Survival Benefit of Experience of Liver Resection for Advanced Recurrent Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated with Sorafenib: A Propensity Score Matching Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
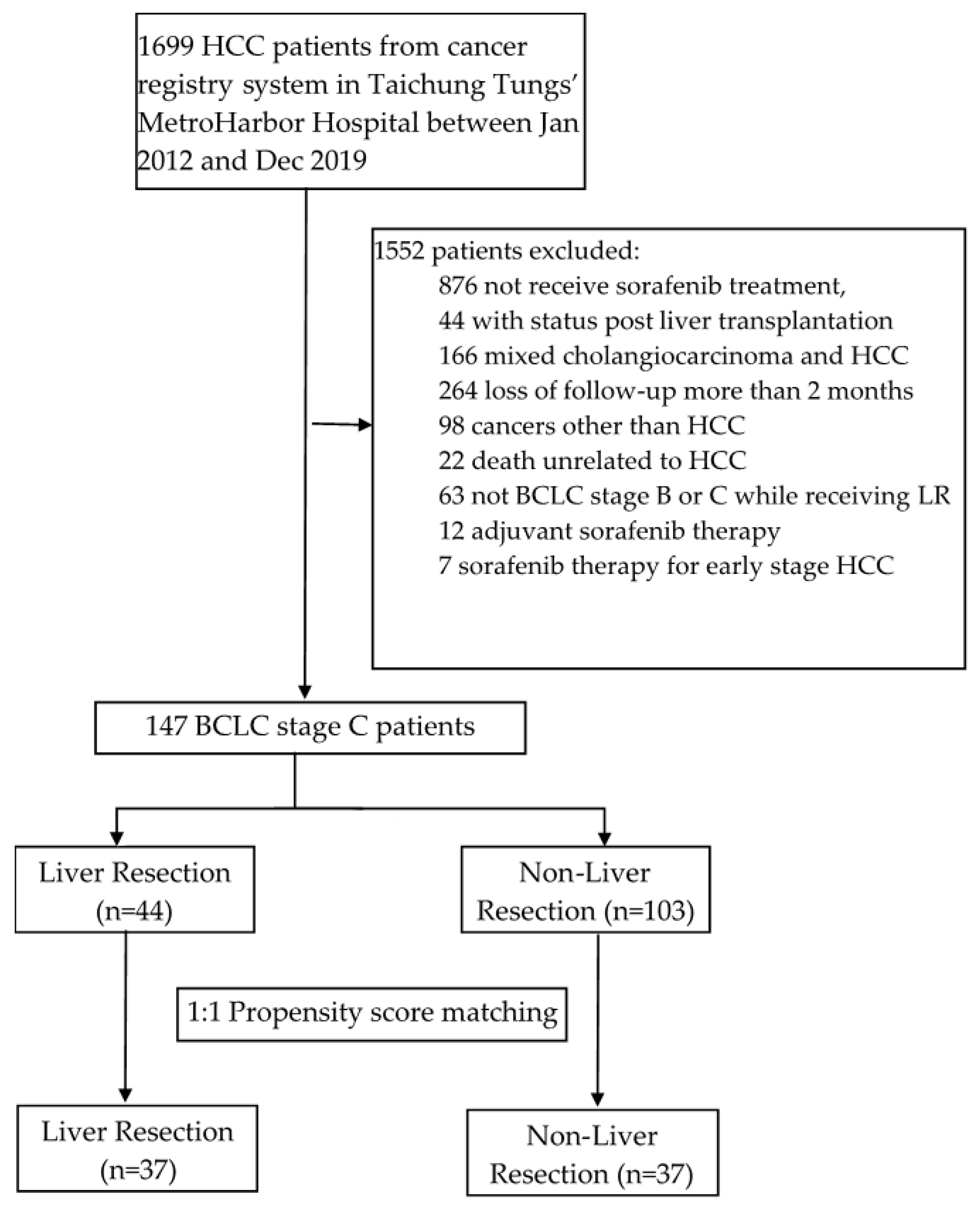
2.1. Patients and Study Design
2.2. Outcomes and Evaluation
2.3. Ethical Considerations
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
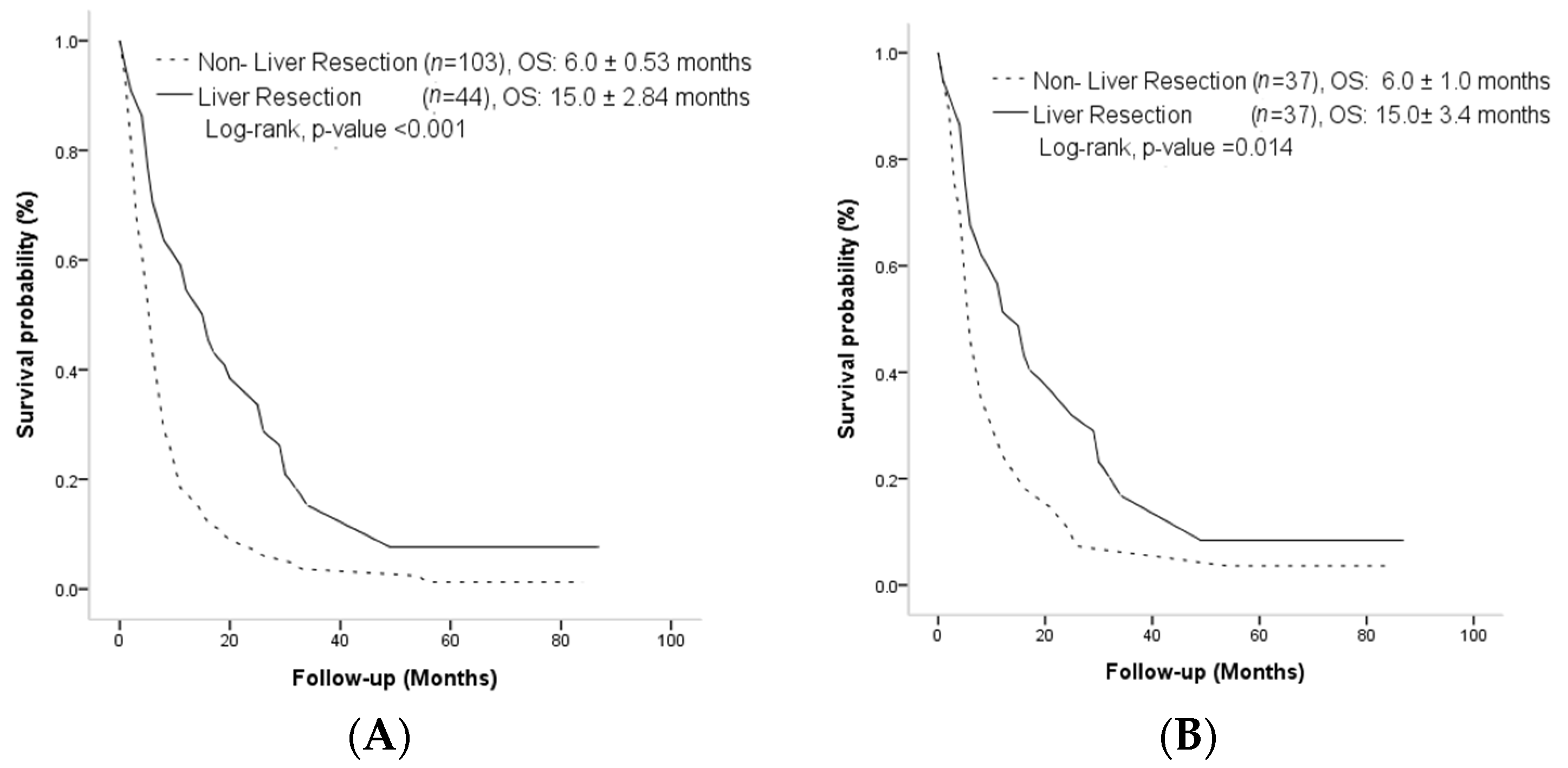
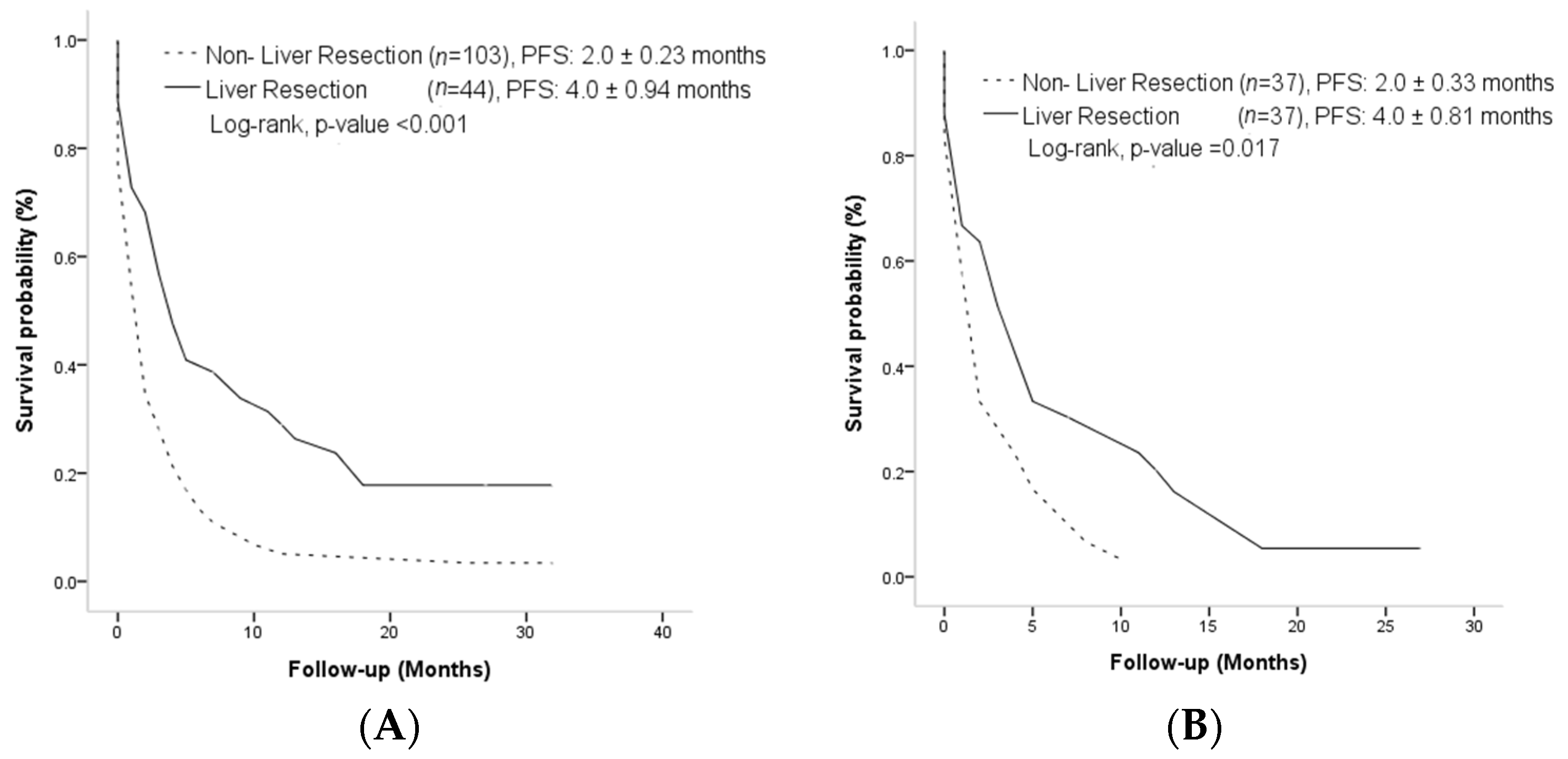
3.2. Overall Survival and Progression-Free Survival Outcome
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fitzmaurice, C.; Allen, C.; Barber, R.M.; Barregard, L.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Brenner, H.; Dicker, D.J.; Chimed-Orchir, O.; Dandona, R.; Dandona, L.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Cancer Incidence, Mortality, Years of Life Lost, Years Lived with Disability, and Disability-Adjusted Life-years for 32 Cancer Groups, 1990 to 2015: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 524–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.M.; Sinn, D.H.; Jung, S.H.; Gwak, G.Y.; Paik, Y.H.; Choi, M.S.; Lee, J.H.; Koh, K.C.; Paik, S.W. The recommended treatment algorithms of the BCLC and HKLC staging systems: Does following these always improve survival rates for HCC patients? Liver Int. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Study Liver 2016, 36, 1490–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serper, M.; Taddei, T.H.; Mehta, R.; D’Addeo, K.; Dai, F.; Aytaman, A.; Baytarian, M.; Fox, R.; Hunt, K.; Goldberg, D.S.; et al. Association of Provider Specialty and Multidisciplinary Care with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treatment and Mortality. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 1954–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J.M.; Brú, C.; Bruix, J. Prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: The BCLC staging classification. Semin. Liver Dis. 1999, 19, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruix, J.; Sherman, M. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma: An update. Hepatology 2011, 53, 1020–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver; European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer. EASL-EORTC clinical practice guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 908–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, C.H.; Yoon, J.H.; Cho, E.; Shin, S.S.; Cho, S.B.; Kim, H.J.; Park, C.H.; Kim, H.S.; Choi, S.K.; Rew, J.S. Barcelona clinic liver cancer-stage C hepatocellular carcinoma: A novel approach to subclassification and treatment. Medicine 2017, 96, e6745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Yan, L.; Wang, W.; Zeng, Y.; LI, B.; Wen, T.; Xu, M.; Yang, J. Barcelona clinic liver cancer stage B hepatocellular carcinoma: Transarterial chemoembolization or hepatic resection? Medicine 2014, 93, e180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torzilli, G.; Donadon, M.; Marconi, M.; Palmisano, A.; Del Fabbro, D.; Spinelli, A.; Botea, F.; Montorsi, M. Hepatectomy for stage B and stage C hepatocellular carcinoma in the Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer classification: Results of a prospective analysis. Arch. Surg. 2008, 143, 1082–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.J.; Chung, K.P.; Chang, Y.J.; Chen, L.J. Long-term survival of patients undergoing liver resection for very large hepatocellular carcinomas. Br. J. Surg. 2016, 103, 1513–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Li, H.; Li, A.J.; Lau, W.Y.; Pan, Z.Y.; Lai, E.C.; Wu, M.C.; Zhou, W.P. Partial hepatectomy vs. transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for resectable multiple hepatocellular carcinoma beyond Milan Criteria: A RCT. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imamura, H.; Matsuyama, Y.; Tanaka, E.; Ohkubo, T.; Hasegawa, K.; Miyagawa, S.; Sugawara, Y.; Minagawa, M.; Takayama, T.; Kawasaki, S.; et al. Risk factors contributing to early and late phase intrahepatic recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy. J. Hepatol. 2003, 38, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J.M.; Ricci, S.; Mazzaferro, V.; Hilgard, P.; Gane, E.; Blanc, J.F.; de Oliveira, A.C.; Santoro, A.; Raoul, J.L.; Forner, A.; et al. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 378–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, A.L.; Kang, Y.K.; Chen, Z.; Tsao, C.J.; Qin, S.; Kim, J.S.; Luo, R.; Feng, J.; Ye, S.; Yang, T.S.; et al. Efficacy and safety of sorafenib in patients in the Asia-Pacific region with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: A phase III randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimbach, J.K.; Kulik, L.M.; Finn, R.S.; Sirlin, C.B.; Abecassis, M.M.; Roberts, L.R.; Zhu, A.X.; Murad, M.H.; Marrero, J.A. AASLD guidelines for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2018, 67, 358–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Zheng, Y.; He, W.; Li, Q.; Shen, J.; Hong, J.; Zou, R.; Qiu, J.; Li, B.; Yuan, Y. Sorafenib therapy following resection prolongs disease-free survival in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma at a high risk of recurrence. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 984–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yau, T.; Park, J.; Finn, R.; Cheng, A.-L.; Mathurin, P.; Edeline, J.; Kudo, M.; Han, K.-H.; Harding, J.; Merle, P. CheckMate 459: A randomized, multi-center phase III study of nivolumab (NIVO) vs sorafenib (SOR) as first-line (1L) treatment in patients (pts) with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (aHCC). Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, v874–v875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, R.K.; Rimassa, L.; Cheng, A.L.; Kaseb, A.; Qin, S.; Zhu, A.X.; Chan, S.L.; Melkadze, T.; Sukeepaisarnjaroen, W.; Breder, V.; et al. Cabozantinib plus atezolizumab versus sorafenib for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (COSMIC-312): A multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 995–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruix, J.; Qin, S.; Merle, P.; Granito, A.; Huang, Y.H.; Bodoky, G.; Pracht, M.; Yokosuka, O.; Rosmorduc, O.; Breder, V.; et al. Regorafenib for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma who progressed on sorafenib treatment (RESORCE): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Alfa, G.K.; Meyer, T.; Cheng, A.L.; El-Khoueiry, A.B.; Rimassa, L.; Ryoo, B.Y.; Cicin, I.; Merle, P.; Chen, Y.; Park, J.W.; et al. Cabozantinib in Patients with Advanced and Progressing Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, A.X.; Kang, Y.K.; Yen, C.J.; Finn, R.S.; Galle, P.R.; Llovet, J.M.; Assenat, E.; Brandi, G.; Pracht, M.; Lim, H.Y.; et al. Ramucirumab after sorafenib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma and increased α-fetoprotein concentrations (REACH-2): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 282–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Shi, J.; Jia, X.; Dang, S.; Wang, W. Cost-effectiveness of Atezolizumab Plus Bevacizumab vs Sorafenib for Patients with Unresectable or Metastatic Hepatocellular Carcinoma. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e214846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, C.L.; Chan, S.K.; Lee, S.F.; Wong, I.O.; Choi, H.C. Cost-effectiveness of Pembrolizumab as a Second-Line Therapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2033761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherrow, C.; Attwood, K.; Zhou, K.; Mukherjee, S.; Iyer, R.; Fountzilas, C. Sequencing Systemic Therapy Pathways for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Cost Effectiveness Analysis. Liver Cancer 2020, 9, 549–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galle, P.R.; Forner, A.; Llovet, J.M.; Mazzaferro, V.; Piscaglia, F.; Raoul, J.L.; Schirmacher, P.; Vilgrain, V. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 182–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omata, M.; Cheng, A.L.; Kokudo, N.; Kudo, M.; Lee, J.M.; Jia, J.; Tateishi, R.; Han, K.H.; Chawla, Y.K.; Shiina, S.; et al. Asia-Pacific clinical practice guidelines on the management of hepatocellular carcinoma: A 2017 update. Hepatol. Int. 2017, 11, 317–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erridge, S.; Pucher, P.H.; Markar, S.R.; Malietzis, G.; Athanasiou, T.; Darzi, A.; Sodergren, M.H.; Jiao, L.R. Meta-analysis of determinants of survival following treatment of recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma. Br. J. Surg. 2017, 104, 1433–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoh, T.; Seo, S.; Taura, K.; Iguchi, K.; Ogiso, S.; Fukumitsu, K.; Ishii, T.; Kaido, T.; Uemoto, S. Surgery for Recurrent Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Achieving Long-term Survival. Ann. Surg. 2021, 273, 792–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weichselbaum, R.R.; Hellman, S. Oligometastases revisited. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 8, 378–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, M.C.; Hasegawa, K.; Chen, X.P.; Nagano, H.; Lee, Y.J.; Chau, G.Y.; Zhou, J.; Wang, C.C.; Choi, Y.R.; Poon, R.T.; et al. Surgery for Intermediate and Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Consensus Report from the 5th Asia-Pacific Primary Liver Cancer Expert Meeting (APPLE 2014). Liver Cancer 2016, 5, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruix, J.; Takayama, T.; Mazzaferro, V.; Chau, G.Y.; Yang, J.; Kudo, M.; Cai, J.; Poon, R.T.; Han, K.H.; Tak, W.Y.; et al. Adjuvant sorafenib for hepatocellular carcinoma after resection or ablation (STORM): A phase 3, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 1344–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Hou, Y.; Cai, X.B.; Liu, B. Sorafenib after resection improves the outcome of BCLC stage C hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 4034–4040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, F.; Wu, L.L.; Lau, W.Y.; Huan, H.B.; Wen, X.D.; Ma, K.S.; Li, X.W.; Bie, P. Adjuvant sorafenib after heptectomy for Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer-stage C hepatocellular carcinoma patients. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 5384–5392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasini, F.; Serenari, M.; Cucchetti, A.; Ercolani, G. Treatment options for recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after surgical resection: Review of the literature and current recommendations for management. Hepatoma Res. 2020, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.P.; Chai, Z.T.; Gao, Y.Z.; Chen, Z.H.; Wang, K.; Shi, J.; Guo, W.X.; Zhou, T.F.; Ding, J.; Cong, W.M.; et al. Postoperative adjuvant sorafenib improves survival outcomes in hepatocellular carcinoma patients with microvascular invasion after R0 liver resection: A propensity score matching analysis. HPB 2019, 21, 1687–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, J.; Hu, K.; Wang, Z. Should we apply sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma patients with microvascular invasion after curative hepatectomy? OncoTargets Ther. 2019, 12, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.N.; Chuang, S.C.; Lee, K.T. Efficacy of sorafenib as adjuvant therapy to prevent early recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after curative surgery: A pilot study. Hepatol. Res. 2014, 44, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Gao, Z.H.; Qu, X.J. The adverse effects of sorafenib in patients with advanced cancers. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2015, 116, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroescu, C.; Dragnea, A.; Ivanov, B.; Pechianu, C.; Herlea, V.; Sgarbura, O.; Popescu, A.; Popescu, I. Expression of p53, Bcl-2, VEGF, Ki67 and PCNA and prognostic significance in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Gastrointestin. Liver Dis. 2008, 17, 411–417. [Google Scholar]
- Tsilimigras, D.I.; Moris, D.; Hyer, J.M.; Bagante, F.; Sahara, K.; Moro, A.; Paredes, A.Z.; Mehta, R.; Ratti, F.; Marques, H.P.; et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma tumour burden score to stratify prognosis after resection. Br. J. Surg. 2020, 107, 854–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muntané, J.; De la Rosa, A.J.; Docobo, F.; García-Carbonero, R.; Padillo, F.J. Targeting tyrosine kinase receptors in hepatocellular carcinoma. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2013, 13, 300–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatzaras, I.; Bischof, D.A.; Fahy, B.; Cosgrove, D.; Pawlik, T.M. Treatment options and surveillance strategies after therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 21, 758–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Before Match (n = 147) | After Match (n = 74) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | LR Group (n = 44) | Non- LR Group (n = 103) | p Value | LR Group (n = 37) | Non-LR Group (n = 37) | p Value |
| Age | 0.17 | 0.35 | ||||
| >60 years, n (%) | 22 (50) | 62 (60.3) | 22 (59.5) | 24 (64.9) | ||
| Gender | 0.26 | 0.24 | ||||
| Male, n (%) | 35 (79.5) | 85 (82.5) | 29 (78.4) | 31 (83.8) | ||
| ECOG | 0.4 | 0.24 | ||||
| PS 1, n (%) | 35 (79.5) | 86 (82.7) | 29 (78.4) | 31 (83.8) | ||
| Etiology of liver disease | 0.97 | 0.73 | ||||
| HBV, n (%) | 21 (47.7) | 43 (41.7) | 16 (43.2) | 16 (43.2) | ||
| HCV, n (%) | 14 (31.8) | 30 (29.1) | 13 (35.1) | 11 (29.7) | ||
| HBC + HCV, n (%) | 3 (6.8) | 4 (3.9) | 2 (5.4) | 3 (8.1) | ||
| CTP score | 0.003 | 1.00 | ||||
| 6, n (%) | 12 (23.7) | 63 (60.6) | 12 (32.4) | 12 (32.4) | ||
| Albumin | 0.01 | 1.00 | ||||
| >3.5 g/L, n (%) | 33 (75.0) | 67 (65) | 26 (70.3) | 26 (70.3) | ||
| Bilirubin | 0.23 | 1.00 | ||||
| >2 mg/dL, n (%) | 43 (97.7) | 96 (93.2) | 37 (100) | 37 (100) | ||
| Ascites | <0.001 | 1.00 | ||||
| Absent, n (%) | 43 (97.7) | 74 (71.8) | 36 (97.3) | 37 (100) | ||
| AFP | 0.88 | 0.66 | ||||
| <400 ng/mL, n (%) | 28 (63.6) | 53 (51.5) | 22 (59.5) | 25 (67.6) | ||
| Tumor burden | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||
| PVT, n (%) | 13 (29.5) | 43 (41.7) | 10(27.0) | 20 (54.1) | ||
| EHS, n (%) | 28 (63.6) | 26 (25.2) | 24(64.9) | 16 (29.7) | ||
| Tumor size > 3 cm or number of tumor nodules > 3, n (%) | 3 (6.8) | 34 (33.0) | 3(8.1) | 6 (16.2) | ||
| Characteristics | Before Propensity Score Matching | After Propensity Score Matching | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Univariable Analysis | Multivariable Analysis | Univariable Analysis | Multivariable Analysis | |||||
| HR (95% CI) | p Value | HR (95% CI) | p Value | HR (95% CI) | p Value | HR (95% CI) | p Value | |
| Treatment | ||||||||
| Non-LR LR | 1 0.45 (0.30–0.66) | <0.001 | 1 0.48 (0.30–0.67) | 0.002 | 1 0.55 (0.33–0.90) | 0.02 | 1 0.48 (0.25–0.91) | 0.02 |
| Age | ||||||||
| >60 ≤60 | 1 0.98 (0.70–1.38) | 0.93 | 1 0.92 (0.55–1.52) | 0.75 | ||||
| Gender | ||||||||
| Male Female | 1 0.85 (0.54–1.34) | 0.49 | 1 0.85 (0.45–1.60) | 0.62 | ||||
| ECOG | ||||||||
| PS 1 PS 0 | 1 0.58 (0.37–0.92) | 0.21 | 1 0.55 (0.28–1.07) | 0.08 | ||||
| Etiology of hepatitis | ||||||||
| NBNC HBV HCV HBC + HCV | 1 0.99 (0.63–1.55) 0.98 (0.61–1.57) 0.98 (0.41–2.39) | 0.98 0.93 0.98 | 1 0.64 (0.20–2.07) 0.89 (0.31–2.56) 0.96 (0.33–2.79) | 0.46 0.89 0.94 | ||||
| CTP score | ||||||||
| 6 5 | 1 0.62 (0.42–0.84) | 0.003 | 1 0.76 (0.45–1.28) | 0.31 | ||||
| Albumin | ||||||||
| ≤3.5 g/dL >3.5 g/dL | 1 0.91 (0.64–1.30) | 0.62 | 1 0.79 (0.43–1.22) | 0.23 | ||||
| Bilirubin | ||||||||
| ≥2 mg/dL <2 mg/dL | 1 0.83 (0.39–1.79) | 0.64 | 1 0.48 (0.62–1.77) | 0.46 | ||||
| Ascites | ||||||||
| Presence Absence | 1 0.48 (0.32–0.74) | <0.001 | 1 (Ref) 0.87 (0.45–1.68) | 0.68 | 1 0.58 (0.14–2.42) | 0.46 | ||
| AFP | ||||||||
| ≥400 ng/mL <400 ng/mL | 1 0.69 (0.49–0.97) | 0.03 | 1 (Ref) 0.84 (0.57–1.23) | 0.37 | 1 0.84 (0.51–1.40) | 0.51 | ||
| Tumor burden | ||||||||
| PTV EHS Tumor size > 3 cm or number of tumor nodules ≥ 3 | 1 0.87 (0.56–1.56) 0.63 (0.40–0.99) | 0.55 0.04 | 0.82 (0.51–1.31) | 0.41 | 1 1.46 (0.66–3.21) 0.99 (0.45–2.19) | 0.34 0.98 | ||
| Characteristics | Before Propensity Score Matching | After Propensity Score Matching | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Univariable Analysis | Multivariable Analysis | Univariable Analysis | Multivariable Analysis | |||||
| HR (95% CI) | p Value | HR (95% CI) | p Value | HR (95% CI) | p Value | HR (95% CI) | p Value | |
| Treatment | ||||||||
| Non-LR LR | 1 0.51 (0.34–0.76) | 0.001 | 1 0.55 (0.34–0.88) | 0.013 | 1 0.45 (0.26–0.77) | 0.004 | 1 0.43 (0.21–0.87) | 0.02 |
| Age | ||||||||
| >60 ≤60 | 1 0.97 (0.68–1.39) | 0.89 | 1 0.58 (0.33–0.99) | 0.83 | ||||
| Gender | ||||||||
| Male Female | 1 0.82 (0.52–1.31) | 0.82 | 1 0.85 (0.45–1.60) | 0.62 | ||||
| ECOG | ||||||||
| PS 1 PS 0 | 1 0.79 (0.50–1.25) | 0.32 | 1 0.55 (0.28–1.07) | 0.08 | ||||
| Etiology of hepatitis | ||||||||
| NBNC HBV HCV HBC + HCV | 1 0.97 (0.61–1.54) 0.79 (0.48–1.30) 0.95 (0.39–2.33) | 0.98 0.36 0.95 | 1 1.38 (0.76–2.85) 1.48 (0.73–3.13) 1.73 (0.55–5.44) | 0.79 0.29 0.46 | ||||
| CTP score | ||||||||
| 6 5 | 1 0.79 (0.50–1.25) | 0.32 | 1 1.35 (0.77–2.18) | 0.31 | ||||
| Albumin | ||||||||
| ≤3.5 g/dL >3.5 g/dL | 1 0. 80 (0.55–1.16) | 0.25 | 1 1.37 (0.81–2.31) | 0.23 | ||||
| Bilirubin | ||||||||
| ≥2 mg/dL <2 mg/dL | 1 0.82 (0.38–1.77) | 0.62 | 1 0.48 (0.62–1.77) | 0.46 | ||||
| Ascites | ||||||||
| Presence Absence | 1 0.49 (0.31–0.76) | 0.002 | 1 (Ref) 0.65 (0.32–1.31) | 0.23 | 1 1.70 (0.41–7.03) | 0.34 | ||
| AFP | ||||||||
| ≥400 ng/mL <400 ng/mL | 1 0.79 (0.56–1.13) | 0.21 | ||||||
| Tumor burden | ||||||||
| PTV EHS Tumor size > 3 cm or number of tumor nodules ≥ 3 | 1 0.81 (0.54–1.21) 0.97 (0.61–1.53) | 0.31 0.91 | 1 0.67 (0.40–1.15) 0.68 (0.31–1.50) | 0.15 0.34 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hsueh, K.-C.; Lee, C.-C.; Huang, P.-T.; Liang, C.-Y.; Yang, S.-F. Survival Benefit of Experience of Liver Resection for Advanced Recurrent Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated with Sorafenib: A Propensity Score Matching Analysis. Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 3206-3216. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30030243
Hsueh K-C, Lee C-C, Huang P-T, Liang C-Y, Yang S-F. Survival Benefit of Experience of Liver Resection for Advanced Recurrent Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated with Sorafenib: A Propensity Score Matching Analysis. Current Oncology. 2023; 30(3):3206-3216. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30030243
Chicago/Turabian StyleHsueh, Kuan-Chun, Cheng-Chun Lee, Pi-Teh Huang, Chih-Yu Liang, and Shun-Fa Yang. 2023. "Survival Benefit of Experience of Liver Resection for Advanced Recurrent Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated with Sorafenib: A Propensity Score Matching Analysis" Current Oncology 30, no. 3: 3206-3216. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30030243
APA StyleHsueh, K.-C., Lee, C.-C., Huang, P.-T., Liang, C.-Y., & Yang, S.-F. (2023). Survival Benefit of Experience of Liver Resection for Advanced Recurrent Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated with Sorafenib: A Propensity Score Matching Analysis. Current Oncology, 30(3), 3206-3216. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30030243






