Abstract
The purpose of this study is to examine the relationship between credit rating scales and debt maturity choices. A liquidity hypothesis is used to formulate the testable proposition and conceptual framework. Generalized linear model (GLM) and pooled ordinary least square (OLS) are utilized by SAS programming to test the proposed hypothesis. Other different estimation techniques are also used for robust evidence. Results suggest that companies with high and low ratings have a shorter debt maturity. Companies with medium ratings have longer debt maturity structure. Liquidity shows a negative association with longer debt maturity structure. It is evident that at high rating scale with high liquidity, and at lower rating scales with lower liquidity firms have a shorter debt maturity. Mid rated firms with a low probability of refinancing risk show longer debt maturity structure. Considering refinancing risk by Asian companies make the nonlinear relationship between credit ratings and debt maturity choices. Results suggest the importance of credit ratings for the optimization of debt maturity structure of Asian firms, which was totally overlooked by the past studies. The findings of this study are consistent with the liquidity hypothesis. The findings also motivating financial managers and investors to consider credit ratings as a measure of financial constraints.
1. Introduction
There are several studies in the finance discipline that are mostly concentrated on the choice between debt and equity in the Asian markets, but there is another area of interest that is debt maturity structure, which can be of the same importance but is generally not a focus of financial research. There is rather little empirical evidence on the determinants of debt maturity structure of Asian firms.
The failure of non-financial institutions such as Lehman Brothers and the Bear Stearns during the recent financial crisis once again focused attention on the risk arising from short-term debts. It is now consistently recognized that the adjacent cause for the collapse of such institutions was their refinancing risk due to larger dependability on short-term debts, (Chen et al. 2013). The theoretical literature has acknowledged the refinancing risk arising from the short-term debt, (Dang and Phan 2016; Parise 2017). Optimal debt maturity choices play a vital role in the firm’s financial structure. It is assumed from previous studies that right proportion of short-term debt and long-term debt can decrease the cost of financing, (Fan et al. 2012; He and Milbradt 2016; Khurana and Wang 2015), agency cost (Flannery 1986), and information asymmetry, (Diamond 1991). (Diamond 1991) shows that in the “presence of credit market frictions, firms may face difficulty in rolling over short-term debt, especially if refinancing coincides with a deterioration in either firm fundamentals or credit market conditions”. The contemporary theoretical literature argues that refinancing or liquidity risk may itself be an additional source of credit risk because short-term debt increases the possibility of a run on the firm and worsen the conflict of interest between debt holders and shareholders, (Dimitrov et al. 2015; He et al. 2017; Wang and Zhang 2017).
Others have argued (Antoniou et al. 2006; Valta 2016) that the optimal debt maturity structure also reduces the cost of capital and bankruptcy risk. Some research (Wang and Zhang 2017) argues that even when there is an equal value of short-term debt and long-term debt, there is still a need for the right decision about the maturity of debt financing to avoid liquidity risk.
The selection of debt financing is dependent on the private information in which the management is concerned about the quality of the firm, (Öztekin and Flannery 2012). This fact can be related to the credit ratings that portray the quality of firms and reduces the information asymmetry between investors and borrowers. There is very little research on the importance of credit ratings in debt maturity choices, (Diamond 1991; Guedes and Opler 1996; Naeem 2012). The study of (Flannery 1986), on debt financing choices, is considered as one of the pioneering studies that put the focus on the importance of signaling in the debt maturity structure.
Credit rating agencies also obtain information from the public and private sectors which is crucial for firms so that they know about current and future economic trends. To be precise, to meet issuers’ demand for financial information, the credit rating agencies provide a clear and realistic financial picture of firms in terms of codes and symbols that fulfill the demands of the issuer. Moreover, credit rating provides accurate pricing of securities, and visibly reduces the cost of each transaction due to use of shortcodes. Therefore, it is expected that rated firms would gain the assistance of credit rating agencies to grab attention from investors. Credit ratings also provide perks of giving financial flexibility, decreasing the chances of incorrect and asymmetric information in the market (Lok and Richardson 2011).
In addition, credit ratings give encouragement to firms to sustain a good level of ratings in the market. Today, credit ratings are used by banks, plan sponsors, fund managers and trustees of financial firms not only in the US but also across the globe for financial portfolio management (Cantor 2004). The stature, pertinence, and value of credit rating agencies have ascended with the passage of time as it is clearly observed that investors and firms depend on these agencies for their output and performance. The inspiration for this investigation started with the perception that an organization’s financial managers, regulatory authorities, investors, and speculators are concerned about credit ratings when making their investment and financing choices. Credit ratings can also helpful for optimal debt maturity choices.
Generally, studies on debt maturity structures are based on the U.S. and European market, among those first papers is that of Morris (1976), which focused on U.S. companies. Moreover, other researchers also cover mainly U.S. firms (Scherr and Hulburt 2001; Stohs and Mauer 2002), and there is only a restricted list of studies focused on cross-country comparisons (Antoniou et al. 2006; Fan et al. 2012). In the emerging economies, there are limited studies on the corporate debt maturity structure, even there is no evidence on the relationship between credit ratings and the debt maturity structure of Asian firms. The aforementioned scenario also highlights the need for a considered approach towards financial risk management that would support firms in a changing financial environment. Asian financial markets, like other regions, have also observed a remarkable growth in the development of credit rating agencies. Therefore, a comprehensive study to examine the effect of credit ratings on the debt maturity structure of Asian firms is required. The main objective of this research is to “examine the relationship between credit ratings and the debt maturity structure of Asian firms”.
Moreover, this study is the first attempt to empirically examines the Diamond (1991) framework to elaborate the influence of each rating scale on the debt maturity choices and further complements it by assuming the importance of refinancing risk. Although there is a big lapse of academic literature on debt maturity structure for the Asian market, it is understood from the previous discussion that a different and distinct setting is presented by Asian markets providing an opportunity to analyze this issue with more elaboration. Therefore, in this context, the key research question of this study is as below:
Do credit rating scales have any explanatory power for the debt maturity structure of Asian companies? Or is there any relevance of the debt maturity structure of firms for credit ratings?
The paper is structured as follows. After the introduction, a literature review and theoretical framework are presented in Section 2. The Section 3 presents an explanation of research methodology and estimation procedure. Section 4 consists of the empirical results and interpretations. The Section 5 presents the conclusion of the paper.
2. Literature Review
Theoretical debate on debt maturity structure started from the proposition of (Stiglitz 1988), that the debt maturity structure of firms is irrelevant to their value in perfect capital markets; a rationale like the irrelevance proposition for capital structure of firms presented by (Modigliani and Miller 1958). As it is evident to understand that none of the capital markets is perfect, due to taxation, cash inflows, and outflows, information asymmetry, agency cost, and interest rate etc. Therefore, there are numerous empirical as well as theoretical studies that negate and challenge the idea of irrelevance propositions for determination of maturity structure of debt. Four theories have been established for studying the irrelevance proposition for debt maturity structure: (i) the hypothesis of agency costs; (ii) the asset maturity hypothesis; (iii) tax liabilities in debt maturity structures; (iv) signaling theories for debt maturity structure as well as information asymmetry.
Agency cost theory stated that the potential or absolute conflict between bondholders and shareholders can be reduced with the help of debt maturity structure (Jensen and Meckling 1976). The conflict can also originate when the firm’s capital structure has a risky debt inclusion to execute positive NPV (net present value) projects. These profits should be shared between bondholders and shareholders (Ataullah et al. 2018; Khurana and Wang 2015). There are some other ways argued by (Myers 1977), that the maturity debt reduction also reduces the underinvestment problems despite having other means of conflict resolution e.g., including restrictive covenants to debt contracts. Asset maturity hypothesis proposed that debt maturity has a risk of being unable to process fixed outflows of cash along with inflows that are generated by business processes. This risk can be mitigated with the matching of cash inflows and outflows (Myers and Majluf 1984). This can be a prevaricating policy for firms so that the maturity of the asset can be compatible with the debt maturity. In such cases, firms should have sufficient funds that are generated from assets.
(Brick and Ravid 1985) argued that a positive relationship is already established between the debt maturity structure and taxation, and the optimal strategy to work on the firms is to increase the long-term debt.
Signaling theory stated that the selection of debt maturity structure is dependent on the private information by which management is concerned about the quality of the firm. (Flannery 1986) are considered as pioneering studies that put the focus on the signaling of debt maturity structure. (Flannery 1986) proposed an argument that debt maturity structure of firms can indicate a firm’s quality to outsiders and can impact an investor’s decision. The model of Flannery proposes the assumption that the short-term debt is issued frequently for a long term can raise the fixed transaction cost of firms as compared to long-term debt.
There are numerous research studies that present an empirical view, specifying important factors established on theoretical models. The research design of many past studies relies on the firm’s level measures such as growth opportunities, size, matching for the maturity of assets, interest ratio, firm’s quality, liquidity etc. (Ataullah et al. 2018; Dang and Phan 2016; Katper et al. 2017). Moreover, some studies have been more focused on institutional or industrial classification, (Debortoli et al. 2017; Fan et al. 2012; Jõeveer 2013; Martins et al. 2017; Naeem 2012).
A firm’s financing decision is significantly affected by the economic environment of the country, particularly in the case of developing countries. Very few studies incorporate macroeconomic factors in financing decisions (Chen et al. 2013; Debortoli et al. 2017; Deesomsak et al. 2004; He et al. 2017; Wang and Zhang 2017; Sajjad and Zakaria 2018).
In advanced and third wave literature is an increasing number of studies investigating whether credit ratings issued by external credit rating agencies, such as Moody’s or Standard and Poor’s, are helpful in explaining firms’ financial structure behaviour (Chen et al. 2013; Chong et al. 2015; De Haan 2017; Efing and Hau 2015; Fracassi et al. 2016; Gopalan et al. 2014; Gul and Goodwin 2010; Naeem 2012; Sajjad and Zakaria 2018).
Since the complexity of financial markets and borrowers’ and lenders’ diversity is increasing, credit rating has now become a reliable parameter to assess the creditworthiness of firms, regulators, and investors (Kedia et al. 2017). The perceptional changes of market participants are mainly influenced by credit ratings issued by rating agencies. After that, numerous borrowers and different financial institutions have settled certain credit standards in the market and has successfully achieved the attention of regulatory bodies in various countries (Wojewodzki et al. 2017). To be precise, the 2008 financial crisis has made it important to search more into the importance of financial decision-making process for firm’s productivity. There are numerous advantages of rated firms i.e., extending the base of investors, accurate security pricing, and reduction of dependence on conventional funding sources e.g., debt markets. It is contended by (Bolton et al. 2012; CFR.org 2015; Chava et al. 2014) that even in the state of financial crises, firms with ratings are not facing any major issue in raising funds.
Two survey-based studies (Graham and Harvey 2000; Mittoo and Zhang 2008), on firms in US and European markets, claim that refinancing risk is another subsequent element which is considered by firms while making debt maturity structure decisions. Liquidity risk is also explored by past studies as an important determinant of debt maturity structure. Firms are likely to get liquidation and more costly financing if they become incapable of rolling over debt to the next period. In these cases, the costs and advantages of selecting a certain level of maturity in the financial structure can be evaluated from the prospect of liquidity risk. (Bancel and Mittoo 2004) show that 70% of a sample consider liquidity risk as the second major factor for debt maturity decisions. The increased liquidity risk of firms is also raised by the intensity of information asymmetry between lenders and borrowers (Bruche and Segura 2015; Chen et al. 2013; Mian and Santos 2017).
Diamond’s model suggests that short-term debt is not the priority of all firms. This fact can be related to the credit ratings that portray the quality of firms when the information is updated in a systematic manner for investors so that the issue of information asymmetry between investors and insiders can be resolved. (Diamond 1991) defines the liquidity risk as ‘... a solvent risk due to which the illiquid borrower becomes unable to attain an interest in refinancing parties’ (p. 710). After that, firms prefer to do trade off costs between the benefits of choosing short-term debt and the cost of liquidity risk. (Diamond 1991), stated that a non-monotonic relationship exists between debt maturity structure and liquidity risk as it is assessed by credit ratings. Low risk and high rated firms, and high risk and low rated firms tend to issue high debt for the short-term and intermediate firms having more issuance of long-term debt.
Numerous empirical studies test the non-monotonicity between credit ratings and financial structure based on the U.S. market. However, a mixed relationship is found. For example, (Barclay and Smith 1995) a study on U.S. firms is inconsistent with the non-monotonic relationship and (Naeem 2012; Stohs and Mauer 2002) find strong evidence of non-monotonicity between debt maturity structure and credit ratings by assuming liquidity risk.
Several studies in the literature have been conducted to determine the optimal debt maturity structure as well as the importance of credit ratings, but no empirical study has been conducted on the relevance of each credit rating scale for the optimization of debt maturity structure in Asian markets. The aforementioned research gaps leave some room for additional research. Hence, the purpose of this research is to investigate the importance of each rating scale for the optimal debt maturity structure of Asian firms. Country factors, firms’ factors, and industry dummies are also used as proxy measures for robust evidence. Therefore, by following the argument made by Diamond (1991), a hypothesis for the present study is suggested as follows:
Hypothesis (H1).
There is a non-linear (inverted U-shaped) relationship between rating scales and debt maturity choices by assuming liquidity risk, with other factors being steady.
Through a literature review, the following variables are identified for the theoretical framework of the present study. The dependent variable is longer debt maturity (DML), the independent variable is individual credit ratings (ICR) because this paper tests the explanatory power of each rating scale on the maturity structure of debts.
Control variables include a firm’s factors such as tangibility (FAR), interest coverage ratio (IR), quality (AR), liquidity (LIR), profitability (PR), size (SIZ). Industry dummies (ID) consist of nine industries classified by DataStream, (Basic material (BMD), consumer goods (CGD), consumer services (CSD), industrial (INDSD), technology (TECD), telecommunication (TELD), utility (UTILD), healthcare (HCD), oil and gas (OGD). Country factors are GDP growth (GD), domestic stock market (SM), real interest rate (RI), inflation rate (INF) (World bank database). Figure 1 shows the conceptual framework of the study.
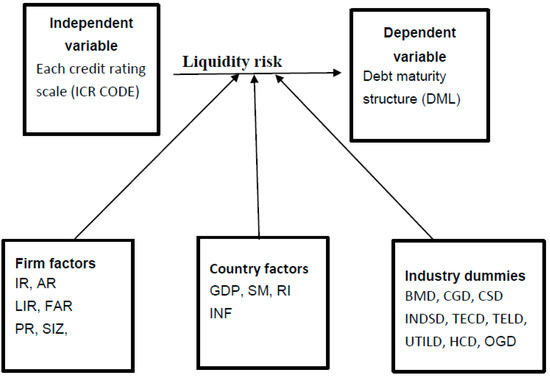
Figure 1.
A conceptual framework.
This study is expected to contribute to both the literature on the maturity structure of debts and on credit ratings by presenting empirical evidence to the formulated theoretical framework, that refinancing risk induces a non-linear inverted u-shaped relationship between each rating scale and the maturity structure of debt.
Although the theoretical and empirical literature identifies liquidity risk as an important determinant of debt maturity structure, (He and Xiong 2012; Parise 2017) but credit rating is totally ignored as an important determinant of debt maturity structure by past studies. Therefore, this study is unique in this context and expected to present novel findings of the non-linear relationship between rating scales and the maturity structure of debt for Asian firms by assuming liquidity risk.
3. Research Methodology
3.1. Model Specification and Data Selection
The research sample consists of non-financial listed Asian companies that are rated by Standard and Poor’s rating agency. A sample of Asian rated firms by Standard and Poor’s are small as compared to non-rated firms and the main objective of the study is to determine the optimal debt maturity structure of rated firms and their behavior according to each rating scale. Therefore, that sample is important to draw an accurate conclusion for a special group of rated firms and their behavior.
Non-financial companies are chosen from eight selected Asian regions (Japan, South Korea, Singapore, China, Hong Kong, Indonesia, Malaysia, India, (JSSCHIMI)). The financial data was extracted from DataStream based on nine industrial classifications. Long-term issuer credit ratings by Standard and Poor’s are used. Macroeconomic data are extracted from the World Bank database. Financial firms and firms with missing observations during sample years are excluded. For the empirical evidence the data set employed consists of the balanced panel data of 137 rated firms; for 17 years (2000–2016), resulting in 2329 observations.
The theoretical framework for this study comprised two aspects i.e., First the research studies on credit ratings and debt maturity structure. Second control variables include a firm’s factors, country factors, and industry dummies. A coding methodology is used to measure the credit ratings of each company and test the influence of credit assessment on debt maturity structure. According to (Kisgen 2006, 2009), coding schemes are established by the actual credit ratings given by Standard and Poor’s rating agency. A numerical code of 1 to 16 is allocated to each rating level or individual rating category (See Table 1).

Table 1.
Long-term issuer ratings and assigned numerical coding.
The theoretical framework is formulated from the extensive literature review and from Diamond’s 1991 liquidity hypothesis. Table 2 shows the selected variables of the current study, such as debt maturity ratio (longer debt maturity) as a dependent variable, credit ratings as an independent variable, control variables, (a firms’ factors, country factors, and industry dummies).

Table 2.
The theoretical framework.
3.2. Model for Maturity Structure of Debt and Credit Ratings
To empirically test the relevance of each rating scales and the debt maturity structure, following equation is specified. ICR2 is used to test the non-monotonic relationship between DML and ICR.
- DML = Debt maturity structure
- ICR = each rating scale/ individual credit rating
- ICR2 = Square of individual credit ratings
All other are control variables such as firm factors (IR, AR, FAR, LIR, PR, SIZ), Industry dummies (ID) and Country factors (GDP, SM, RI, INF).
3.3. Estimation Techniques
Generally, past studies on the corporate debt maturity structure were using pooled OLS. The present study is using a new technique that is a generalized linear model (GLM) along with pooled OLS for strong evidence. GLM represent a class of regression models that allow generalizing the linear regression to adjust many types of response variables including binary, count, continuous, positive and proportion distributions, (Fox 2008; Wulff 2007). It is considered a valuable statistical technique due to its flexibility in solving different statistical complication and is widely used. According to (Fox 2008), in the past twenty years, GLM has been referred as the most substantial development in regression analysis. GLM has “the ability to handle a larger class of error distributions and data types and this is the key improvement of GLMs over linear models”.
Moreover, for robust evidence and solving the different problems of data, such as endogeneity, autocorrelation and heteroskedasticity, estimation techniques such as fixed effect (FE), heteroskedastic consistent variance (HCV) and generalized method of moment (GMM) are employed to examine the influence of each rating scale on the debt maturity structure.
According to prior studies, dynamic panel models play a significant role in corporate finance research. Currently, GMM is extensively used for estimating dynamic financial structure decision, (Antoniou et al. 2008; Cheng 2014; Lu et al. 2015; Öztekin and Flannery 2012). The two-step GMM is employed in this study. For dynamic panel data, GMM is generally used in situations like heteroskedasticity, autocorrelation, fixed individual effect, endogeneity and if the data sample has small T time period and large individuals N”, (Cheng 2014; Sajjad and Zakaria 2018).
4. Results and Discussion
Descriptive statistics are presented before properly examining the link between the debt maturity structures and credit ratings. Table 3 shows the statistical summary of all variables including the dependent, independent, and control variables.

Table 3.
Descriptive statistics.
It is shown that the average longer debt maturity (DML) of the Asian companies is 0.510, and shorter debt maturity is 0.499. It is evident that the firms on average have a slightly higher amount of long-term debt. The deviations within the sample are considerable (standard deviation = 0.29). The result indicates that mainly companies wanted longer maturity in their debt maturity structure, which could be due to avoiding liquidity risk and underdeveloped bond market in Asia. Control variables also show some differences in the debt maturity structure of the Asian firms. In particular, the standard deviation is too much high in the interest coverage ratio (IR) = 177.4, and in the domestic stock market (SM) = 367.7. This could be due to firms being selected from heterogeneous markets from highly developed markets like Korea, Japan to less developed such as Indonesia and India etc.
Table 4 displays the mean of the shorter debt maturity and the longer debt maturity of the sample with respect to each credit rating scale. The higher-rated firms show mixed evidence for debt maturity structure. At AA+ rating with 1 coding number shows more short-term debts 0.53 (SM), and at code 1, and 2 with AA, AA− credit rating scales, long-term debts are higher in the debt maturity structure of firms, 0.542, 0.542, respectively. The average short-term debts are high at the top rating scales A+, A, A–. Moreover, at the lowest rating scale from BB+ to B–, firms show high short-term debt as compared to long-term debts, while BBB+, BBB, BBB– category of firms have the highest average longer debt maturity. The distribution of average short-term debt and long-term debt ratios provides initial evidence of being consistent with the theory of Diamond (1991), and with the intended hypotheses that suggested a non-linear association of credit rating scales and the debt maturity structure of Asian firms.

Table 4.
Mean of shorter and longer debt maturity at each rating scale.
Figure 2 illustrates the maturity structure of debt (DML) of the Asian firms with respect to each rating scale (ICR). Consistent with the results in Table 3, the maturity structure of debt shows a non-linear association with credit-rating scales.
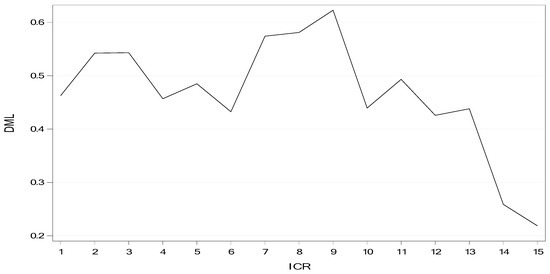
Figure 2.
Longer debt maturity and individual credit rating.
Proc Panel was used for pooled OLS, FE and GMM estimations, and Proc Genmod was used for the GLM technique in SAS programming.
Table 5 shows the findings of pooled OLS and generalized linear model (GLM). The individual credit rating ICR and its square ICR2 both are significant at a coefficient estimate of 0.039 *** and −0.0031 *** in the GLM. Results of pooled OLS also show that each credit rating (ICR) and its square ICR2 are significantly related to debt maturity structure (DML) at a coefficient estimate of 0.0392 *** and −0.0030 *** respectively. Moreover, a negative sign with ICR2 shows that with increasing rating scales longer debt maturity is decreasing. Results indicate that the longer-term debt maturity structure of firms in Asia varies with their credit ratings.

Table 5.
Influence of rating scales on the debt maturity structure.
It is evident that there is a non-linear association of credit rating scale with debt maturity structure of Asian firms. The coefficient estimates show that the debt maturity ratio increases by 3.9 percentage points with the exacerbation of each credit rating levels, but this rise has a declining rate of 0.31 percentage points with every squared individual credit rating level in both GLM and pooled OLS. The findings of the study supported the formulated hypothesis that “There is a non-linear (inverted U-shaped) relationship between rating scales and debt maturity choices by assuming liquidity risk, with other factors being steady”. It is also evident that at each rating scale the behavior of firm toward debt maturity choices is different and consideration of liquidity risk at different rating scale induces non-linear inverted u-shaped relationship between credit ratings and maturity choices of debt.
High-rated firms possess shorter maturity as compared to mid-level rating firms due to lower concerns about liquidity risk. Low-rated firms, even when they are prone to high liquidity risk, have shorter maturity. This is because of limited accessibility to the long-term debt market. This is an important piece of evidence and it has practical implications for the optimization of the debt maturity structure of Asian firms. The evidence is also supported by Diamond (1991) and is consistent with the U.S.-based studies (Barclay and Smith 1995; Stohs and Mauer 2002) and U.K. based studies (Naeem 2012).
Liquidity (LIR), shows a negative and significant relationship with longer debt maturity structure with coefficient estimates of −0.011***, and it is approximately the same in both the estimation techniques. The findings clearly show that when there is higher liquidity ratio, firms are inclined toward shorter debt financing into the firm’s financial structure. When there is a lower liquidity ratio or a higher rollover risk, then firms will prefer long-term debt financing in their debt maturity structure. Results also indicate that among the firm’s factors liquidity has larger and significant Wald-chi square (9.08) in GLM and (−3.0) in pooled OLS as compared to the firm’s other variables.
Interest coverage ratio (IR) and total assets turnover ratio (AR) show a negative and significant relationship with a longer debt maturity structure by both GLM and pooled OLS estimations. The tangibility ratio (FAR), shows a positive and significant relationship with longer debt maturity. Size (SIZ) shows a positive and less significant association with debt maturity structure. Profitability ratio (PR), shows a positive but insignificant relationship with the longer debt maturity structure.
Macroeconomic factors show mixed evidence in the current study. GDP growth (GD), shows negative and less significant association with a longer debt maturity of companies. Domestic stock market (SM,) shows a negative and significant relationship with longer debt maturity ratios. Inflation (INF), and real interest ratios (RI) show positive and significant association with longer debt maturity structure by both GLM and pooled OLS estimations.
All industrial dummies show a positive and significant relationship with longer debt maturity structure of Asian firms except the healthcare industry, which shows a positive and insignificant relationship with the longer debt maturity structure of Asian firms. It is evident that it is mainly industries in Asia that have longer debt maturity structure. This could be one of the reasons for avoiding liquidity or rollover risk in their corporate financial decisions.
Robust Check by Other Estimation Techniques
Table 6 shows the impact of each rating scale on the debt maturity structure by the fixed effect method (FE), heteroskedastic consistent variance (HCV), and generalized method of moment (GMM). The evidence is consistent with the findings of the generalized linear model (GLM) and pooled OLS estimations.

Table 6.
Credit ratings and maturity structure of debt.
Longer debt maturity shows a positive and significant relationship with each rating scale at 0.0692 ***, 0.03922 ***, 0.22130 *** coefficient estimates respectively by all three estimation techniques. Moreover, ICR2 shows a negative and significant relationship with longer debt maturity structure at −0.0045 ***, −0.003 ***, and −0.012 *** respectively, by fixed effect (FE), heteroskedastic consistent variance (HCV) and generalized method of moment (GMM). It is evident that the impact of each rating scale on the debt maturity structure is non-linear and inverted U-shaped. FAR and SM are used as an exogenous instrument. The Sargan test statistic 50.67 (PR = 0.168) shows that the selected instrumental variables are valid and does not show any over-identification problem in the GMM estimation. All variables jointly explain 13% variation within the debt maturity structure by the heteroskedastic consistent variance (HCV) estimation. R2 by fixed effect (FE) increased and explains 48% variation in debt maturity structure by all variables. Control variables show mixed evidence. Liquidity (LIR) shows a negative and significant relationship with longer debt maturity structure by HCV and GMM estimations but shows a positive and insignificant relationship with longer debt maturity structure by the fixed effect (FE) model.
5. Conclusions
The purpose of the study is to examine the impact of each rating scale on debt maturity structure. The study proposed a conceptual framework of credit ratings (ICR) and debt maturity structure (DML) with control variables such as firms’ factors, industry dummies, and macroeconomic variables. The study also empirically tested Diamond’s liquidity hypothesis, which gives the theoretical basis for two variables DMT and ICR. Estimation techniques such as the generalized linear model (GLM), pooled OLS, fixed effect (FE), heteroskedastic consistent variance (HCV) and generalized method of moment (GMM) were used. The findings of the study indicate that high-rated firms show mixed evidence and have slightly more short-term debt, but long-term debts are also not too low that can be due to less information asymmetry which decreases the liquidity risk and easy access to financial markets. Low-rated firms face high refinancing risk due to the deterioration in credit ratings and consequently face restricted access to long-term debt markets, and so they have short-term debt in their debt maturity structure. Only mid-rated firms prefer more long-term debt because they have an option for long-term debt maturity and they also have a certain amount of liquidity risk, which stops them from increasing shorter maturity in their debt maturity structures. Results also indicate that maximum industry dummies show a positive and significant association with the longer debt maturity structure of Asian companies. Among financial variables of firms, liquidity shows a significant and negative association with longer debt maturity structure. Macroeconomic factors also show a substantial effect on the debt maturity structure of Asian companies.
The findings of the study have answered the main research question and proved the hypothesis that there is a non-monotonic relationship between the credit-rating scales and debt maturity choices of Asian firms. The evidence is also supported by Diamond’s (1991) theoretical framework and is consistent with U.S.-based studies (Barclay and Smith 1995; Stohs and Mauer 2002) and U.K. based studies (Naeem 2012), Moreover, the importance of credit ratings in the financial structure is also supported by previous studies (Bedendo and Siming 2016; Daniels et al. 2010; Gul and Goodwin 2010; Lütkebohmert et al. 2017; Naeem 2012). The study also reveals that credit rating has a substantial effect on the optimization of debt maturity structure of Asian companies.
Credit ratings should be considered as a key determinant for making financing decisions. Credit rating agency assigns credit rating codes after analyzing internal and external factors of firms that help to reduce information asymmetry. Findings also suggested that credit ratings have significant explanatory power for debt maturity structure and gives unique insight to capture the behavior of firms toward debt financing choices by considering the cost and benefits of credit ratings such as, liquidity risk, creditworthiness of firms, the loyalty of customers and suppliers, restriction to enter into debt market, costly covenants, access to commercial paper market etc.
This study is useful for chief financial officers (CFOs) in firms wishing to make optimal financing decisions. Regulatory bodies and policymakers can benefit by considering credit ratings as a regulatory tool in financial market development and should monitor and regulate credit-rating agencies for transparent credit-rating outcomes.
Like most research studies, this study also has some limitations. This study has a limited number of rated Asian firms from Standard and Poor’s rating agency. Thus, it cannot investigate the impact on a broader range of data. Future studies on the debt maturity structure may also employ different financial and macroeconomic ratios. Different rating categories and rating indexes can also be implied in future research. Data from local and other international rating agencies can also be used for further research.
Supplementary Files
Supplementary File 1Author Contributions
F.S. wrote the paper and M.Z. supervised and edited the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Antoniou, Antonios, Yilmaz Guney, and Krishna Paudyal. 2006. The Determinants of Debt Maturity Structure: Evidence from France, Germany and UK. European Financial Management 12: 161–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniou, Antonios, Yilmaz Guney, and Krishna Paudyal. 2008. The Determinants of Capital Structure: Capital Market-Oriented versus Bank-Oriented Institutions. Journal of Financial and Quantitative Analysis 43: 59–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataullah, Ali, Andrew Vivian, and Bin Xu. 2018. Time-varying managerial overconfidence and corporate debt maturity structure. European Journal of Finance 24: 157–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bancel, Franck, and Usha R. Mittoo. 2004. The Determinants of Capital Structure Choice : A Survey of European Firms. Financial Management 33: 103–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barclay, Michael J., and Clifford W. Smith, Jr. 1995. The Maturity Structure of Corporate Debt. The Journal of Finance 50: 609–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedendo, Mascia, and Linus Siming. 2016. Debt structure and credit ratings. Working Paper. Available online: ftp://ftp.repec.org/opt/ReDIF/RePEc/baf/papers/cbafwp1622.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2018).
- Bolton, Patrick, Xavier Freixas, and Joel Shapiro. 2012. The credit ratings game. Journal of Finance 67: 85–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brick, Ivan E., and S. Abraham Ravid. 1985. On the Relevance of Debt Maturity Structure. The Journal of Finance 40: 1423–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruche, Max, and Anatoli Segura. 2015. Debt maturity and the liquidity of secondary debt markets. Journal of Financial Economics 124: 599–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantor, Richard. 2004. An introduction to recent research on credit ratings. Journal of Banking and Finance 28: 2565–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Credit Rating Controversy. 2015. CFR Backgrounders. pp. 1–5. Available online: http://www.cfr.org/financial-crises/credit-rating-controversy/p22328 (accessed on 20 January 2018).
- Chava, Sudheer, Rohan Ganduri, and Chayawat Ornthanalai. 2014. Are Credit Ratings Still Relevant? Working Paper. Available online: https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.2023998 (accessed on 20 January 2018).
- Chen, Hui, Yu Xu, and Jun Yang. 2013. Systematic Risk, Debt Maturity, and the Term Structure of Credit Spreads. Working Paper No. 18367. Cambridge, MA, USA: National Bureau of Economic Research. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Hang. 2014. Determinants of Capital Structure in Asian Firms: New Evidence on the Role of Firm-Level Factors, Industry Characteristics, and Institutions. Ph.D. dissertation, University of Leicester, Leicester, UK. unpublished. [Google Scholar]
- Chong, Byung, In Deokand Hwang, and Young Sang Kim. 2015. Credit ratings and short-term debt financing: An empirical analysis of listed firms in Korea. Asia-Pacific Journal of Financial Studies 44: 88–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Viet A., and Hieu V. Phan. 2016. CEO inside debt and corporate debt maturity structure. Journal of Banking and Finance 70: 38–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, Kenneth, Demissew Diro Ejara, and Jayaraman Vijayakumar. 2010. Debt maturity, credit risk, and information asymmetry: The case of municipal bonds. Financial Review 45: 603–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debortoli, Davide, Ricardo Nunes, and Pierre Yared. 2017. Optimal time-consistent government debt maturity. Quarterly Journal of Economics 132: 55–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deesomsak, Rataporn, Krishna Paudyal, and Gioia Pescetto. 2004. The determinants of capital structure: Evidence from the Asia Pacific region. Journal of Multinational Financial Management 14: 387–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Haan, Ed. 2017. The financial crisis and corporate credit ratings. Accounting Review 9: 161–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, Douglas W. 1991. Debt Maturity Structure and Liquidity Risk. Quarterly Journal of Economics 106: 709–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, Valentinand, Darius Palia, and Leo Tang. 2015. Impact of the Dodd-Frank act on credit ratings. Journal of Financial Economics 115: 505–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efing, Matthias, and Harald Hau. 2015. Structured debt ratings: Evidence on conflicts of interest. Journal of Financial Economics 116: 46–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fan, Joseph P.H., Sheridan Titman, and Garry Twite. 2012. An International Comparison of Capital Structure and Debt Maturity Choices. Journal of Financial and Quantitative Analysis 47: 23–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flannery, Mark J. 1986. Asymmetric Information and Risky Debt Maturity Choice. The Journal of Finance 41: 19–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, John. 2008. Generalized Linear Models. Applied Regression Analysis and Generalized Linear Models 135: 379–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fracassi, Cesare, Stefan Petry, and Geoffrey Tate. 2016. Does rating analyst subjectivity affect corporate debt pricing? Journal of Financial Economics 120: 514–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalan, Radhakrishnan, Fenghua Song, and Vijay Yerramilli. 2014. Debt Maturity Structure and Credit Quality. Journal of Financial and Quantitative Analysis 49: 817–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, John R., and Campbell R. Harvey. 2000. The Theory and Practice of Corporate Finance: Evidence from the Field. Available online: http://ecsocman.hse.ru/data/030/124/1231/Empirich_issled_po_byudzh_i_dr_Graham2000.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2018).
- Guedes, Jose, and Tim Opler. 1996. The Determinants of the Maturity of Corporate Debt Issues. The Journal of Finance 51: 1809–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, Ferdinand A., and John Goodwin. 2010. Short-Term debt maturity structures, credit ratings, and the pricing of audit services. Accounting Review 85: 877–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Zhiguo, and Konstantin Milbradt. 2016. Dynamic Debt Maturity. Review of Financial Studies 29: 2677–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Zhiguo, and Wei Xiong. 2012. Rollover Risk and Credit Risk. Journal of Finance 67: 391–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Xue Zhong, Eva Lütkebohmert, and Yajun Xiao. 2017. Rollover risk and credit risk under time-varying margin. Quantitative Finance 17: 455–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, Michael C., and William H. Meckling. 1976. Theory of the firm: Managerial behavior, agency costs, and ownership structure. Journal of Financial Economics 3: 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jõeveer, Karin. 2013. Firm, country and macroeconomic determinants of capital structure: Evidence from transition economies. Journal of Comparative Economics 41: 294–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katper, Naveeda K., Aziman Madun, Karim Bux Syed, and Muhammad Nawaz Tunio. 2017. Determinants of debt maturity structure in Shariah and non-Shariah firms in Pakistan: A comparative study. Journal of Applied Economic Sciences 12: 1210–25. [Google Scholar]
- . Kedia, Simi, Shivaram Rajgopal, and Xing Alex Zhou. 2017. Large shareholders and credit ratings. Journal of Financial Economics 124: 632–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurana, Inder K., and Changjiang Wang. 2015. Debt maturity structure and accounting conservatism. Journal of Business Finance and Accounting 42: 167–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisgen, Darren J. 2006. Credit ratings and capital structure. The Journal of Finance 61: 1035–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisgen, Darren J. 2009. Do firms target credit ratings or leverage levels? Journal of Financial and Quantitative Analysis 44: 1323–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lok, Stephen, and Scott Richardson. 2011. Credit markets and financial information. Review of Accounting Studies 16: 487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Yang Cheng, Yu Chen Wei, and Tsang Yao Chang. 2015. The effects and applicability of financial media reports on corporate default ratings. International Review of Economics and Finance 36: 69–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lütkebohmert, Eva, Daniel Oeltz, and Yajun Xiao. 2017. Endogenous Credit Spreads and Optimal Debt Financing Structure in the Presence of Liquidity Risk. European Financial Management 23: 55–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, Henrique C., Eduardo Schiehll, and Paulo R. S. Terra. 2017. Country-level governance quality, ownership concentration, and debt maturity: A comparative study of Brazil and Chile. Corporate Governance: An International Review 25: 236–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mian, Atif, and João A.C. Santos. 2017. Liquidity risk and maturity management over the credit cycle. Journal of Financial Economics 127: 264–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittoo, Usha R., and Zhou Zhang. 2008. The capital structure of multinational corporations: Canadian versus U.S. evidence. Journal of Corporate Finance 14: 706–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modigliani, Franco, and Merton H. Miller. 1958. The Cost of Capital, Corporation Finance and the Theory of Investment. American Economic Review 48: 261–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, James R. 1976. On Corporate Debt Maturity Strategies. Journal of Finance 31: 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- . Myers, Stewart C. 1977. Determinants of corporate structure. Journal of Financial Economics 5: 147–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- . Myers, Stewart C., and Nicholas S. Majluf. 1984. Corporate financing and investmentdecisions when firms have information that investors do not have. Journal of Financial Economics 13: 187–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeem, Shammyla. 2012. Financial Structure of UK Firms: The Influence of Credit Rating. Ph.D. thesis, University of Glasgow, Glasgow, UK; p. 371. [Google Scholar]
- Öztekin, Özde, and Mark J. Flannery. 2012. Institutional determinants of capital structure adjustment speeds. Journal of Financial Economics 103: 88–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parise, Gianpaolo. 2017. Threat of entry and debt maturity: Evidence from airlines. Journal of Financial Economics 127: 226–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faiza Sajjad, Muhammad Zakaria. 2018. Credit Rating as a Mechanism for Capital Structure Optimization: Empirical Evidence from Panel Data Analysis. International Journal of Financial Studies 6: 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CScherr, Frederick, and Heather M. Hulburt. 2001. The debt maturity structure of small firms. Financial Management 30: 85–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiglitz, Joseph E. 1988. Why Financial Structure Matters. Journal of Economic Perspectives 2: 121–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mark Hoven Stohs, David C. Mauer. 2002. The Determinants of Corporate Debt Maturity Structure. Journal of Business 69: 279–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valta, Philip. 2016. Strategic Default, Debt Structure, and Stock Returns. Journal of Financial and Quantitative Analysis 51: 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Haiping, and Jing Zhang. 2017. Fair value accounting and corporate debt structure. Advances in Accounting 37: 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojewodzki, Michal, Winnie P.H. Poon, and Jianfu Shen. 2017. The role of credit ratings on capital structure and its speed of adjustment: An international study. European Journal of Finance 24: 735–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulff, Shaun S. 2007. SAS for Mixed Models. The American Statistician 61: 184–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).