High Outcome-Reporting Bias in Randomized-Controlled Trials of Acupuncture for Cancer Chemotherapy-Induced Nausea and Vomiting: A Systematic Review and Meta-Epidemiological Study
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
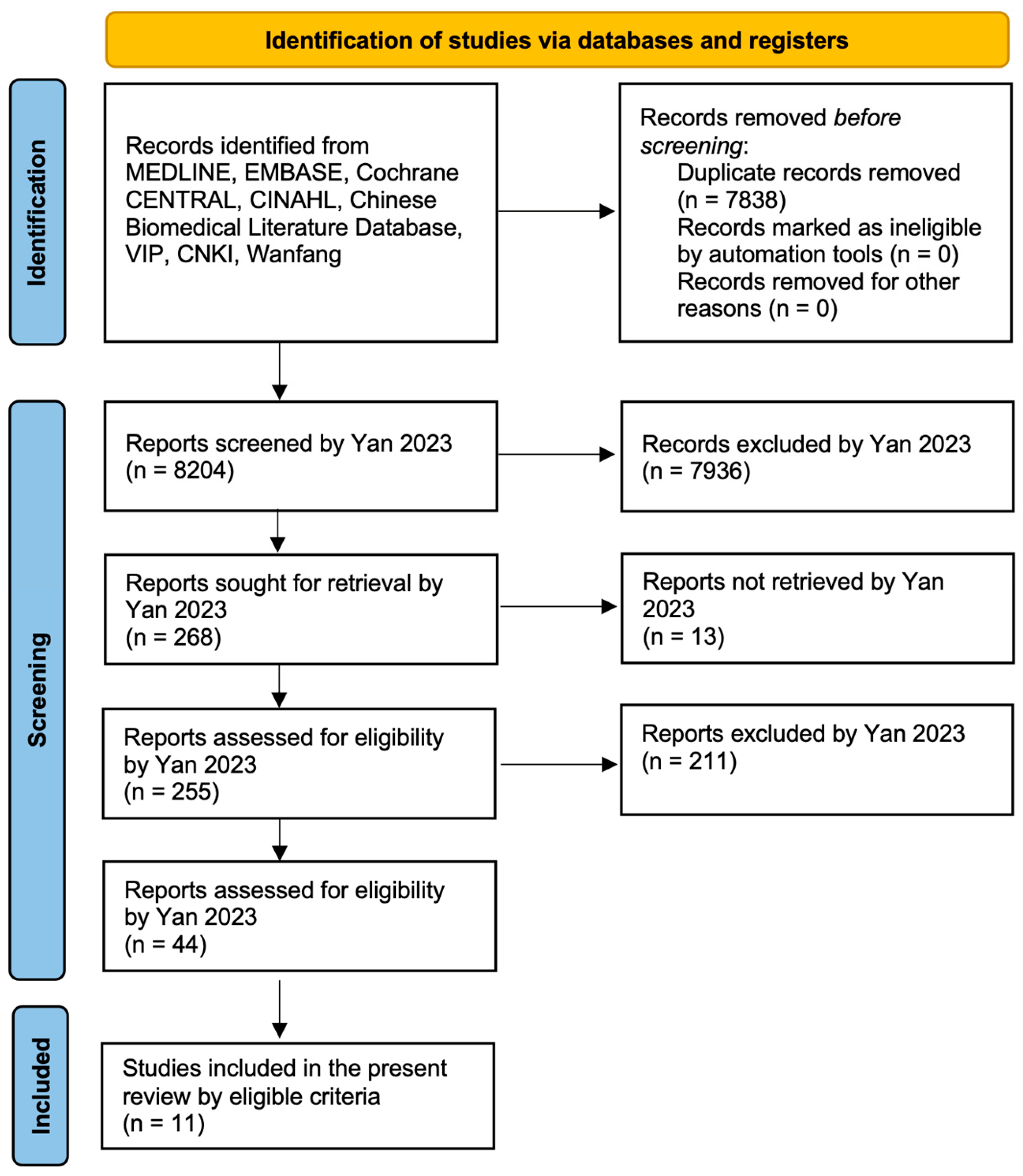
2. Materials and Methods
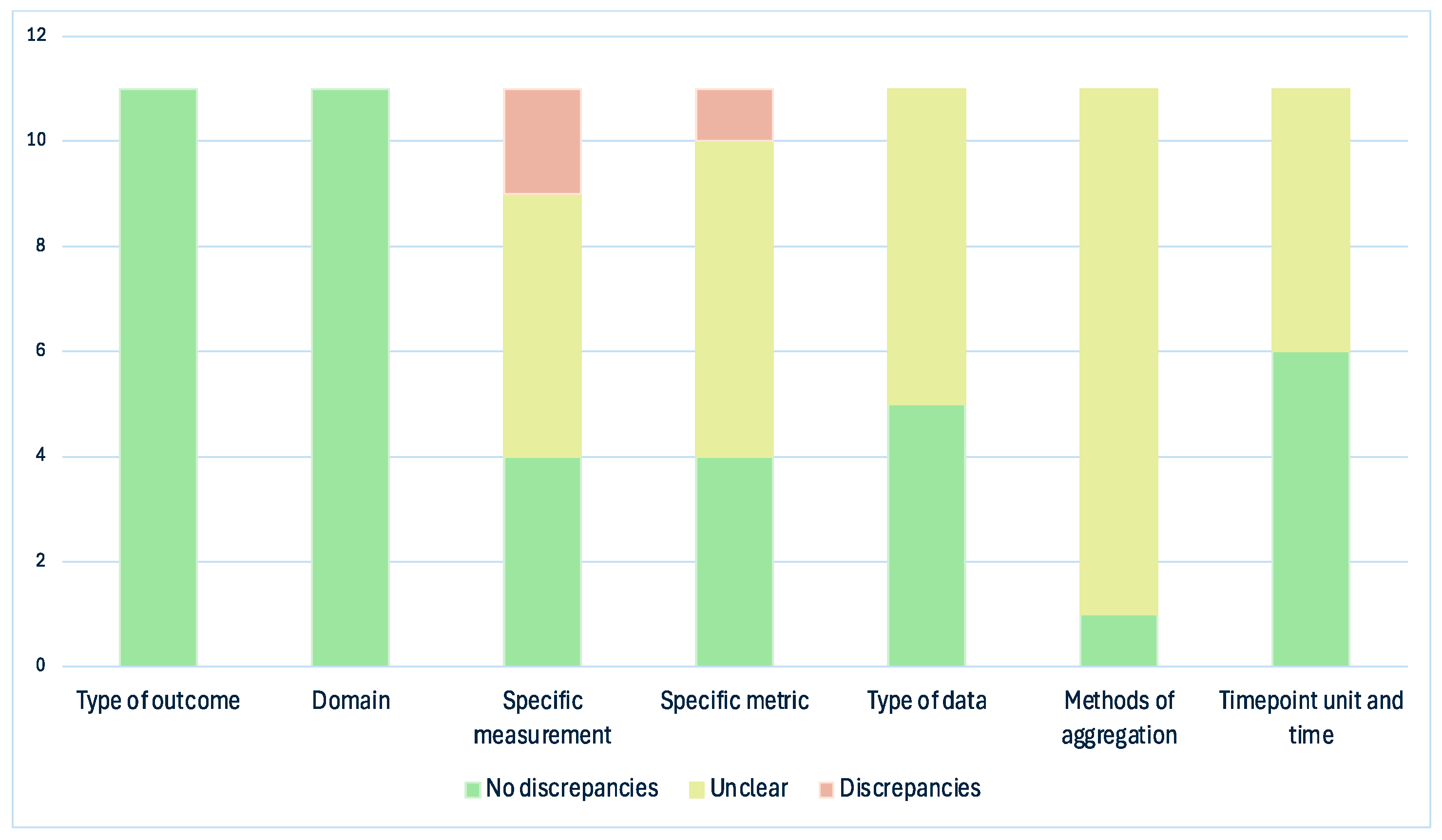
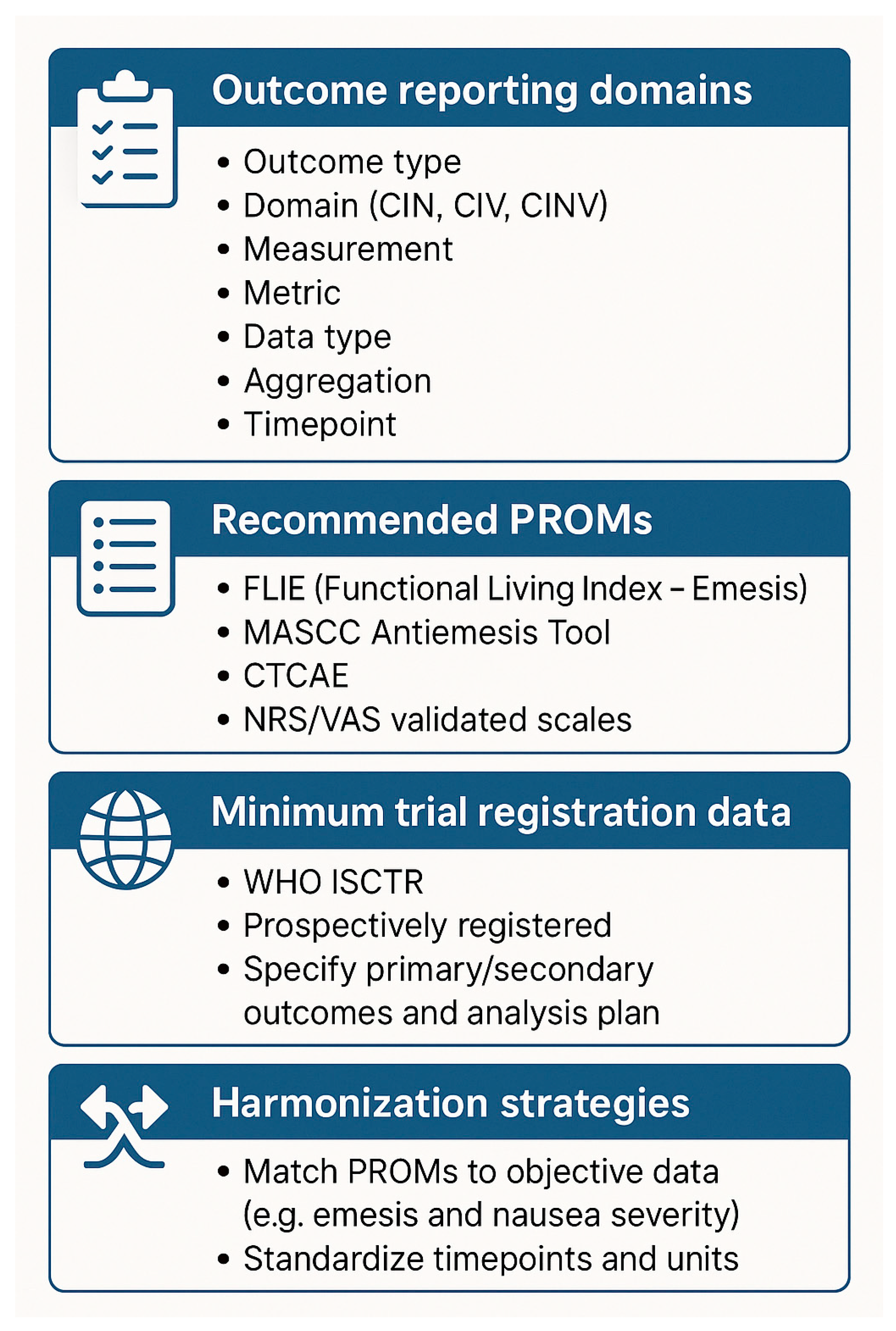
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RCTs | Randomized Controlled Trials |
| TCM | Traditional Chinese Medicine |
| CINV | Chemotherapy-Induced Nausea and Vomiting |
| CIN | Chemotherapy-Induced Nausea |
| CIV | Chemotherapy-Induced Vomiting |
| VAS | Visual Analogue Scale |
| PROMs | Patient-Reported Outcome Measures |
| IS-CTR | International Standards for Clinical Trial Registries |
| MASCC | Multinational Association of Supportive Care in Cancer |
References
- Nankervis, H.; Baibergenova, A.; Williams, H.C.; Thomas, K.S. Prospective Registration and Outcome-Reporting Bias in Randomized Controlled Trials of Eczema Treatments: A Systematic Review. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 2727–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkham, J.J.; Dwan, K.M.; Altman, D.G.; Gamble, C.; Dodd, S.; Smyth, R.; Williamson, P.R. The impact of outcome reporting bias in randomised controlled trials on a cohort of systematic reviews. BMJ 2010, 340, c365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutron, I.; Page, M.J.; Higgins, J.P.T.; Altman, D.G.; Lundh, A.; Hróbjartsson, A. Chapter 7: Considering bias and conflicts of interest among the included studies. In Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 6.4 (Updated August 2023); Higgins, J.P.T., Thomas, J., Chandler, J., Cumpston, M., Li, T., Page, M.J., Welch, V.A., Eds.; Cochrane: London, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.P.; Han, M.; Li, X.X.; Mu, Y.-J.; Lewith, G.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Witt, C.M.; Yang, G.-Y.; Manheimer, E.; Snellingen, T.; et al. Prospective registration, bias risk and outcome-reporting bias in randomised clinical trials of traditional Chinese medicine: An empirical methodological study. BMJ Open 2013, 3, e002968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, C.X.; Han, M.; Ren, J.; Li, W.Y.; Yue, S.J.; Hao, Y.F.; Liu, J.P. Empirical evidence for outcome reporting bias in randomized clinical trials of acupuncture: Comparison of registered records and subsequent publications. Trials 2015, 16, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vera-Badillo, F.E.; Napoleone, M.; Krzyzanowska, M.K.; Alibhai, S.M.; Chan, A.W.; Ocana, A.; Seruga, B.; Templeton, A.J.; Amir, E.; Tannock, I.F. Bias in reporting of randomised clinical trials in oncology. Eur. J. Cancer 2016, 61, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, B.; Fairman, C.M.; Christensen, J.F.; Bolam, K.A.; Twomey, R.; Nunan, D.; Lahart, I.M. Outcome Reporting bias in Exercise Oncology trials (OREO): A cross-sectional study. medRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; López-Alcalde, J.; Zhang, L.; Siebenhüner, A.R.; Witt, C.M.; Barth, J. Acupuncture for the prevention of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting in cancer patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Med. 2023, 12, 12504–12517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldanha, I.J.; Dickersin, K.; Wang, X.; Li, T. Outcomes in Cochrane Systematic Reviews Addressing Four Common Eye Conditions: An Evaluation of Completeness and Comparability. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Beith, J.M.; Oh, B.; Chatfield, M.D.; Davis, E.; Venkateswaran, R. Electroacupuncture for Nausea, Vomiting, and Myelosuppression in Women Receiving Adjuvant Chemotherapy for Early Breast Cancer: A Randomized Controlled Pilot Trial. Med. Acupunct. 2012, 24, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkhaus, B.; Kirschbaum, B.; Stöckigt, B.; Binting, S.; Roll, S.; Carstensen, M.; Witt, C.M. Prophylactic acupuncture treatment during chemotherapy with breast cancer: A randomized pragmatic trial with a retrospective nested qualitative study. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 178, 617–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rithirangsriroj, K.; Manchana, T.; Akkayagorn, L. Efficacy of acupuncture in prevention of delayed chemotherapy induced nausea and vomiting in gynecologic cancer patients. Gynecol. Oncol. 2015, 136, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dundee, J.W.; Ghaly, R.G.; Fitzpatrick, K.T.J. Randomised comparison ofthe anti-emetic effects of metoclopramide and electro acupuncture in cancer chemotherapy. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1988, 6, 678–679. [Google Scholar]
- Dundee, J.W.; Ghaly, R.G.; Fitzpatrick, K.T.J.; Lynch, G.A.; Abram, W.P. Acupuncture to prevent cisplatin-associated vomiting. Lancet 1987, 329, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.W.; Yu, M.W.; Wang, X.M.; Yang, G.-W.; Wang, H.; Zhang, C.-X.; Xue, N.; Xu, W.-R.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, P.-Y.; et al. Efficacy of acupuncture in the prevention and treatment of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting in patients with advanced cancer: A multi-center, single-blind, randomized, sham-controlled clinical research. Chin Med. 2020, 15, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKeon, C.; Smith, C.A.; Gibbons, K.; Hardy, J.; Haugstetter, C.; Anderson, H. Ea versus Sham Acupuncture and no Acupuncture for the Control of Acute and Delayed Chemotherapy-Induced Nausea and Vomiting: A Pilot Study. Acupunct. Med. 2015, 33, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraswati, W.; Dahlan, E.G.; Saputra, K.; Sutrisno, T.C. Effect of Electroacupuncture on Natural-Killer Cells and Tumor Size in Patients with Cervical Squamous-Cell Carcinoma: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Med. Acupunct. 2019, 31, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Wenger, N.; Glaspy, J.; Hays, R.D.; Albert, P.S.; Choi, C.; Schkelle, P.G. Electroacupuncture for Control of Myeloablative Chemotherapy–Induced Emesis: A Randomized Controlled Trial. JAMA 2000, 284, 2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streitberger, K.; Friedrich-Rust, M.; Bardenheuer, H.; Unnebrink, K.; Windeler, J.; Goldschmidt, H.; Egerer, G. Effect of acupuncture compared with placebo-acupuncture at P6 as additional antiemetic prophylaxis in high-dose chemotherapy and autologous peripheral blood stem cell transplantation: A randomized controlled single-blind trial. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 2538–2544. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Fang, L.; Wu, W.Y.; He, F.; Zhang, X.L.; Zhou, X.; Xiong, Z.J. The Effect of Acupuncture on Chemotherapy-Associated Gastrointestinal Symptoms in Gastric Cancer. Curr. Oncol. 2017, 24, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Park, S.B.; Battaglini, E.; King, M.T.; Kiernan, M.C.; Goldstein, D.; Rutherford, C. Assessing chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy with patient reported outcome measures: A systematic review of measurement properties and considerations for future use. Qual. Life Res. 2022, 31, 3091–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molassiotis, A.; Coventry, P.A.; Stricker, C.T.; Clements, C.; Eaby, B.; Velders, L.; Rittenberg, C.; Gralla, R.J. Validation and psychometric assessment of a short clinical scale to measure chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting: The MASCC antiemesis tool. J. Pain Symptom Manag. 2007, 34, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decker, G.M.; DeMeyer, E.S.; Kisko, D.L. Measuring the maintenance of daily life activities using the functional living index-emesis (FLIE) in patients receiving moderately emetogenic chemotherapy. J. Support. Oncol. 2006, 4, 52. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Walker, K.F.; Stevenson, G.; Thornton, J.G. Discrepancies between registration and publication of randomised controlled trials: An observational study. JRSM Open 2014, 5, 204253331351768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Li, C.; Qin, R.; Wang, Y.; Yu, D.; Dodd, J.; Wang, D.; Cornelius, V. Comparison of Clinical Trial Changes in Primary Outcome and Reported Intervention Effect Size Between Trial Registration and Publication. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e197242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, Y.M.; Tong, C.K.; Chutatape, T.T.; Seah, C.N.; Cui, S.L.; Tan, K.H.; Chan, D.X. Survey of patients’ perspectives on the use of acupuncture as a complementary treatment for chronic pain. Bali J. Anesthesiol. 2022, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greville-Harris, M.; Hughes, J.; Lewith, G.; Liossi, C.; White, P.; Graham, C.A.; Bishop, F. Assessing knowledge about acupuncture: A survey of people with back pain in the UK. Complement. Ther. Med. 2016, 29, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernooij, M.; Marcelissen, F. Measuring patient reported outcomes of acupuncture treatment on pain patients’ health status. Complement. Ther. Clin. Pract. 2017, 28, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrstedt, J.; Clark-Snow, R.; Ruhlmann, C.H.; Jordan, K.; Scotté, F. MASCC/ESMO antiemetic guidelines: Introduction to the 2023 guidelines update. Support. Care Cancer 2023, 32, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odone, A.; Sgueglia, A.C.; Bertuccio, P.; Vecchio, R.; Meloni, A.; Gianfredi, V.; Traverso, L.; Gaeta, M.; Vigezzi, G.P. “Leo&Giulia standing for public health”: An animated series to promote the values of public health among school-aged children. Best practices and field-trial protocol. Ann. Ig. 2024, 36, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayo-Wilson, E.; Li, T.; Fusco, N.; Bertizzolo, L.; Canner, J.K.; Cowley, T.; Doshi, P.; Ehmsen, J.; Gresham, G.; Guo, N.; et al. Cherry-picking by trialists and meta-analysts can drive conclusions about intervention efficacy. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2017, 91, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
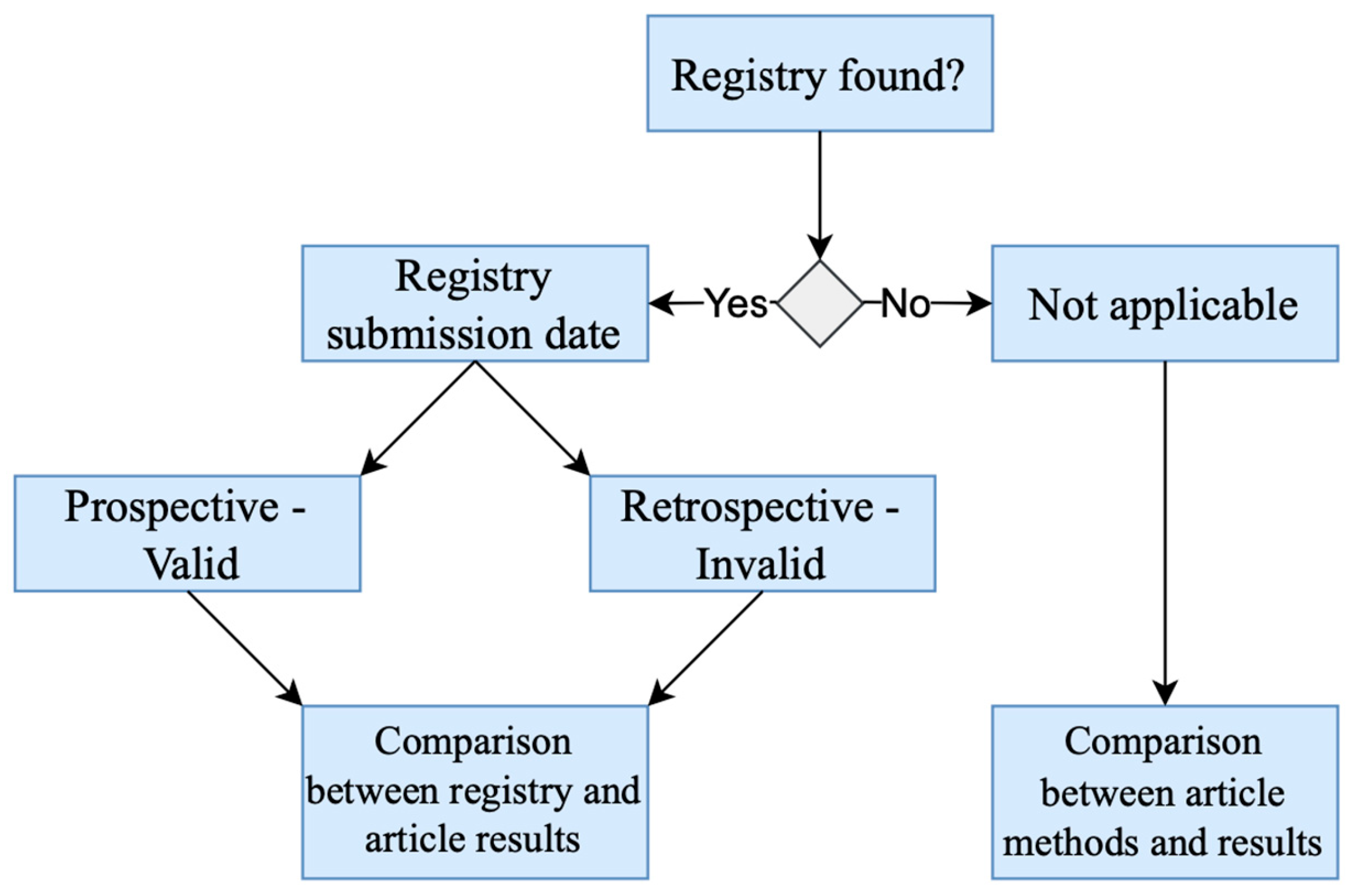
| First Author | Year | Country | Study Design | Sample Size | Study ID | Study Registration | 1st Recruitment Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dundee [15] | 1987 | Ireland | Randomized trial | 10 | Not found | Not found | Not found |
| Dundee [14] | 1988 | Ireland | Randomized trial | 20 | Not found | Not found | Not found |
| Shen [19] | 2000 | California | Three-arm, parallel-group, randomized controlled trial | 104 | Not found | Unclear | Not applicable |
| Streitberger [20] | 2003 | Germany | Randomized placebo-controlled single-blind trial | 220 | Not found | Unclear | Not applicable |
| Beith [11] | 2012 | Australia | Randomized controlled pilot trial | 32 | Not found | Unclear | Not applicable |
| McKeon [17] | 2015 | Australia | Single-centre, pilot, randomised trial | 153 | ACTRN 126090010554202 | 09/12/09 | April 2009 |
| Rithirangsriroj [13] | 2015 | Thailand | Randomized trial, crossover study | 70 | TCTR 20121105001 | 16/05/13 | May 2013 |
| Zhou [21] | 2017 | China | Randomized controlled trial | 56 | Not found | Unclear | Not applicable |
| Brinkhaus [12] | 2019 | Germany | Randomized pragmatic trial | 150 | NCT 01727362 | 16/11/12 | October 2012 |
| Saraswati [18] | 2019 | Indonesia | Randomized, experimental clinical study | 53 | Not found | Unclear | Not applicable |
| Li [22] | 2020 | China | Multi-center, single-blind, randomized, sham-controlled clinical trial | 134 | NCT 02369107 | 23/02/15 | March 2015 |
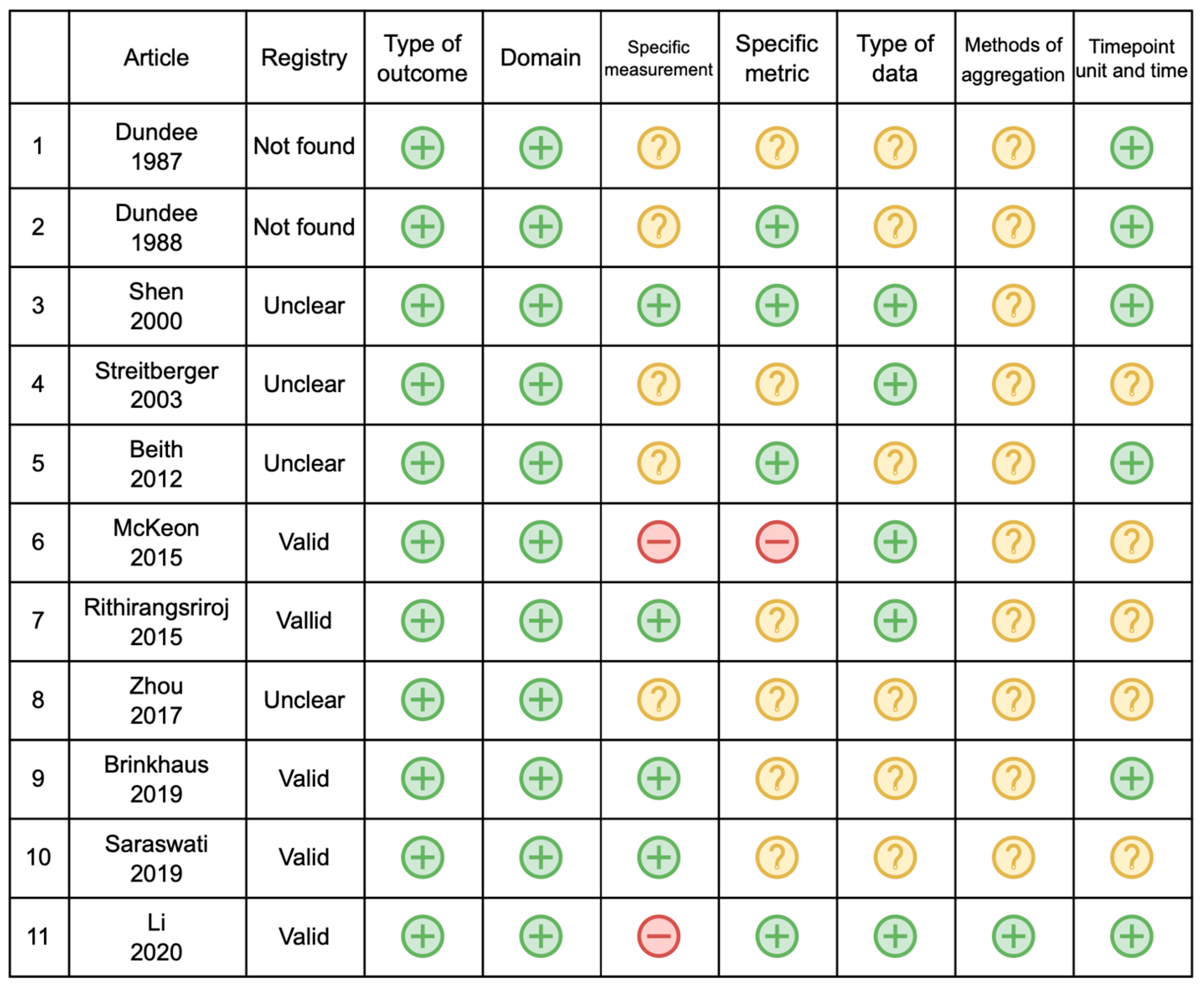
| First Author, Year | Outcome | Type | Domain | Measurement | Specific Metric | Type of Data | Method of Aggregation | Timepoints Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dundee, 1987 [15] | Nausea and vomit | PO | CINV | Four grades of sickness | Not reported | Discrete | Grade of severity | Not reported |
| Dundee, 1988 [14] | Nausea and vomit | PO | CINV | Number of subjects with symptoms | Endpoint | Discrete | Total number of patients | Hours |
| Shen, 2000 [19] | Vomit | PO | CIN | Total number of emesis episodes | Value at a timepoint | Discrete | Total, median, range, mean, percentiles | Days |
| Streitberger, 2003 [20] | Nausea and vomit | PO and non -PO | CINV | Number of patients, frequency of vomit, duration of nausea | Value at a timepoint | Discrete | Total number of patients | Days |
| Beit, 2012 [11] | Nausea and vomit | PO | CINV | Multinational Association of Supportive Care in Cancer (MASCC) antiemetic tool | Endpoint | Discrete | Total number of patients and percent age | Days |
| McKeon, 2015 [17] | Nausea and vomit | PO | CINV | Function Living Index—Emesis, Vomit and Nausea NRS | Change from baseline and Endpoint | Discrete | Median and IQR | Days |
| Rithirangs riroj, 2015 [13] | Nausea and vomit | PO | CINV | Number of emesis and nausea degree | Endpoint | Discrete | Median and range | Not reported |
| Zhou, 2017 [21] | Nausea and vomit | PO | CINV | Frequency of vomit, duration of nausea | Value at a timepoint | Value at a timepoint | Mean | Days |
| Brinkhaus, 2019 [12] | Nausea | Non -PO | CIN | Single item FACT B | Change from the baseline | Discrete | Mean and 95% CI | Months |
| Saraswati, 2019 [18] | Nausea and vomit | Non -PO | CINV | Modified Rhodes Index of Nausea and Vomiting | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported |
| Li, 2020 [22] | Nausea and vomit | PO | CINV | CTCAE grade | Change from baseline | Discrete | Mean + SD | Days |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Penati, R.; Vecchio, R.; Gatto, R.; Odone, A.; Deandrea, S. High Outcome-Reporting Bias in Randomized-Controlled Trials of Acupuncture for Cancer Chemotherapy-Induced Nausea and Vomiting: A Systematic Review and Meta-Epidemiological Study. Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32, 462. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32080462
Penati R, Vecchio R, Gatto R, Odone A, Deandrea S. High Outcome-Reporting Bias in Randomized-Controlled Trials of Acupuncture for Cancer Chemotherapy-Induced Nausea and Vomiting: A Systematic Review and Meta-Epidemiological Study. Current Oncology. 2025; 32(8):462. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32080462
Chicago/Turabian StylePenati, Rachele, Riccardo Vecchio, Roberto Gatto, Anna Odone, and Silvia Deandrea. 2025. "High Outcome-Reporting Bias in Randomized-Controlled Trials of Acupuncture for Cancer Chemotherapy-Induced Nausea and Vomiting: A Systematic Review and Meta-Epidemiological Study" Current Oncology 32, no. 8: 462. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32080462
APA StylePenati, R., Vecchio, R., Gatto, R., Odone, A., & Deandrea, S. (2025). High Outcome-Reporting Bias in Randomized-Controlled Trials of Acupuncture for Cancer Chemotherapy-Induced Nausea and Vomiting: A Systematic Review and Meta-Epidemiological Study. Current Oncology, 32(8), 462. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32080462






