The Predictive Value of CD3+/CD8+ Lymphocyte Infiltration and PD-L1 Expression in Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Patients and Tissue Specimens
2.2. Tissue Microarray and Immunohistochemistry
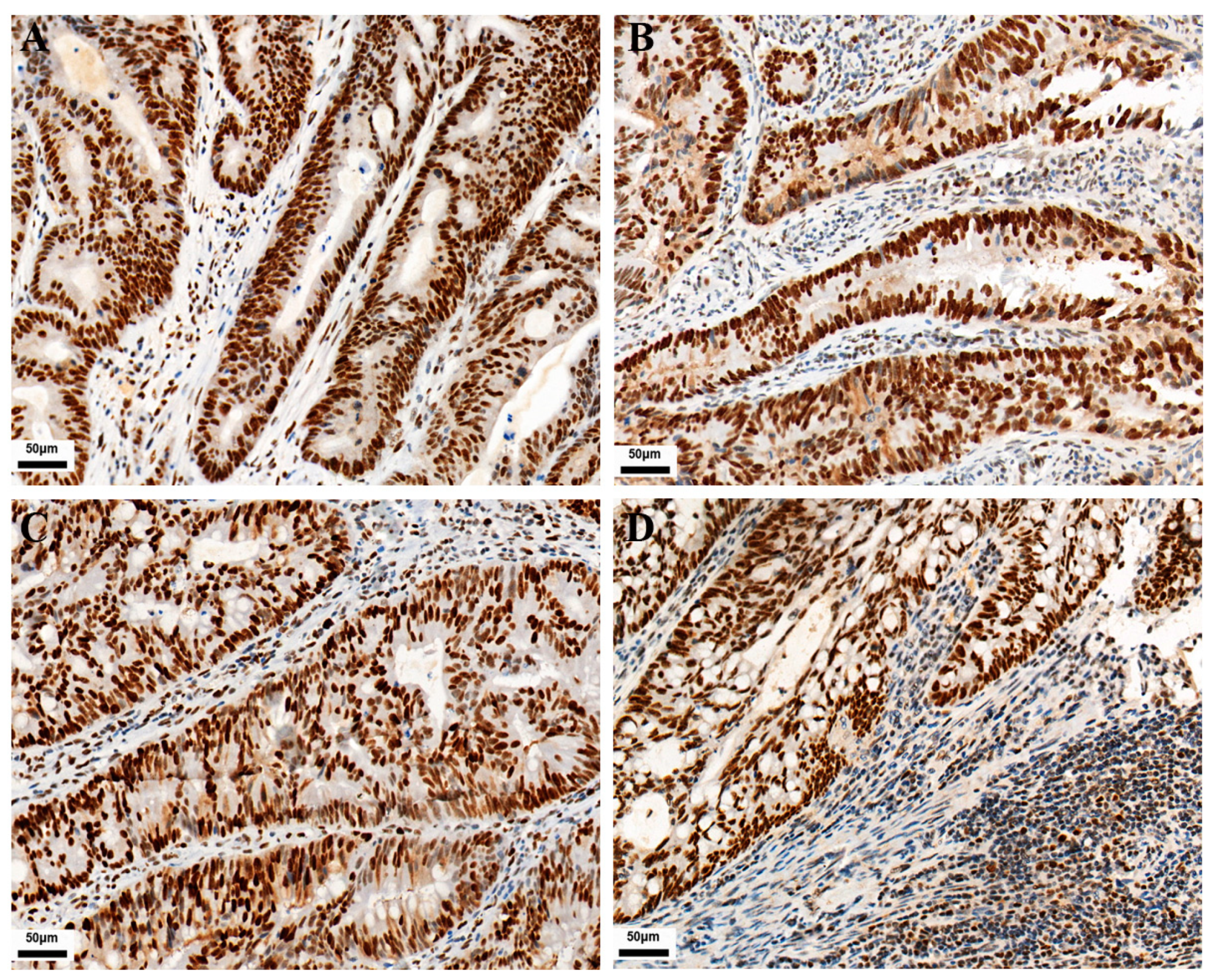
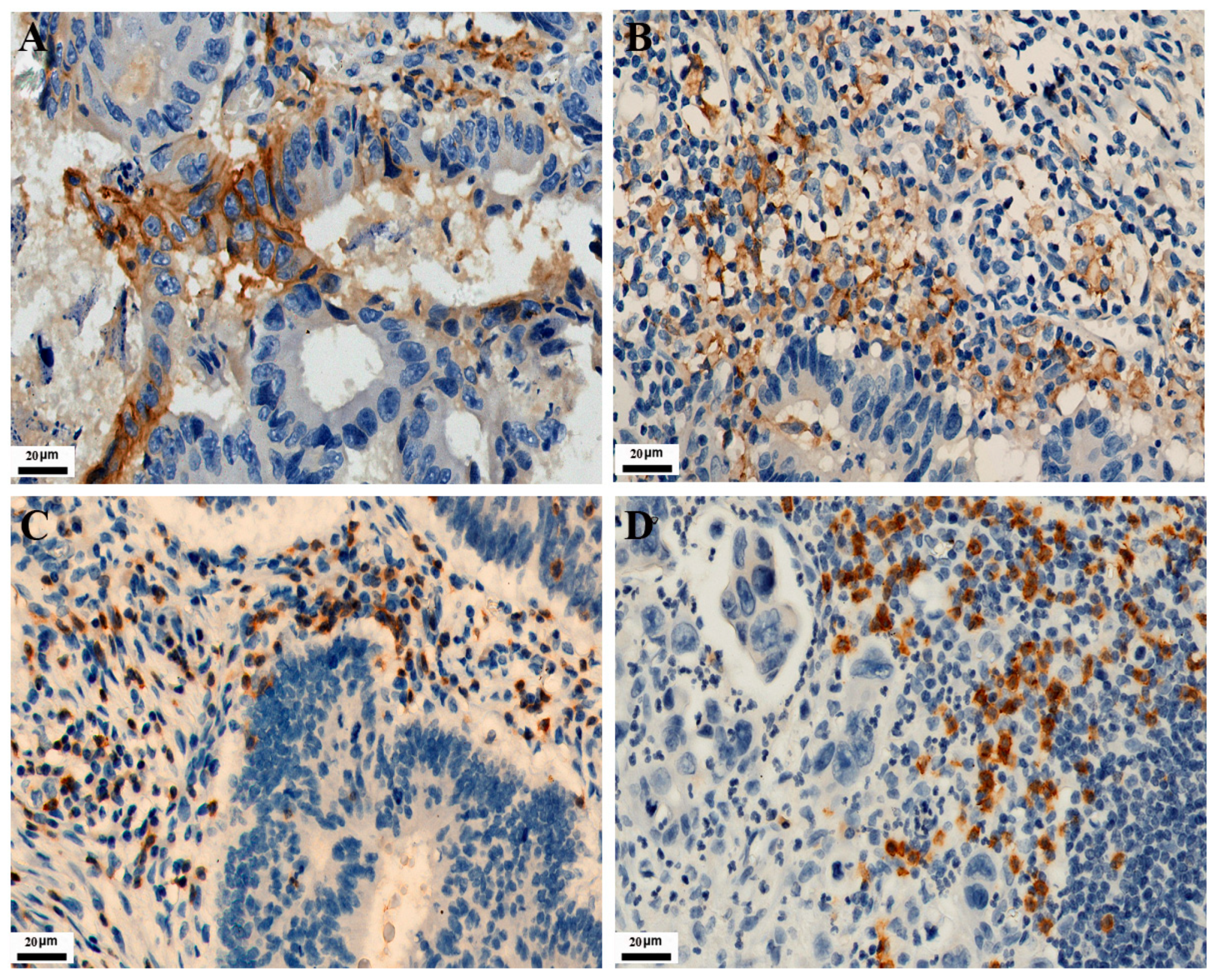
2.3. Immunoreactivity Evaluation
2.4. MMR Protein Detection
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Result
3.1. Expression of PD-L1, CD3/CD8 Proteins, and MMR in 771 CRCs
3.2. The Correlation of PD-L1 and CD3/CD8 Expression with MMR Proteins Expression and Clinicopathological Parameters in 771 CRCs
3.3. The Relationship among the Expression of PD-L1, CD3, CD8, and MMR and the Prognosis of Postoperative CRC Patients
| Variable | Univariate | Multivariate | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR | 95% CI | p Value | HR | 95% CI | p Value | |
| Age | 2.091 | 1.582–2.764 | 0.000 * | 2.237 | 1.685–2.968 | 0.000 * |
| Gender | 0.886 | 0.681–1.152 | 0.365 | 0.916 | 0.803–1.488 | 0.571 |
| Tumor location | 1.114 | 0.832–1.492 | 0.467 | 1.093 | 0.803–1.488 | 0.571 |
| Histological grade | 1.770 | 1.191–2.631 | 0.005 * | 1.405 | 0.753–2.624 | 0.285 |
| Histological type | 2.247 | 1.368–3.689 | 0.001 * | 1.321 | 0.609–2.864 | 0.481 |
| Lymph node metastasis | 2.360 | 1.809–3.080 | 0.000 * | 0.774 | 0.531–1.128 | 0.182 |
| TNM stage | 3.503 | 2.587–4.744 | 0.000 * | 4.437 | 2.898–6.792 | 0.000 * |
| CD3 | 0.892 | 0.624–1.275 | 0.530 | 0.814 | 0.551–1.202 | 0.300 |
| CD8 | 1.172 | 0.876–1.568 | 0.285 | 1.217 | 0.888–1.666 | 0.222 |
| PD-L1 in TC | 0.572 | 0.365–0.897 | 0.015 * | 0.713 | 0.439–1.158 | 0.172 |
| PD-L1 in IC | 0.696 | 0.520–0.932 | 0.015 * | 0.826 | 0.595–1.148 | 0.256 |
| MMR proteins expression | 0.412 | 0.240–0.709 | 0.001 * | 0.429 | 0.245–0.750 | 0.003 * |

4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Jemal, A.; Bray, F.; Center, M.M.; Ferlay, J.; Ward, E.; Forman, D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2011, 61, 69–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koudougou, C.; Bonneville, M.; Matysiak-Budnik, T.; Touchefeu, Y. Review article: Antitumoural immunity in colorectal cancer–current and potential future implications in clinical practice. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 38, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, J.; Li, S.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, R.; Yang, Y.; Li, X. Exploring immunotherapy in colorectal cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 15, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcus, L.; Lemery, S.J.; Keegan, P.; Pazdur, R. FDA Approval Summary: Pembrolizumab for the Treatment of Microsatellite Instability-High Solid Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 3753–3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, D.T.; Kim, T.W.; Van Cutsem, E.; Geva, R.; Jäger, D.; Hara, H.; Burge, M.; O’Neil, B.; Kavan, P.; Yoshino, T.; et al. Phase II Open-Label Study of Pembrolizumab in Treatment-Refractory, Microsatellite Instability-High/Mismatch Repair-Deficient Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: KEYNOTE-164. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenz, H.-J.; Van Cutsem, E.; Limon, M.L.; Wong, K.Y.M.; Hendlisz, A.; Aglietta, M.; García-Alfonso, P.; Neyns, B.; Luppi, G.; Cardin, D.B.; et al. First-Line Nivolumab Plus Low-Dose Ipilimumab for Microsatellite Instability-High/Mismatch Repair-Deficient Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: The Phase II CheckMate 142 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L. Co-inhibitory molecules of the B7–CD28 family in the control of T-cell immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 4, 336–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latchman, Y.; Wood, C.R.; Chernova, T.; Chaudhary, D.; Borde, M.; Chernova, I.; Iwai, Y.; Long, A.J.; Brown, J.A.; Nunes, R.; et al. PD-L2 is a second ligand for PD-1 and inhibits T cell activation. Nat. Immunol. 2001, 2, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keir, M.E.; Liang, S.C.; Guleria, I.; Latchman, Y.E.; Qipo, A.; Albacker, L.A.; Koulmanda, M.; Freeman, G.J.; Sayegh, M.H.; Sharpe, A.H. Tissue expression of PD-L1 mediates peripheral T cell tolerance. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 883–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keir, M.E.; Butte, M.J.; Freeman, G.J.; Sharpe, A.H. PD-1 and its ligands in tolerance and immunity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 26, 677–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, O.; Robert, C.; Daud, A.; Hodi, F.S.; Hwu, W.J.; Kefford, R.; Wolchok, J.D.; Hersey, P.; Joseph, R.W.; Weber, J.S.; et al. Safety and tumor responses with lambrolizumab (anti-PD-1) in melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbst, R.S.; Soria, J.C.; Kowanetz, M.; Fine, G.D.; Hamid, O.; Gordon, M.S.; Sosman, J.A.; McDermott, D.F.; Powderly, J.D.; Gettinger, S.N.; et al. Predictive correlates of response to the anti-PD-L1 antibody MPDL3280A in cancer patients. Nature 2014, 515, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powles, T.; Eder, J.P.; Fine, G.D.; Braiteh, F.S.; Loroit, Y.; Cruz, C.; Bellmunt, J.; Burris, H.A.; Petrylak, D.P.; Teng, S.L.; et al. MPDL3280A (anti-PD-L1) treatment leads to clinical activity in metastatic bladder cancer. Nature 2014, 515, 558–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topalian, S.L.; Hodi, F.S.; Brahmer, J.R.; Gettinger, S.N.; Smith, D.C.; McDermott, D.F.; Powderly, J.D.; Carvajal, R.D.; Sosman, J.A.; Atkins, M.B.; et al. Safety, activity, and immune correlates of anti-PD-1 antibody in cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 2443–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rittmeyer, A.; Barlesi, F.; Waterkamp, D.; Park, K.; Ciardiello, F.; von Pawel, J.; Gadgeel, S.M.; Hida, T.; Kowalski, D.M.; Dols, M.C.; et al. Atezolizumab versus docetaxel in patients with previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer (OAK): A phase 3, open-label, multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Park, H.E.; Cho, N.Y.; Lee, H.S.; Kang, G.H. Characterisation of PD-L1-positive subsets of microsatellite-unstable colorectal cancers. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 115, 490–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masugi, Y.; Nishihara, R.; Yang, J.; Mima, K.; Da Silva, A.; Shi, Y.; Inamura, K.; Cao, Y.; Song, M.; Nowak, J.A.; et al. Tumour CD274 (PD-L1) expression and T cells in colorectal cancer. Gut 2017, 66, 1463–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenbaum, M.W.; Bledsoe, J.R.; Morales-Oyarvide, V.; Huynh, T.G.; Mino-Kenudson, M. PD-L1 expression in colorectal cancer is associated with microsatellite instability, BRAF mutation, medullary morphology and cytotoxic tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes. Mod. Pathol. 2016, 29, 1104–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liang, L.; Dai, W.; Cai, G.; Xu, Y.; Li, X.; Li, Q.; Cai, S. Prognostic impact of programed cell death-1 (PD-1) and PD-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression in cancer cells and tumor infiltrating lymphocytes in colorectal cancer. Mol. Cancer 2016, 15, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.S.; Kwak, Y.; Ahn, S.; Shin, E.; Oh, H.K.; Kim, D.W.; Kang, S.B.; Choe, G.; Kim, W.H.; Lee, H.S. Prognostic implication of CD274 (PD-L1) protein expression in tumor-infiltrating immune cells for microsatellite unstable and stable colorectal cancer. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2017, 66, 927–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Qin, H.; Huang, Z.; Li, S.; Zhu, X.; He, J.; Yang, J.; Yu, X.; Yi, X. Clinical significance of programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1) in colorectal serrated adenocarcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 9351–9359. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Smith-Garvin, J.E.; Koretzky, G.A.; Jordan, M.S. T cell activation. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 27, 591–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Q.-Z.; Pan, K.; Zhao, J.J.; Chen, J.-G.; Li, J.J.; Lv, L.; Wang, D.D.; Zheng, H.X.; Jiang, S.S.; Zhang, X.F.; et al. Decreased expression of interleukin-36α correlates with poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2013, 62, 1675–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naito, Y.; Saito, K.; Shiiba, K.; Ohuchi, A.; Saigenji, K.; Nagura, H.; Ohtani, H. CD8+ T cells infiltrated within cancer cell nests as a prognostic factor in human colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 3491–3494. [Google Scholar]
- Deschoolmeester, V.; Baay, M.; Lardon, F.; Pauwels, P.; Peeters, M. Immune Cells in Colorectal Cancer: Prognostic Relevance and Role of MSI. Cancer Microenviron. 2011, 4, 377–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fridman, W.H.; Pagès, F.; Sautès-Fridman, C.; Galon, J. The immune contexture in human tumours: Impact on clinical outcome. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadzadeh, M.; Johnson, L.A.; Heemskerk, B.; Wunderlich, J.R.; Dudley, M.E.; White, D.E.; Rosenberg, S.A. Tumor antigen–specific CD8 T cells infiltrating the tumor express high levels of PD-1 and are functionally impaired. Blood 2009, 114, 1537–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, M.-C.; Hsiao, J.R.; Chang, K.C.; Wu, Y.H.; Su, I.J.; Jin, Y.T.; Chang, Y. Increase of programmed death-1-expressing intratumoral CD8 T cells predicts a poor prognosis for nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Mod. Pathol. 2010, 23, 1393–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konishi, J.; Yamazaki, K.; Azuma, M.; Kinoshita, I.; Dosaka-Akita, H.; Nishimura, M. B7-H1 expression on non-small cell lung cancer cells and its relationship with tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and their pd-1 expression. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 5094–5100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modrich, P. Mechanisms in E. coli and Human Mismatch Repair (Nobel Lecture). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2016, 55, 8490–8501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaanan, A.; Meunier, K.; Sangar, F.; Fléjou, J.F.; Praz, F. Microsatellite instability in colorectal cancer: From molecular oncogenic mechanisms to clinical implications. Cell. Oncol. 2011, 34, 155–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, R.; Sinha, S.; Paul, R.N. The impact of microsatellite stability status in colorectal cancer. Curr. Probl. Cancer 2018, 42, 548–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermel, D.J.; Sigal, D. The Emerging Role of Checkpoint Inhibition in Microsatellite Stable Colorectal Cancer. J. Pers. Med. 2019, 9, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahmer, J.R.; Tykodi, S.S.; Chow, L.Q.; Hwu, W.J.; Topalian, S.L.; Hwu, P.; Drake, C.G.; Camacho, L.H.; Kauh, J.; Odunsi, K.; et al. Safety and activity of anti-PD-L1 antibody in patients with advanced cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 2455–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topalian, S.L.; Sznol, M.; McDermott, D.F.; Kluger, H.M.; Carvajal, R.D.; Sharfman, W.H.; Brahmer, J.R.; Lawrence, D.P.; Atkins, M.B.; Powderly, J.D.; et al. Survival, durable tumor remission, and long-term safety in patients with advanced melanoma receiving nivolumab. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 1020–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunshine, J.; Taube, J.M. PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2015, 23, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehrenbacher, L.; von Pawel, J.; Park, K.; Rittmeyer, A.; Gandara, D.R.; Aix, S.P.; Han, J.Y.; Gadgeel, S.M.; Hida, T.; Cortinovis, D.L.; et al. Updated Efficacy Analysis Including Secondary Population Results for OAK: A Randomized Phase III Study of Atezolizumab versus Docetaxel in Patients with Previously Treated Advanced Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1156–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postow, M.A.; Callahan, M.K.; Wolchok, J.D. Immune Checkpoint Blockade in Cancer Therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 1974–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.; Chen, L. Inhibitory B7-family molecules in the tumour microenvironment. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Jungbluth, A.A.; Frosina, D.; Alzumaili, B.; Aleynick, N.; Slodkowska, E.; Higgins, K.; Ho, A.; Morris, L.; Ghossein, R.; et al. The immune microenvironment and expression of PD-L1, PD-1, PRAME and MHC I in salivary duct carcinoma. Histopathology 2019, 75, 672–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatalica, Z.; Snyder, C.; Maney, T.; Ghazalpour, A.; Holterman, D.A.; Xiao, N.; Overberg, P.; Rose, I.; Basu, G.D.; Vranic, S.; et al. Programmed cell death 1 (PD-1) and its ligand (PD-L1) in common cancers and their correlation with molecular cancer type. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2014, 23, 2965–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llosa, N.J.; Cruise, M.; Tam, A.; Wicks, E.C.; Hechenbleikner, E.M.; Taube, J.M.; Blosser, R.L.; Fan, H.; Wang, H.; Luber, B.S.; et al. The vigorous immune microenvironment of microsatellite instable colon cancer is balanced by multiple counter-inhibitory checkpoints. Cancer Discov. 2015, 5, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inaguma, S.; Lasota, J.; Wang, Z.; Felisiak-Golabek, A.; Ikeda, H.; Miettinen, M. Clinicopathologic profile, immunophenotype, and genotype of CD274 (PD-L1)-positive colorectal carcinomas. Mod. Pathol. 2017, 30, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.S.; Park, S.; Lee, W.Y.; Yun, S.H.; Chun, H.-K. Clinical impact of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes for survival in stage II colon cancer. Cancer 2010, 116, 5188–5199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-Y.; Chiang, S.F.; Ke, T.W.; Chen, T.-W.; You, Y.S.; Chen, W.T.L.; Chao, K.S.C. Clinical significance of programmed death 1 ligand-1 (CD274/PD-L1) and intra-tumoral CD8+ T-cell infiltration in stage II-III colorectal cancer. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Dai, Y.; Cheng, J.N.; Gong, Z.; Feng, Y.; Sun, C.; Jia, Q.; Zhu, B. Immune Landscape of Colorectal Cancer Tumor Microenvironment from Different Primary Tumor Location. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minoo, P.; Zlobec, I.; Peterson, M.; Terracciano, L.; Lugli, A. Characterization of rectal, proximal and distal colon cancers based on clinicopathological, molecular and protein profiles. Int. J. Oncol. 2010, 37, 707–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, A.; Durant, L.; Dilke, S.M.; Man, R.; Martin, I.; Patel, R.; Hoyles, L.; Pring, E.T.; Latchford, A.; Clark, S.K.; et al. Altered Mucosal Immune-Microbiota Interactions in Familial Adenomatous Polyposis. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2022, 13, e00428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, T.; Mimura, K.; Okayama, H.; Nakayama, Y.; Saito, K.; Yamada, L.; Endo, E.; Sakamoto, W.; Fujita, S.; Endo, H.; et al. A subset of patients with MSS/MSI-low-colorectal cancer showed increased CD8(+) TILs together with up-regulated IFN-γ. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 18, 5977–5985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Jing, H.; Liu, J.; Bu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, T.; Lu, K.; Xu, Y.; Cheng, M.; Liu, J.; et al. Correlation between schistosomiasis and CD8+ T cell and stromal PD-L1 as well as the different prognostic role of CD8+ T cell and PD-L1 in schistosomal-associated colorectal cancer and non-schistosomal-associated colorectal cancer. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 19, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concha-Benavente, F.; Srivastava, R.M.; Trivedi, S.; Lei, Y.; Chandran, U.; Seethala, R.R.; Freeman, G.J.; Ferris, R.L. Identification of the Cell-Intrinsic and -Extrinsic Pathways Downstream of EGFR and IFNγ That Induce PD-L1 Expression in Head and Neck Cancer. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 1031–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J.; Jun, S.Y.; Lee, I.H.; Kang, B.W.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Park, J.S.; Choi, G.S.; Yoon, G.; Kim, J.G. CD274, LAG3, and IDO1 expressions in tumor-infiltrating immune cells as prognostic biomarker for patients with MSI-high colon cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 144, 1005–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nosho, K.; Baba, Y.; Tanaka, N.; Shima, K.; Hayashi, M.; Meyerhardt, J.A.; Giovannucci, E.; Dranoff, G.; Fuchs, C.S.; Ogino, S. Tumour-infiltrating T-cell subsets, molecular changes in colorectal cancer, and prognosis: Cohort study and literature review. J. Pathol. 2010, 222, 350–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Q.; Ying, J.; Lyu, N.; Guo, L.; Zhi, W.; Zhou, A.; Wang, J. Correlations between DNA mismatch repair (MMR) and prognosis and prediction of treatment efficacy in stage II/II colon cancer. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi 2014, 36, 844–848. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, L.; Güngör, C.; Tan, F.; Zhou, Z.; Li, C.; Song, X.; Wang, D.; Pei, Q.; Liu, W. The main contributor to the upswing of survival in locally advanced colorectal cancer: An analysis of the SEER database. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2019, 12, 1756284819862154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaghoubi, N.; Soltani, A.; Ghazvini, K.; Hassanian, S.M.; Hashemy, S.I. PD-1/PD-L1 blockade as a novel treatment for colorectal cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 110, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variable | Cases | PD-L1+ in TC | p | PD-L1+ in IC | p | CD3+ | p | CD8+ | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | |||||||||
| ≤60 | 351 | 62 (17.7%) | 0.142 | 142 (40.5%) | 0.041 | 71 (20.2%) | 0.123 | 103 (29.3%) | 0.097 |
| >60 | 420 | 58 (13.8%) | 140 (33.3%) | 67 (16.0%) | 101 (24.0%) | ||||
| Gender | |||||||||
| Male | 430 | 65 (15.1%) | 0.700 | 156 (36.3%) | 0.848 | 83 (19.3%) | 0.254 | 116 (27.0%) | 0.714 |
| Female | 341 | 55 (16.1%) | 126 (37.0%) | 55 (16.1%) | 88 (25.8%) | ||||
| Tumor location | |||||||||
| Left colon | 574 | 78 (13.6%) | 0.010 * | 210 (36.6%) | 0.993 | 95 (16.6%) | 0.096 | 132 (23.0%) | 0.000 * |
| Right colon | 197 | 42 (21.3%) | 72 (36.5%) | 43 (21.8%) | 72 (36.5%) | ||||
| Histological grade | |||||||||
| Low grade | 692 | 104 (15%) | 0.225 | 255 (36.8%) | 0.640 | 118 (17.1%) | 0.069 | 179 (25.9%) | 0.270 |
| High grade | 79 | 16 (20.3%) | 27 (34.2%) | 20 (25.3%) | 25 (31.6%) | ||||
| Histological type | |||||||||
| Adenocarcinoma | 734 | 119 (16.2%) | 0.020 * | 274 (37.3%) | 0.053 | 131 (17.8%) | 0.868 | 194 (26.4%) | 0.936 |
| Mucinous adenocarcinoma | 37 | 1 (2.7%) | 8 (21.6%) | 7 (18.9%) | 10 (27.0%) | ||||
| Lymph node metastasis | |||||||||
| No | 408 | 65 (15.9%) | 0.766 | 160 (39.2%) | 0.107 | 43 (10.5%) | 0.000 * | 91 (22.3%) | 0.006 * |
| Yes | 363 | 55 (15.2%) | 122 (33.6%) | 95 (26.2%) | 113 (31.1%) | ||||
| TNM stage | |||||||||
| I-II | 335 | 56 (16.7%) | 0.439 | 137 (40.9%) | 0.029 * | 34 (10.1%) | 0.000 * | 76 (22.7%) | 0.037 * |
| III-IV | 436 | 64 (14.7%) | 145 (33.3%) | 104 (23.9%) | 128 (29.4%) | ||||
| CD3 expression | |||||||||
| Low | 633 | 77 (12.2%) | 0.000 * | 188 (29.7%) | 0.000 * | \ | 135 (21.3%) | 0.000 * | |
| High | 138 | 43 (31.2%) | 94 (68.1%) | 69 (50.0%) | |||||
| CD8 expression | |||||||||
| Low | 567 | 71 (12.5%) | 0.000 * | 166 (29.3%) | 0.000 * | \ | \ | ||
| High | 204 | 49 (24.0%) | 116 (56.9%) | ||||||
| MMR proteins expression | |||||||||
| pMMR | 678 | 98 (14.5%) | 0.022 * | 246 (36.3%) | 0.649 | 124 (18.3%) | 0.445 | 184 (27.1%) | 0.248 |
| dMMR | 93 | 22 (23.7%) | 36 (38.7%) | 14 (15.1%) | 20 (21.5%) | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Li, J.; Luo, F.; Wu, S.; Li, B.; Liu, K. The Predictive Value of CD3+/CD8+ Lymphocyte Infiltration and PD-L1 Expression in Colorectal Cancer. Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 9647-9659. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30110699
Liu J, Li J, Luo F, Wu S, Li B, Liu K. The Predictive Value of CD3+/CD8+ Lymphocyte Infiltration and PD-L1 Expression in Colorectal Cancer. Current Oncology. 2023; 30(11):9647-9659. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30110699
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jihong, Jinbang Li, Feng Luo, Shigang Wu, Bingquan Li, and Kunping Liu. 2023. "The Predictive Value of CD3+/CD8+ Lymphocyte Infiltration and PD-L1 Expression in Colorectal Cancer" Current Oncology 30, no. 11: 9647-9659. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30110699
APA StyleLiu, J., Li, J., Luo, F., Wu, S., Li, B., & Liu, K. (2023). The Predictive Value of CD3+/CD8+ Lymphocyte Infiltration and PD-L1 Expression in Colorectal Cancer. Current Oncology, 30(11), 9647-9659. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol30110699





