The Impact of Peri-Operative Nutritional Status on Survival in Gastroesophageal Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Outcomes
2.2. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Demographics
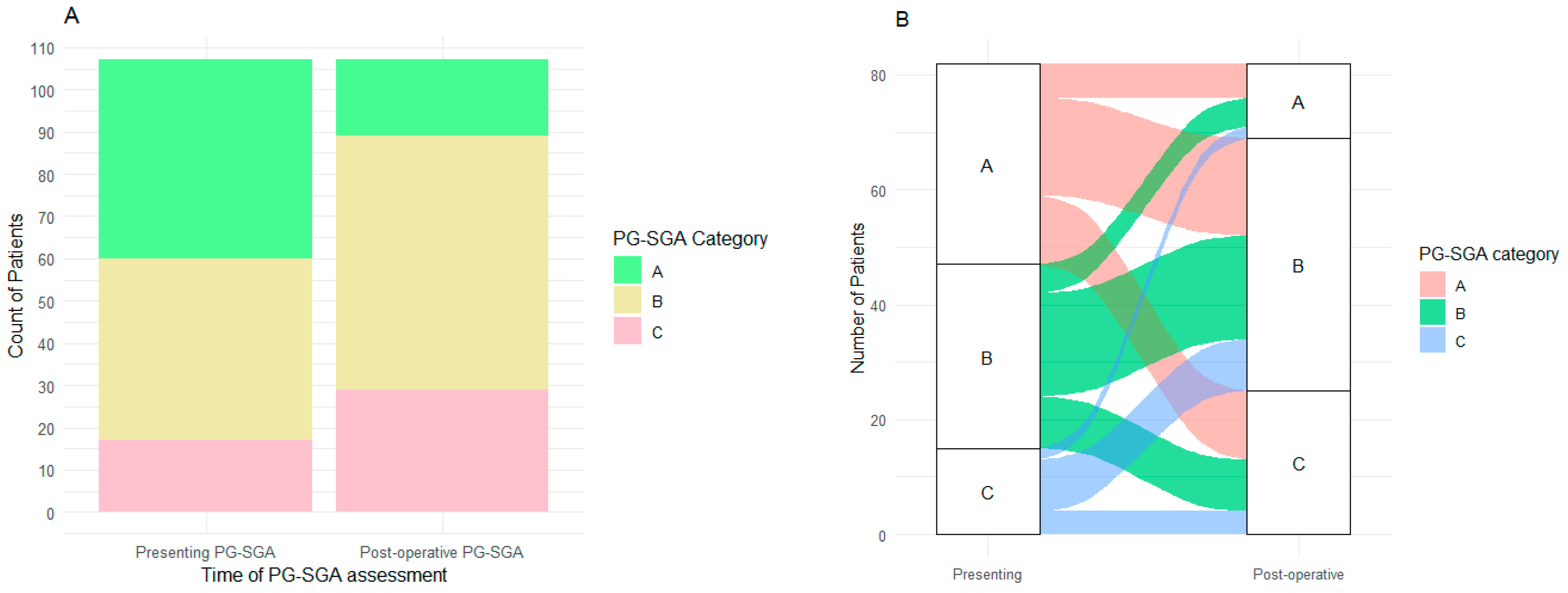
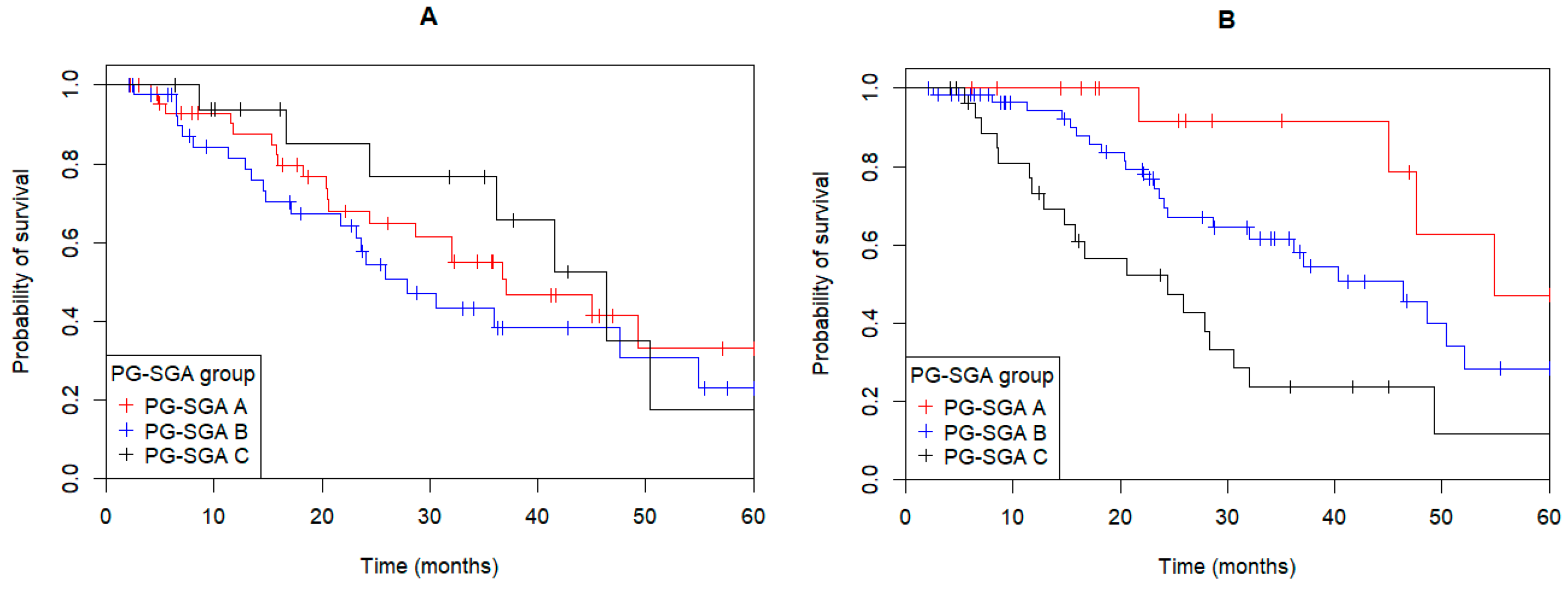
3.2. Nutritional Status
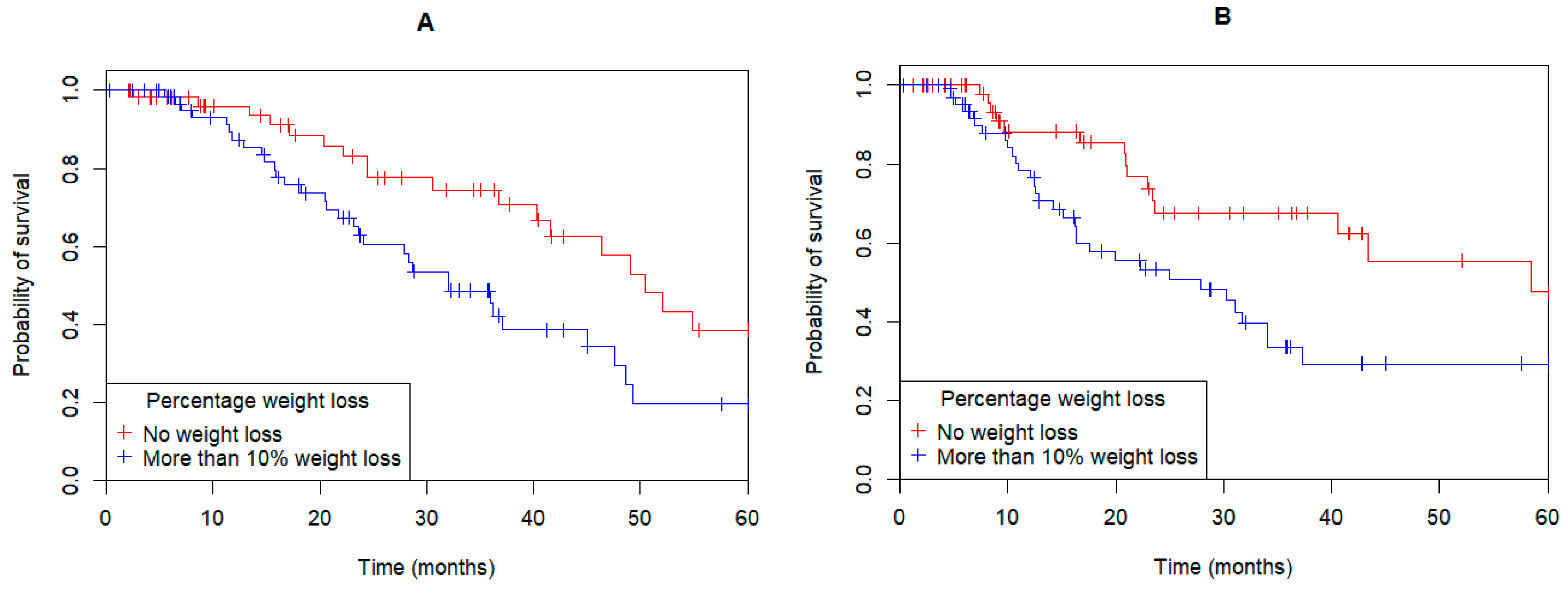
3.3. Weight Loss
3.4. Univariate and Multivariate Models
4. Discussion
Limitations of Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GOC | gastric, gastroesophageal junction and esophageal adenocarcinoma |
| PG-SGA | patient-generated subjective global assessment |
| OS | overall survival |
| DFS | disease-free survival |
References
- Cancer Australia. Oesophageal Cancer in Australia [Online]. NSW, Australia. 2025. Available online: https://www.canceraustralia.gov.au/cancer-types/oesophageal-cancer/oesophageal-cancer-australia (accessed on 19 March 2025).
- Cong, M.; Song, C.; Xu, H.; Song, C.; Wang, C.; Fu, Z.; Ba, Y.; Wu, J.; Xie, C.; Chen, G.; et al. The patient-generated subjective global assessment is a promising screening tool for cancer cachexia. BMJ Support. Palliat. Care 2022, 12, e39–e46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deftereos, I.; Kiss, N.; Isenring, E.; Carter, V.M.; Yeung, J.M. A systematic review of the effect of preoperative nutrition support on nutritional status and treatment outcomes in upper gastrointestinal cancer resection. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 46, 1423–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Malnutrition Geneva, Switzerland. 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/questions-and-answers/item/malnutrition (accessed on 5 December 2023).
- Obermannova, R.; Alsina, M.; Cervantes, A.; Leong, T.; Lordick, F.; Nilsson, M.; van Grieken, N.C.T.; Vogel, A.; Smyth, E.C. Oesophageal cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, 992–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lordick, F.; Carneiro, F.; Cascinu, S.; Fleitas, T.; Haustermans, K.; Piessen, G.; Vogel, A.; Smyth, E.C. Gastric cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, 1005–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schizas, D.; Lidoriki, I.; Moris, D.; Liakakos, T. Nutritional Management of Esophageal Cancer Patients. In Esophageal Abnormalities; Jianyuan, C., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2017; p. Ch. 6. [Google Scholar]
- Rosania, R.; Chiapponi, C.; Malfertheiner, P.; Venerito, M. Nutrition in Patients with Gastric Cancer: An Update. Gastrointest. Tumors 2016, 2, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arends, J.; Baracos, V.; Bertz, H.; Bozzetti, F.; Calder, P.C.; Deutz, N.E.P.; Erickson, N.; Laviano, A.; Lisanti, M.P.; Lobo, D.N.; et al. ESPEN expert group recommendations for action against cancer-related malnutrition. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 1187–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pressoir, M.; Desné, S.; Berchery, D.; Rossignol, G.; Poiree, B.; Meslier, M.; Traversier, S.; Vittot, M.; Simon, M.; Gekiere, J.P.; et al. Prevalence, risk factors and clinical implications of malnutrition in French Comprehensive Cancer Centres. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 102, 966–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiya, K.; Kawamura, T.; Omae, K.; Makuuchi, R.; Irino, T.; Tokunaga, M.; Tanizawa, Y.; Bando, E.; Terashima, M. Impact of Malnutrition After Gastrectomy for Gastric Cancer on Long-Term Survival. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 25, 974–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, S.; Powell, C.; Carter, B.; Hurt, C.; Mukherjee, S.; Crosby, T.D. Role of nutritional status and intervention in oesophageal cancer treated with definitive chemoradiotherapy: Outcomes from SCOPE1. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 115, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, J.; Capra, S.; Ferguson, M. Use of the scored Patient-Generated Subjective Global Assessment (PG-SGA) as a nutrition assessment tool in patients with cancer. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2002, 56, 779–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jager-Wittenaar, H.; Ottery, F.D. Assessing nutritional status in cancer: Role of the Patient-Generated Subjective Global Assessment. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2017, 20, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ottery, F.D. Definition of standardized nutritional assessment and interventional pathways in oncology. Nutrition 1996, 12, S15–S19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, M.C.; Wang, S.H.; Chuah, S.K.; Lin, Y.H.; Lan, J.; Rau, K.M. A Prognostic Model Using Inflammation- and Nutrition-Based Scores in Patients With Metastatic Gastric Adenocarcinoma Treated With Chemotherapy. Medicine 2016, 95, e3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poziomyck, A.K.; Weston, A.C.; Lameu, E.B.; Cassol, O.S.; Coelho, L.J.; Moreira, L.F. Preoperative nutritional assessment and prognosis in patients with foregut tumors. Nutr. Cancer 2012, 64, 1174–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.J. Involuntary Weight Loss. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2014, 98, 625–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hager, K.K. Management of Weight Loss in People With Cancer. J. Adv. Pract. Oncol. 2016, 7, 336–338. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.H.; Park, B.; Joo, J.; Kook, M.-C.; Kim, Y.-I.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, C.G.; Choi, I.J.; Eom, B.W.; Yoon, H.M.; et al. Body mass index and mortality in patients with gastric cancer: A large cohort study. Gastric Cancer 2018, 21, 913–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorusso, A.; Bichev, D.; Högner, A.; Bartels, P.; Ballhausen, A.; Treese, C.; Biebl, M.; Thuss-Patience, P. Prognostic Relevance of Weight and Weight Loss during Multimodal Therapy for Oesophagogastric Tumours. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 2706–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansoor, W.; Roeland, E.J.; Chaudhry, A.; Liepa, A.M.; Wei, R.; Knoderer, H.; Abada, P.; Chatterjee, A.; Klempner, S.J. Early Weight Loss as a Prognostic Factor in Patients with Advanced Gastric Cancer: Analyses from REGARD, RAINBOW, and RAINFALL Phase III Studies. Oncologist 2021, 26, e1538–e1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.B.; Edge, S.B.; Greene, F.L.; Byrd, D.R.; Brookland, R.K.; Washington, M.K.; Gershenwald, J.E.; Compton, C.C.; Hess, K.R.; Sullivan, D.C. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual, 8th ed.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Batran, S.-E.; Homann, N.; Pauligk, C.; Goetze, T.O.; Meiler, J.; Kasper, S.; Kopp, H.-G.; Mayer, F.; Haag, G.M.; Luley, K.; et al. Perioperative chemotherapy with fluorouracil plus leucovorin, oxaliplatin, and docetaxel versus fluorouracil or capecitabine plus cisplatin and epirubicin for locally advanced, resectable gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction adenocarcinoma (FLOT4): A randomised, phase 2/3 trial. Lancet 2019, 393, 1948–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, D.; Allum, W.H.; Stenning, S.P.; Thompson, J.N.; Van de Velde, C.J.; Nicolson, M.; Scarffe, J.H.; Lofts, F.J.; Falk, S.J.; Iveson, T.J.; et al. Perioperative chemotherapy versus surgery alone for resectable gastroesophageal cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagen, P.v.; Hulshof, M.C.C.M.; Lanschot, J.J.B.v.; Steyerberg, E.W.; Henegouwen, M.I.v.B.; Wijnhoven, B.P.L.; Richel, D.J.; Nieuwenhuijzen, G.A.P.; Hospers, G.A.P.; Bonenkamp, J.J.; et al. Preoperative Chemoradiotherapy for Esophageal or Junctional Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 2074–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garth, A.K.; Newsome, C.M.; Simmance, N.; Crowe, T.C. Nutritional status, nutrition practices and post-operative complications in patients with gastrointestinal cancer. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2010, 23, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grace, E.M.; Shaw, C.; Lalji, A.; Mohammed, K.; Andreyev, H.J.N.; Whelan, K. Nutritional status, the development and persistence of malnutrition and dietary intake in oesophago-gastric cancer: A longitudinal cohort study. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2018, 31, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajchman, S.K.; Tucker, A.M.; Cardenas-Turanzas, M.; Nates, J.L. Validation Study of Energy Requirements in Critically Ill, Obese Cancer Patients. JPEN J. Parenter. Enteral Nutr. 2016, 40, 806–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, H.; Okamoto, Y.; Kawai, A.; Ueno, D.; Kubota, H.; Murakami, H.; Higashida, M.; Hirai, T. Prognosis Prediction for Postoperative Esophageal Cancer Patients Using Onodera’s Prognostic Nutritional Index. Nutr. Cancer 2017, 69, 849–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Soom, T.; El Bakkali, S.; Gebruers, N.; Verbelen, H.; Tjalma, W.; van Breda, E. The effects of chemotherapy on energy metabolic aspects in cancer patients: A systematic review. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 1863–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schricker, T.; Lattermann, R. Perioperative catabolism. Can. J. Anaesth. 2015, 62, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thibault, R.; Abbasoglu, O.; Ioannou, E.; Meija, L.; Ottens-Oussoren, K.; Pichard, C.; Rothenberg, E.; Rubin, D.; Siljamäki-Ojansuu, U.; Vaillant, M.-F.; et al. ESPEN guideline on hospital nutrition. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 5684–5709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkura, Y.; Miyata, H.; Konno, H.; Udagawa, H.; Ueno, M.; Shindoh, J.; Kumamaru, H.; Wakabayashi, G.; Gotoh, M.; Mori, M. Development of a model predicting the risk of eight major postoperative complications after esophagectomy based on 10 826 cases in the Japan National Clinical Database. J. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 121, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Cheng, N.; Chen, P.; Zhang, M.; Li, N.; Lin, X.; He, X.; Wang, Y.; Xu, H.; Guo, W.; et al. Association of Malnutrition, as Defined by the PG-SGA, ESPEN 2015, and GLIM Criteria, With Complications in Esophageal Cancer Patients After Esophagectomy. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 632546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movahed, S.; Norouzy, A.; Ghanbari-Motlagh, A.; Eslami, S.; Khadem-Rezaiyan, M.; Emadzadeh, M.; Nematy, M.; Ghayour-Mobarhan, M.; Varshoee Tabrizi, F.; Bozzetti, F.; et al. Nutritional Status in Patients with Esophageal Cancer Receiving Chemoradiation and Assessing the Efficacy of Usual Care for Nutritional Managements. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2020, 21, 2315–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.; Fang, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhang, X.; Xin, X.; He, Y.; Cao, Y.; Jiao, X.; Sun, T.; Pang, Y.; et al. Early Interdisciplinary Supportive Care in Patients With Previously Untreated Metastatic Esophagogastric Cancer: A Phase III Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 748–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triantafillidis, J.K.; Papakontantinou, J.; Antonakis, P.; Konstadoulakis, M.M.; Papalois, A.E. Enteral Nutrition in Operated-On Gastric Cancer Patients: An Update. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscaritoli, M.; Arends, J.; Bachmann, P.; Baracos, V.; Barthelemy, N.; Bertz, H.; Bozzetti, F.; Hütterer, E.; Isenring, E.; Kaasa, S.; et al. ESPEN practical guideline: Clinical Nutrition in cancer. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 2898–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.; Yu, D.; Bikdeli, B.; Yu, S. Sarcopenia and Adverse Post-Surgical Outcomes in Geriatric Patients: A Scoping Review. J. Frailty Aging 2021, 10, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, S.M.; Fontaine, J.P.; Dam, A.N.; Hoffe, S.E.; Cameron, M.; Frakes, J.; Mehta, R.; Gurd, E.; Pimiento, J.M. Is Preoperative G-Tube Use Safe for Esophageal Cancer Patients? J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2020, 39, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, S.J.; West, M.A.; Rahman, S.A.; Underwood, T.J.; Marino, L.V. Oesophageal cancer: The effect of early nutrition support on clinical outcomes. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2021, 42, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhya, L.; Devi Sreenivasan, N.; Goenka, L.; Dubashi, B.; Kayal, S.; Solaiappan, M.; Govindarajalou, R.; Kt, H.; Ganesan, P. Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Study of Olanzapine for Chemotherapy-Related Anorexia in Patients With Locally Advanced or Metastatic Gastric, Hepatopancreaticobiliary, and Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 2617–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variable | Total Population |
|---|---|
| Number (n) | 148 |
| Age: Median (range, years) | 69.1 (40, 89) |
| Male (n, %) | 109 (73.6) |
| ECOG (n, %) | |
| 0 | 82 (61.7) |
| 1 | 43 (34.6) |
| 2 or 3 | 5 (3.8) |
| Tumor location | |
| Esophagus | 46 (31.1) |
| GOJ | 46 (31.1) |
| Gastric | 56 (37.8) |
| Tumor stage | |
| I | 17 (11.5) |
| II | 41 (27.7) |
| III | 76 (51.4) |
| IV | 14 (9.5) |
| Tumor Differentiation (n, %) | |
| Well | 20 (15) |
| Moderate | 58 (43.6) |
| Poor | 55 (41.4) |
| Pre-operative regimen (n, %) | |
| Chemotherapy | 25 (16.9) |
| Chemoradiotherapy | 63 (42.5) |
| Nil | 60 (40.5) |
| Presenting PG-SGA (n, %) | |
| A: well nourished | 47 (32) |
| B: moderate/suspected malnutrition | 43 (29) |
| C: Severely malnourished | 17 (11) |
| Not reported | 41 (28) |
| Total Patients (n = 121) | Upfront Surgery (n = 41) | Pre-Operative Treatment (n = 80) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| % weight change (median, range) | −10.4 (+13.0, −27.4) | −9.7 (+13, −25.7) | −11.1 (+2.8, −27.4) | <0.001 |
| Number more than 5% weight loss (%) | 106 (87.6) | 33 (80.5) | 73 (91.3) | <0.001 |
| Number more than 10% weight loss (%) | 65 (53.7) | 19 (46.3) | 46 (57.5) | 0.039 |
| Variable | Univariate OS | Multivariate OS | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR | 95% Confidence Interval | p-Value | HR | 95% Confidence Interval | p-Value | |
| PG-SGA “Nourished/Improved” vs. “Deteriorated/Malnourished” | 2.71 | 1.23–5.94 | 0.007 | 2.81 | 1.15–6.83 | 0.03 |
| Age categorical <65 vs. >65 | 1.24 | 0.73–2.12 | 0.42 | |||
| Gender Female vs. Male | 1.66 | 0.91–3.02 | 0.08 | 1.98 | 0.55–3.44 | 0.02 |
| Stage | 0.005 | 0.008 | ||||
| I vs. II | 0.63 | 0.22–1.82 | 1.72 | 0.34–8.69 | ||
| I vs. III | 1.60 | 0.67–3.78 | 3.49 | 0.78–15.59 | ||
| I vs. IV | 3.21 | 1.13–9.06 | 10.09 | 1.89–53.70 | ||
| Tumor location (ref: gastric) | 0.02 | |||||
| GOJ | 1.45 | 0.77–2.72 | ||||
| Esophagus | 1.73 | 0.93–3.21 | ||||
| Presenting ECOG performance status (ref: 0) | 0.09 | |||||
| 1 | 1.63 | 0.94–2.83 | ||||
| 2 or 3 | 3.07 | 0.92–10.28 | ||||
| Neoadjuvant treatment | 1.54 | 0.90–2.66 | 0.11 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tincknell, G.; Bosward, T.; Fildes, K.; Batchelor, H.; Freeman, B.; Jaber, M.; Ranson, M.; Haughton, J.; Brungs, D. The Impact of Peri-Operative Nutritional Status on Survival in Gastroesophageal Adenocarcinoma. Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32, 186. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32040186
Tincknell G, Bosward T, Fildes K, Batchelor H, Freeman B, Jaber M, Ranson M, Haughton J, Brungs D. The Impact of Peri-Operative Nutritional Status on Survival in Gastroesophageal Adenocarcinoma. Current Oncology. 2025; 32(4):186. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32040186
Chicago/Turabian StyleTincknell, Gary, Tamara Bosward, Karen Fildes, Hayley Batchelor, Bronwyn Freeman, Mouhannad Jaber, Marie Ranson, Jennifer Haughton, and Daniel Brungs. 2025. "The Impact of Peri-Operative Nutritional Status on Survival in Gastroesophageal Adenocarcinoma" Current Oncology 32, no. 4: 186. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32040186
APA StyleTincknell, G., Bosward, T., Fildes, K., Batchelor, H., Freeman, B., Jaber, M., Ranson, M., Haughton, J., & Brungs, D. (2025). The Impact of Peri-Operative Nutritional Status on Survival in Gastroesophageal Adenocarcinoma. Current Oncology, 32(4), 186. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32040186





