Real-World Effectiveness and Safety of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Combined with Chemotherapy in Taiwanese Patients with Extensive-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Data Collection
2.2. Adverse Events Classification
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participates Enrollment
3.2. Basic Characteristics
3.3. Treatment Response and Adverse Events
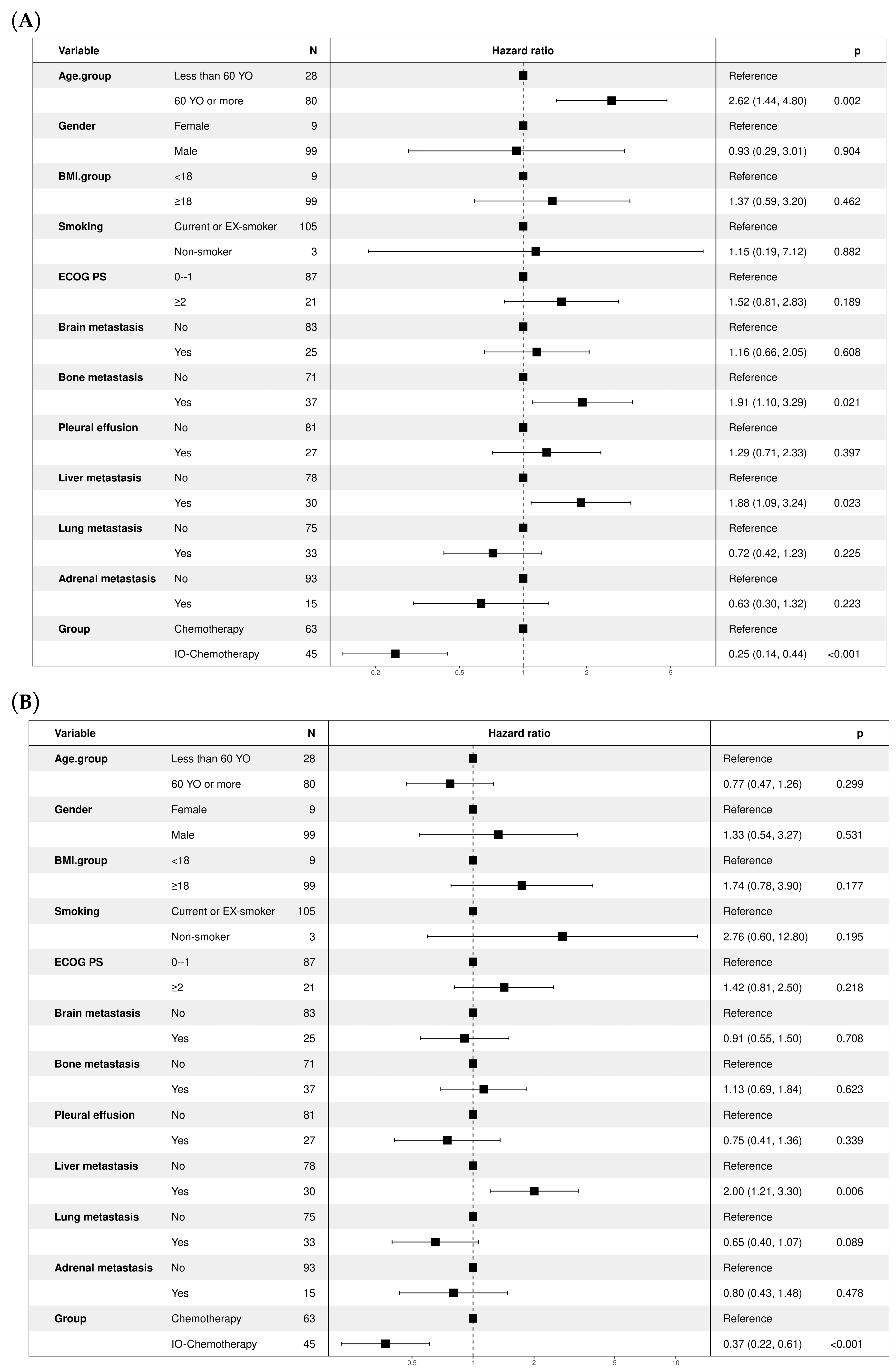
3.4. Treatment Outcomes and Patient Survival
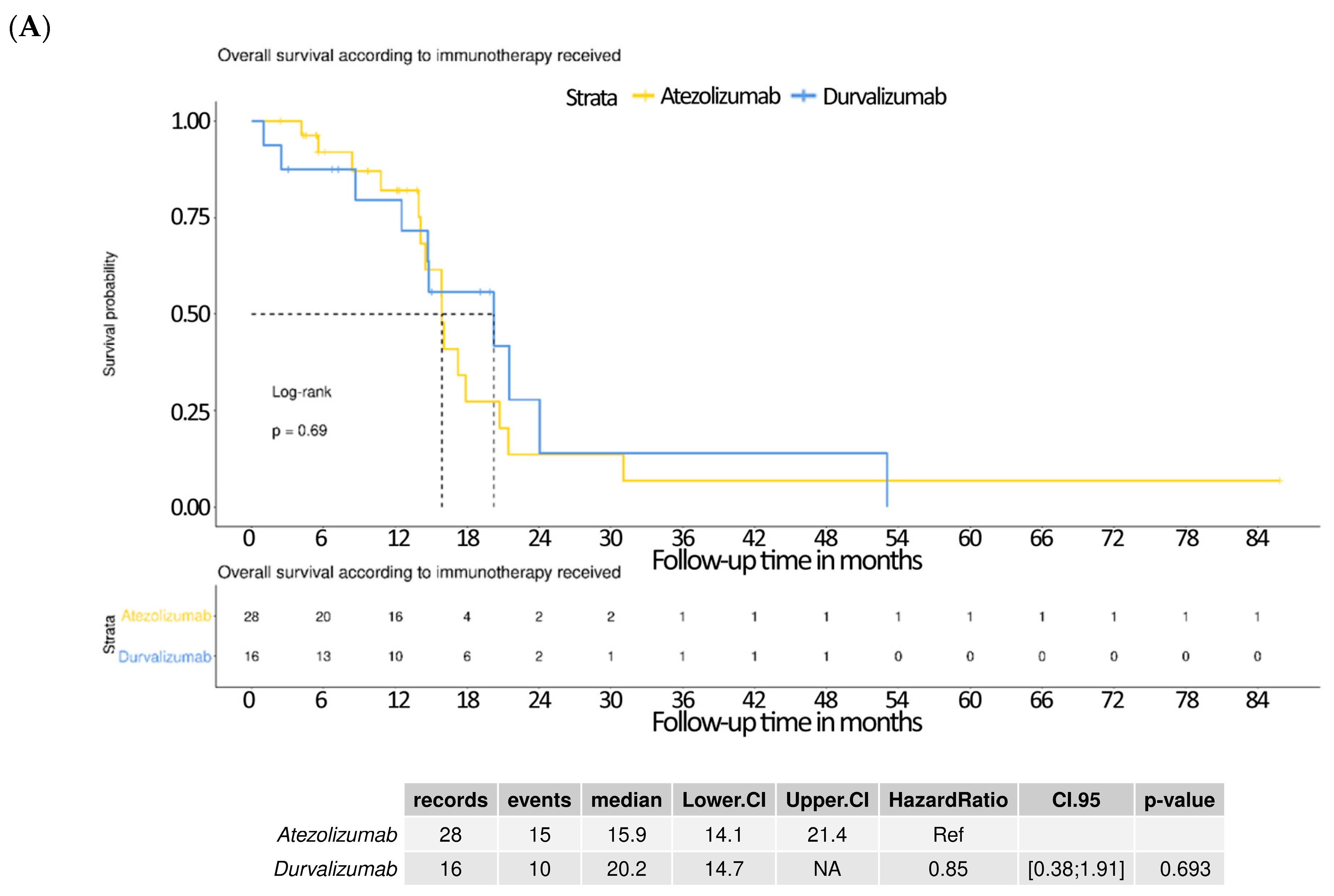
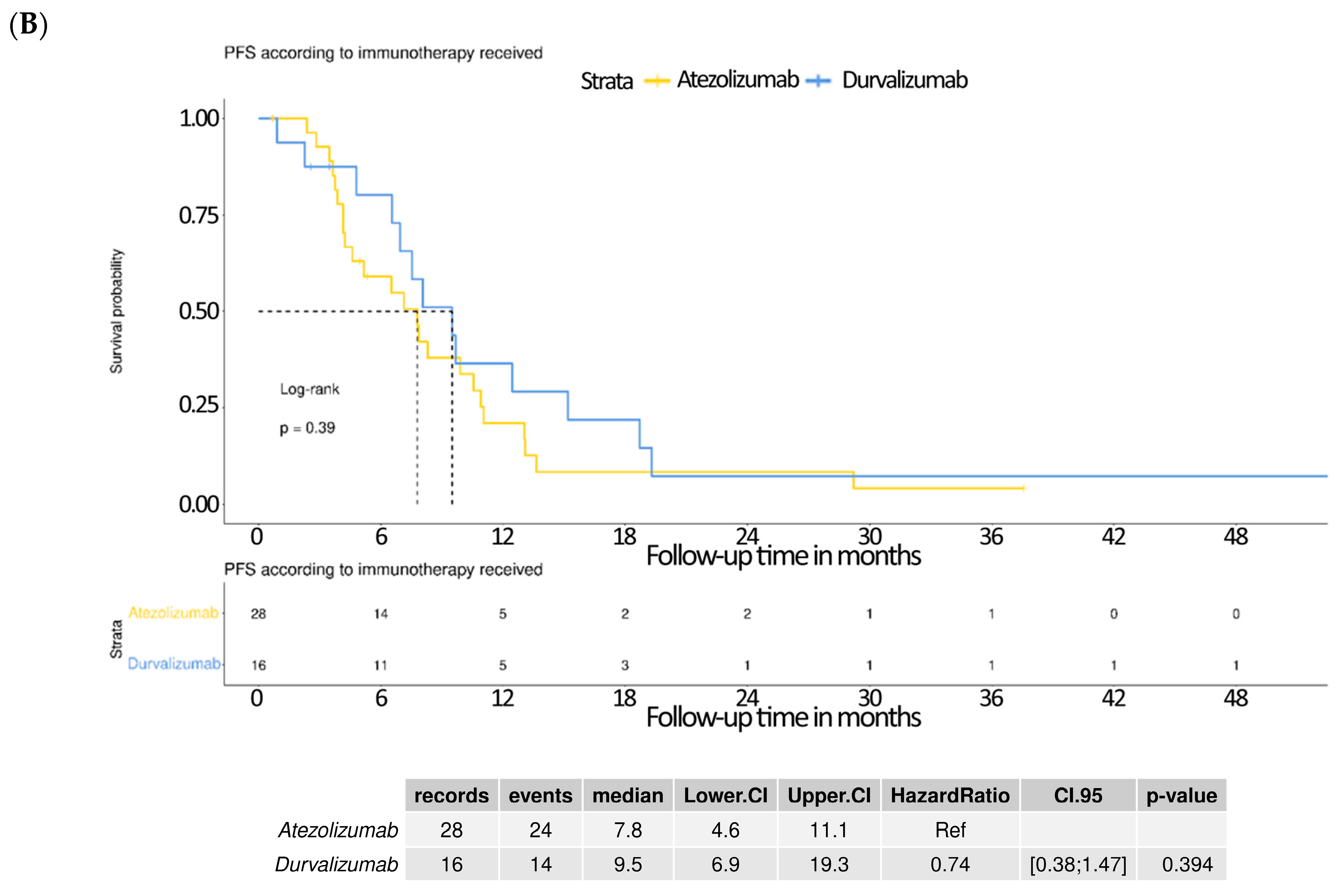
3.5. Subgroup Analysis Comparing Atezolizumab and Durvalumab
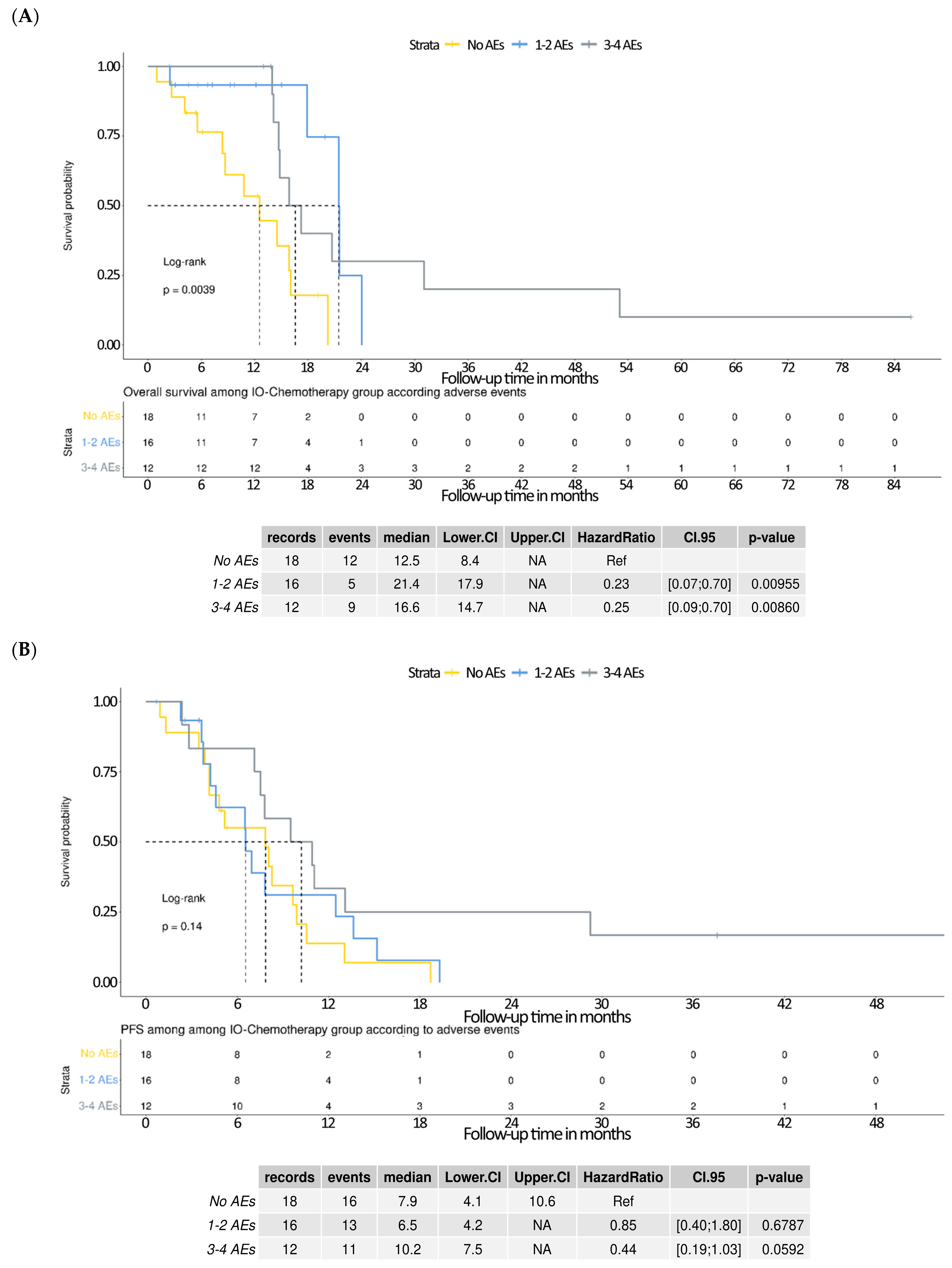
3.6. Survival Outcomes Stratified by Adverse Events in the IO–Chemotherapy Group
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, S.Y.; Park, H.S.; Chiang, A.C. Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Review. JAMA 2025, 333, 1906–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, S.; Stanley, K.E.; Yesner, R.; Kuang, D.T.; Morris, J.F. Small-cell carcinoma of the lung—Survival according to histologic subtype: A veterans administration lung group study. Cancer 1981, 47, 1863–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, K.; Gay, C.M.; Byers, L.A.; Zhang, J. The current and emerging immunotherapy paradigm in small-cell lung cancer. Nat. Cancer 2025, 6, 954–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, A.; Di Maio, M.; Chiodini, P.; Rudd, R.M.; Okamoto, H.; Skarlos, D.V.; Früh, M.; Qian, W.; Tamura, T.; Samantas, E.; et al. Carboplatin- or Cisplatin-Based Chemotherapy in First-Line Treatment of Small-Cell Lung Cancer: The COCIS Meta-Analysis of Individual Patient Data. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 1692–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horn, L.; Mansfield, A.S.; Szczęsna, A.; Havel, L.; Krzakowski, M.; Hochmair, M.J.; Huemer, F.; Losonczy, G.; Johnson, M.L.; Nishio, M.; et al. First-Line Atezolizumab plus Chemotherapy in Extensive-Stage Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2220–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paz-Ares, L.; Dvorkin, M.; Chen, Y.; Reinmuth, N.; Hotta, K.; Trukhin, D.; Statsenko, G.; Hochmair, M.J.; Özgüroğlu, M.; Ji, J.H.; et al. Durvalumab plus platinum–etoposide versus platinum–etoposide in first-line treatment of extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (CASPIAN): A randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2019, 394, 1929–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudin, C.M.; Awad, M.M.; Navarro, A.; Gottfried, M.; Peters, S.; Csőszi, T.; Cheema, P.K.; Rodriguez-Abreu, D.; Wollner, M.; Yang, J.C.-H.; et al. Pembrolizumab or Placebo Plus Etoposide and Platinum as First-Line Therapy for Extensive-Stage Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Randomized, Double-Blind, Phase III KEYNOTE-604 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 2369–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damiano, P.; Stefani, A.; Avancini, A.; Belluomini, L.; Bria, E.; Pilotto, S. Real-world evidence in extensive disease small cell lung cancer: The missing piece of the puzzle. Crit. Rev. Oncol. 2025, 207, 104618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Ye, J.; Shao, Z.; Rossi, A.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, S. Prognostic value of baseline clinicopathological characteristics in first-line chemotherapy ± immunotherapy for extensive-stage small cell lung cancer: A retrospective cohort study. J. Thorac. Dis. 2024, 16, 5348–5360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragavan, M.; Das, M. Systemic Therapy of Extensive Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer in the Era of Immunotherapy. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2020, 21, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatori, T.; Numata, T.; Shiozawa, T.; Taguchi, M.; Sakurai, H.; Tamura, T.; Kanazawa, J.; Tachi, H.; Kondo, K.; Miyazaki, K.; et al. Prognostic Factors for Patients with Small-Cell Lung Cancer Treated with Chemoimmunotherapy: A Retrospective Multicenter Study. Curr. Oncol. 2024, 31, 6502–6511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vince, M.; Naqvi, S.M.H.; Pellini, B.; Verbosky, M.; Melzer, D. Real-world comparison of the efficacy and safety of atezolizumab versus durvalumab in extensive-stage small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2024, 198, 107999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, E.; Kraehenbuehl, L.; Ketosugbo, K.; Kern, J.A.; Lacouture, M.E.; Leung, D.Y. Immune-related cutaneous adverse events due to checkpoint inhibitors. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2021, 126, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Lee, S.Y. Clinical Characteristics and Treatment of Immune-Related Adverse Events of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Immune Netw. 2020, 20, e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos-Casals, M.; Brahmer, J.R.; Callahan, M.K.; Flores-Chávez, A.; Keegan, N.; Khamashta, M.A.; Lam-Botte, O.; Mariette, X.; Prat, A.; Suárez-Almazor, M.E. Immune-related adverse events of checkpoint in-hibitors. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2020, 6, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akamatsu, H.; Murakami, E.; Oyanagi, J.; Shibaki, R.; Kaki, T.; Takase, E.; Tanaka, M.; Harutani, Y.; Yamagata, N.; Okuda, Y.; et al. Immune-Related Adverse Events by Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Significantly Predict Durable Efficacy Even in Responders with Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Oncologist 2019, 25, e679–e683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussaini, S.; Chehade, R.; Boldt, R.G.; Raphael, J.; Blanchette, P.; Vareki, S.M.; Fernandes, R. Association between immune-related side effects and efficacy and benefit of immune checkpoint inhibitors—A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2021, 92, 102134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Gao, A.; Wang, S.; Sun, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, D.; Ge, Y.; Li, J.; Sun, H.; Cheng, Q.; et al. Correlation between immune-related adverse events and efficacy of PD-(L)1 inhibitors in small cell lung cancer: A multi-center retrospective study. Respir. Res. 2024, 25, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Characteristic | Chemotherapy N = 68 1 | IO–Chemotherapy N = 46 1 | p-Value 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 70 (60, 77) | 68 (59, 75) | 0.5 |
| Unknown | 1 | 0 | |
| Gender | 0.8 | ||
| Male | 61 (91%) | 41 (89%) | |
| Female | 6 (9.0%) | 5 (11%) | |
| Unknown | 1 | 0 | |
| BMI | 22.8 (20.8, 24.4) | 23.1 (19.7, 26.4) | 0.5 |
| Smoking | >0.9 | ||
| Current or ex-smoker | 66 (97%) | 44 (98%) | |
| Non-smoker | 2 (2.9%) | 1 (2.2%) | |
| Unknown | 0 | 1 | |
| ECOG PS | 0.021 | ||
| 0–1 | 47 (73%) | 41 (91%) | |
| ≥2 | 17 (27%) | 4 (8.9%) | |
| Unknown | 4 | 1 | |
| Brain metastasis | 0.091 | ||
| No | 48 (71%) | 38 (84%) | |
| Yes | 20 (29%) | 7 (16%) | |
| Unknown | 0 | 1 | |
| Bone metastasis | 0.5 | ||
| No | 43 (63%) | 31 (69%) | |
| Yes | 25 (37%) | 14 (31%) | |
| Unknown | 0 | 1 | |
| Pleural effusion | 0.3 | ||
| No | 48 (71%) | 36 (80%) | |
| Yes | 20 (29%) | 9 (20%) | |
| Unknown | 0 | 1 | |
| Lung metastasis | 0.2 | ||
| No | 45 (66%) | 35 (78%) | |
| Yes | 23 (34%) | 10 (22%) | |
| Unknown | 0 | 1 | |
| Liver metastasis | 0.8 | ||
| No | 49 (72%) | 34 (74%) | |
| Yes | 19 (28%) | 12 (26%) | |
| Adrenal metastasis | 0.6 | ||
| No | 60 (88%) | 38 (84%) | |
| Yes | 8 (12%) | 7 (16%) | |
| Unknown | 0 | 1 | |
| WBC | 8.2 (5.9, 10.3) | 7.9 (6.2, 9.1) | 0.4 |
| Unknown | 0 | 1 | |
| Seg | 73 (63, 83) | 72 (65, 79) | 0.5 |
| Unknown | 0 | 1 | |
| Lymphocyte | 16 (9, 26) | 18 (13, 24) | 0.3 |
| Unknown | 0 | 1 | |
| NLR | 4.7 (2.4, 8.8) | 3.9 (2.7, 5.8) | 0.3 |
| Unknown | 0 | 1 | |
| AST | 26 (19, 43) | 24 (18, 31) | 0.2 |
| Unknown | 6 | 1 | |
| ALT | 24 (14, 39) | 20 (15, 25) | 0.4 |
| Unknown | 1 | 1 | |
| Total bilirubin | 0.54 (0.40, 0.67) | 0.47 (0.38, 0.62) | 0.2 |
| Unknown | 2 | 2 | |
| Serum creatinine | 0.90 (0.70, 1.10) | 0.84 (0.70, 1.06) | 0.5 |
| Unknown | 0 | 1 | |
| Chemotherapy cycles no. | 5.00 (2.00, 6.00) | 5.00 (4.00, 6.00) | 0.2 |
| Unknown | 1 | 1 | |
| Response | 0.005 | ||
| Partial response | 22 (33%) | 28 (64%) | |
| Progressive disease | 37 (56%) | 12 (27%) | |
| Stable disease | 7 (11%) | 4 (9.1%) | |
| Unknown | 2 | 2 | |
| Brain metastasis progression | 0.090 | ||
| No | 48 (73%) | 38 (86%) | |
| Yes | 18 (27%) | 6 (14%) | |
| Unknown | 2 | 2 | |
| Skin rash | <0.001 | ||
| No | 66 (97%) | 34 (76%) | |
| Grade 1–2 ADR | 2 (2.9%) | 11 (24%) | |
| Unknown | 0 | 1 | |
| Liver toxicity | 0.4 | ||
| No | 60 (88%) | 43 (96%) | |
| Grade 1–2 ADR | 7 (10%) | 2 (4.4%) | |
| Grade ≥3 ADR | 1 (1.5%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Unknown | 0 | 1 | |
| Diarrhea | 0.2 | ||
| No | 62 (91%) | 37 (82%) | |
| Grade 1–2 ADR | 6 (8.8%) | 8 (18%) | |
| Unknown | 0 | 1 | |
| Interstitial lung disease | 0.4 | ||
| No | 68 (100%) | 44 (98%) | |
| Grade 1–2 ADR | 0 (0%) | 1 (2.2%) | |
| Unknown | 0 | 1 | |
| Endocrinal disorders | 0.081 | ||
| No | 67 (99%) | 41 (91%) | |
| Grade 1-2 ADR | 1 (1.5%) | 4 (8.9%) | |
| Unknown | 0 | 1 | |
| AKI | 0.4 | ||
| No | 63 (93%) | 44 (98%) | |
| Grade 1–2 ADR | 5 (7.4%) | 1 (2.2%) | |
| Unknown | 0 | 1 | |
| Neutropenia | 0.5 | ||
| No | 49 (72%) | 35 (78%) | |
| Yes | 19 (28%) | 10 (22%) | |
| Unknown | 0 | 1 | |
| Anemia | 0.3 | ||
| No | 48 (71%) | 36 (80%) | |
| Yes | 20 (29%) | 9 (20%) | |
| Unknown | 0 | 1 | |
| Thrombocytopenia | 0.2 | ||
| No | 53 (78%) | 30 (67%) | |
| Yes | 15 (22%) | 15 (33%) | |
| Unknown | 0 | 1 | |
| Treatment-related discontinuation | 0.5 | ||
| No | 66 (97%) | 45 (100%) | |
| Yes | 2 (2.9%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Unknown | 0 | 1 | |
| Treatment-related death | >0.9 | ||
| No | 67 (99%) | 45 (100%) | |
| Yes | 1 (1.5%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Unknown | 0 | 1 | |
| Duration of follow-up | 9 (3, 12) | 13 (6, 17) | 0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, C.-Y.; Wei, Y.-F.; Chang, S.-C.; Chen, C.-Y. Real-World Effectiveness and Safety of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Combined with Chemotherapy in Taiwanese Patients with Extensive-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer. Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32, 472. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32080472
Chang C-Y, Wei Y-F, Chang S-C, Chen C-Y. Real-World Effectiveness and Safety of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Combined with Chemotherapy in Taiwanese Patients with Extensive-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer. Current Oncology. 2025; 32(8):472. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32080472
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Cheng-Yu, Yu-Feng Wei, Shih-Chieh Chang, and Chung-Yu Chen. 2025. "Real-World Effectiveness and Safety of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Combined with Chemotherapy in Taiwanese Patients with Extensive-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer" Current Oncology 32, no. 8: 472. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32080472
APA StyleChang, C.-Y., Wei, Y.-F., Chang, S.-C., & Chen, C.-Y. (2025). Real-World Effectiveness and Safety of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Combined with Chemotherapy in Taiwanese Patients with Extensive-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer. Current Oncology, 32(8), 472. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32080472






