A Scientometric Study on Management Literature in Southeast Asia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Methods
4. Results
4.1. Descriptive Results
4.1.1. Types and Quantity of Papers
4.1.2. Annual Publication Trend
4.2. Author, Affiliation, Country, and Article Performances
4.2.1. Authors’ Productivity
4.2.2. Affiliation’s Productivity
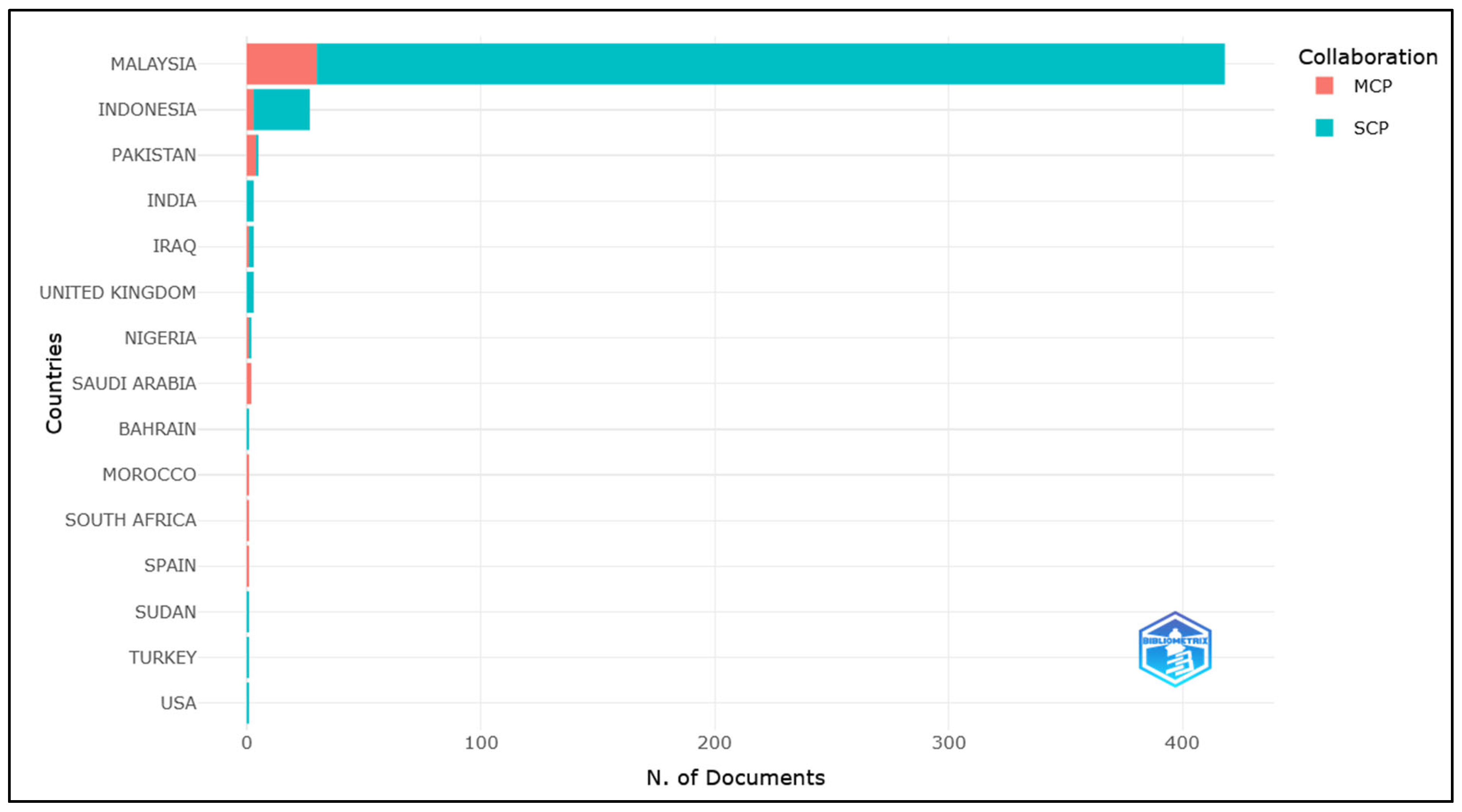
4.2.3. Corresponding Author’s Country and Total Citations
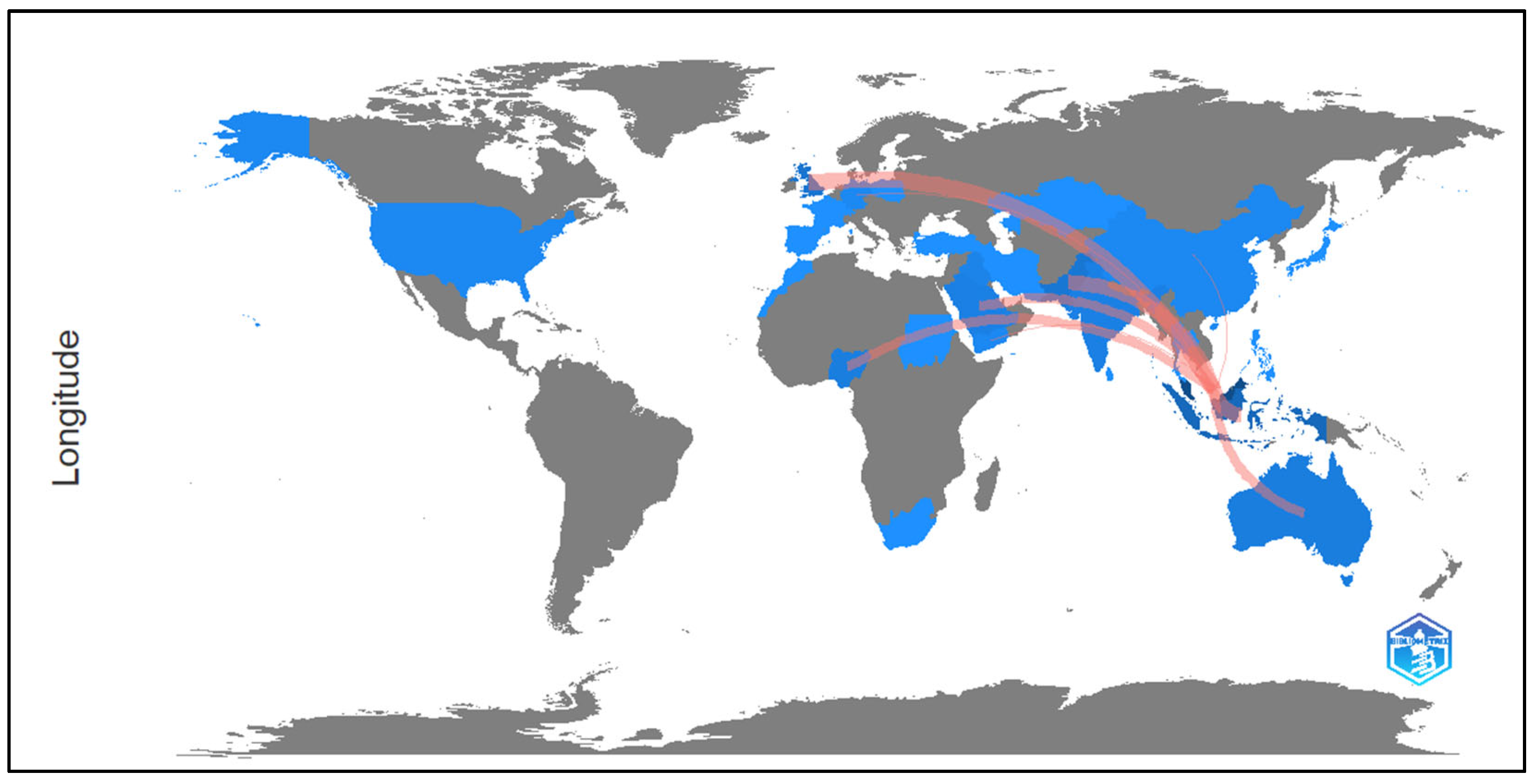
4.2.4. Country Collaboration Map
4.2.5. Article Performance
4.3. Research Topics
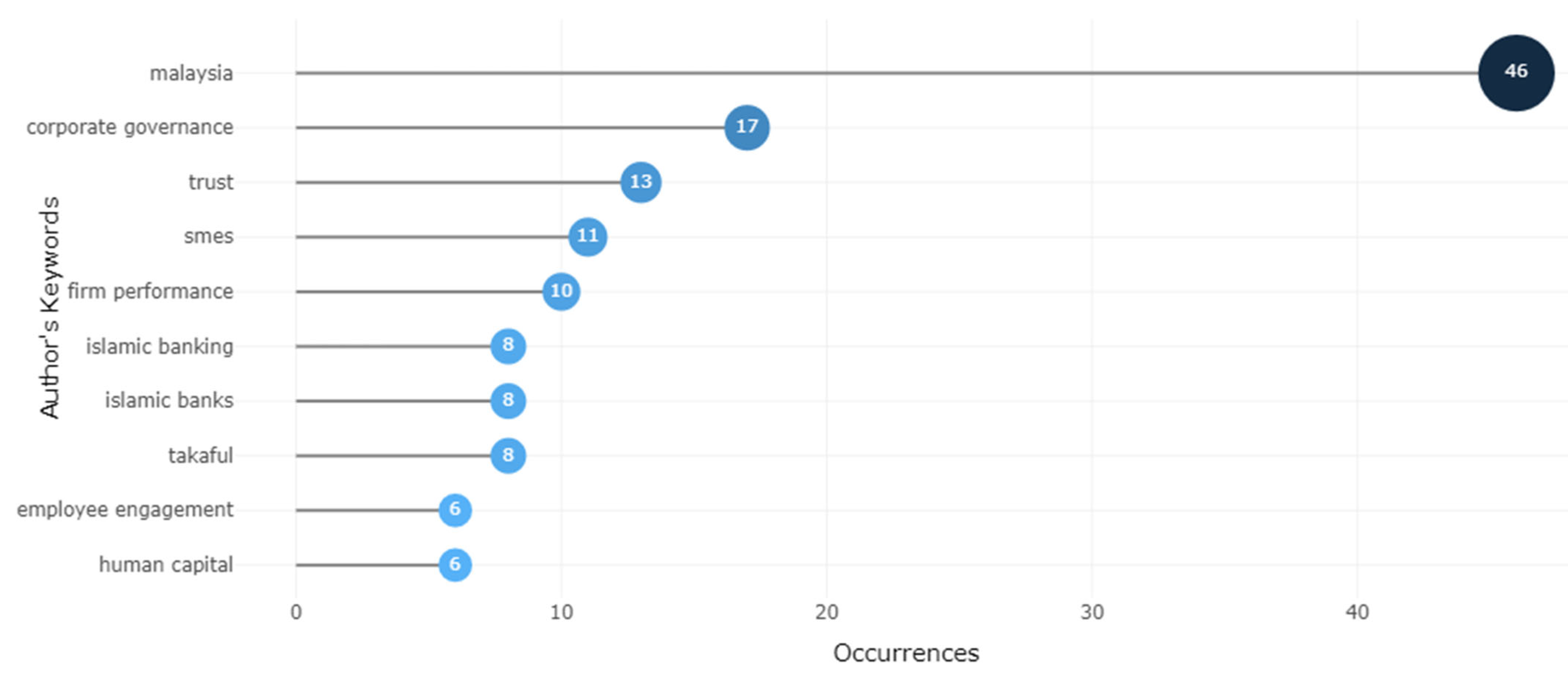
4.3.1. Most Frequent Word
4.3.2. Trend Topics
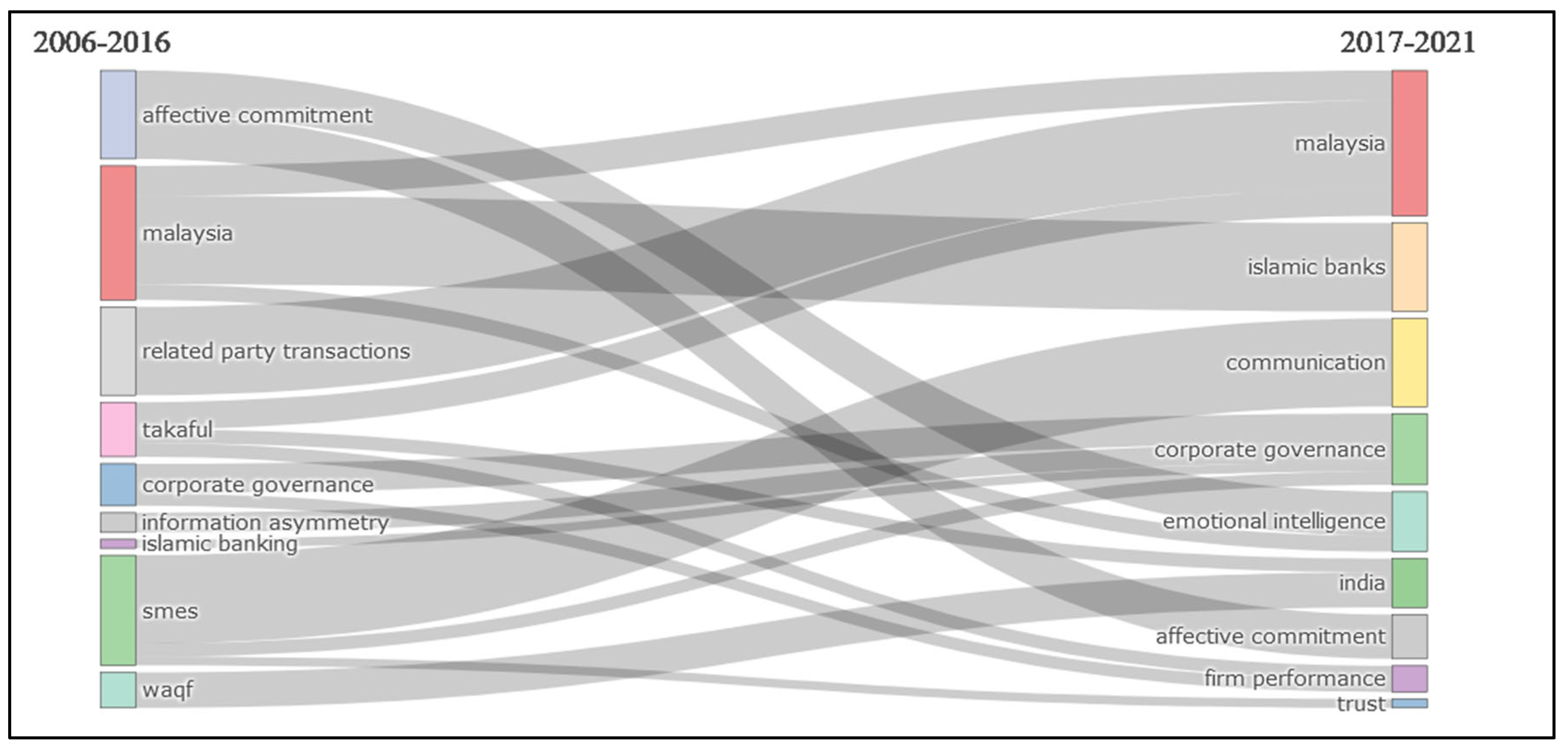
4.3.3. Thematic Evolution
5. Managerial Implication
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ab Hamid, Siti Ngayesah, Wan Jamaliah Wan Jusoh, and Suharni Maulan. 2021. The Influence of Spiritual Brand Attributes towards the Corporate Brand Image of Islamic Banking Institutions in Malaysia. Jurnal Pengurusan 61: 31–41. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, Alhamzah F., Ahmad Jusoh, Adaviah Mas’od, Ahmed H. Alsharif, Javed Ali, and Albert W. K. Tan. 2022. Cogent Business & Management Bibliometrix Analysis of Information Sharing in Social Media Bibliometrix Analysis of Information Sharing in Social Media. Cogent Business & Management 9: 2016556. [Google Scholar]
- Abdullah, Maizatulakma, and Zaleha Abdul Shukor. 2017. The Comparative Moderating Effect of Risk Management Committee and Audit Committee on the Association Between Voluntary Risk Management Disclosure and Firm Performance. Jurnal Pengurusan 51: 159–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, Shamsul Nahar, and Ku Nor Izah Ku Ismail. 2013. Gender, Ethnic and Age Diversity of the Boards of Large Malaysian Firms and Performance. Jurnal Pengurusan 38: 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aisyah, Abd Rahman, and Zaleha Zaid. 2015. Developing a Framework of Islamic Bank Operational Risk Management: ‘People Risk’. Jurnal Pengurusan 44: 129–39. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Hawari, Mohammad A. 2011. The Role of Bank Automated Services in Gaining Customers’ Trust: A Practical Study in UAE. Jurnal Pengurusan 33: 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- Alshater, Muneer Maher Mahmoud, Mohammad Kabir Hassan, Ashraf Khan, and Irum Saba. 2021. Influential and Intellectual Structure of Islamic Finance: A Bibliometric Review. International Journal of Islamic and Middle Eastern Finance and Management 14: 339–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aman, Aini, and Ruhanita Maelah. 2011. Relational Risks and Trust: A Case Study of Accounting Outsourcing in Malaysia. Jurnal Pengurusan 32: 13–20. [Google Scholar]
- Aria, Masimo, and Corrado Cuccurullo. 2017. Bibliometrix: An R-Tool for Comprehensive Science Mapping Analysis. Journal of Informetrics 11: 959–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashar, Abu, Shalini Singh, and Vivek Kumar Pathak. 2022. A Bibliometric Review of Online Impulse Buying Behaviour. International Journal of Electronic Business 17: 162–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baz, Jamal El, and Sadia Iddik. 2022. Green Supply Chain Management and Organizational Culture: A Bibliometric Analysis Based on Scopus Data (2001–2020). International Journal of Organizational Analysis 30: 156–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidin, Zainol, Kamil Md Idris, and Faridahwati Mohd Shamsudin. 2009. Predicting Compliance Intention on Zakah on Employment Income in Malaysia: An Application of Reasoned Action Theory. Jurnal Pengurusan 28: 85–102. [Google Scholar]
- Buniamin, Sharifah, Bakhtiar Alrazi, Nor Hasimah Johari, and Noor Raida Abd Rahman. 2011. Corporate Governance Practices and Environmental Reporting of Companies in Malaysia: Finding Possibilities of Double Thumbs Up (Amalan Tadbir Urus Korporat Dan Pelaporan Alam Sekitar Syarikat Di Malaysia: Mengkaji Kemungkinan Hubungan Baik Antara Kedua-Du. Jurnal Pengurusan 32: 55–71. [Google Scholar]
- Chun, Yong Kah, Chung Jee Fenn, and Akram Abdulraqeb Sultan Al-Khaled. 2021. The Relationship between Socio-Demographics and Financial Literacy with Financial Planning Among Young Adults in Klang Valley, Malaysia. Jurnal Pengurusan 63: 17–30. [Google Scholar]
- Cobo, Manuel Jesús, Antonio Gabriel López Herrera, Enrique Herrera-Viedma, and Francisco Herrera. 2012. SciMAT: A New Science Mapping Analysis Software Tool. Journal of The Association for Information Science and Technology 3: 1609–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de las Heras-Rosas, Carlos, and Juan Herrera. 2021. Research Trends in Open Innovation and the Role of the University. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity 7: 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Embong, Mohd Rodzi, Roshaiza Taha, and Mohd Nazli Mohd Nor. 2013. Role of Zakat to Eradicate Poverty in Malaysia. Jurnal Pengurusan 39: 141–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Hui. 2021. Analysis of the New Scopus CiteScore. Scientometrics 126: 5321–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firmansyah, Egi Arvian, Amelia Rizky Alamanda, and Teguh Santoso. 2020. An Evaluation of Scholarly Works in Zakat: A Bibliometric Analysis of Islamic Economics Journals in Indonesia. Amwaluna: Jurnal Ekonomi dan Keuangan Syariah 4: 311–23. [Google Scholar]
- Firmansyah, Egi Arvian, and Budi Harsanto. 2022. Islamic Fintech Research: Systematic Review Using Mainstream Databases. Etikonomi 21: 355–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunardi, Ardi, Aldrin Herwany, Erie Febrian, and Mokhamad Anwar. 2021. Research on Islamic Corporate Social Responsibility and Islamic Bank Disclosures. Journal of Sustainable Finance and Investment 12: 1308–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, Manish, and Musarrat Shaheen. 2017. The Relationship between Psychological Capital and Turnover Intention: Work Engagement as Mediator and Work Experience as Moderator. Jurnal Pengurusan 49: 117–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasbullah, Nurul Adilah, and Asmak Ab Rahman. 2021. Strategies for Managing Endowment Funds: Case Studies of Selected Malaysian Public Universities. Jurnal Pengurusan 62: 17–26. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, Mohammad Kabir, Fahmi Ali Hudaefi, and Ahmad Agung. 2022. Evaluating indonesian islamic banking scholarly publications: A data analytics. Journal of Islamic Monetary Economics and Finance 8: 341–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodi, Nazia Abdul, and Zaiton Hassan. 2021. Relationship between Organizational Trust, Employee Voice and Silence Behaviour: The Moderator Effect of Power Distance. Jurnal Pengurusan 62: 131–44. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, Hazril Izwar, Wan Maisara Wan Mohamad, and Khairul Anuar Mohammad Shah. 2020. Investigating Information and Communication Technology (ICT) Usage, Knowledge Sharing and Innovative Behavior among Engineers in Electrical and Electronic MNCs in Malaysia. Jurnal Pengurusan 58: 133–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingale, Kavita Karan, and Ratna Achuta Paluri. 2022. Financial Literacy and Financial Behaviour: A Bibliometric Analysis. Review of Behavioral Finance 14: 130154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffar, Romlah, Dina Mardinah, and Azlina Ahmad. 2013. Corporate Governance and Voluntary Disclosure Practices: Evidence from a Two Tier Board Systems in Indonesia. Jurnal Pengurusan 39: 83–92. [Google Scholar]
- Jaffar, Romlah, Razieh RaziAziendeh, Zaleha Abdul Shukor, and Mara Ridhuan Che Abdul Rahman. 2018. Environmental Performance: Does Corporate Governance Matter? Jurnal Pengurusan 52: 133–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Joshi, Aditi. 2016. Comparison Between Scopus & ISI Web of Science. Journal Global Values VII: 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Kadir, Osman, Mohd Zaidi Omar, and Mohamad Sattar Rasul. 2021. The Impact of Psychological Well-Being, Employability and Work-Life Balance on Organizational Mobility of Women Engineering Technology Graduate. Jurnal Pengurusan 63: 99–113. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, Waris Ali, Ramraini Ali Hassan, Muhammad Zulqarnain Arshad, and Umair Kashif. 2020. Does Innovation Affect the Firm Performance in Developing Countries? A Conceptual Framework. Jurnal Pengurusan 59: 117–27. [Google Scholar]
- Mabkhot, Hashed Ahmad, Hasnizam Shaari, and Salniza Md Salleh. 2017. The Influence of Brand Image and Brand Personality on Brand Loyalty, Mediating by Brand Trust: An Empirical Study. Jurnal Pengurusan 50: 71–82. [Google Scholar]
- Marzuki, Marziana Madah, and Roslina Salwani Haji Shukri. 2019. Directors’ Remuneration, Firm Performance and Political Connection: Evidence from State-Owned Enterprise (SOE) in Malaysia. Jurnal Pengurusan 57: 184–97. [Google Scholar]
- Maulod, Sharul Azlan, Rasidah Arshad, and Ida Rosnita Ismail. 2020. Hubungan Antara Konflik Dan Tingkah Laku Buli Dalam Unit Kerja: Peranan Kepercayaan Sebagai Pengantara. Jurnal Pengurusan (UKM Journal of Management) 59: 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, Mohd Faiz, Joni Tamkin Borhan, and Nurhanani Romli. 2016. Shariah Governance of Takaful Industry in Malaysia: Implications of Post Islamic Financial Services Act 2013. Jurnal Pengurusan 47: 91–103. [Google Scholar]
- Mohd Nor, Shifa, and Noor Azuan Hashim. 2015. CSR and Sustainability of Islamic Banking: The Bankers View (CSR Dan Kemampanan Perbankan Islam: Pandangan Pegawai Bank). Jurnal Pengurusan 45: 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizar, Nadifa Salsabila, and Falikhatun. 2021. Islamic Intellectual Capital and Takaful Financial Performance. Jurnal Pengurusan 62: 91–99. [Google Scholar]
- Nor, Hamezah Md, and Ku Nor Izah Ku Ismail. 2017. The Moderating Effects of Independent Directors ‘ Human Capital on the Relationship between Related Party Transactions and Firm Performance: Evidence from Malaysia. Jurnal Pengurusan 51: 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, Nor Asiah, Hasnan Md Aris, and Muhamad Azrin Nazri. 2016. The Effect of Entrepreneurial Orientation, Innovation Capability and Knowledge Creation on Firm Performance A Perspective on Small Scale Entrepreneurs. Jurnal Pengurusan 48: 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, Nor Asiah, Muhamad Azrin Nazri, Syed Shah Alam, and Mohd Helmi Ali. 2017. Consumer Retaliation to Halal Violation Incidents: The Mediating Role of Trust Recovery. Jurnal Pengurusan 51: 101–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdemir, Mücahit, and Mervan Selçuk. 2021. A Bibliometric Analysis of the the International Journal of Islamic and Middle Eastern Finance and Management. International Journal of Islamic and Middle Eastern Finance and Management 14: 767–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puri-Mirza, Amna. 2021. Leading Countries in Islamic Banking Assets Worldwide in 2019. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1090903/worldwide-leading-countries-in-islamic-banking-assets-by-value/ (accessed on 30 September 2022).
- Ramli, Nathasa Mazna, Abdul Rahim Abdul Rahman, Ainulashikin Marzuki, and Marziana Madah Marzuki. 2021. Implementation of IFRS 13 Fair Value Measurement: Issues and Challenges Faced by the Islamic Financial Institutions in Malaysia. Jurnal Pengurusan 63: 51–60. [Google Scholar]
- Reuters, Thomson. 2008. Whitepaper Using Bibliometrics. Thomson Reuters 2008: 12. [Google Scholar]
- Saad, Natrah, Abdulsalam Mas’ud, Saliza Abdul Aziz, Nor Azizah Abdul Manaf, and Muhammad Aqbal Mashadi. 2021. Tax Noncompliance of High Net-Worth Individuals (HNWIS) in Malaysia: Perspectives of Tax Professionals. Jurnal Pengurusan 63: 85–98. [Google Scholar]
- Shaladdin, Zaida Farhana Mohd, Mohd Zulkifli Mokhtar, and Nur Haiza Muhammad Zawawi. 2018. Determinants of Customer Satisfaction in Takaful (Islamic Insurance) Services in Malaysia. Jurnal Pengurusan 54: 205–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sufian, Fadzlan, Fakarudin Kamarudin, and Nor Halida Haziaton Mohd Noor. 2013. Assessing the Revenue Efficiency of Domestic and Foreign Islamic Banks: Empirical Evidence from Malaysia. Jurnal Pengurusan 37: 77–90. [Google Scholar]
- Suhaili, Nur Aqidah, Mohd Rizal Palil, and Rohayati Husin. 2018. Wakaf CSR: An Emperical Study of Polycentric Collaborative Waqf Governance. Jurnal Pengurusan 53: 133–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taqi, Muhamad, Aam Slamet Rusydiana, Nanik Kustiningsih, and Irman Firmansyah. 2021. Environmental Accounting: A Scientometric Using Biblioshiny. International Journal of Energy Economics and Policy 11: 369–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teh, Boon Heng, Tze San Ong, Adedeji Babatunji Samuel, and Sin Huei Ng. 2016. An Empirical Study of Auditors Switching, Corporate Governance and Financial Performances of Malaysian Public Listed Companies (PLCs). Jurnal Pengurusan 47: 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaker, Mohamed Asmy Mohd Thas, and Hassanudin Mohd Thas Thaker. 2015. Exploring the Contemporary Issues of Corporate Share Waqf Model in Malaysia with the Reference to the Waqaf An-Nur Corporation Berhad. Jurnal Pengurusan 45: 165–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thing, Ng Suat, Mohd Hasimi Yaacob, and Norazlan Alias. 2021. Information Asymmetry and Industry 4.0 among Small and Medium Enterprise (SME) in Malaysian Halal Industry. Jurnal Pengurusan 63: 31–49. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, Asha, and Vikas Gupta. 2021. Tacit Knowledge in Organizations: Bibliometrics and a Framework-Based Systematic Review of Antecedents, Outcomes, Theories, Methods and Future Directions. Journal of Knowledge Management 26: 1014–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapp, Jamie V. 2020. The New Scopus CiteScore Formula and the Journal Impact Factor: A Look at Top Ranking Journals and Middle Ranking Journals in the Scopus Categories of General Physics and Astronomy, Materials Science, General Medicine and Social Sciences. Physical and Engineering Sciences in Medicine 43: 739–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, Muhammad, and Asmak Ab Rahman. 2021. Financing Higher Education through Waqf in Pakistan: Issues and Challenges. Jurnal Pengurusan 62: 159–71. [Google Scholar]
- van Eck, Nees Jan, and Ludo Waltman. 2010. Software Survey: VOSviewer, a Computer Program for Bibliometric Mapping. Scientometrics 84: 523–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, Othman. 2007. Investor Demand, Size Effect and Performance of Malaysian Initial Public Offerings: Evidence from Post-1997 Financial Crisis. Jurnal Pengurusan 26: 25–47. [Google Scholar]
- Yong, Othman. 2011. Winner’s Curse and Bandwagon Effect in Malaysian IPOs: Evidence from 2001–2009. Jurnal Pengurusan 32: 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Zainudin, Zalina, Izani Ibrahim, Hafezali Iqbal Hussain, and Abdul Razak Abdul Hadi. 2017. Debt and Financial Performance of REITs in Malaysia: An Optimal Debt Threshold Analysis. Jurnal Ekonomi Malaysia 51: 73–85. [Google Scholar]
- Zaki, Hafizah Omar, and Siti Ngayesah Ab Hamid. 2021. The Influence of Time Availability, Happiness, and Weariness on Consumers’ Impulse Buying Tendency amidst Covid-19 Partial Lockdown in Malaysia. Jurnal Pengurusan 62: 81–90. [Google Scholar]



| Type | Quantity | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Article | 472 | 94.40% |
| Review | 27 | 5.40% |
| Conference paper | 1 | 0.20% |
| Total | 500 | 100% |
| Rank | Authors | Number of Document |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Omar NA | 14 |
| 2 | Arshad R | 12 |
| 3 | Adham KA | 9 |
| 4 | Ali MH | 9 |
| 5 | Isa RM | 9 |
| 6 | Nor FM | 9 |
| 7 | Saleh NM | 9 |
| 8 | Abdullah NL | 8 |
| 9 | Janor H | 8 |
| 10 | Maelah R | 8 |
| 11 | Nazri MA | 8 |
| 12 | Abdul-Rahman A | 7 |
| 13 | Hassan MS | 7 |
| 14 | Rahim RA | 7 |
| 15 | Shukor ZA | 7 |
| 16 | Ahmad A | 6 |
| 17 | Alam SS | 6 |
| 18 | Aziz NA | 6 |
| 19 | Hamzah N | 6 |
| 20 | Ismail A | 6 |
| Rank | Affiliation | Number of Document |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia | 303 |
| 2 | Universiti Utara Malaysia | 57 |
| 3 | Universiti Sains Malaysia | 32 |
| 4 | Universiti Putra Malaysia | 30 |
| 5 | Universiti Sains Islam Malaysia | 25 |
| 6 | Universiti Teknologi Mara | 20 |
| 7 | Multimedia University | 18 |
| 8 | Universiti Malaysia Sabah | 15 |
| 9 | International Islamic University Malaysia | 11 |
| 10 | Universiti Malaysia Terengganu | 11 |
| 11 | University of Malaya | 10 |
| 12 | Universiti Malaya | 9 |
| 13 | Universiti Utara Malaysia UUM | 8 |
| 14 | Universiti Malaysia Sarawak | 6 |
| 15 | Inti International University | 5 |
| 16 | Universitas Airlangga | 5 |
| 17 | Universiti Malaysia Kelantan | 5 |
| 18 | Universiti Pendidikan Sultan Idris | 5 |
| 19 | Universiti Sultan Zainal Abidin | 5 |
| 20 | Universiti Teknologi Malaysia | 5 |
| No | Country | Total Citations | Average Article Citations |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Malaysia | 1359 | 3.251 |
| 2 | Indonesia | 89 | 3.296 |
| 3 | India | 29 | 9.667 |
| 4 | United Kingdom | 18 | 6 |
| 5 | Sudan | 15 | 15 |
| 6 | Saudi Arabia | 13 | 6.5 |
| 7 | Pakistan | 10 | 2 |
| 8 | Nigeria | 5 | 2.5 |
| 9 | Iraq | 2 | 0.667 |
| 10 | Morocco | 2 | 2 |
| No | Author and Publication Year | Title | Total Citations (TC) | TC Per Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Abdullah and Ismail (2013) | “Gender, Ethnic and Age Diversity of the Boards of Large Malaysian Firms and Performance” | 45 | 4.5 |
| 2 | Bidin et al. (2009) | “Predicting Compliance Intention on Zakah on Employment Income in Malaysia: An Application of Reasoned Action Theory” | 43 | 3.0714 |
| 3 | Mabkhot et al. (2017) | “The influence of brand image and brand personality on brand loyalty, mediating by brand trust: An empirical study” | 27 | 4.5 |
| 4 | Zainudin et al. (2017) | “Debt and Financial Performance of REITs in Malaysia: A Moderating Effect of Financial Flexibility” | 26 | 4.3333 |
| 5 | Sufian et al. (2013) | “Assessing the Revenue Efficiency of Domestic and Foreign Islamic Banks: Empirical Evidence from Malaysia” | 26 | 2.6 |
| 6 | Buniamin et al. (2011) | “Corporate Governance Practices and Environmental Reporting of Companies in Malaysia: Finding Possibilities of Double Thumbs Up” | 25 | 2.0833 |
| 7 | Yong (2011) | “Winner’s Curse and Bandwagon Effect in Malaysian IPOs: Evidence from 2001–2009” | 20 | 1.6667 |
| 8 | Gupta and Shaheen (2017) | “The Relationship between Psychological Capital and Turnover Intention: Work Engagement as Mediator and Work Experience as Moderator” | 19 | 3.1667 |
| 9 | Embong et al. (2013) | “Role of zakat to eradicate poverty in Malaysia” | 18 | 1.8 |
| 10 | Yong (2007) | “Investor demand, size effect and performance of Malaysian initial public offerings: Evidence from post-1997 financial crisis” | 18 | 1.125 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Firmansyah, E.A.; Wahid, H.; Gunardi, A.; Hudaefi, F.A. A Scientometric Study on Management Literature in Southeast Asia. J. Risk Financial Manag. 2022, 15, 507. https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm15110507
Firmansyah EA, Wahid H, Gunardi A, Hudaefi FA. A Scientometric Study on Management Literature in Southeast Asia. Journal of Risk and Financial Management. 2022; 15(11):507. https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm15110507
Chicago/Turabian StyleFirmansyah, Egi Arvian, Hairunnizam Wahid, Ardi Gunardi, and Fahmi Ali Hudaefi. 2022. "A Scientometric Study on Management Literature in Southeast Asia" Journal of Risk and Financial Management 15, no. 11: 507. https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm15110507
APA StyleFirmansyah, E. A., Wahid, H., Gunardi, A., & Hudaefi, F. A. (2022). A Scientometric Study on Management Literature in Southeast Asia. Journal of Risk and Financial Management, 15(11), 507. https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm15110507






