Case Report: A Presentation of Early-Onset Immune-Mediated Bullous Pemphigoid in a Patient with Urothelial Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
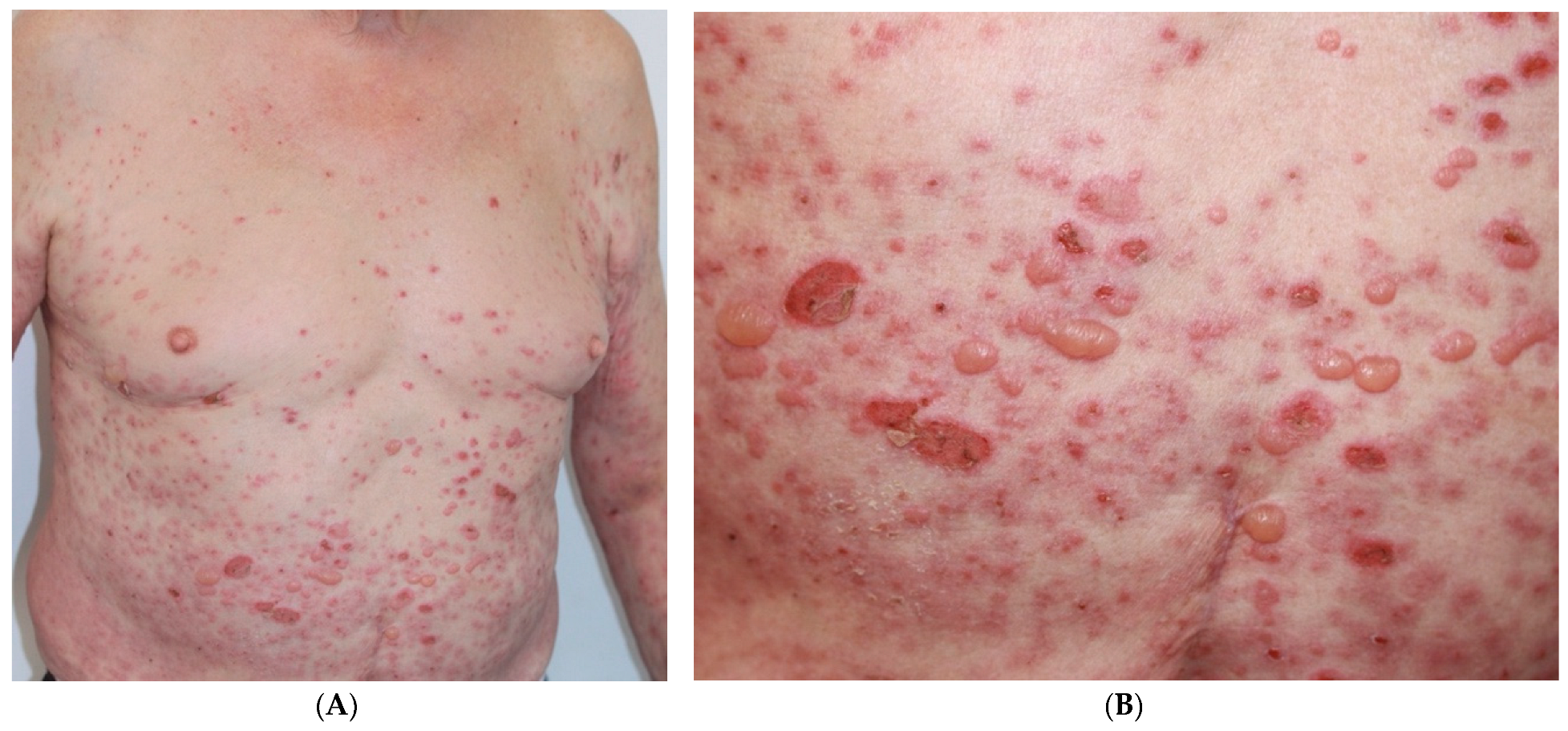
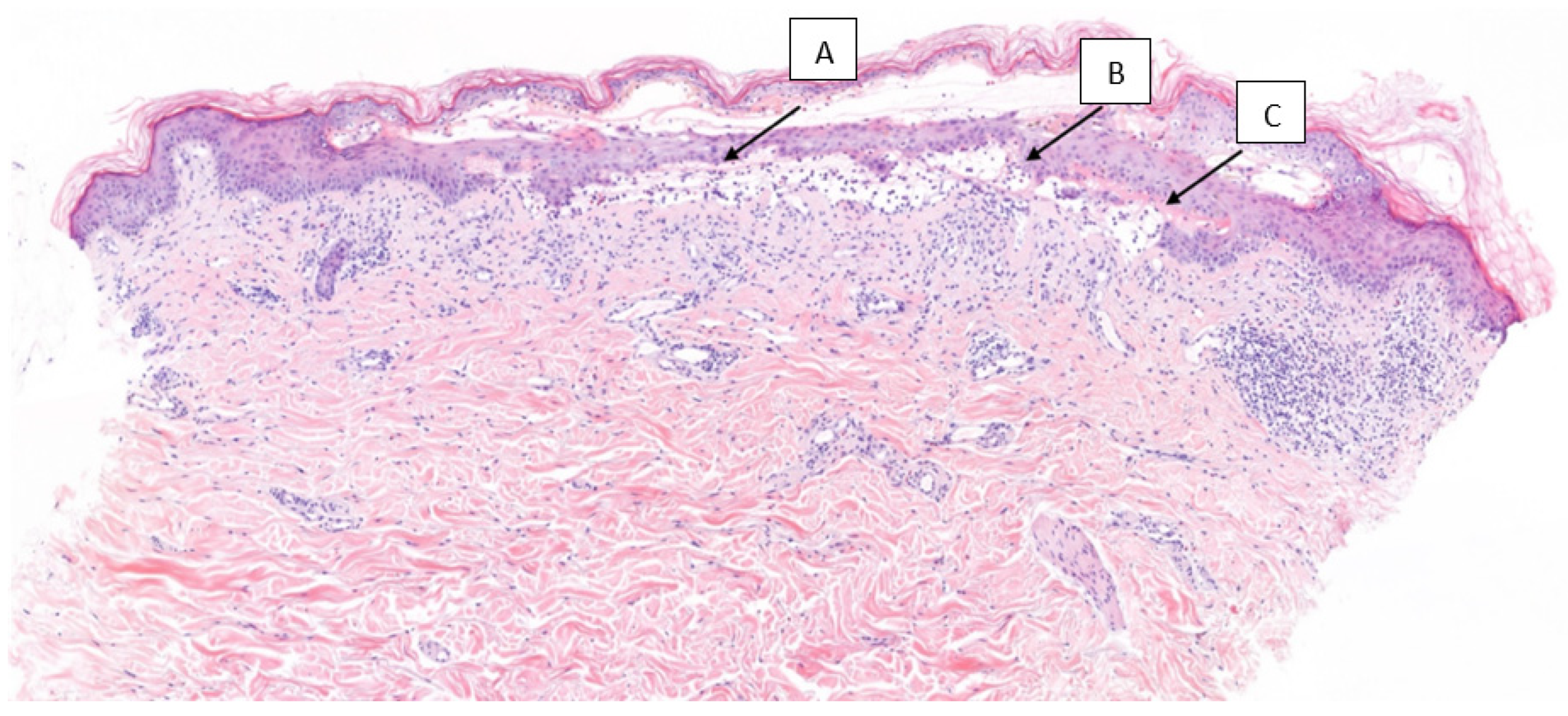
2. Presentation of the Case
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Franzin, R.; Netti, G.S.; Spadaccino, F.; Porta, C.; Gesualdo, L.; Stallone, G.; Castellano, G.; Ranieri, E. The use of immune checkpoint inhibitors in oncology and the occurrence of AKI: Where do we stand? Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 574271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Reynolds, K.L.; Lyon, A.R.; Palaskas, N.; Neilan, T.G. The Evolving Immunotherapy Landscape and the Epidemiology, Diagnosis, and Management of Cardiotoxicity. JACC CardioOncology 2021, 3, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.Y.; Salem, J.E.; Cohen, J.V.; Chandra, S.; Menzer, C.; Ye, F.; Zhao, S.; Das, S.; Beckermann, K.E.; Ha, L.; et al. Fatal Toxic Effects Associated with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cathcart-Rake, E.J.; Sangaralingham, L.R.; Henk, H.J.; Shah, N.D.; Bin Riaz, I.; Mansfield, A.S. A Population-based Study of Immunotherapy-related Toxicities in Lung Cancer. Clin. Lung Cancer 2020, 21, 421–427.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, S.; Zibelman, M.; Bertino, E.; Yucebay, F.; Reynolds, K. Managing Immuno-Oncology Toxicity: Top 10 Innovative Institutional Solutions. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2019, 39, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, F.; Sofiya, L.; Sykiotis, G.P.; Lamine, F.; Maillard, M.; Fraga, M.; Shabafrouz, K.; Ribi, C.; Cairoli, A.; Guex-Crosier, Y.; et al. Adverse effects of immune-checkpoint inhibitors: Epidemiology, management and surveillance. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 16, 563–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.B.; Balko, J.M.; Compton, M.L.; Chalkias, S.; Gorham, J.; Xu, Y.; Hicks, M.; Puzanov, I.; Alexander, M.R.; Bloomer, T.L.; et al. Fulminant Myocarditis with Combination Immune Checkpoint Blockade. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1749–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibaud, V. Dermatologic reactions to immune checkpoint inhibitors: Skin toxicities and immunotherapy. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2018, 19, 345–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio-Infante, N.; Ramírez-Flores, Y.A.; Castillo, E.C.; Lozano, O.; García-Rivas, G.; Torre-Amione, G. Cardiotoxicity associated with immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy: A meta-analysis. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2021, 23, 1739–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, M.; Begum, N.; Grainge, M.; Harman, K.; Grindlay, D.; Gran, S. The global incidence of bullous pemphigoid: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2021, 186, 414–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhao, W.; Jin, H.; Li, L. Risk Factors for Mucosal Involvement in Bullous Pemphigoid and the Possible Mechanism: A Review. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 680871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curry, J.L.; Tetzlaff, M.T.; Nagarajan, P.; Drucker, C.; Diab, A.; Hymes, S.R.; Duvic, M.; Hwu, W.-J.; Wargo, J.A.; Torres-Cabala, C.A.; et al. Diverse types of dermatologic toxicities from immune checkpoint blockade therapy. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2016, 44, 158–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, S.R.; Vierra, A.T.; Millsop, J.W.; Lacouture, M.E.; Kiuru, M. Dermatologic toxicities to immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy: A review of histopathologic features. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020, 83, 1130–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Li, S.; Yang, Q. Risk of dermatologic and mucosal adverse events associated with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors in cancer patients. Medicine 2019, 98, e15731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhaya, S.; Watts, I.; Ng, K.; Mustapha, R.; Powles, T.; Sharma, A.; Vasdev, N. Role of Perioperative Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer. Oncol. Ther. 2023, 11, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Beltran, A.; Cimadamore, A.; Blanca, A.; Massari, F.; Vau, N.; Scarpelli, M.; Cheng, L.; Montironi, R. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors for the Treatment of Bladder Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, M.; Zheng, X.; Niu, M.; Zhu, S.; Ge, H.; Wu, K. Combination strategies with PD-1/PD-L1 blockade: Current advances and future directions. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, T.; Ishikawa, H.; Nagumo, Y.; Sekino, Y.; Kageyama, Y.; Ushijima, H.; Kawai, T.; Yamashita, H.; Azuma, H.; Nihei, K.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Bladder Preservation Therapy in Combination with Atezolizumab and Radiation Therapy (BPT-ART) for Invasive Bladder Cancer: Interim Analysis from a Multicenter, Open-label, Prospective Phase 2 Trial. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2023, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galsky, M.D.; Arija, J.Á.A.; Bamias, A.; Davis, I.D.; De Santis, M.; Kikuchi, E.; Garcia-del-Muro, X.; De Giorgi, U.; Mencinger, M.; Izumi, K.; et al. Atezolizumab with or without chemotherapy in metastatic urothelial cancer (IMvigor130): A multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. The Lancet 2020, 395, 1547–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacovino, M.L.; Miceli, C.C.; De Felice, M.; Barone, B.; Pompella, L.; Chiancone, F.; Di Zazzo, E.; Tirino, G.; Della Corte, C.M.; Imbimbo, C.; et al. Novel Therapeutic Opportunities in Neoadjuvant Setting in Urothelial Cancers: A New Horizon Opened by Molecular Classification and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.J.; Lee, H.J., Jr.; Farmer, J.R.; Reynolds, K.L. Mechanisms Driving Immune-Related Adverse Events in Cancer Patients Treated with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2021, 23, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geisler, A.N.; Phillips, G.S.; Barrios, D.M.; Wu, J.; Leung, D.Y.M.; Moy, A.P.; Kern, J.A.; Lacouture, M.E. Immune checkpoint inhibitor–related dermatologic adverse events. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020, 83, 1255–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Les, I.; Pérez-Francisco, I.; Cabero, M.; Sánchez, C.; Hidalgo, M.; Teijeira, L.; Arrazubi, V.; Domínguez, S.; Anaut, P.; Eguiluz, S.; et al. Prediction of Immune-Related Adverse Events Induced by Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors with a Panel of Autoantibodies: Protocol of a Multicenter, Prospective, Observational Cohort Study. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 894550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, E.L.; Olamiju, B.; Leventhal, J.S. The life-threatening eruptions of immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy. Clin. Dermatol. 2019, 38, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadik, C.D.; Langan, E.A.; Grätz, V.; Zillikens, D.; Terheyden, P. Checkpoint Inhibition May Trigger the Rare Variant of Anti-LAD-1 IgG-Positive, Anti-BP180 NC16A IgG-Negative Bullous Pemphigoid. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, C.; Borradori, L.; Amber, K.T. Deciphering the Contribution of BP230 Autoantibodies in Bullous Pemphigoid. Antibodies 2022, 11, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verheyden, M.; Bilgic, A.; Murrell, D. A Systematic Review of Drug-Induced Pemphigoid. Acta Derm.-Venereol. 2020, 100, adv00224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bur, D.; Patel, A.B.; Nelson, K.; Huen, A.; Pacha, O.; Phillips, R.; Heberton, M. A retrospective case series of 20 patients with immunotherapy-induced bullous pemphigoid with emphasis on management outcomes. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2022, 87, 1394–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Sui, D.; Wang, D.; Zhang, L.; Wang, R. Case Report: A Rare Case of Pembrolizumab-Induced Bullous Pemphigoid. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 731774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leavitt, E.; Holland, V. A case of atezolizumab-induced photodistributed bullous pemphigoid. Dermatol. Ther. 2019, 32, e12924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, A.T.; Khanna, T.; Antonov, N.; Audrey-Bayan, C.; Geskin, L. A review of bullous pemphigoid associated with PD-1 and PD-L1 inhibitors. Int. J. Dermatol. 2018, 57, 664–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosche, C.; Owen, J.L.; Sadowsky, L.M.; Choi, J.N. Bullous dermatoses secondary to anti-PD-L1 agents: A case report and review of the literature. Dermatol. Online J. 2019, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro, F.; Fania, L.; Sinagra, J.L.M.; Salemme, A.; Di Zenzo, G. Bullous Pemphigoid: Trigger and Predisposing Factors. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopkins, A.M.; Rowland, A.; Kichenadasse, G.; Wiese, M.D.; Gurney, H.; A McKinnon, R.; Karapetis, C.S.; Sorich, M.J. Predicting response and toxicity to immune checkpoint inhibitors using routinely available blood and clinical markers. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 117, 913–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manson, G.; Norwood, J.; Marabelle, A.; Kohrt, H.; Houot, R. Biomarkers associated with checkpoint inhibitors. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 1199–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chennamadhavuni, A.; Abushahin, L.; Jin, N.; Presley, C.J.; Manne, A. Risk Factors and Biomarkers for Immune-Related Adverse Events: A Practical Guide to Identifying High-Risk Patients and Rechallenging Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 779691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Hsu, D.Y.; Brieva, J.; Silverberg, N.B.; Langan, S.M.; Silverberg, J.I. Hospitalization, inpatient burden and comorbidities associated with bullous pemphigoid in the USA. Br. J. Dermatol. 2017, 176, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwa, M.C.; Silverberg, J.I. Association Between Inflammatory Skin Disease and Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Co-Morbidities in US Adults: Analysis of Nationwide Inpatient Sample Data. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2017, 18, 813–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzani, E.; Gasparini, G.; Burlando, M.; Drago, F.; Parodi, A. Atypical presentations of bullous pemphigoid: Clinical and immunopathological aspects. Autoimmun. Rev. 2015, 14, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Béné, J.; Jacobsoone, A.; Coupe, P.; Auffret, M.; Babai, S.; Hillaire-Buys, D.; Jean-Pastor, M.-J.; Vonarx, M.; Vermersch, A.; Tronquoy, A.-F.; et al. Bullous pemphigoid induced by vildagliptin: A report of three cases. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2014, 29, 112–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giusti, D.; Gatouillat, G.; Le Jan, S.; Plée, J.; Bernard, P.; Antonicelli, F.; Pham, B.N. Eosinophil Cationic Protein (ECP), a predictive marker of bullous pemphigoid severity and outcome. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedeschi, A.; Marzano, A.; Lorini, M.; Balice, Y.; Cugno, M. Eosinophil cationic protein levels parallel coagulation activation in the blister fluid of patients with bullous pemphigoid. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2014, 29, 813–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Zhang, L.; Qi, R.; Gao, X.; Chen, H.; Xiao, T. miR-1291 Functions as a Potential Serum Biomarker for Bullous Pemphigoid. Dis. Markers 2020, 2020, 9505312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, Y.; Liu, J.; Ye, Y.; Pan, L.; Deng, H.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Diao, L.; Lin, S.H.; Mills, G.B.; et al. Multi-omics prediction of immune-related adverse events during checkpoint immunotherapy. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romão, R.; Mendes, A.S.; Ranchor, R.; Ramos, M.J.; Coelho, J.; Pichel, R.C.; Azevedo, S.X.; Fidalgo, P.; Araújo, A. Impact of Immune-Related Adverse Events on Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Treated Cancer Patients’ Survival: Single Center Experience and Literature Review. Cancers 2023, 15, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Zhang, J.; Xu, L.; Yang, H.; Liang, N.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, X. Safety and Efficacy of the Rechallenge of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors After Immune-Related Adverse Events in Patients with Cancer: A Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 730320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apalla, Z.; Sibaud, V. Immunotherapy-mediated dermatological adverse events: The urgent need for a common, clinically meaningful, management strategy. Support. Care Cancer 2020, 28, 5597–5599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sabaté Ortega, J.; Fort Culillas, R.; Escoda Garcia, M.; Vásquez-Dongo, C.A.; Sala González, N. Case Report: A Presentation of Early-Onset Immune-Mediated Bullous Pemphigoid in a Patient with Urothelial Cancer. Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 7802-7809. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30090566
Sabaté Ortega J, Fort Culillas R, Escoda Garcia M, Vásquez-Dongo CA, Sala González N. Case Report: A Presentation of Early-Onset Immune-Mediated Bullous Pemphigoid in a Patient with Urothelial Cancer. Current Oncology. 2023; 30(9):7802-7809. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30090566
Chicago/Turabian StyleSabaté Ortega, Josep, Roser Fort Culillas, Marina Escoda Garcia, Carmen Amalia Vásquez-Dongo, and Núria Sala González. 2023. "Case Report: A Presentation of Early-Onset Immune-Mediated Bullous Pemphigoid in a Patient with Urothelial Cancer" Current Oncology 30, no. 9: 7802-7809. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30090566
APA StyleSabaté Ortega, J., Fort Culillas, R., Escoda Garcia, M., Vásquez-Dongo, C. A., & Sala González, N. (2023). Case Report: A Presentation of Early-Onset Immune-Mediated Bullous Pemphigoid in a Patient with Urothelial Cancer. Current Oncology, 30(9), 7802-7809. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30090566




