Clinical, Radiological, and Pathological Features of Intraosseous Hibernoma: A Systematic Review of Case Reports and Case Series
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy and Study Selection
2.2. Data Extraction and Quality Assessment
2.3. Data Synthesis and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
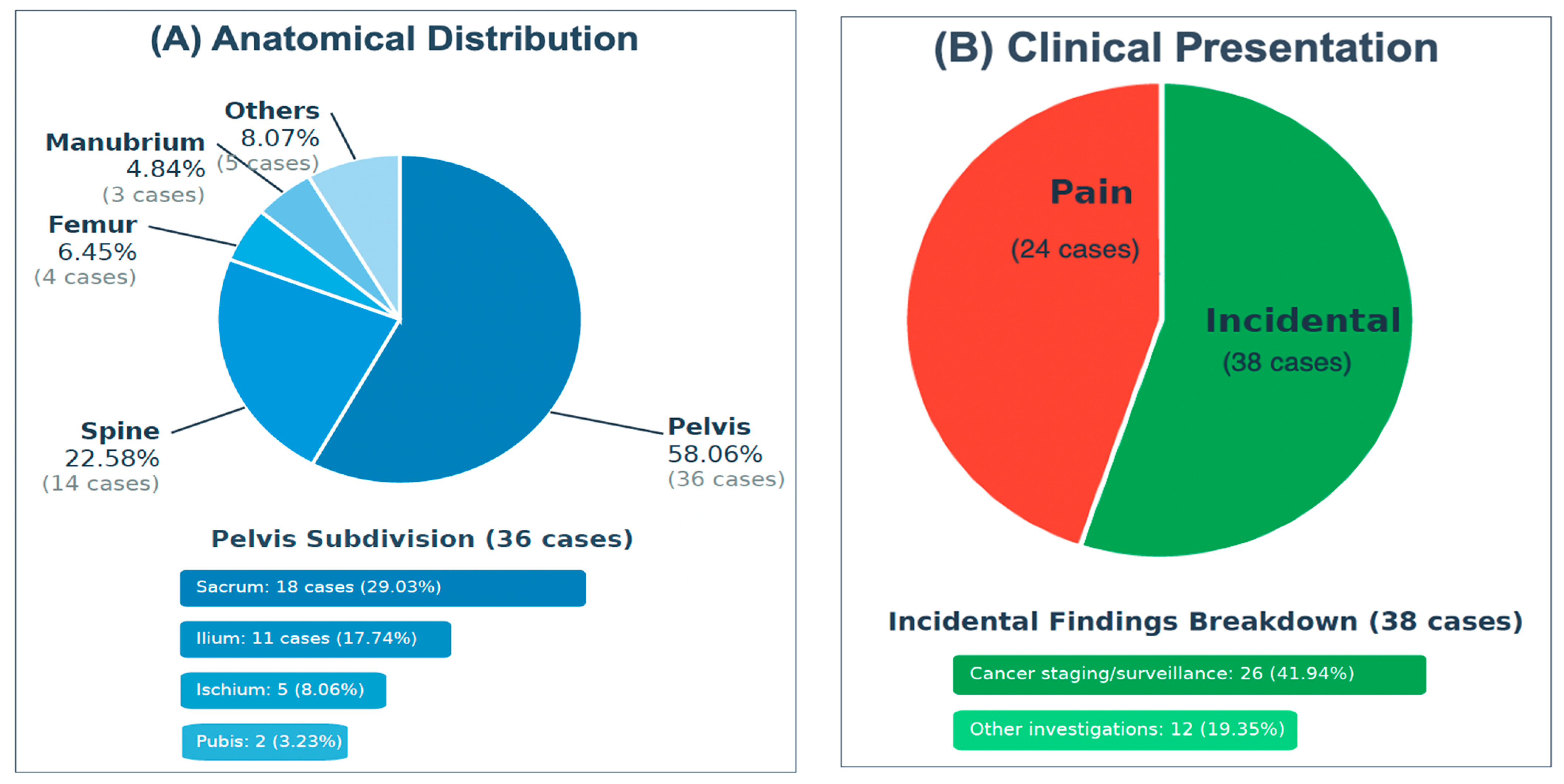
3.1. Demographics and Characteristics of Intraosseous Hibernoma Cases
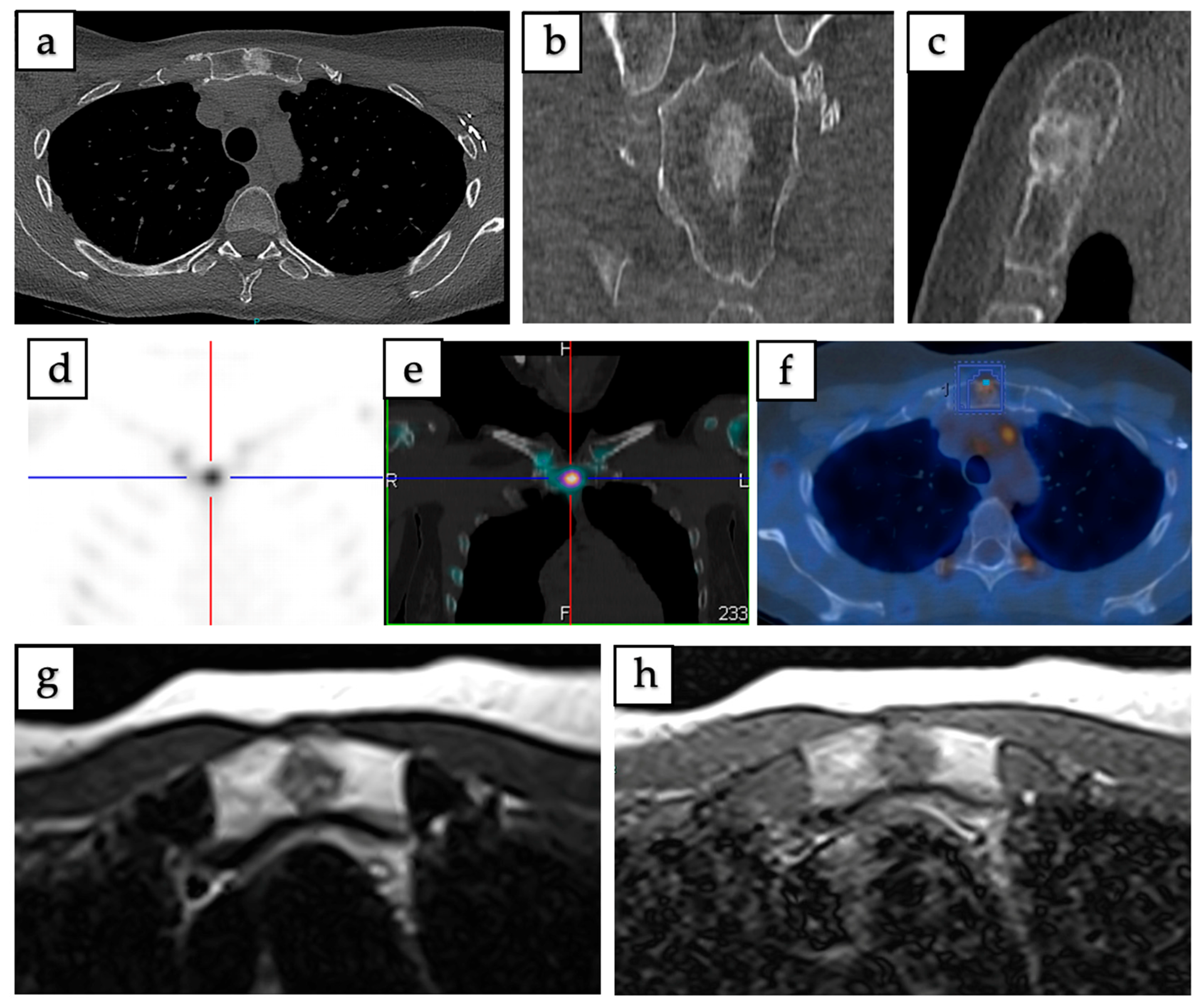
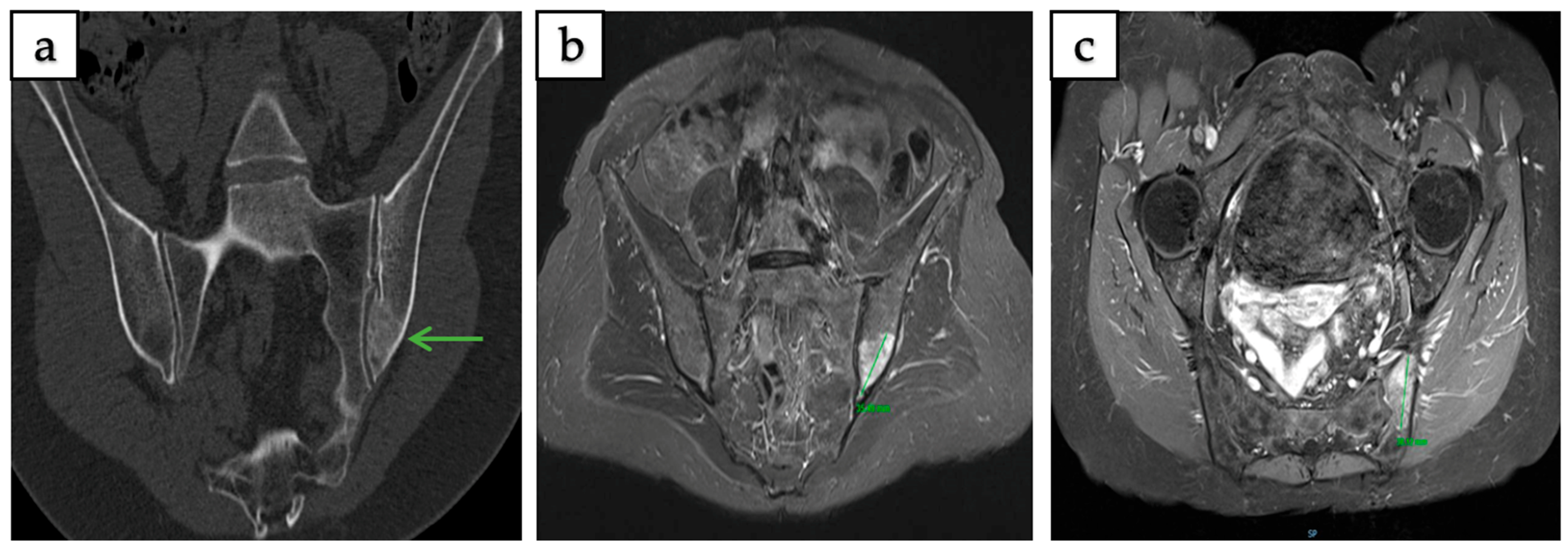
3.2. Radiological Features and Imaging Patterns
3.3. Comparative Radiological Features of IOH and Metastatic Lesions
3.4. Immunohistochemical Features
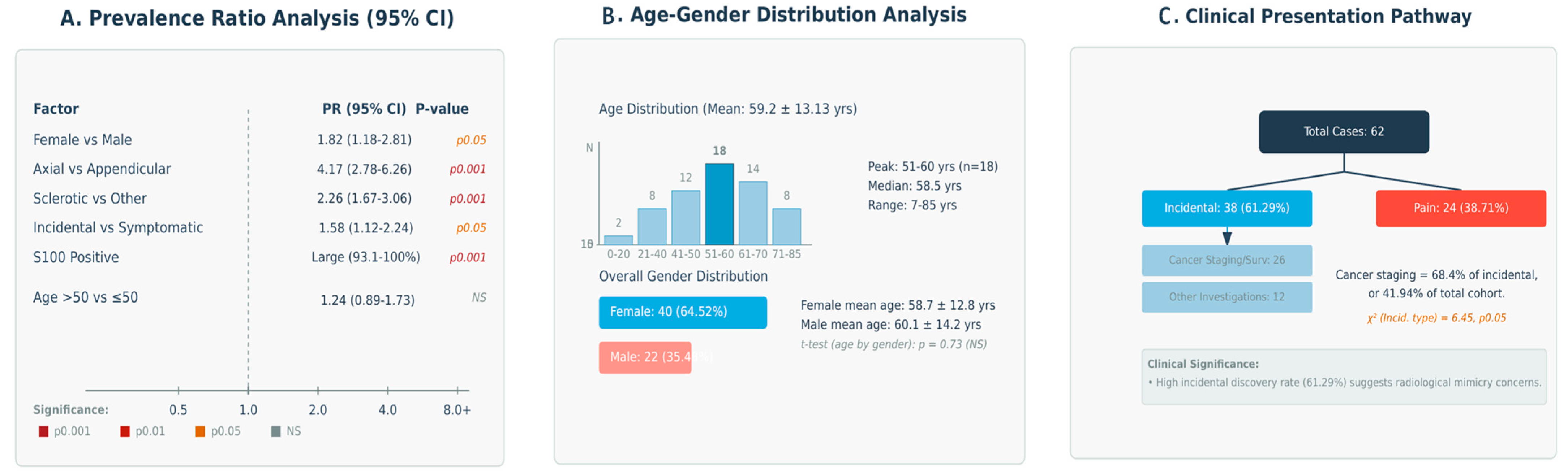
3.5. Multi-Dimensional Analysis of Clinical-Radiological Associations
3.6. Multiparameter Cross-Correlation
3.7. Risk of Bias Assessment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Evers, L.H.; Gebhard, M.; Lange, T.; Siemers, F.; Mailänder, P. Hibernoma-Case Report and Literature Review. Am. J. Dermatopathol. 2009, 31, 685–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furlong, M.A.; Fanburg-Smith, J.C.; Miettinen, M. The Morphologic Spectrum of Hibernoma: A Clinicopathologic Study of 170 Cases. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2001, 25, 809–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassos, N.; Lell, M.; Hohenberger, W.; Croner, R.S.; Agaimy, A. Deep-Seated Huge Hibernoma of Soft Tissue: A Rare Differential Diagnosis of Atypical Lipomatous Tumor/Well Differentiated Liposarcoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2013, 6, 2178–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goossens, G.H. The Role of Adipose Tissue Dysfunction in the Pathogenesis of Obesity-Related Insulin Resistance. Physiol. Behav. 2008, 94, 206–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, W.; Chen, W.; Sun, W.; Li, X.; Suo, Z.; Jiang, G.; Gao, P.; Li, Q. Mitochondrial Activity Regulates the Differentiation of Skin-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells into Brown Adipocytes to Contribute to Hypertension. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2021, 12, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samargandi, R.; Le Nail, L.-R.; de Pinieux, G.; Tallegas, M.; Miquelestorena-Standley, E. Intraosseous Hibernoma: A Rare Entity in Orthopedics With Peculiar Radiological Features. Cureus 2025, 15, e39883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorns, C.; Schardt, C.; Katenkamp, D.; Kähler, C.; Merz, H.; Feller, A.C. Hibernoma-like Brown Fat in the Bone Marrow: Report of a Unique Case. Virchows Arch. 2008, 452, 343–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Ryu, H.J.; Lee, C.; Moon, K.C. Intraosseous Hibernoma: A Rare and Unique Intraosseous Lesion. J. Pathol. Transl. Med. 2017, 51, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, A.; Rowell, C.C.; Vogler, J.B.; Samoilov, D.E. Intraosseous Hibernoma: A Metastatic Mimicker to Consider on the Differential. Radiol. Case Rep. 2020, 15, 2677–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, S.; Mies, C.; Stephenson, J.; Zhang, P.J. Intraosseous Hibernoma: A Potential Mimic of Metastatic Carcinoma. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2013, 17, 204–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolte, S.J.; Geiger, H.; Forrer, F.; Rodriguez, R.; Müller, J. Case Report: Intraosseous Hibernoma (IOH) Mimics Osseous Metastasis: Another Rare Pitfall in FDG-PET-CT. Front. Nucl. Med. 2023, 3, 1150143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, S.N.; Mohla, A.; Zhu, G.G.; Gutowski, C.; Kim, T.W.B.; Amin, R. Intraosseous Hibernoma: Two Case Reports and a Review of the Literature. Radiol. Case Rep. 2022, 17, 2477–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myslicki, F.A.; Rosenberg, A.E.; Chaitowitz, I.; Subhawong, T.K. Intraosseous Hibernoma: Five Cases and a Review of the Literature. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2019, 43, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peer, S.; Kühberger, R.; Dessl, A.; Judmaier, W. MR Imaging Findings in Hibernoma. Skelet. Radiol. 1997, 26, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murad, M.H.; Sultan, S.; Haffar, S.; Bazerbachi, F. Methodological Quality and Synthesis of Case Series and Case Reports. BMJ Evid.-Based Med. 2018, 23, 60–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlychou, M.; Inagaki, Y.; Stacey, R.; Athanasou, N.A. Primary Intraosseous Meningioma: An Osteosclerotic Bone Tumour Mimicking Malignancy. Clin. Sarcoma Res. 2016, 6, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafeez, I.; Shankman, S.; Michnovicz, J.; Vigorita, V.J. Intraosseous Hibernoma: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Spine 2015, 40, E558–E561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jerman, A.; Snoj, Ž.; Kuzmanov, B.G.; Limpel Novak, A.K. Intraosseous Hibernoma: Case Report and Tumor Characterization. BJR Case Rep. 2015, 1, 20150204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westacott, L.; Collins, A.; Dickenson, I. Intraosseous Hibernoma in the Sacrum of an Adult. Int. J. Surg. Pathol. 2016, 24, 749–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yahia, M.; Laabidi, B.; M’sakni, I.; Bougrine, F.; Bouziani, A. Intraosseous Hibernoma: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Tunis. Med. 2016, 94, 622–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botchu, R.; Puls, F.; Hock, Y.L.; Davies, A.M.; Wafa, H.; Grimer, R.J.; Bröcker, V.; James, S. Intraosseous Hibernoma: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Skelet. Radiol. 2013, 42, 1003–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Deaver, M.T.; Czerniak, B.A.; Madewell, J.E. Intraosseous Hibernoma. Skelet. Radiol. 2011, 40, 641–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonar, S.F.; Watson, G.; Gragnaniello, C.; Seex, K.; Magnussen, J.; Earwaker, J. Intraosseous Hibernoma: Characterization of Five Cases and Literature Review. Skelet. Radiol. 2014, 43, 939–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faropoulos, K.; Apostolopoulou, K.; Gkermpesi, M. Sacral Hibernoma: Presentation of a Rare Case and a Treatment Algorithm. Neurochirurgie 2019, 65, 430–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degnan, A.J.; Maldjian, C.; Pantanowitz, L.; Kofler, J.K. Rare Case of a Radiographically Occult Sacral Lesion Detected on MRI Presenting with Intractable Back Pain. BJR Case Rep. 2015, 1, 20150002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dannheim, K.; Bhargava, P. A Rare Finding of Brown Fat in Bone Marrow as a Mimic for Metastatic Disease. Am. J. Hematol. 2016, 91, 545–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zuidberg-van der Gronde, K.; der Gronde, K.Z.; Klazen, C.; van Baarlen, J.; Bezooijen, R. A Rare Sternal Lesion on Magnetic Resonance Mammography Mimicking a Metastasis in a Patient With a History of Mamma Carcinoma: A Case Report. J. Med. Cases 2017, 8, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Woodford, H.; Le, K.; Bui, C.; Mansberg, R. Hibernoma Demonstrated on 68Ga-DOTATATE PET/CT. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2019, 44, 491–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, S.; Rai, A.K.; Rahman, S.H.; Hadole, B.S.; Bandebuche, A.R.; Prabhu, R.M. Diagnosis of Intraosseous Hibernoma of an Appendicular Skeleton in an Adult—A Rare Case Report. J. Orthop. Case Rep. 2022, 12, 40–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, M.; Liu, H.; Zhang, L.; Gao, L. Intraosseous Hibernoma in the Rib. Interdiscip. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2023, 36, ivac287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Um, M.-K.; Lee, E.; Lee, J.W.; Lee, K.S.; Kang, Y.; Ahn, J.M.; Kang, H.S. Spinal Intraosseous Hibernoma: A Case Report and Review of Literature. Taehan Yongsang Uihakhoe Chi 2020, 81, 965–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonkaz, G.; Cakir, E.; Tonkaz, M.; Sengul, D. Femoral Hibernoma: Unique Intraosseous Tumor. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2024, 136, 581–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaikh, A.; Basha, A.; Ray, G.; Bishop, J.A.; Chhabra, A. Intraosseous Hibernoma Mimicking Sclerotic Bone Metastasis-A Case Report. Skelet. Radiol. 2025, 54, 1139–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitto, S.; Doeleman, T.; van de Sande, M.A.J.; van Langevelde, K. Intraosseous Hibernoma of the Appendicular Skeleton. Skelet. Radiol. 2022, 51, 1325–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringe, K.I.; Rosenthal, H.; Länger, F.; Callies, T.; Wacker, F.; Raatschen, H.-J. Radiofrequency Ablation of a Rare Case of an Intraosseous Hibernoma Causing Therapy-Refractory Pain. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. JVIR 2013, 24, 1754–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangahar, C.N.; Dehner, C.A.; Wang, D.P.; Amini, B.; Hillen, T.; O’Conor, C.; Jennings, S.N.; Byrnes, K.; Montgomery, E.A.; Czerniak, B.A.; et al. Intraosseous Hibernoma: Clinicopathologic and Imaging Analysis of 18 Cases. Histopathology 2023, 83, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, D.T.; Dabney, R.S.; Andrews, J.M. Intraosseous Hibernoma or Unusual Location of Brown Fat? J. Hematop. 2013, 6, 151–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celi, F.S. Brown Adipose Tissue--When It Pays to Be Inefficient. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 1553–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, P.; Levy, J.D.; Zhang, Y.; Frontini, A.; Kolodin, D.P.; Svensson, K.J.; Lo, J.C.; Zeng, X.; Ye, L.; Khandekar, M.J.; et al. Ablation of PRDM16 and Beige Adipose Causes Metabolic Dysfunction and a Subcutaneous to Visceral Fat Switch. Cell 2014, 156, 304–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodacre, T.; Ball, T.; Cox, P. Epidemiology of Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip within the UK: Refining the Risk Factors. J. Child. Orthop. 2016, 10, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mrózek, K.; Karakousis, C.P.; Bloomfield, C.D. Band 11q13 Is Nonrandomly Rearranged in Hibernomas. Genes. Chromosomes Cancer 1994, 9, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertens, F.; Rydholm, A.; Brosjö, O.; Willén, H.; Mitelman, F.; Mandahl, N. Hibernomas Are Characterized by Rearrangements of Chromosome Bands 11q13-21. Int. J. Cancer 1994, 58, 503–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maire, G.; Forus, A.; Foa, C.; Bjerkehagen, B.; Mainguené, C.; Kresse, S.H.; Myklebost, O.; Pedeutour, F. 11q13 Alterations in Two Cases of Hibernoma: Large Heterozygous Deletions and Rearrangement Breakpoints near GARP in 11q13.5. Genes. Chromosomes Cancer 2003, 37, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Characteristic | Value |
|---|---|
| Patient Demographics: | |
| Age, years, mean ± SD (range) | 59.2 ± 13.13 (7–85) |
| Sex | |
| Male, n (%) | 22 (35.48%) |
| Female, n (%) | 40 (64.52%) |
| Clinical Presentation: | |
| Incidental findings, n (%) | 38 (61.29%) |
| - During cancer staging/surveillance | 26 (41.94%) |
| - During other medical investigations | 12 (19.35%) |
| Pain, n (%) | 24 (38.71%) |
| Lesion Characteristics: | |
| Size in mm, mean ± SD (range) | 21.8 ± 15.7 (1.5–90) |
| Anatomical Location: | |
| Pelvis, total: | 36 (58.06%) |
| - Sacrum | 18 (29.03%) |
| - Ilium | 11 (17.74%) |
| - Ischium | 5 (8.06%) |
| - Pubis | 2 (3.23%) |
| Spine, total: | 14 (22.58%) |
| - Thoracic | 8 (12.90%) |
| - Lumbar | 6 (9.68%) |
| Femur | 4 (6.45%) |
| Manubrium sterni | 3 (4.84%) |
| Humerus | 2 (3.23%) |
| Ribs | 2 (3.23%) |
| Tibia | 1 (1.61%) |
| Management | |
| Conservative (biopsy only) | 54 (87%) |
| Surgical excision/curettage | 5 (8%) |
| percutaneous thermal ablation (RFA, MWA) | 3 (5%) |
| Author, Year | Country | Study Design | Sample Size | Tumor Location | Investigation Reason | Imaging Modality Used |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shaikh et al., 2025 [34] | USA | Case Report | 1 | Left iliac bone (pelvis) | Found incidentally during investigation of fall injury | CT, MRI |
| Tonkaz et al., 2024 [33] | Turkey | Case Report | 1 | Femur (greater trochanter) | Discovered incidentally after a fall | CT, MRI, Bone scintigraphy/SPECT |
| Gangahar et al., 2023 [37] | USA | Case Series | 18 | Multiple locations: femur (7), pelvis (4), spine (3), humerus (2), tibia (1), ribs (1) | Various (surveillance, back pain, staging, limping, weight loss, sciatica) | CT, MRI, 18F-FDG PET/CT, Bone scintigraphy/SPECT, 68Ga-DOTATATE PET/CT |
| Samargandi et al., 2023 [6] | France | Case Report | 2 | Manubrium sterni, left iliac bone | Incidentally found during breast cancer staging, incidental bony lesion on MRI | CT, MRI, 18F-FDG PET/CT, Bone scintigraphy/SPECT |
| Song M et al., 2023 [31] | China | Case Report | 1 | Left seventh rib | Paroxysmal left-sided thoracic pain for 2 months | CT |
| Stolte et al., 2023 [11] | Switzerland | Case Report | 1 | Upper left pubic bone (pelvis) | Lesion discovered incidentally on 18F-FDG PET/CT during lung cancer staging | CT, 18F-FDG PET/CT |
| Gitto et al., 2022 [35] | Netherlands | Case Report | 1 | Right proximal humerus | Shoulder MRI incidentally revealed an osseous lesion | MRI |
| Srinivasan et al., 2022 [30] | India | Case Report | 1 | Left proximal tibia | Painless solitary mass, slowly growing over 2 years | MRI, 18F-FDG PET/CT |
| Weiss et al., 2022 [12] | USA | Case Report | 2 | Right sacral wing, right sacral ala | Chronic right hip pain, chronic midline lumbar back pain | CT, MRI, 18F-FDG PET/CT |
| Ko et al., 2020 [9] | USA | Case Report | 1 | T3 vertebral body (spine) | Incidental finding during ovarian cancer workup | CT, MRI |
| Mi-Kyung Um et al., 2020 [32] | South Korea | Case Report | 1 | T7 vertebral body (spine) | Discovered incidentally on chest CT during tuberculosis screening | CT, MRI, 18F-FDG PET/CT |
| Faropoulos et al., 2019 [25] | Greece | Case Report | 1 | Left sacral vertebra S4 (spine) | Low back pain extending to the left buttock, causalgia | CT, MRI |
| Myslicki et al., 2019 [13] | USA | Case Series | 5 | L2 vertebral body, right sacral ala, Right hemisacrum at S2, left posterior superior iliac spine, left proximal femur | Various (incidental findings, pelvic pain) | CT, MRI, Bone scintigraphy/SPECT |
| Woodford et al., 2019 [29] | Australia | Case Report | 1 | Right sacral ala (pelvis) | Identified on 68Ga-DOTATATE PET/CT during neuroendocrine tumor staging | CT, 18F-FDG PET/CT, 68Ga-DOTATATE PET/CT |
| Song B et al., 2017 [8] | South Korea | Case Series | 6 | L3 vertebral body, T12 vertebral body (2), sacral ala, distal femur, L3–4 vertebral body | Five patients with musculoskeletal pain, one incidental finding | CT, MRI, 18F-FDG PET/CT, Bone scintigraphy/SPECT |
| Zuidberg-van der Gronde et al., 2017 [28] | Netherlands | Case Report | 1 | Manubrium sterni | Found during annual MRI breast cancer follow-up | CT, MRI, Bone scintigraphy/SPECT |
| Dannheim et al., 2016 [27] | USA | Case Report | 1 | Right sacral ala (pelvis) | Incidental finding during staging of breast cancer work-up | CT, 18F-FDG PET/CT |
| Yahia et al., 2016 [21] | Tunisia | Case Report | 1 | Right fourth rib | Right chest pain for 6 months | CT, Bone scintigraphy/SPECT |
| Vlychou et al., 2016 [17] | United Kingdom | Case Report | 1 | Left ischium (pelvis) | Left sacral/hip pain radiating down the left leg, worse at night | CT, MRI, 18F-FDG PET/CT |
| Westacott et al., 2016 [20] | Australia | Case Report | 1 | Sacrum (pelvis) | Right hip and lower back pain | CT |
| Degnan et al., 2015 [26] | USA | Case Report | 1 | Right S2 sacral lesion (spine) | Persistent lower back and right buttock pain for months | CT, MRI |
| Hafeez et al., 2015 [18] | USA | Case Report | 1 | L3 vertebral body (spine) | No pain reported; identified incidentally during imaging | CT, MRI |
| Jerman et al., 2015 [19] | Slovenia | Case Report | 1 | Left sacrum (pelvis) | Chronic lower back pain (lumbago, worse after physical activity) | CT, MRI, 18F-FDG PET/CT, Bone scintigraphy/SPECT |
| Bonar et al., 2014 [24] | Australia | Case Series | 5 | T5 vertebral body, Manubrium sterni, left ischiopubic ramus, T12 vertebral body, left iliac crest | All incidental findings during staging investigations | CT, MRI, 18F-FDG PET/CT, Bone scintigraphy/SPECT |
| Bai et al., 2013 [10] | USA | Case Report | 1 | Right ilium (pelvis) | Posterolateral right hip pain worsened by activity | CT, MRI, 18F-FDG PET/CT |
| Botchu et al., 2013 [22] | United Kingdom | Case Report | 1 | Right posterior ilium (pelvis) | Low back and buttock pain for six months | CT, MRI, Bone scintigraphy/SPECT |
| Lynch et al., 2013 [38] | USA | Case Report | 1 | Left iliac crest (pelvis) | Incidental finding as part of workup for essential thrombocytopenia | NR * |
| Ringe et al., 2013 [36] | Germany | Case Report | 1 | Left sacral bone (pelvis) | Lower back pain radiating to the left foot, especially at night; therapy-refractory | CT, MRI |
| Kumar et al., 2011 [23] | USA | Case Report | 1 | Left sacral ala (pelvis) | Low back pain radiating to the left lower limb | CT, MRI |
| Thorns et al., 2008 [7] | Germany | Case Report | 1 | Ilium (pelvis) | Incidental finding during workup | NR * |
| Imaging Modality and Characteristics | Number (%) |
|---|---|
| CT Findings: (n = 62) | |
| Appearance pattern | |
| - Sclerotic | 43 (69.35%) |
| - Lytic | 6 (9.68%) |
| - Mixed (sclerotic + lytic) | 4 (6.45%) |
| - Occult | 3 (4.84%) |
| - Not reported | 6 (9.68%) |
| MRI Characteristics:(n = 46) | |
| T1-weighted signal | |
| - Hypointense/low—Isointense | 44 (95.65%) |
| - Hyperintense/high | 2 (4.35%) |
| - Heterogeneous | Common finding |
| T2-weighted signal/STIR | |
| - Hyperintense/high | 43 (93.48%) |
| - Hypointense/low—Isointense | 3 (6.52%) |
| Post-contrast enhancement | |
| - Present (mild to moderate) | Majority of reported cases |
| - Absent | Minority of reported cases |
| 18F-FDG PET/CT Findings (n = 16): | |
| Mean SUV (3.31 ± 0.67) | |
| - No uptake | 4 (25%) |
| - Uptake | 11 (68.75%) |
| Mild | 9 |
| Moderate | 1 |
| High | 1 |
| - Not reported | 1 (6.25%) |
| Bone scintigraphy/SPECT Findings (n = 18): | |
| - Increased uptake | 13 (72.22%) |
| - No uptake | 2 (11.11%) |
| - Not reported | 3 (16.67%) |
| 68Ga-DOTATATE PET/CT Findings (n = 4): | |
| - No uptake | 1 (25%) |
| - Mild uptake | 1 (25%) |
| - Moderate uptake | 1 (25%) |
| - High uptake | 1 (25%) |
| Feature | Intraosseous Hibernoma | Metastatic Lesion |
|---|---|---|
| Number | Almost always solitary | Solitary or multiple |
| Margins | Well-defined | Less defined, irregular |
| Density on CT | Sclerotic, sometimes mixed/lytic and rarely occult | Sclerotic, lytic, or mixed |
| MRI Signal (T1/T2) | Low/intermediate T1; hyperintense T2 | Low T1; variable T2 |
| Contrast Enhancement | Heterogeneous, low to moderate, peripheral possible | Diffuse, intense |
| 18F-FDG PET/CT | Mild or moderate uptake, SUV usually low-to-intermediate | Markedly hypermetabolic, SUV often high |
| Bone Scintigraphy/SPECT | Mild uptake, may be variable | Typically, increased uptake |
| Preservation of Trabeculae | Common | Often destroyed/disrupted |
| Cortical Breach/Soft Tissue | Rare | Possible, especially aggressive tumors |
| Typical Location | Common in axial skeleton | Any bone |
| Marker | Positive n (%) | Negative n (%) | Not Reported n (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| S100 | 52 (83.87%) | 0 | 10 (16.13%) |
| Adipophilin | 7 (11.29%) | 0 | 55 (88.71%) |
| FABP4/AP2 | 1 (1.61%) | 0 | 61 (98.39%) |
| CD68 | 1 (1.61%) | 32 (51.61%) | 29 (46.77%) |
| CD45 | 0 | 12 (19.35%) | 50 (80.65%) |
| CD163 | 0 | 14 (22.58%) | 48 (77.42%) |
| Cytokeratin AE1/AE3 | 0 | 42 (67.74%) | 20 (32.26%) |
| Brachyury | 0 | 14 (22.58%) | 48 (77.42%) |
| HMB45 | 0 | 9 (14.52%) | 53 (85.48%) |
| MDM2 | 0 | 2 (3.23%) | 60 (96.77%) |
| Melan A | 0 | 7 (11.29%) | 55 (88.71%) |
| Parameter | Stratification | Observed Frequency | Proportion (95% CI) 1 | Prevalence Ratio 2 | Estimated Representation 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender-Based Distribution: | |||||
| Female preponderance | Overall population | 40/62 | 64.5% (52.1–75.3%) | 1.82 | +++ |
| Axial distribution subset | 4 | 4 | 4 | ++ | |
| Appendicular distribution subset | 4 | 4 | 4 | +++ | |
| Male representation | Overall population | 22/62 | 35.5% (24.7–47.9%) | 0.55 | ++ |
| Anatomical Distribution Analysis: | |||||
| Axial skeleton involvement | Aggregate analysis | 50/62 | 80.6% (69.1–88.6%) | 4.17 | ++++ |
| - Pelvis | Subgroup analysis | 36/62 | 58.1% (45.7–69.5%) | 1.39 | +++ |
| - Spine | Subgroup analysis | 14/62 | 22.6% (13.8–34.8%) | 0.29 | ++ |
| Appendicular skeleton | Comparative analysis | 12/62 | 19.4% (11.4–30.9%) | 0.24 | + |
| Radiological Manifestation Patterns: | |||||
| Sclerotic presentation | Primary pattern | 43/62 | 69.4% (57.0–79.4%) | 2.26 | ++++ |
| Lytic presentation | Alternative pattern | 6/62 | 9.7% (4.5–19.5%) | 0.11 | + |
| Mixed/Other presentations | Variant patterns | 13/62 | 21.0% (12.5–33.0%) | 0.26 | ++ |
| Clinical-Pathological Correlation: | |||||
| Incidental discovery | Diagnostic pathway analysis | 38/62 | 61.3% (48.9–72.4%) | 1.58 | +++ |
| Pain manifestation | Symptomatic presentation | 24/62 | 38.7% (27.6–51.1%) | 0.63 | ++ |
| Immunohistochemical Profile Stratification: | |||||
| S100 positivity | Diagnostic marker efficacy | 52/52 | 100% (93.1–100%) 5 | ∞ | ++++ |
| Variable | Anatomical Distribution | Radiological Pattern | Gender Predilection | Age Distribution | Clinical Presentation | Immunological Profile |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anatomical Distribution | 1.00 | 0.78 ** | 0.56 * | 0.22 | 0.73 ** | 0.18 |
| Radiological Pattern | 0.78 ** | 1.00 | 0.47 * | 0.19 | 0.54 * | 0.21 |
| Gender Predilection | 0.56 * | 0.47 * | 1.00 | 0.25 | 0.52 * | 0.15 |
| Age Distribution | 0.22 | 0.19 | 0.25 | 1.00 | 0.27 | 0.14 |
| Clinical Presentation | 0.73 ** | 0.54 * | 0.52 * | 0.27 | 1.00 | 0.23 |
| Immunological Profile | 0.18 | 0.21 | 0.15 | 0.14 | 0.23 | 1.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Albashri, J.; Albashri, A.; Alhamrani, M.; Hassan, A.; Shamah, H.; Alhefzi, R.; Alshahrani, N.Z.; Algethami, M.R.; Le Nail, L.-R.; Samargandi, R. Clinical, Radiological, and Pathological Features of Intraosseous Hibernoma: A Systematic Review of Case Reports and Case Series. Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32, 535. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32100535
Albashri J, Albashri A, Alhamrani M, Hassan A, Shamah H, Alhefzi R, Alshahrani NZ, Algethami MR, Le Nail L-R, Samargandi R. Clinical, Radiological, and Pathological Features of Intraosseous Hibernoma: A Systematic Review of Case Reports and Case Series. Current Oncology. 2025; 32(10):535. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32100535
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlbashri, Jawad, Ahmed Albashri, Muhannad Alhamrani, Abdulrahman Hassan, Hisham Shamah, Rayan Alhefzi, Najim Z. Alshahrani, Mohammed R. Algethami, Louis-Romée Le Nail, and Ramy Samargandi. 2025. "Clinical, Radiological, and Pathological Features of Intraosseous Hibernoma: A Systematic Review of Case Reports and Case Series" Current Oncology 32, no. 10: 535. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32100535
APA StyleAlbashri, J., Albashri, A., Alhamrani, M., Hassan, A., Shamah, H., Alhefzi, R., Alshahrani, N. Z., Algethami, M. R., Le Nail, L.-R., & Samargandi, R. (2025). Clinical, Radiological, and Pathological Features of Intraosseous Hibernoma: A Systematic Review of Case Reports and Case Series. Current Oncology, 32(10), 535. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32100535






