Deep Learning Algorithm for Tumor Segmentation and Discrimination of Clinically Significant Cancer in Patients with Prostate Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection Criteria
2.2. MRI Technique
2.3. Data Processing
2.4. DL Architecture for Tumor and Gland Segmentation
2.5. DL Architecture for Tumor Classification
2.5.1. Training Architecture
2.5.2. External Validation
2.6. Reference Standard
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Demographics
3.2. Diagnostic Performance of DLA
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arif, M.; Schoots, I.G.; Tovar, J.C.; Bangma, C.H.; Krestin, G.P.; Roobol, M.J.; Niessen, W.; Veenland, J.F. Clinically significant prostate cancer detection and segmentation in low-risk patients using a convolutional neural network on multi-parametric MRI. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 6582–6592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, X.; Cao, R.; Shakeri, S.; Scalzo, F.; Lee, Y.; Enzmann, D.R.; Wu, H.H.; Raman, S.S.; Sung, K. Deep transfer learning-based prostate cancer classification using 3 Tesla multi-parametric MRI. Abdom. Radiol. 2019, 44, 2030–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaeffer, E.M.; Srinivas, S.; Adra, N.; An, Y.; Barocas, D.; Bitting, R.; Bryce, A.; Chapin, B.; Cheng, H.H.; D’Amico, A.V.; et al. NCCN Guidelines® Insights: Prostate Cancer, Version 1.2023. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2022, 20, 1288–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.C.; Rumble, R.B.; Loblaw, D.A.; Finelli, A.; Ehdaie, B.R.; Cooperberg, M.R.; Morgan, S.C.; Tyldesley, S.; Haluschak, J.J.; Tan, W.; et al. Active Surveillance for the Management of Localized Prostate Cancer (Cancer Care Ontario Guideline): American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline Endorsement. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 2182–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corcoran, N.M.; Hong, M.K.; Casey, R.G.; Hurtado-Coll, A.; Peters, J.; Harewood, L.; Goldenberg, S.L.; Hovens, C.M.; Costello, A.J.; Gleave, M.E. Upgrade in Gleason score between prostate biopsies and pathology following radical prostatectomy significantly impacts upon the risk of biochemical recurrence. BJU Int. 2011, 108, E202–E210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, M.S.; Hanley, R.S.; Kurteva, T.; Ruthazer, R.; Silverman, M.L.; Sorcini, A.; Hamawy, K.; Roth, R.A.; Tuerk, I.; Libertino, J.A. Comparing the Gleason prostate biopsy and Gleason prostatectomy grading system: The Lahey Clinic Medical Center experience and an international meta-analysis. Eur. Urol. 2008, 54, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghesi, M.; Ahmed, H.; Nam, R.; Schaeffer, E.; Schiavina, R.; Taneja, S.; Weidner, W.; Loeb, S. Complications after systematic, random, and image-guided prostate biopsy. Eur. Urol. 2017, 71, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkadi, R.; Taher, F.; El-Baz, A.; Werghi, N. A deep learning-based approach for the detection and localization of prostate cancer in T2 magnetic resonance images. J. Digit. Imaging 2019, 32, 793–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schelb, P.; Kohl, S.; Radtke, J.P.; Wiesenfarth, M.; Kickingereder, P.; Bickelhaupt, S.; Kuder, T.A.; Stenzinger, A.; Hohenfellner, M.; Schlemmer, H.-P.; et al. Classification of cancer at prostate MRI: Deep learning versus clinical PI-RADS assessment. Radiology 2019, 293, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, Y.D.; Yan, X.; Liu, H.; Zhou, M.; Hu, B.; Yang, G. Computer-aided diagnosis of prostate cancer using a deep convolutional neural network from multiparametric MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2018, 48, 1570–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampun, A.; Zheng, L.; Malcolm, P.; Tiddeman, B.; Zwiggelaar, R. Computer-aided detection of prostate cancer in T2-weighted MRI within the peripheral zone. Phys. Med. Biol. 2016, 61, 4796–4825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishioka, J.; Matsuoka, Y.; Uehara, S.; Yasuda, Y.; Kijima, T.; Yoshida, S.; Yokoyama, M.; Saito, K.; Kihara, K.; Numao, N.; et al. Computer-aided diagnosis of prostate cancer on magnetic resonance imaging using a convolutional neural network algorithm. BJU Int. 2018, 122, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkel, D.J.; Tong, A.; Lou, B.; Kamen, A.; Comaniciu, D.; Disselhorst, J.A.; Rodríguez-Ruiz, A.; Huisman, H.; Szolar, D.; Shabunin, I. A novel deep learning based computer-aided diagnosis system improves the accuracy and efficiency of radiologists in reading biparametric magnetic resonance images of the prostate: Results of a multireader, multicase study. Investig. Radiol. 2021, 56, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niaf, E.; Lartizien, C.; Bratan, F.; Roche, L.; Rabilloud, M.; Mège-Lechevallier, F.; Rouvière, O. Prostate focal peripheral zone lesions: Characterization at multiparametric MR imaging-influence of a computer-aided diagnosis system. Radiology 2014, 271, 761–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhayana, R.; O’Shea, A.; Anderson, M.A.; Bradley, W.R.; Gottumukkala, R.V.; Mojtahed, A.; Pierce, T.T.; Harisinghani, M. PI-RADS versions 2 and 2.1: Interobserver agreement and diagnostic performance in peripheral and transition zone lesions among six radiologists. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2021, 217, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenkrantz, A.B.; Hindman, N.; Lim, R.P.; Das, K.; Babb, J.S.; Mussi, T.C.; Taneja, S.S. Diffusion-weighted imaging of the prostate: Comparison of b1000 and b2000 image sets for index lesion detection. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2013, 38, 694–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamada, T.; Kanomata, N.; Sone, T.; Jo, Y.; Miyaji, Y.; Higashi, H.; Yamamoto, A.; Ito, K. High b value (2000 s/mm2) diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in prostate cancer at 3 Tesla: Comparison with 1000 s/mm2 for tumor conspicuity and discrimination of aggressiveness. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Siddiquee, M.U. A Nested U-Net Architecture for medical Image Segmentation. In Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis and Multimodal Learning for Clinical Decision Support, Proceedings of the 4th International Workshop, DLMIA 2018, and 8th International Workshop, ML-CDS 2018, Held in Conjunction with Miccai 2018, Granada, Spain, 20 September 2018; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Vanhoucke, V.; Ioffe, S.; Shlens, J.; Wojna, Z. Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 2818–2826. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Van Der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K. Densely connected convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Epstein, J.I.; Egevad, L.; Amin, M.B.; Delahunt, B.; Srigley, J.R.; Humphrey, P.A. The 2014 International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) consensus conference on Gleason grading of prostatic carcinoma. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2016, 40, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ploussard, G.; Epstein, J.I.; Montironi, R.; Carroll, P.R.; Wirth, M.; Grimm, M.-O.; Bjartell, A.S.; Montorsi, F.; Freedland, S.J.; Erbersdobler, A. The contemporary concept of significant versus insignificant prostate cancer. Eur. Urol. 2011, 60, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dice, L.R. Measures of the Amount of Ecologic Association Between Species. Ecology 1945, 26, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vural, M.; Ertaş, G.; Onay, A.; Acar, Ö.; Esen, T.; Sağlıcan, Y.; Zengingönül, H.P.; Akpek, S. Conspicuity of peripheral zone prostate cancer on computed diffusion-weighted imaging: Comparison of cDWI1500, cDWI2000, and cDWI3000. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 768291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha, S.Y.; Kim, E.; Park, S.Y. Why Is a b-value Range of 1500–2000 s/mm2 Optimal for Evaluating Prostatic Index Lesions on Synthetic Diffusion-Weighted Imaging? Korean J. Radiol. 2021, 22, 922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


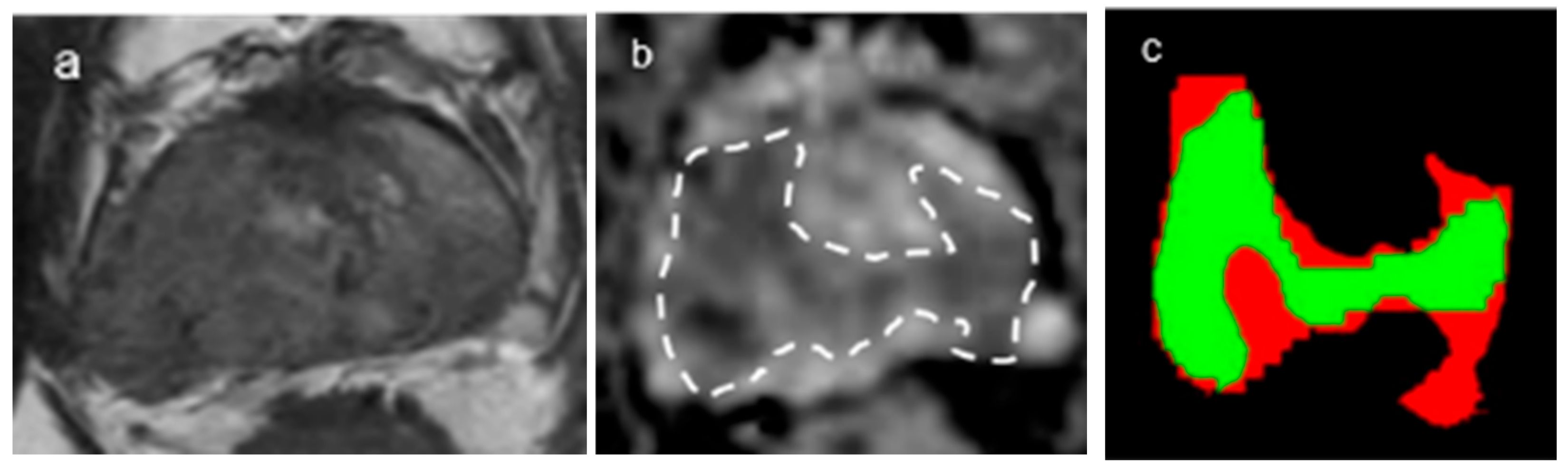

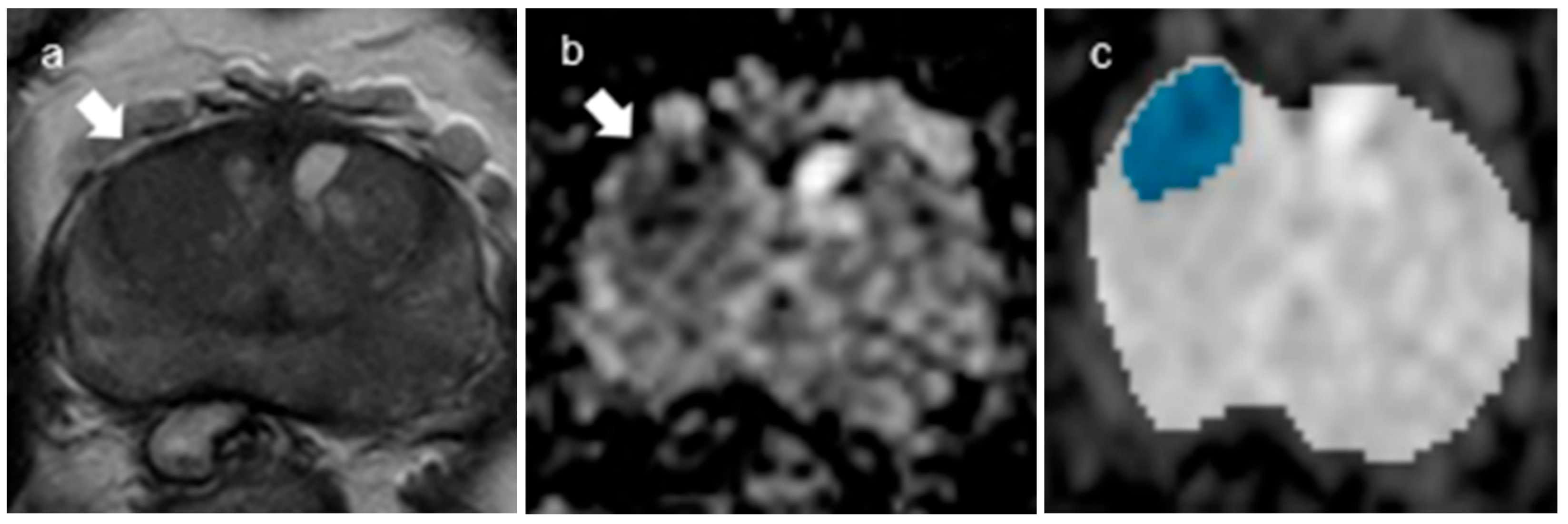
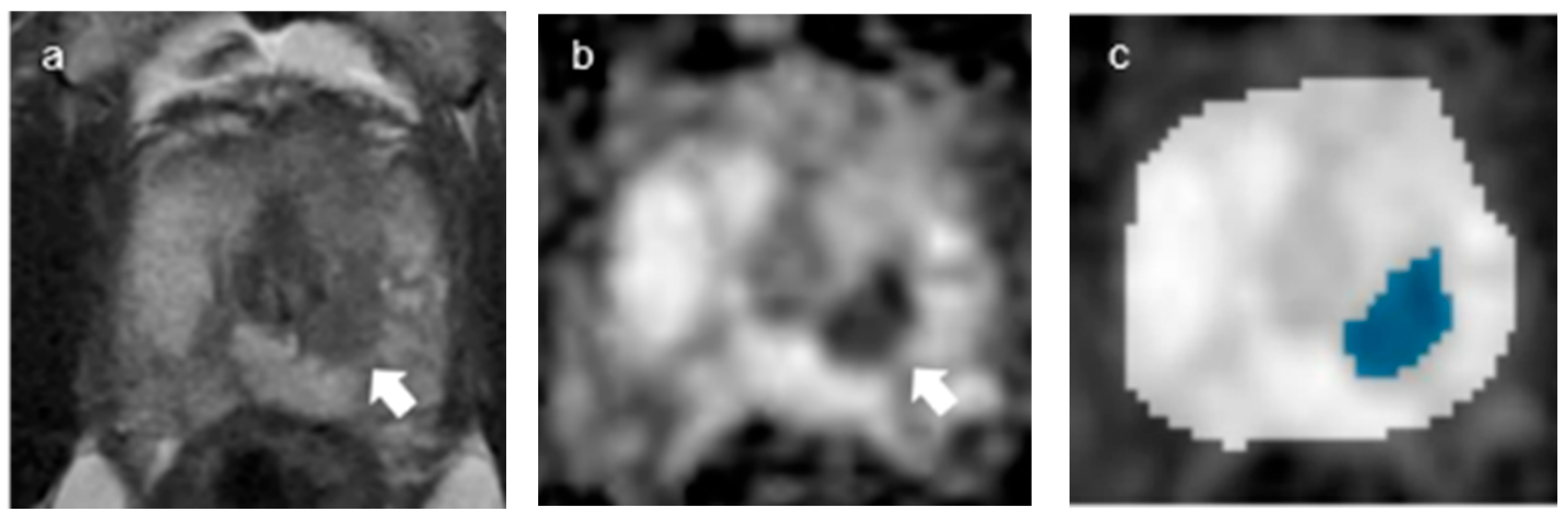
| Parameters | T2-Weighted Axial, Sagittal, and Coronal TSE | DWI (b = 0, 100, 1000 and 2000 s/mm2) |
|---|---|---|
| TR (msec) | 3370.7 | 5725 |
| TE (msec) | 100 | 77.8 |
| Slice thickness (mm) | 3 | 3 |
| Slice gap (mm) | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| Matrix size | 316 × 272 | 120 × 118 |
| NEX | 1 | 1 |
| FOV (mm × mm) | 220 × 220 | 240 × 240 |
| Number of slices | 30 | 30 |
| Parameter | All | Training and Internal Validation Sets (n = 149) | External Validation Set (n = 22) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Age, years [range] | 69.2982 [47–84] | 69.2483 [47–84] | 69.6364 [56–80] | 0.8049 |
| Mean PSA, ng/mL [range] | 14.6315 [0.85–149] | 14.4478 [0.85–149] | 21.1709 [3.0–131] | 0.3597 |
| GS, n (%) | ||||
| 6 | 46 (27) | 40 (27) | 6 (27) | 0.9307 |
| 7 | 125 (73) | 109 (73) | 16 (73) | 0.9912 |
| 3 + 4 | 89 | 76 | 13 | |
| 4 + 3 | 36 | 33 | 3 | |
| PIRADS v2.1, n (%) | ||||
| 3 | 17 (10) | 17 (11) | 0 (0) | 0.1131 |
| 4 | 55 (32) | 49 (33) | 6 (27) | 0.7006 |
| 5 | 99 (58) | 83 (56) | 16 (73) | 0.3307 |
| Tumor location, n (%) | ||||
| Peripheral zone | 92 (54) | 81 (54) | 11 (50) | 0.8245 |
| Transitional zone | 48 (28) | 38 (26) | 10 (45) | 0.1204 |
| Fibromuscular zone | 4 (2) | 4 (3) | 0 (0) | 0.4422 |
| Diffuse | 27 (16) | 26 (17) | 1 (5) | 0.1453 |
| Accuracy (%) | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | PPV (%) | NPV (%) | Dice Score | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gland | ||||||
| Internal validation | 96 | 95 | 96 | 95 | 96 | 0.951 |
| External validation | 95 | 92 | 97 | 96 | 93 | 0.9413 |
| Tumor | ||||||
| Internal validation | 93 | 82 | 96 | 83 | 96 | 0.822 |
| External validation | 92 | 77 | 95 | 79 | 95 | 0.7776 |
| Accuracy (%) | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | PPV (%) | NPV (%) | AUC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Internal validation set | ||||||
| CSC | 73 | 72 | 74 | 74 | 72 | |
| External validation set | ||||||
| CSC | 75 | 84 | 48 | 82 | 52 | 0.6269 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hong, S.; Kim, S.H.; Yoo, B.; Kim, J.Y. Deep Learning Algorithm for Tumor Segmentation and Discrimination of Clinically Significant Cancer in Patients with Prostate Cancer. Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 7275-7285. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30080528
Hong S, Kim SH, Yoo B, Kim JY. Deep Learning Algorithm for Tumor Segmentation and Discrimination of Clinically Significant Cancer in Patients with Prostate Cancer. Current Oncology. 2023; 30(8):7275-7285. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30080528
Chicago/Turabian StyleHong, Sujin, Seung Ho Kim, Byeongcheol Yoo, and Joo Yeon Kim. 2023. "Deep Learning Algorithm for Tumor Segmentation and Discrimination of Clinically Significant Cancer in Patients with Prostate Cancer" Current Oncology 30, no. 8: 7275-7285. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30080528
APA StyleHong, S., Kim, S. H., Yoo, B., & Kim, J. Y. (2023). Deep Learning Algorithm for Tumor Segmentation and Discrimination of Clinically Significant Cancer in Patients with Prostate Cancer. Current Oncology, 30(8), 7275-7285. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30080528





