Abstract
The aim of this study was to evaluate the incidence, clinical features, and risk factors of sustaining inferior rectus (IR) palsy in a group of pediatric patients with orbital floor blowout fractures. We performed a retrospective case review of sequential cases of pediatric orbital floor blowout fractures (<18 years old) from 2000 to 2013 in a tertiary ophthalmic center in Singapore. A total of 48 patients were included in our study, of whom 5 had IR palsy (10.4%). Patients with IR palsy had a higher mean age (16.4 ± 1.5 years) compared with patients without IR palsy (12.4 ± 3.3 years), had significantly (p < 0.05) worse preoperative motility, and had significantly greater proportion developing postoperative hypertropia (100%) compared with patients without IR palsy (4.7%). Our series of pediatric blowout fractures demonstrated IR palsy prevalence and clinical features for IR palsy which may be distinct to the pediatric group.
Isolated inferior rectus (IR) muscle palsy may occur after orbital trauma [1,2,3,4,5,6]. Various mechanisms have been proposed, including muscle contusion, longitudinal splitting of the muscle, transection or destruction of the muscle, posterior muscle slippage within its sheath, and nerve injury (damage to the oculomotor nerve) [7,8,9,10,11]. IR palsy secondary to periorbital blowout fractures have been well described in adults [1,2,3,4,5,6,8,9]. However, there is lack of clinical information on IR palsies in pediatric blowout fractures.
Two theories of blowout fractures have been proposed—the “buckling” theory and “hydraulic” theory. In the former, blowout fractures are believed to occur through force transmission from the more rigid infraorbital rim to the relatively weak orbital floor [12,13,14]. In the “hydraulic” theory, blunt force is transmitted to the orbital floor via impact on the globe and extraocular muscles against the orbital walls [15].
However, there is limited bony fragmentation in the pediatric group due to greater bone pliability, incomplete aeration of the maxillary sinus, thicker periosteum, and incompletely fused suture lines [16,17,18]. We therefore believe that there are potential differences in factors predisposing pediatric patients with periorbital blowout fractures to IR palsies. In this study, we aimed to evaluate the incidence, clinical features, as well as clinical and radiological risk factors for sustaining IR palsy in a group of pediatric patients.
Methods
We performed a retrospective case review of sequential cases of pediatric orbital floor blowout fractures in patients (<18 years old) who had undergone surgical repair from 2000 to 2013 in a tertiary ophthalmic center in Singapore. In pediatric blowout fractures, in addition to the usual criteria for adult blowout fractures (signs of entrapment of orbital tissue, diplopia on primary gaze or within 30 degrees of primary gaze, and large fractures of more than 50% of the floor), all cases with restricted eye movement were operated on as we usually do not wait to see if it improves unlike in adults. Hence, all pediatric floor fractures with suspected IR palsies were operated on as they had restricted eye movements. Repair was performed via transconjunctival approach by two senior oculoplastic surgeons (S.A., G.S.). A periosteal incision was made along the anterior orbital rim and the periosteum was reflected to expose the orbital floor fracture. Entrapped tissue was freed from all edges of the fracture and elevated from the adjacent paranasal sinus cavity into the orbit. Care was taken to avoid damage to the infraorbital neurovascular bundle, as well as the anterior and posterior ethmoidal arteries where applicable. We ensured the medial, lateral, and especially posterior edges of the fracture site were well visualized and exposed prior to the insertion of the implant. Institutional review board approval was obtained.
Blowout orbital floor fracture was defined as an isolated fracture of the orbital floor not involving the orbital rim. IR palsy was defined as deficiency of depression in abduction with negative forced duction testing after the release of IR entrapment.
Exclusion criteria included patients with incomplete clinical data, paralysis or underaction of other extraocular muscles, primary superior oblique overaction or tightness mimicking contralateral IR underaction, multiple fractures, and poor quality computed tomographic (CT) images.
Demographic, radiological, and clinical data were collected and analyzed. Underaction of the IR was graded on a scale of 0 to −4, with 0 representing no limitation and −4 representing no movement into the tested field of gaze. All cases had CT face done and evaluated by a radiologist and oculoplastic surgeon. Coronal CT images were used. Fracture extent was assessed and classified into three groups (Figure 1) [19]: A1, floor lateral to infraorbital canal; A2, floor medial to infraorbital canal; A3, involving the inferomedial strut; A4, medial blowout fracture (not applicable in our study).
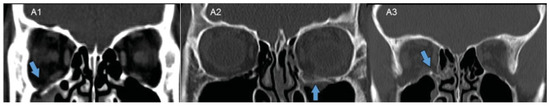
Figure 1.
Fracture extent assessed and classified into three groups—A1: floor lateral to infraorbital canal; A2: floor medial to infraorbital canal; A3: involving the inferomedial strut. The fracture site is represented by the blue arrows.
Fracture quantification was as follows (Figure 2): Measurements were made from the medial anatomical landmark (strut between medial wall and floor) to the medial (X) and lateral (Y) border of the fracture in each CT slice. The anterior and posterior borders were determined by relating the CT slices that displayed the fracture. Data were expressed as a two-dimensional (2D) diagram in Microsoft Excel, and the area was quantified by Image J software (version 1.49n).
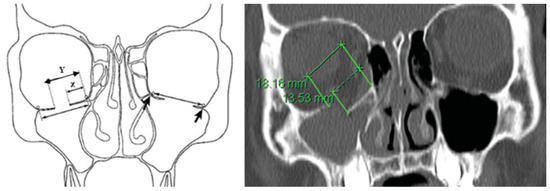
Figure 2.
Fracture quantification: measurements were made from the medial anatomical landmark (orbital strut between medial wall and floor) to the medial (X) and lateral (Y) border of the fracture in each CT slice. The arrows represent the normal anatomical landmarks of the medial and lateral borders of the orbital floor.
Table 1 shows an example of orbital floor fracture measurement in a patient (patient 12). Figure 3 shows the 2D diagram of orbital fracture measurement (patient 12). Orbital floor area quantification was as described earlier, with the anterior border determined as the first CT slice with a visible maxillary sinus, and posterior border at the apex of the orbit.

Table 1.
Example of orbital floor fracture measurement (patient 12).
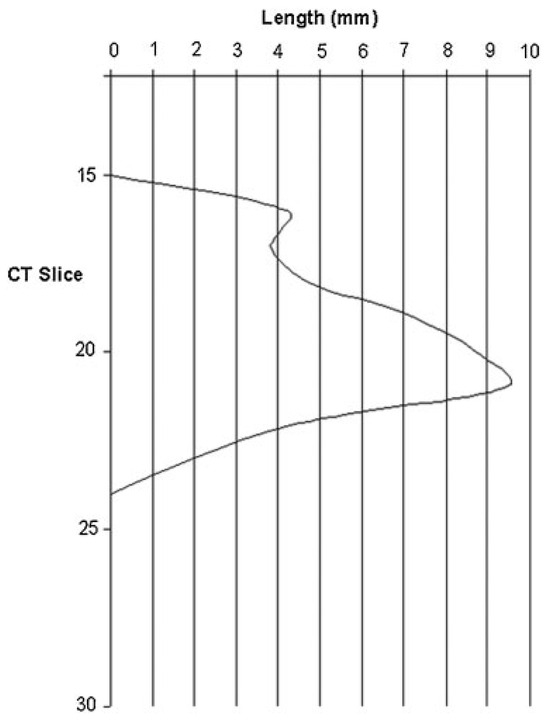
Figure 3.
Two-dimensional diagram of orbital fracture measurement in a sample patient.
Frequencies were tabulated for categorical variables and continuous variables were summarized either as means with standard deviations or as medians with interquartile ranges (IQR). Continuous variables, such as age, areas, and durations, were compared using the Mann–Whitney test or independent samples t-test. Categorical data such as gender, race, fracture configuration, and preoperative orthoptics were compared using the Fisher’s exact test. Data analysis was performed using IBM SPSS Statistics (version 22; IBM Corp, New York, NY, USA) and R (version 3.1.2; The R Foundation for Statistical Computing).
Results
A total of 48 patients were included in our study, of whom 5 had IR palsy (10.4%). Table 2 shows the demographics of the study patients. There was no significant difference between patients with IR palsy and patients without IR palsy. Males comprised the majority in both groups, and assault was the most common mechanism of injury. However, patients with IR palsy had a significantly higher mean age (16.4 ± 1.5 years) compared with those without IR palsy (12.4 ± 3.3 years).

Table 2.
Demographics.
Table 3 shows the comparison of clinical features between the patients with and without IR palsy. Patients in the IR palsy group had significantly worse preoperative motility, especially on upgaze and downgaze. There was no significant difference between the two groups in terms of orthoptics preoperatively, but postoperatively, the IR group had significantly greater proportion with hypertropia. The mechanism of injury in both groups of patients with and without IR palsy was similar, although the group with IR palsy had a greater proportion with assault (60%) compared with the group without IR palsy (14.0%).

Table 3.
Comparison of clinical features between patients with and without IR palsy.
Intraoperatively, all patients with IR palsy had findings of impingement of the IR by edges of the floor fracture, although only two had minimal prolapse of the muscle within the fracture. Three had impingement on the posterior aspect of the IR, one on the anterior aspect, and one on the middle aspect.
The clinical characteristics of the five patients with IR palsy are summarized in Table 4. Preoperatively, most were orthophoric in primary gaze, although all had limitation on up-and-down gazes. Postoperatively, all had varying degrees of hypertropia, ranging from 10 to 20 prism diopters (PD). Fortunately, the IR palsy resolved spontaneously, taking 4 to 10 weeks from the time of surgery.

Table 4.
Clinical characteristics of patients with inferior rectus (IR) palsy.
Radiological studies (Table 5) of patients with and without IR palsy showed no significant difference in terms of fracture type A1, A2, or A3 (Figure 4). However, the mean fracture area in patients with IR palsy was significantly larger (1.8 ± 0.7 cm2) than those without (0.7 ± 0.2 cm2).

Table 5.
Radiological characteristics of patients with and without inferior rectus (IR) palsy.
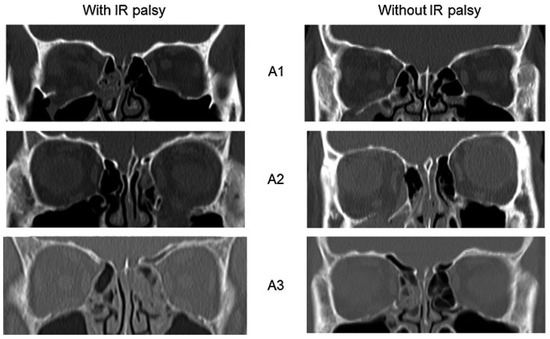
Figure 4.
Patients with and without inferior rectus (IR) palsy, each group having fracture type A1, A2, and A3.
Discussion
In our study of pediatric patients with orbital floor blowout fractures, 10.4% had evidence of IR palsy. There is currently little in the literature on IR palsy after pediatric blowout fractures and hence it is difficult to compare our prevalence rate with known norms. However, it is a good number to have at the back of our minds when we see pediatric patients with blowout floor fractures, for our own knowledge as well as for counseling preoperatively and postoperatively.
Similar to Kushner’s case series on IR palsy post–orbit facial trauma, our patients were orthophoric in the primary position but troublesome diplopia on upgaze and downgaze [20]. Forced duction test (done intraoperatively for most of the cases) was not useful in determining if a particular patient had IR palsy. A positive forced duction indicated mechanical limitation of eye movement rather than an underaction from muscle palsy. In contrast, a forced generation test could help distinguish between paralytic and restrictive ophthalmopareses, as a paretic muscle generated only a fraction of this normal force, and muscles functioning against a tethered extraocular muscle seemed to generate supranormal forces. However, a forced generation test was not possible to perform in most of the pediatric cases preoperatively, as it required patient cooperation. The very fact that these patients did not present with hypertropia indicated that the hypertropia was masked by some amount of restrictive element and once the surgery was done to release the muscle, the full extent of hypertropia became obvious. The authors believe that patients with IR palsy have both restrictive IR action (hence unable to move eye up fully) and IR weakness (hence unable to look down fully). The resultant force may lead to the mild hypertropia or orthophoria. The preoperative risk factor to highlight is the limitation of eye movement in downgaze and negative forced duction in downgaze which helps distinguish this group of patients with IR palsy.
The diagnosis of IR palsy is traditionally based on the clinical finding of limitation ofdepression, worse in abduction. However, in the setting of trauma, it is usually a retrospective diagnosis due to the compounding presence of edema or entrapment. In our study, these patients with IR palsy were significantly older in age, had larger fracture areas, had restriction in up and down gazes preoperatively, and were more likely to develop hypertropia immediate postoperatively.
Various mechanisms have been proposed as a cause of IR underaction after trauma. Possible hypotheses include that of muscle contusion, scarring within and around the orbital fibrous sheath network, longitudinal splitting or a flap tear of the muscle, direct avulsion, or transection of the muscle [4,5,6,7,8,9,20,21]. In addition, the inferior division of the oculomotor nerve branches just inside the orbital apex and divides into three separate roots that travel medially to the medial rectus muscle, laterally to the inferior oblique muscle and ciliary ganglion, and inferiorly to the IR. The sudden force driving the IR into the fracture can cause stretching and shearing of the nerve, resulting in paresis of the muscle. Isolated direct trauma to the nerve to the IR muscle is also a possible mechanism in isolated IR paresis [22,23].
Development of hypertropia on the first postoperative day, as seen in all our patients with IR palsy, raises concern over surgical damage to the IR. However, the presence of moderate to severe limitation of infraduction preoperatively suggests that IR weakness was already present, as the extent of infraduction limitation was greater than that which could be explained by posttraumatic tissue edema. We believe that releasing the IR and restoring the orbital floor unmasks the IR weakness.
We hypothesize that IR palsy occurs in the older pediatric age group, as the compliance of the bony orbit is less [24]. This also explains the larger size of the orbital floor fractures in these patients. With a greater change in pressure within the orbit transiently, the periorbita and IR would likely herniate through the fracture with greater force, leading to significant nerve paresis and functional limitation.
There are several limitations to our study. It is a retrospective study and the number of patients with IR palsy in our series is not large. Given the variable timing from injury to surgery, and the self-limiting clinical course, it is possible that some patients without IR palsy might have manifested if surgical repair was performed earlier. The diverse causes of IR underaction in the study made detailed individual analysis of each cause difficult. The process of postoperative healing and edema may have compounded the presentation of hypertropia. In addition, the possibility of intraoperative damage of the IR giving rise to postoperative hypertropia, while unlikely, still exists.
In summary, our series of pediatric blowout fractures had an approximately 10% prevalence of IR palsy. Risk factors for IR palsy in the pediatric group include older age and larger fracture area measured on CT, while clinical features suggestive of IR palsy include restriction in both up and down gazes preoperatively, and presentation of hypertropia on first postoperative day. Preoperative and early postoperative suspicion of IR palsy is important to advise patients on the development of postoperative hypertropia, albeit its self-limiting clinical course.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wojno, T.H. The incidence of extraocular muscle and cranial nerve palsy in orbital floor blow-out fractures. Ophthalmology 1987, 94, 682–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sloan, B.; McNab, A.A. Inferior rectus rupture following blowout fracture. Aust N Z J Ophthalmol 1998, 26, 171–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yano, H.; Minagawa, T.; Masuda, K.; Hirano, A. Urgent rescue of ‘missing rectus’ in blowout fracture. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 2009, 62, e301–e304. [Google Scholar]
- Iliff, N.; Manson, P.N.; Katz, J.; Rever, L.; Yaremchuk, M. Mechanisms of extraocular muscle injury in orbital fractures. Plast Reconstr Surg 1999, 103, 787–799. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lyon, D.B.; Newman, S.A. Evidence of direct damage to extraocular muscles as a cause of diplopia following orbital trauma. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg 1989, 5, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Noorden, G.K.; Hansell, R. Clinical characteristics and treatment of isolated inferior rectus paralysis. Ophthalmology 1991, 98, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awadein, A. Clinical findings, orbital imaging, and intraoperative findings in patients with isolated inferior rectus muscle paresis or underaction. J AAPOS 2012, 16, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, I.H.; Brown, M.S. Flap tear of rectus muscles: An underlying cause of strabismus after orbital trauma. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg 2002, 18, 443–449, Discussion 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, C.C.; Jain, A.; McCann, J.D.; Demer, J.L. Inferior rectus muscle transection: A cause of diplopia after non-penetrating orbital trauma. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 2006, 244, 1698–1700. [Google Scholar]
- Chatzistefanou, K.I.; Kushner, B.J.; Gentry, L.R. Magnetic resonance imaging of the arc of contact of extraocular muscles: Implications regarding the incidence of slipped muscles. J AAPOS 2000, 4, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushner, B.J. Surgical treatment of paralysis of the inferior division of the oculomotor nerve. Arch Ophthalmol 1999, 117, 485–489. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tessier, P. The classic reprint: Experimental study of fractures of the upper jaw. 3. René Le Fort, M.D., Lille, France. Plast Reconstr Surg 1972, 50, 600–607. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tessier, P. The classic reprint. Experimental study of fractures of the upper jaw. I and II. René Le Fort, M.D. Plast Reconstr Surg 1972, 50, 497–506. [Google Scholar]
- Le Fort, R. Etude experimentale sur les fractures de la machoire superieure. Rev Chir Paris 1901, 23, 208–279. [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer, R.L. Traumatic enophthalmos. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc 1943, 41, 293–306. [Google Scholar]
- Haug, R.H.; Foss, J. Maxillofacial injuries in the pediatric patient. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 2000, 90, 126–134. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, K.C.; Seo, M.S.; Park, Y.G. Orbital trapdoor fracture in children. J Korean Med Sci 2003, 18, 881–885. [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, S.; Kassira, W.; Thaller, S.R. Overview of pediatric orbital fractures. J Craniofac Surg 2011, 22, 1330–1332. [Google Scholar]
- Ploder, O.; Klug, C.; Voracek, M.; Burggasser, G.; Czerny, C. Evaluation of computer-based area and volume measurement from coronal computed tomography scans in isolated blowout fractures of the orbital floor. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2002, 60, 1267–1272, Discussion 1273–1274. [Google Scholar]
- Kushner, B.J. Paresis and restriction of the inferior rectus muscle after orbital floor fracture. Am J Ophthalmol 1982, 94, 81–86. [Google Scholar]
- Kashima, T.; Akiyama, H.; Kishi, S. Longitudinal tear of the inferior rectus muscle in orbital floor fracture. Orbit 2012, 31, 171–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warwick, W.; Williams, P.L. Gray’s Anatomy, 35th ed.; Longman Group: London, UK, 1973; pp. 997–999. [Google Scholar]
- Zayed, M.G.; Quhill, H.; Burke, J.P. Inferior rectus muscle palsy with constant diplopia following orbito-facial trauma. Br Ir Orthopt J 2014, 11, 50–52. [Google Scholar]
- Baumann, A.; Troulis, M.J.; Kaban, L.B. Facial trauma I: Midfacial fractures. In Pediatric Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery; Kaban, L.B., Troulis, M.J., Eds.; Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2004; pp. 425–440. [Google Scholar]
© 2017 by the author. The Author(s) 2017.