Associations of Clinical and Dosimetric Parameters with Urinary Toxicities after Prostate Brachytherapy: A Long-Term Single-Institution Experience
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Population
2.2. LDR-BT
2.3. Follow-Up
2.4. Outcome Measures
2.5. Statistical Analyses
2.6. Ethical Considerations
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganjoho. Projected Cancer Statistics. 2022. Available online: https://ganjoho.jp/reg_stat/statistics/stat/short_pred_en.htmlt (accessed on 1 October 2022).
- Grimm, P.D.; Blasko, J.C.; Sylvester, J.E.; Meier, R.M.; Cavanagh, W. 10-year biochemical (prostate-specific antigen) control of prostate cancer with (125) I brachytherapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2001, 51, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimm, P.; Sylvester, J. Advances in brachytherapy. Rev. Urol. 2004, 6 (Suppl. S4), S37–S48. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lehto, U.S.; Tenhola, H.; Taari, K.; Aromaa, A. Patients’ perceptions of the negative effects following different prostate cancer treatments and the impact on psychological well-being: A nationwide survey. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 116, 864–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veccia, A.; Caffo, O.; Fellin, G.; Mussari, S.; Ziglio, F.; Maines, F.; Tomio, L.; Galligioni, E. Impact of post-implant dosimetric parameters on the quality of life of patients treated with low-dose rate brachytherapy for localised prostate cancer: Results of a single-institution study. Radiat. Oncol. 2015, 10, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farris, J.C.; Hughes, R.T.; Steber, C.R.; Craven, T.E.; Frizzell, B.A. Patient assessment of lower urinary tract symptoms using the international prostate symptom score following low-dose-rate prostate brachytherapy. Brachytherapy 2021, 20, 1107–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyce-Fappiano, D.; Bathala, T.K.; Ye, R.; Pasalic, D. Predictors of urinary toxicity with MRI-assisted radiosurgery for low-dose-rate prostate brachytherapy. Brachytherapy 2020, 19, 574–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, J.N.; Araujo, C.; Crook, J.M. MRI-defined treatment margins, uriary toxicity, and PSA response in LDR prostate brachytherapy. Brachytherapy 2022, 21, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriguchi, T.; Yorozu, A.; Kuroiwa, N.; Yagi, Y.; Nishiyama, T.; Saito, S.; Toya, K.; Hanada, T.; Shiraishi, Y.; Ohashi, T.; et al. Predictive factors for urinary toxicity after iodine-125 prostate brachytherapy with or without supplemental external beam radiotherapy. Brachytherapy 2016, 15, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzarini, C.; Rancati, T.; Carillo, V.; Civardi, F. Multi-variable models predicting specific patient-reported acute urinary symptoms after radiotherapy for prostate cancer: Results of a cohort study. Radiother. Oncol. 2015, 116, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, M.; Tanaka, N.; Asakawa, I.; Hori, S.; Morizawa, Y. Assessment of lower urinary symptom flare with overactive bladder symptom score and International Prostate Symptom Score in patients treated with iodine-125 implant brachytherapy: Long-term follow-up experience at a single institute. BMC Urol. 2017, 17, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aaltomaa, S.H.; Kataja, V.V.; Lahtinen, T.; Palmgren, J.E.; Forsell, T. Eight years experience of local prostate cancer treatment with permanent I125 seed brachytherapy. Morbidity and outcome results. Radiother. Oncol. 2009, 91, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, C.K.; Choi, E.P.; Chan, S.W.; Tsu, J.H.; Fan, C.W.; Chu, P.S.; Cheung, F.K.; Ma, W.K.; Mah, I.S.F.; Yip, S.K.; et al. Use of the International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS) in Chinese male patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia. Aging Male 2017, 20, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, D.C.; Sanda, M.G.; Dunn, R.L. Long-term outcomes among localized prostate cancer survivors: Health-related quality-of-life changes after radical prostatectomy, external radiation, and brachy-therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 2772–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakayori, M.; Ohashi, T.; Momma, T.; Kaneda, T.; Nishimura, S.; Sutani, S.; Yamashita, S.; Shigematsu, N. Quantitative analysis of genitourinary toxicity after iodine-125 brachytherapy for localized prostate cancer: Follow up of the International Prostate Symptom Score and Overactive Bladder Symptom Score. Brachytherapy 2017, 16, 806–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelblum, D.Y.; Potters, L.; Ashley, R.; Waldbaum, R.; Wang, X.H.; Leibel, S. Urinary morbidity following ultrasound-guided transperineal prostate seed implantation. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1999, 45, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onishi, K.; Tanaka, N.; Miyake, M.; Nakai, Y.; Anai, S.; Torimoto, K.; Yamaki, K.; Asakawa, I.; Hasegawa, M.; Fujii, T.; et al. Changes in lower urinary tract symptoms after iodine-125 brachytherapy for prostate cancer. Clin. Transl. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 14, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohashi, T.; Yorozu, A.; Toya, K.; Saito, S.; Momma, T. Serial changes of international prostate symptom score following I-125 prostate brachytherapy. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 11, 320–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neill, M.; Studer, G.; Le, L.; McLean, M.; Yeung, I.; Pond, G.; Crook, J.M. The nature and extent of urinary morbidity in relation to prostate brachytherapy urethral dosimetry. Brachytherapy 2007, 6, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.; Keyes, M.; Liu, M.; Moravan, V. Segmental urethral dosimetry and urinary toxicity in patients with no urinary symptoms before permanent prostate brachytherapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2008, 72, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earley, J.J.; Abdelbaky, A.M.; Cunningham, M.J.; Chadwick, E.; Langley, S.E.M.; Laing, R.W. Correlation between prostate brachytherapy-related urethral stricture and peri-apical urethral dosimetry: A matched case-control study. Radiother. Oncol. 2012, 104, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steggerda, M.J.; Witteveen, T.; Van Den Boom, F.; Moonen, L.M.F. Is there a relation between the radiation dose to the different sub-segments of the lower urinary tract and urinary morbidity after brachytherapy of the prostate with I-125 seeds? Radiother. Oncol. 2013, 109, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roeloffzen, E.M.A.; Monninkhof, E.M.; Battermann, J.J.; Van Roermund, J.G.H.; Moerland, M.A.; Van Vulpen, M. Acute urinary retention after I-125 prostate brachytherapy in relation to dose in different regions of the prostate. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2011, 80, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cesaretti, J.A.; Stone, N.N.; Stock, R.G. Urinary symptom flare following I-125 prostate brachytherapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2003, 56, 1085–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyes, M.; Miller, S.; Pickles, T.; Halperin, R.; Kwan, W.; Lapointe, V.; McKenzie, M.; Spadinger, I.; Pai, H.; Chan, E.K.; et al. Late urinary side effects 10 years after low-dose-rate prostate brachytherapy: Population-based results from a multiphysician practice treating with a standardized protocol and uniform dosimetric goals. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2014, 90, 570–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, R.A.; Buckstein, M.; Stone, N.N.; Stock, R. Treatment outcomes and morbidity following definitive brachytherapy with or without external beam radiation for the treatment of localized prostate cancer: 20-year experience at Mount Sinai Medical Center. Urol. Oncol. 2014, 32, 38.e1–38.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, N.N.; Winoker, J.S.; Kaplan, S.A.; Stock, R.G. Factors influencing long-term urinary symptoms after prostate brachytherapy. BJU Int. 2018, 122, 831–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elizabeth, T.; William, B. Ultra-long-term toxicity of prostate brachytherapy. Brachytherapy 2021, 20, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salembier, C.; Lavagnini, P.; Nickers, P.; Mangili, P.; Rijnders, A.; Polo, A.; Venselaar, J.; Hoskin, P.R. Tumour and target volumes in permanent prostate brachytherapy: A supplement to the ESTRO/EAU/EORTC recommendations on prostate brachytherapy. Radiother. Oncol. 2007, 83, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, Z.A.; Merrick, G.S.; Butler, W.M.; Wallner, K.E.; Kurko, B.; Anderson, R.L.; Murray, B.C.; Galbreath, R.W. Detailed urethral dosimetry in the evaluation of prostate brachytherapy-related urinary morbidity. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2005, 62, 981–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
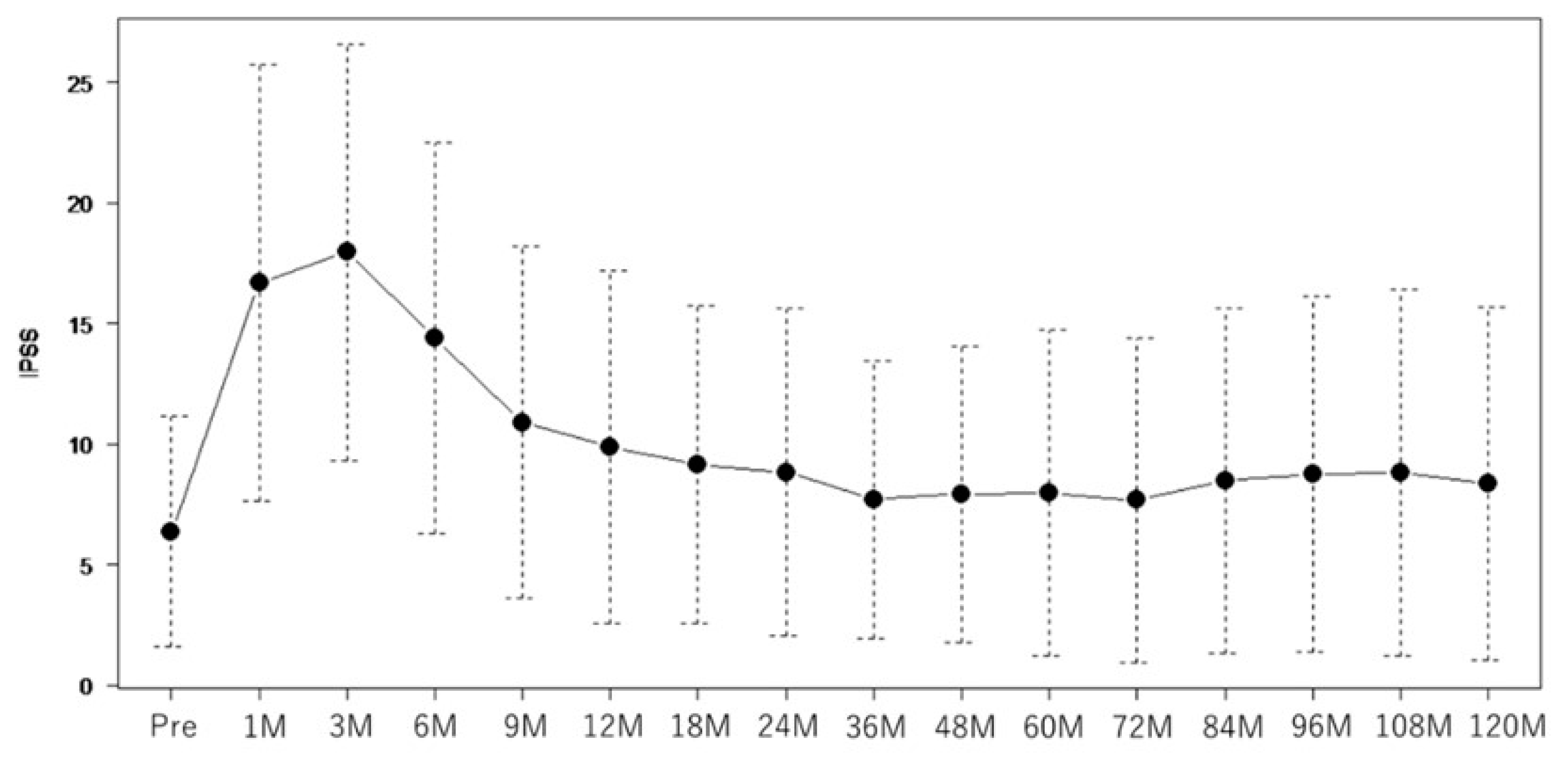
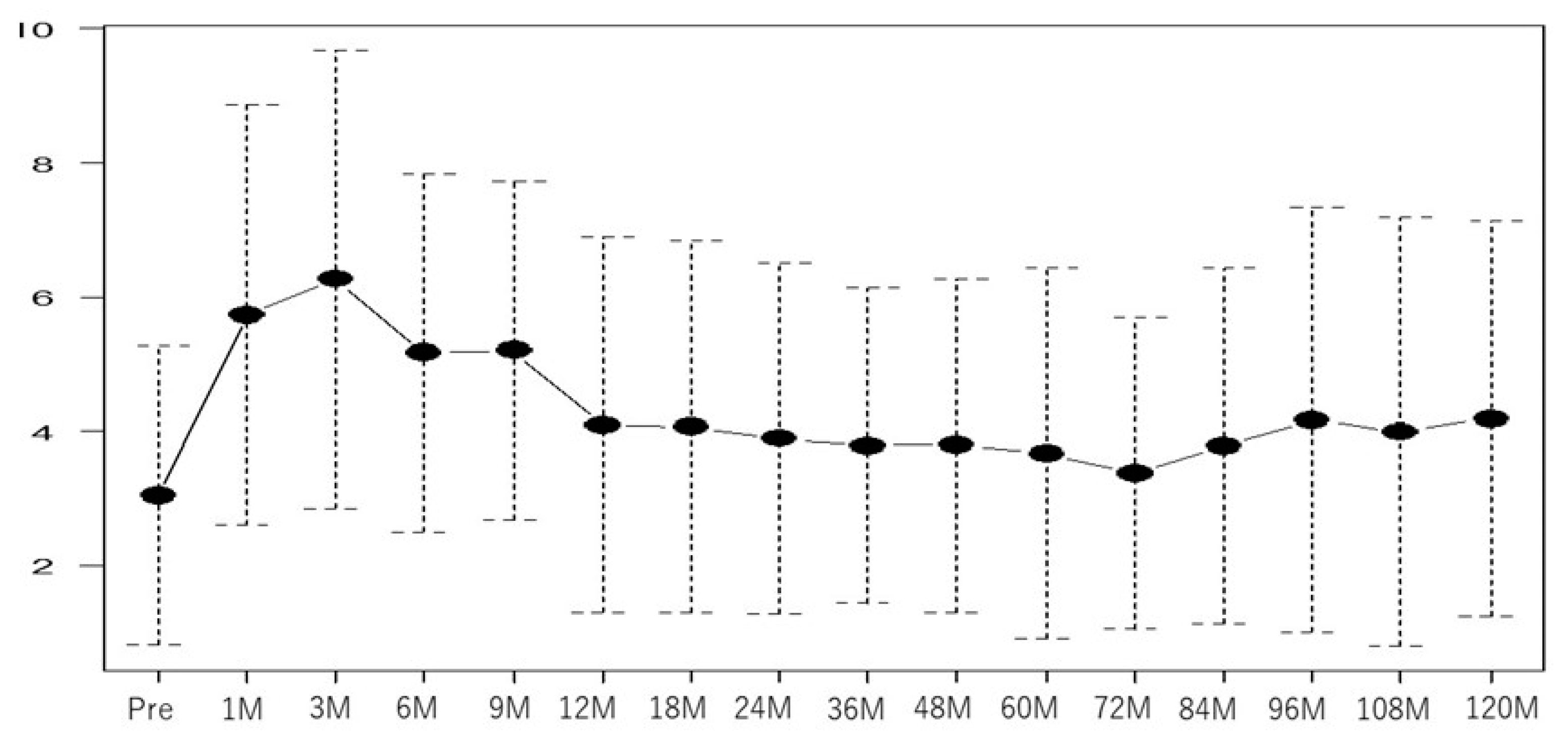
| Factor | Total 203 | |
|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 66 (50–78) | |
| Gleason score | 6 | 143 (50.7) |
| 7 | 59 (49.3) | |
| PSA | 6 (1.1–14.7) | |
| cTstage | T1c | 165 |
| NADT | T2a | 37 |
| T2b | 2 | |
| Yes | 159 (78.3) | |
| No | 44 (21.7) | |
| IPSS | 5 (0–25) | |
| OABSS | 2 (0–15) | |
| OAB | Yes | 39 (23.4) |
| No | 128 (76.6) | |
| UFM (mL/s) | 10 (10–49) | |
| Intra_PV (mL) | 25.4 (8.77–46.88) |
| Factor | Median | Range |
|---|---|---|
| Needle | 22 | 13–35 |
| Seed | 75 | 35–108 |
| PD90 (Gy) | 172 | 105–241 |
| PV100 (%) | 96 | 77–100 |
| UD5 (Gy) | 235 | 171–400 |
| UD10 (Gy) | 222 | 168–332 |
| UD30 (Gy) | 218 | 159–319 |
| UD90 (Gy) | 141 | 63–241 |
| 2 Years | 5 Years | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moderate (n = 98) | Severe (n = 15) | Moderate (n = 75) | Severe (n = 12) | |||||||||
| Factor | UVA | MVA | UVA | MVA | UVA | MVA | UVA | MVA | ||||
| p | OR (95% CI) | p | p | OR (95% CI) | p | p | OR (95% CI) | p | p | OR (95% CI) | p | |
| Age | 0.61 | 0.72 | 0.19 | 0.99 (0.91–1.07) | 0.83 | 0.35 | ||||||
| GS | 0.34 | 0.56 | 0.53 | 1.00 | ||||||||
| PSA | 0.76 | 0.42 | 0.59 | 0.71 | ||||||||
| NADT | 0.22 | 0.09 | 0.65 (0.11–3.94) | 0.64 | 0.86 | 0.14 | 0.55 (0.21–1.46) | 0.23 | ||||
| Needle | 0.41 | 0.71 | 0.73 | 0.72 | ||||||||
| Seed | 0.11 | 1.02 (1.00–1.04) | 0.02 | 0.20 | 1.02 (0.96–1.07) | 0.56 | 0.59 | 0.94 | ||||
| Intra_PV | 0.53 | 0.37 | 0.24 | 0.61 | ||||||||
| PD90 | 0.82 | 0.37 | 0.63 | 0.21 | ||||||||
| PV100 | 0.41 | 0.75 | 0.53 | 0.33 | ||||||||
| UD5 | 0.49 | 0.25 | 0.78 | 0.62 | ||||||||
| UD10 | 0.16 | 1.00 (0.99–1.01) | 0.97 | 0.10 | 0.97 (0.94–1.01) | 0.18 | 0.20 | 1.00 (0.98–1.02) | 0.90 | 0.11 | 0.99 (0.98–1.04) | 0.91 |
| UD30 | 0.56 | 0.38 | 0.71 | 0.76 | ||||||||
| UD90 | 0.83 | 0.47 | 0.84 | 0.20 | ||||||||
| Baseline IPSS | <0.01 | 1.3 (1.18–1.42) | <0.01 | 0.08 | 1.12 (0.95–1.31) | 0.17 | <0.01 | 1.19 (1.10–1.29) | <0.01 | 0.02 | 1.18 (1.06–1.31) | <0.01 |
| Baseline UFM | 0.53 | 0.72 | 0.60 | 0.09 | 1.01 (0.94–1.08) | 0.75 | ||||||
| OAB at 2 Years (n = 60) | OAB at 5 Years (n = 40) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UVA | MVA | UVA | MVA | |||
| p | OR (95% CI) | p | p | OR (95% CI) | p | |
| Age | 0.52 | 0.45 | ||||
| GS | 0.12 | 0.97 | ||||
| PSA | 0.71 | 0.27 | ||||
| NADT | 0.56 | 0.19 | ||||
| Needle | 0.84 | 0.86 | ||||
| Seed | 0.16 | 0.22 | ||||
| Intra_PV | 0.24 | 0.47 | ||||
| PD90 | 0.42 | 0.72 | ||||
| PV100 | 0.99 | 0.87 | ||||
| UD5 | 0.23 | 0.75 | ||||
| UD10 | 0.19 | 0.99 (0.98–1.01) | 0.78 | 0.40 | ||
| UD30 | 0.40 | 0.75 | ||||
| UD90 | 0.92 | 0.61 | ||||
| Baseline OABSS | <0.01 | 1.77 (1.35–2.31) | <0.01 | 0.03 | 2.5 (1.10–5.80) | 0.02 |
| Baseline UFM | 0.02 | 1.11 (1.03–1.20) | <0.01 | 0.61 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ito, M.; Makita, C.; Mori, T.; Takano, H.; Kumano, T.; Matsuo, M.; Iinuma, K.; Kawase, M.; Nakane, K.; Nakano, M.; et al. Associations of Clinical and Dosimetric Parameters with Urinary Toxicities after Prostate Brachytherapy: A Long-Term Single-Institution Experience. Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 5680-5689. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30060426
Ito M, Makita C, Mori T, Takano H, Kumano T, Matsuo M, Iinuma K, Kawase M, Nakane K, Nakano M, et al. Associations of Clinical and Dosimetric Parameters with Urinary Toxicities after Prostate Brachytherapy: A Long-Term Single-Institution Experience. Current Oncology. 2023; 30(6):5680-5689. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30060426
Chicago/Turabian StyleIto, Masaya, Chiyoko Makita, Takayuki Mori, Hirota Takano, Tomoyasu Kumano, Masayuki Matsuo, Koji Iinuma, Makoto Kawase, Keita Nakane, Masahiro Nakano, and et al. 2023. "Associations of Clinical and Dosimetric Parameters with Urinary Toxicities after Prostate Brachytherapy: A Long-Term Single-Institution Experience" Current Oncology 30, no. 6: 5680-5689. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30060426
APA StyleIto, M., Makita, C., Mori, T., Takano, H., Kumano, T., Matsuo, M., Iinuma, K., Kawase, M., Nakane, K., Nakano, M., & Koie, T. (2023). Associations of Clinical and Dosimetric Parameters with Urinary Toxicities after Prostate Brachytherapy: A Long-Term Single-Institution Experience. Current Oncology, 30(6), 5680-5689. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30060426






