Chronic Kidney Disease of Unknown Etiology: A Global Health Threat in Rural Agricultural Communities—Prevalence, Suspected Causes, Mechanisms, and Prevention Strategies
Abstract
1. Introduction
CKDu: Definition, Clinical Profile and Histopathology
2. Geographical Distribution and Prevalence of CKDu
2.1. Mesoamerican Nephropathy (MeN)
2.2. Sri Lankan Nephropathy
2.3. Indian CKDu
2.3.1. Uddanam Nephropathy
2.3.2. Tondaimandalam Nephropathy
2.4. Other CKDu Hotspots
3. Possible Etiological Factors of CKDu
3.1. Agrochemicals
3.2. Heavy Metals
3.3. Dehydration/Heat Stress
3.4. Hard Water
3.5. Nephrotoxic Agents
3.6. Infections
3.7. Altitude
3.8. Mycotoxins
3.9. Genetic Factors
4. Possible Molecular Mechanisms That Could Induce Renal Injury
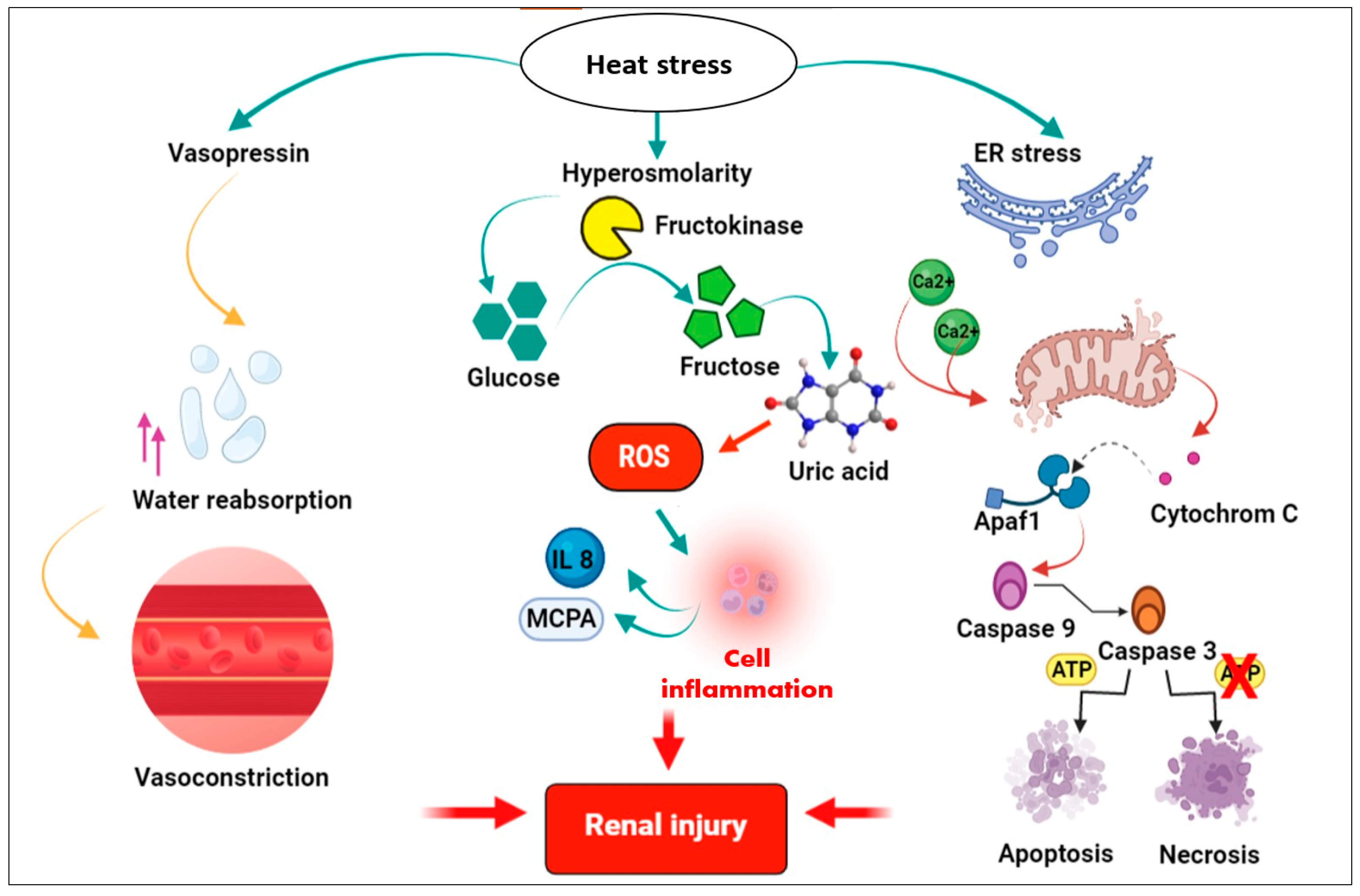
4.1. Molecular Mechanisms of Heat Stress and Dehydration-Induced Renal Injury
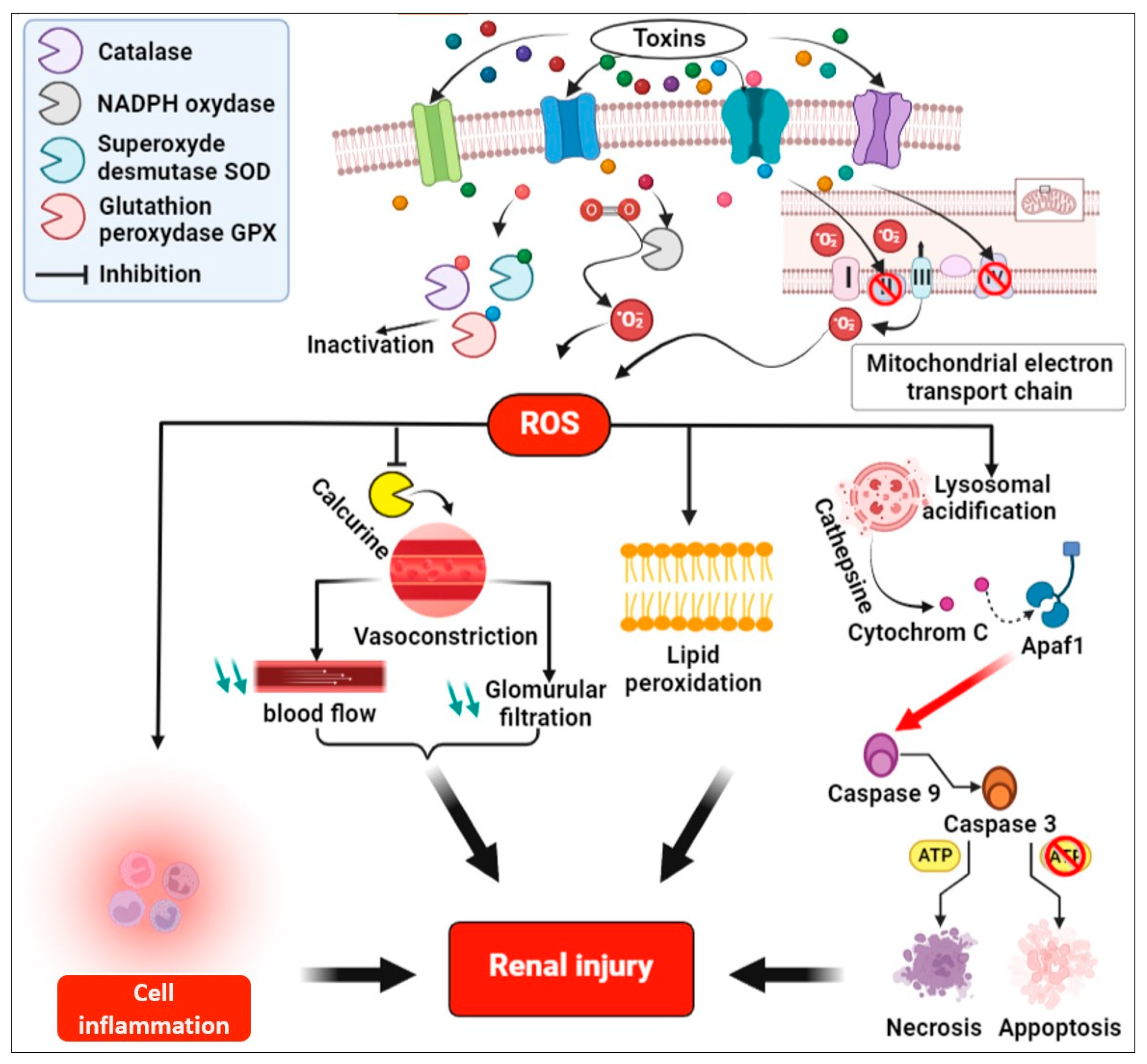
4.2. Molecular Mechanisms of Toxins Induced Renal Injury
4.3. Point of View
5. Early Detection of CKDu
6. Treatment
7. Prevention
7.1. Changing Agricultural Practices
7.2. Fight Against the Consumption of Alcohol and Tobacco
7.3. Environmental Protection
7.4. Early Detection of the Disease
7.5. Research Program
7.6. Effective Prospective Monitoring to Ensure Toxin-Free Drinking Water
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jha, V.; Garcia-Garcia, G.; Iseki, K.; Li, Z.; Naicker, S.; Plattner, B.; Saran, R.; Wang, A.Y.-M.; Yang, C.-W. Chronic kidney disease: Global dimension and perspectives. Lancet 2013, 382, 260–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ene-Iordache, B.; Perico, N.; Bikbov, B.; Carminati, S.; Remuzzi, A.; Perna, A.; Islam, N.; Bravo, R.F.; Aleckovic-Halilovic, M.; Zou, H.; et al. Chronic kidney disease and cardiovascular risk in six regions of the world (ISN-KDDC): A cross-sectional study. Lancet Glob. Health 2016, 4, e307–e319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redmon, J.H.; Elledge, M.F.; Womack, D.S.; Wickremashinghe, R.; Wanigasuriya, K.P.; Peiris-John, R.J.; Lunyera, J.; Smith, K.; Raymer, J.H.; Levine, K.E. Additional perspectives on chronic kidney disease of unknown aetiology (CKDu) in Sri Lanka—Lessons learned from the WHO CKDu population prevalence study. BMC Nephrol. 2014, 15, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez-Rubio, O.; McClean, M.D.; Amador, J.J.; Brooks, D.R. An epidemic of chronic kidney disease in Central America: An overview. Postgrad. Med. J. 2013, 89, 123–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulathunga, M.R.D.L.; Wijayawardena, M.A.A.; Naidu, R.; Wijeratne, A.W. Chronic kidney disease of unknown aetiology in Sri Lanka and the exposure to environmental chemicals: A review of literature. Environ. Geochem. Health 2019, 41, 2329–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilar, D.J.; Madero, M. Other Potential CKD Hotspots in the World: The Cases of Mexico and the United States. Semin. Nephrol. 2019, 39, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gifford, F.J.; Gifford, R.M.; Eddleston, M.; Dhaun, N. Endemic Nephropathy Around the World. Kidney Int. Rep. 2016, 2, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dueymes, J.; Gbaguidi, H.; Davoudoun, T.; Gbaguidi, T. La néphropathie méso-américaine: Une pathologie intertropicale mondiale? Étude préliminaire. Nephrol. Ther. 2018, 14, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadde, P.; Sanikommu, S.; Manumanthu, V.R.; Akkaloori, A. Uddanam nephropathy in India: A challenge for epidemiologists. Bull. World Health Organ. 2017, 95, 848–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, S.; Ps, P.; Sahoo, J.; Vairappan, B.; Parameswaran, S. Seasonal Changes in Kidney Function in CKD of Uncertain Etiology. Kidney Int. Rep. 2021, 6, 2918–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floris, M.; Lepori, N.; Angioi, A.; Cabiddu, G.; Piras, D.; Loi, V.; Swaminathan, S.; Rosner, M.H.; Pani, A. Chronic Kidney Disease of Undetermined Etiology around the World. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2021, 46, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernando, A.; Sivakumaran, N. A comprehensive review of Chronic Kidney Disease of Unknown Etiology. Int. J. Sci. Tech. Res. Eng. 2018, 3, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, R.; Orantes, C.M.; Almaguer, M.; Alfonso, P.; Bayarre, H.D.; Leiva, I.M.; Smith, M.J.; Cubias, R.A.; Almendárez, W.O.; Cubias, F.R.; et al. Clinical characteristics of chronic kidney disease of nontraditional causes in Salvadoran farming communities. MEDICC Rev. 2014, 16, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seneff, S.; Orlando, L.F.; Salvador, E. Is Glyphosate a Key Factor in Mesoamerican Nephropathy? J. Environ. Anal. Toxicol. 2018, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khlifa, K.H.; Ghali, R.; Mazigh, C.; Aouni, Z.; Machgoul, S.; Hedhili, A. Ochratoxin A levels in human serum and foods from nephropathy patients in Tunisia: Where are you now? Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2012, 64, 509–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Khadda, Z.; Berni, I.; Houssaini, T.S. Prevalence and risk factors associated with chronic kidney disease in Moroccan rural communes: Fez-Meknes region. Nephrol. Ther. 2022, 18, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farag, Y.M.K.; Subramanian, K.K.; Singh, V.A.; Tatapudi, R.R.; Singh, A.K. Occupational risk factors for chronic kidney disease in Andhra Pradesh: ‘Uddanam Nephropathy’. Ren. Fail. 2020, 42, 1032–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaser, J.; Lemery, J.; Rajagopalan, B.; Diaz, H.F.; García-Trabanino, R.; Taduri, G.; Madero, M.; Amarasinghe, M.; Abraham, G.; Anutrakulchai, S.; et al. Climate Change and the Emergent Epidemic of CKD from Heat Stress in Rural Communities: The Case for Heat Stress Nephropathy. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 11, 1472–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babich, R.; Ulrich, J.C.; Ekanayake, E.D.V.; Massarsky, A.; De Silva, P.M.C.; Manage, P.M.; Jackson, B.P.; Ferguson, P.L.; Di Giulio, R.T.; Drummond, I.A.; et al. Kidney developmental effects of metal-herbicide mixtures: Implications for chronic kidney disease of unknown etiology. Environ. Int. 2020, 144, 106019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valcke, M.; Levasseur, M.-E.; da Silva, A.S.; Wesseling, C. Pesticide exposures and chronic kidney disease of unknown etiology: An epidemiologic review. Environ. Health 2017, 16, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weaver, V.M.; Fadrowski, J.J.; Jaar, B.G. Global dimensions of chronic kidney disease of unknown etiology (CKDu): A modern era environmental and/or occupational nephropathy? BMC Nephrol. 2015, 16, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Broe, M.E.; Vervaet, B.A. Is an Environmental Nephrotoxin the Primary Cause of CKDu (Mesoamerican Nephropathy)? PRO. Kidney360 2020, 1, 591–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almaguer, M.; Herrera, R.; Orantes, C.M. Chronic kidney disease of unknown etiology in agricultural communities. MEDICC Rev. 2014, 16, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olano, C.G.; Guevara, N.A.; Salinas, C.A.; Orantes, C.; Barba, L.M.; Akram, S.M. Dysmorphic Lysosomes, Pathognomonic of Chronic Interstitial Nephritis in Agricultural Communities (CINAC). J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 32, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.J.; Wesseling, C.; Newman, L.S. Chronic Kidney Disease of Unknown Cause in Agricultural Communities. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1843–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasumana, C.; Orantes, C.; Herrera, R.; Almaguer, M.; Lopez, L.; Silva, L.C.; Ordunez, P.; Siribaddana, S.; Gunatilake, S.; De Broe, M.E. Chronic interstitial nephritis in agricultural communities: A worldwide epidemic with social, occupational and environmental determinants. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2017, 32, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vervaet, B.A.; Schreurs, G.; Nast, C.C.; Santa-Cruz, F.; De Broe, M.E. Chronic Interstitial Nephritis in Agricultural Communities: A Patient in Paraguay. Kidney Int. Rep. 2022, 7, 1131–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo, C.; Nawarathne, P.; Jayasinghe, S. Chronic interstitial nephritis in agricultural communities (CINAC) and lysosomal tubulopathy: Is there a place for anti-oxidants? Med. Hypotheses 2021, 146, 110414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haas, M. Uncovering the etiology of CINAC, a complex and mysterious renal syndrome: The invaluable role of histopathology and electron microscopy. Kidney Int. 2020, 97, 258–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vervaet, B.A.; Nast, C.C.; Jayasumana, C.; Schreurs, G.; Roels, F.; Herath, C.; Kojc, N.; Samaee, V.; Rodrigo, S.; Gowrishankar, S.; et al. Chronic interstitial nephritis in agricultural communities is a toxin-induced proximal tubular nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2020, 97, 350–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa-Rotter, R.; Wesseling, C.; Johnson, R.J. CKD of Unknown Origin in Central America: The Case for a Mesoamerican Nephropathy. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2014, 63, 506–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdivia Mazeyra, M.F.; Muñoz Ramos, P.; Serrano, R.; Alonso Riaño, M.; Gil Giraldo, Y.; Quiroga, B. Mesoamerican nephropathy: A not so unknown chronic kidney disease. Nefropatía endémica mesoamericana: Una enfermedad renal crónica de origen no tan desconocido. Nefrologia 2021, 41, 612–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa-Rotter, R.; García-Trabanino, R. Mesoamerican Nephropathy. Semin. Nephrol. 2019, 39, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courville, K.; Bustamante, N.; Hurtado, B.; Pecchio, M.; Rodríguez, C.; Núñez-Samudio, V.; Landires, I. Chronic kidney disease of nontraditional causes in central Panama. BMC Nephrol. 2022, 23, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerdas, M. Chronic kidney disease in Costa Rica. Kidney Int. 2005, 68, S31–S33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Trabanino, R.; Jarquín, E.; Wesseling, C.; Johnson, R.J.; González-Quiroz, M.; Weiss, I.; Glaser, J.; Vindell, J.J.; Stockfelt, L.; Roncal, C.; et al. Heat stress, dehydration, and kidney function in sugarcane cutters in El Salvador—A cross-shift study of workers at risk of Mesoamerican nephropathy. Environ. Res. 2015, 142, 746–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balasooriya, S.; Munasinghe, H.; Herath, A.T.; Diyabalanage, S.; Ileperuma, O.A.; Manthrithilake, H.; Daniel, C.; Amann, K.; Zwiener, C.; Barth, J.A.C.; et al. Possible links between groundwater geochemistry and chronic kidney disease of unknown etiology (CKDu): An investigation from the Ginnoruwa region in Sri Lanka. Expo. Health 2019, 12, 823–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, G.; Agarwal, S.K.; Gowrishankar, S.; Vijayan, M. Chronic Kidney Disease of Unknown Etiology: Hotspots in India and Other Asian Countries. Semin. Nephrol. 2019, 39, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatapudi, R.R.; Rentala, S.; Gullipalli, P.; Komarraju, A.L.; Singh, A.K.; Tatapudi, V.S.; Goru, K.B.; Bhimarasetty, D.M.; Narni, H. High Prevalence of CKD of Unknown Etiology in Uddanam, India. Kidney Int. Rep. 2018, 4, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekara, T.; De Silva, P.M.C.; Herath, C.; Siribaddana, S.; Siribaddana, N.; Jayasumana, C.; Jayasinghe, S.; Cardenas-Gonzalez, M.; Jayasundara, N. The Utility of Novel Renal Biomarkers in Assessment of Chronic Kidney Disease of Unknown Etiology (CKDu): A Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 9522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paidi, G.; Jayarathna, A.I.I.; Salibindla, D.B.A.M.R.; Amirthalingam, J.; Karpinska-Leydier, K.; Alshowaikh, K.; Ergin, H.E. Chronic Kidney Disease of Unknown Origin: A Mysterious Epidemic. Cureus 2021, 13, e17132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parameswaran, S.; Rinu, P.K.; Kar, S.S.; Harichandrakumar, K.T.; James, T.D.; Priyamvada, P.S.P.; Haridasan, S.; Mohan, S.; Radhakrishnan, J. A Newly Recognized Endemic Region of CKD of Undetermined Etiology (CKDu) in South India—“Tondaimandalam Nephropathy”. Kidney Int. Rep. 2020, 5, 2066–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, S.; Hassen, W.; Achour, A.; Skhiri, H.; Maaroufi, K.; Ellouz, F.; Creppy, E.; Bacha, H. Ochratoxin A and human chronic nephropathy in Tunisia: Is the situation endemic? Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2003, 22, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ballat, M.A.-F.; El-Sayed, M.A.; Emam, H.K. Epidemiology of End Stage Renal Disease Patients on Regular Hemodialysis in El-Beheira Governorate, Egypt. Egypt. J. Hosp. Med. 2019, 76, 3618–3625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Minshawy, O.; Kamel, E.G. Diabetics on hemodialysis in El-Minia Governorate, Upper Egypt: Five-year study. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2010, 43, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Zorkany, K.M. Maintenance hemodialysis in Menoufia governorate, Egypt: Is there any progress? J. Egypt. Soc. Nephrol. Transplant. 2017, 17, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, E.; El-Minshawy, O. Environmental Factors Incriminated in the Development of End Stage Renal Disease in El-Minia Governorate, Upper Egypt. Nephro-Urol Mon. 2010, 2, 431–437. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, M. NLRP3 inflammasome activation regulated by NF-κB and DAPK contributed to paraquat-induced acute kidney injury. Immunol. Res. 2017, 65, 687–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smpokou, E.-T.; González-Quiroz, M.; Martins, C.; Alvito, P.; Le Blond, J.; Glaser, J.; Aragón, A.; Wesseling, C.; Nitsch, D.; Pearce, N.; et al. Environmental exposures in young adults with declining kidney function in a population at risk of Mesoamerican nephropathy. Occup. Environ. Med. 2019, 76, 920–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sombatsawat, E.; Barr, D.B.; Panuwet, P.; Robson, M.G.; Siriwong, W. Pesticide-induced changes in cholinesterase activity and chronic kidney disease of unknown etiology among farmers in Nakhon Ratchasima, Thailand. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assessment Int. J. 2021, 27, 2038–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, E.; Haby, M.M.; Illanes, E.; Sanchez-Viamonte, J.; Elias, V.; Reveiz, L. Risk factors for chronic kidney disease of non-traditional causes: A systematic review. Rev. Panam. De Salud Publica-Pan Am. J. Public Health 2019, 43, e35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VanDervort, D.R.; López, D.L.; Orantes, C.M.; Rodríguez, D.S. Spatial Distribution of Unspecified Chronic Kidney Disease in El Salvador by Crop Area Cultivated and Ambient Temperature. MEDICC Rev. 2014, 16, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajapaksha, H.; Pandithavidana, D.R.; Dahanayake, J.N. Demystifying Chronic Kidney Disease of Unknown Etiology (CKDu): Computational Interaction Analysis of Pesticides and Metabolites with Vital Renal Enzymes. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lentini, P.; Zanoli, L.; Granata, A.; Signorelli, S.S.; Castellino, P.; Dellaquila, R. Kidney and heavy metals—The role of environmental exposure. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 15, 3413–3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orr, S.E.; Bridges, C.C. Chronic Kidney Disease and Exposure to Nephrotoxic Metals. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Channa, J. Possible link of Chronic arsenic toxicity with Chronic Kidney Disease of unknown etiology in Sri Lanka. J. Nat. Sci. Res. 2013, 3, 64–73. [Google Scholar]
- Jayalal, T.B.A.; Bandara, T.W.M.A.J.; Mahawithanage, S.T.C.; Wansapala, M.A.J.; Galappaththi, S.P.L. A quantitative analysis of chronic exposure of selected heavy metals in a model diet in a CKD hotspot in Sri Lanka. BMC Nephrol. 2019, 20, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasumana, C.; Paranagama, P.; Agampodi, S.; Wijewardane, C.; Gunatilake, S.; Siribaddana, S. Drinking well water and occupational exposure to Herbicides is associated with chronic kidney disease, in Padavi-Sripura, Sri Lanka. Environ. Health 2015, 14, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, K.E.; Redmon, J.H.; Elledge, M.F.; Wanigasuriya, K.P.; Smith, K.; Munoz, B.; Waduge, V.A.; Periris-John, R.J.; Sathiakumar, N.; Harrington, J.M.; et al. Quest to identify geochemical risk factors associated with chronic kidney disease of unknown etiology (CKDu) in an endemic region of Sri Lanka—A multimedia laboratory analysis of biological, food, and environmental samples. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, R.T.; Dayananda, N.; Botheju, S.; Liyanage, J.; Ranasinghe, A.; Karunarathna, R.H.; Kumara, G.P. Heavy metal contamination in surface sediments of major tanks in Anuradhapura district: A CKDu endemic district in Sri Lanka. EQA—Int. J. Environ. Qual. 2021, 41, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roncal-Jimenez, C.; Lanaspa, M.A.; Jensen, T.; Sanchezlozada, L.G.; Johnson, R.J. Mechanisms by Which Dehydration May Lead to Chronic Kidney Disease. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2015, 66 (Suppl. 3), 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wesseling, C.; Aragón, A.; González, M.; Weiss, I.; Glaser, J.; Rivard, C.J.; Roncal-Jiménez, C.; Correa-Rotter, R.; Johnson, R.J. Heat stress, hydration and uric acid: A cross-sectional study in workers of three occupations in a hotspot of Mesoamerican nephropathy in Nicaragua. BMJ Open 2016, 6, e011034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayasekara, K.; Kulasooriya, P.; Wijayasiri, K.; Rajapakse, E.; Dulshika, D.; Bandara, P.; Fried, L.; De Silva, A.; Albert, S. Relevance of heat stress and dehydration to chronic kidney disease (CKDu) in Sri Lanka. Prev. Med. Rep. 2019, 15, 100928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siriwardhana, E.A.R.I.E.; Perera, P.A.J.; Sivakanesan, R.; Abeysekara, T.; Nugegoda, D.; Jayaweera, J.A.A.S. Dehydration and malaria augment the risk of developing chronic kidney disease in Sri Lanka. Indian J. Nephrol. 2015, 25, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortez, O.D. Heat stress assessment among workers in a Nicaraguan sugarcane farm. Glob. Health Action 2009, 2, 2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, M.; Kjellstrom, T.; Baldasseroni, A. Impact of climate change on occupational health and productivity: A systematic literature review focusing on workplace heat. Med. Lav. 2018, 109, 163–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herath, C.; Jayasumana, C.; De Silva, P.M.C.; De Silva, P.C.; Siribaddana, S.; De Broe, M.E. Kidney Diseases in Agricultural Communities: A Case Against Heat-Stress Nephropathy. Kidney Int. Rep. 2017, 3, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanayakkara, S.; Senevirathna, S.T.M.L.D.; Abeysekera, T.; Chandrajith, R.; Ratnatunga, N.; Gunarathne, E.D.L.; Yan, J.; Hitomi, T.; Muso, E.; Komiya, T.; et al. An Integrative Study of the Genetic, Social and Environmental Determinants of Chronic Kidney Disease Characterized by Tubulointerstitial Damages in the North Central Region of Sri Lanka. J. Occup. Health 2014, 56, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickramarathna, S.; Balasooriya, S.; Diyabalanage, S.; Chandrajith, R. Tracing environmental aetiological factors of chronic kidney diseases in the dry zone of Sri Lanka—A hydrogeochemical and isotope approach. J. Trace Elements Med. Biol. 2017, 44, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dissanayake, C.B.; Chandrajith, R. Fluoride and hardness in groundwater of tropical regions—Review of recent evidence indicating tissue calcification and calcium phosphate nanoparticle formation in kidney tubules. Ceylon J. Sci. 2019, 48, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasana, H.M.S.; Aluthpatabendi, D.; Kularatne, W.M.T.D.; Wijekoon, P.; Weerasooriya, R.; Bandara, J. Drinking water quality and chronic kidney disease of unknown etiology (CKDu): Synergic effects of fluoride, cadmium and hardness of water. Environ. Geochem. Health 2015, 38, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imbulana, S.; Oguma, K.; Takizawa, S. Evaluation of groundwater quality and reverse osmosis water treatment plants in the endemic areas of Chronic Kidney Disease of Unknown Etiology (CKDu) in Sri Lanka. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 745, 140716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gobalarajah, K.; Subramaniam, P.; Jayawardena, U.A.; Rasiah, G.; Rajendra, S.; Prabagar, J. Impact of water quality on Chronic Kidney Disease of unknown etiology (CKDu) in Thunukkai Division in Mullaitivu District, Sri Lanka. BMC Nephrol. 2020, 21, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrajith, R.; Dissanayake, C.; Ariyarathna, T.; Herath, H.; Padmasiri, J. Dose-dependent Na and Ca in fluoride-rich drinking water —Another major cause of chronic renal failure in tropical arid regions. Sci. Total. Environ. 2011, 409, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botheju, W.S.M.; Liyanage, S.A. The Role of Fluoride, Cadmium and Water Hardness in Drinking Water: A Critical Study of Potential Factors of Chronic Kidney Disease of Unknown Etiology (CKDu) in the Prevalence Area, Sri Lanka. In Proceedings of the 20th International Postgraduate Conference (IPRC 2019), Colombo, Sri Lanka, 30 December 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Dharma-Wardana, M.W.C. Chronic kidney disease of unknown etiology and the effect of multiple-ion interactions. Environ. Geochem. Health 2017, 40, 705–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farmer, J.W.; Singhal, S.; Dempster, L.; Quiñonez, C. Effectiveness, safety, and acceptance of silver diamine fluoride therapy and its implications for dental hygiene practice: Position paper and statement from the Canadian Dental Hygienists Association. Can. J. Dent. Hyg. 2018, 52, 192–207. [Google Scholar]
- Vupputuri, S.; Parks, C.G.; Nylander-French, L.A.; Owen-Smith, A.; Hogan, S.L.; Sandler, D.P. Occupational Silica Exposure and Chronic Kidney Disease. Ren. Fail. 2011, 34, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascarenhas, S.; Mutnuri, S.; Ganguly, A. Deleterious role of trace elements—Silica and lead in the development of chronic kidney disease. Chemosphere 2017, 177, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Shi, T.; Cui, X.; Rong, Y.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Shen, Y.; Chen, W. Effects of silica exposure on the cardiac and renal inflammatory and fibrotic response and the antagonistic role of interleukin-1 beta in C57BL/6 mice. Arch. Toxicol. 2014, 90, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Xie, Y.; Guo, M.; Rosner, M.H.; Yang, H.; Ronco, C. Nephrotoxicity and Chinese herbal medicine. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 13, 1605–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, M.A.; Rottura, M.; Cicala, G.; Mandraffino, R.; Marino, S.; Irrera, N.; Mannucci, C.; Santoro, D.; Squadrito, F.; Arcoraci, V. Chronic Kidney Disease Management in General Practice: A Focus on Inappropriate Drugs Prescriptions. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, H.-Y.; Huang, H.-L.; Li, C.-H.; Chen, H.-A.; Yeh, C.-L.; Chiu, S.-H.; Lin, W.-C.; Cheng, Y.-P.; Tsai, T.-F.; Ho, S.-Y. Increased Risk of Chronic Kidney Disease in Rheumatoid Arthritis Associated with Cardiovascular Complications—A National Population-Based Cohort Study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luyckx, V.A. Nephrotoxicity of Alternative Medicine Practice. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2012, 19, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petejova, N.; Martinek, A.; Zadrazil, J.; Teplan, V. Acute toxic kidney injury. Ren. Fail. 2019, 41, 576–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanifer, J.W.; Kilonzo, K.; Wang, D.; Su, G.; Mao, W.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Nayak-Rao, S.; Miranda, J.J. Traditional Medicines and Kidney Disease in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: Opportunities and Challenges. Semin. Nephrol. 2017, 37, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.-Y.; Chiu, Y.-W.; Chang, J.-S.; Lin, H.-L.; Lee, C.T.-C.; Chiu, G.-F.; Kuo, M.-C.; Wu, M.-T.; Chen, H.-C.; Hwang, S.-J. Association of prescribed Chinese herbal medicine use with risk of end-stage renal disease in patients with chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2015, 88, 1365–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhiya, N.; Arlt, V.M.; Bahn, A.; Burckhardt, G.; Phillips, D.H.; Glatt, H. Molecular evidence for an involvement of organic anion transporters (OATs) in aristolochic acid nephropathy. Toxicology 2009, 264, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsin, Y.-H.; Cheng, C.-H.; Tzen, J.T.C.; Wu, M.-J.; Shu, K.-H.; Chen, H.-C. Effect of aristolochic acid on intracellular calcium concentration and its links with apoptosis in renal tubular cells. Apoptosis 2006, 11, 2167–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Ozols, E.; Ma, F.Y.; Leong, K.G.; Tesch, G.H.; Jiang, X.; Nikolic-Paterson, D.J. c-Jun Amino Terminal Kinase Signaling Promotes Aristolochic Acid-Induced Acute Kidney Injury. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 599114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozdzik, A.; Salmon, I.; Debelle, F.; Decaestecker, C.; Branden, C.V.D.; Verbeelen, D.; Deschodt-Lanckman, M.; Vanherweghem, J.-L.; Nortier, J. Aristolochic acid induces proximal tubule apoptosis and epithelial to mesenchymal transformation. Kidney Int. 2008, 73, 595–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudoux, T.; Jadot, I.; Declèves, A.-E.; Antoine, M.-H.; Colet, J.-M.; Botton, O.; De Prez, E.; Pozdzik, A.; Husson, C.; Caron, N.; et al. Experimental Aristolochic Acid Nephropathy: A Relevant Model to Study AKI-to-CKD Transition. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 822870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Zheng, X.; Wang, L.; Du, H.; Wang, P.; Bai, X. Hantavirus infection: A global zoonotic challenge. Virol. Sin. 2017, 32, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sion, M.L.; Hatzitolios, A.I.; Armenaka, M.C.; Toulis, E.N.; Kalampalika, D.; Mikoudi, K.D. Acute renal failure caused by leptospirosis and Hantavirus infection in an urban hospital. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2002, 13, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.-W. Leptospirosis Renal Disease: Emerging Culprit of Chronic Kidney Disease Unknown Etiology. Nephron 2018, 138, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Andon, M.F.; Quellard, N.; Fernandez, B.; Ratet, G.; Lacroix-Lamandé, S.; Vandewalle, A.; Boneca, I.G.; Goujon, J.-M.; Werts, C. Leptospira Interrogans Induces Fibrosis in the Mouse Kidney through Inos-Dependent, TLR- and NLR-Independent Signaling Pathways. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veron, D.; Aggarwal, P.K.; Velazquez, H.; Kashgarian, M.; Moeckel, G.; Tufro, A. Podocyte-Specific VEGF-A Gain of Function Induces Nodular Glomerulosclerosis in eNOS Null Mice. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 25, 1814–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo-Larco, R.M.; Altez-Fernandez, C.; Acevedo-Rodriguez, J.G.; Ortiz-Acha, K.; Ugarte-Gil, C. Leptospirosis as a risk factor for chronic kidney disease: A systematic review of observational studies. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarathkumara, Y.D.; Gamage, C.D.; Lokupathirage, S.; Muthusinghe, D.S.; Nanayakkara, N.; Gunarathne, L.; Shimizu, K.; Tsuda, Y.; Arikawa, J.; Yoshimatsu, K. Exposure to Hantavirus is a Risk Factor Associated with Kidney Diseases in Sri Lanka: A Cross Sectional Study. Viruses 2019, 11, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimatsu, K.; Gamage, C.D.; Sarathkumara, Y.D.; Kulendiran, T.; Muthusinghe, D.S.; Nanayakkara, N.; Gunarathne, L.; Shimizu, K.; Tsuda, Y.; Arikawa, J. Thailand orthohantavirus infection in patients with chronic kidney disease of unknown aetiology in Sri Lanka. Arch. Virol. 2018, 164, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamage, C.D.; Sarathkumara, Y.D. Chronic kidney disease of uncertain etiology in Sri Lanka: Are leptospirosis and Hantaviral infection likely causes? Med. Hypotheses 2016, 91, 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalvazo, P.; Carriazo, S.; Martin-Cleary, C.; Ortiz, A. Aguascalientes: One of the hottest chronic kidney disease (CKD) hotspots in Mexico and a CKD of unknown aetiology mystery to be solved. Clin. Kidney J. 2021, 14, 2285–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peraza, S.; Wesseling, C.; Aragon, A.; Leiva, R.; García-Trabanino, R.A.; Torres, C.; Jakobsson, K.; Elinder, C.G.; Hogstedt, C. Decreased Kidney Function Among Agricultural Workers in El Salvador. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2012, 59, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Quiroz, M.; Pearce, N.; Caplin, B.; Nitsch, D. What do epidemiological studies tell us about chronic kidney disease of undetermined cause in Meso-America? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Kidney, J. 2017, 11, 496–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arestegui, A.H.; Fuquay, R.; Sirota, J.; Swenson, E.R.; Schoene, R.B.; Jefferson, J.A.; Chen, W.; Yu, X.-Q.; Kelly, J.P.; Johnson, R.J.; et al. High Altitude Renal Syndrome (HARS). J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 22, 1963–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurtado, A.; Escudero, E.; Pando, J.; Sharma, S.; Johnson, R.J. Cardiovascular and renal effects of chronic exposure to high altitude. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2012, 27, iv11–iv16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitria, L.; Prihartono, N.A.; Ramdhan, D.H.; Wahyono, T.Y.M.; Kongtip, P.; Woskie, S. Environmental and Occupational Risk Factors Associated with Chronic Kidney Disease of Unknown Etiology in West Javanese Rice Farmers, Indonesia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmon, J.H.; Levine, K.E.; Lebov, J.; Harrington, J.; Kondash, A. A comparative review: Chronic Kidney Disease of unknown etiology (CKDu) research conducted in Latin America versus Asia. Environ. Res. 2020, 192, 110270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desalegn, B.; Nanayakkara, S.; Harada, K.H.; Hitomi, T.; Chandrajith, R.; Karunaratne, U.; Abeysekera, T.; Koizumi, A. Mycotoxin Detection in Urine Samples from Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease of Uncertain Etiology in Sri Lanka. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2011, 87, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meucci, V.; Luci, G.; Vanni, M.; Guidi, G.; Perondi, F.; Intorre, L. Serum levels of ochratoxin A in dogs with chronic kidney disease (CKD): A retrospective study. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2017, 79, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, J.M.; Moxey-Mims, M.M.; Eggers, P.W.; Narva, A.S.; Star, R.A.; Kimmel, P.L.; Rodgers, G.P. Social Determinants of Racial Disparities in CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 27, 2576–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunyera, J.; Mohottige, D.; Von Isenburg, M.; Jeuland, M.; Patel, U.D.; Stanifer, J.W. CKD of Uncertain Etiology: A Systematic Review. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 11, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanayakkara, S.; Senevirathna, S.T.M.L.D.; Parahitiyawa, N.B.; Abeysekera, T.; Chandrajith, R.; Ratnatunga, N.; Hitomi, T.; Kobayashi, H.; Harada, K.H.; Koizumi, A. Whole-exome sequencing reveals genetic variants associated with chronic kidney disease characterized by tubulointerstitial damages in North Central Region, Sri Lanka. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2015, 20, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ma, J.; Yang, Q.; Hwang, S.-J.; Fox, C.S.; Chu, A.Y. Genetic risk score and risk of stage 3 chronic kidney disease. BMC Nephrol. 2017, 18, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nerbass, F.B.; Pecoits-Filho, R.; Clark, W.F.; Sontrop, J.M.; McIntyre, C.W.; Moist, L. Occupational Heat Stress and Kidney Health: From Farms to Factories. Kidney Int. Rep. 2017, 2, 998–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, C.A.R.; Ishimoto, T.; Lanaspa, M.A.; Rivard, C.J.; Nakagawa, T.; Ejaz, A.A.; Cicerchi, C.; Inaba, S.; Le, M.; Miyazaki, M.; et al. Fructokinase activity mediates dehydration-induced renal injury. Kidney Int. 2014, 86, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, E.; Glaser, J.; Jakobsson, K.; Weiss, I.; Wesseling, C.; Lucas, R.A.I.; Wei, J.L.K.; Ekström, U.; Wijkström, J.; Bodin, T.; et al. Pathophysiological Mechanisms by which Heat Stress Potentially Induces Kidney Inflammation and Chronic Kidney Disease in Sugarcane Workers. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarian, A.; Michiels, J.; DeGroote, J.; Majdeddin, M.; Golian, A.; De Smet, S. Association between heat stress and oxidative stress in poultry; mitochondrial dysfunction and dietary interventions with phytochemicals. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2016, 7, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Di, H.-S.; Guo, L.; Li, Z.-H.; Wang, G.-L. Hyperthermia causes bovine mammary epithelial cell death by a mitochondrial-induced pathway. J. Therm. Biol. 2007, 33, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.-L.; Fujiwara, Y.; Kondo, T. Mechanism of cell death induction by nitroxide and hyperthermia. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2006, 40, 1131–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, R.; Dong, X.; Feng, L.; Li, S.; Hu, Z. The Effect of Heat Stress on Autophagy and Apoptosis of Rumen, Abomasum, Duodenum, Liver and Kidney Cells in Calves. Animals 2019, 9, 854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brustovetsky, N. The Role of Adenine Nucleotide Translocase in the Mitochondrial Permeability Transition. Cells 2020, 9, 2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haak, J.L.; Buettner, G.R.; Spitz, D.R.; Kregel, K.C. Aging augments mitochondrial susceptibility to heat stress. Am. J. Physiol. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2009, 296, R812–R820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallée, D.; Blanc, M.; Lebeaupin, C.; Bailly-Maitre, B. The stress response of the endoplasmic reticulum in the pathophysiology of chronic liver diseases. M/S-Med. Sci. 2020, 36, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belhadj Slimen, I.; Najar, T.; Ghram, A.; Dabbebi, H.; Ben Mrad, M.; Abdrabbah, M. Reactive oxygen species, heat stress and oxidative-induced mitochondrial damage. A review. Int. J. Hyperth. 2014, 30, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naranmandura, H.; Xu, S.; Sawata, T.; Hao, W.H.; Liu, H.; Bu, N.; Ogra, Y.; Lou, Y.J.; Suzuki, N. Mitochondria are the main target organelle for trivalent monomethylarsonous acid (MMAIII)-induced cytotoxicity. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 24, 1094–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Dusting, G.J. NADPH Oxidase-Mediated Redox Signaling: Roles in Cellular Stress Response, Stress Tolerance, and Tissue Repair. Pharmacol. Rev. 2011, 63, 218–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Gill, A.S.; Singh, Z.; Kaur, C.; Vijaya, P. Nephrotoxic Effects of Arsenic in Albino Mice. Am. J. Biosci. 2016, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zheng, H.J.; Zhang, X.; Guo, J.; Zhang, W.; Ai, S.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Y.; Liu, W.J. Lysosomal dysfunction–induced autophagic stress in diabetic kidney disease. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 8276–8290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.-M.; Mizushima, N. At the end of the autophagic road: An emerging understanding of lysosomal functions in autophagy. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2014, 39, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Gómez-Sintes, R.; Boya, P. Lysosomal membrane permeabilization and cell death. Traffic 2018, 19, 918–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwan, H.; Pal, S.; Sabnam, S.; Pal, A. High glucose augments ROS generation regulates mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis via stress signalling cascades in keratinocytes. Life Sci. 2020, 241, 117148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, Y.-T.; Chou, S.-H.; Cheng, C.-Y.; Ho, C.-T.; Lin, H.-C.; Jung, S.-M.; Chu, P.-H.; Ko, F.-H. The preferential accumulation of cadmium ions among various tissues in mice. Toxicol. Rep. 2022, 9, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wang, X.-Y.; Zhou, X.-P.; Liu, Z.-P.; Song, X.-B.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Wang, L. Cadmium disrupts autophagic flux by inhibiting cytosolic Ca 2+ -dependent autophagosome-lysosome fusion in primary rat proximal tubular cells. Toxicology 2017, 383, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaushal, G.P.; Shah, S.V. Autophagy in acute kidney injury. Kidney Int. 2016, 89, 779–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dikic, I.; Elazar, Z. Mechanism and medical implications of mammalian autophagy. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 349–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Jin, X.; Fan, R.; Xing, M.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Xu, S. Cadmium-mediated miR-30a-GRP78 leads to JNK-dependent autophagy in chicken kidney. Chemosphere 2019, 215, 710–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, A.; Ishida, Y.; Nosaka, M.; Kuninaka, Y.; Hama, M.; Kawaguchi, T.; Sakamoto, S.; Shinozaki, K.; Iwahashi, Y.; Takayasu, T.; et al. Exaggerated arsenic nephrotoxicity in female mice through estrogen-dependent impairments in the autophagic flux. Toxicology 2016, 339, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boroushaki, M.T.; Arshadi, D.; Jalili-Rasti, H.; Asadpour, E.; Hosseini, A. Protective effect of pomegranate seed oil against acute toxicity of diazinon in rat kidney. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. IJPR 2013, 12, 821–827. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Attar, A.M. Physiological and Histopathological Investigations on the Effects of-Lipoic Acid in Rats Exposed to Malathion. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2010, 2010, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Possamai, F.; Fortunato, J.; Feier, G.; Agostinho, F.; Quevedo, J.; Filho, D.W.; Dal-Pizzol, F. Oxidative stress after acute and sub-chronic malathion intoxication in Wistar rats. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2006, 23, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satar, S.; Satar, D.; Mete, U.O.; Suchard, J.R.; Topal, M.; Kaya, M. Ultrastructural Effects of Acute Organophosphate Poisoning on Rat Kidney. Ren. Fail. 2005, 27, 623–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Li, S.; Qi, L.; Xu, W.; Wang, H.; Zhao, X.; Sun, C. Effect of quercetin against dichlorvos induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2014, 66, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, N.S.; Mohamed, A.S.; Abdel-Wahhab, M.A. Chlorpyrifos-induced oxidative stress and histological changes in retinas and kidney in rats: Protective role of ascorbic acid and alpha tocopherol. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2010, 98, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukaszewicz-Hussain, A. Role of oxidative stress in organophosphate insecticide toxicity—Short review. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2010, 98, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, R.; Park, Y.U.; Ji, E.; Yeo, E.-J.; Kim, S.Y. Malathion increases apoptotic cell death by inducing lysosomal membrane permeabilization in N2a neuroblastoma cells: A model for neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. Cell Death Discov. 2017, 3, 17007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Xu, B.; Chen, H.; Qiang, J.; Feng, H.; Li, X.; Chu, M.; Pan, E.; Dong, J. Crosstalk of oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptosis, and autophagy under reactive oxygen stress involved in difenoconazole-induced kidney damage in carp. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2022, 132, 108508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Hu, Z.; Xu, W.; Xu, S.; Niu, Q. Impaired V-ATPase leads to increased lysosomal pH, results in disrupted lysosomal degradation and autophagic flux blockage, contributes to fluoride-induced developmental neurotoxicity. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 236, 113500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolli, R.T.; Gunasekara, S.C.; Foster, M.W.; Adduri, S.; Strasma, A.; Wyatt, C.; Konduru, N.V.; De Silva, M.C.S.; Jayasundara, N. The urinary proteome infers dysregulation of mitochondrial, lysosomal, and protein reabsorption processes in chronic kidney disease of unknown etiology (CKDu). Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2023, 324, F387–F403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eman, R.Y.; Agha, F.E.; El-Toukhy, S.E.; El-Naggar, S.M.M.; Selim, A.A.I.; Ibrahim, A.M.M. The protective effect of orange juice on Glyphosate toxicity in adult male mice. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2016, 8, 13–28. [Google Scholar]
- Ognjanović, B.; Marković, S.; Pavlović, S.; Žikić, R.; Štajn, A.; Saičić, Z. Effect of chronic cadmium exposure on antioxidant defense system in some tissues of rats: Protective effect of selenium. Physiol. Res. 2008, 57, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, F.; Endre, Z.H.; Pickering, J.W.; Jayamanne, S.; Palangasinghe, C.; Shahmy, S.; Chathuranga, U.; Wijerathna, T.; Shihana, F.; Gawarammana, I.; et al. Mechanism-specific injury biomarkers predict nephrotoxicity early following glyphosate surfactant herbicide (GPSH) poisoning. Toxicol. Lett. 2016, 258, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, B.; Lin, Y.; Jiang, S.; Huang, L.; Yao, H.; Zhuang, Q.; Zhao, R.; Liu, H.; He, C.; Lin, Z. Endoplasmic reticulum stress eIF2α–ATF4 pathway-mediated cyclooxygenase-2 induction regulates cadmium-induced autophagy in kidney. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaeth, M.; Feske, S. NFAT control of immune function: New Frontiers for an Abiding Trooper. F1000Research 2018, 7, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klee, C.B.; Ren, H.; Wang, X. Regulation of the Calmodulin-stimulated Protein Phosphatase, Calcineurin. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 13367–13370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.-J.; Yoo, S.-A.; Kim, M.; Kim, W.-U. The Role of Calcium–Calcineurin–NFAT Signaling Pathway in Health and Autoimmune Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan, P.G. Calcium–NFAT transcriptional signalling in T cell activation and T cell exhaustion. Cell Calcium 2017, 63, 66–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Mester, C.; Stemmer, P.M.; Reid, G.E. Oxidation-Induced Conformational Changes in Calcineurin Determined by Covalent Labeling and Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Biochemistry 2014, 53, 6754–6765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karolin, A.; Escher, G.; Rudloff, S.; Sidler, D. Nephrotoxicity of Calcineurin Inhibitors in Kidney Epithelial Cells is Independent of NFAT Signaling. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 12, 789080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, S.; Usui, J.; Takahashi, K.; Kimura, T.; Hoshi, A.; Nishiyama, H.; Oda, T.; Yamagata, K. P0002A NEW INSIGHT INTO THE MECHANISM OF HYPERCHLOREMIC METABOLIC ACIDOSIS IN KIDNEY TRANSPLANT RECIPIENTS: INCREASED POSTGLOMERULAR PERITUBULAR BLOOD FLOW IS A KEY CONDITION FOR THE DEVELOPEMENT OF CALCINEURIN INHIBITOR-INDUCED RENAL TUBULAR ACIDOSIS. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2020, 35 (Suppl. S3). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enan, E.; Matsumura, F. Specific inhibition of calcineurin by type II synthetic pyrethroid insecticides. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1992, 43, 1777–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreurs, G.; Maudsley, S.; Nast, C.; Praet, M.; Fernandes, S.D.S.; Boor, P.; D’haese, P.; De Broe, M.E.; Vervaet, B.A. Chronic dehydration induces injury pathways in rats, but does not mimic histopathology of chronic interstitial nephritis in agricultural communities. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 18119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasumana, C.; Gunatilake, S.; Senanayake, P. Glyphosate, Hard Water and Nephrotoxic Metals: Are They the Culprits Behind the Epidemic of Chronic Kidney Disease of Unknown Etiology in Sri Lanka? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 2125–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdés, R.H.; Orantes, C.M.; López, M.A.; Marín, L.L.; Arévalo, P.A.; González, M.J.S.; Morales, F.E.; Bacallao, R.; Bayarre, H.D.; Parada, X.F.V. Clinical characteristics of chronic kidney disease of non-traditional causes in women of agricultural communities in El Salvador. Clin. Nephrol. 2015, 83, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayanthooran, S.; Magana-Arachchi, D.N.; Gunerathne, L.; Abeysekara, T. Potential diagnostic biomarkers for chronic kidney disease of unknown etiology (CKDu) in Sri Lanka: A pilot study. BMC Nephrol. 2017, 18, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, W.; Smith, S.; Kretzler, M. Genomic biomarkers for chronic kidney disease. Transl. Res. 2012, 159, 290–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fassett, R.G.; Venuthurupalli, S.K.; Gobe, G.C.; Coombes, J.S.; Cooper, M.A.; Hoy, W.E. Biomarkers in chronic kidney disease: A review. Kidney Int. 2011, 80, 806–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mischak, H.; Delles, C.; Vlahou, A.; Vanholder, R. Proteomic biomarkers in kidney disease: Issues in development and implementation. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2015, 11, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taherkhani, A.; Yekta, R.F.; Mohseni, M.; Saidijam, M.; Oskouie, A.A. Chronic kidney disease: A review of proteomic and metabolomic approaches to membranous glomerulonephritis, focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, and IgA nephropathy biomarkers. Proteome Sci. 2019, 17, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongboonkerd, V. Recent progress in urinary proteomics. Proteom.—Clin. Appl. 2007, 1, 780–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirolli, V.; Pieroni, L.; Di Liberato, L.; Urbani, A.; Bonomini, M. Urinary Peptidomic Biomarkers in Kidney Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 21, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, D.M.; Zürbig, P.; Argilés, À.; Bauer, H.W.; Behrens, G.; Coon, J.J.; Dakna, M.; Decramer, S.; Delles, C.; Dominiczak, A.F.; et al. Naturally Occurring Human Urinary Peptides for Use in Diagnosis of Chronic Kidney Disease. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2010, 9, 2424–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cañadas-Garre, M.; Anderson, K.; McGoldrick, J.; Maxwell, A.; McKnight, A. Proteomic and metabolomic approaches in the search for biomarkers in chronic kidney disease. J. Proteom. 2018, 193, 93–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duffield, J.S. Cellular and molecular mechanisms in kidney fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 2299–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, P.T.; Mehta, R.L.; Shaw, A.; Ronco, C.; Endre, Z.H.; Kellum, J.A.; Chawla, L.S.; Cruz, D.N.; Ince, C.; Okusa, M.D. ADQI 10 workgroup Potential use of biomarkers in acute kidney injury: Report and summary of recommendations from the 10th Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative consensus conference. Kidney Int. 2014, 85, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonventre, J.V. Kidney injury molecule-1: A translational journey. Trans. Am. Clin. Climatol. Assoc. 2014, 125, 293–299. [Google Scholar]
- Buonafine, M.; Martinez-Martinez, E.; Jaisser, F. More than a simple biomarker: The role of NGAL in cardiovascular and renal diseases. Clin. Sci. 2018, 132, 909–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyssoulis, G.P.; Tousoulis, D.; Antoniades, C.; Dimitrakopoulos, S.; Zervoudaki, A.; Stefanadis, C. α-1 Microglobulin as a New Inflammatory Marker in Newly Diagnosed Hypertensive Patients. Am. J. Hypertens. 2007, 20, 1016–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kristiansson, A.; Gram, M.; Flygare, J.; Hansson, S.R.; Åkerström, B.; Storry, J.R. The Role of α1-Microglobulin (A1M) in Erythropoiesis and Erythrocyte Homeostasis—Therapeutic Opportunities in Hemolytic Conditions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinkai, S.; Chaves, P.H.M.; Fujiwara, Y.; Watanabe, S.; Shibata, H.; Yoshida, H.; Suzuki, T. β2-Microglobulin for Risk Stratification of Total Mortality in the Elderly PopulationComparison with Cystatin C and C-Reactive Protein. Arch. Intern. Med. 2008, 168, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Prizment, A.E.; Linabery, A.M.; Lutsey, P.L.; Selvin, E.; Nelson, H.H.; Folsom, A.R.; Church, T.R.; Drake, C.G.; Platz, E.A.; Joshu, C. Circulating Beta-2 Microglobulin and Risk of Cancer: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study (ARIC). Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2016, 25, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zong, R.; Li, H.; Yin, X.; Fu, M.; Yao, L.; Sun, J.; Yang, F. Distribution of urinary N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminidase and the establishment of reference intervals in healthy adults. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2021, 35, e23748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoud, A.A.; Mostafa, N.M.; Mesbah, O.; Sabry, O.M.; Al-Barshomy, S.M. Study of Urinary N-Acetyl-Beta-D-Glucosaminidase as a biomarker of Diabetic Nephropathy. Egypt. J. Hosp. Med. 2021, 82, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Aranda, M.; Serrano, A.; Redondo, M. Regulation of Clusterin Gene Expression. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2018, 19, 612–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, M.R.; Zoubeidi, A. Clusterin as a therapeutic target. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2016, 21, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Icer, M.A.; Gezmen-Karadağ, M. The multiple functions and mechanisms of osteopontin. Clin. Biochem. 2018, 59, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Sakatsume, M.; Nishi, S.; Narita, I.; Arakawa, M.; Gejyo, F. Expression, roles, receptors, and regulation of osteopontin in the kidney. Kidney Int. 2001, 60, 1645–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satirapoj, B. Tubulointerstitial Biomarkers for Diabetic Nephropathy. J. Diabetes Res. 2018, 2018, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Zhu, Q.; Zhu, B.; Wu, T.; Wang, G.; Liu, S.; Luo, Q. Increased Serum MCP-1 Levels in Systemic Vasculitis Patients with Renal Involvement. J. Interf. Cytokine Res. 2018, 38, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, P.M.C.S.; Abdul, K.S.M.; Eakanayake, E.M.D.V.; Jayasinghe, S.S.; Jayasumana, C.; Asanthi, H.B.; Perera, H.S.D.; Chaminda, G.G.T.; Chandana, E.P.S.; Siribaddana, S.H. Urinary Biomarkers KIM-1 and NGAL for Detection of Chronic Kidney Disease of Uncertain Etiology (CKDu) among Agricultural Communities in Sri Lanka. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, B.N.T.W.; Alli-Shaik, A.; Hemage, R.K.D.; Badurdeen, Z.; Hettiarachchi, T.W.; Abeysundara, H.T.K.; Abeysekara, T.D.J.; Wazil, A.; Rathnayake, S.; Gunaratne, J.; et al. Pilot Study of Renal Urinary Biomarkers for Diagnosis of CKD of Uncertain Etiology. Kidney Int. Rep. 2019, 4, 1401–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orantes Navarro, C.; Herrera-Valdés, R.; Almaguer-López, M.; Brizuela-Díaz, E.; Alvarado-Ascencio, N.; Morales, E.; Bayarre, H.; Calero-Brizuela, D.; Vela Parada, X.; Zelaya-Quezada, S. Chronic Kidney Disease in Children and Adolescents in Salvadoran Farming Communities: NefroSalva Pediatric Study (2009–2011). MEDICC Rev. 2016, 18, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abeyagunawardena, A.S.; Shroff, R. CKDu: The known unknowns. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2020, 36, 219–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köttgen, A.; Gall, E.C.-L.; Halbritter, J.; Kiryluk, K.; Mallett, A.J.; Parekh, R.S.; Rasouly, H.M.; Sampson, M.G.; Tin, A.; Antignac, C.; et al. Genetics in chronic kidney disease: Conclusions from a Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Controversies Conference. Kidney Int. 2022, 101, 1126–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groopman, E.E.; Marasa, M.; Cameron-Christie, S.; Petrovski, S.; Aggarwal, V.S.; Milo-Rasouly, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Nestor, J.; Krithivasan, P.; et al. Diagnostic Utility of Exome Sequencing for Kidney Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, Y.H.; Lee, C.; Kim, N.K.D.; Park, E.; Kang, H.G.; Ha, I.-S.; Park, W.-Y.; Cheong, H.I. Targeted Exome Sequencing Provided Comprehensive Genetic Diagnosis of Congenital Anomalies of the Kidney and Urinary Tract. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hureaux, M.; Heidet, L.; Vargas-Poussou, R.; Dorval, G. Les grandes avancées en néphro-génétique pédiatrique [Major advances in pediatric nephro-genetics]. Med. Sci. 2023, 39, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehm, H.L.; Berg, J.S.; Brooks, L.D.; Bustamante, C.D.; Evans, J.P.; Landrum, M.J.; Ledbetter, D.H.; Maglott, D.R.; Martin, C.L.; Nussbaum, R.L.; et al. ClinGen—The Clinical Genome Resource. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2235–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, J.A.; Hamza, E.; Guerrero-Hue, M.; Rayego-Mateos, S.; García-Caballero, C.; Vallejo-Mudarra, M.; Metzinger, L.; Meuth, V.M.-L. Non-Coding RNAs in Kidney Diseases: The Long and Short of Them. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majidpour, M.; Saravani, R.; Sargazi, S.; Harati-Sadegh, M.; Khorrami, S.; Sarhadi, M.; Alidadi, A. A Study on Associations of Long Noncoding RNA HOTAIR Polymorphisms With Genetic Susceptibility to Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2024, 38, e25086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moresco, R.N.; Bochi, G.V.; Stein, C.S.; De Carvalho, J.A.; Cembranel, B.M.; Bollick, Y.S. Urinary kidney injury molecule-1 in renal disease. Clin. Chim. Acta 2018, 487, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrajith, R.; Nanayakkara, S.; Itai, K.; Aturaliya, T.N.C.; Dissanayake, C.B.; Abeysekera, T.; Harada, K.; Watanabe, T.; Koizumi, A. Chronic kidney diseases of uncertain etiology (CKDue) in Sri Lanka: Geographic distribution and environmental implications. Environ. Geochem. Health 2010, 33, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanayakkara, N.; Wazil, A.; Gunerathne, L.; Dickowita, S.; Rope, R.; Ratnayake, C.; Saxena, A.; Anand, S. Tackling the Fallout From Chronic Kidney Disease of Unknown Etiology: Why We Need to Focus on Providing Peritoneal Dialysis in Rural, Low-Resource Settings. Kidney Int. Rep. 2016, 2, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, B.; Courtney, M.; Pauly, R.P.; Jindal, K.; Klarenbach, S. Cost Analysis of In-Centre Nocturnal Compared with Conventional Hemodialysis. Can. J. Kidney Health Dis. 2014, 1, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varughese, S.; Agarwal, S.; Raju, T.; Khanna, T. Options of renal replacement therapy in CKDu. Indian, J. Nephrol. 2020, 30, 261–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polo, V.S.; Garcia-Trabanino, R.; Rodriguez, G.; Madero, M. Mesoamerican Nephropathy (MeN): What We Know so Far. Int. J. Nephrol. Renov. Dis. 2020, 13, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roncal-Jimenez, C.A.; Sato, Y.; Milagres, T.; Hernando, A.A.; García, G.; Bjornstad, P.; Dawson, J.B.; Sorensen, C.; Newman, L.; Krisher, L.; et al. Experimental heat stress nephropathy and liver injury are improved by allopurinol. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2018, 315, F726–F733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trachtman, H.; Valderrama, E.; Futterweit, S. Nephrotoxicity of allopurinol is enhanced in experimental hypertension. Hypertension 1991, 17, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goraya, N.; Wesson, D.E. Clinical evidence that treatment of metabolic acidosis slows the progression of chronic kidney disease. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2019, 28, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Lozada, L.-G.; García-Arroyo, F.E.; Gonzaga, G.; Silverio, O.; Blas-Marron, M.G.; Muñoz-Jimenez, I.; Tapia, E.; Osorio-Alonso, H.; Madero, M.; Roncal-Jiménez, C.A.; et al. Kidney Injury from Recurrent Heat Stress and Rhabdomyolysis: Protective Role of Allopurinol and Sodium Bicarbonate. Am. J. Nephrol. 2018, 48, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalau, J.; Kajbaf, F.; de Broe, M. La metformine dans l’insuffisance rénale: Place (enfin) aux faits. Médecine Mal. Métaboliques 2018, 12, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacCallum, L.; Senior, P.A. Safe Use of Metformin in Adults With Type 2 Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease: Lower Dosages and Sick-Day Education Are Essential. Can. J. Diabetes 2018, 43, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ben Khadda, Z.; Lahmamsi, H.; El Karmoudi, Y.; Ezrari, S.; El Hanafi, L.; Sqalli Houssaini, T. Chronic Kidney Disease of Unknown Etiology: A Global Health Threat in Rural Agricultural Communities—Prevalence, Suspected Causes, Mechanisms, and Prevention Strategies. Pathophysiology 2024, 31, 761-786. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology31040052
Ben Khadda Z, Lahmamsi H, El Karmoudi Y, Ezrari S, El Hanafi L, Sqalli Houssaini T. Chronic Kidney Disease of Unknown Etiology: A Global Health Threat in Rural Agricultural Communities—Prevalence, Suspected Causes, Mechanisms, and Prevention Strategies. Pathophysiology. 2024; 31(4):761-786. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology31040052
Chicago/Turabian StyleBen Khadda, Zineb, Haitam Lahmamsi, Yahya El Karmoudi, Said Ezrari, Laila El Hanafi, and Tarik Sqalli Houssaini. 2024. "Chronic Kidney Disease of Unknown Etiology: A Global Health Threat in Rural Agricultural Communities—Prevalence, Suspected Causes, Mechanisms, and Prevention Strategies" Pathophysiology 31, no. 4: 761-786. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology31040052
APA StyleBen Khadda, Z., Lahmamsi, H., El Karmoudi, Y., Ezrari, S., El Hanafi, L., & Sqalli Houssaini, T. (2024). Chronic Kidney Disease of Unknown Etiology: A Global Health Threat in Rural Agricultural Communities—Prevalence, Suspected Causes, Mechanisms, and Prevention Strategies. Pathophysiology, 31(4), 761-786. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology31040052






