Simple Summary
Breast cancers arising before the age of 45 years, also known as early-onset breast cancers, have a more aggressive behavior and worse prognosis than late-onset breast cancers. Therefore, there is an urgent need to identify potential therapeutic targets for this group of tumors. In the last decade, angiopoietin-like protein 4 and insulin-like growth factor-1 have attracted attention in clinical research as independent markers of the progression and prognosis of malignancies. In this study, we investigated the expression of both proteins in breast carcinoma tissue from young patients and examined whether their expression can be predicted by clinicopathological parameters.
Abstract
Biomarker identification is imperative for invasive breast carcinoma, which is more aggressive and associated with higher mortality and worse prognosis in younger patients (<45 years) than in older patients (>50 years). The current study aimed to investigate angiopoietin-like protein 4 (ANGPTL4) and insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) protein expression in breast tissue from young patients with breast carcinoma. Immunohistochemical staining was applied in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded samples of breast carcinoma tissue from young patients aged <45 years at the time of diagnosis. Both proteins were expressed in the majority of cases. The highest frequency of positive ANGPTL4 and IGF-1 expression was observed in the luminal A subtype, whereas the HER2-overexpression subtype exhibited the lowest expression frequency for both proteins. There was no significant association between ANGPTL4 (p = 0.897) and IGF-1 (p = 0.091) expression and molecular subtypes of breast carcinoma. The histological grade was a significant predictor of ANGPTL4 expression (grade 1 vs. grade 3, adjusted odds ratio = 12.39, p = 0.040). Therefore, ANGPTL-4 and IGF-1 expressions are common in young breast carcinoma tissue. There is a potential use of them as biomarkers in breast carcinoma.
1. Introduction
Breast carcinoma is the most common malignancy affecting women worldwide and the second leading cause of cancer-related death in women following lung cancer [1]. After a diagnosis of breast carcinoma, patient management starts with determining the prognostic and predictive parameters that provide an overview of how the tumor will behave and respond to therapy [2]. Several prognostic and predictive parameters have been described for breast carcinoma, starting with conventional parameters such as the hormone receptors status, histological tumor type, histological grade, tumor size, lymph node involvement, lymphovascular invasion, proliferative markers, ending with molecular markers that aid in predicting clinical outcome [3]. However, no parameters are specific for the managing young age patients (≤45 years), even though early-onset breast cancer is more aggressive and associated with worse outcomes than older-onset breast cancer.
Angiopoietin-like protein 4 (ANGPTL4) is a secretory glycoprotein belonging to the angiopoietin family. It is expressed in several tissues including liver, adipose, pancreatic, placenta, kidney, intestinal, and ischemic tissue. ANGPTL4 has important roles in lipid and glucose metabolism as well as angiogenesis [4,5]. In 2011, Nakayama and colleagues suggested that ANGPTL4 contributes to progression, venous invasion, and distant metastasis in human colorectal cancer [6]. In 2013, Adhikary et al. reported that the repression of ANGPTL4 gene transcription resulted in the inhibition of breast cancer cell invasion in vitro, suggesting the potential role of ANGPTL4 as a therapeutic target for breast cancer [7]. Furthermore, a recent study reported that higher tissue expression of ANGPTL4 was correlated with breast tumor progression and distant metastasis, as well as shorter overall survival and disease-free survival [8]. The mechanism through which ANGPTL-4 promotes breast cancer progression was described by Padua et al., where they found that the cytokine transforming growth factor-B (TGF-B) induces breast cancer cell metastasis to the lungs, and the key molecule in this process was the overexpressed ANGPTL-4 through SMAD signaling pathway [9] (Figure 1).
In contrast to these findings, Cai et al. found that overexpression of ANGPTL4 inhibits triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) cell adhesion, migration, and invasion in vitro, suggesting that the enhancement of ANGPTL4 expression can prevent progression in TNBC cells [10].
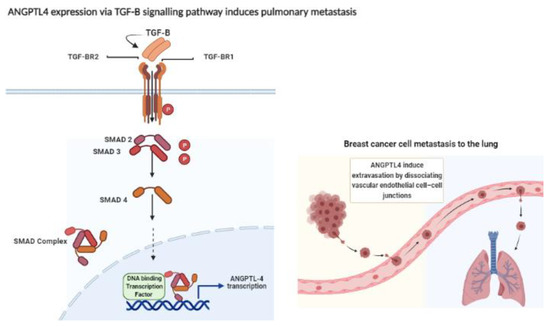
Figure 1.
Expression of ANGPTL4 through TGF-B–SMAD signaling enhances the extravasation of the breast cancer cell to the lungs by disrupting of the vascular endothelial cell-cell -junction. Transforming growth factor-B (TGF-B) ligand binds to transforming growth Factor-B receptor I (TGFBR1) and transforming growth factor-B II (TGFBR2). TGFBR2 phosphorylates (P) TGFBR1, which in turn activates SMAD2 and SMAD3 via phosphorylation. Activated SMAD2 and SMAD3 form complex with SMAD4. The complex translocates into the nucleus where it interacts with other DNA-binding transcription factors, co-activators as well as co-repressors. Following this, the complex binds to the promoter regions of TGF target genes and regulates their transcription. The overexpression of angiopoietin-like 4 (ANGPTL-4) induces the extravasation of breast cancer cell by disrupting the vascular endothelial cell-cell junction, Figure created with BioRender.com [9,11].
Another important marker in breast cancer is insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1), which is a polypeptide encoded by the IGF-1 gene located on chromosome 12. IGF-1 is produced mainly in the liver under direct stimulation by growth hormone [12]. Under normal physiological conditions, IGF-1 induces mitosis and inhibits apoptosis. In contrast, under pathological conditions, it is well established that IGF-1 functions as a potent mitogen that contributes to tumor progression, increasing metastatic potential and resistance to apoptosis induced by cytotoxic drugs. In prior studies, IGF-1 overexpression was associated with aggressive tumors and poor prognosis [13,14]. In breast cancer, IGF-1 regulates cell growth through stimulation of the insulin growth factor receptor (IGF-1R), which consequently phosphorylates either insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1) or insulin receptor substrate-2 (IRS-2). IRS-1/2 activates downstream signaling proteins such as PI3K/AKT/mTOR and Ras/Raf/MAPK, and this role has been documented in all molecular subtypes of breast cancer (Figure 2) [15].
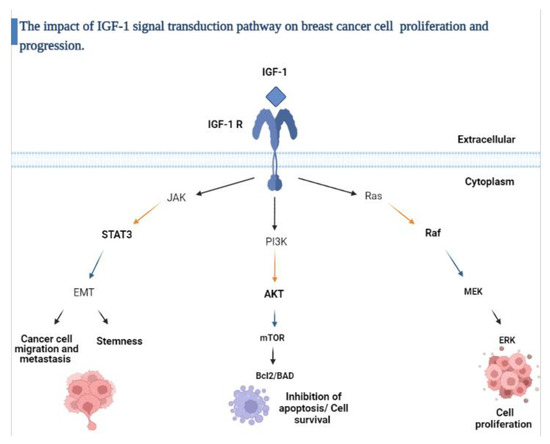
Figure 2.
Schematic overview of the IGF-1 signaling pathway.
The insulin growth factor-1 (IGF-1) signaling axis is activated by the binding of (IGF-1) to the insulin growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R); this binding activates several downstream molecular pathways including PI3K/AKT which inhibits apoptosis, increases protein synthesis and glucose metabolism, RAS/MAPK that promotes cell proliferation and JAK/STAT which induces epithelial- mesenchymal transition (EMT) and cancer cell stemness. Figure created with BioRender.com [12,16,17].
In the present study, we investigated the protein expression of ANGPTL4 and IGF-1 in breast carcinoma tissue from young age patients and determined whether there is an association between the expression of both proteins and the breast carcinoma molecular subtype and if the expression of both proteins can be predicted by tumor clinicopathological characteristics.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design, Participants, and Specimen
This cross-sectional study was carried in the Department of Pathology—Hospital Universiti Sains Malaysia, Kelantan, Malaysia. All patients who were histopathologically diagnosed with breast carcinoma between 1 January 2007 and 31 December 2017 and were ≤45 years at the time of diagnosis were included. Patients with unavailable tissue blocks or who had a tissue block but with inadequate material for immunohistochemical staining were excluded. Additionally, patients who received neoadjuvant therapy before surgery were also excluded. The study included 75 patients who fulfilled the study inclusion criteria. Demographic and clinicopathological characteristics of patients including age, specimen type, tumor size, histopathological type, tumor grade, lymph node status, expression of estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR), HER2 by immunohistochemistry and HER2 status by the dual-color dual-hapten brightfield in situ hybridization method (DDISH) were retrieved from the electronic medical records of the department of pathology and patient case records.
2.2. Immunohistochemical Staining and Scoring System
Briefly, tissue sections of 3–4 µm thickness were cut from formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue blocks. Following this, tissue sections were deparaffinized by xylene and rehydrated through a series of graded alcohol. The slides were then placed in an ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid- containing buffer in a pressure cooker for 3 min; the purpose of this step is to retrieve the antigen. Following this, slides were immersed in 3% hydrogen peroxide for 5 min to block endogenous peroxidase activity. Subsequently, for each case one slide was incubated with a rabbit polyclonal ANGPTL4 antibody (1:500; ab196746, Abcam, Cambridge, UK). The second slide was incubated with rabbit polyclonal IGF-1 antibody (1:500; ab9572, Abcam UK) for one hour at room temperature. 3, 3′-diaminobenzidine tetrahydrochloride (DAB) from (DAKO, Glostrup, Hovedstaden, Denmark) was used to visualize the antigen–antibody complex. Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma tissue was used as positive controls for the ANGPTL4 antibody, and placenta tissue was used as positive controls for the IGF-1 antibody, as recommended by the manufacturer. The same tissues were also used as negative controls by omitting the primary antibody incubation step from the protocol.
We used a semi-quantitative scoring system for both antibodies. The scoring system determined the staining intensity and percentage of positive malignant cells. The staining intensity of malignant cells was measured on a scale from 0 to 3 as shown in Table 1. To obtain the immunostaining score, the scale of staining intensity and the percentage of positive malignant cells were multiplied, a total score of ≥4 was defined as a positive expression, whereas a total score of <4 indicated negative expression [18].

Table 1.
Scoring system of ANGPTL4 and IGF1 expression.
Nuclear immunoreactivity of control tissue was necessary for the ANGPTL4 antibody, whereas cytoplasmic immunoreactivity of control tissue was required for the IGF-1 antibody. All slides were scored independently by two well-trained pathologists who were blinded to the clinicopathological data.
2.3. Statistical Analysis
Double data entry was performed independently using Microsoft Excel 2010 by two researchers. Data analysis was conducted using R software version 4.0.3 in the R studio environment. Descriptive statistics were performed to describe the sociodemographic as well as the clinicopathological characteristics of the study participants. For age, mean and standard deviation (SD) was presented, for all other variables, frequency (n) and percentage (%) were presented.
Associations of ANGPTL4 and IGF-1 expression with molecular subtypes of breast carcinoma were assessed using Pearson’s chi-square test and Fisher’s exact test. Multiple logistic regression analysis was conducted to determine the clinicopathological predictors of ANGPTL4 and IGF-1 expression. Data were presented as adjusted ORs, 95% CIs, and p-values.
3. Results
The ages of the 75 patients included in this study range between 23 and 44 years with a mean age of 37 years (SD, 5.37 years). Based on the modified Bloom–Richardson grading system, this study included 10 (13.3%) and 65 (86.7%) patients with low-grade (grade I) and high-grade (grades II or III) breast carcinoma, respectively (Figure 3). In addition, 42 (56.0%) and 36 (48.0%) of patients were positive for ER and PR, respectively. Majority of the patients n = 40 (53.3%) were HER2-negative (score 0 or 1), whereas 13 (17.3%) patients were equivocal (score, 2) and 22 (29.3%) patients were HER2-positive (score, 3). The most common molecular subtype was Luminal A accounting for 29 (38.7%) cases, followed by triple-negative, luminal B, and HER2-overexpression 20 (26.7%), 15 (20%), and 11 (14.7%), respectively. Further details of the cases clinicopathological characteristics are presented in (Table 2).
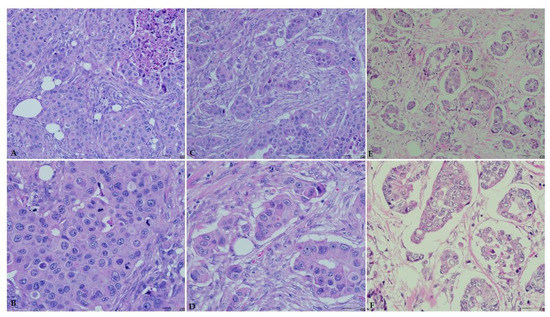
Figure 3.
Breast carcinoma histological grade according to the Bloom–Richardson grading system. Hematoxylin and eosin staining (×20 and ×40). (A) High grade (grade III, ×20). (B) High grade (grade III, ×40). (C) High grade (grade II, ×20). (D) High grade (grade II, ×40). (E) Low grade (grade I, ×20). (F) Low grade (grade I, ×40).

Table 2.
Clinicopathological characteristics of the patients (n = 75).
3.1. Immunohistochemical Expression of ANGPTL-4 and IGF-1
As shown in Table 3, the majority of the cases showed immunoreactivity for ANGPTL4 and IGF-1 antibodies in 50 (66.7%) and 67 (89.3%) cases, respectively. Figure 4 and Figure 5 illustrates the immunostaining and scoring of ANGPTL4 and IGF-1 antibodies, respectively.

Table 3.
Expression of ANGPTL-4 and IGF-1 in young patients with breast cancer (n = 75).
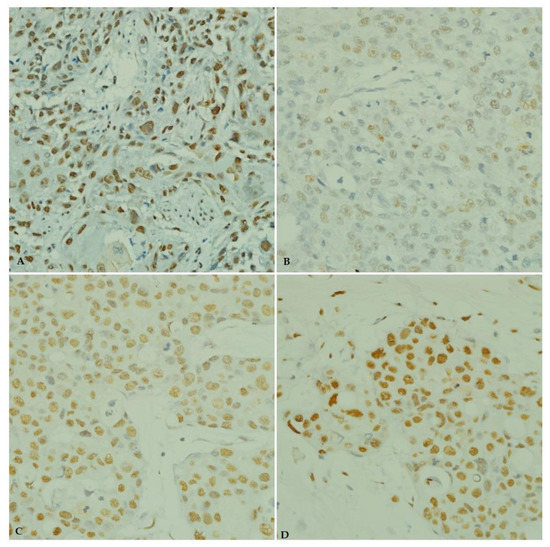
Figure 4.
Immunohistochemical staining of ANGPTL4 in breast carcinoma tissue from young patients. (A) ANGPTL4 positive control (esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, ×40). (B) Weak ANGPTL4 immunostaining. (C) Moderate ANGPTL4 immunostaining (×40). (D) Strong ANGPTL4 immunostaining (×40).
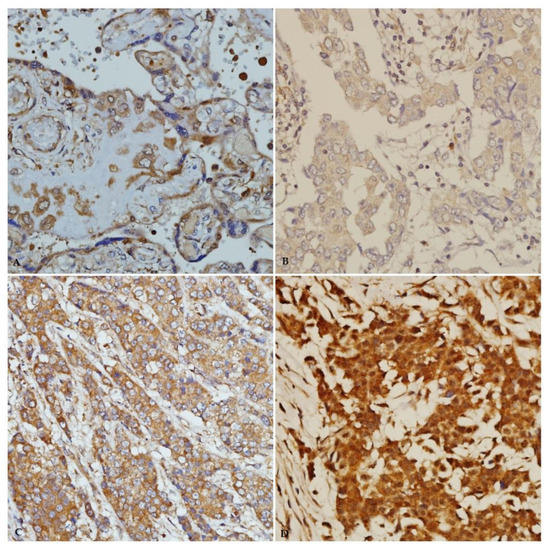
Figure 5.
IGF-1 immunohistochemical staining in breast carcinoma tissue from young patients. (A) Immunostaining of positive-control placenta tissue (×40). (B) Weak IGF-1 immunostaining (×40). (C) Moderate IGF-1 immunostaining (×40). (D) Strong IGF-1 immunostaining (×40).
3.2. Associations of ANGPTL-4 and IGF-1 Expression with Breast Carcinoma Molecular Subtypes
The frequency of ANGPTL4 immunoreactivity varied among different molecular subtypes of breast carcinoma, higher frequency was observed in the luminal A subtype (n = 19 (38.0%)), followed by triple-negative (n = 14 (28.0%)) and luminal B (n = 9 (18.0%)), while the lowest rate of ANGPTL4 immunoreactivity was observed in the HER2-overexpression subtype (n = 8 (16.0%)). However, the chi-square test did not detect a significant association between ANGPTL4 expression and specific molecular subtypes of invasive breast carcinoma in young women (p = 0.897) (Table 4).

Table 4.
Association of ANGPTL-4 expression with breast carcinoma molecular subtypes in young patients (n = 75).
Similarly, frequency of IGF-1 immunoreactivity among different molecular subtypes of breast carcinoma was mimicking that observed in ANGPTL4. A high rate of IGF-1 immunoreactivity was observed in the luminal A subtype (n = 27 (40.3%)) and the lowest rate of IGF-1 immunoreactivity was found in the HER2-overexpression subtype (n = 10 (14.9%)), whereas both the luminal B and triple-negative subtypes showed equal rates of IGF-1 immunoreactivity (n = 15 (22.4%)). However, there was no significant association between IGF-1 expression and molecular subtypes (p = 0.091) (Table 5).

Table 5.
Association of IGF-1 expression with breast carcinoma molecular subtypes in young patients (n = 75).
3.3. Clinicopathological Predictors of ANGPTL-4 and IGF-1 Expression
3.3.1. Clinicopathological Predictors of ANGPTL4 Expression
Histological grade, tumor size, lymph node, ER and PR status, HER2 expression, and molecular subtype were included in multiple logistic regression analysis. Table 6 presents the clinicopathological characteristics of patients based on the ANGPTL4 status. Likewise, patients with an unknown tumor size or unknown lymph node status were excluded from the analysis.

Table 6.
Patients’ clinicopathological characteristics based on the ANGPTL4 status (n = 75).
In multivariate analysis, patients with grade 1 tumors had 12.39-fold higher odds of positive ANGPTL4 expression than patients with grade 3 tumors following adjustment for all other clinicopathological characteristics (adjusted OR = 12.39, p = 0.040; Table 7).

Table 7.
Multiple logistic regression analysis of the clinicopathological predictors of ANGPTL4 expression (n = 75).
3.3.2. Clinicopathological Predictors of IGF-1
Similar variables as described previously were included in multivariate analysis to identify the clinicopathological predictors of IGF-1 expression. Table 8 presents the patients’ clinicopathological characteristics based on the IGF-1 status.

Table 8.
Patients’ clinicopathological characteristics based on the IGF-1 status (n = 75).
In multiple logistic regression analyses, the OR could not be computed for histological grade 1 compared to grade 3 because none of the patients with grade 1 tumors was negative for IGF-1 expression. None of the clinicopathological characteristics were predictive of IGF-1 expression (Table 9).

Table 9.
Multiple logistic regression analysis of the clinicopathological predictors of IGF-1 expression (n = 75).
4. Discussion
The purpose of the current study was to investigate the protein expression of ANGPTL4 and IGF-1 in primary breast carcinoma tissue and its association with breast cancer molecular subtypes in patients younger than 45 years. Furthermore, we assessed whether the expression of both proteins can be predicted by various clinicopathological parameters.
Shafik et al. and Cai et al. reported expression of ANGPTL4 in the cytoplasm of breast carcinoma cells [10,19]. However, in this study we observed ANGPTL4 expression in the nucleus; we attributed this variation to the dual location of ANGPTL4 in the cell, based on information available in The Human Protein Atlas and GeneCards, ANGPTL4 localized in nucleoplasm as well as vesicles [20]. More than half of patients in the present study displayed immunoreactivity for ANGPTL4 (67%), this in concordance with previous studies investigated ANGPTL4 expression in breast and prostate cancer tissues [19,21]. This finding was expected because ANGPTL4 expression is upregulated in the hypoxic microenvironment, which is a hallmark of most solid tumors including breast cancer [22,23]. Using multiple logistic regression analysis, all clinicopathological parameters, including tumor size, lymph node status, ER and PR status, HER2 expression, and molecular subtype, failed to predict the expression of ANGPTL4. This is in line with a previous study that found no relationships between ANGPTL4 expression and clinicopathological parameters in patients with TNBC [10]. However, when we carried multivariate analysis, patients with grade 1 tumor had 12.39-fold higher odds of positive ANGPTL4 expression than those with grade 3 tumors after adjustment for all other clinicopathological characteristics (adjusted OR = 12.39, p = 0.040), this is in contrast to Shafiq et al.’s findings where ANGPTL4 mRNA transcript and serum levels were significantly higher in high grade breast carcinoma samples compared to low grade and control samples. When we compared our data with this study the only difference is the age of breast cancer patients [19]. Thus, further study is needed to elucidate the mechanism behind the variation of ANGPTL-4 expression among different disease grades mainly in young age patients. Findings in this area are controversial. Although several studies concluded that ANGPTL4 expression is associated with tumor progression and metastasis [19,24], many studies implicated ANGPTL4 in the inhibition of tumor angiogenesis and metastasis [25,26]. This conflict of function was explained by Tan et al., who found that ANGPTL4 function was context- and tissue type-dependent [27].
The majority of patients in the current study (89%) exhibited positive staining for IGF-1. This percentage was comparable to that reported by Shiratsuchi et al. in colorectal cancer tissue (80%) [28]. This high frequent expression might be attributed to the role of the growth hormone/IGF-1 axis in oncogenesis and progression of cancer. Specifically, higher plasma levels of IGF-1 were reported previously to be associated with malignancy, whereas deficiencies of growth hormone and IGF-1 were related to the absence of cancers [29]. Most patients with positive staining for IGF-1 had a luminal A subtype, while lower expression was seen in patients with Triple negative subtype. This finding in line with a previous genomic study that found that breast tumors which were known to be well differentiated and have favorable outcomes such as luminal A and normal subtypes exhibited higher expression of the IGF-1 ligand genomic signature, whereas the basal-like subtype which have poor outcomes have lower expression of the IGF-1 ligand genomic signature; furthermore, the study reported results of network analysis, where breast cancer group with high IGF-1 ligand signature shows downregulation in component of proliferation pathways (AKT/MAPK) and upregulation of component of differentiation pathways (adipocyte growth factors, PPAR-gamma), this explains the favorable outcome of tumors with a high IGF-1 ligand signature [30]. Another explanation of the higher expression of IGF-1 in luminal A subtype tumors is the strong crosstalk between ER and IGF-1 signaling pathways [31]. It is well established that components of the IGF-1 signaling pathway are regulated by estrogen [32,33]. Although IGF-1 expression was more frequent in the luminal A subtype and less frequent in the Triple negative subtype, fisher’s exact test failed to find an association between IGF-1 expression and young age breast carcinoma molecular subtypes. Moreover, no clinico–pathological parameter was predictive of IGF-1 expression in breast cancer tissue in young patients.
5. Conclusions
In this cross-sectional study we investigated the expression of ANGPTL-4 and IGF-1 in primary breast carcinoma tissue samples from young age patients ≤45 years. Both proteins were expressed by the majority of patients. However, no association was detected between expression of both proteins and breast carcinoma molecular subtype. However, all clinicopathological parameters investigated in the current study failed to predict the tissue expression of both proteins. ANGPTL-4 showed significant higher expression in tumors with lower histopathological grades compared to tumors of higher grades. Further study with a larger sample size may verify our findings.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.K., W.F.W.A.R.; methodology, Z.K. and W.F.W.A.R.; formal analysis, N.M.Y., Z.K.; investigation, Z.K.; writing—original draft preparation, A.S.; writing—review and editing, A.S., A.K.L.; supervision, W.F.W.A.R.; funding acquisition, W.F.W.A.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Universiti Sains Malaysia Bridging Grant (304/PPSP/6316162) and Fundamental Research Grant Scheme by Ministry of Higher Education Malaysia, grant number 203.PPSP.6171249.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approval to conduct this study was obtained from the Human Ethical Committee of School of Medical Sciences, Universiti Sains Malaysia (USM/JEPeM/17110598).
Informed Consent Statement
According to Malaysian regulations, written informed consent from the patients was not required for this study and patient consents was waived. All data were rendered anonymous before access and analysis.
Data Availability Statement
All data present within the main article.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge the administration office of Universiti Sains Malaysia, Kubang Kerian, Kelantan for facilitating our work. Additionally, we are thankful for the Ministry of higher education Malaysia (MOHE) for supporting us with the Fundamental Research Grant Scheme to carry this work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2016, 66, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Donegan, W.L. Tumor-related prognostic factors for breast cancer. CA Cancer J. Clin. 1997, 47, 28–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolini, A.; Ferrari, P.; Duffy, M.J. Prognostic and predictive biomarkers in breast cancer: Past, present and future. Semin Cancer Biol. 2018, 52 (Pt 1), 56–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, P.; Goh, Y.Y.; Chin, H.F.A.; Kersten, S.; Tan, N.S. Angiopoietin-like 4: A decade of research. Biosci. Rep. 2011, 32, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oike, Y.; Akao, M.; Kubota, Y.; Suda, T. Angiopoietin-like proteins: Potential new targets for metabolic syndrome therapy. Trends Mol. Med. 2005, 11, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, T.; Hirakawa, H.; Shibata, K.; Nazneen, A.; Abe, K.; Nagayasu, T.; Taguchi, T. Expression of angiopoietin-like 4 (ANGPTL4) in human colorectal cancer: ANGPTL4 promotes venous invasion and distant metastasis. Oncol. Rep. 2011, 25, 929–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhikary, T.; Brandt, D.T.; Kaddatz, K.; Stockert, J.C.; Naruhn, S.; Meissner, W.A.; Finkernagel, F.; Obert, J.; Lieber, S.; Scharfe, M.; et al. Inverse PPARβ/δ agonists suppress oncogenic signaling to the ANGPTL4 gene and inhibit cancer cell invasion. Oncogene 2013, 32, 5241–5252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, J.; Liu, J.; Wu, N.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, S.; Li, L.; Wang, M. ANGPTL4 overexpression is associated with progression and poor prognosis in breast cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 20, 2499–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padua, D.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Q.; Nadal, C.; Gerald, W.L.; Gomis, R.; Massagué, J. TGFβ Primes Breast Tumors for Lung Metastasis Seeding through Angiopoietin-like 4. Cell 2008, 133, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, Y.-C.; Yang, H.; Wang, K.-F.; Chen, T.-H.; Jiang, W.-Q.; Shi, Y.-X. ANGPTL4 overexpression inhibits tumor cell adhesion and migration and predicts favorable prognosis of triple-negative breast cancer. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikushima, H.; Miyazono, K. TGFβ signalling: A complex web in cancer progression. Nat. Cancer 2010, 10, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christopoulos, P.F.; Msaouel, P.; Koutsilieris, M. The role of the insulin-like growth factor-1 system in breast cancer. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chong, Y.M.; Subramanian, A.; Sharma, A.K.; Mokbel, K. The potential clinical applications of insulin-like growth factor-1 ligand in human breast cancer. Anticancer Res. 2007, 27, 1617–1624. [Google Scholar]
- Dunn, S.E.; Hardman, R.A.; Kari, F.W.; Barrett, J.C. Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) alters drug sensitivity of HBL100 human breast cancer cells by inhibition of apoptosis induced by diverse anticancer drugs. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 2687–2693. [Google Scholar]
- Ekyalongo, R.C.; Yee, D. Revisiting the IGF-1R as a breast cancer target. Npj Precis. Oncol. 2017, 1, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murphy, N.; Knuppel, A.; Papadimitriou, N.; Martin, R.M.; Tsilidis, K.K.; Smith-Byrne, K.; Fensom, G.; Perez-Cornago, A.; Travis, R.C.; Key, T.J.; et al. Insulin-like growth factor-1, insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3, and breast cancer risk: Observational and Mendelian randomization analyses with ~430,000 women. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ianza, A.; Sirico, M.; Bernocchi, O.; Generali, D. Role of the IGF-1 Axis in Overcoming Resistance in Breast Cancer. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaemmerer, D.; Peter, L.; Lupp, A.; Schulz, S.; Sänger, J.; Baum, R.P.; Prasad, V.; Hommann, M. Comparing of IRS and Her2 as immunohistochemical scoring schemes in gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2012, 5, 187–194. [Google Scholar]
- Shafik, N.M.; Mohamed, D.A.; Bedder, A.E.; El-Gendy, A.M. Significance of tissue expression and serum levels of angiopoietin-like protein 4 in breast cancer progression: Link to NF-κB/P65 activity and pro-inflammatory cytokines. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2016, 16, 8579–8587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Atlas, T.H.P. ANGPTL4. Available online: https://www.proteinatlas.org/ENSG00000167772-ANGPTL4/cell (accessed on 1 June 2021).
- Hata, S.; Nomura, T.; Iwasaki, K.; Sato, R.; Yamasaki, M.; Sato, F.; Mimata, H. Hypoxia-induced angiopoietin-like protein 4 as a clinical biomarker and treatment target for human prostate cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milani, M.; Harris, A.L. Targeting tumour hypoxia in breast cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2008, 44, 2766–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, T.; Li, J.-Z.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, C.-Y.; Li, Q.; Mao, J.; Li, L.-H. The mechanism between epithelial mesenchymal transition in breast cancer and hypoxia microenvironment. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 80, 393–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, K.; Nakayama, T.; Hirakawa, H.; Hidaka, S.; Nagayasu, T. Clinicopathological significance of angiopoietin-like protein 4 expression in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J. Clin. Pathol. 2010, 63, 1054–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, Y.; Oike, Y.; Yasunaga, K.; Hamada, K.; Miyata, K.; Matsumoto, S.-I.; Sugano, S.; Tanihara, H.; Masuho, Y.; Suda, T. Inhibition of angiogenesis and vascular leakiness by angiopoietin-related protein 4. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 6651–6657. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Galaup, A.; Cazes, A.; Le Jan, S.; Philippe, J.; Connault, E.; Le Coz, E.; Mekid, H.; Mir, L.M.; Opolon, P.; Corvol, P.; et al. Angiopoietin-like 4 prevents metastasis through inhibition of vascular permeability and tumor cell motility and invasiveness. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 18721–18726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, M.J.; Teo, Z.; Sng, M.K.; Zhu, P.; Tan, N.S. Emerging Roles of Angiopoietin-like 4 in Human Cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2012, 10, 677–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shiratsuchi, I.; Akagi, Y.; Kawahara, A.; Kinugasa, T.; Romeo, K.; Yoshida, T.; Ryu, Y.; Gotanda, Y.; Kage, M.; Shirouzu, K. Expression of IGF-1 and IGF-1R and their relation to clinicopathological factors in colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res. 2011, 31, 2541–2545. [Google Scholar]
- Chhabra, Y.; Waters, M.J.; Brooks, A. Role of the growth hormone–IGF-1 axis in cancer. Expert Rev. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 6, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, L.; Tuck, D.; Katsaros, D.; Lu, L.; Schulz, V.; Perincheri, S.; Menato, G.; Scarampi, L.; Harris, L.; Yu, H. Favorable outcome associated with an IGF-1 ligand signature in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 133, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahlert, S.; Nuedling, S.; van Eickels, M.; Vetter, H.; Meyer, R.; Grohé, C. Estrogen Receptor α Rapidly Activates the IGF-1 Receptor Pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 18447–18453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Casa, A.J.; Potter, A.S.; Malik, S.; Lazard, Z.; Kuiatse, I.; Kim, H.-T.; Tsimelzon, A.; Creighton, C.J.; Hilsenbeck, S.G.; Brown, P.H.; et al. Estrogen and insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) independently down-regulate critical repressors of breast cancer growth. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2011, 132, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macias, H.; Hinck, L. Mammary gland development. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Dev. Biol. 2012, 1, 533–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).