Prognostic Relevance of PDL1 and CA19-9 Expression in Gallbladder Cancer vs. Inflammatory Lesions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics, Consent, and Sample Collection
2.2. ELISA Assay
2.3. RT-PCR
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
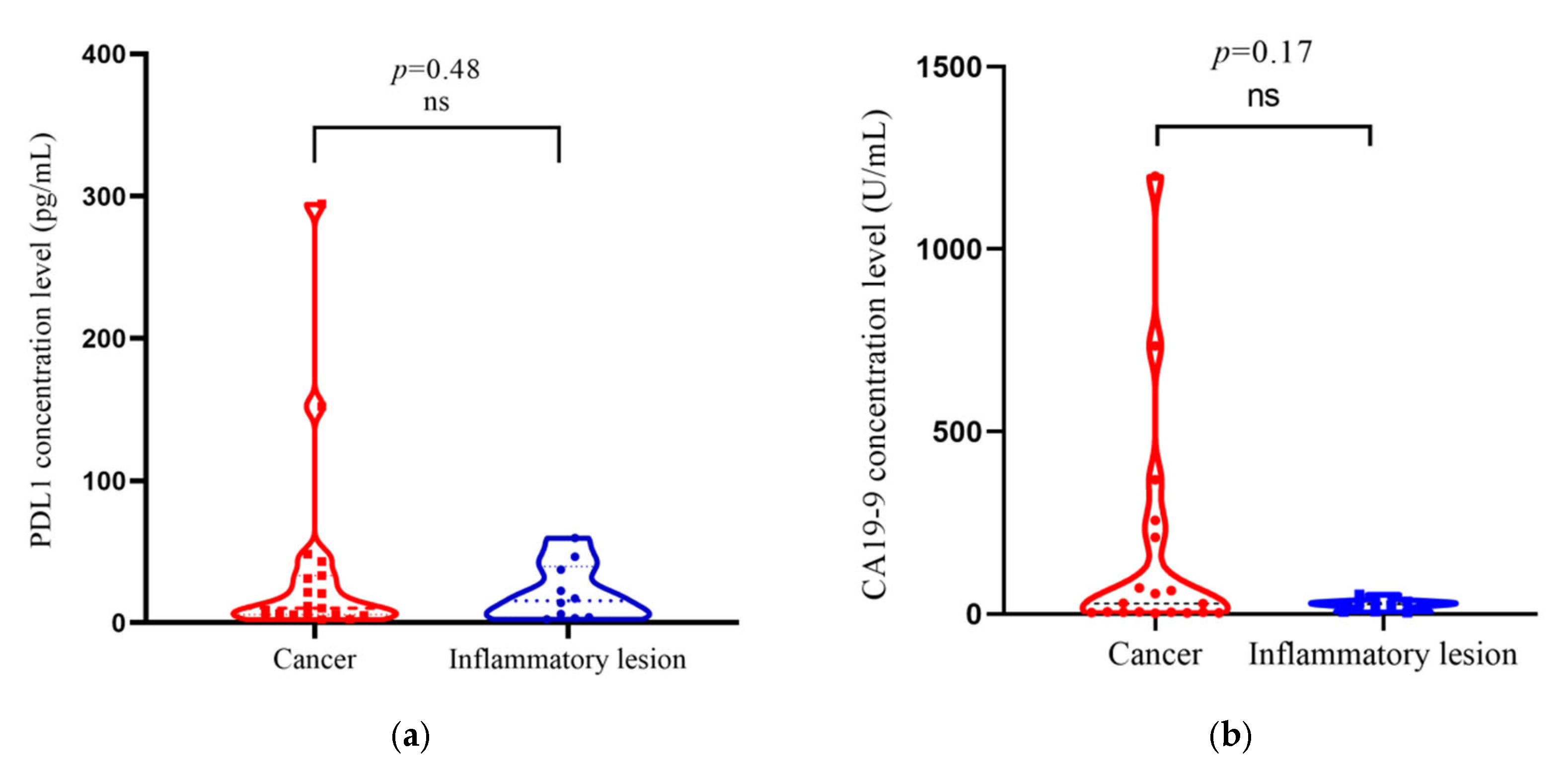
3.1. PDL1 and CA19-9 Concentration in Cancer Casesand Inflammatory Lesion of Gallbladder
3.2. Clinico-Pathological Correlations of Gallbladder Cancer/Inflammatory Cases with PDL1 and CA19-9 Concentration Level
3.2.1. PDL1
3.2.2. CA19-9
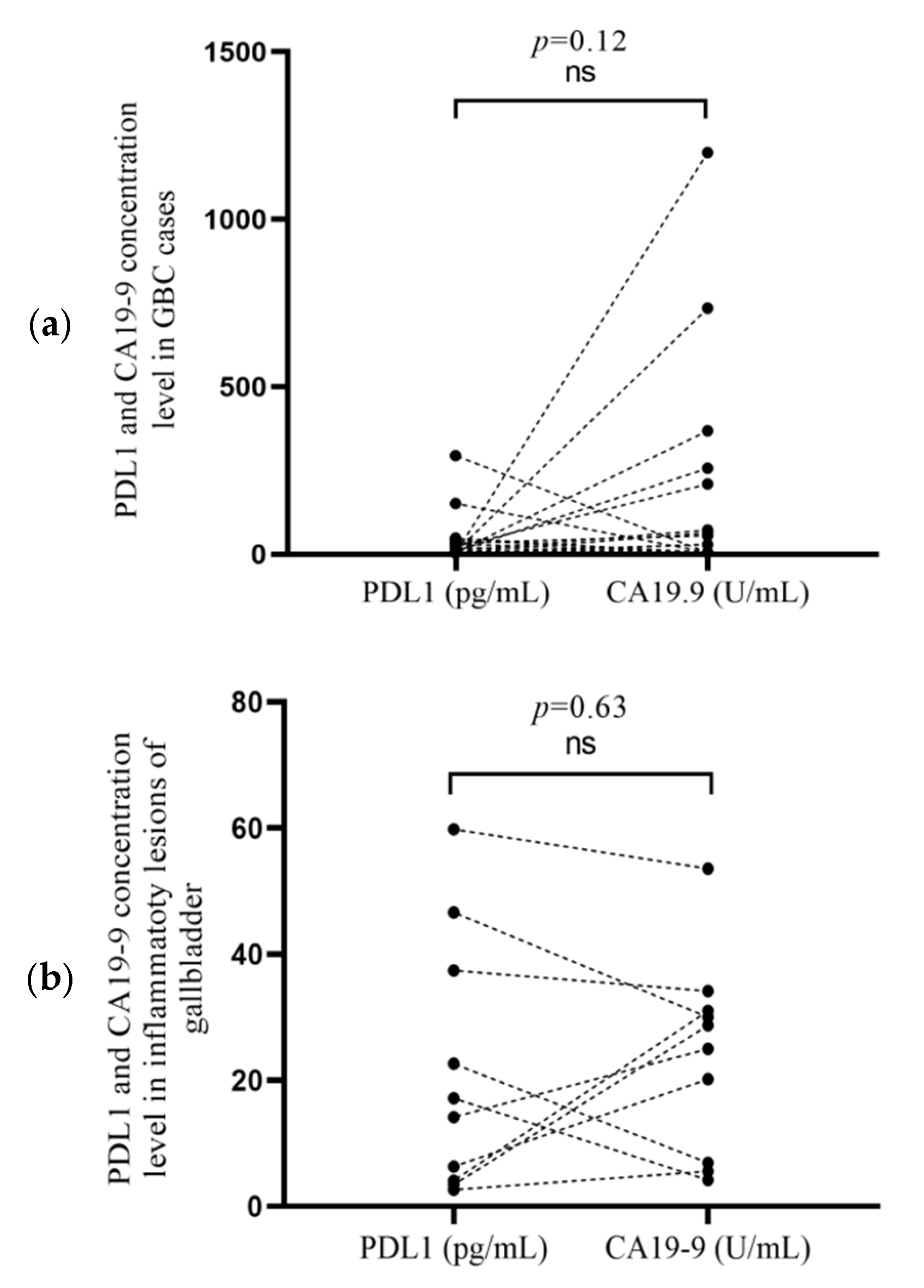
3.3. Correlation of PDL1 and CA19-9 Concentrationsin Cancer Cases and Inflammatory Lesion
3.4. Correlation of PDL1 Protein Concentration with Relative PDL1 mRNA Expression
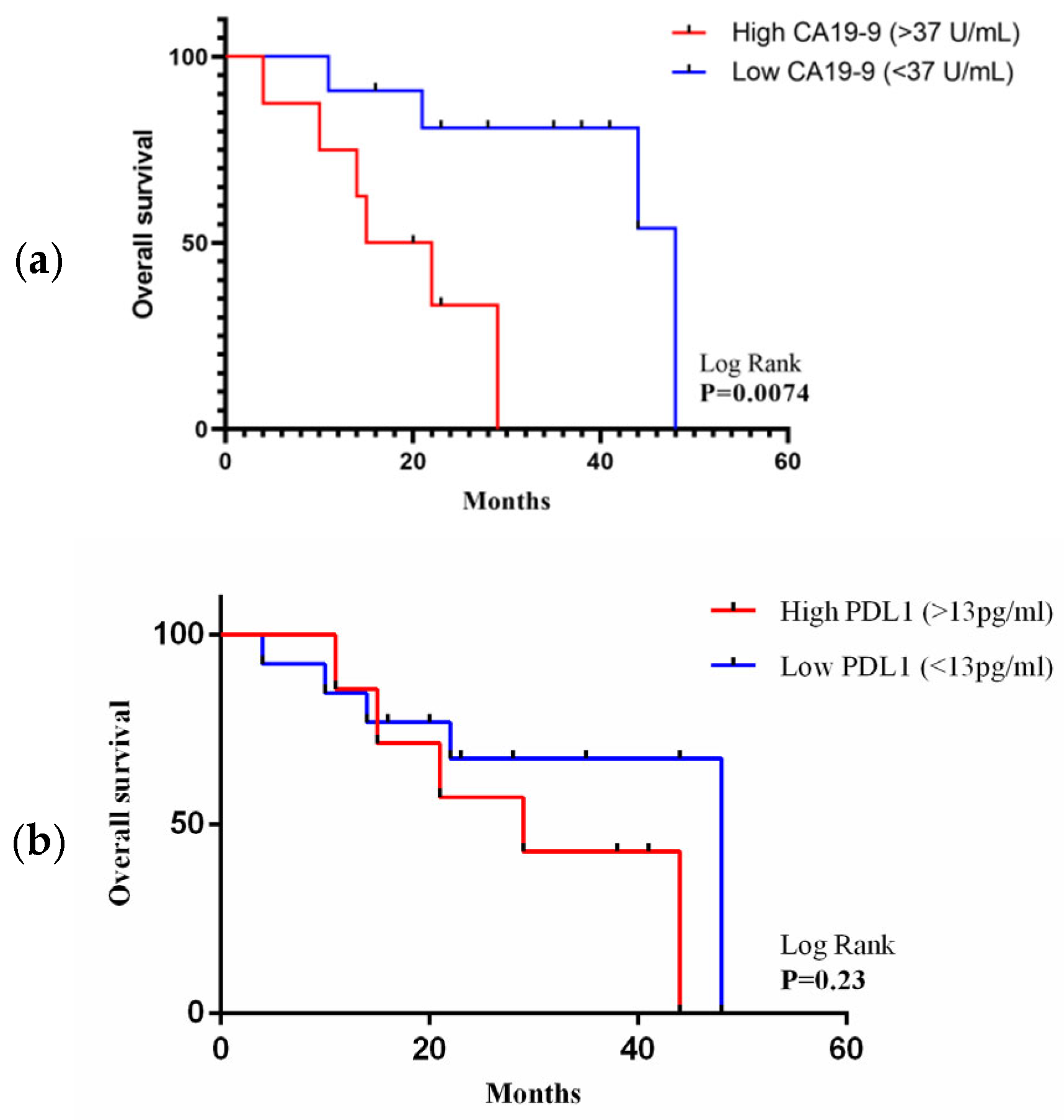
3.5. Association of PDL1 and CA19-9 Concentration with Overall Survival
3.6. Univariate and Multivariate Analysis of Prognostic Factors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mehrotra, B. Gallbladder Cancer: Epidemiology, Risk Factors, Clinical Features, and Diagnosis. Up Date 2013. Available online: https://medilib.ir/uptodate/show/2491 (accessed on 24 January 2023).
- Goetze, T.O. Gallbladder carcinoma: Prognostic factors and therapeutic options. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 12211–12217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, C.H.E.; Lau, W.Y. Gallbladder cancer—A comprehensive review. Surgeon 2008, 6, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldin, R.D.; Roa, J.C. Gallbladder cancer: A morphological and molecular update. Histopathology 2009, 55, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albores-Saavedra, J.; Tuck, M.; McLaren, B.K.; Carrick, K.S.; Henson, D.E. Papillary carcinomas of the gallbladder: Analysis of noninvasive and invasive types. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2005, 129, 905–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hundal, R.; Shaffer, E.A. Gallbladder cancer: Epidemiology and outcome. Clin. Epidemiol. 2014, 6, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, U.; Bush, N.; Kalsi, D.; Popli, P.; Kapoor, V.K. Epidemiology of gallbladder cancer in India. Chin. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 8, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roa, I.; Ibacache, G.; Roa, J.; Araya, J.; De Aretxabala, X.; Muñoz, S. Gallstones and gallbladder cancer-volume and weight of gallstones are associated with gallbladder cancer: A case-control study. J. Surg. Oncol. 2006, 93, 624–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wistuba, I.I.; Gazdar, A.F. Gallbladder cancer: Lessons from a rare tumour. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 695–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilgrim, C.H.C.; Groeschl, R.T.; Christians, K.K.; Gamblin, T.C. Modern perspectives on factors predisposing to the development of gallbladder cancer. HPB 2013, 15, 839–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsing, A.W.; Bai, Y.; Andreotti, G.; Rashid, A.; Deng, J.; Chen, J.; Goldstein, A.M.; Han, T.-Q.; Shen, M.-C.; Fraumeni, J.F., Jr.; et al. Family history of gallstones and the risk of biliary tract cancer and gallstones: A population-based study in Shanghai, China. Int. J. Cancer 2007, 121, 832–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinidis, I.T.; Deshpande, V.; Genevay, M.; Berger, D.; Castillo, C.F.-D.; Tanabe, K.K.; Zheng, H.; Lauwers, G.Y.; Ferrone, C.R. Trends in presentation and survival for gallbladder cancer during a period of more than 4 decades: A single-institution experience. Arch. Surg. 2009, 144, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Agarwal, A.; Gupta, V.; Singh, P.K.; Pantola, C.; Amit, S. Expression and clinicopathological significance of estrogen and progesterone receptors in gallbladder cancer. Gastrointest. Cancer Res. 2012, 5, 41–47. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, M.; Sakhuja, P.; Singh, S.; Agarwal, A. P53 and beta-catenin expression in gallbladder tissues and correlation with tumor progression in gallbladder cancer. Saudi J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, K.-I.; Kijima, H.; Imaizumi, T.; Hirabayashi, K.; Matsuyama, M.; Yazawa, N.; Dowaki, S.; Tobita, K.; Ohtani, Y.; Tanaka, M.; et al. Clinical significance of wall invasion pattern of subserosa-invasive gallbladder carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2012, 28, 1531–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Hu, Y.; Li, Y.; Shao, R.; Liu, F.; Liu, Y. Overview of current targeted therapy in gallbladder cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, K.; Kim, M.; Kim, Y.M.; Suh, J.H.; Cha, H.J.; Choi, H.J. Programmed death-ligand 1 expression and its correlation with clinicopathological parameters in gallbladder cancer. J. Pathol. Transl. Med. 2020, 54, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fluss, R.; Faraggi, D.; Reiser, B. Estimation of the Youden Index and its associated cutoff point. Biom. J. 2005, 47, 458–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Tong, M.; Hu, H.; Huang, C.; Li, D. Diagnostic value of CA 19-9 and carcinoembryonic antigen for pancreatic cancer: A meta-analysis. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2018, 2018, 8704751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neyaz, A.; Husain, N.; Kumari, S.; Gupta, S.; Shukla, S.; Arshad, S.; Anand, N.; Chaturvedi, A. Clinical relevance of PDL1 expression in gallbladder cancer: A potential target for therapy. Histopathology 2018, 73, 622–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachan, A.; Saluja, S.S.; Nekarakanti, P.K.; Nimisha; Mahajan, B.; Nag, H.H.; Mishra, P.K. Raised CA19-9 and CEA have prognostic relevance in gallbladder carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bind, M.; Mishra, R.; Kumar, V.; Misra, V.; Singh, P. Serum CA 19-9 and CA 125 as a diagnostic marker in carcinoma of gallbladder. Indian J. Pathol. Microbiol. 2021, 64, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, A.; Huminer, D. The role of estrogen receptors in the development of gallstones and gallbladder cancer. Med. Hypotheses 1991, 36, 259–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singletary, B.K.; van Thiel, D.H.; Eagon, P.K. Estrogen and progesterone receptors in human gallbladder. Hepatology 1986, 6, 574–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hould, F.S.; Fried, G.M.; Fazekas, A.G.; Tremblay, S.; Mersereau, W.A. Progesterone receptors regulate gallbladder motility. J. Surg. Res. 1988, 45, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalgnault, P.G.; Fazekas, A.G.; Rosenthall, L.; Fried, G.M. Relationship between gallbladder contraction and progesterone receptors in patients will gallstones. Am. J. Surg. 1988, 155, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskaran, V.; Vij, U.; Sahni, P.; Tandon, R.K.; Nundy, S. Do the progesterone receptors have a role to play in gallbladder cancer? Int. J. Gastrointest. Cancer 2005, 35, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, S.; Muro, H.; Suzuki, S. Estrogen and progesterone receptors in gallbladder cancer. Jpn. J. Surg. 1989, 19, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saranga Bharathi, R.; Singh, R.; Gupta, R.; Verma, G.R.; Kalra, N.; Kiran, K.; Joshi, K. Female Sex Hormone Receptors in Gallbladder Cancer. J. Gastrointest. Cancer 2015, 46, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; Sharma, K.L.; Srivastava, N.; Misra, S.; Mittal, B. Significant role of estrogen and progesterone receptor sequence variants in gallbladder cancer predisposition: A multi-analytical strategy. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, C.; Yang, X.; Pan, H.; Han, W. Estrogen Receptor Downregulates Expression of PD1/PDL1 and Infiltration of CD8+ T Cells by Inhibiting IL-17 Signaling Transduction in Breast Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 582863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manson, Q.F.; ter Hoeve, N.D.; Buerger, H.; Moelans, C.B.; van Diest, P.J. PD-1 and PDL1 Expression in Male Breast Cancer in Comparison with Female Breast Cancer. Target. Oncol. 2018, 13, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Tang, Y.Y.; Wan, J.X.; Zou, J.Y.; Lu, C.G.; Zhu, H.S.; Sheng, S.Y.; Wang, Y.F.; Liu, H.C.; Yang, J.; et al. Sex difference in the expression of PD-1 of non-small cell lung cancer. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1026214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, T.; Brinkmann, F.; Albrecht, M.; Lonsdorf, A.; Mehrabi, A.; Hoffmann, K.; Kulu, Y.; Charbel, A.; Vogel, M.; Rupp, C.; et al. Programmed death ligand-1 (Pdl1) is an independent negative prognosticator in western-world gallbladder cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Xiao, P.; Lei, S.; Deng, F.; Xiao, G.G.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, L.; Wu, S.; Chen, Y.; et al. How is mRNA expression predictive for protein expression? A correlation study on human circulating monocytes. Acta Biochim. Biophys. 2008, 40, 426–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Long, J.; Wan, X.; Chen, J.; Bai, Y.; Wang, A.; Yang, X.; Wu, Y.; Robson, S.C.; Sang, X.; et al. Classification of gallbladder cancer by assessment of CD8+ TIL and PDL1 expression. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, C.; Peng, X.; Gong, X.; Fan, Y.; Wu, S.; Liu, N.; Li, L.; Huang, J.; Zheng, G.; Long, Z. Prognostic role of programmed death-ligand 1 expression in patients with biliary tract cancer: A meta-analysis. Aging 2019, 11, 12568–12580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.; Si, A.; Yang, J.; Yang, P.; Yang, X.; Liu, H.; Yan, X.; Li, W.; Zhang, B. Elevation of CA19-9 and CEA is associated with a poor prognosis in patients with resectable gallbladder carcinoma. HPB 2017, 19, 951–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballehaninna, U.K.; Chamberlain, R.S. The clinical utility of serum CA 19-9 in the diagnosis, prognosis and management of pancreatic adenocarcinoma: An evidence based appraisal. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2012, 3, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, R.; Yazawa, T.; Uemura, S.; Matsunaga, Y.; Ota, T.; Araida, T.; Furukawa, T.; Yamamoto, M. Examination of prognostic factors affecting long-term survival of patients with stage 3/4 gallbladder cancer without distant metastasis. Cancers 2020, 12, 2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ClinicalTrials. Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov (accessed on 25 December 2022).

| Characteristics | PDL1 | p Value | CA19-9 | p Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low Expression (≤13.03 pg/mL) | High Expression (≥13.03 pg/mL) | Low Expression (≤37 U/mL) | High Expression (≥37 U/mL) | ||||
| Age above 60 | 2 (33.3%) | 4 (66.6%) | 0.31 | 3 (50%) | 3 (50%) | 0.25 | |
| Age below 60 | 13 (56.5%) | 10 (43.4%) | 17 (73.91%) | 6 (26.09%) | |||
| Liver metastasis | 4 (66.6%) | 2 (33.3%) | 0.59 | 1 (16.67%) | 5 (83.33%) | 0.0043 * | |
| Liver without metastasis | 7 (53.8%) | 6 (46%) | 11 (84.62%) | 2 (15.38%) | |||
| Gender | Female | 11 (68.75%) | 5 (31.25%) | 0.04 * | 11 (68.75%) | 5 (31.25%) | 0.97 |
| Male | 4 (31%) | 9 (69%) | 9 (69.23%) | 4 (30.77%) | |||
| Lymph node metastasis | N0 | 8 (61.5%) | 5 (38.4) | 0.82 | 9 (64.29%) | 5 (35.71%) | 0.3 |
| N1 | 4 (66.6%) | 2 (33.3%) | 2 (40%) | 3 (60%) | |||
| Differentiation | Well/moderate | 11 (64.7%) | 6 (35.2%) | 0.0796 | 9 (52.9%) | 8 (47.05%) | 0.2 |
| Poor | 0 (0%) | 2 (100%) | 2 (100%) | 0 | |||
| Tumor size | T1 | 2 (100%) | 0 (0%) | 0.96 | 2 (100%) | 0 | 0.004 * |
| T2 | 4 (44.4%) | 5 (55.5%) | 8 (88.8%) | 1 (11.1%) | |||
| T3 | 4 (66.6%) | 2 (33.3%) | 0 | 6 (100%) | |||
| T4 | 1 (50%) | 1 (50%) | 1 (50%) | 1 (50%) | |||
| Characteristics | n | Univariate Cox Regression | Multivariate Cox Regression | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Ratio [95CI] | p Value | Hazard Ratio | p Value | |||
| PDL1 concentration level | <13 pg/mL | 11 | 0.6672 [0.1669–2.384] | 0.615 | 0.913 [0.1194–6.440] | 0.9250 |
| >13 pg/mL | 8 | |||||
| CA19-9 concentration level | <37 U/mL | 11 | 3.875 [1.065–15.76] | 0.0424 * | 1.073 [0.05903–13.64] | 0.9588 |
| >37 U/mL | 8 | |||||
| Lymphnode metastasis | without metastasis | 13 | 3.081 [0.8462–11.22] | 0.0785 | 3.416 [0.8119–16.13] | 0.0938 |
| with metastasis | 6 | |||||
| Differentiation | poor | 2 | 0.9740 [0.1809–18.03] | 0.9801 | 0.9785 [0.04478–43.82] | 0.9894 |
| well/moderate | 17 | |||||
| Liver metastasis | without metastasis | 13 | 7.159 [1.645–36.96] | 0.0102 * | 8.185 [0.8095–154.5] | 0.1131 |
| with metastasis | 6 | |||||
| Age | <60 | 4 | 1.699 [0.3638–6.167] | 0.4452 | 1.374 [1.078–12.67] | 0.7846 |
| >60 | 15 | |||||
| Tumor size | T1/T2 | 11 | 7.692 [2.045–36.82] | 0.0041 * | - | - |
| T3/T4 | 8 | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rawal, N.; Awasthi, S.; Dash, N.R.; Kumar, S.; Das, P.; Ranjan, A.; Chopra, A.; Khan, M.A.; Saluja, S.; Hussain, S.; et al. Prognostic Relevance of PDL1 and CA19-9 Expression in Gallbladder Cancer vs. Inflammatory Lesions. Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 1571-1584. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30020121
Rawal N, Awasthi S, Dash NR, Kumar S, Das P, Ranjan A, Chopra A, Khan MA, Saluja S, Hussain S, et al. Prognostic Relevance of PDL1 and CA19-9 Expression in Gallbladder Cancer vs. Inflammatory Lesions. Current Oncology. 2023; 30(2):1571-1584. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30020121
Chicago/Turabian StyleRawal, Neetu, Supriya Awasthi, Nihar Ranjan Dash, Sunil Kumar, Prasenjit Das, Amar Ranjan, Anita Chopra, Maroof Ahmad Khan, Sundeep Saluja, Showket Hussain, and et al. 2023. "Prognostic Relevance of PDL1 and CA19-9 Expression in Gallbladder Cancer vs. Inflammatory Lesions" Current Oncology 30, no. 2: 1571-1584. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30020121
APA StyleRawal, N., Awasthi, S., Dash, N. R., Kumar, S., Das, P., Ranjan, A., Chopra, A., Khan, M. A., Saluja, S., Hussain, S., & Tanwar, P. (2023). Prognostic Relevance of PDL1 and CA19-9 Expression in Gallbladder Cancer vs. Inflammatory Lesions. Current Oncology, 30(2), 1571-1584. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30020121






