Low Renalase Levels in Newly Diagnosed CML: Dysregulation Sensitive to Modulation by Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
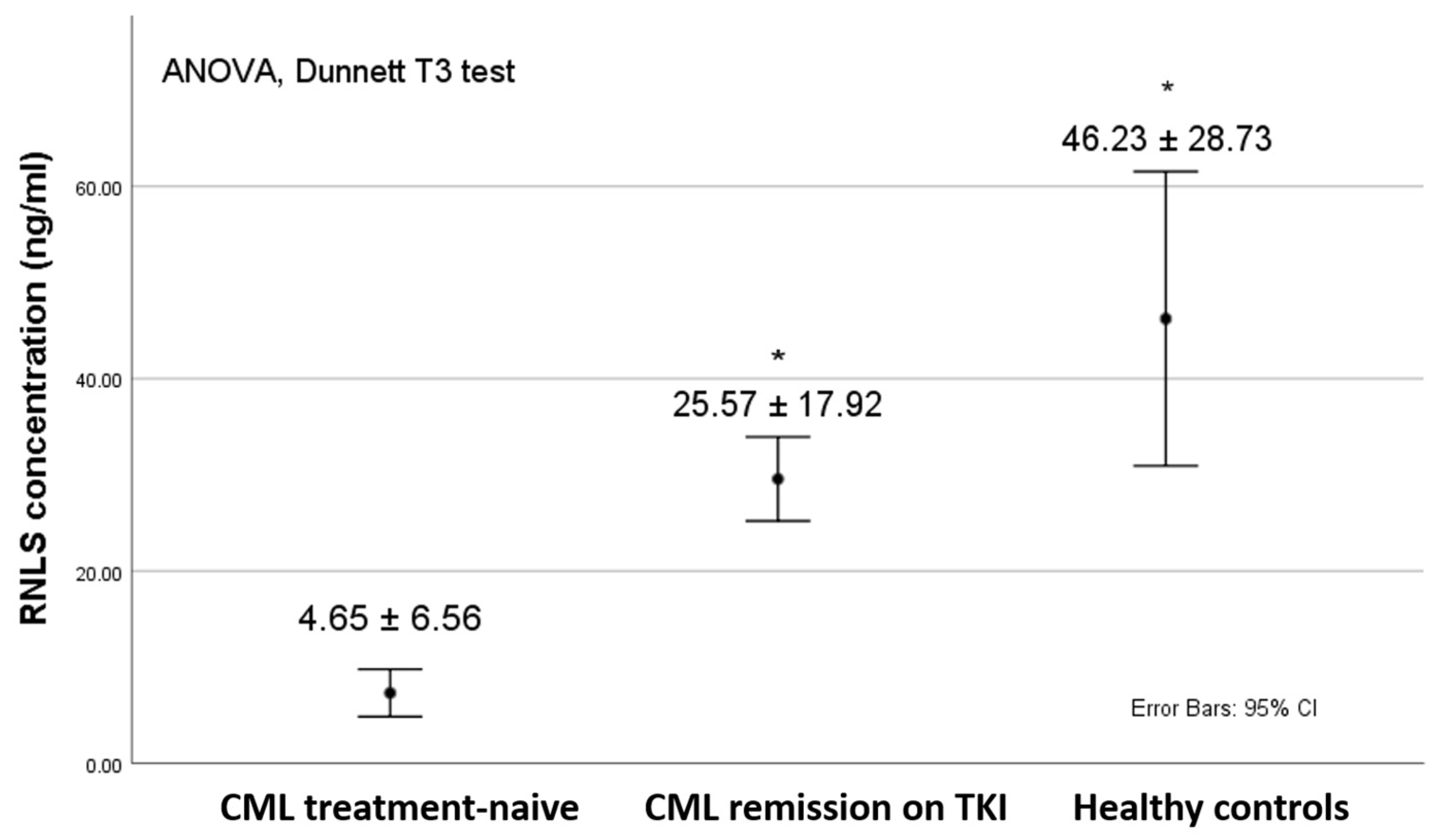
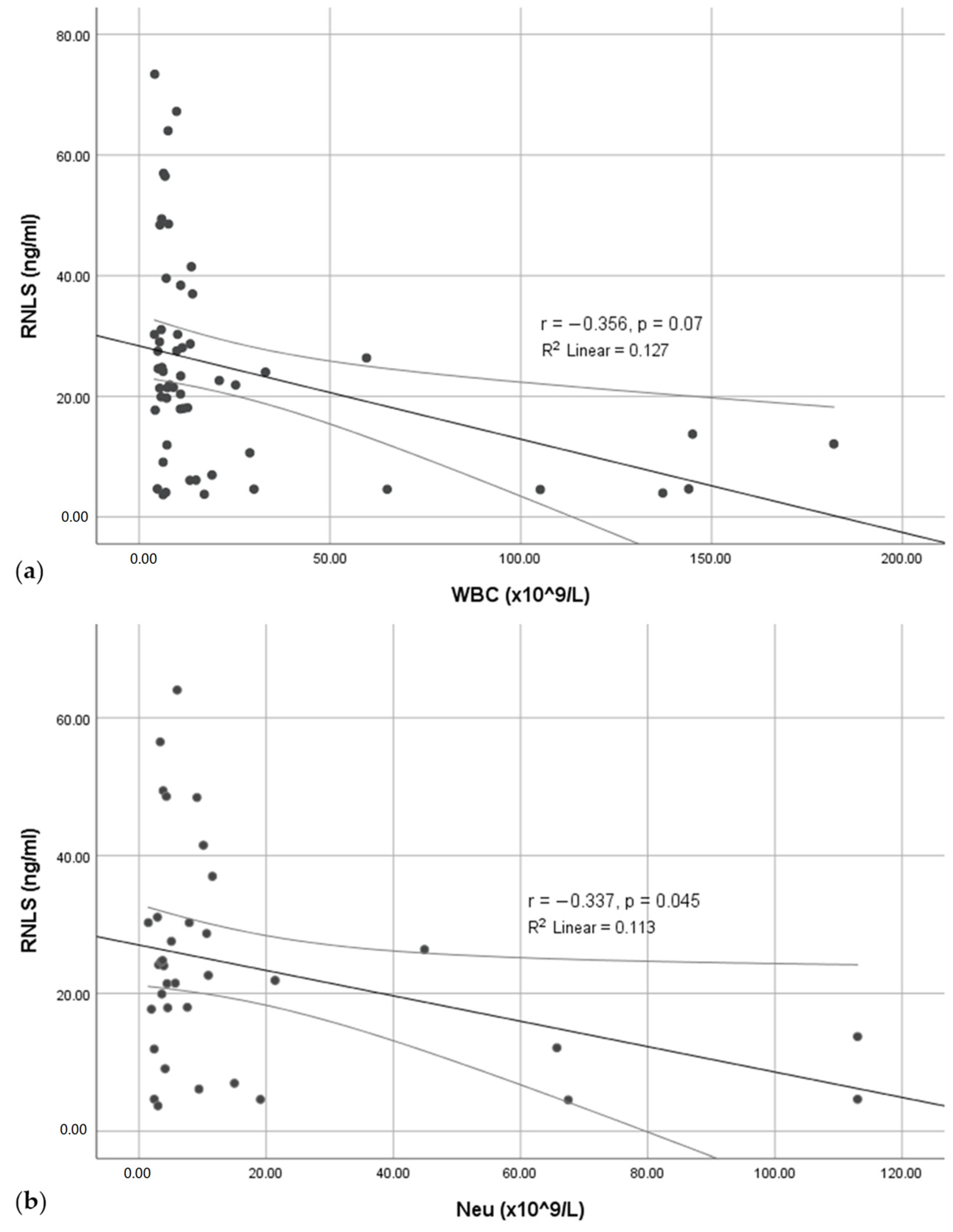
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fisher, D.A.C.; Fowles, J.S.; Zhou, A.; Oh, S.T. Inflammatory Pathophysiology as a Contributor to Myeloproliferative Neoplasms. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 683401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallipoli, P.; Pellicano, F.; Morrison, H.; Laidlaw, K.; Allan, E.K.; Bhatia, R.; Copland, M.; Jørgensen, H.G.; Holyoake, T.L. Autocrine TNF-alpha production supports CML stem and progenitor cell survival and enhances their proliferation. Blood 2013, 122, 3335–3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoury, J.D.; Solary, E.; Abla, O.; Akkari, Y.; Alaggio, R.; Apperley, J.F.; Bejar, R.; Berti, E.; Busque, L.; Chan, J.K.C.; et al. The 5th edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Haematolymphoid Tumours: Myeloid and Histiocytic/Dendritic Neoplasms. Leukemia 2022, 36, 1703–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welner, R.S.; Amabile, G.; Bararia, D.; Czibere, A.; Yang, H.; Zhang, H.; Pontes, L.L.; Ye, M.; Levantini, E.; Di Ruscio, A.; et al. Treatment of chronic myelogenous leukemia by blocking cytokine alterations found in normal stem and progenitor cells. Cancer Cell 2015, 27, 671–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, N.; Liu, S.; Cui, J.; Li, Q.; You, Y.; Zhong, Z.; Cheng, F.; Guo, A.Y.; Zou, P.; Yuan, G.; et al. Tumor necrosis factor α knockout impaired tumorigenesis in chronic myeloid leukemia cells partly by metabolism modification and miRNA regulation. Onco Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 2355–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pophali, P.A.; Patnaik, M.M. The Role of New Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Cancer J. 2016, 22, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amarante-Mendes, G.P.; Rana, A.; Datoguia, T.S.; Hamerschlak, N.; Brumatti, G. BCR-ABL1 Tyrosine Kinase Complex Signaling Transduction: Challenges to Overcome Resistance in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleppe, M.; Kwak, M.; Koppikar, P.; Riester, M.; Keller, M.; Bastian, L.; Hricik, T.; Bhagwat, N.; McKenney, A.S.; Papalexi, E.; et al. JAK-STAT pathway activation in malignant and nonmalignant cells contributes to MPN pathogenesis and therapeutic response. Cancer Discov. 2015, 5, 316–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, J.J.; Ong, S.T. Therapy Resistance and Disease Progression in CML: Mechanistic Links and Therapeutic Strategies. Curr. Hematol. Malig. Rep. 2022, 17, 181–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudel, G.; Tolland, M.G.; Hughes, T.P.; Pagani, I.S. Mechanisms of Resistance and Implications for Treatment Strategies in Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia. Cancers 2022, 14, 3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrà, G.; Torti, D.; Crivellaro, S.; Panuzzo, C.; Taulli, R.; Cilloni, D.; Guerrasio, A.; Saglio, G.; Morotti, A. The BCR-ABL/NF-κB signal transduction network: A long lasting relationship in Philadelphia positive Leukemias. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 66287–66298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zuo, X. Cytokines frequently implicated in myeloproliferative neoplasms. Cytokine: X 2019, 1, 100005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pointer, T.C.; Gorelick, F.; Desir, G.V. Renalase: A Multi-Functional Signaling Molecule with Roles in Gastrointestinal Disease. Cells 2021, 10, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czerwińska, K.; Poręba, R.; Gać, P. Renalase—A new understanding of its enzymatic and non-enzymatic activity and its implications for future research. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2022, 49, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuepper, M.K.; Bütow, M.; Herrmann, O.; Ziemons, J.; Chatain, N.; Maurer, A.; Kirschner, M.; Maié, T.; Costa, I.G.; Eschweiler, J.; et al. Stem cell persistence in CML is mediated by extrinsically activated JAK1-STAT3 signaling. Leukemia 2019, 33, 1964–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanovic, D.; Stojanovic, M.; Milenkovic, J.; Velickov, A.; Ignjatovic, A.; Milojkovic, M. The Multi-Faceted Nature of Renalase for Mitochondrial Dysfunction Improvement in Cardiac Disease. Cells 2023, 12, 1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czubilińska-Łada, J.; Gliwińska, A.; Badeński, A.; Szczepańska, M. Associations between renalase concentration and the occurrence of selected diseases. Endokrynol. Pol. 2020, 71, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Safirstein, R.; Velazquez, H.; Guo, X.J.; Hollander, L.; Chang, J.; Chen, T.M.; Mu, J.J.; Desir, G.V. Extracellular renalase protects cells and organs by outside-in signalling. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2017, 21, 1260–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanovic, D.; Stojanovic, M.; Milenkovic, J.; Velickov, A.; Ignjatovic, A.; Milojkovic, M. Renalase Challenges the Oxidative Stress and Fibroproliferative Response in COVID-19. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2022, 2022, 4032704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaupre, B.A.; Hoag, M.R.; Roman, J.; Försterling, F.H.; Moran, G.R. Metabolic function for human renalase: Oxidation of isomeric forms of β-NAD(P)H that are inhibitory to primary metabolism. Biochemistry 2015, 54, 795–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Han, P.; Wang, J.; Sun, H.; Shao, M. Renalase overexpression in ER-positive breast cancer. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2018, 11, 1297–1307. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Jessel, S.; Qu, R.; Kluger, Y.; Chen, T.M.; Hollander, L.; Safirstein, R.; Nelson, B.; Cha, C.; Bosenberg, M.; et al. Inhibition of renalase drives tumour rejection by promoting T cell activation. Eur. J. Cancer 2022, 165, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Hollander, L.; MacPherson, D.; Wang, L.; Velazquez, H.; Chang, J.; Safirstein, R.; Cha, C.; Gorelick, F.; Desir, G.V. Inhibition of renalase expression and signaling has antitumor activity in pancreatic cancer. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollander, L.; Guo, X.; Velazquez, H.; Chang, J.; Safirstein, R.; Kluger, H.; Cha, C.; Desir, G.V. Renalase Expression by Melanoma and Tumor-Associated Macrophages Promotes Tumor Growth through a STAT3-Mediated Mechanism. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 3884–3894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, M.; Guo, X.; Hu, J.; Chen, T.M.; Finn, S.M.B.; Lacy, J.; Kunstman, J.W.; Cha, C.H.; Bellin, M.D.; et al. Renalase is a novel tissue and serological biomarker in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0250539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, L.; Deng, D.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, W. Renalase Protects against Renal Fibrosis by Inhibiting the Activation of the ERK Signaling Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safdar, B.; Wang, M.; Guo, X.; Cha, C.; Chun, H.J.; Deng, Y.; Dziura, J.; El-Khoury, J.M.; Gorelick, F.; Ko, A.I.; et al. Association of renalase with clinical outcomes in hospitalized patients with COVID-19. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0264178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branford, S. Why is it critical to achieve a deep molecular response in chronic myeloid leukemia? Haematologica 2020, 105, 2730–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaker, E.; Nouri, N.; Sorkhizadeh, S.; Ghasemirad, H.; Hossein Hajijafari, A.; Zare, F. The importance of personalized medicine in chronic myeloid leukemia management: A narrative review. Egypt. J. Med. Hum. Genet. 2023, 24, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonawane, P.J.; Gupta, V.; Sasi, B.K.; Kalyani, A.; Natarajan, B.; Khan, A.A.; Sahu, B.S.; Mahapatra, N.R. Transcriptional regulation of the novel monoamine oxidase renalase: Crucial roles of transcription factors Sp1, STAT3, and ZBP89. Biochemistry 2014, 53, 6878–6892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayakumar, A.; Mahapatra, N.R. Renalase: A novel regulator of cardiometabolic and renal diseases. Hypertens. Res. 2022, 45, 1582–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serwin, N.; Cecerska-Heryć, E.; Pius-Sadowska, E.; Serwin, K.; Niedźwiedź, A.; Wiśniewska, M.; Roszak, M.; Grygorcewicz, B.; Skwirczyńska, E.; Machaliński, B.; et al. Renal and Inflammation Markers-Renalase, Cystatin C, and NGAL Levels in Asymptomatic and Symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infection in a One-Month Follow-Up Study. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gok Oguz, E.; Akoglu, H.; Ulusal Okyay, G.; Karaveli Gursoy, G.; Yildirim, T.; Merhametsiz, O.; Cimen, T.; Canbakan, B.; Yeter, E.; Ayli, M.D. Increased serum renalase in peritoneal dialysis patients: Is it related to cardiovascular disease risk? Nefrol. Publ. Soc. Esp. Nefrol. 2017, 37, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madapura, H.S.; Nagy, N.; Ujvari, D.; Kallas, T.; Kröhnke, M.C.L.; Amu, S.; Björkholm, M.; Stenke, L.; Mandal, P.K.; McMurray, J.S.; et al. Interferon γ is a STAT1-dependent direct inducer of BCL6 expression in imatinib-treated chronic myeloid leukemia cells. Oncogene 2017, 36, 4619–4628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warsch, W.; Grundschober, E.; Sexl, V. Adding a new facet to STAT5 in CML: Multitasking for leukemic cells. Cell Cycle 2013, 12, 1813–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Brachet-Botineau, M.; Polomski, M.; Neubauer, H.A.; Juen, L.; Hédou, D.; Viaud-Massuard, M.C.; Prié, G.; Gouilleux, F. Pharmacological Inhibition of Oncogenic STAT3 and STAT5 Signaling in Hematopoietic Cancers. Cancers 2020, 12, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wingelhofer, B.; Neubauer, H.A.; Valent, P.; Han, X.; Constantinescu, S.N.; Gunning, P.T.; Müller, M.; Moriggl, R. Implications of STAT3 and STAT5 signaling on gene regulation and chromatin remodeling in hematopoietic cancer. Leukemia 2018, 32, 1713–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vainchenker, W.; Kralovics, R. Genetic basis and molecular pathophysiology of classical myeloproliferative neoplasms. Blood 2017, 129, 667–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, S.R.; Nelson, E.A.; Yeh, J.E.; Pinello, L.; Yuan, G.C.; Frank, D.A. STAT5 outcompetes STAT3 to regulate the expression of the oncogenic transcriptional modulator BCL6. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013, 33, 2879–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ujvari, D.; Malyukova, A.; Zovko, A.; Yektaei-Karin, E.; Madapura, H.S.; Keszei, M.; Nagy, N.; Lotfi, K.; Björn, N.; Wallvik, J.; et al. IFNγ directly counteracts imatinib-induced apoptosis of primary human CD34+ CML stem/progenitor cells potentially through the upregulation of multiple key survival factors. Oncoimmunology 2022, 11, 2109861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.B.; Nemkov, T.; Stefanoni, D.; Benavides, G.A.; Bassal, M.A.; Crown, B.L.; Matkins, V.R.; Camacho, V.; Kuznetsova, V.; Hoang, A.T.; et al. Metabolic alterations mediated by STAT3 promotes drug persistence in CML. Leukemia 2021, 35, 3371–3382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Beauchamp, L.; Himonas, E.; Helgason, G.V. Mitochondrial metabolism as a potential therapeutic target in myeloid leukaemia. Leukemia 2022, 36, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, A.; Qiu, S.; Chacko, B.K.; Li, H.; Paterson, A.; He, J.; Agarwal, P.; Shah, M.; Welner, R.; Darley-Usmar, V.M.; et al. SIRT1 regulates metabolism and leukemogenic potential in CML stem cells. J. Clin. Invest. 2019, 129, 2685–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tošić, I.; Frank, D.A. STAT3 as a mediator of oncogenic cellular metabolism: Pathogenic and therapeutic implications. Neoplasia 2021, 23, 1167–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Gu, J.; Guo, J.; Chen, K.; Li, H.; Wang, J. Renalase Attenuates Mouse Fatty Liver Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury through Mitigating Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Damage via Activating SIRT1. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2019, 2019, 7534285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Adane, B.; Khan, N.; Sullivan, T.; Minhajuddin, M.; Gasparetto, M.; Stevens, B.; Pei, S.; Balys, M.; Ashton, J.M.; et al. Leukemic Stem Cells Evade Chemotherapy by Metabolic Adaptation to an Adipose Tissue Niche. Cell Stem Cell 2016, 19, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bode, K.; Wei, S.; Gruber, I.; Kissler, S.; Yi, P. Beta Cells Deficient for Renalase Counteract Autoimmunity by Shaping Natural Killer Cell Activity. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1403752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| CML No Treatment | CML with TKI | Controls | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 58.5 ± 19.2 | 59.2 ± 12.6 | 55.7 ± 11.1 |
| Gender, male (n (%)) | 11 (55%) | 24 (43.6%) | 10 (50%) |
| Sokal score | - | ||
| low | 7 (35%) | 17 (31%) | - |
| intermediate | 12 (60%) | 38 (69%) | - |
| high | 1 (5%) | 0 | - |
| WBC (×109/L) | 25.00 ± 99.90 *,† | 7.50 ± 5.20 | 5.72 ± 0.87 |
| NEU (×109/L) | 17.05 ± 58.21 * | 4.40 ± 5.78 | 3.05 ± 0.85 |
| LYM (×109/L) | 6.30 ± 14.61 * | 2.70 ± 1.81 | 2.20 ± 0.21 |
| BAS (×109/L) | 0.56 ± 3.81 | 0.14 ± 1.89 | 0.61 ± 0.73 |
| PLT (×109/L) | 376.66 ± 258.09 *,† | 294.36 ± 204.00 † | 204.75 ± 25.15 |
| RBC (×1012/L) | 3.29 ± 0.93 *,† | 4.32 ± 0.92 † | 4.45 ± 0.46 |
| HGB (g/L) | 114.50 ± 27.73 | 128.15 ± 24.49 | 133.17 ± 12.90 |
| CRP (mg/L) | 4.00 ± 7.35 † | 3.10 ± 3.18 † | 0.12 ± 0.06 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Milenkovic, J.; Stojanovic, D.; Velickovic, S.; Djordjevic, B.; Marjanovic, G.; Milojkovic, M. Low Renalase Levels in Newly Diagnosed CML: Dysregulation Sensitive to Modulation by Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Pathophysiology 2024, 31, 787-796. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology31040053
Milenkovic J, Stojanovic D, Velickovic S, Djordjevic B, Marjanovic G, Milojkovic M. Low Renalase Levels in Newly Diagnosed CML: Dysregulation Sensitive to Modulation by Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Pathophysiology. 2024; 31(4):787-796. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology31040053
Chicago/Turabian StyleMilenkovic, Jelena, Dijana Stojanovic, Sanja Velickovic, Branka Djordjevic, Goran Marjanovic, and Maja Milojkovic. 2024. "Low Renalase Levels in Newly Diagnosed CML: Dysregulation Sensitive to Modulation by Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors" Pathophysiology 31, no. 4: 787-796. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology31040053
APA StyleMilenkovic, J., Stojanovic, D., Velickovic, S., Djordjevic, B., Marjanovic, G., & Milojkovic, M. (2024). Low Renalase Levels in Newly Diagnosed CML: Dysregulation Sensitive to Modulation by Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Pathophysiology, 31(4), 787-796. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology31040053







