Detection of Potential Mutated Genes Associated with Common Immunotherapy Biomarkers in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cohorts and Samples
2.1.1. Case Inclusion Criteria
2.1.2. Case Exclusion Criteria
2.2. Somatic Mutation Detection
2.3. Screening Specific Genes
2.4. Functional Annotation
2.5. Characteristics of Immune Microenvironment
2.6. Drug Analysis
2.7. TCGA Verification
3. Results
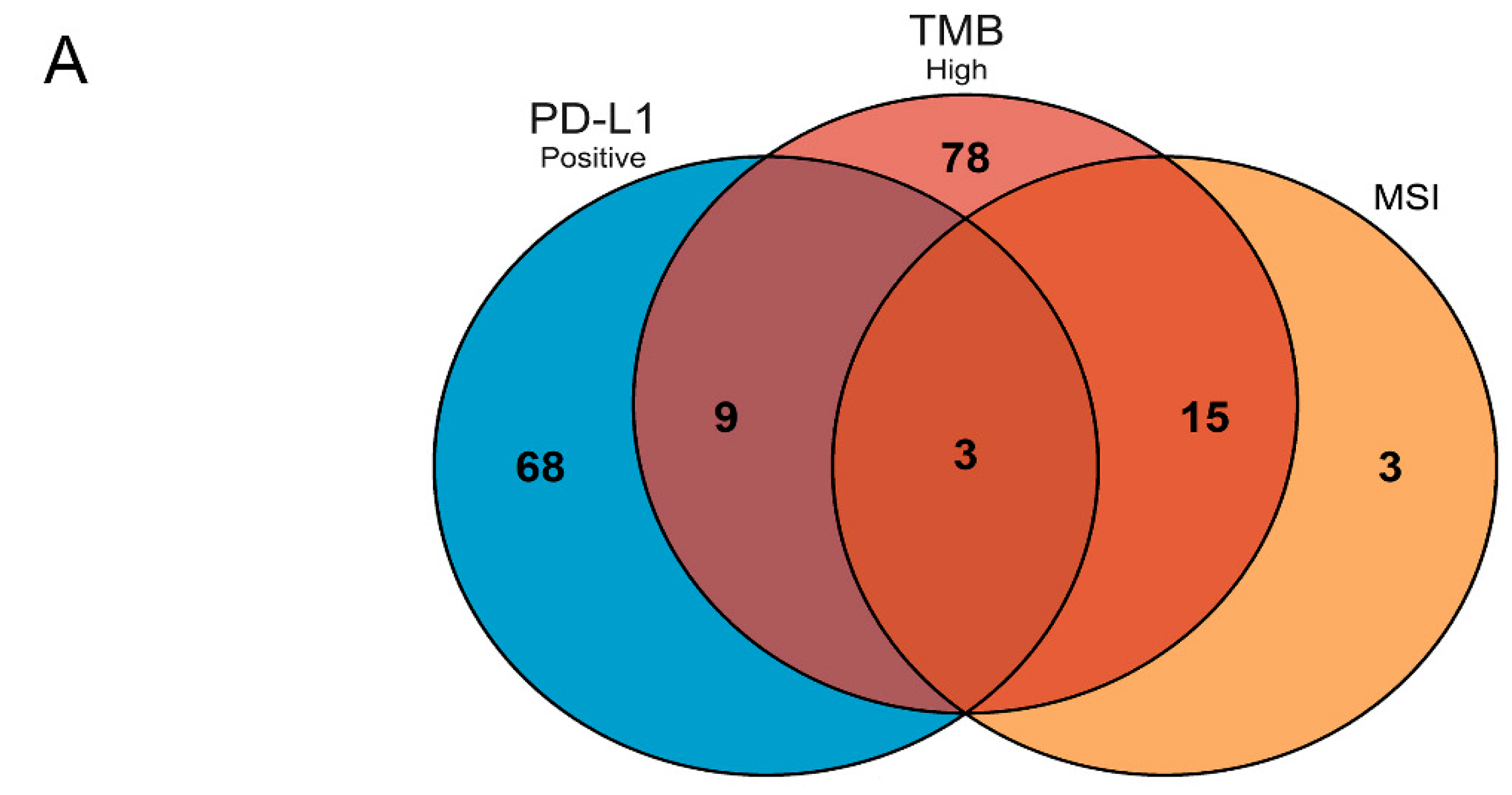
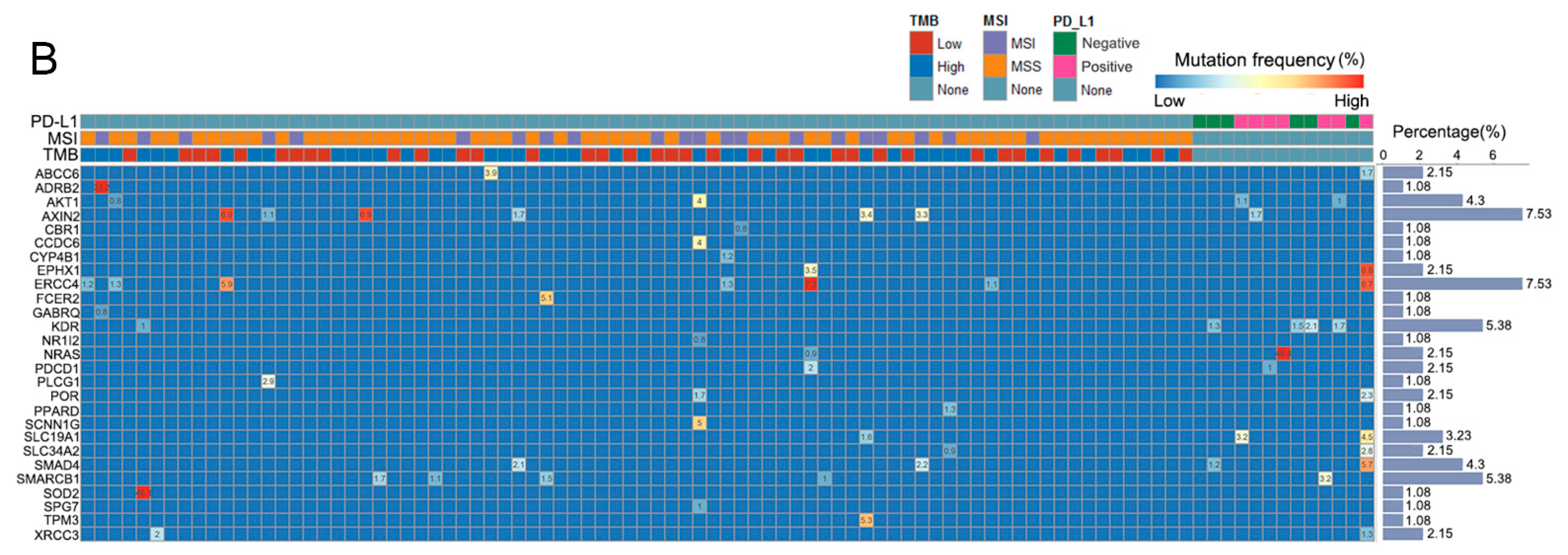
3.1. Patients and Mutated Gene Characteristics in Different Groups
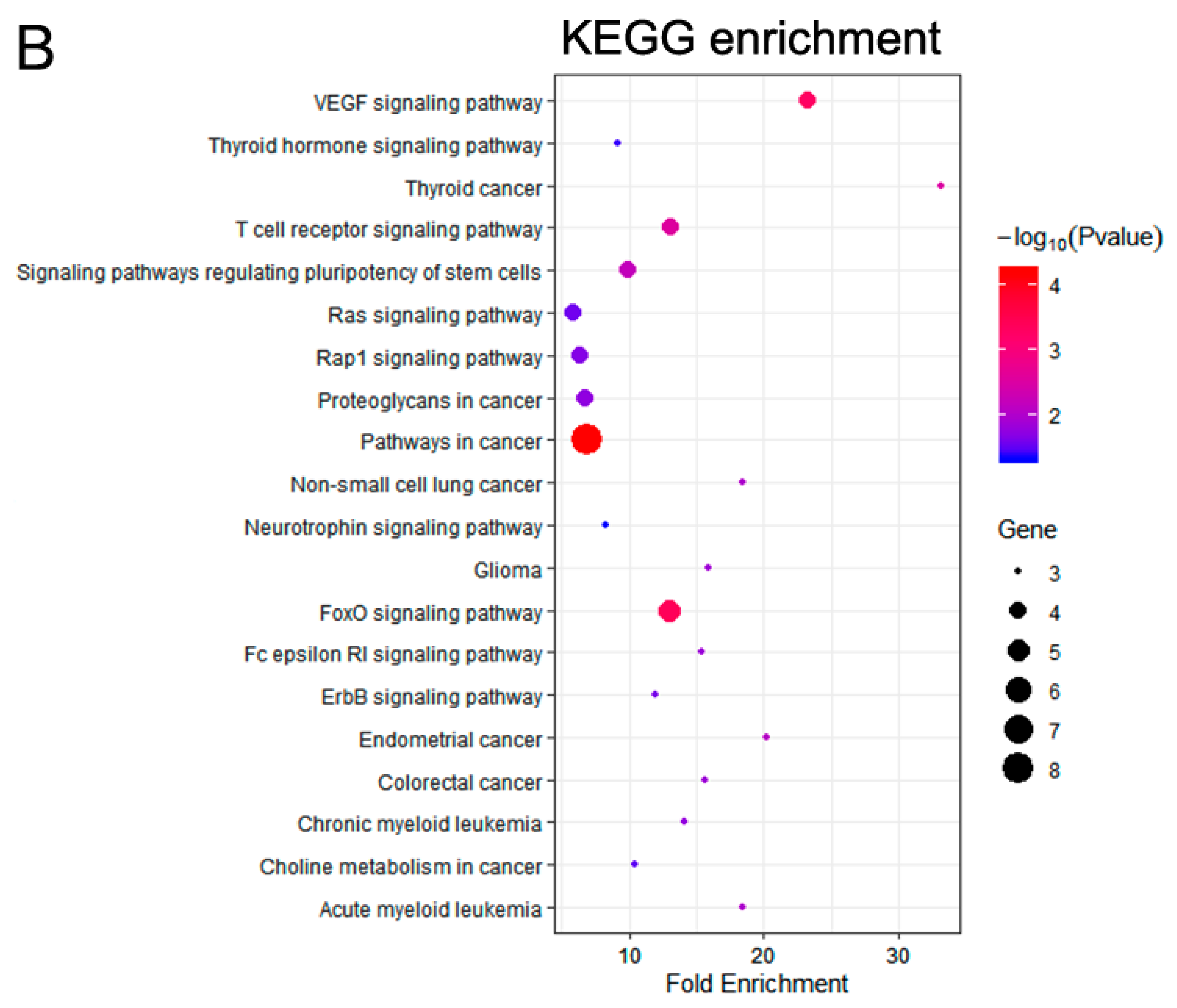
3.2. Functional Enrichment Analysis
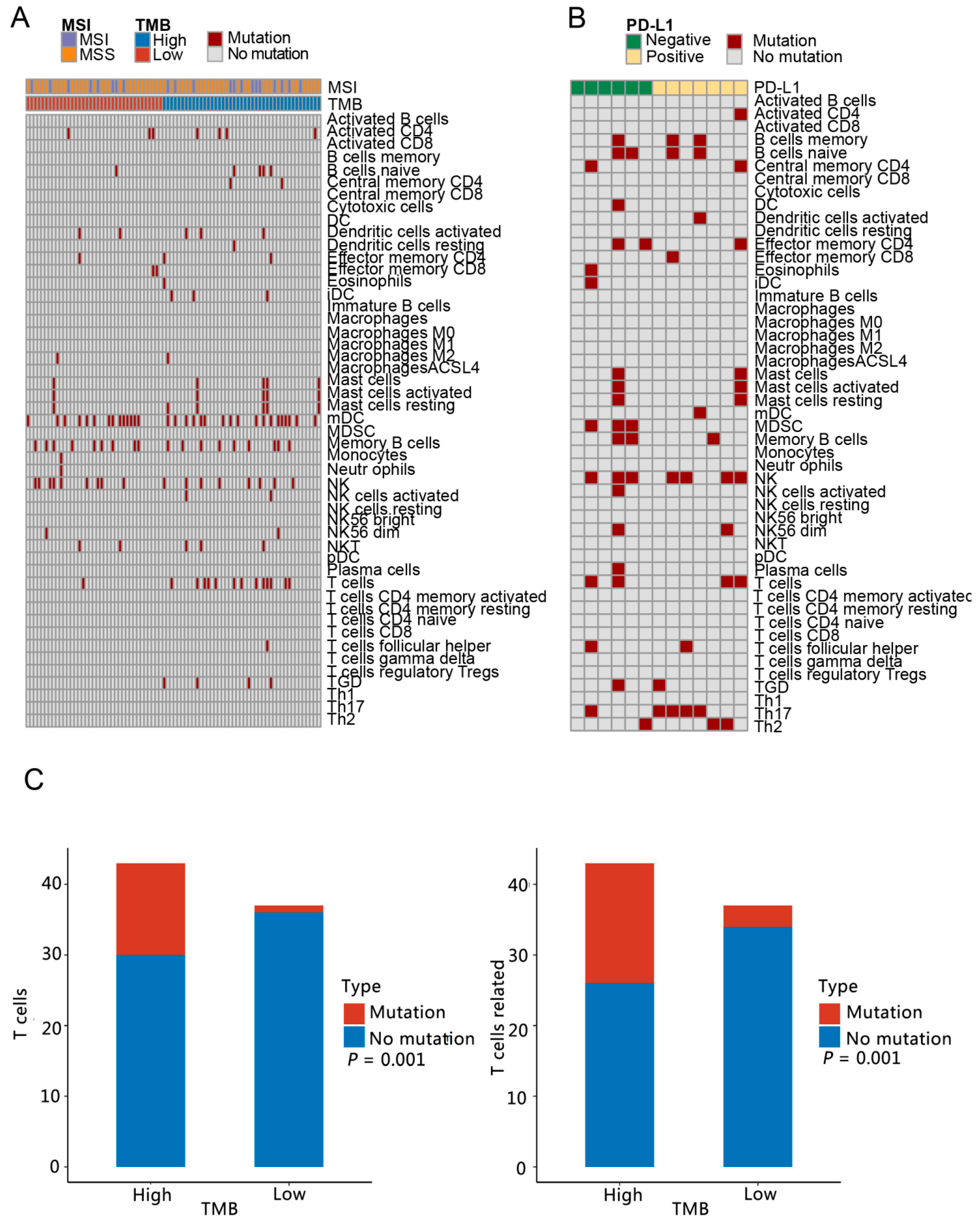
3.3. Analysis of Immune Microenvironment Characteristics
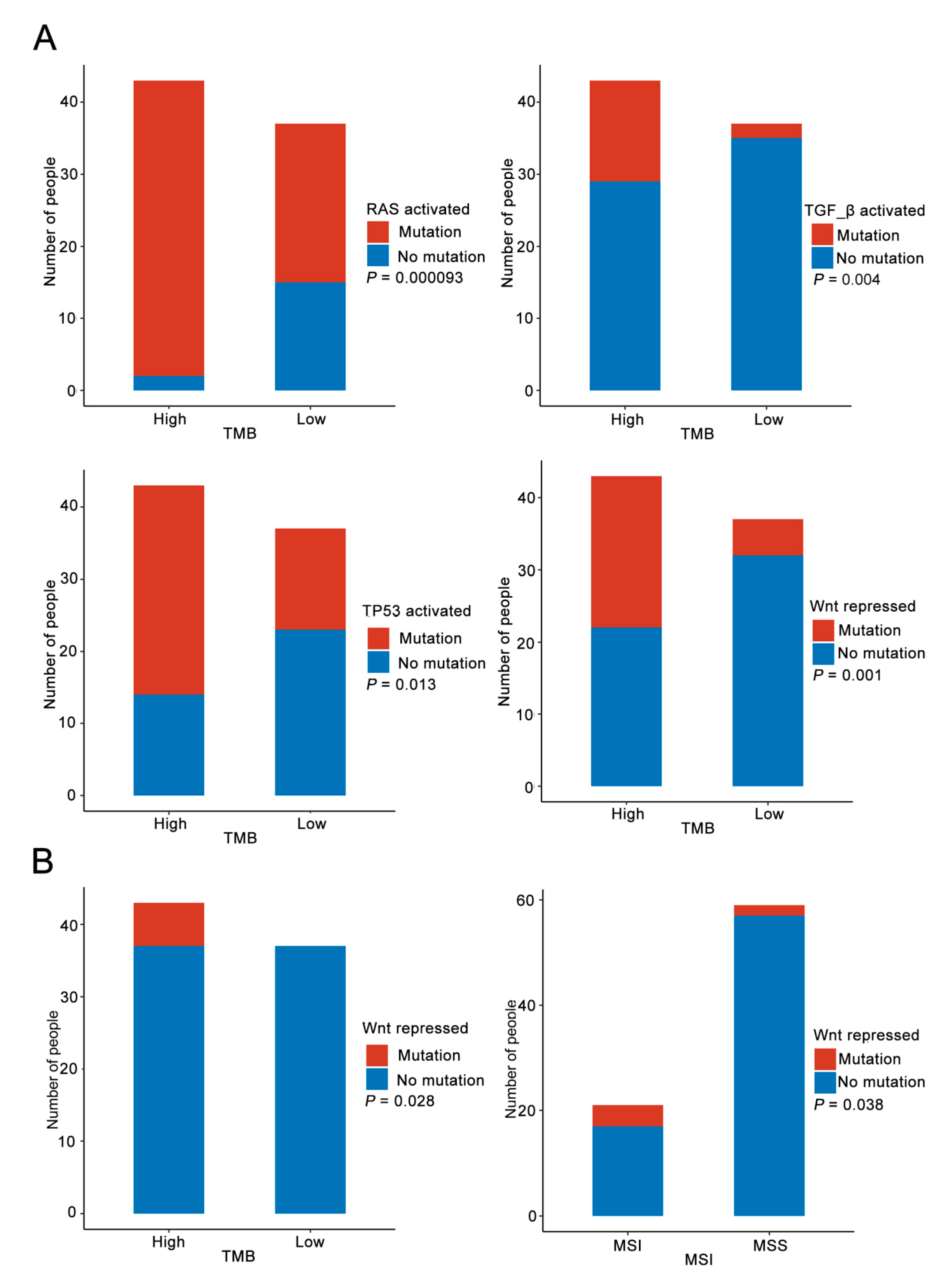
3.4. Immune Pathway Analysis
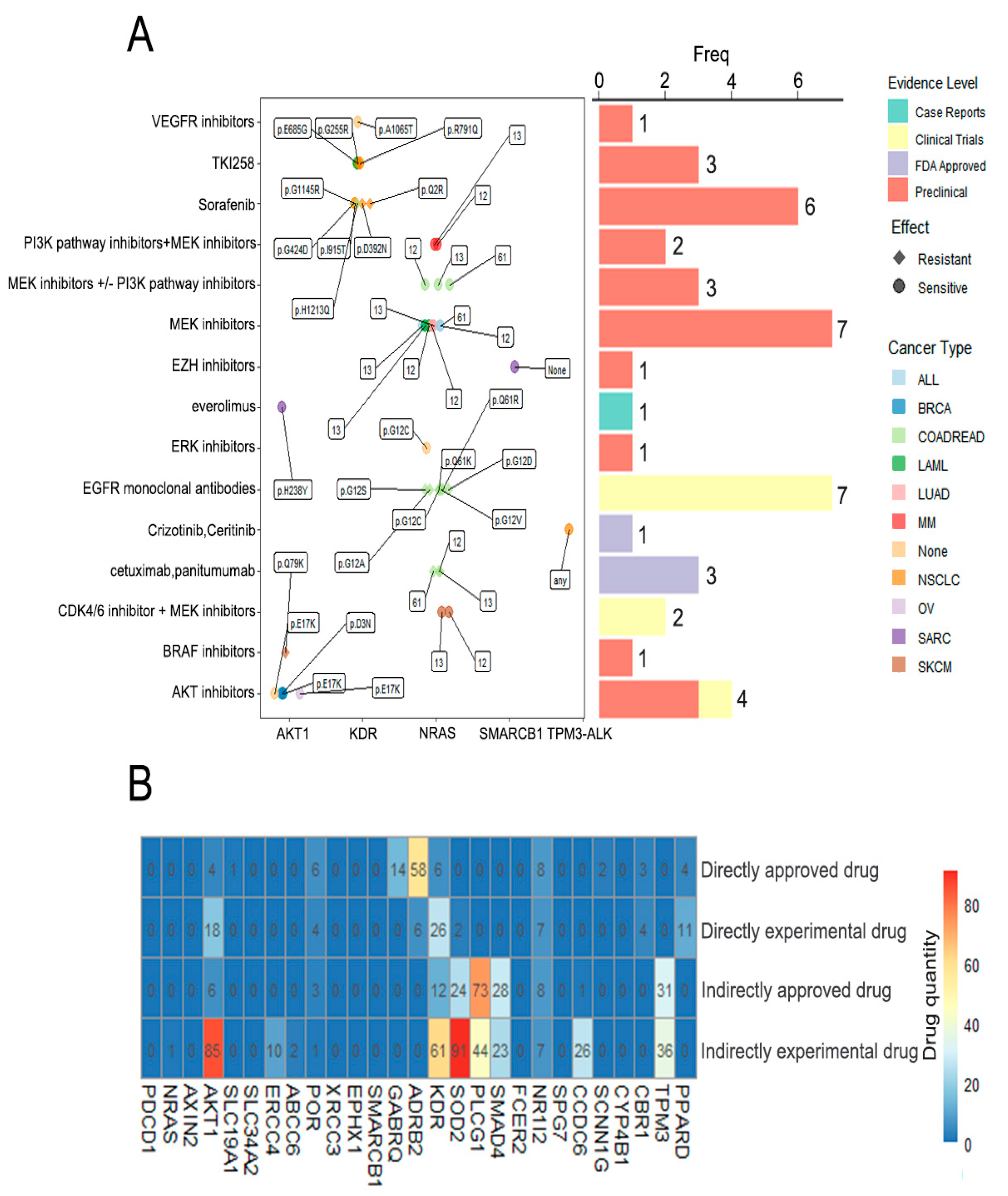
3.5. Drug Analysis
3.6. Validation of 27 Genes Screened in TCGA Database
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 7–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsch, F.R.; Scagliotti, G.V.; Mulshine, J.L.; Kwon, R.; Curran, W.J., Jr.; Wu, Y.L.; Paz-Ares, L. Lung cancer: Current therapies and new targeted treatments. Lancet 2017, 389, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.J.; Shaw, A.T. Resisting Resistance: Targeted Therapies in Lung Cancer. Trends Cancer 2016, 2, 350–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malhotra, J.; Jabbour, S.K.; Aisner, J. Current state of immunotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2017, 6, 196–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emens, L.A.; Silverstein, S.C.; Khleif, S.; Marincola, F.M.; Galon, M.J. Toward integrative cancer immunotherapy: Targeting the tumor microenvironment. J. Transl. Med. 2012, 10, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, G.E.; Podack, E.R.; Raez, L.E. Immunotherapy as a strategy for the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer. Therapy 2011, 8, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkwill, F.R.; Capasso, M.; Hagemann, T. The tumor microenvironment at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 5591–5596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, F.-F.; Han, B.-H. Mechanisms of resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors and strategies to reverse drug resistance in lung cancer. Chin. Med. J. 2020, 133, 2444–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salik, B.; Smyth, M.J.; Nakamura, K. Targeting immune checkpoints in hematological malignancies. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Kefford, R.; Carlino, M. PD-1 and PD-L1 inhibitors in melanoma treatment: Past success, present application and future challenges. Immunotherapy 2016, 8, 733–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishino, M.; Ramaiya, N.H.; Hatabu, H.; Hodi, F.S. Monitoring immune-checkpoint blockade: Response evaluation and biomarker development. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 655–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, D.B.; Rioth, M.J.; Horn, L. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in NSCLC. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2014, 15, 658–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Postow, M.A.; Callahan, M.K.; Wolchok, J.D. Immune Checkpoint Blockade in Cancer Therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 1974–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoneda, K.; Imanishi, N.; Ichiki, Y.; Tanaka, F. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors (ICIs) in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC). J. UOEH 2018, 40, 173–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spigel, D.R.; Schrock, A.B.; Fabrizio, D.; Frampton, G.M.; Sun, J.; He, J.; Gowen, K.; Johnson, M.L.; Bauer, T.M.; Kalemkerian, G.P.; et al. Total mutation burden (TMB) in lung cancer (LC) and relationship with response to PD-1/PD-L1 targeted therapies. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34 (Suppl. 15), 9017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudley, J.C.; Lin, M.-T.; Le, D.T.; Eshleman, J.R. Microsatellite Instability as a Biomarker for PD-1 Blockade. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passiglia, F.; Bronte, G.; Bazan, V.; Natoli, C.; Rizzo, S.; Galvano, A.; Listì, A.; Cicero, G.; Rolfo, C.; Santini, D.; et al. PD-L1 expression as predictive biomarker in patients with NSCLC: A pooled analysis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 19738–19747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bathke, J.; Lühken, G. OVarFlow: A resource optimized GATK 4 based Open source Variant calling workFlow. BMC Bioinform. 2021, 22, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, Y.-C.; Hsiao, Y.-T.; Kao, T.-Y.; Chang, J.-G.; Shieh, G.S. Detection of Somatic Mutations in Exome Sequencing of Tumor-only Samples. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- França, M.M.; Funari, M.F.A.; Lerario, A.M.; Santos, M.G.; Nishi, M.Y.; Domenice, S.; Moraes, D.R.; Costalonga, E.F.; Maciel, G.A.R.; Maciel-Guerra, A.T.; et al. Screening of targeted panel genes in Brazilian patients with primary ovarian insufficiency. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0240795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tischer, B.; Kim, E.S.; Peters, M.J.; Hirsh, V. P3.02b-023 Physician Patterns of Care in Patients with EGFR Mutation+ NSCLC: An International Survey into Testing and Treatment Choice: Topic: EGFR Biomarkers. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, S1199–S1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hirsch, F.R.; McElhinny, A.; Stanforth, D.; Ranger-Moore, J.; Jansson, M.; Kulangara, K.; Richardson, W.; Towne, P.; Hanks, D.; Vennapusa, B.; et al. PD-L1 Immunohistochemistry Assays for Lung Cancer: Results from Phase 1 of the Blueprint PD-L1 IHC Assay Comparison Project. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 208–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VanderWalde, A.; Spetzler, D.; Xiao, N.; Gatalica, Z.; Marshall, J. Microsatellite instability status determined by next-generation sequencing and compared with PD-L1 and tumor mutational burden in 11,348 patients. Cancer Med. 2018, 7, 746–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alevizakos, M.; Kaltsas, S.; Syrigos, K.N. The VEGF pathway in lung cancer. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2013, 72, 1169–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Wang, R.C.; Cheng, K.; Ring, B.Z.; Su, L. Roles of Rap1 signaling in tumor cell migration and invasion. Cancer Biol. Med. 2017, 14, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hoque, M.O.; Brait, M.; Rosenbaum, E.; Poeta, M.L.; Pal, P.; Begum, S.; Dasgupta, S.; Carvalho, A.L.; Ahrendt, S.A.; Westra, W.H.; et al. Genetic and Epigenetic Analysis of erbB Signaling Pathway Genes in Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2010, 5, 1887–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starczynowski, D.T.; Lockwood, W.W.; Deléhouzée, S.; Chari, R.; Wegrzyn, J.; Fuller, M.; Tsao, M.S.; Lam, S.; Gazdar, A.F.; Lam, W.F.; et al. TRAF6 is an amplified oncogene bridging the RAS and NF-κB pathways in human lung cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 4095–4105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matherly, L.H.; Hou, Z.; Deng, Y. Human reduced folate carrier: Translation of basic biology to cancer etiology and therapy. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2007, 26, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Chen, W.; Wang, J.; Tan, Y.F.; Zhou, Y.; Ding, W.L.; Hua, Z.L.; Shen, J.; Xu, Y.C.; Shen, H.B. Reduced folate carrier gene G80A polymorphism is associated with an increased risk of gastroesophageal cancers in a chinese population. Eur. J. Cancer 2006, 42, 3206–3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.-J.; Jiang, H.; Fang, X.-J.; Ye, H.-L.; Liu, M.-H.; Liu, Y.-W.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.-Y.; Yuan, C.-L.; et al. Polymorphisms in thymidylate synthase and reduced folate carrier (SLC19A1) genes predict survival outcome in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with pemetrexed-based chemotherapy. Oncol. Lett. 2013, 5, 1165–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, B.W.T.; Kiyamova, R.; Chua, R.; Caballero, O.L.; Gout, I.; Gryshkova, V.; Bhaskaran, N.; Souchelnytskyi, S.; Hellman, U.; Filonenko, V.; et al. Monoclonal antibody MX35 detects the membrane transporter NaPi2b (SLC34A2) in human carcinomas. Cancer Immun. Arch. 2008, 8, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Rangel, L.B.A. The cotransporter NaPi-IIb: Characteristics, regulation and its role in carcinogenesis. Appl. Cancer Res. 2010, 30, 197–203. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Ye, S.; Zhang, M.; Wu, J.; Yan, H.; Li, X.; He, J. High expression of SLC34A2 is a favorable prognostic marker in lung adenocarcinoma patients. Tumor Biol. 2017, 39, 1010428317720212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flück, C.E.; Nicolo, C.; Pandey, A.V. Clinical, structural and functional implications of mutations and polymorphisms in human NADPH P450 oxidoreductase. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2007, 21, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, D.P.; Gandara, D.R.; Antonia, S.J.; Zielinski, C.; Paz-Ares, L. Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Role of the Immune System and Potential for Immunotherapy. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 974–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagamu, H.; Kitano, S.; Yamaguchi, O.; Yoshimura, K.; Horimoto, K.; Kitazawa, M.; Fukui, K.; Shiono, A.; Mouri, A.; Nishihara, F.; et al. CD4+ T-cell Immunity in the Peripheral Blood Correlates with Response to Anti-PD-1 Therapy. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2020, 8, 334–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.-S.; Ramani, V.; Kobayashi, M.; Fattah, F.J.; Popat, V.; Zhang, S.; Cruz, P.D., Jr.; Gerber, D.E.; Ariizumi, K. DC-HIL/Gpnmb Is a Negative Regulator of Tumor Response to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 1449–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Liang, H.; Xu, Y.; Liu, L.; Ren, X.; Zhang, S.; Wei, S.; Xu, P. The Role of Circulating T Follicular Helper Cells and Regulatory Cells in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients. Scand. J. Immunol. 2017, 86, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khazaie, K.; Blatner, N.R.; Khan, M.W.; Gounari, F.; Gounaris, E.; Dennis, K.; Bonertz, A.; Tsai, F.-N.; Strouch, M.J.T.; Cheon, E.; et al. The significant role of mast cells in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2011, 30, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlini, M.J.; Dalurzo, M.C.L.; Lastiri, J.M.; Smith, D.E.; Vasallo, B.C.; Puricelli, L.I.; de Cidre, L.S.L. Mast cell phenotypes and microvessels in non–small cell lung cancer and its prognostic significance. Hum. Pathol. 2010, 41, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, Y.; Tanemura, A.; Tada, Y.; Katayama, I.; Kumanogoh, A.; Nishikawa, H. Clinical response to PD-1 blockade correlates with a sub-fraction of peripheral central memory CD4+ T cells in patients with malignant melanoma. Int. Immunol. 2017, 30, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.-Y.; Huang, D.-Y.; Zhang, H.-J.; Chen, J.; Miller, W.; Chen, X.-F. Function of follicular helper T cell is impaired and correlates with survival time in non-small cell lung cancer. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2016, 41, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heavey, S.; O’Byrne, K.J.; Gately, K. Strategies for co-targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in NSCLC. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2014, 40, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrzesinski, S.H.; Wan, Y.Y.; Flavell, R.A. Transforming Growth Factor-β and the Immune Response: Implications for Anticancer Therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 5262–5270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordian, E.; Welsh, E.A.; Gimbrone, N.; Siegel, E.M.; Shibata, D.; Creelan, B.C.; Cress, W.D.; Eschrich, S.A.; Haura, E.B.; Muñoz-Antonia, T. Transforming growth factor β-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal signature predicts metastasis-free survival in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 810–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.L.; Jiang, X.M.; Huang, M.Y.; Feng, Z.L.; Chen, X.P.; Wang, Y.T.; Li, H.; Li, A.; Lin, L.G.; Lu, J.J. Nagilactone E suppresses TGF-β1-induced epithelial–mesenchymal transition, migration and invasion in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Phytomedicine 2019, 52, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Meng, Z.; Chen, R.; Guan, K.-L. The Hippo Pathway: Biology and Pathophysiology. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2019, 88, 577–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rensburg, H.J.J.; Yang, X. The roles of the Hippo pathway in cancer metastasis. Cell Signal. 2016, 28, 1761–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, B.; Yang, Y.L.; Xu, Z.; Dai, Y.Y.; Liu, S.; Mao, J.H.; Tetsu, O.; Li, H.; Jablons, D.M.; You, L. Inhibition of ERK1/2 down-regulates the Hippo/YAP signaling pathway in human NSCLC cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 4357–4368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, D.J. Wnt Signaling Pathway in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2014, 106, djt356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolos, F.; Thomas, C.; Rajapaksa, G.; Bado, I.; Gustafsson, J.Å. ERβ Regulates NSCLC Phenotypes by Controlling Oncogenic RAS Signaling. Mol. Cancer Res. 2014, 12, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Gene Symbol | Drug(s) |
|---|---|
| PDCD1 | CT-011; Nivolumab; Pembrolizumab |
| AKT1 | Adenosine triphosphate; Arsenic trioxide; Inositol 1,3,4,5-Tetrakisphosphate; N-[2-(5-methyl-4H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)phenyl]-7H-pyrrolo [2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-amine; 5-(5-chloro-7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1H-imidazo[4,5-c]pyridine |
| POR | Flavin adenine dinucleotide; Riboflavin Monophosphate; 2′-Monophosphoadenosine 5′-Diphosphoribose |
| GABRQ | Temazepam; Midazolam; Flurazepam; Diazepam; Oxazepam; Triazolam; Ethanol; Bromazepam; Nitrazepam |
| ADRB2 | Betaxolol; Isoetarine; Cabergoline; Metoprolol; Atenolol; Norepinephrine; Mirtazapine; Timolol; Phenylpropanolamine; Dipivefrin; Sotalol; Carteolol; Propranolol; Labetalol; Bisoprolol; Epinephrine; Orciprenaline; Dobutamine; Pseudoephedrine; Alprenolol; Ritodrine; Terbutaline; Bitolterol; Phenoxybenzamine; Salmeterol; Pindolol; Formoterol; Salbutamol; Isoprenaline; Arbutamine; Carvedilol; Desipramine; Acebutolol; Nadolol; Levobunolol; Metipranolol; Arformoterol; Fenoterol; Pirbuterol; Bevantolol; Penbutolol; Ephedra; Procaterol; Clenbuterol; Bambuterol; Oxprenolol; Celiprolol; Nebivolol; Indacaterol; NCX 950; Asenapine; Droxidopa; (2S)-1-(9H-Carbazol-4-yloxy)-3-(isopropylamino)propan-2-ol; Bopindolol; Bupranolol; Olodaterol; Vilanterol |
| KDR | Sorafenib; Sunitinib; N-(4-{4-AMINO-6-[4-(METHYLOXY)PHENYL]FURO[2,3-D]PYRIMIDIN-5-YL}PHENYL)-N’-[2-FLUORO-5-(TRIFLUOROMETHYL)PHENYL]UREA; AZD2171; Vatalanib; XL999; XL880; TG100801; XL820; XL184; CYC116; Ramucirumab; ABT-869; IMC-1C11; Pazopanib; Axitinib; 4-[[2-[[4-chloro-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]amino]-3H-benzimidazol-5-yl]oxy]-N-methyl-pyridine-2-carboxamide; N-(4-phenoxyphenyl)-2-[(pyridin-4-ylmethyl)amino]nicotinamide; N-cyclopropyl-6-[(6,7-dimethoxyquinolin-4-yl)oxy]naphthalene-1-carboxamide; 6-chloro-N-pyrimidin-5-yl-3-{[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]amino}-1,2-benzisoxazole-7-carboxamide; N-(CYCLOPROPYLMETHYL)-4-(METHYLOXY)-3-({5-[3-(3-PYRIDINYL)PHENYL]-1,3-OXAZOL-2-YL}AMINO)BENZENESULFONAMIDE; N-[5-(ETHYLSULFONYL)-2-METHOXYPHENYL]-5-[3-(2-PYRIDINYL)PHENYL]-1,3-OXAZOL-2-AMINE; 3-(2-aminoquinazolin-6-yl)-1-(3,3-dimethylindolin-6-yl)-4-methylpyridin-2(1H)-one; 3-(2-aminoquinazolin-6-yl)-4-methyl-1-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]pyridin-2(1H)-one; N’-(6-aminopyridin-3-yl)-N-(2-cyclopentylethyl)-4-methyl-benzene-1,3-dicarboxamide; N~4~-methyl-N~4~-(3-methyl-1H-indazol-6-yl)-N~2~-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)pyrimidine-2,4-diamine; N~4~-(3-methyl-1H-indazol-6-yl)-N~2~-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)pyrimidine-2,4-diamine; Cabozantinib; Regorafenib; Ponatinib; Lenvatinib; Nintedanib |
| SOD2 | Benzylsulfinic Acid; 3-Fluorotyrosine |
| NR1I2 | Vitamin E; Erlotinib; Estradiol; Ethinyl Estradiol; Rifampicin; Rifaximin; Paclitaxel; Docetaxel; Prasterone; Hyperforin; SR12813; N-(2,2,2-TRIFLUOROETHYL)-N-{4-[2,2,2-TRIFLUORO-1-HYDROXY-1-(TRIFLUOROMETHYL)ETHYL]PHENYL}BENZENESULFONAMIDE; Rilpivirine |
| SCNN1G | Triamterene; Amiloride |
| CBR1 | 2-(2-{2-[2-(2-{2-[2-(2-Ethoxy-Ethoxy)-Ethoxy]-Ethoxy}-Ethoxy)-Ethoxy]-Ethoxy}-Ethoxy)-Ethanol; Polyethyleneglycol Peg400; 3-(4-Amino-1-Tert-Butyl-1h-Pyrazolo[3,4-D]Pyrimidin-3-Yl)Phenol |
| PPARD | Icosapent; Treprostinil; Sulindac; Bezafibrate; Heptyl-Beta-D-Glucopyranoside; (11E)-OCTADEC-11-ENOIC ACID; GFT505; KD3010; (2S)-2-{3-[({[2-fluoro-4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]carbonyl}amino)methyl]-4-methoxybenzyl}butanoic acid; 2-({[3-(3,4-dihydroisoquinolin-2(1H)-ylsulfonyl)phenyl]carbonyl}amino)benzoic acid; 3-{5-methoxy-1-[(4-methoxyphenyl)sulfonyl]-1H-indol-3-yl}propanoic acid; {4-[3-(4-acetyl-3-hydroxy-2-propylphenoxy)propoxy]phenoxy}acetic acid |
| Characteristic | TCGA-05-4402 | TCGA-05-4424 | TCGA-05-5425 | TCGA-49-6742 | TCGA-73-A9RS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Female | Male | Male | Male | Male |
| Age | 57 | 70 | 68 | 70 | 41 |
| Pathologic stage | Stage IV | Stage IIB | Stage IIB | Stage IIA | Stage IIB |
| Primary diagnosis | Adenocarcinoma with mixed subtypes | Adenocarcinoma with mixed subtypes | Adenocarcinoma with mixed subtypes | Mucinous adenocarcinoma | Adenocarcinoma, NOS |
| Site of resection or biopsy | Lower lobe, lung | Upper lobe, lung | Lung, NOS | Upper lobe, lung | Upper lobe, lung |
| Therapy drug name | Erlotinib | Erlotinib | Gefitinib Erlotinib | MDX-1106 clinical trial | Bevacizumab |
| Vital status | Dead | Alive | Alive | Dead | Dead |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, L.; Cao, Z.; Liu, H.; Liang, N.; Bing, Z.; Tian, C.; Li, S. Detection of Potential Mutated Genes Associated with Common Immunotherapy Biomarkers in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 5715-5730. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29080451
Cao L, Cao Z, Liu H, Liang N, Bing Z, Tian C, Li S. Detection of Potential Mutated Genes Associated with Common Immunotherapy Biomarkers in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients. Current Oncology. 2022; 29(8):5715-5730. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29080451
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Lei, Zhili Cao, Hongsheng Liu, Naixin Liang, Zhongxing Bing, Caijuan Tian, and Shanqing Li. 2022. "Detection of Potential Mutated Genes Associated with Common Immunotherapy Biomarkers in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients" Current Oncology 29, no. 8: 5715-5730. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29080451
APA StyleCao, L., Cao, Z., Liu, H., Liang, N., Bing, Z., Tian, C., & Li, S. (2022). Detection of Potential Mutated Genes Associated with Common Immunotherapy Biomarkers in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients. Current Oncology, 29(8), 5715-5730. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29080451





