Unraveling Survival Determinants in Patients with Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer with EGFR Exon 20 Insertions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
- (1)
- Study design: This multicenter, retrospective study was conducted at a top-tier medical center (a hospital providing advanced and specialized care) and three regional hospitals in Taiwan.
- (2)
- Patients: We included all patients with stage IV NSCLC who had EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations and received treatment at our institution between January 2016 and December 2020. However, patients who were referred only for best supportive care or those who participated in clinical trials were excluded. The mutational status of all included patients was determined using polymerase chain reactions (PCRs).
- (3)
- Data collection: We collected demographic and clinical data related to lung cancer, including age, sex, smoking status, tumor size, cancer staging, initial metastatic sites, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) at diagnosis, type of therapy, co-morbidities, and the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Performance Status (ECOG PS) score.
- (4)
- Statistical analysis: The primary endpoint was progression-free survival (PFS), while the secondary endpoint was overall survival (OS). Kaplan–Meier analysis with the log-rank test was used to analyze progression-free survival and overall survival, further stratified by different regimens of first-line treatment, including first-generation EGFR-TKI and platinum-based chemotherapy. Univariate and multivariable Cox regression analyses were used to identify the predictive factors of progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS).
- (5)
- Ethics statement: The study protocol received approval from the institutional review board at each participating center: the National Yang-Ming Chiao Tung University Hospital, Yilan, 260, Taiwan (IRB No.: 2021A022), the Far-Eastern Memorial Hospital, New Taipei City, 220, Taiwan (IRB No.: 113050-E), E-DA Hospital, Kaohsiung, 824, Taiwan (IRB No.: EMRP-110-147), and the National Taiwan University Hospital, Yunlin Branch, Yunlin, 640, Taiwan (IRB No.: 201611059RINB).
3. Results
- (1)
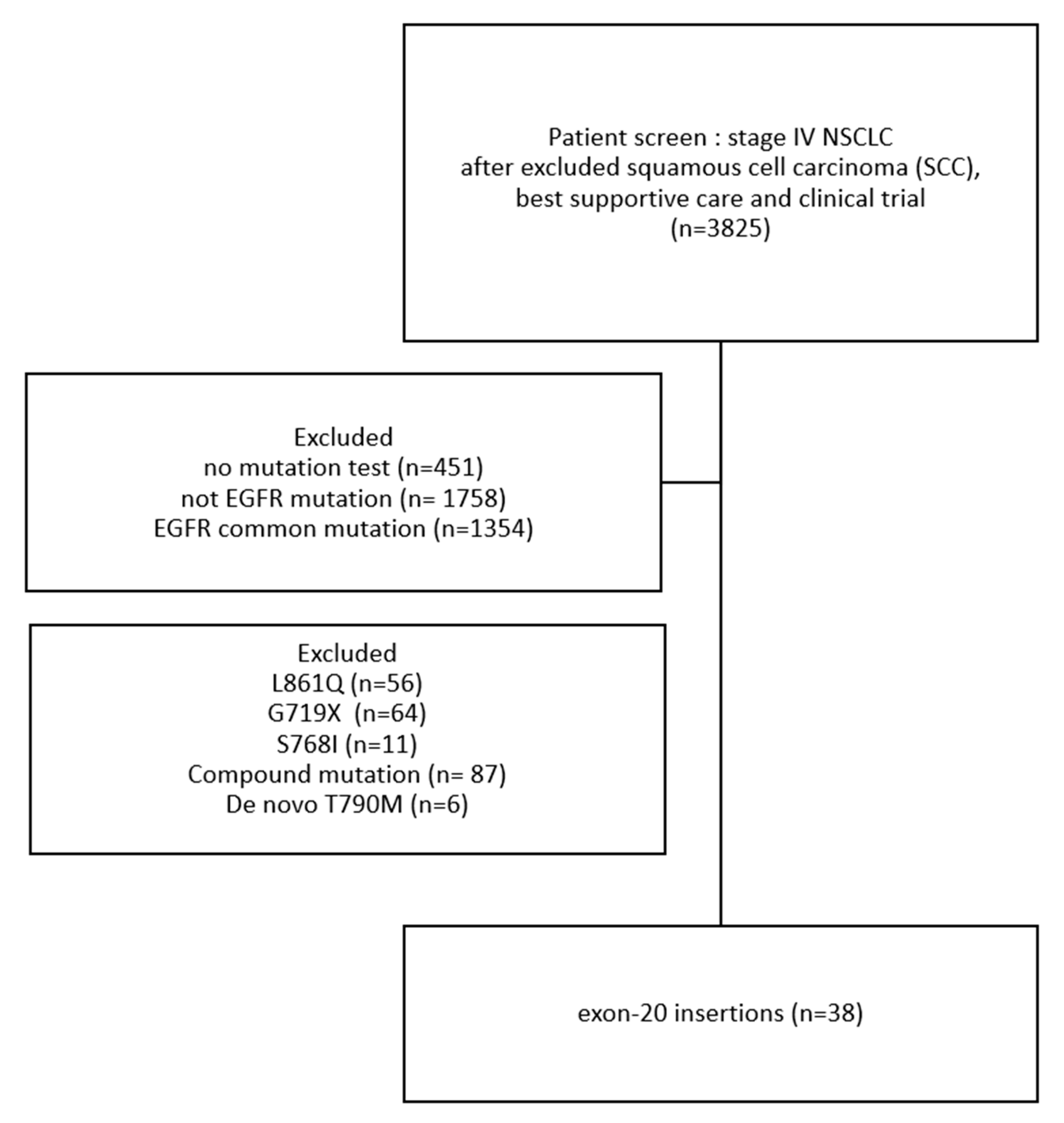
- Patient characteristics: Among patients from these four hospitals, we excluded those with squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), those receiving only best supportive care, and those enrolled in clinical trials, leaving a total of 3825 patients. After applying additional exclusion criteria, 38 patients with EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations were identified (Figure 1). This study enrolled these 38 patients with metastatic NSCLC with EGFR exon 20 insertions. Their demographic data are presented in Table 1. Their median age was 65.5 years (range = 39–84 years). Most participants were female (60.5%), had never smoked (72.0%), and had an ECOG-PS score of 0–1 (81.0%). All participants had stage IV lung cancer at diagnosis, and the most common sites of distant metastases were the brain (n = 13, 34.2%) and bones (n = 13, 34.2%). A total of 4 (10.5%) patients had distant metastasis with ≥3 sites.
- (2)
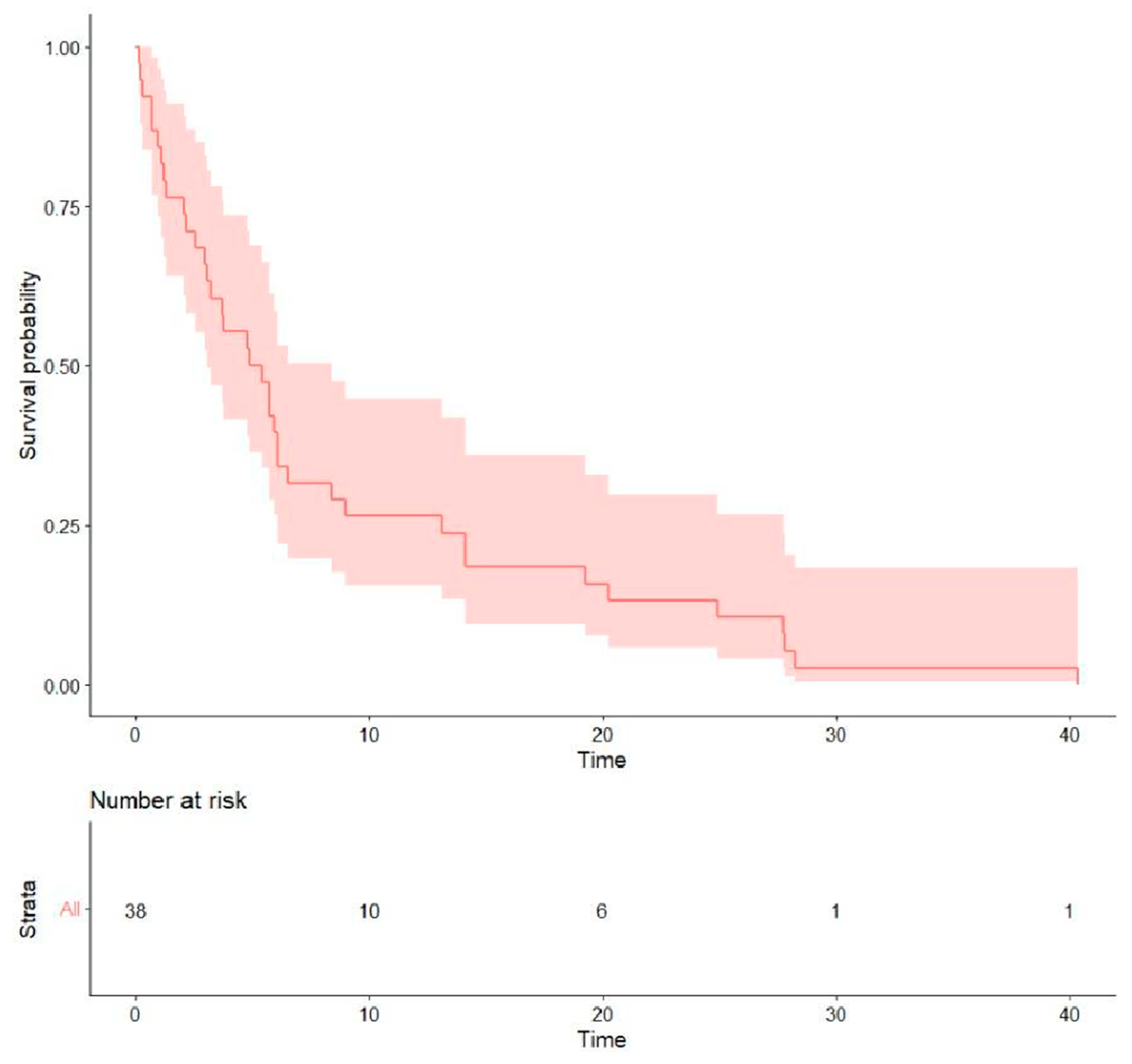
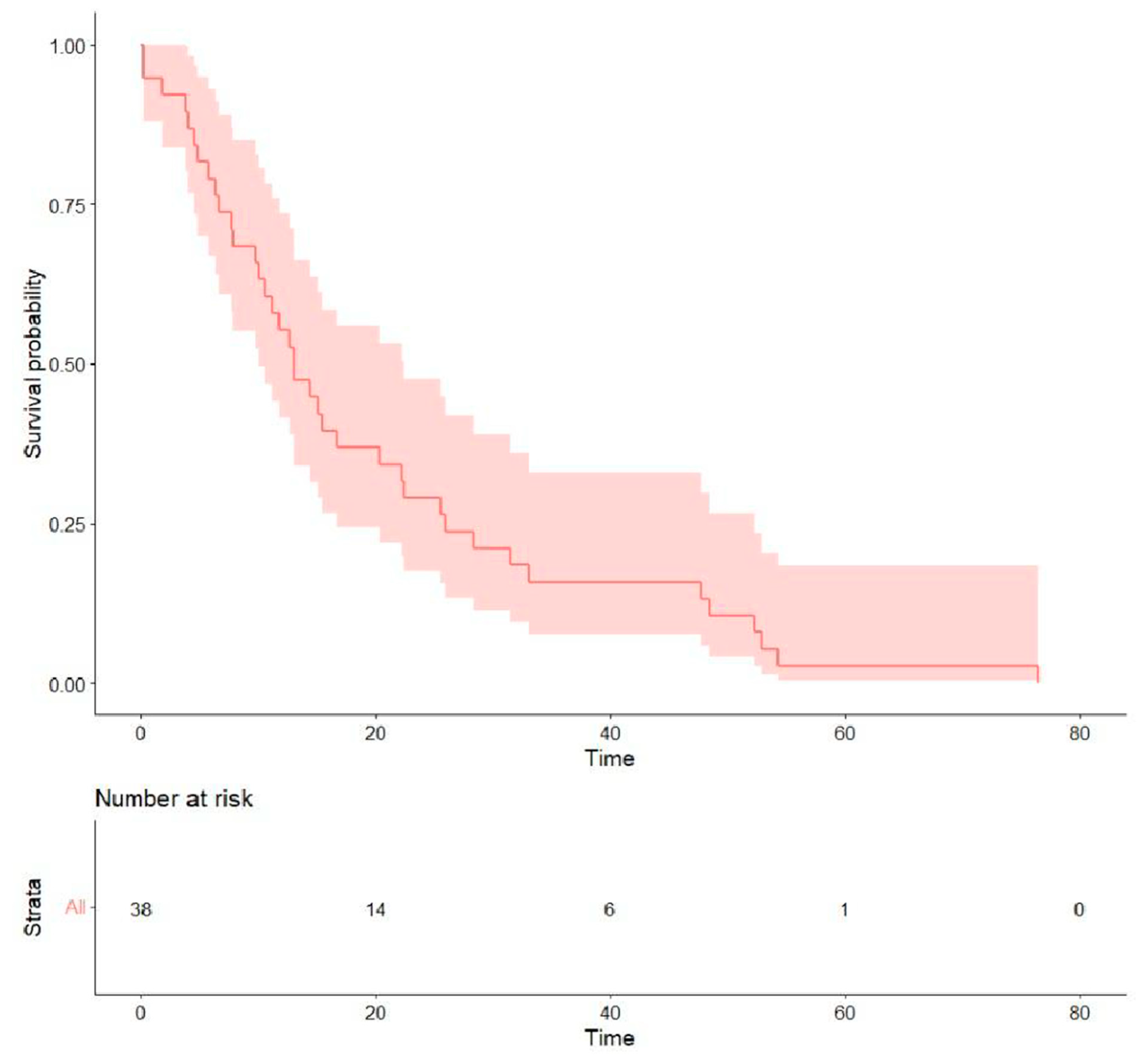
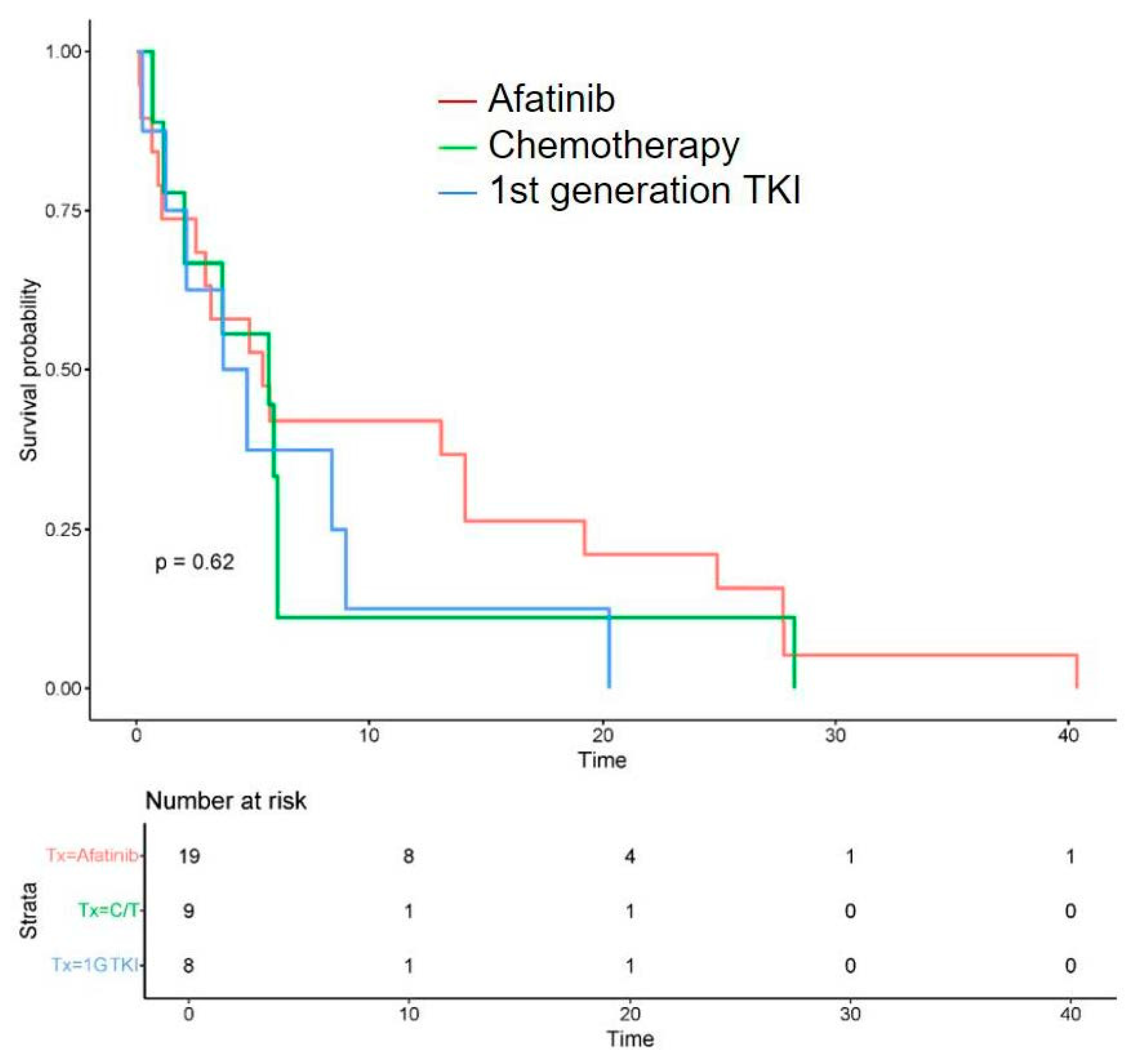
- Treatment outcomes: Regarding the initial first-line treatment, most participants were treated with EGFR-TKIs: 19 (50.0%) with afatinib, 8 (21.1%) with first-generation EGFR-TKIs, and 2 (5.3%) with osimertinib. The other nine (23.7%) patients received platinum-based doublet chemotherapy (Table 2). The rates of objective response and disease control were 31.6% and 57.9% for afatinib, 22.2% and 44.4% for platinum-based chemotherapy, and 12.5% and 37.5% for first-generation EGFR-TKIs, respectively. The median PFS of all was 5.15 months (0.13–40.4), the median OS was 13.0 months (0.13–76.5) (Table 3), and the survival probability curves are shown in Figure 2 and Figure 3, respectively. PFS was examined with respect to the drugs used as first-line treatments (Figure 4). The median PFS was 5.4 months (3.0–24.9) for afatinib, 5.7 months (2.1–NA) for chemotherapy, and 4.3 months (2.2–NA) for first-generation TKIs.
- (3)
4. Discussion
5. Limitation
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hassanein, S.S.; Ibrahim, S.A.; Abdel-Mawgood, A.L. Cell Behavior of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Is at EGFR and MicroRNAs Hands. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naidoo, J.; Sima, C.S.; Rodriguez, K.; Busby, N.; Nafa, K.; Ladanyi, M.; Riely, G.J.; Kris, M.G.; Arcila, M.E.; Yu, H.A. Epidermal growth factor receptor exon 20 insertions in advanced lung adenocarcinomas: Clinical outcomes and response to erlotinib. Cancer 2015, 121, 3212–3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcila, M.E.; Nafa, K.; Chaft, J.E.; Rekhtman, N.; Lau, C.; Reva, B.A.; Zakowski, M.F.; Kris, M.G.; Ladanyi, M. EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations in lung adenocarcinomas: Prevalence, molecular heterogeneity, and clinicopathologic characteristics. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasuda, H.; Park, E.; Yun, C.-H.; Sng, N.J.; Lucena-Araujo, A.R.; Yeo, W.-L.; Huberman, M.S.; Cohen, D.W.; Nakayama, S.; Ishioka, K.; et al. Structural, biochemical, and clinical characterization of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) exon 20 insertion mutations in lung cancer. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 216ra177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.-Y.; Yu, C.-J.; Chang, Y.-C.; Yang, C.-H.; Shih, J.-Y.; Yang, P.-C. Effectiveness of tyrosine kinase inhibitors on “uncommon” epidermal growth factor receptor mutations of unknown clinical significance in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 3812–3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Jin, B.; Chu, T.; Dong, X.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, D.; Lou, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; et al. EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) harboring uncommon EGFR mutations: A realworld study in China. Lung Cancer 2016, 96, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Yang, H.; Jiang, T.; Li, X.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, S.; Liu, X.; Jia, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Uncommon EGFR mutations in a cohort of Chinese NSCLC patients and outcomes of first-line EGFR-TKIs and platinum-based chemotherapy. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 2017, 29, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, C.-H.; Yang, C.-T.; Shih, J.-Y.; Huang, M.-S.; Su, W.-C.; Lai, R.-S.; Wang, C.-C.; Hsiao, S.-H.; Lin, Y.-C.; Ho, C.-L.; et al. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Treatment Response in Advanced Lung Adenocarcinomas with G719X/L861Q/ S768I Mutations. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 793–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Tang, K.-J.; Cho, B.C.; Liu, B.; Paz-Ares, L.; Cheng, S.; Kitazono, S.; Thiagarajan, M.; Goldman, J.W.; Sabari, J.K.; et al. Amivantamab plus Chemotherapy in NSCLC with EGFR Exon 20 Insertions. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 2039–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCCN. Clinical Guidelines in Oncology. Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer, Version 3.2025. Available online: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/nscl.pdf (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- Bazhenova, L.; Minchom, A.; Viteri, S.; Bauml, J.M.; Ou, S.-H.I.; Gadgeel, S.M.; Trigo, J.M.; Backenroth, D.; Li, T.; Londhe, A.; et al. Comparative clinical outcomes for patients with advanced NSCLC harboring EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations and common EGFR mutations. Lung Cancer 2021, 162, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-T.; Liu, Y.-N.; Wu, S.-G.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Shih, J.-Y. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor-Sensitive Exon 19 Insertion and Exon 20 Insertion in Patients with Advanced Non-Small-cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Lung Cancer. 2017, 18, 324–332.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beau-Faller, M.; Prim, N.; Ruppert, A.-M.; Nanni-Metéllus, I.; Lacave, R.; Lacroix, L.; Escande, F.; Lizard, S.; Pretet, J.-L.; Rouquette, I.; et al. Rare EGFR exon 18 and exon 20 mutations in non-small-cell lung cancer on 10 117 patients: A multicentre observational study by the French ERMETIC-IFCT network. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voon, P.J.; Tsui, D.W.Y.; Rosenfeld, N.; Chin, T.M. EGFR exon 20 insertion A763-Y764insFQEA and response to erlotinib—Letter. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 2614–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oxnard, G.R.; Lo, P.C.; Nishino, M.; Dahlberg, S.E.; Lindeman, N.I.; Butaney, M.; Jackman, D.M.; Johnson, B.E.; Jänne, P.A. Natural history and molecular characteristics of lung cancers harboring EGFR exon 20 insertions. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2013, 8, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.C.-H.; Schuler, M.; Popat, S.; Miura, S.; Park, K.; Passaro, A.; De Marinis, F.; Solca, F.; Märten, A.; Kim, E.S. Afatinib for the Treatment of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Harboring Uncommon EGFR Mutations: An Updated Database of 1023 Cases Brief Report. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 834704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.-Y.; Wu, S.-G.; Yang, C.-H.; Gow, C.-H.; Chang, Y.-L.; Yu, C.-J.; Shih, J.-Y.; Yang, P.-C. Lung cancer with epidermal growth factor receptor exon 20 mutations is associated with poor gefitinib treatment response. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 4877–4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, H.-W.; Shie, S.-S.; Chiu, C.-T.; Wang, C.-L.; Yang, T.-Y.; Chou, S.-C.; Liu, C.-Y.; Kuo, C.-H.S.; Lin, Y.-C.; Li, L.-F.; et al. Association of smoking status with non-small cell lung cancer patients harboring uncommon epidermal growth factor receptor mutation. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1011092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.; Haura, E.B.; Leighl, N.B.; Mitchell, P.; Shu, C.A.; Girard, N.; Viteri, S.; Han, J.-Y.; Kim, S.-W.; Lee, C.K. Amivantamab in EGFR ex-on 20 insertion–mutated non–small-cell lung cancer progressing on platinum chemotherapy: Initial results from the CHRYSALIS phase I study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 3391–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anne, P.; Wang, B.; Cho, B.; Zhao, J.; Li, J.; Hochmair, M.; Peters, S.; Besse, B.; Kato, T.; Wu, Y. EXCLAIM-2, Phase III trial of first-line mobocertinib versus platinum-based chemotherapy in patients with epidermal growth factor receptor exon 20 insertion locally advanced/metastatic NSCLC. In Annals of Oncology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. S1663–S1664. [Google Scholar]
- Janne, P.A.; Wang, M.; Camidge, D.R.; Mitchell, P.; Fang, J.; Nian, W.; Chiu, C.-H.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, Y.; Su, W.-C.; et al. Antitumor activity of sunvozertinib in NSCLC patients with EGFR Exon20 insertion mutations after platinum and anti-PD (L)1 treatment failures. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 9015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Fan, Y.; Sun, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Jin, B.; Hu, Y.; Han, Z.; Song, X.; Liu, A.; et al. Sunvozertinib for the treatment of NSCLC with EGFR Exon20 insertion mutations: The first pivotal study results. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 9002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Branstetter, S.; Lazarus, P.; Muscat, J.E. Smoking, Lung Cancer Stage, and Prognostic Factors—Findings from the National Lung Screening Trial. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2024, 21, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Huang, C.; Xie, X.; Wu, Z.; Tian, X.; Wu, Y.; Du, X.; Shi, L. The impact of smoking status on the progression-free survival of non-small cell lung cancer patients receiving molecularly target therapy or immunotherapy versus chemotherapy: A meta-analysis. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2021, 46, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Romero-Gutierrez, C.W.; Kothari, J.; Shafer, A.; Li, Y.; Christiani, D.C. Prediagnosis Smoking Cessation and Overall Survival Among Patients with Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2311966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soria, J.-C.; Ohe, Y.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Chewaskulyong, B.; Lee, K.H.; Dechaphunkul, A.; Imamura, F.; Nogami, N.; Kurata, T.; et al. Osimertinib in Untreated EGFR-Mutated Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Wu, Y.L.; Chen, G.; Feng, J.; Liu, X.-Q.; Wang, C.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhou, S.; Ren, S.; et al. Final overall survival results from a randomised, phase III study of erlotinib versus chemotherapy as first-line treatment of EGFR mutation-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (OPTIMAL, CTONG-0802). Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 1877–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Number of Patients | 38 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Median (Range) | |||
| Age (years), | 66 (39–84) | ||
| BSA | 1.61 (1.32–2.12) | ||
| Target tumor size | 3.4 (0.6–11.4) | ||
| CEA level | 35.92 (0.45–1037.26) | ||
| n | % | ||
| Age | |||
| <65 | 17 | 44.7 | |
| >65 | 21 | 55.3 | |
| Gender | |||
| Female | 23 | 60.5 | |
| Male | 15 | 39.5 | |
| ECOG PS | |||
| 0 | 18 | 47.4 | |
| 1 | 13 | 34.2 | |
| 2 | 4 | 10.5 | |
| 3 | 3 | 7.9 | |
| Smoking status | |||
| Smoking | |||
| Yes | 14 | 36.8 | |
| No | 24 | 63.2 | |
| Metastasis | |||
| Site | ≥3 | 4 | 10.5 |
| <3 | 34 | 89.5 | |
| Brain | YES | 13 | 34.2 |
| NO | 25 | 65.8 | |
| Lung | YES | 7 | 18.4 |
| NO | 31 | 81.6 | |
| Malignant effusion | YES | 11 | 28.9 |
| NO | 27 | 71.1 | |
| Liver | YES | 0 | 0.0 |
| NO | 38 | 100.0 | |
| Bone | YES | 13 | 34.2 |
| NO | 25 | 65.8 | |
| Adrenal gland | YES | 1 | 2.6 |
| NO | 37 | 97.4 | |
| Co-morbidity | |||
| YES | 16 | 42.1 | |
| NO | 22 | 57.9 | |
| Hypertension | |||
| YES | 11 | 28.9 | |
| NO | 27 | 71.1 | |
| Diabetes mellitus | |||
| YES | 2 | 5.3 | |
| NO | 36 | 94.7 | |
| Liver disease | |||
| YES | 1 | 2.6 | |
| NO | 37 | 97.4 | |
| COPD | |||
| YES | 4 | 10.5 | |
| NO | 34 | 89.5 | |
| Neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio | |||
| (Blood) | ≥5 | 14 | 36.8 |
| <5 | 24 | 63.2 | |
| n | % | |
|---|---|---|
| Afatinib | 19 | 50.0 |
| Osimertinib | 2 | 5.3 |
| Chemotherapy | 9 | 23.7 |
| First generation TKIs | 8 | 21.1 |
| Median (Range) | |
|---|---|
| PFS (months) | |
| 5.15 (0.13–40.4) | |
| OS (months) | |
| 13.0 (0.13–76.5) |
| Univariate | Multivariable | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | HR (95% CI) | p Value | Adj. HR (95% CI) | p Value |
| Age | ||||
| <65 | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| ≥65 | 0.98 [0.51–1.90] | 0.963 | 1.12 [0.46–2.72] | 0.801 |
| Gender | ||||
| Female | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| Male | 1.35 [0.69–2.66] | 0.381 | 1.58 [0.68–3.69] | 0.290 |
| ECOG PS | ||||
| 0–1 | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| ≥2 | 1.45 [0.63–3.34] | 0.405 | 2.16 [0.70–6.66] | 0.179 |
| Smoking status | ||||
| No | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| Yes | 1.17 [0.85–1.61] | 0.360 | 1.15 [0.81–1.62] | 0.433 |
| Metastatic sites | ||||
| <3 | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| ≥3 | 1.35 [0.46–3.97] | 0.580 | 2.39 [0.61–9.42] | 0.212 |
| Brain metastasis | ||||
| No | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| Yes | 0.96 [0.49–1.92] | 0.918 | 0.73 [0.31–1.72] | 0.468 |
| NLR | ||||
| No | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| Yes | 1.06 [0.54–2.09] | 0.869 | 0.83 [0.38–1.82] | 0.638 |
| Univariate | Multivariable | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | HR (95% CI) | p Value | Adj. HR (95% CI) | p Value |
| Age | ||||
| <65 | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| ≥65 | 1.15 [0.60–2.21] | 0.667 | 1.48 [0.53–4.09] | 0.452 |
| Gender | ||||
| Female | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| Male | 1.26 [0.65–2.43] | 0.500 | 1.30 [0.46–3.69] | 0.617 |
| ECOG PS | ||||
| 0–1 | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| ≥2 | 1.67 [0.71,3.90] | 0.260 | 1.83 [0.60–5.60] | 0.289 |
| Smoking status | ||||
| No | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| Yes | 1.10 [0.57–2.15] | 0.772 | 1.73 [0.63–7.72] | 0.286 |
| Metastatic sites | ||||
| <3 | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| ≥3 | 2.11 [0.72–6.15] | 0.173 | 4.24 [0.95–19.03] | 0.059 |
| Re-biopsy | ||||
| No | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| Yes | 0.45 [0.18–1.13] | 0.089 | 0.57 [0.16–1.40] | 0.176 |
| Brain metastasis | ||||
| No | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| Yes | 1.14 [0.57–2.26] | 0.712 | 0.71 [0.30–1.70] | 0.445 |
| NLR | ||||
| No | Ref. | Ref. | ||
| Yes | 1.23 [0.63–2.39] | 0.548 | 1.09 [0.50–2.36] | 0.838 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, K.-Y.; Chang, S.-C.; Wei, Y.-F.; Hung, J.-C.; Chen, C.-Y.; Chang, C.-Y. Unraveling Survival Determinants in Patients with Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer with EGFR Exon 20 Insertions. Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32, 174. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32030174
Wang K-Y, Chang S-C, Wei Y-F, Hung J-C, Chen C-Y, Chang C-Y. Unraveling Survival Determinants in Patients with Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer with EGFR Exon 20 Insertions. Current Oncology. 2025; 32(3):174. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32030174
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Kung-Yang, Shih-Chieh Chang, Yu-Feng Wei, Jui-Chi Hung, Chung-Yu Chen, and Cheng-Yu Chang. 2025. "Unraveling Survival Determinants in Patients with Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer with EGFR Exon 20 Insertions" Current Oncology 32, no. 3: 174. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32030174
APA StyleWang, K.-Y., Chang, S.-C., Wei, Y.-F., Hung, J.-C., Chen, C.-Y., & Chang, C.-Y. (2025). Unraveling Survival Determinants in Patients with Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer with EGFR Exon 20 Insertions. Current Oncology, 32(3), 174. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32030174






