Can STEreotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT) Improve the Prognosis of Unresectable Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer? Long-Term Clinical Outcomes, Toxicity and Prognostic Factors on 142 Patients (STEP Study)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
- Age ≥ 18 years old
- Minimum Karnofsky Performance Status of 70%
- Histologically and/or radiologically proven locally advanced unresectable PC
- Tumor diameter < 5 cm
- Absence of nodal and metastatic disease
- Other malignancies diagnosed within 5 years
- Previous abdominal SBRT
- Gastric or duodenal obstruction
- Nodal metastases
- Metastatic disease
- Concomitant ChT
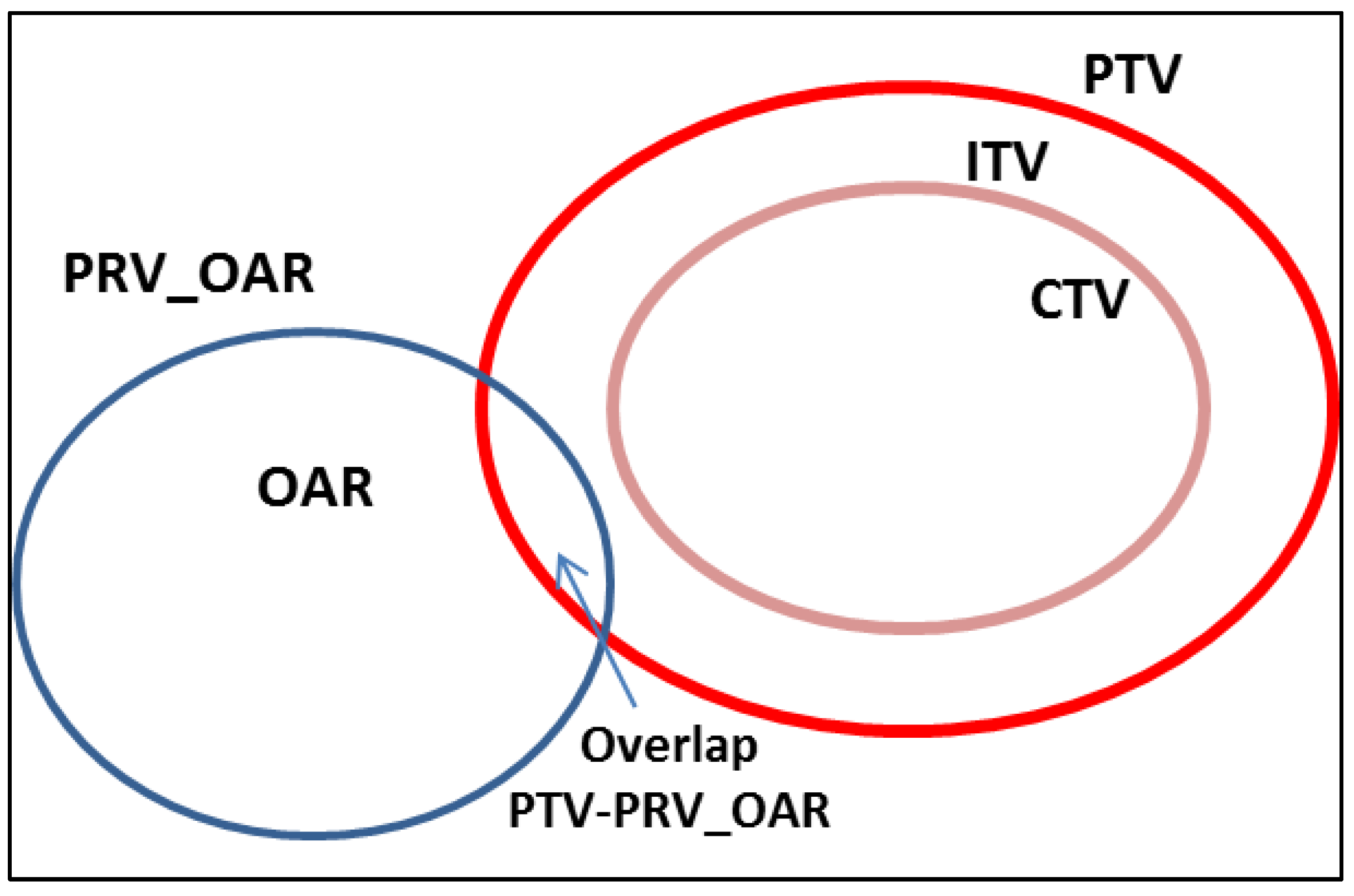
2.2. Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy
2.3. Response Evaluation
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
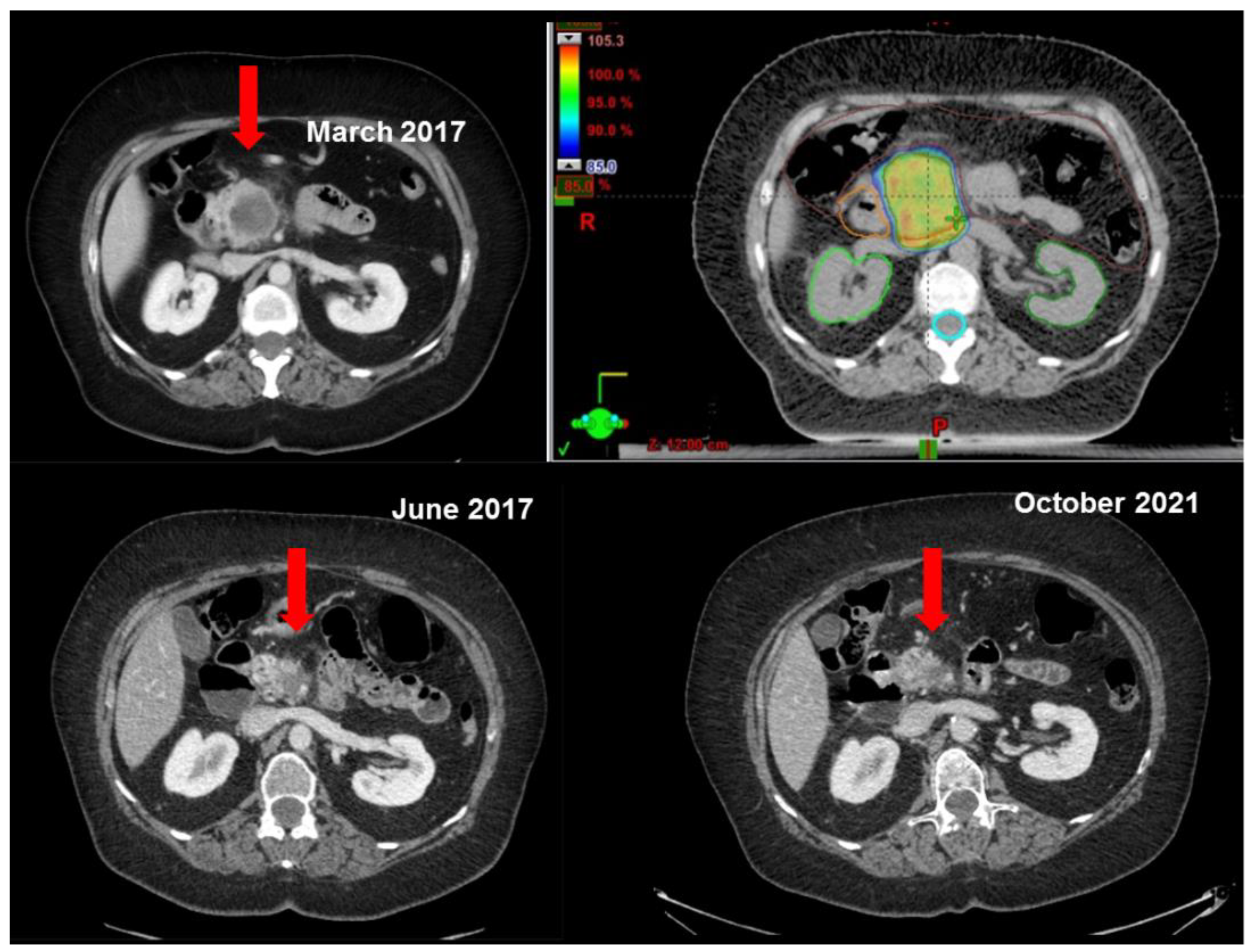
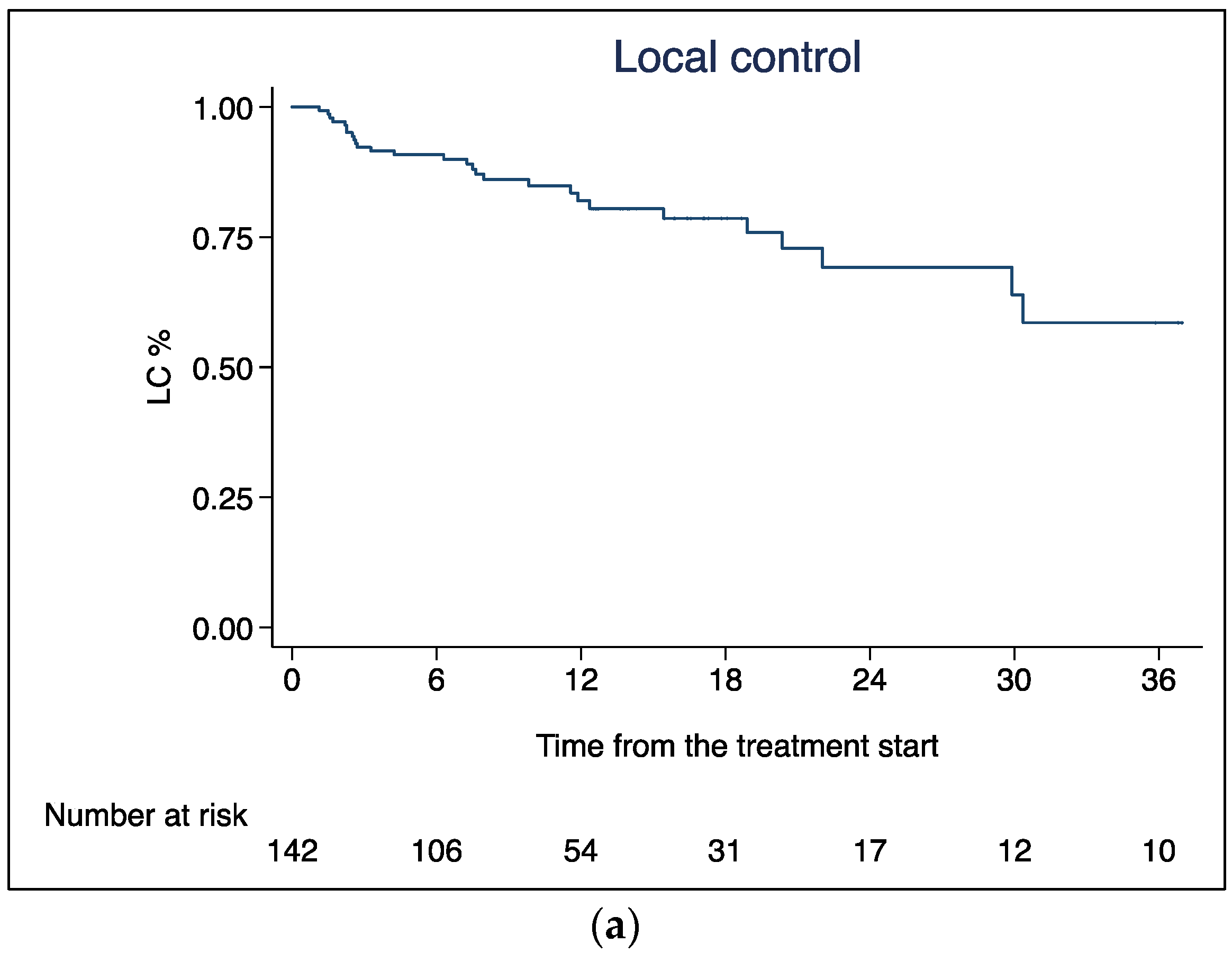
3.1. Local Control
3.2. Distant Progression Free Survival
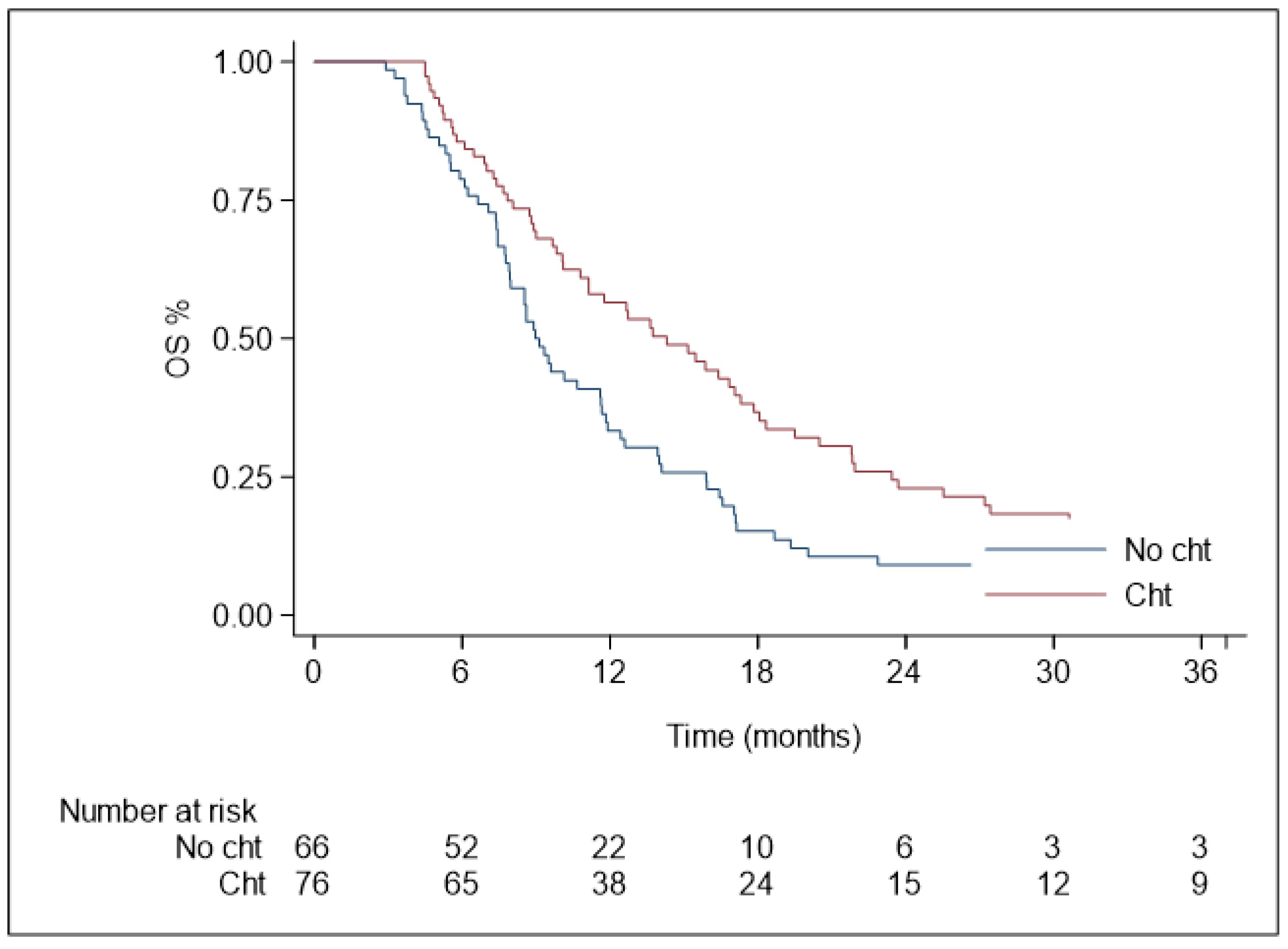
3.3. Overall Survival
3.4. Toxicity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carioli, G.; Bertuccio, P.; Boffetta, P.; Levi, F.; La Vecchia, C.; Negri, E.; Malvezzi, M. European cancer mortality predictions for the year 2020 with a focus on prostate cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 650–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahib, L.; Smith, B.D.; Aizenberg, R.; Rosenzweig, A.B.; Fleshman, J.M.; Matrisian, L.M. Projecting cancer incidence and deaths to 2030: The unexpected burden of thyroid, liver, and pancreas cancers in the United States. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 2913–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizrahi, J.D.; Surana, R.; Valle, J.W.; Shroff, R.T. Pancreatic cancer. Lancet 2020, 395, 2008–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balaban, E.P.; Mangu, P.B.; Khorana, A.A.; Shah, M.A.; Mukherjee, S.; Crane, C.H.; Javle, M.M.; Eads, J.R.; Allen, P.; Ko, A.H.; et al. Locally Advanced, Unresectable Pancreatic Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 2654–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacobuzio-Donahue, C.A.; Fu, B.; Yachida, S.; Luo, M.; Abe, H.; Henderson, C.M.; Vilardell, F.; Wang, Z.; Keller, J.W.; Banerjee, P.; et al. DPC4 Gene Status of the Primary Carcinoma Correlates with Patterns of Failure in Patients with Pancreatic Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 1806–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crane, C.H.; Varadhachary, G.R.; Yordy, J.S.; Staerkel, G.A.; Javle, M.M.; Safran, H.; Haque, W.; Hobbs, B.D.; Krishnan, S.; Fleming, J.B.; et al. Phase II Trial of Cetuximab, Gemcitabine, and Oxaliplatin Followed by Chemoradiation with Cetuximab for Locally Advanced (T4) Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma: Correlation of Smad4(Dpc4) Immunostaining with Pattern of Disease Progression. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 3037–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huguet, F.; André, T.; Hammel, P.; Artru, P.; Balosso, J.; Selle, F.; Deniaud-Alexandre, E.; Ruszniewski, P.; Touboul, E.; Labianca, R.; et al. Impact of chemotherapy in locally advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma in GERCOR phase II and III studies. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, S.; Rana, V.; Janjan, N.A.; Varadhachary, G.R.; Abbruzzese, J.L.; Das, P.; Delclos, M.E.; Gould, M.S.; Evans, D.B.; Wolff, R.A.; et al. Induction chemotherapy selects patients with locally advanced, unresectable pancreatic cancer for optimal benefit from consolidative chemoradiation therapy. Cancer 2007, 110, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, J.M.; Koong, A. Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy: A New Standard Option for Pancreatic Cancer? J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2014, 12, 1489–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurka, M.K.; Collins, S.P.; Slack, R.; Tse, G.; Charabaty, A.; Ley, L.; Berzcel, L.; Lei, S.; Suy, S.; Haddad, N.; et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy with concurrent full-dose gemcitabine for locally advanced pancreatic cancer: A pilot trial demonstrating safety. Radiat. Oncol. 2013, 8, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tozzi, A.; Comito, T.; Alongi, F.; Navarria, P.; Iftode, C.; Mancosu, P.; Reggiori, G.; Clerici, E.; Rimassa, L.; Zerbi, A.; et al. SBRT in unresectable advanced pancreatic cancer: Preliminary results of a mono-institutional experience. Radiat. Oncol. 2013, 8, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herman, J.M.; Chang, D.T.; Goodman, K.A.; Dholakia, A.S.; Raman, S.P.; Hacker-Prietz, A.; Iacobuzio-Donahue, C.A.; Griffith, M.E.; Pawlik, T.M.; Ba, J.S.P.; et al. Phase 2 multi-institutional trial evaluating gemcitabine and stereotactic body radiotherapy for patients with locally advanced unresectable pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Cancer 2014, 121, 1128–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comito, T.; Cozzi, L.; Clerici, E.; Franzese, C.; Tozzi, A.; Iftode, C.; Navarria, P.; D’agostino, G.; Rimassa, L.; Carnaghi, C.; et al. Can Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy Be a Viable and Efficient Therapeutic Option for Unresectable Locally Advanced Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma? Results of a Phase 2 Study. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2017, 16, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teriaca, M.; Loi, M.; Suker, M.; Eskens, F.; van Eijck, C.; Nuyttens, J. A phase II study of stereotactic radiotherapy after FOLFIRINOX for locally advanced pancreatic cancer (LAPC-1 trial): Long-term outcome. Radiother. Oncol. 2020, 155, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen-Zhao, X.; Hernando, O.; López, M.; Sánchez, E.; Montero, A.; García-Aranda, M.; Ciérvide, R.; Valero, J.; Alonso, R.; Cárdenas-Rebollo, J.M.; et al. A prospective observational study of the clinical and pathological impact of stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) as a neoadjuvant strategy of chemoradiation in pancreatic cancer. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2020, 22, 1499–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Cao, Y.; Lu, M.; Zhao, X.; Jiang, L.; Ye, Y.; Ju, X.; Zhang, H. Stereotactic body radiation therapy with sequential S-1 for patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer and poor performance status: An open-label, single-arm, phase 2 trial. Radiother. Oncol. 2021, 162, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moningi, S.; Dholakia, A.S.; Raman, S.P.; Blackford, A.; Cameron, J.L.; Le, D.T.; De Jesus-Acosta, A.M.C.; Hacker-Prietz, A.; Rosati, L.M.; Assadi, R.K.; et al. The Role of Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Pancreatic Cancer: A Single-Institution Experience. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 22, 2352–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellon, E.A.; Hoffe, S.E.; Springett, G.M.; Frakes, J.M.; Strom, T.J.; Hodul, P.J.; Malafa, M.P.; Chuong, M.D.; Shridhar, R. Long-term outcomes of induction chemotherapy and neoadjuvant stereotactic body radiotherapy for borderline resectable and locally advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Acta Oncol. 2015, 54, 979–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurka, M.K.; Kim, C.B.; He, A.R.; Charabaty, A.; Haddad, N.; Turocy, J.B.; Johnson, L.; Jackson, P.; Weiner, L.M.; Marshall, J.L.; et al. Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT) Combined with Chemotherapy for Unresected Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 40, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Li, F.; Ju, X.; Cao, F.; Cao, Y.; Fang, F.; Qing, S.; Shen, Y.; Jia, Z.; Zhang, H. Prognostic role of stereotactic body radiation therapy for elderly patients with advanced and medically inoperable pancreatic cancer. Cancer Med. 2017, 6, 2263–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzola, R.; Fersino, S.; Aiello, D.; Gregucci, F.; Tebano, U.; Corradini, S.; Di Paola, G.; Cirillo, M.; Tondulli, L.; Ruffo, G.; et al. Linac-based stereotactic body radiation therapy for unresectable locally advanced pancreatic cancer: Risk-adapted dose prescription and image-guided delivery. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2018, 194, 835–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toesca, D.A.; Ahmed, F.; Kashyap, M.; Baclay, J.R.M.; von Eyben, R.; Pollom, E.L.; Koong, A.C.; Chang, D.T. Intensified systemic therapy and stereotactic ablative radiotherapy dose for patients with unresectable pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Radiother. Oncol. 2020, 152, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Z.-T.; Zhou, H.; Li, A.-M.; Ji, X.-Q.; Jiang, C.-C.; Yuan, X.; Li, B.; Zhu, X.-X.; Huang, G.-C. Clinical outcomes and prognostic factors of stereotactic body radiation therapy combined with gemcitabine plus capecitabine for locally advanced unresectable pancreatic cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 146, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koong, A.C.; Le, Q.T.; Ho, A.; Fong, B.; Fisher, G.; Cho, C.; Ford, J.; Poen, J.; Gibbs, I.C.; Mehta, V.K.; et al. Phase I study of stereotactic radiosurgery in patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2004, 58, 1017–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schellenberg, D.; Goodman, K.A.; Lee, F.; Chang, S.; Kuo, T.; Ford, J.M.; Fisher, G.A.; Quon, A.; Desser, T.S.; Norton, J.; et al. Gemcitabine Chemotherapy and Single-Fraction Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy for Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2008, 72, 678–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schellenberg, D.; Kim, J.; Christman-Skieller, C.; Chun, C.L.; Columbo, L.A.; Ford, J.M.; Fisher, G.A.; Kunz, P.L.; Van Dam, J.; Quon, A.; et al. Single-Fraction Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy and Sequential Gemcitabine for the Treatment of Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2011, 81, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callery, M.P.; Chang, K.J.; Fishman, E.K.; Talamonti, M.S.; Traverso, L.W.; Linehan, D.C. Pretreatment Assessment of Resectable and Borderline Resectable Pancreatic Cancer: Expert Consensus Statement. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2009, 16, 1727–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenhauer, E.A.; Therasse, P.; Bogaerts, J.; Schwartz, L.H.; Sargent, D.; Ford, R.; Dancey, J.; Arbuck, S.; Gwyther, S.; Mooney, M.; et al. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: Revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur. J. Cancer 2009, 45, 228–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahl, R.L.; Jacene, H.; Kasamon, Y.; Lodge, M.A. From RECIST to PERCIST: Evolving Considerations for PET Response Criteria in Solid Tumors. J. Nucl. Med. 2009, 50 (Suppl. 1), 122S–150S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) Version 5; US Department of Health and Human Services, National Institutes of Health, National Cancer Institute: Frederick, MD, USA, 2017.
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network, NCCN Guidelines, Version 2.2021, Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Available online: www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/pancreatic.pdf (accessed on 30 May 2023).
- Palta, M.; Godfrey, D.; Goodman, K.A.; Hoffe, S.; Dawson, L.A.; Dessert, D.; Hall, W.A.; Herman, J.M.; Khorana, A.A.; Merchant, N.; et al. Radiation Therapy for Pancreatic Cancer: Executive Summary of an ASTRO Clinical Practice Guideline. Pract. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 9, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollom, E.L.; Alagappan, M.; von Eyben, R.; Kunz, P.L.; Fisher, G.A.; Ford, J.A.; Poultsides, G.A.; Visser, B.C.; Norton, J.A.; Kamaya, A.; et al. Single- versus Multifraction Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma: Outcomes and Toxicity. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2014, 90, 918–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Ju, X.; Cao, Y.; Shen, Y.; Cao, F.; Qing, S.; Fang, F.; Jia, Z.; Zhang, H. Patterns of Local Failure after Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy and Sequential Chemotherapy as Initial Treatment for Pancreatic Cancer: Implications of Target Volume Design. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2019, 104, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oar, A.; Lee, M.; Le, H.; Hruby, G.; Dalfsen, R.; Pryor, D.; Lee, D.; Chu, J.; Holloway, L.; Briggs, A.; et al. Australasian Gastrointestinal Trials Group (AGITG) and Trans-Tasman Radiation Oncology Group (TROG) Guidelines for Pancreatic Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT). Pract. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 10, e136–e146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernard, V.; Herman, J.M. Pancreas SBRT: Who, What, When, Where, and How. Pract. Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 10, 183–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colbert, L.; Rebueno, N.; Moningi, S.; Beddar, S.; Sawakuchi, G.O.; Herman, J.M.; Koong, A.C.; Das, P.; Holliday, E.B.; Koay, E.J.; et al. Dose escalation for locally advanced pancreatic cancer: How high can we go? Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 3, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzarotto, R.; Simoni, N.; Guariglia, S.; Rossi, G.; Micera, R.; De Robertis, R.; Pierelli, A.; Zivelonghi, E.; Malleo, G.; Paiella, S.; et al. Dosimetric Feasibility Study of Dose Escalated Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT) in Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer (LAPC) Patients: It Is Time to Raise the Bar. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, T.B.; Nestle, U.; Grosu, A.-L.; Partridge, M. SBRT in pancreatic cancer: What is the therapeutic window? Radiother. Oncol. 2015, 114, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrelli, F.; Comito, T.; Ghidini, A.; Torri, V.; Scorsetti, M.; Barni, S. Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer: A Systematic Review and Pooled Analysis of 19 Trials. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2017, 97, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dholakia, A.S.; Chaudhry, M.; Leal, J.P.; Chang, D.T.; Raman, S.P.; Hacker-Prietz, A.; Su, Z.; Pai, J.; Oteiza, K.E.; Griffith, M.E.; et al. Baseline Metabolic Tumor Volume and Total Lesion Glycolysis Are Associated with Survival Outcomes in Patients with Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer Receiving Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2014, 89, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Author | Patients | Clinical Stage | SBRT (Dose/Fraction) | Pre-, Post-SBRT Therapy | mFU (Months) | LC | PFS | OS | Gastrointestinal Toxicity ≥ G3 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gurka et al., 2013 [11] | 11 | LAPC | 25 Gy/5 fr | Gemcitabine pre + post-SBRT | Na | Na | mPFS: 6.8 months | mOS: 12.2 months | Acute ≥ G3: 0% Late ≥ G3: 0% |
| Tozzi et al., 2013 [12] | 30 | LAPC Local Relapse | 45 Gy/6 fr | Multiple ChT schemes pre + post-SBRT | 11 | 1y: 77% 2y: 75% | mPFS: 8 months | mOS: 11 months 1y: 47% | Acute ≥ G3: 0% Late ≥ G3: 0% |
| Herman et al., 2015 [13] | 49 | LAPC | 33 Gy/5 fr | Gemcitabine pre + post-SBRT | 13.9 | 1y: 78% | mPFS: 7.8 months 1y: 32% 2y: 10% | mOS: 13.9 months 1y: 59% 2y: 18% | Acute G3: 10.2%; G4: 2% Late G3: 6.4%; G4: 2% |
| Comito et al., 2017 [14] | 45 | LAPC | 45 Gy/6 fr | Multiple ChT schemes (71% pre-SBRT and 41% post-SBRT) | 13.5 | mLC: 26 months 1y: 87% 2y: 87% | mPFS: 8 months 1y: 39% 2y: 15% | mOS: 13 months 1y: 59% 2y: 18% | Acute ≥ G3: 0% Late ≥ G3: 0% |
| Teriaca et al., 2021 [15] | 39 | LAPC | 40 Gy/5 fr | FOLFIRINOX pre-SBRT (8 cycles) + surgery post-SBRT (14%) | 13 | mLC: 36.3 months 1y: 81% 3y: 53% | mPFS: 10.7 months 1y: 43% 3y: 15% | mOS: 18 months 1y: 77% 3y: 13% | Acute G3: 10.2% |
| Chen Zhao et al., 2020 [16] | 45 | LAPC (20) BRPC (25) | 40–62 Gy/5–10 fr | Multiple ChT schemes pre-SBRT + surgery post-SBRT (71.1%) | 14.7 | 1y: 95% | 1y: 72% 2y: 58% | mOS: 13.8 months 1y: 67% 2y: 36% | Acute ≥ G3: 0% Late ≥ G3: 0% |
| Zhu et al., 2021 [17] | 63 | LAPC | 35-40Gy/5 fr | S-1 (6 cycles) post-SBRT | 15.8 | Na | mPFS: 10.1 months | 14.4 months | Acute G3: 14.3% Late G3: 4.8% |
| Author | Patients | Clinical Stage | SBRT (Dose/Fraction) | Pre-, Post-SBRT Therapy | mFU (Months) | LC | PFS | OS | Gastrointestinal Toxicity ≥ G3 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moningi et al., 2015 [18] | 88 | LAPC (74) BRPC (14) | 25–33 Gy/5 fr | Multiple ChT schemes pre-SBRT (87.5%) | 13.1 | mLC: 13.9 months 1y: 61% 2y: 14% | mPFS: 9.9 months 1y: 41% 2y: 11% | mOS: 18.4 months 1y: 73% 2y: 24% | Acute G3: 3.4% Late G3: 5.7% |
| Mellon et al., 2015 [19] | 159 | LAPC (49) BRPC (110) | 20–50 Gy/5 fr | Multiple ChT schemes pre-SBRT + surgery post-SBRT (38%) | 14 | mLC: 12.7 months 1y: 78% | Na | mOS: 18.1 months | Acute ≥ G3: 7% Late ≥ G3: 7% |
| Gurka et al., 2017 [20] | 38 | LAPC (28) BRPC (6) Unresectable for clinical comorbidities (4) | 25–30 Gy/5 fr | Multiple ChT schemes pre-SBRT | Na | Na | mPFS: 9.2 months | mOS: 14.3 months | Acute G3: 5.2% Late G3: 5.2%; G4: 2.6%; G5: 2.6% |
| Zhu et al., 2017 [21] | 417 | LAPC (218) BRPC (105) Metastatic (94) | 30–46.8 Gy/5–8 fr | Multiple ChT schemes pre-SBRT + post-SBRT (11.2%) | 11 | mLC: 10 months 1y: 26.6% | mPFS: 8 months 1y: 18.2% | mOS: 10 months 1y: 35.5% | Acute G4: 0.5% Late G3: 0% |
| Mazzola et al., 2018 [22] | 33 | LAPC | 42-45 Gy/6 fr | Multiple ChT schemes pre-SBRT (72%) + post-SBRT (60%) and surgery post-SBRT (18%) | 18 | 1y: 81% | Na | 1y: 75% | Acute ≥ G3: 0% Late ≥ G3: 0% |
| Toesca et al., 2020 [23] | 149 | LAPC | 20–45Gy/3-6 fr | Multiple ChT schemes pre-SBRT | 15 | 1y: 86% | Na | 16 months | Acute ≥ G3: 13% Late ≥ G3: 0% |
| Shen et al., 2020 [24] | 56 | LAPC | 40 Gy (30–50 Gy)/5 fr | GEM-CAP (2 cycles) and concurrent to RT (4 cycles) | 17 | 1y: 85% | mPFS: 12 months 1y: 48.2% 2y: 14.3% | mOS: 19 months 1y: 82.1% 2y: 35.7% | Acute G3: 10.8% Late G3: 5.4% |
| Median age (range) | 71 years (41–91) |
| <70 years | 63 patients |
| ≥70 years | 79 patients |
| Tumor location (number of patients, %) | |
| Head | 91 (64.1%) |
| Uncinate process | 23 (16.2%) |
| Body | 20 (14.1%) |
| Tail | 3 (2.1%) |
| Isthmus | 5 (3.5%) |
| CA19.9 before SBRT | 124 (87.3%) |
| <300 U/mL | 79 (63.7%) |
| ≥300 U/mL | 45 (36.3%) |
| Not available | 18 (12.7%) |
| Median (range) [U/mL] | 102.75 (0.8–12.000) |
| CA19.9 after SBRT | |
| Median value (range) [U/mL] | 35 (0.4–8594) |
| Median diameter (cm, range) | 3.7 (1.4–9.3) |
| Median volume (cc, range) | |
| CTV | 31.6 (2.75–187) |
| PTV | 71.3 (17.6–321) |
| Chemotherapy before SBRT | |
| Yes | 76 (53.5%) |
| No | 66 (46.5%) |
| Chemotherapy scheme before SBRT | |
| Gemcitabine | 7 (9.2%) |
| FOLFIRINOX | 18 (23.7%) |
| Gemcitabine + nab-paclitaxel | 17 (22.3%) |
| GEMOX | 21 (27.6%) |
| PEX-G | 10 (13.2%) |
| Others | 3 (4%) |
| Chemotherapy after SBRT | |
| Yes | 42 (29.6%) |
| No | 100 (70.4%) |
| Chemotherapy scheme after SBRT | |
| Capecitabine-based | 5 (12%) |
| FOLFIRINOX | 6 (14.3%) |
| Gemcitabine-based | 22 (52.4%) |
| Irinotecan | 2 (4.7%) |
| Others | 7 (16.6%) |
| Tumor Response | Number of Patients (%) |
|---|---|
| Complete Response | 1 (0.7%) |
| Partial Response | 31 (22%) |
| Stable Disease | 81 (57%) |
| Progression Disease | 29 (20.3%) |
| Local Control | Overall Survival | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR | 95%CI | p Value | HR | 95%CI | p Value | |
| Age > 70 years | 1.11 | 0.53–2.32 | 0.776 | 1.46 | 1.02–2.08 | 0.037 |
| Tumor Diameter | 0.98 | 0.95–1.01 | 0.346 | 1.00 | 0.99–1.02 | 0.400 |
| CTV Volume | 0.99 | 0.98–1.01 | 0.881 | 1.00 | 0.99–1.01 | 0.163 |
| PTV Volume | 0.99 | 0.99–1.00 | 0.865 | 1.00 | 0.99–1.00 | 0.075 |
| Time from diagnosis to SBRT | 0.97 | 0.91–1.04 | 0.487 | 0.98 | 0.96–1.01 | 0.460 |
| CA19-9 before SBRT | 1.00 | 0.99–1.00 | 0.740 | 1.00 | 0.99–1.00 | 0.417 |
| CA19-9 after SBRT | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| ChT before SBRT | 0.85 | 0.40–1.79 | 0.675 | 0.59 | 0.41–0.84 | 0.004 |
| ChT after SBRT | 1.71 | 0.81–3.57 | 0.155 | 0.63 | 0.43–0.92 | 0.019 |
| Local progression | - | - | - | 0.90 | 0.60–1.37 | 0.655 |
| Distant progression | 1.10 | 0.26–4.70 | 0.890 | 0.89 | 0.45–1.77 | 0.758 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Comito, T.; Massaro, M.; Teriaca, M.A.; Franzese, C.; Franceschini, D.; Navarria, P.; Clerici, E.; Di Cristina, L.; Bertolini, A.; Tomatis, S.; et al. Can STEreotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT) Improve the Prognosis of Unresectable Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer? Long-Term Clinical Outcomes, Toxicity and Prognostic Factors on 142 Patients (STEP Study). Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 7073-7088. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30070513
Comito T, Massaro M, Teriaca MA, Franzese C, Franceschini D, Navarria P, Clerici E, Di Cristina L, Bertolini A, Tomatis S, et al. Can STEreotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT) Improve the Prognosis of Unresectable Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer? Long-Term Clinical Outcomes, Toxicity and Prognostic Factors on 142 Patients (STEP Study). Current Oncology. 2023; 30(7):7073-7088. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30070513
Chicago/Turabian StyleComito, Tiziana, Maria Massaro, Maria Ausilia Teriaca, Ciro Franzese, Davide Franceschini, Pierina Navarria, Elena Clerici, Luciana Di Cristina, Anna Bertolini, Stefano Tomatis, and et al. 2023. "Can STEreotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT) Improve the Prognosis of Unresectable Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer? Long-Term Clinical Outcomes, Toxicity and Prognostic Factors on 142 Patients (STEP Study)" Current Oncology 30, no. 7: 7073-7088. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30070513
APA StyleComito, T., Massaro, M., Teriaca, M. A., Franzese, C., Franceschini, D., Navarria, P., Clerici, E., Di Cristina, L., Bertolini, A., Tomatis, S., Reggiori, G., Bresolin, A., Bozzarelli, S., Rimassa, L., Bonifacio, C., Carrara, S., Santoro, A., Zerbi, A., & Scorsetti, M. (2023). Can STEreotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT) Improve the Prognosis of Unresectable Locally Advanced Pancreatic Cancer? Long-Term Clinical Outcomes, Toxicity and Prognostic Factors on 142 Patients (STEP Study). Current Oncology, 30(7), 7073-7088. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30070513







