Circulating Levels of Endothelin-1 and Big Endothelin-1 in Patients with Essential Hypertension
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Characteristics of the Study Population
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria in the Study
2.2.1. Inclusion Criteria for Patients
- Male or female aged ≥35 years and ≤80 years;
- Patients with essential HTN (either SBP ≥ 140 mmHg, DBP ≥ 90 mmHg or both);
- Willingness to voluntarily participate in the study and sign an informed consent form.
2.2.2. Exclusion Criteria for Patients
- Male or female aged ≤35 years and ≥80 years;
- Secondary HTN and pulmonary HTN;
- Chronic renal disease, heart failure, liver dysfunction, and malignant tumor;
- Inability or unwillingness to participate in the study or to sign an informed consent form.
2.2.3. Inclusion Criteria for Control Subjects
- Healthy men or women aged ≥35 years and ≤80 years;
- Individuals with normal BP (SBP 120–129 mmHg and DBP 80–84 mmHg);
- Willingness to voluntarily participate in the study and sign an informed consent form.
2.3. Blood Pressure Measurement
2.4. Immunological Assays
2.4.1. Determination of ET-1
2.4.2. Determination of Big ET-1
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
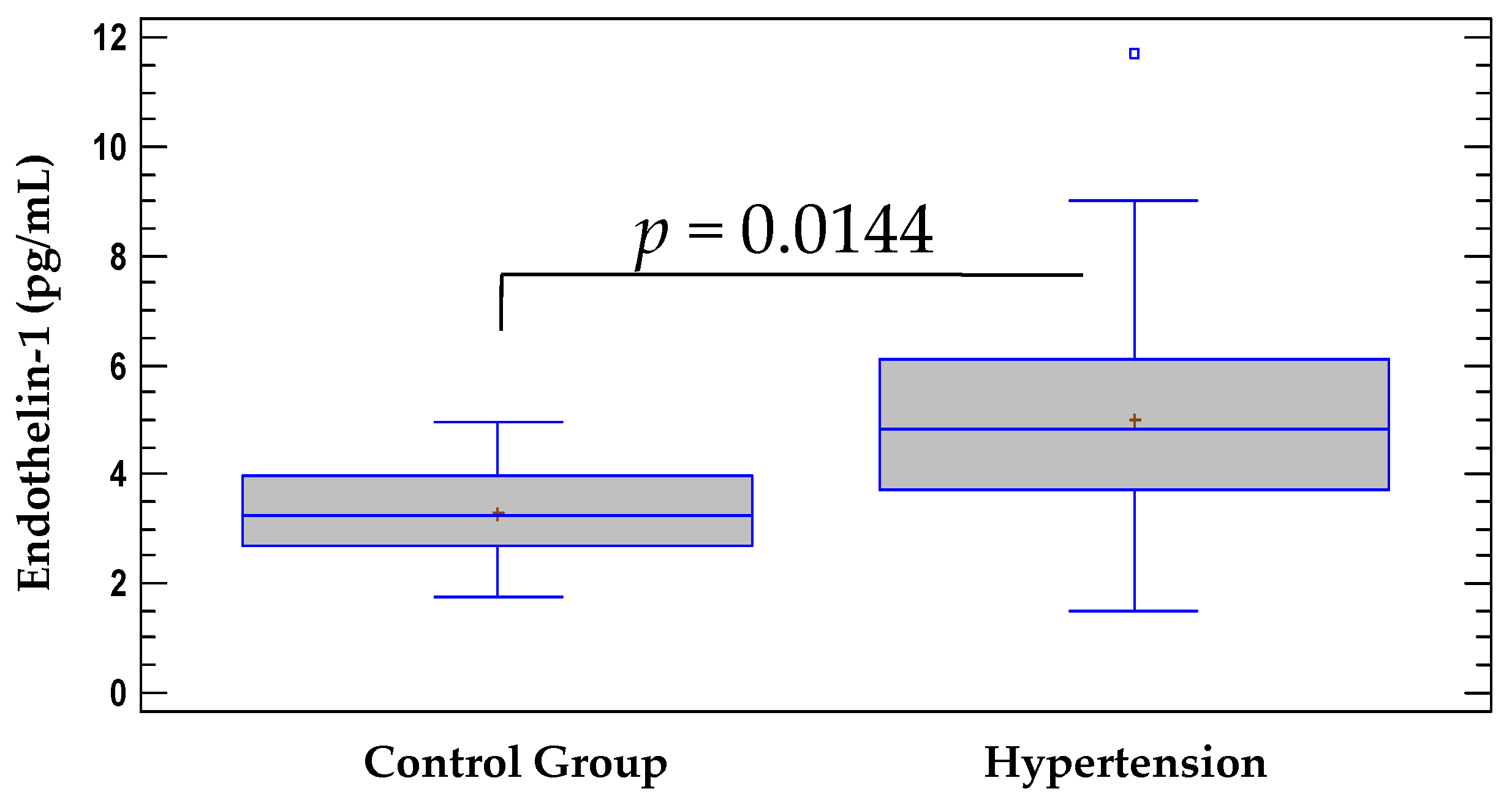
3.1. Comparison of Serum Levels of ET-1 between the Hypertensive Group and the Control Group
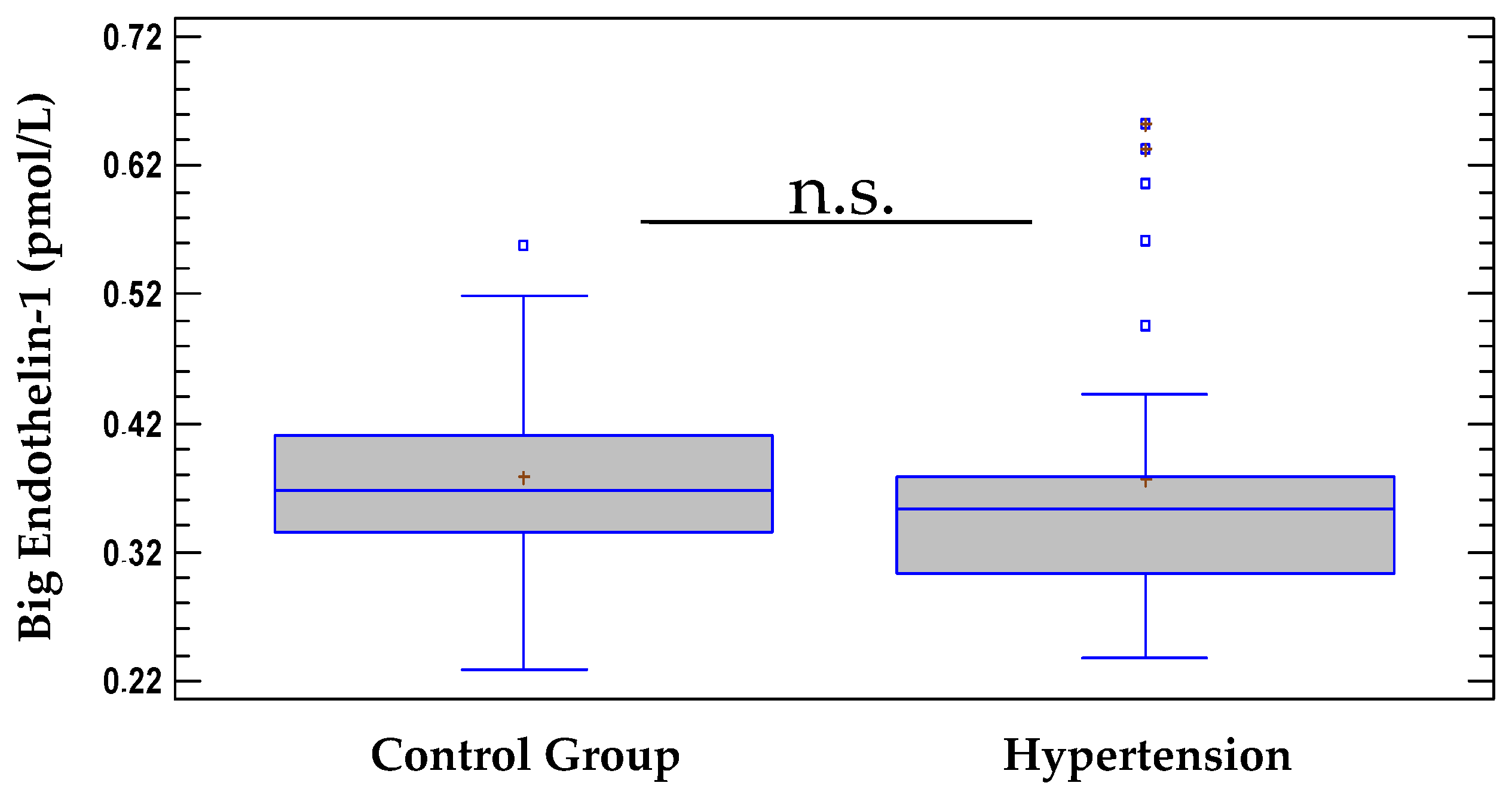
3.2. Comparison of Serum Levels of Big ET-1 between the Hypertensive Group and the Control Group
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oparil, S.; Acelajado, M.C.; Bakris, G.L.; Berlowitz, D.R.; Cífková, R.; Dominiczak, A.F.; Grassi, G.; Jordan, J.; Poulter, N.R.; Rodgers, A.; et al. Hypertension. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 18014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touyz, R.M.; Feldman, R.D.; Harrison, D.G.; Schiffrin, E.L. A new look at the mosaic theory of hypertension. Can. J. Cardiol. 2020, 36, 591–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Félétou, M.; Köhler, R.; Vanhoutte, P.M. Endothelium-derived vasoactive factors and hypertension: Possible roles in pathogenesis and as treatment targets. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2010, 12, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konukoglu, D.; Uzun, H. Endothelial dysfunction and hypertension. Hypertens. Basic Res. Clin. Pract. 2016, 2, 511–540. [Google Scholar]
- Masaki, T.; Sawamura, T. Endothelin and endothelial dysfunction. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B Phys. Biol. Sci. 2006, 82, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagisawa, M.; Kurihara, H.; Kimura, S.; Tomobe, Y.; Kobayashi, M.; Mitsui, Y.; Yazaki, Y.; Goto, K.; Masaki, T. A Novel potent vasoconstrictor peptide produced by vascular endothelial cells. Nature 1988, 332, 411–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollock, D.M.; Keith, T.L.; Highsmith, R.F. Endothelin receptors and calcium signaling. FASEB J. 1995, 9, 1196–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hynynen, M.M.; Khalil, R.A. The vascular endothelin system in hypertension–recent patents and discoveries. Recent Pat. Cardiovasc. Drug Discov. 2006, 1, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffrin, E.L. Does endothelin-1 raise or lower blood pressure in humans? Nephron 2018, 139, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostov, K.; Blazhev, A.; Atanasova, M.; Dimitrova, A. Serum concentrations of endothelin-1 and matrix metalloproteinases-2, -9 in pre-hypertensive and hypertensive patients with type 2 diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, E.; Islam, K.; Yeasmin, F.; Karim, M.R.; Rahman, M.; Agarwal, S.; Hossain, S.; Aziz, A.; Al Mamun, A.; Sheikh, A.; et al. Elevated levels of plasma Big endothelin-1 and its relation to hypertension and skin lesions in individuals exposed to arsenic. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2012, 259, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, B.; Mancia, G.; Spiering, W.; Agabiti Rosei, E.; Azizi, M.; Burnier, M.; Clement, D.L.; Coca, A.; de Simone, G.; Dominiczak, A.; et al. ESC/ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: The Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Society of Hypertension (ESH). Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 3021–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powierza, K.; Sawicka-Powierza, J.; Urban, B.; Żelazowska-Rutkowska, B.; Cylwik, B.; Mikołuć, B.; Kowalewska, O.; Bakunowicz-Łazarczyk, A. Endothelin-1 serum concentration in pediatric chronic idiopathic uveitis. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2021, 15, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Omari, M.A.; Khaleghi, M.; Mosley, T.H.; Morgenthaler, N.G.; Struck, J.; Bergmann, A.; Kullo, I.J. Plasma C-terminal pro-endothelin-1 is associated with left ventricular mass index and aortic root diameter in African-American adults with hypertension. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2011, 25, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kohan, D.E.; Rossi, N.F.; Inscho, E.W.; Pollock, D.M. Regulation of blood pressure and salt homeostasis by endothelin. Physiol. Rev. 2011, 91, 1–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oishi, S.; Sasaki, M.; Sato, T. Elevated immunoreactive endothelin levels in patients with pheochromocytoma. Am. J. Hypertens. 1994, 7, 717–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokokawa, K.; Tahara, H.; Kohno, M.; Murakawa, K.I.; Yasunari, K.; Nakagawa, K.; Hamada, T.; Otani, S.; Yanagisawa, M.; Takeda, T. Hypertension associated with endothelin-secreting malignant hemangioendothelioma. Ann. Intern. Med. 1991, 114, 213–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, M.; Yanagisawa, M. Endothelin: 20 years from discovery to therapy. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2008, 86, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumagae, S.I.; Adachi, H.; Jacobs, D.R., Jr.; Hirai, Y.; Enomoto, M.; Fukami, A.; Otsuka, M.; Nanjo, Y.; Esaki, E.; Kumagai, E.; et al. High level of plasma endothelin-1 predicts development of hypertension in normotensive subjects. Am. J. Hypertens. 2010, 23, 1103–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krum, H.; Viskoper, R.J.; Lacourciere, Y.; Budde, M.; Charlon, V. The effect of an endothelin-receptor antagonist, bosentan, on blood pressure in patients with essential hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 338, 784–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roumen, N.; Egon, P.; Siegfried, E. Darusentan: An effective endothelina receptor antagonist for treatment of hypertension. Am. J. Hypertens. 2002, 15, 583–589. [Google Scholar]
- Black, H.R.; Bakris, G.L.; Weber, M.A.; Weiss, R.; Shahawy, M.E.; Marple, R.; Tannoury, G.; Linas, S.; Wiens, B.L.; Linseman, J.V. Efficacy and safety of darusentan in patients with resistant hypertension: Results from a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled dose-ranging study. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2007, 9, 760–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakris, G.L.; Lindholm, L.H.; Black, H.R.; Krum, H.; Linas, S.; Linseman, J.V.; Arterburn, S.; Sager, P.; Weber, M. Divergent results using clinic and ambulatory blood pressures: Report of a darusentan-resistant hypertension trial. Hypertension 2010, 56, 824–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, Y.; Nakao, K.; Mukoyama, M.; Imura, H. Increased plasma endothelin level in patients with essential hypertension. N. Engl. J. Med. 1990, 322, 205. [Google Scholar]
- Shichiri, M.; Hirata, Y.; Ando, K.; Emori, T.; Ohta, K.; Kimoto, S.; Ogura, M.; Inoue, A.; Marumo, F. Plasma endothelin levels in hypertension and chronic renal failure. Hypertension 1990, 15, 493–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohno, M.; Yasunari, K.; Murakawa, K.I.; Yokokawa, K.; Horio, T.; Fukui, T.; Takeda, T. Plasma immunoreactive endothelin in essential hypertension. Am. J. Med. 1990, 88, 614–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Januszewicz, A.; Łapiński, M.; Symonides, B.; Dabrowska, E.; Kuch-Wocial, A.; Trzepla, E.; Ignatowska-Świtalska, H.; Wocial, B.; Chodakowska, J.; Januszewicz, W. Elevated endothelin-1 plasma concentration in patients with essential hypertension. Eur. J. Cardiovasc. Prev. Rehabil. 1994, 1, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoroso, A.; Cossu, M.; Mariotti, A.; Guido, F.; Ferri, G.; De Rosa, F.; Sportelli, G. Increased plasma levels of endothelin in patients with essential arterial hypertension. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 1996, 18, 33–37. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, M.P.; Hilgers, K.F.; Klingbeil, A.U.; John, S.; Veelken, R.; Schmieder, R.E. Plasma endothelin is increased in early essential hypertension. Am. J. Hypertens. 2000, 13, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostov, K.; Dimitrova, A.; Grigoryan, A.; Tisheva, S.; Ruseva, A.; Atanasova, M.; Gospodinov, C.; Blazhev, A. Changes in the serum levels of endothelin-1, matrix metalloproteinases-2,-9 and C-reactive protein in patients with mild and severe degree of arterial hypertension. C. R. Acad. Bulg. Sci. 2014, 67, 427–434. [Google Scholar]
- Barton, M.; Shaw, S.; d’Uscio, L.V.; Moreau, P.; Lüscher, T.F. Angiotensin II increases vascular and renal endothelin-1 and functional endothelin converting enzyme activity in vivo: Role of ETA receptors for endothelin regulation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1997, 238, 861–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffrin, E.L. Role of endothelin-1 in hypertension and vascular disease. Am. J. Hypertens. 2001, 14, 83S–89S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doumas, M.N.; Douma, S.N.; Petidis, K.M.; Vogiatzis, K.V.; Bassagiannis, I.C.; Zamboulis, C.X. Different effects of losartan and moxonidine on endothelial function during sympathetic activation in essential hypertension. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2004, 6, 682–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haug, C.; Koenig, W.; Hoeher, M.; Kochs, M.; Hombach, V.; Gruenert, A.; Osterhues, H. Direct enzyme immunometric measurement of plasma big endothelin-1 concentrations and correlation with indicators of left ventricular function. Clin. Chem. 1998, 44, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, R.; Yang, Y.M.; Yu, L.T.; Tan, H.Q.; Zhu, J. Elevated plasma big endothelin-1 at admission is associated with poor short-term outcomes in patients with acute decompensated heart failure. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubens, C.; Ewert, R.; Halank, M.; Wensel, R.; Orzechowski, H.D.; Schultheiss, H.P.; Hoeffken, G. Big endothelin-1 and endothelin-1 plasma levels are correlated with the severity of primary pulmonary hypertension. Chest 2001, 120, 1562–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, S.; Schmeisser, A.; Hoeffken, G.; Halank, M. Plasma big-endothelin in pre- versus postcapillary pulmonary hypertension. Pneumologie 2009, 63, A4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Li, T.; Cong, X.; Hou, Z.; Lu, B.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, X. Association between circulating big endothelin-1 and noncalcified or mixed coronary atherosclerotic plaques. Coron. Artery Dis. 2019, 30, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, M.H.; Guo, Y.L.; Zhu, C.G.; Xu, R.X.; Dong, Q.; Li, J.J. Plasma big endothelin-1 level and the severity of new-onset stable coronary artery disease. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2015, 22, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkaliagkousi, E.; Gavriilaki, E.; Triantafyllou, A.; Nikolaidou, B.; Anyfanti, P.; Koletsos, N.; Vamvakis, A.; Dipla, K.; Lazaridis, A.; Douma, S. Asymmetric dimethylarginine levels are associated with augmentation index across naïve untreated patients with different hypertension phenotypes. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2018, 20, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkaliagkousi, E.; Gavriilaki, E.; Triantafyllou, A.; Douma, S. Clinical significance of endothelial dysfunction in essential hypertension. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2015, 17, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostov, K. The causal relationship between endothelin-1 and hypertension: Focusing on endothelial dysfunction, arterial stiffness, vascular remodeling, and blood pressure regulation. Life 2021, 11, 986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Number of Examined Individuals (n = 80) | Control Group (n = 20) | Hypertensive Group (n = 60) |
|---|---|---|
| Sex, Male/Female | 10/10 | 24/36 |
| Age, years 1 | 47.9 ± 11.3 | 65.3 ± 11.5 |
| Duration of HTN 1 | N/A 2 | 8.6 ± 5.9 |
| SBP, mmHg 1 | 124.0 ± 3.7 | 155.4 ± 4.8 |
| DBP, mmHg 1 | 82.2 ± 4.1 | 87.1 ± 2.6 |
| ET-1, pg/mL 1 | 3.2 ± 1.0 | 5.01 ± 2.1 |
| Big ET-1, pmol/L 1 | 0.378 ± 0.07 | 0.377 ± 0.1 |
| TC, mmol/L 1 | 3.9 ± 0.7 | 4.8 ± 1.2 |
| LDL-C, mmol/L 1 | 2.5 ± 0.6 | 3.2 ± 1.1 |
| HDL-C, mmol/L 1 | 1.1 ± 0.3 | 1.02 ± 0.2 |
| TG, mmol/L 1 | 1.3 ± 0.6 | 1.5 ± 1.3 |
| CRP, mg/L 1 | 1.07 ± 0.9 | 7.5 ± 9.6 |
| Hypertensive CVD: | N/A 2 | (n = 12) |
| -Coronary Artery Disease | N/A 2 | (n = 5) |
| -Kidney Damage | N/A 2 | (n = 3) |
| -Brain Damage | N/A 2 | (n = 2) |
| -Eye Damage | N/A 2 | (n = 2) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kostov, K.; Blazhev, A. Circulating Levels of Endothelin-1 and Big Endothelin-1 in Patients with Essential Hypertension. Pathophysiology 2021, 28, 489-495. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology28040031
Kostov K, Blazhev A. Circulating Levels of Endothelin-1 and Big Endothelin-1 in Patients with Essential Hypertension. Pathophysiology. 2021; 28(4):489-495. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology28040031
Chicago/Turabian StyleKostov, Krasimir, and Alexander Blazhev. 2021. "Circulating Levels of Endothelin-1 and Big Endothelin-1 in Patients with Essential Hypertension" Pathophysiology 28, no. 4: 489-495. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology28040031
APA StyleKostov, K., & Blazhev, A. (2021). Circulating Levels of Endothelin-1 and Big Endothelin-1 in Patients with Essential Hypertension. Pathophysiology, 28(4), 489-495. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology28040031







