Predictive Value of Inflammatory and Nutritional Indexes in the Pathology of Bladder Cancer Patients Treated with Radical Cystectomy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Screening Cohort and Baseline Characteristics
2.2. Inflammatory and Nutritional Index Calculations
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Globocan. 2020. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/today/data/factsheets/populations/900-world-fact-sheets.pdf (accessed on 22 September 2022).
- Cumberbatch, M.G.K.; Jubber, I.; Black, P.C.; Esperto, F.; Figueroa, J.D.; Kamat, A.M.; Kiemeney, L.; Lotan, Y.; Pang, K.; Silverman, D.T.; et al. Epidemiology of Bladder Cancer: A Systematic Review and Contemporary Update of Risk Factors in 2018. Eur. Urol. 2018, 74, 784–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shariat, S.F.; Sfakianos, J.P.; Droller, M.J.; Karakiewicz, P.I.; Meryn, S.; Bochner, B.H. The effect of age and gender on bladder cancer: A critical review of the literature. BJU Int. 2010, 105, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobruch, J.; Daneshmand, S.; Fisch, M.; Lotan, Y.; Noon, A.P.; Resnick, M.J.; Shariat, S.F.; Zlotta, A.R.; Boorjian, S.A. Gender and Bladder Cancer: A Collaborative Review of Etiology, Biology, and Outcomes. Eur. Urol. 2016, 69, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Yang, T.; Na, R.; Hu, M.; Zhang, L.; Fu, Y.; Jiang, H.; Ding, Q. The impact of female gender on bladder cancer-specific death risk after radical cystectomy: A meta-analysis of 27,912 patients. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2015, 47, 951–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, P.; Bogillot, O.; Cordier, S.; Greiser, E.; Schill, W.; Vineis, P.; Lopez-Abente, G.; Tzonou, A.; Chang-Claude, J.; Bolm-Audorff, U.; et al. Cigarette smoking and bladder cancer in men: A pooled analysis of 11 case-control studies. Int. J. Cancer 2000, 86, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, M.; Catto, J.W.F.; Dalbagni, G.; Grossman, H.B.; Herr, H.; Karakiewicz, P.; Kassouf, W.; Kiemeney, L.A.; La Vecchia, C.; Shariat, S.; et al. Epidemiology and Risk Factors of Urothelial Bladder Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2013, 63, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, N.; Shariat, S.F.; Guo, C.C.; Fernandez, M.I.; Kassouf, W.; Choudhury, A.; Gao, J.; Williams, S.B.; Galsky, M.D.; Taylor, J.A., 3rd; et al. What Is the Significance of Variant Histology in Urothelial Carcinoma? Eur. Urol. Focus 2020, 6, 653–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montironi, R.; López-Beltrán, A. The 2004 WHO Classification of Bladder Tumors: A Summary and Commentary. Int. J. Surg. Pathol. 2005, 13, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MMoschini, M.; Sharma, V.; Dell’Oglio, P.; Cucchiara, V.; Gandaglia, G.; Cantiello, F.; Zattoni, F.; Pellucchi, F.; Briganti, A.; Damiano, R.; et al. Comparing long-term outcomes of primary and progressive carcinoma invading bladder muscle after radical cystectomy. BJU Int. 2015, 117, 604–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, J.P.; Lieskovsky, G.; Cote, R.; Groshen, S.; Feng, A.-C.; Boyd, S.; Skinner, E.; Bochner, B.; Thangathurai, D.; Mikhail, M.; et al. Radical Cystectomy in the Treatment of Invasive Bladder Cancer: Long-Term Results in 1,054 Patients. J. Clin. Oncol. 2001, 19, 666–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EAU Guidelines. In Proceedings of the EAU Annual Congress, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1–4 July 2022; ISBN 978-94-92671-16-5.
- Zhang, L.; Wu, B.; Zha, Z.; Qu, W.; Zhao, H.; Yuan, J. Clinicopathological factors in bladder cancer for cancer-specific survival outcomes following radical cystectomy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathieu, R.; Lucca, I.; Rouprêt, M.; Briganti, A.; Shariat, R.M.I.L.S.F. The prognostic role of lymphovascular invasion in urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2016, 13, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arends, J.; Bachmann, P.; Baracos, V.; Barthelemy, N.; Bertz, H.; Bozzetti, F.; Fearon, K.; Hütterer, E.; Isenring, E.; Kaasa, S.; et al. ESPEN guidelines on nutrition in cancer patients. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 11–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diem, S.; Schmid, S.; Krapf, M.; Flatz, L.; Born, D.; Jochum, W.; Templeton, A.J.; Früh, M. Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and Platelet-to-Lymphocyte ratio (PLR) as prognostic markers in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) treated with nivolumab. Lung Cancer 2017, 111, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Yao, X.; Xie, X.; Wu, X.; Zheng, C.; Xia, W.; Ma, S. Prognostic value of preoperative NLR, dNLR, PLR and CRP in surgical renal cell carcinoma patients. World J. Urol. 2016, 35, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.-H.; Zhai, E.-T.; Yuan, Y.; Wu, K.-M.; Xu, J.-B.; Peng, J.-J.; Chen, C.-Q.; He, Y.-L.; Cai, S.-R. Systemic immune-inflammation index for predicting prognosis of colorectal cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 6261–6272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Jing, J. Inflammation-related parameter serve as prognostic biomarker in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 900305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, Z.; Zhang, L.; Cao, J.; Ai, K.; Xu, R. Pretreatment Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio as a Predictor in Bladder Cancer and Metastatic or Unresectable Urothelial Carcinoma Patients: A Pooled Analysis of Comparative Studies. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 46, 1352–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojerholm, E.; Smith, A.; Hwang, W.T.; Baumann, B.C.; Tucker, K.N.; Lerner, S.P.; Mamtani, R.; Boursi, B.; Christodouleas, J.P. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a bladder cancer biomarker: Assessing prognostic and predictive value in SWOG 8710. Cancer 2017, 123, 794–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarmuzek, P.; Kot, M.; Defort, P.; Stawicki, J.; Komorzycka, J.; Nowak, K.; Tylutka, A.; Zembron-Lacny, A. Prognostic Values of Combined Ratios of White Blood Cells in Glioblastoma: A Retrospective Study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liposits, G.; Skuladottir, H.; Ryg, J.; Winther, S.B.; Möller, S.; Hofsli, E.; Shah, C.H.; Poulsen, L.Ø.; Berglund, Å.; Qvortrup, C.; et al. The Prognostic Value of Pre-Treatment Circulating Biomarkers of Systemic Inflammation (CRP, dNLR, YKL-40, and IL-6) in Vulnerable Older Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Receiving Palliative Chemotherapy-The Randomized NORDIC9-Study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tachibana, M.; Miyakawa, A.; Tazaki, H.; Nakamura, K.; Kubo, A.; Hata, J.; Nishi, T.; Amano, Y. Autocrine growth of transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder induced by granulocyte-colony stimulating factor. Cancer Res. 1995, 55, 3438–3443. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Coffelt, S.B.; De Visser, K.E. Inflammation lights the way to metastasis. Nature 2014, 507, 48–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantovani, A.; Allavena, P.; Sica, A.; Balkwill, F. Cancer-related inflammation. Nature 2008, 454, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inman, K.; Francis, A.A.; Murray, N.R. Complex role for the immune system in initiation and progression of pancreatic cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 11160–11181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhu, B.; Li, Y. Resolution of Cancer-Promoting Inflammation: A New Approach for Anticancer Therapy. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo-Martinez, L.; Castro-Eguiluz, A.D.; Copca-Mendoza, E.T.; Pérez-Camargo, D.A.; Reyes-Torres, C.A.; Damasco, E.; López-Córdova, G.; Fuentes-Hernández, M.R.; Cetina-Pérez, L.; Milke-García, M.D.P. Nutritional Assessment Tools for the Identification of Malnutrition and Nutritional Risk Associated with Cancer Treatment. Rev. Investig. Clin. 2018, 70, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkwill, F.; Mantovani, A. Inflammation and cancer: Back to Virchow? Lancet 2001, 357, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhou, S.; Jiang, W.; Huang, M.; Dai, X. Effects of ganopoly (a Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide extract) on the immune functions in advanced-stage cancer patients. Immunol. Investig. 2003, 32, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzby, G.P.; Mullen, J.L.; Matthews, D.C.; Hobbs, C.L.; Rosato, E.F. Prognostic nutritional index in gastrointestinal surgery. Am. J. Surg. 1980, 139, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogar, P.; Sperti, C.; Basso, D.; Sanzari, M.C.; Greco, E.; Davoli, C.; Navaglia, F.; Zambon, C.-F.; Pasquali, C.; Venza, E.; et al. Decreased Total Lymphocyte Counts in Pancreatic Cancer: An Index of Adverse Outcome. Pancreas 2006, 32, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djaladat, H.; Bruins, H.M.; Miranda, G.; Cai, J.; Skinner, E.C.; Daneshmand, S. The association of preoperative serum albumin level and American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) score on early complications and survival of patients undergoing radical cystectomy for urothelial bladder cancer. BJU Int. 2013, 113, 887–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, M.; Miyoshi, N.; Fujino, S.; Ogino, T.; Takahashi, H.; Uemura, M.; Matsuda, C.; Yamamoto, H.; Mizushima, T.; Mori, M.; et al. The Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index predicts postoperative complications and prognosis in elderly patients with colorectal cancer after curative surgery. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouillanne, O.; Morineau, G.; Dupont, C.; Coulombel, I.; Vincent, J.-P.; Nicolis, I.; Benazeth, S.; Cynober, L.; Aussel, C. Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index: A new index for evaluating at-risk elderly medical patients. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 82, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; McKenney, J.K. Urinary Bladder Pathology: World Health Organization Classification and American Joint Committee on Cancer Staging Update. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2018, 143, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- TNM Classification of Malignant Tumors. UICC International Union against Cancer, 8th ed.; Brierley, J.D., Gospodarowicz, M.K., Wittekind, C., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell and UICC: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, K.D.; Siegel, R.L.; Lin, C.C.; Mariotto, A.B.; Kramer, J.L.; Rowland, J.H.; Stein, K.D.; Alteri, R.; Jemal, A. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2016, 66, 271–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colotta, F.; Allavena, P.; Sica, A.; Garlanda, C.; Mantovani, A. Cancer-related inflammation, the seventh hallmark of cancer: Links to genetic instability. Carcinogenesis 2009, 30, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.; Johnstone, C.N.; Stewart, A.G. Annexin A1 influences in breast cancer: Controversies on contributions to tumour, host and immunoediting processes. Pharmacol. Res. 2017, 119, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, K.; Umeda, Y.; Yoshida, R.; Nobuoka, D.; Kuise, T.; Fushimi, T.; Fujiwara, T.; Yagi, T. Preoperative Controlling Nutritional Status Score Predicts Mortality after Hepatectomy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Dig. Surg. 2018, 36, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Cao, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, S.; Yang, Y.; Du, P. Diagnostic Value of Inflammatory Factors in Pathology of Bladder Cancer Patients. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 575483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, H.; Shang, Z.; Jia, C.; Wu, J.; Cui, B.; Wang, Q.; Ou, T. Predictive Values of Preoperative Prognostic Nutritional Index and Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index for Long-Term Survival in High-Risk Non-Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer Patients: A Single-Centre Retrospective Study. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 9471–9483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dicken, B.J.; Graham, K.; Hamilton, S.M.; Andrews, S.; Lai, R.; Listgarten, J.; Jhangri, G.S.; Saunders, L.D.; Damaraju, S.; Cass, C. Lymphovascular invasion is associated with poor survival in gastric cancer: An application of gene-expression and tissue array techniques. Ann. Surg. 2006, 243, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander-Sefre, F.; Nibbs, R.; Rafferty, T.; Ayhan, A.; Singh, N.; Jacobs, I. Clinical Value of Immunohistochemically Detected Lymphatic and Vascular Invasions in Clinically Staged Endometrioid Endometrial Cancer. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2009, 19, 1074–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiser, M.R.; Landmann, R.G.; Kattan, M.W.; Gonen, M.; Shia, J.; Chou, J.; Paty, P.B.; Guillem, J.G.; Temple, L.K.; Schrag, D.; et al. Individualized Prediction of Colon Cancer Recurrence Using a Nomogram. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginzberg, H.H.; Cherapanov, V.; Dong, Q.; Cantin, A.; McCulloch, C.A.; Shannon, P.T.; Downey, G.P. Neutrophil-mediated epithelial injury during transmigration: Role of elastase. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2001, 281, G705–G717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-M.; Russell, A.; Hellawell, G. Predictive value of pretreatment inflammation-based prognostic scores (neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio, and lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio) for invasive bladder carcinoma. Korean J. Urol. 2015, 56, 749–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novara, G.; Svatek, R.S.; Karakiewicz, P.I.; Skinner, E.; Ficarra, V.; Fradet, Y.; Lotan, Y.; Isbarn, H.; Capitanio, U.; Bastian, P.J.; et al. Soft Tissue Surgical Margin Status is a Powerful Predictor of Outcomes After Radical Cystectomy: A Multicenter Study of More Than 4,400 Patients. J. Urol. 2010, 183, 2165–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.E.; Byun, S.-S.; Hong, S.K.; Chang, I.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Gill, M.C.; Song, S.H.; Kim, K.T. Significance of cancer involvement at the ureteral margin detected on routine frozen section analysis during radical cystectomy. Urol. Int. 2006, 77, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, X.; Li, T.; Ling, F.; Yang, D.; Hou, L.; Li, F.; Tan, W. Impact of surgical margin status on the outcome of bladder cancer treated by radical cystectomy: A meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2016, 8, 17258–17269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.Y.; Qin, Y.Y.; Qin, J.Q.; Zhang, X.; Lin, F.Q. Diagnostic value of derived neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in patients with ovarian cancer. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2019, 33, e22833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.T.; Lam, W.W.; Yu, M.Y.; Cheung, T.H.; Metreweli, C. Comparison of dynamic helical CT and dynamic MR imaging in the evaluation of pelvic lymph nodes in cervical carcinoma. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2000, 175, 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Choi, B.I.; Lee, H.P.; Kang, S.B.; Choi, Y.M.; Han, M.C.; Kim, C.W. Uterine cervical carcinoma: Comparison of CT and MR findings. Radiology 1990, 175, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, T.B.L. Optimizing the diagnosis of pelvic lymph node metastasis in bladder cancer using computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. Cancer Commun. 2018, 38, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buzby, G.P.; Williford, W.O.; Peterson, O.L.; Crosby, L.O.; Page, C.P.; Reinhardt, G.F.; Mullen, J.L. A randomized clinical trial of total parenteral nutrition in malnourished surgical patients: The rationale and impact of previous clinical trials and pilot study on protocol design. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1988, 47 (Suppl. 2), 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robbins, L.J. Evaluation of weight loss in the elderly. Geriatrics 1989, 44, 31–34, 37. [Google Scholar]
- Komatsu, M.; Okazaki, M.; Tsuchiya, K.; Kawaguchi, H.; Nitta, K. Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index Is a Simple Predictor of Mortality in Chronic Hemodialysis Patients. Blood Purif. 2015, 39, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, H.; Yang, J.; Jiang, L.; Yang, J.; Wu, H.; Wen, T.; Yan, L. Geriatric nutritional risk index predicts prognosis after hepatectomy in elderly patients with hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, H.; Tei, H.; Fujisawa, M. Geriatric Nutrition Risk Index is an Important Predictor of CancerSpecific Survival, but not Recurrence-Free Survival, in Patients Undergoing Surgical Resection for NonMetastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma. Curr. Urol. 2017, 10, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, T.; Hatakeyama, S.; Narita, S.; Takahashi, M.; Sakurai, T.; Kawamura, S.; Hoshi, S.; Ishida, M.; Kawaguchi, T.; Ishidoya, S.; et al. Impact of nutritional status on the prognosis of patients with metastatic hormone-naïve prostate cancer: A multicenter retrospective cohort study in Japan. World J. Urol. 2018, 37, 1827–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | Total |
|---|---|
| Patients, n | 491 |
| Gender, n (%) | |
| Male | 387 (78.8%) |
| Female | 104 (21.2%) |
| Age, median (IQR) | 67.00 (62.00–72.00) |
| Body mass index, median (IQR) | 25.74(23.44–28.08) |
| Tobacco smoking, n (%) | |
| No | 158 (32.2%) |
| Current/former smoker | 333 (67.8%) |
| ECOG, n (%) | |
| 0 | 202 (41.1%) |
| 1 | 242 (49.3%) |
| 2 | 40 (8.1%) |
| 3 | 7 (1.4%) |
| Pathological stage, n (%) | |
| pT0 | 13 (2.6%) |
| pTa + pTis | 12 (2.4%) |
| pT1 | 37 (7.5%) |
| pT2 | 160 (32.6%) |
| pT3 | 154 (31.4%) |
| pT4 | 115 (23.4%) |
| Muscle invasion, n (%) | |
| NMIBC | 49 (10.3%) |
| MIBC | 429 (89.7%) |
| Histological type, n (%) | |
| Urothelial cancer (UC) | 456 (95.4%) |
| Other type of cancer | 22 (4.6%) |
| Lymphovascular invasion, n (%) | |
| Present | 334 (70.6%) |
| Absent | 139 (29.4%) |
| Surgical margins, n (%) | |
| Positive | 76 (15.5%) |
| Negative | 415 (84.5%) |
| Lymph nodes, n (%) | |
| Positive | 81 (23.2%) |
| Negative | 268 (76.8%) |
| Parameter | Median (IQR) |
|---|---|
| Hemoglobin (g/L) | 126.00 (107.00–141.00) |
| Leukocytes (×109/L) | 7.60 (6.20–9.20) |
| Neutrophils (×109/L) | 4.70 (3.60–6.10) |
| Lymphocytes (×109/L) | 1.80 (1.40–2.25) |
| Monocytes (×109/L) | 0.60 (0.47–0.75) |
| Platelets (×109/L) | 245.00 (203.00–307.00) |
| NLR | 2.68 (1.84–3.80) |
| dNLR | 1.71(1.26–2.38) |
| SII | 638.08 (420.00–1032.77) |
| SIRI | 1.53 (0.97–2.45) |
| LMR | 3.08 (2.26–4.00) |
| PLR | 135.90 (107.27–190.00) |
| Albumin (g/L) | 40.00 (37.00–43.00) |
| PNI | 49.00 (45.00–53.00) |
| GNRI | 107.99 (100.95–115.33) |
| Parameter | Correlation Coefficient a | p Value |
|---|---|---|
| NLR | 0.225 | <0.001 |
| dNLR | 0.228 | <0.001 |
| SII | 0.234 | <0.001 |
| SIRI | 0.227 | <0.001 |
| LMR | −0.152 | 0.001 |
| PLR | 0.174 | <0.001 |
| PNI | −0.182 | <0.001 |
| GNRI | −0.155 | 0.001 |
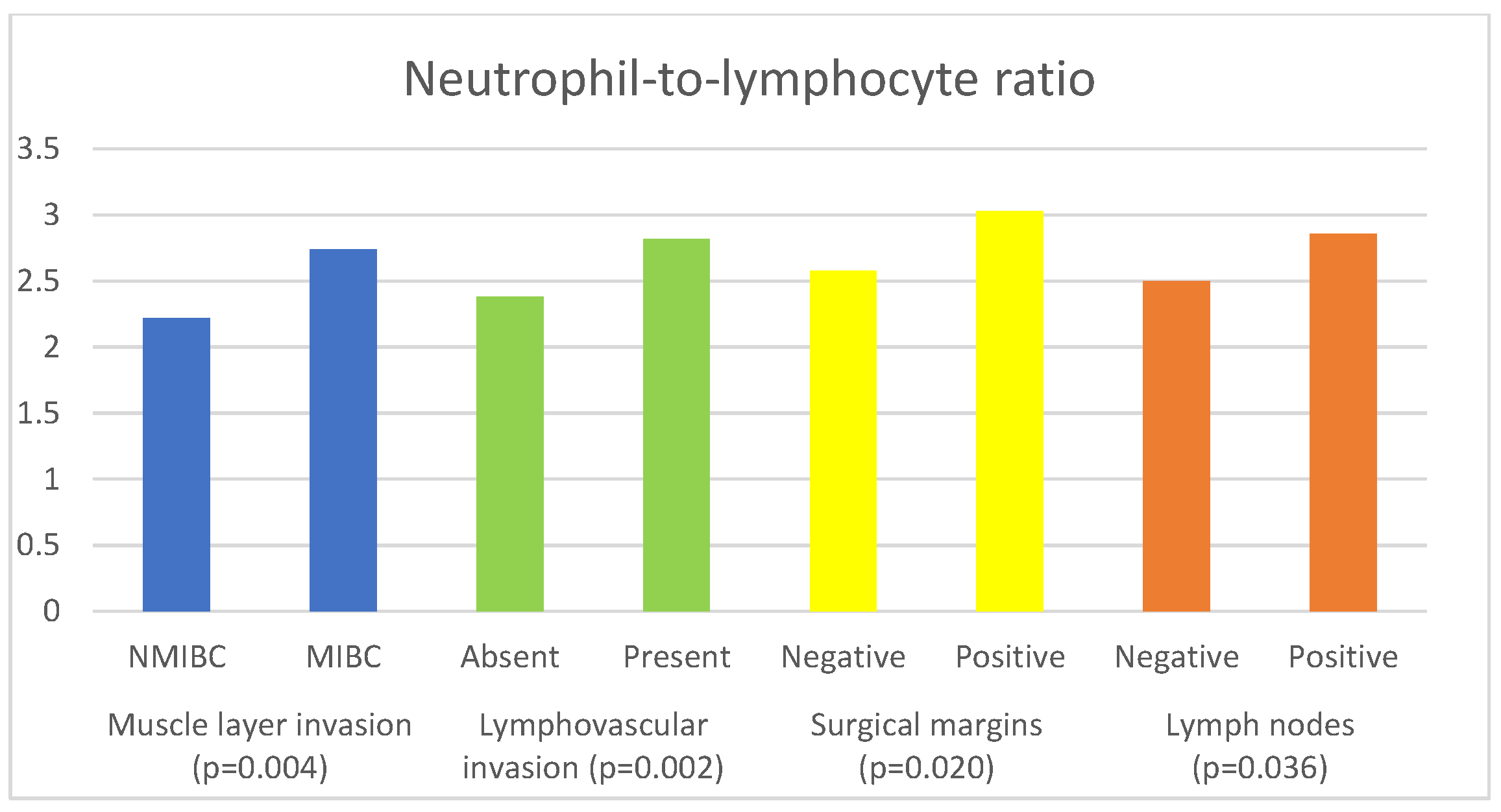
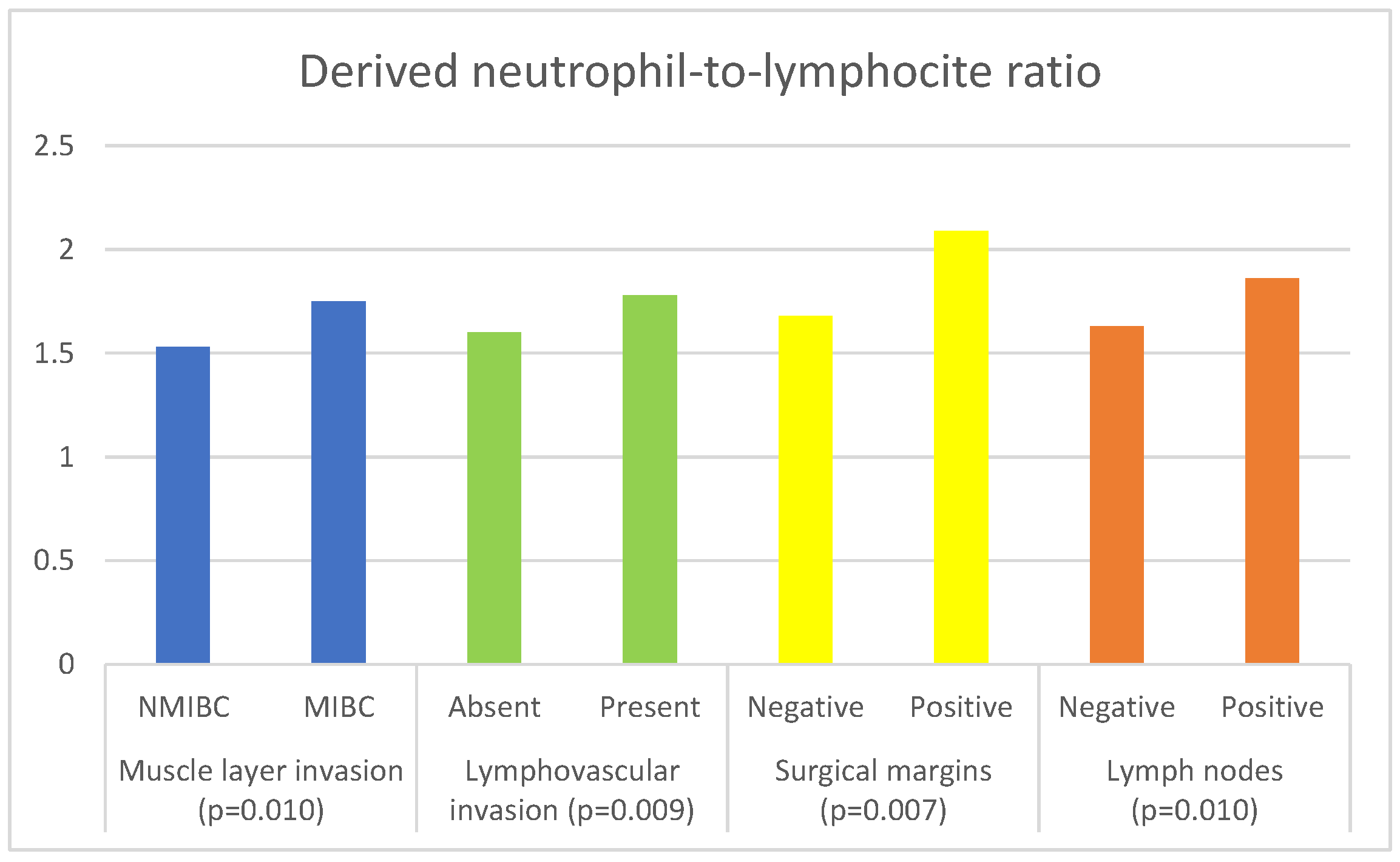
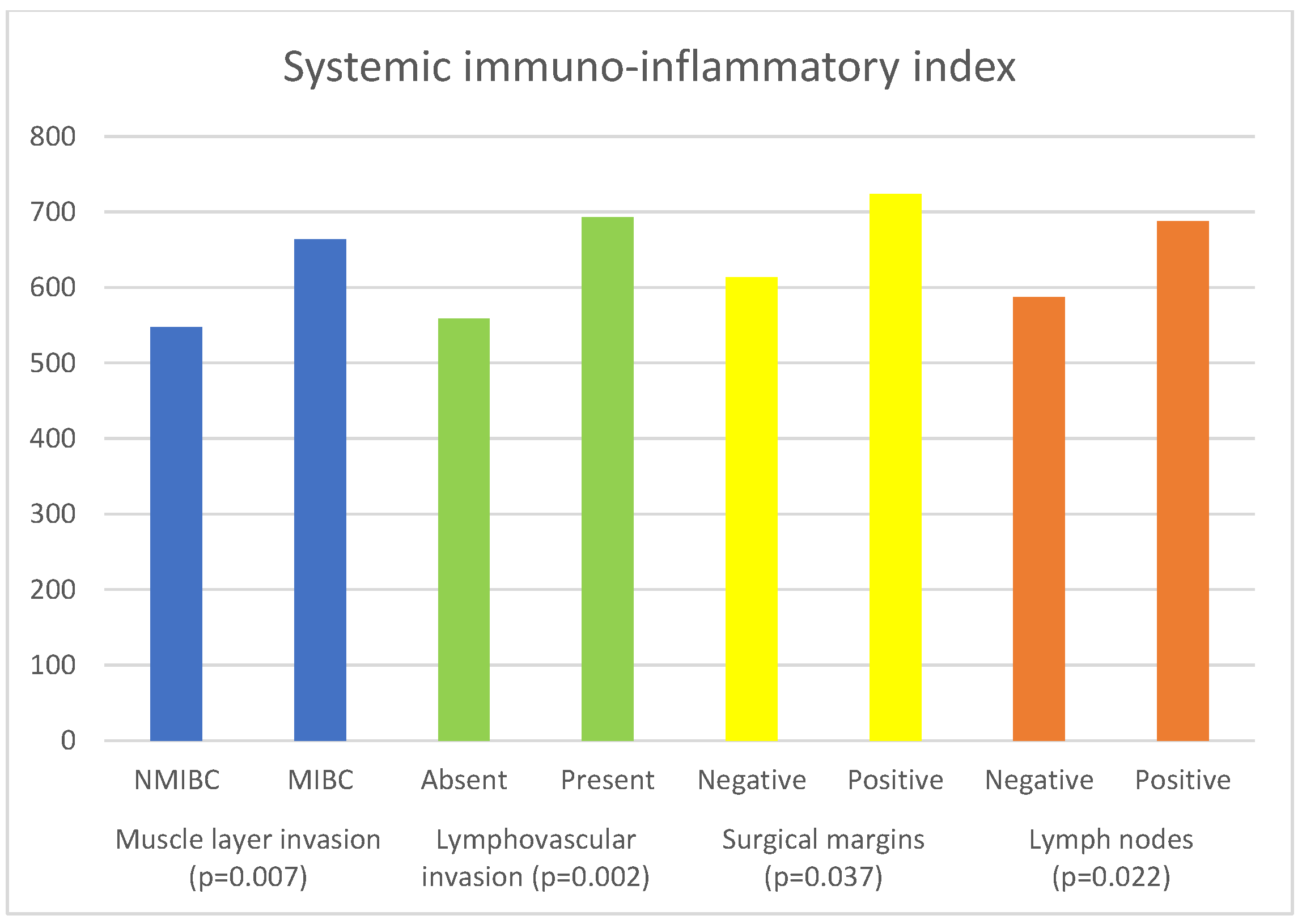
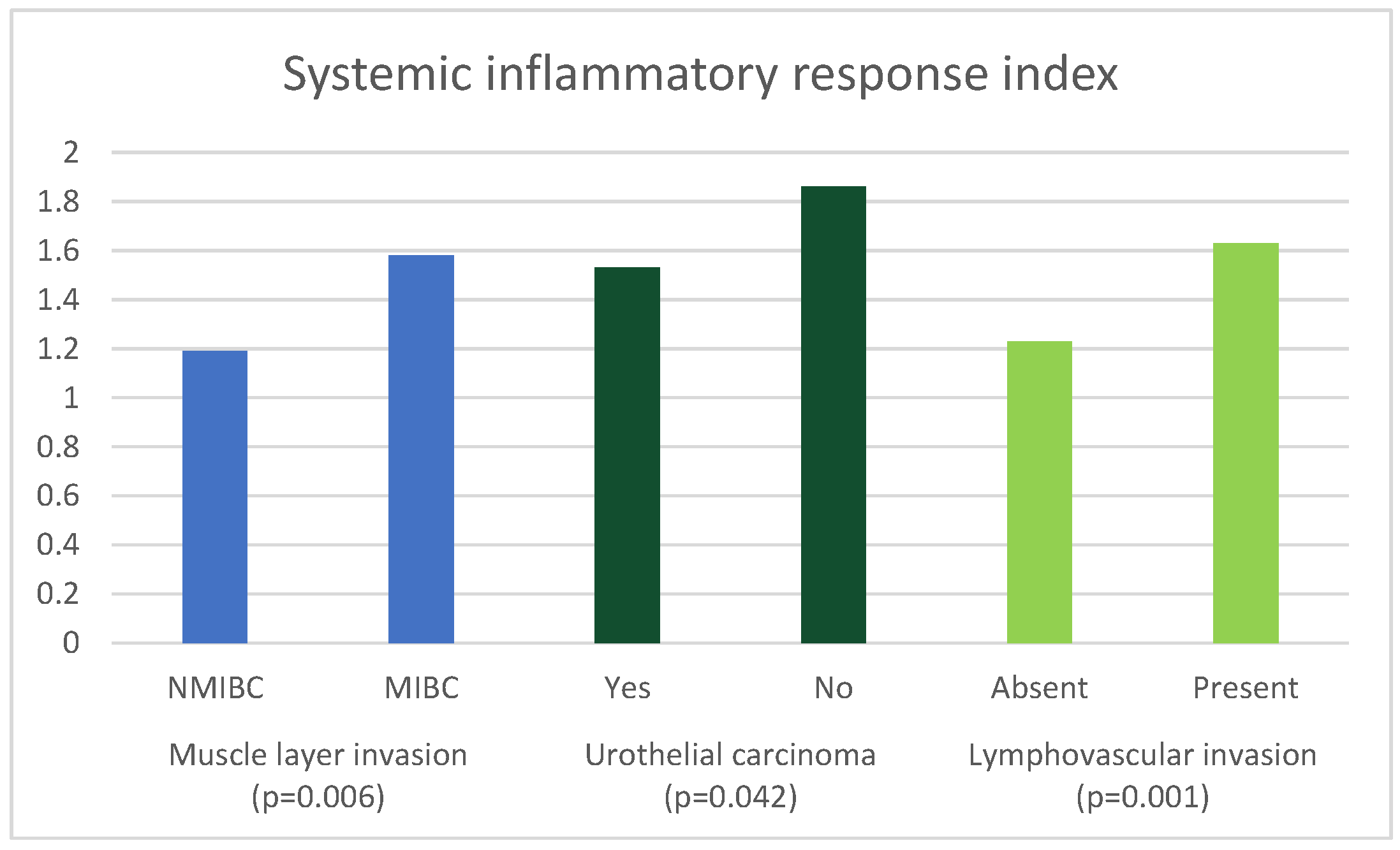
| Parameter | Muscle Invasion | Median (IQR) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| NLR | NMIBC | 2.22 (1.55–2.92) | 0.004 a |
| MIBC | 2.74 (1.87–3.92) | ||
| dNLR | NMIBC | 1.53 (1.22–1.89) | 0.010 a |
| MIBC | 1.75 (1.29–2.44) | ||
| SII | NMIBC | 547.62 (340.20–739.6 | 0.007 a |
| MIBC | 663.88 (441.37–1074.73) | ||
| SIRI | NMIBC | 1.19 (0.76–1.97) | 0.006 a |
| MIBC | 1.58 (1.01–2.53) | ||
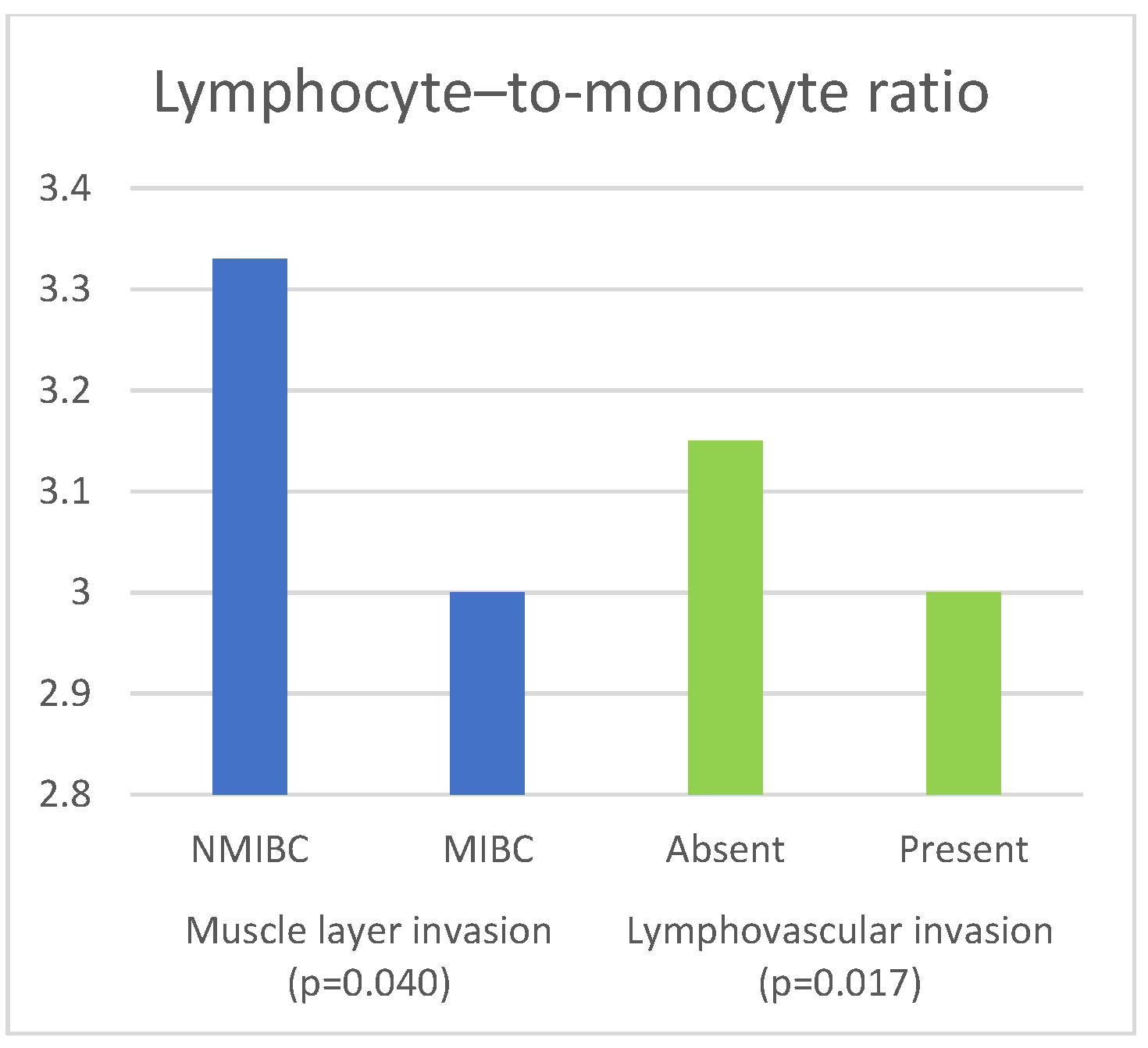
| LMR | NMIBC | 3.33 (2.40–4.25) | 0.040 a |
| MIBC | 3.00 (2.25–4.00) | ||
| PLR | NMIBC | 125.88 (97.92–165.12) | 0.075 a |
| MIBC | 137.83 (108.30–195.06) | ||
| PNI | NMIBC | 51.00 (47.50–54.60) | 0.062 b |
| MIBC | 48.50 (45.00–52.80) | ||
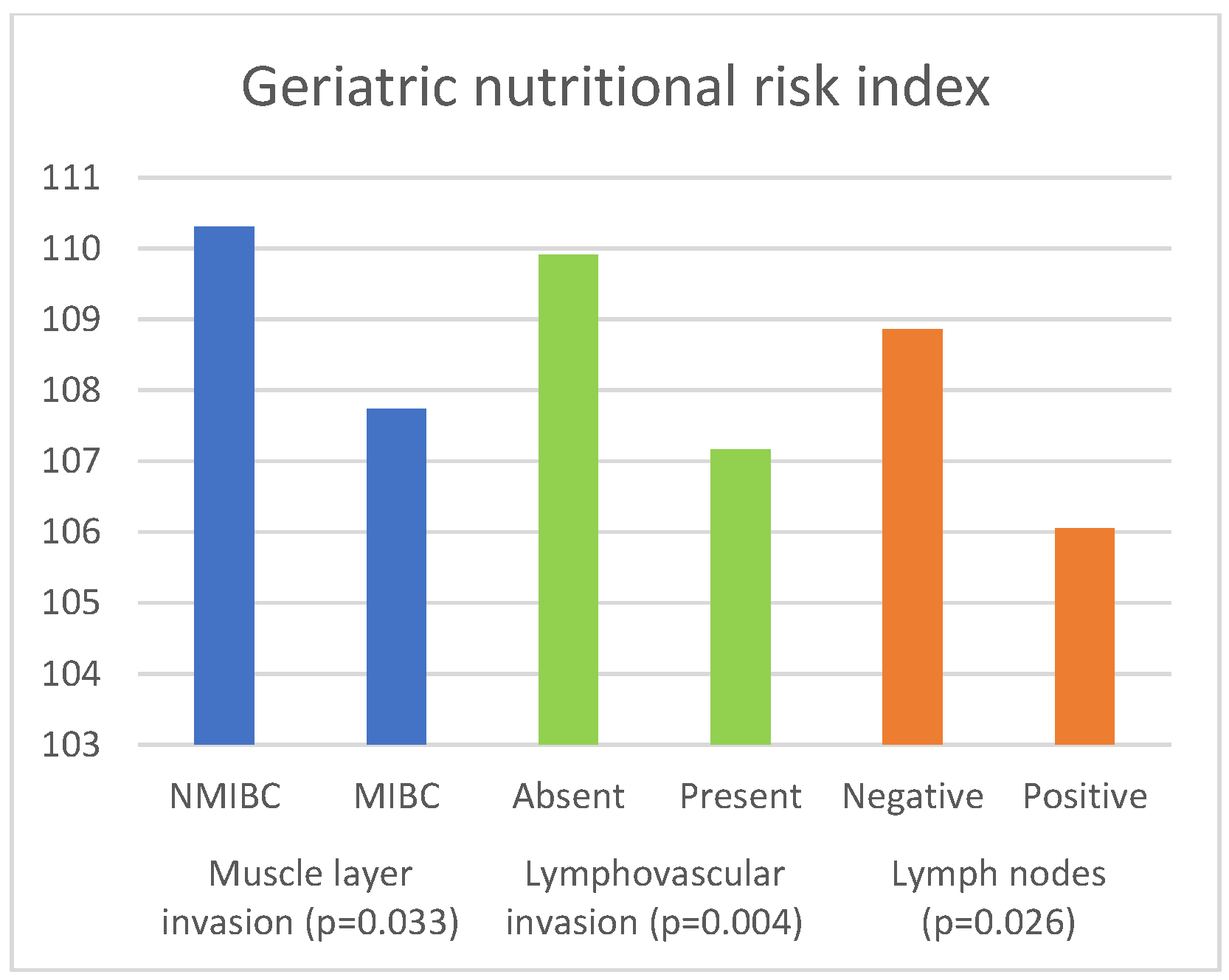
| GNRI | NMIBC | 110.31 (103.37–115.99) | 0.033 a |
| MIBC | 107.74 (100.87–114.97) |
| Parameter | Urothelial Carcinoma | Median (IQR) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| NLR | Yes | 2.67 (1.83–3.75) | 0.105 a |
| No | 3.14 (2.16–4.08) | ||
| dNLR | Yes | 1.73 (1.26–2.37) | 0.176 a |
| No | 1.94 (1.59–2.45) | ||
| SII | Yes | 635.50 (423.41–1027.10) | 0.283 a |
| No | 774.86 (490.50–1093.47) | ||
| SIRI | Yes | 1.53 (0.98–2.40) | 0.042 a |
| No | 1.86 (1.24–3.24) | ||
| LMR | Yes | 3.08 (2.31–4.00) | 0.104 a |
| No | 2.37 (1.75–3.75) | ||
| PLR | Yes | 135.89 (107.48–189.09) | 0.744 a |
| No | 151.31 (108.89–195.26) | ||
| PNI | Yes | 49.00 (45.00–53.00) | 0.428 a |
| No | 48.78 (45.50–53.20) | ||
| GNRI | Yes | 107.84 (100.93–115.04) | 0.697 b |
| No | 108.55 (101.18–117.77) |
| Parameter | Lymphovascular Invasion | Median (IQR) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| NLR | Absent | 2.38 (1.63–3.26) | 0.002 a |
| Present | 2.82 (1.93–4.09) | ||
| dNLR | Absent | 1.60 (1.20–2.09) | 0.009 a |
| Present | 1.78 (1.31–2.45) | ||
| SII | Absent | 558.54 (376.18–893.33) | 0.002 a |
| Present | 693.00 (450.78–1095.88) | ||
| SIRI | Absent | 1.23 (0.86–2.07) | 0.001 a |
| Present | 1.63 (1.02–2.57) | ||
| LMR | Absent | 3.15 (2.49–4.25) | 0.017 a |
| Present | 3.00 (2.20–4.00) | ||
| PLR | Absent | 132.50 (100.91–172.00) | 0.161 a |
| Present | 137.93 (108.57–197.50) | ||
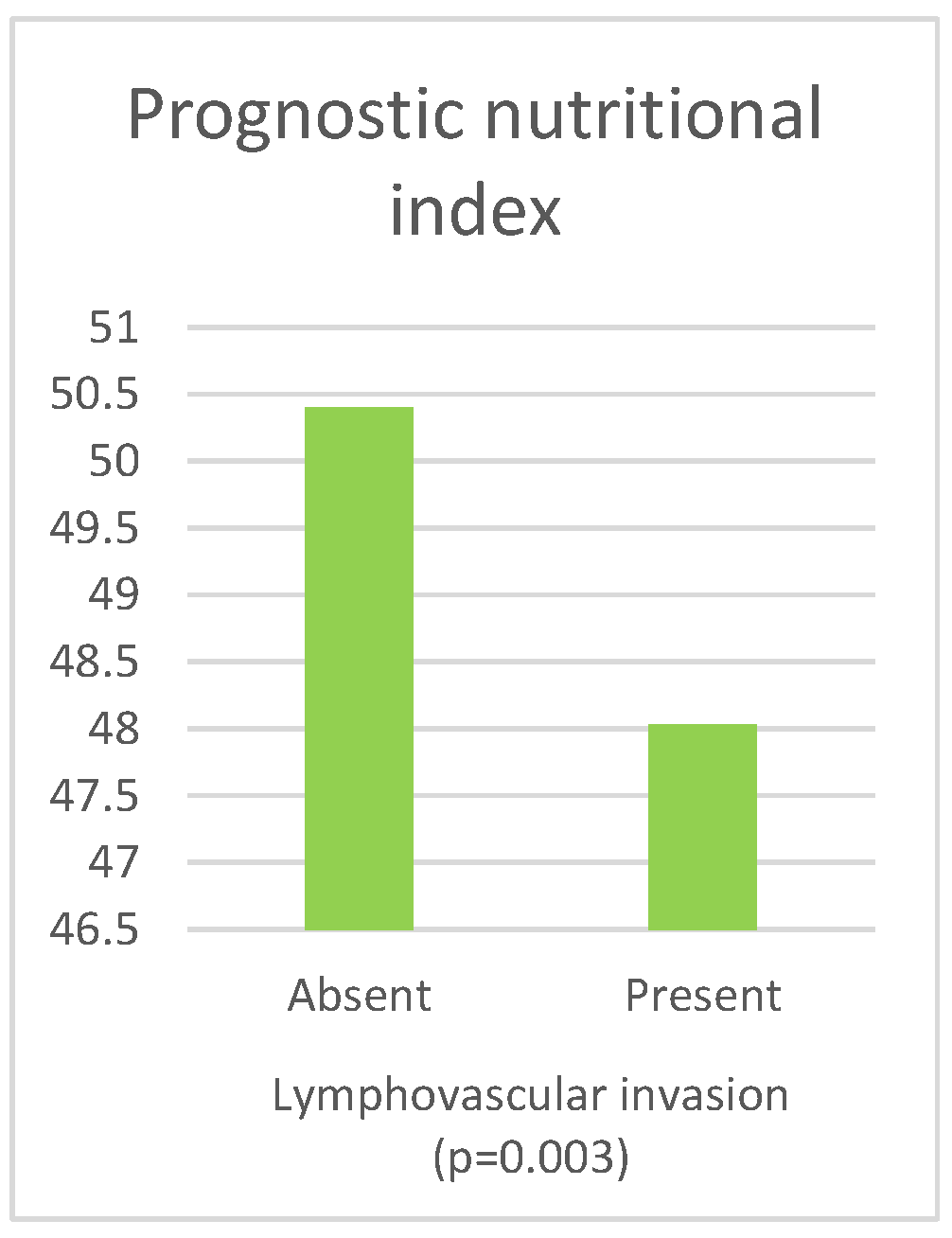
| PNI | Absent | 50.40 (46.55–53.50) | 0.003 b |
| Present | 48.03 (44.50–52.50) | ||
| GNRI | Absent | 109.91 (104.29–116.16) | 0.004 b |
| Present | 107.17 (100.11–114.72) |
| Parameter | Surgical Margin | Median | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| NLR | Negative | 2.58 (1.79–3.69) | 0.020 a |
| Positive | 3.03 (2.21–4.29) | ||
| dNLR | Negative | 1.68 (1.24–2.31) | 0.007 a |
| Positive | 2.09 (1.48–2.58) | ||
| SII | Negative | 613.60 (409.09–1005.81) | 0.037 a |
| Positive | 723.67 (502.43–1221.01) | ||
| SIRI | Negative | 1.50 (0.97–2.40) | 0.119 a |
| Positive | 1.69 (1.19–3.13) | ||
| LMR | Negative | 3.11 (2.32–4.00) | 0.659 a |
| Positive | 3.00 (2.14–4.18) | ||
| PLR | Negative | 134.88 (106.94–186.11) | 0.525 a |
| Positive | 146.93 (107.87–197.08) | ||
| PNI | Negative | 49.00 (45.40–53.00) | 0.440 b |
| Positive | 48.28 (44.15–52.80) | ||
| GNRI | Negative | 108.40 (101.29–115.33) | 0.328 b |
| Positive | 105.57 (100.24–115.12) |
| Parameter | Lymph Nodes | Median (IQR) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| NLR | Negative | 2.50 (1.72–3.54) | 0.036 a |
| Positive | 2.86 (2.09–4.03) | ||
| dNLR | Negative | 1.63 (1.21–2.23) | 0.010 a |
| Positive | 1.86 (1.46–2.58) | ||
| SII | Negative | 587.32 (394.27–951.27) | 0.022 a |
| Positive | 687.50 (510.00–1108.42) | ||
| SIRI | Negative | 1.49 (0.94–2.36) | 0.192 a |
| Positive | 1.63 (1.02–2.56) | ||
| LMR | Negative | 3.13 (2.33–4.15) | 0.613 a |
| Positive | 3.12 (2.33–4.00) | ||
| PLR | Negative | 131.51 (101.12–174.07) | 0.084 a |
| Positive | 143.57 (117.00–195.26) | ||
| PNI | Negative | 49.45 (45.75–53.45) | 0.351 b |
| Positive | 48.50 (45.70–52.10) | ||
| GNRI | Negative | 108.86 (103.90–115.34) | 0.026 b |
| Positive | 106.05 (100.01–112.76) |
| Parameter | Muscle Layer Invasion | Histological Type | Lymphovascular Invasion | Positive Surgical Margins | Positive Lymph Nodes | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | p | OR (95% CI) | p | OR (95% CI) | p | OR (95% CI) | p | OR (95% CI) | p | |
| Gender (female) | 0.693 (0.346–1.388) | 0.301 | 1.449 (0.546–3.845) | 0.456 | 1.060 (0.634–1.772) | 0.825 | 2.544 (1.480–4.373) | 0.001 | 1.443 (0.786–2.647) | 0.237 |
| Age | 1.009 (0.964–1.056) | 0.711 | 0.942 (0.891–0.996) | 0.034 | 0.980 (0.950–1.012) | 0.225 | 0.968 (0.934–1.002) | 0.068 | 0.984 (0.947–1.022) | 0.403 |
| ECOG | 1.472 (0.802–2.701) | 0.212 | 1.344 (0.669–0.698) | 0.406 | 1.332 (0.892–1.990) | 0.160 | 1.247 (0.806–1.928) | 0.321 | 1.065 (0.661–1.716) | 0.796 |
| NLR | 0.946 (0.385–2.328) | 0.904 | - | - | 1.201 (0.763–1.890) | 0.428 | 0.796 (0.561–1.130) | 0.202 | 0.915 (0.743–1.126) | 0.400 |
| dNLR | 1.168 (0.313–4.349) | 1.168 | - | - | 0.718 (0.373–1.380) | 0.320 | 1.908 (1.058–3.443) | 0.032 | 1.612 (0.997–2.607) | 0.052 |
| SII | 1.001 (0.999–1.002) | 0.426 | - | - | 1.000 (0.999–1.000) | 0.534 | 1.000 (0.999–1.000) | 0.760 | 1.000 (0.999–1.000) | 0.444 |
| SIRI | 1.248 (0.742–2.098) | 0.404 | 1.033 (0.937–1.139) | 0.511 | 1.332 (1.006–1.765) | 0.045 | - | - | - | |
| LMR | 1.064 (0.866–1.306) | 0.554 | - | - | 1.135 (0.946–1.362) | 0.127 | - | - | - | |
| PNI | - | - | - | - | 0.971 (0.919–1.027) | 0.309 | - | - | - | |
| GNRI | 0.999 (0.968–1.030) | 0.932 | - | - | 0.985 (0.959–1.012) | 0.289 | - | - | 0.971 (0.945–0.996) | 0.026 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Prijovic, N.; Acimovic, M.; Santric, V.; Stankovic, B.; Nikic, P.; Vukovic, I.; Soldatovic, I.; Nale, D.; Kovacevic, L.; Nale, P.; et al. Predictive Value of Inflammatory and Nutritional Indexes in the Pathology of Bladder Cancer Patients Treated with Radical Cystectomy. Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 2582-2597. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30030197
Prijovic N, Acimovic M, Santric V, Stankovic B, Nikic P, Vukovic I, Soldatovic I, Nale D, Kovacevic L, Nale P, et al. Predictive Value of Inflammatory and Nutritional Indexes in the Pathology of Bladder Cancer Patients Treated with Radical Cystectomy. Current Oncology. 2023; 30(3):2582-2597. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30030197
Chicago/Turabian StylePrijovic, Nebojsa, Miodrag Acimovic, Veljko Santric, Branko Stankovic, Predrag Nikic, Ivan Vukovic, Ivan Soldatovic, Djordje Nale, Luka Kovacevic, Petar Nale, and et al. 2023. "Predictive Value of Inflammatory and Nutritional Indexes in the Pathology of Bladder Cancer Patients Treated with Radical Cystectomy" Current Oncology 30, no. 3: 2582-2597. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30030197
APA StylePrijovic, N., Acimovic, M., Santric, V., Stankovic, B., Nikic, P., Vukovic, I., Soldatovic, I., Nale, D., Kovacevic, L., Nale, P., Marinkovic, A., & Babic, U. (2023). Predictive Value of Inflammatory and Nutritional Indexes in the Pathology of Bladder Cancer Patients Treated with Radical Cystectomy. Current Oncology, 30(3), 2582-2597. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30030197





