Risk Stratification in Post-ERCP Pancreatitis: How Do Procedures, Patient Characteristics and Clinical Indicators Influence Outcomes?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
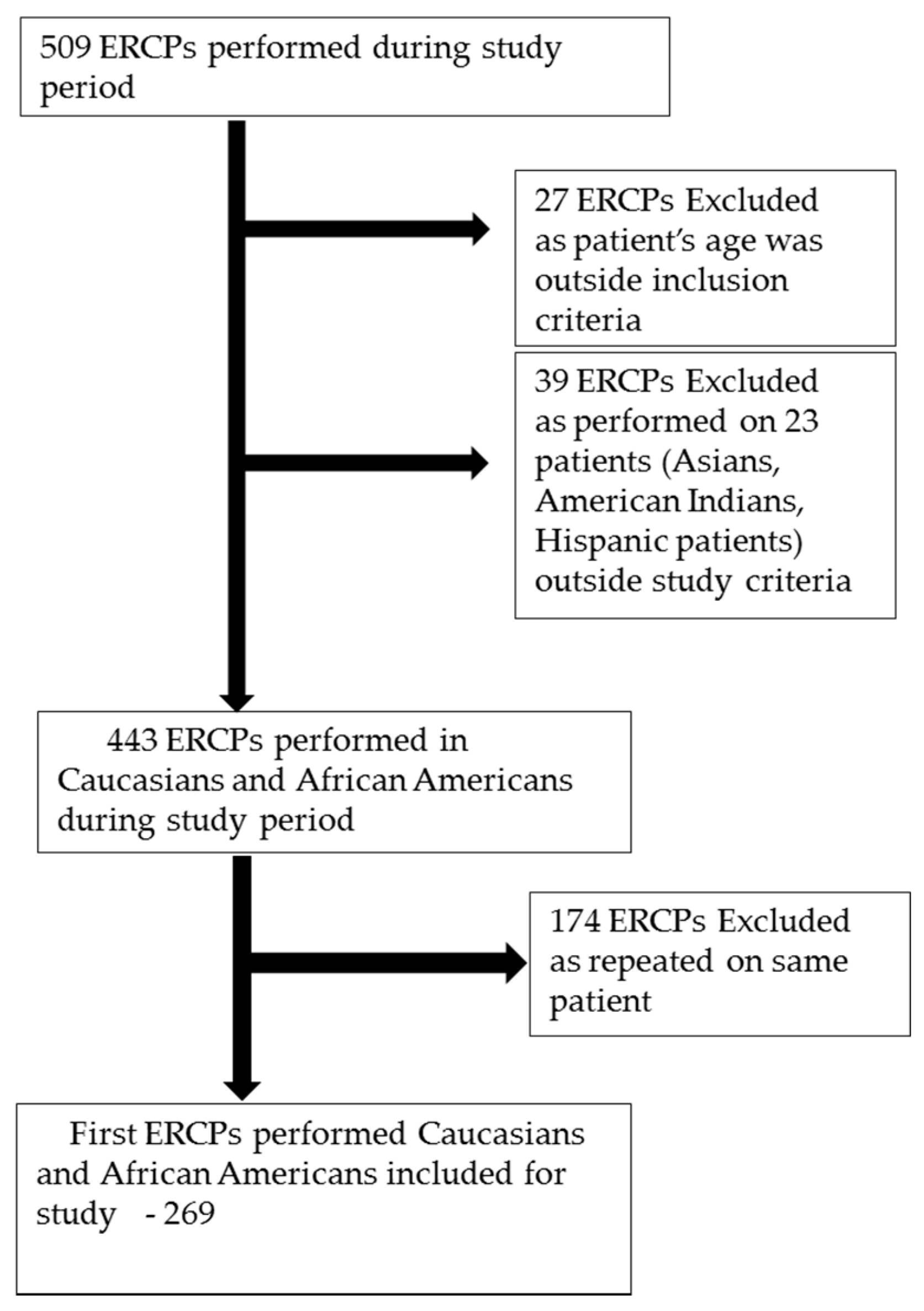
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Study Protocol and Data Collection
2.3. Definition
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
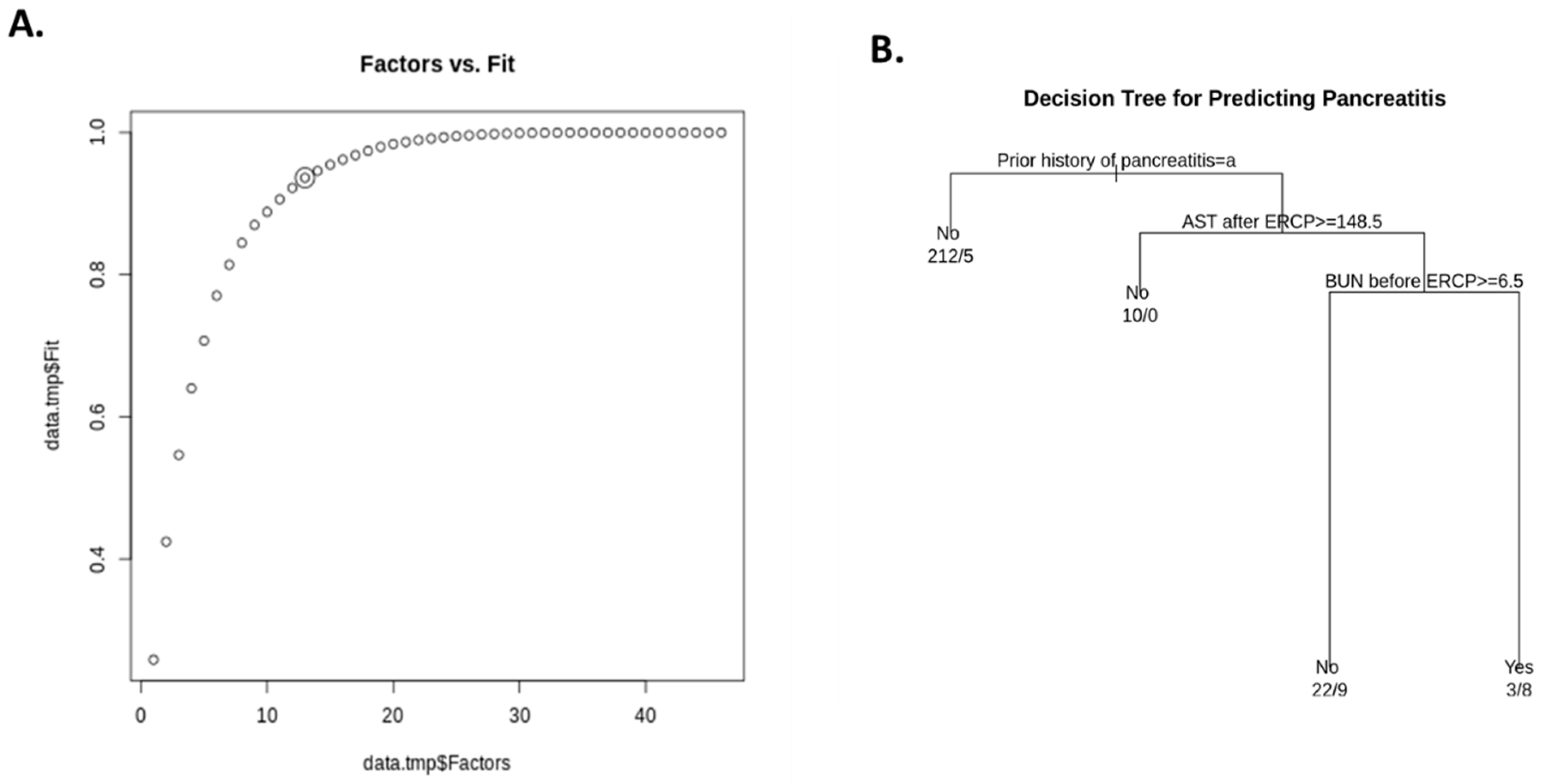
Factor Analysis and Decision Tree Learning
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chandrasekhara, V.; Khashab, M.A.; Muthusamy, V.R.; Acosta, R.D.; Agrawal, D.; Bruining, D.H.; Eloubeidi, M.A.; Fanelli, R.D.; Faulx, A.L.; Gurudu, S.R.; et al. Adverse events associated with ERCP. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2017, 85, 32–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, S.; Kylänpää, L.; Mustonen, H.; Halttunen, J.; Lindström, O.; Jokelainen, K.; Udd, M.; Färkkilä, M. Risk factors for post-ERCP pancreatitis: A prospective multicenter study. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 101, 139–147. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, K.Y.; Montes, H.; Sossenheimer, M.J.; Tham, T.C.; Ruymann, F.; Van Dam, J.; Carr-Locke, D.L. Features that may predict hospital admission following outpatient therapeutic ERCP. Gastrointest. Endosc. 1999, 49, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loperfido, S.; Angelini, G.; Benedetti, G.; Chilovi, F.; Costan, F.; De Berardinis, F.; De Bernardin, M.; Ederle, A.; Fina, P.; Fratton, A. Major early complications from diagnostic and therapeutic ERCP: A prospective multicenter study. Gastrointest. Endosc. 1998, 48, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, M.L.; Nelson, D.B.; Sherman, S.; Haber, G.B.; Herman, M.E.; Dorsher, P.J.; Moore, J.P.; Fennerty, M.B.; Ryan, M.E.; Shaw, M.J.; et al. Complications of endoscopic biliary sphincterotomy. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 335, 909–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabenstein, T.; Schneider, H.T.; Bulling, D.; Nicklas, M.; Katalinic, A.; Hahn, E.G.; Martus, P.; Ell, C. Analysis of the risk factors associated with endoscopic sphincterotomy techniques: Preliminary results of a prospective study, with emphasis on the reduced risk of acute pancreatitis with low-dose anticoagulation treatment. Endoscopy 2000, 32, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masci, E.; Toti, G.; Mariani, A.; Curioni, S.; Lomazzi, A.; Dinelli, M.; Minoli, G.; Crosta, C.; Comin, U.; Fertitta, A.; et al. Complications of diagnostic and therapeutic ERCP: A prospective multicenter study. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2001, 96, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, M.L.; DiSario, J.A.; Nelson, D.B.; Fennerty, M.B.; Lee, J.G.; Bjorkman, D.J.; Overby, C.S.; Aas, J.; Ryan, M.E.; Bochna, G.S.; et al. Risk factors for post-ERCP pancreatitis: A prospective, multicenter study. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2001, 54, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandervoort, J.; Soetikno, R.M.; Tham, T.C.; Wong, R.C.; Ferrari, A.P., Jr.; Montes, H.; Roston, A.D.; Slivka, A.; Lichtenstein, D.R.; Ruymann, F.W.; et al. Risk factors for complications after performance of ERCP. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2002, 56, 652–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, M.; Matzen, P.; Schulze, S.; Rosenberg, J. Complications of ERCP: A prospective study. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2004, 60, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheon, Y.K.; Cho, K.B.; Watkins, J.L.; McHenry, L.; Fogel, E.L.; Sherman, S.; Lehman, G.A. Frequency and severity of post-ERCP pancreatitis correlated with extent of pancreatic ductal opacification. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2007, 65, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, E.J.; Taylor, S.; Fairclough, P.; Hamlyn, A.; Logan, R.F.; Martin, D.; Riley, S.A.; Veitch, P.; Wilkinson, M.L.; Williamson, P.R.; et al. Risk factors for complication following ERCP; results of a large-scale, prospective multicenter study. Endoscopy 2007, 39, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Li, Z.S.; Liu, F.; Ren, X.; Lu, N.H.; Fan, Z.N.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, X.; He, L.P.; Sun, W.S.; et al. Risk factors for ERCP-related complications: A prospective multicenter study. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 104, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cotton, P.B.; Garrow, D.A.; Gallagher, J.; Romagnuolo, J. Risk factors for complications after ERCP: A multivariate analysis of 11,497 procedures over 12 years. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2009, 70, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andriulli, A.; Loperfido, S.; Napolitano, G.; Niro, G.; Valvano, M.R.; Spirito, F.; Pilotto, A.; Forlano, R. Incidence rates of post-ERCP complications: A systematic survey of prospective studies. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 102, 1781–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enochsson, L.; Swahn, F.; Arnelo, U.; Nilsson, M.; Lohr, M.; Persson, G. Nationwide, population-based data from 11,074 ERCP procedures from the Swedish Registry for Gallstone Surgery and ERCP. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2010, 72, 1175–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kochar, B.; Akshintala, V.S.; Afghani, E.; Elmunzer, B.J.; Kim, K.J.; Lennon, A.M.; Khashab, M.A.; Kalloo, A.N.; Singh, V.K. Incidence, severity, and mortality of post-ERCP pancreatitis: A systematic review by using randomized, controlled trials. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2015, 81, 143–149.e149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christoforidis, E.; Goulimaris, I.; Kanellos, I.; Tsalis, K.; Demetriades, C.; Betsis, D. Post-ERCP pancreatitis and hyperamylasemia: Patient-related and operative risk factors. Endoscopy 2002, 34, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, E.; Leung, J. Pharmacotherapy for the prevention of post-ERCP pancreatitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 102, 52–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Y. Risk factors for post-ERCP pancreatitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Surgeon 2015, 13, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maitin-Casalis, N.; Neeman, T.; Thomson, A. Protective effect of advanced age on post-ERCP pancreatitis and unplanned hospitalisation. Intern. Med. J. 2015, 45, 1020–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finkelmeier, F.; Tal, A.; Ajouaou, M.; Filmann, N.; Zeuzem, S.; Waidmann, O.; Albert, J. ERCP in elderly patients: Increased risk of sedation adverse events but low frequency of post-ERCP pancreatitis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2015, 82, 1051–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, S.T.; Slivka, A. Incidence, risk factors, and prevention of post-ERCP pancreatitis. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 2007, 36, 259–276, vii–viii. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakutani, H.; Hino, S.; Ikeda, K.; Koyama, S.; Mori, N.; Imazu, H.; Kawamura, M.; Tajiri, H. Risk factors of post-ERCP pancreatitis at a tertiary referral center in Japan. Surg. Laparosc. Endosc. Percutan. Tech. 2014, 24, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Therneau, T.; Atkinson, B.; Ripley, B. “Package ‘rpart’: Recursive Partitioning and Regression Trees”. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/rpart/rpart.pdf (accessed on 12 April 2019).
- Breimann, L.; Friedman, J.; Stone, C.J.; Olshen, R.A. Classification and Regression Trees. In Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery; Wadsworth: Belmont, CA, USA, 1984; ISBN 978-0412048418. [Google Scholar]

| Indication for ERCP | n (%) |
|---|---|
| CBD Stone/Obstructive Jaundice | |
| 195 (72.4%) | |
| CBD Stricture | 20 (7.4%) |
| Cholangitis | 10 (3.7%) |
| Pancreatitis | 11 (4.0%) |
| Dilated CBD | 6 (2.2%) |
| Bile Leak | 20 (7.4%) |
| Unknown | 7 (2.6%) |
| Techniques | n (%) |
|---|---|
| CBD Stone removal | 54 (20%) |
| CBD Stricture Dilatation | 29 (10.7%) |
| Endoscopic sphincteroplasty | 8 (2.9%) |
| Balloon Sweeps | 103 (38.2%) |
| CBD Stent placement | 154 (57.2%) |
| Endoscopic sphincterotomy | 139 (51.6%) |
| Pancreatic duct stent placement | 42 (15.6%) |
| Variables Divided by Race and Gender | n/N (% or SD) or Value as Defined | p Value |
|---|---|---|
| Caucasian Males | ||
| Prior history of pancreatitis | PEP group = 6/8 (75%) Non-PEP group = 9/46(19.5%) | 0.009 |
| Hemoglobin before ERCP | PEP group = 12.2 (SD = 1.76) Non-PEP group = 12.8 (SD = 1.92) | 0.02 |
| BUN before ERCP | PEP group = 7.8 (SD = 4.12) Non-PEP group = 13.6 (SD = 0.75) | 0.01 |
| Creatinine before ERCP | PEP group = 0.86 (SD = 0.18) Non-PEP group = 1.17 (SD = 1.10) | 0.07 |
| BUN after ERCP | PEP group = 7.6 (SD = 3.15) Non-PEP group = 13 (SD = 11.8) | 0.01 |
| Creatinine after ERCP | PEP group = 0.82 (SD = 0.23) Non-PEP group = 1.19 (SD = 1.17) | 0.07 |
| Caucasian Females | p value | |
| WBC count before ERCP | PEP group = 12.3 (SD = 3.43) Non-PEP group = 8.66 (SD = 4.29) | 0.08 |
| Amylase after ERCP | PEP group = 87 (SD = 42.43) Non-PEP group = 80.18 (SD = 83.35) | 0.10 |
| Bilirubin after ERCP | PEP group = 1.18 (SD = 1.04) Non-PEP group = 2.23 (SD = 2.03) | 0.09 |
| AST after ERCP | PEP group = 47.60 (SD = 34.40) Non-PEP group = 85.60 (SD = 96.76) | 0.08 |
| African-American Males | p value | |
| Weight in kilograms | PEP group = 70.8 (SD = 6.01) Non-PEP group = 84.3 (SD = 20.18) | 0.0001 |
| Height in Inches | PEP group = 69 (SD = 4.35) Non-PEP group = 70.5 (SD = 3.16) | 0.0005 |
| Alkaline phosphatase before ERCP | PEP group = 122 (SD = 64) Non-PEP group = 423 (SD = 464) | 0.0002 |
| AST before ERCP | PEP group = 61 (SD = 42) Non-PEP group = 152 (SD = 199) | 0.04 |
| ALT before ERCP | PEP group = 74 (SD = 46) Non-PEP group = 171 (SD = 147) | 0.03 |
| Alkaline phosphatase after ERCP | PEP group = 131 (SD = 55) Non-PEP group = 412 (SD = 422) | 0.002 |
| AST after ERCP | PEP group = 47 (SD = 29) Non-PEP group = 125 (SD = 115) | 0.01 |
| ALT after ERCP | PEP group = 66 (SD = 29) Non-PEP group = 171 (SD = 148) | 0.004 |
| African-American Females | p value | |
| Prior history of pancreatitis | PEP group = 4/6 (66.6%) Non-PEP group = 9/85 (10.5%) | 0.004 |
| Lipase before ERCP | PEP group = 5620 (SD = 3006) Non-PEP group = 1209 (SD = 5073) | 0.0001 |
| Lipase after ERCP | PEP group = 925 (SD = 1281) Non-PEP group = 1462 (SD = 3852) | 0.05 |
| Risk with pancreatic duct cannulation | PEP group = 3/6 (50%) Non-PEP group = 38/85 (45.8%) | 0.0001 |
| Risk with pancreatic duct injection | PEP group = 1/6 (16.6%) Non-PEP group = 11/85 (12.9%) | 0.0001 |
| Risk with biliary sphincterotomy | PEP group = 5/6 (83.3%) Non-PEP group = 68/85 (80%) | 0.0001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kohli, K.; Samant, H.; Khan, K.; Pandit, S.; Morgan, K.; Cvek, U.; Kilgore, P.; Trutschl, M.; Mijalis, E.; Jordan, P.; et al. Risk Stratification in Post-ERCP Pancreatitis: How Do Procedures, Patient Characteristics and Clinical Indicators Influence Outcomes? Pathophysiology 2021, 28, 76-85. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology28010007
Kohli K, Samant H, Khan K, Pandit S, Morgan K, Cvek U, Kilgore P, Trutschl M, Mijalis E, Jordan P, et al. Risk Stratification in Post-ERCP Pancreatitis: How Do Procedures, Patient Characteristics and Clinical Indicators Influence Outcomes? Pathophysiology. 2021; 28(1):76-85. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology28010007
Chicago/Turabian StyleKohli, Kapil, Hrishikesh Samant, Kashif Khan, Sudha Pandit, Kelli Morgan, Urska Cvek, Phillip Kilgore, Marjan Trutschl, Eleni Mijalis, Paul Jordan, and et al. 2021. "Risk Stratification in Post-ERCP Pancreatitis: How Do Procedures, Patient Characteristics and Clinical Indicators Influence Outcomes?" Pathophysiology 28, no. 1: 76-85. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology28010007
APA StyleKohli, K., Samant, H., Khan, K., Pandit, S., Morgan, K., Cvek, U., Kilgore, P., Trutschl, M., Mijalis, E., Jordan, P., Morris, J., Boktor, M., & Alexander, J. S. (2021). Risk Stratification in Post-ERCP Pancreatitis: How Do Procedures, Patient Characteristics and Clinical Indicators Influence Outcomes? Pathophysiology, 28(1), 76-85. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathophysiology28010007







