The Impact of Dense Breasts on the Stage of Breast Cancer at Diagnosis: A Review and Options for Supplemental Screening
Abstract
1. Background: Screening Mammography
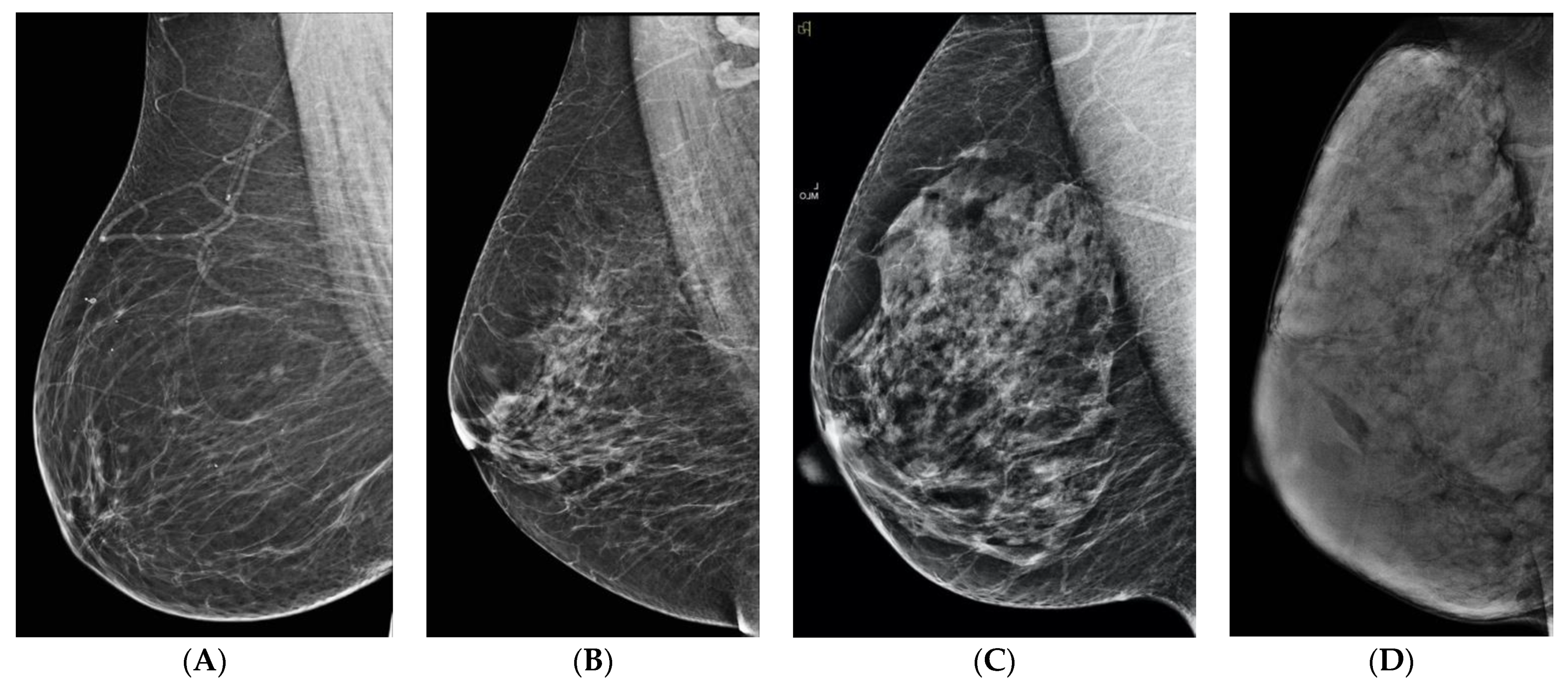
2. What Is Breast Density?
3. What Is the Significance of Dense Breasts?
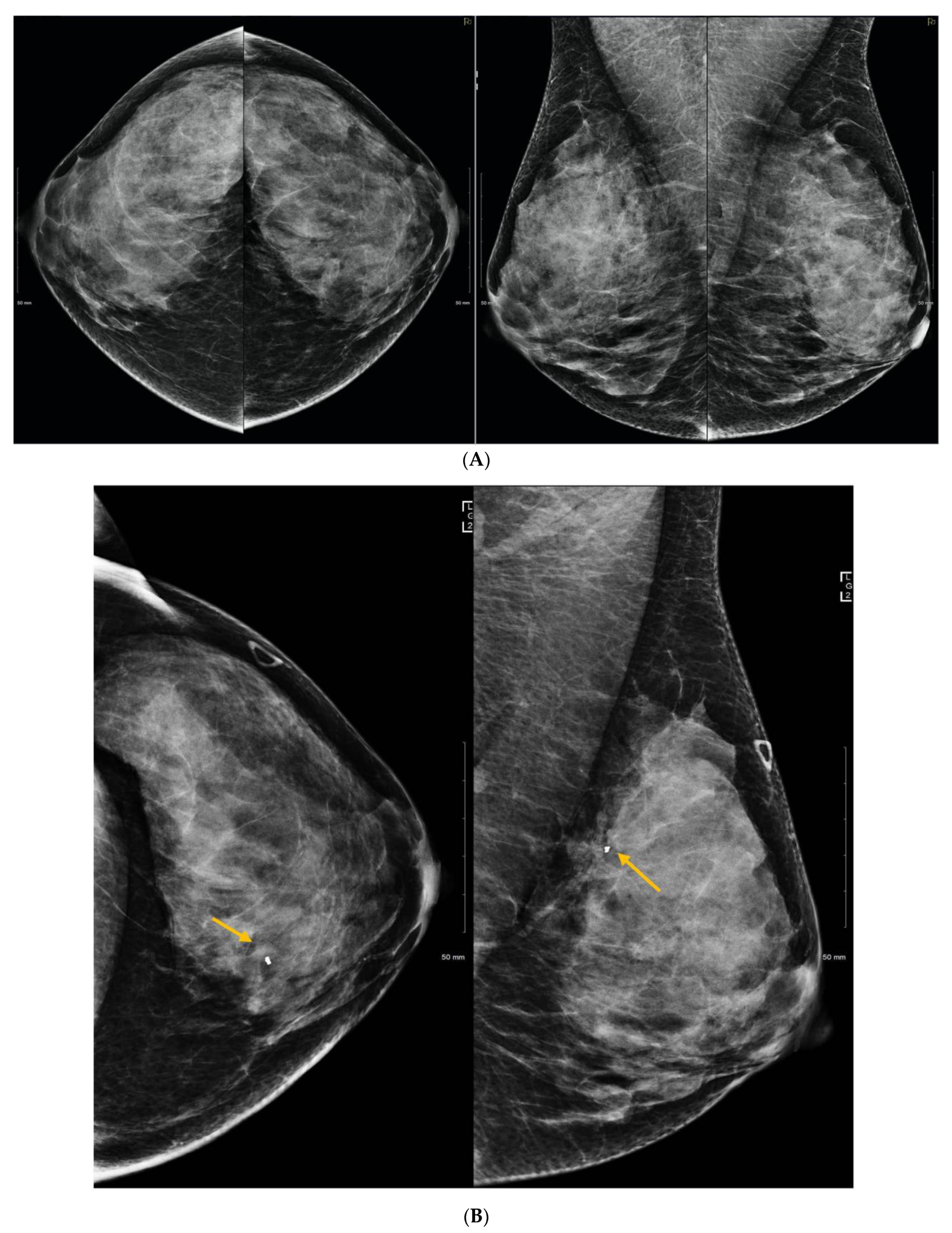
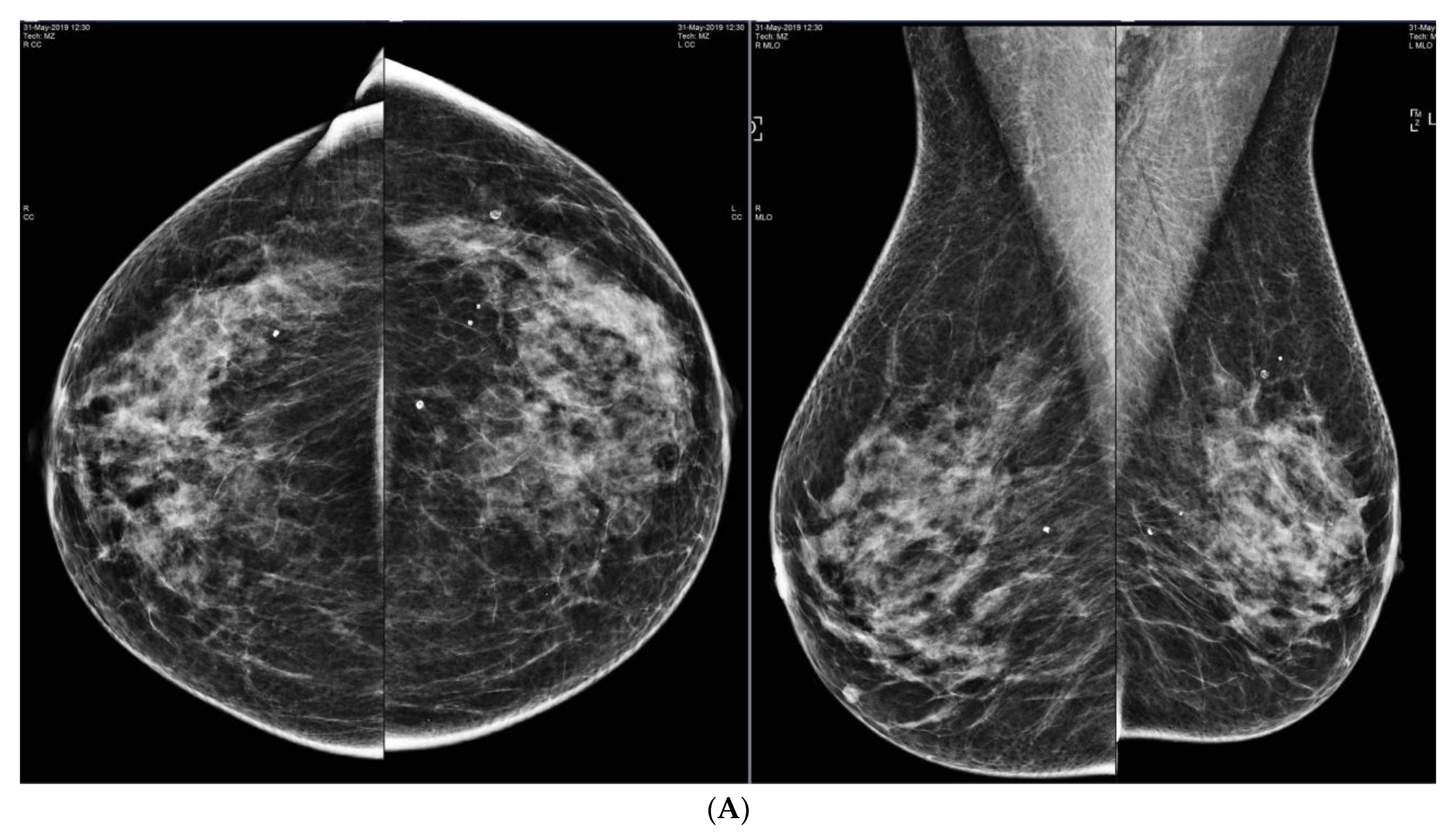
4. Density and Interval Cancers
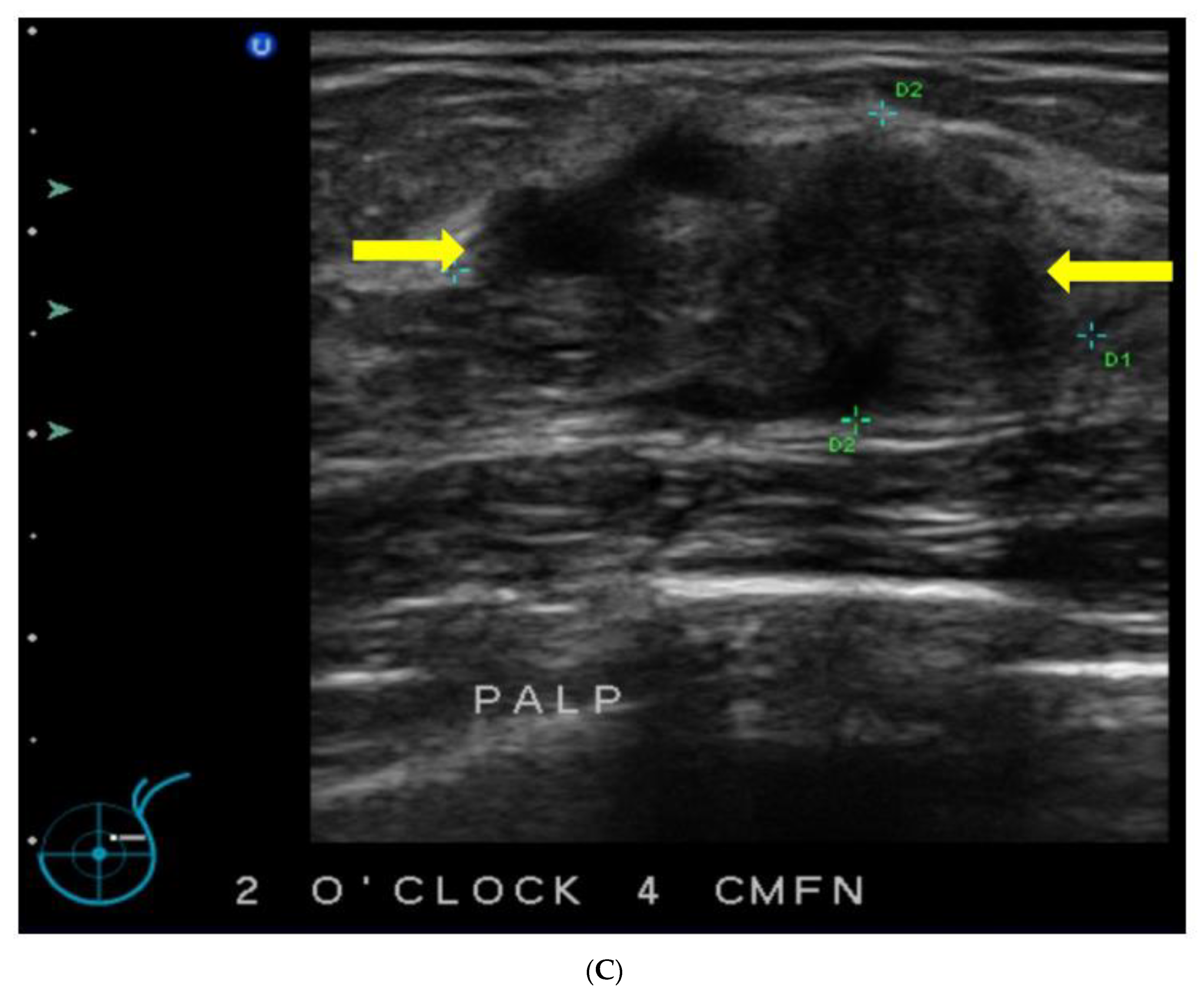
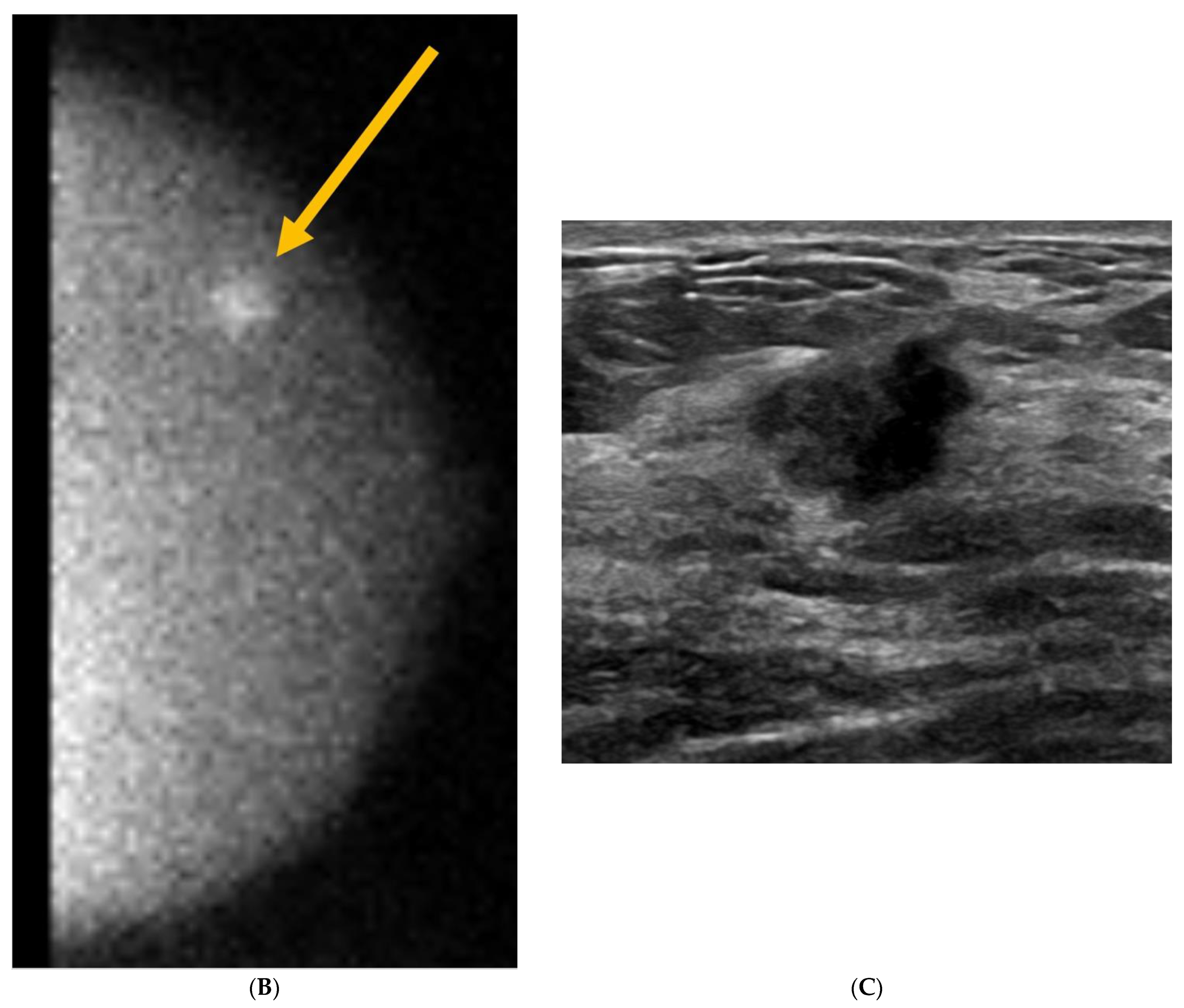
5. Ultrasound (US)
6. Digital Breast Tomosynthesis (DBT)
7. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
8. Contrast-Enhanced Mammography (CEM)
9. Molecular Breast Imaging (MBI)
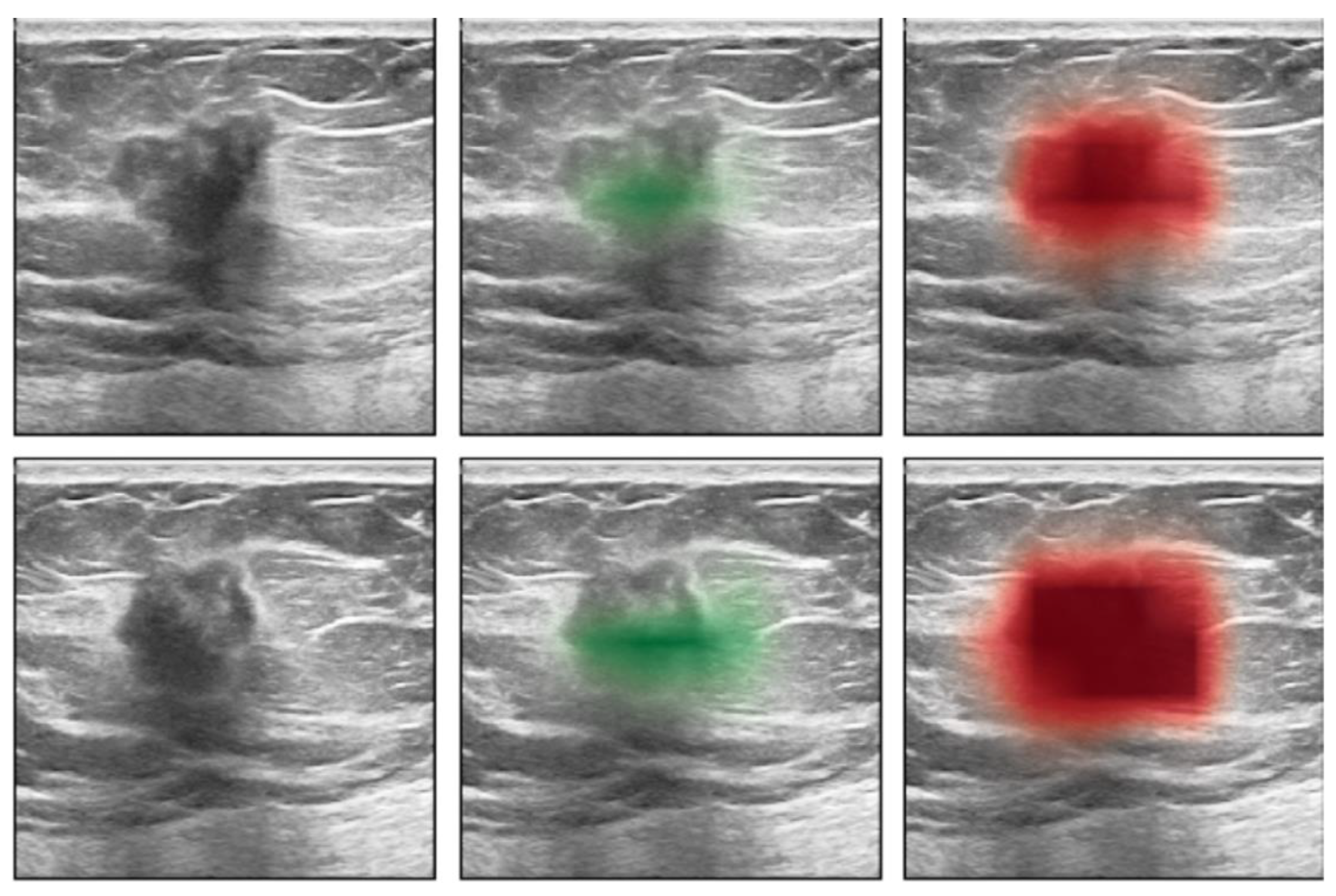
10. Artificial Intelligence (AI)
11. Summary of Benefits vs. Risks
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RCT | Randomized Controlled Trial |
| ACR | American College of Radiology |
| BI-RADS | Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System |
| FFDM | Full Field Digital Mammography |
| IC | Interval Cancer |
| ER | Estrogen Receptor |
| PR | Progesterone Receptor |
| US | Ultrasound |
| DBT | Digital Breast Tomosynthesis |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| CEM | Contrast-Enhanced Mammography |
| MBI | Molecular Breast Imaging |
| DCIS | Ductal Carcinoma In-situ |
| ICDR | Incremental Cancer Detection Rate |
| ACRIN | American College of Radiology Imaging Network |
| PPV | Positive Predictive Value |
| J-START | Japan Strategic Anti-cancer Randomized Trial |
| FDA | United States Food and Drug Administration |
| 2D | Two Dimensional |
| MLO | Mediolateral Oblique |
| CC | Craniocaudal |
| QUALYs | Quality-Adjusted Life-Years |
| EUSOBI | European Society of Breast Imaging |
| DW MRI | Diffusion-Weighted MRI |
| CE MRI | Contrast-enhanced MRI |
| AB MRI | Abbreviated MRI |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
| IV | Intravenous |
| kVp | Kilovoltage peak |
References
- Coldman, A.; Phillips, N.; Wilson, C.; Decker, K.; Chiarelli, A.M.; Brisson, J.; Zhang, B.; Payne, J.; Doyle, G.; Ahmad, R. Pan-Canadian study of mammography screening and mortality from breast cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2014, 106, dju261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabár, L.; Dean, P.B.; Chen, T.H.H.; Yen, A.M.; Chen, S.L.; Fann, J.C.; Chiu, S.Y.; Ku, M.M.; Wu, W.Y.; Hsu, C.Y.; et al. The incidence of fatal breast cancer measures the increased effectiveness of therapy in women participating in mammography screening. Cancer 2019, 125, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broeders, M.; Moss, S.; Nystrom, L.; Njor, S.; Jonsson, H.; Paap, E.; Massat, N.; Duffy, S.; Lynge, E.; Paci, E. The impact of mammographic screening on breast cancer mortality in Europe: A review of observational studies. J. Med. Screen. 2012, 19 (Suppl. S1), 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprague, B.L.; Gangnon, R.E.; Burt, V.; Trentham-Dietz, A.; Hampton, J.M.; Wellman, R.D.; Kerlikowske, K.; Miglioretti, D.L. Prevalence of mammographically dense breasts in the United States. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2014, 106, dju255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Moore, J.X.; Colditz, G.A.; Toriola, A.T. Family History of Breast Cancer and Mammographic Breast Density in Premenopausal Women. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2148983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyd, N.F.; Guo, H.; Martin, L.J.; Sun, L.; Stone, J.; Fishell, E.; Jong, R.A.; Hislop, G.; Chiarelli, A.; Minkin, S.; et al. Mammographic density and the risk and detection of breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerlikowske, K.; Zhu, W.; Tosteson, A.N.A.; Sprague, B.L.; Tice, J.A.; Lehman, C.D.; Miglioretti, D.L.; Breast Cancer Surveillance Consortium. Identifying women with dense breasts at high risk for interval cancer a cohort study. Ann. Intern. Med. 2015, 162, 673–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weigel, S.; Heindel, W.; Heidrich, J.; Hense, H.W.; Heidinger, O. Digital mammography screening: Sensitivity of the programme dependent on breast density. Eur. Radiol. 2017, 27, 2744–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Waal, D.; Ripping, T.M.; Verbeek, A.L.M.; Broeders, M.J.M. Breast cancer screening effect across breast density strata: A case–control study. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 140, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, S.Y.H.; Duffy, S.; Yen, A.M.F.; Tabár, L.; Smith, R.A.; Chen, H.H. Effect of baseline breast density on breast cancer incidence, stage, mortality, and screening parameters: 25-Year follow-up of a Swedish mammographic screening. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2010, 19, 1219–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engmann, N.J.; Golmakani, M.K.; Miglioretti, D.L.; Sprague, B.L.; Kerlikowske, K. Population-attributable risk proportion of clinical risk factors for breast cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 1228–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyd, N.F.; Dite, G.S.; Stone, J.; Gunasekara, A.; English, D.R.; McCredie, M.R.; Giles, G.G.; Tritchler, D.; Chiarelli, A.; Yaffe, M.J.; et al. Heritability of mammographic density, a risk factor for breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 886–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCormack, V.A.; dos Santos Silva, I. Breast density and parenchymal patterns as markers of breast cancer risk: A meta-analysis. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2006, 15, 1159–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertrand, K.A.; Tamimi, R.M.; Scott, C.G.; Jensen, M.R.; Pankratz, V.; Visscher, D.; Norman, A.; Couch, F.; Shepherd, J.; Fan, B.; et al. Mammographic Density and Risk of Breast Cancer by Age and Tumor Characteristics. Breast Cancer Res. 2013, 15, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 1Gram, I.T.; Funkhouser, E.; Tabár, L. The Tabár classification of mammographic parenchymal patterns. Eur. J. Radiol. 1997, 24, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skarping, I.; Förnvik, D.; Sartor, H.; Heide-Jørgensen, U.; Zackrisson, S.; Borgquist, S. Mammographic density is a potential predictive marker of pathological response after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodard, G.A.; Ray, K.M.; Joe, B.N.; Price, E.R. Qualitative radiogenomics: Association between oncotype DX test recurrence score and BI-RADS mammographic and breast MR imaging features. Radiology 2018, 286, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.S.; Chen, J.L.Y.; Huang, C.S.; Kuo, S.H.; Jaw, F.S.; Tseng, Y.H.; Ko, W.C.; Chang, Y.C. High mammographic breast density predicts locoregional recurrence after modified radical mastectomy for invasive breast cancer: A case-control study. Breast Cancer Res. 2016, 18, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, L.; Czene, K.; Rosenberg, L.; Humphreys, K.; Hall, P. Possible Influence of Mammographic Density on Local and Locoregional Recurrence of Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2013, 15, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, P.L.; El-Bastawissi, A.Y.; Mandelson, M.T.; Lin, M.G.; Khalid, N.; Watney, E.A.; Cousens, L.; White, D.; Taplin, S.; White, E. Breast Tumor Character-Istics as Predictors of Mammographic Detection: Comparison of Interval-and Screen-Detected Cancers. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2022, 114, 483–484. [Google Scholar]
- Domingo, L.; Salas, D.; Zubizarreta, R.; Baré, M.; Sarriugarte, G.; Barata, T.; Ibáñez, J.; Blanch, J.; Puig-Vives, M.; Fernández, A.; et al. Tumor Phenotype and Breast Density in Distinct Categories of Interval Cancer: Results of Population-Based Mammography Screening in Spain. Breast Cancer Res. 2014, 16, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houssami, N.; Hunter, K. The epidemiology, radiology and biological characteristics of interval breast cancers in population mammography screening. Npj Breast Cancer 2017, 3, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilliland, F.D.; Joste, N.; Stauber, P.M.; Hunt, W.C.; Rosenberg, R.; Redlich, G.; Key, C.R. Biologic Characteristics of Interval and Screen-Detected Breast Cancers. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2000, 92, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirsh, V.A.; Chiarelli, A.M.; Edwards, S.A.; O’Malley, F.P.; Shumak, R.S.; Yaffe, M.J.; Boyd, N.F. Tumor characteristics associated with mammographic detection of breast cancer in the Ontario breast screening program. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2011, 103, 942–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, A.M.; Friebel-Klingner, T.; Ehsan, S.; He, W.; Welch, M.; Chen, J.; Kontos, D.; Domchek, S.M.; Conant, E.F.; Semine, A.; et al. Relationship of established risk factors with breast cancer subtypes. Cancer Med. 2021, 10, 6456–6467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehman, C.D.; Arao, R.F.; Sprague, B.L.; Lee, J.M.; Buist, D.S.; Kerlikowske, K.; Henderson, L.M.; Onega, T.; Tosteson, A.N.; Rauscher, G.H.; et al. National Performance Benchmarks for Modern Screening Digital Mammography: Update from the Breast Cancer Surveillance Consortium. Radiology 2017, 283, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seely, J.M.; Peddle, S.E.; Yang, H.; Chiarelli, A.M.; McCallum, M.; Narasimhan, G.; Zakaria, D.; Earle, C.C.; Fung, S.; Bryant, H.; et al. Breast Density and Risk of Interval Cancers: The Effect of Annual Versus Biennial Screening Mammography Policies in Canada. Can. Assoc. Radiol. J. = J. L’association Can. Des Radiol. 2022, 73, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiarelli, A.M.; Kirsh, V.A.; Klar, N.S.; Shumak, R.; Jong, R.; Fishell, E.; Yaffe, M.J.; Boyd, N.F. Influence of patterns of hormone replacement therapy use and mammographic density on breast cancer detection. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2006, 15, 1856–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavanagh, A.M.; Byrnes, G.B.; Nickson, C.; Cawson, J.N.; Giles, G.G.; Hopper, J.L.; Gertig, D.M.; English, D.R. Using mammographic density to improve breast cancer screening outcomes. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2008, 17, 2818–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciatto, S.; Visioli, C.; Paci, E.; Zappa, M. Breast density as a determinant of interval cancer at mammographic screening. Br. J. Cancer 2004, 90, 393–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strand, F.; Azavedo, E.; Hellgren, R.; Humphreys, K.; Eriksson, M.; Shepherd, J.; Hall, P.; Czene, K. Localized mammographic density is associated with interval cancer and large breast cancer: A nested case-control study. Breast Cancer Res. 2019, 21, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niraula, S.; Biswanger, N.; Hu, P.Z.; Lambert, P.; Decker, K. Incidence, Characteristics, and Outcomes of Interval Breast Cancers Compared with Screening-Detected Breast Cancers. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e2018179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhl, C.K.; Baltzer, P. You Get What You Pay For: Breast MRI Screening of Women with Dense Breasts Is Cost-effective. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2021, 113, 1439–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, A.S. Intermediate Determinants of Mortality in the Evaluation of Screening. Int. J. Epidemiol. 1991, 20, 642–650. Available online: https://academic.oup.com/ije/article/20/3/642/654391 (accessed on 12 March 2022). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sickles, E.A.; Filly, R.A.; Callen, P.W. Breast cancer detection with sonography and mammography: Comparison using state-of-the-art equipment. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1983, 140, 843–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassett, L.W.; Kimme-Smith, C.; Sutherland, L.K.; Gold, R.H.; Sarti, D.; King, W. Automated and hand-held breast US: Effect on patient management. Radiology 1987, 165, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilton, S.V.W.; Leopold, G.R.; Olson, L.K.; Wiiison, S.A.; Hilton, S.V.W. Real-Time Breast Sonography: Application in 300 Consecutive Patients. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1986, 147, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, A.P.; Kelly-Fry, E.; Noe, J.S.; Bies, J.R.; Jackson, V.P. Ultrasound in the evaluation of solid breast masses. Radiology 1983, 146, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavros, A.T.; Thickman, D.; Rapp, C.L.; Dennis, M.A.; Parker, S.H.; Sisney, G.A. Solid breast nodules: Use of sonography to distinguish between benign and malignant lesions. Radiology 1995, 196, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, P.B.; Goldenberg, S.L. Malignant breast masses detected only by ultrasound. A retrospective review. Cancer 1995, 76, 626–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchberger, W.; Geiger-Gritsch, S.; Knapp, R.; Gautsch, K.; Oberaigner, W. Combined screening with mammography and ultrasound in a population-based screening program. Eur. J. Radiol. 2018, 101, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, S.S. Clinical utility of bilateral whole-breast US in the evaluation of women with dense breast tissue. Radiology 2001, 221, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolb, T.M.; Lichy, J.; Newhouse, J.H. Comparison of the performance of screening mammography, physical examination, and breast US and evaluation of factors that influence them: An analysis of 27,825 patient evaluations. Radiology 2002, 225, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crystal, P.; Strano, S.D.; Shcharynski, S.; Koretz, M.J. Using sonography to screen women with mammographically dense breasts. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2003, 181, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leconte, I.; Feger, C.; Galant, C.; Berlière, M.; Berg, B.V.; D’Hoore, W.; Maldague, B. Mammography and subsequent whole-breast sonography of nonpalpable breast cancers: The importance of radiologic breast density. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2003, 180, 1675–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, W.A. Supplemental screening sonography in dense breasts. Radiol. Clin. N. Am. 2004, 42, 845–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, W.A.; Zhang, Z.; Lehrer, D.; Jong, R.A.; Pisano, E.D.; Barr, R.G.; Böhm-Vélez, M.; Mahoney, M.C.; Evans, W.P., 3rd; Larsen, L.H.; et al. Detection of breast cancer with addition of annual screening ultrasound or a single screening MRI to mammography in women with elevated breast cancer risk. JAMA 2012, 307, 1394–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, R.G.; Zhang, Z.; Cormack, J.B.; Mendelson, E.B.; Berg, W.A. Probably Benign Lesions at Screening Breast US in a Population with Elevated Risk: Prevalence and Rate of Malignancy in the ACRIN 6666 Trial 1. Radiology 2013, 269, 701–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooley, R.J.; Greenberg, K.L.; Stackhouse, R.M.; Geisel, J.L.; Butler, R.S.; Philpotts, L.E. Screening US in patients with mammographically dense breasts: Initial experience with Connecticut public act 09-41. Radiology 2012, 265, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philpotts, L.; Raghu, M.; Durand, M.A.; Horvath, L.J.; Butler, R.S.; Levesque, P.H.; Hooley, R.J. Update on Technologist-performed, Screening Breast Ultrasound in Women with Dense Tissue 5 Years after CT Public Act No. 09-41: How Are We Doing Now? In Radiological Society of North America 2015 Scientific Assembly and Annual Meeting; RSNA: Oak Brook, IL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Weigert, J.; Steenbergen, S. The connecticut experiment: The role of ultrasound in the screening of women with dense breasts. Breast J. 2012, 18, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigert, J.M. The Connecticut Experiment; The Third Installment: 4 Years of Screening Women with Dense Breasts with Bilateral Ultrasound. Breast J. 2017, 23, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dense Breast Info. US States with Legislation Mandating Insurance Coverage for Supplemental Screening. Available online: https://densebreast-info.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/Table.laws_.insurance.ALPHA_.3.8.22.copyright.pdf (accessed on 12 March 2022).
- BC Cancer Screening. Breast Density Notification in BC. Available online: http://www.bccancer.bc.ca/screening/Documents/Breast_20191104_BDProviderGuidance_V07_OPT.pdf (accessed on 12 March 2022).
- Medical Services Plan of BC. Ultrasound for Dense Breast. Available online: https://www2.gov.bc.ca/assets/gov/health/practitioner-pro/medical-services-plan/ultrasound-policy-for-breast-density.pdf (accessed on 12 March 2022).
- Wu, T.; Warren, L.J. The Added Value of Supplemental Breast Ultrasound Screening for Women with Dense Breasts: A Single Center Canadian Experience. Can. Assoc. Radiol. J. 2022, 73, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, L.J. (University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada). Personal communication, 2021.
- Corsetti, V.; Houssami, N.; Ghirardi, M.; Ferrari, A.; Speziani, M.; Bellarosa, S.; Remida, G.; Gasparotti, C.; Galligioni, E.; Ciatto, S. Evidence of the effect of adjunct ultrasound screening in women with mammography-negative dense breasts: Interval breast cancers at 1 year follow-up. Eur. J. Cancer 2011, 47, 1021–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohuchi, N.; Suzuki, A.; Sobue, T.; Kawai, M.; Yamamoto, S.; Zheng, Y.F.; Shiono, Y.N.; Saito, H.; Kuriyama, S.; Tohno, E.; et al. Sensitivity and specificity of mammography and adjunctive ultrasonography to screen for breast cancer in the Japan Strategic Anti-cancer Randomized Trial (J-START): A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2016, 387, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada-Shoji, N.; Suzuki, A.; Ishida, T.; Zheng, Y.F.; Narikawa-Shiono, Y.; Sato-Tadano, A.; Ohta, R.; Ohuchi, N. Evaluation of Adjunctive Ultrasonography for Breast Cancer Detection among Women Aged 40–49 Years with Varying Breast Density Undergoing Screening Mammography: A Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2121505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leong, S.P.L.; Shen, Z.Z.; Liu, T.J.; Agarwal, G.; Tajima, T.; Paik, N.S.; Sandelin, K.; Derossis, A.; Cody, H.; Foulkes, W.D. Is Breast cancer the same disease in Asian and Western countries? World J. Surg. 2010, 34, 2308–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhl, C.K. A Call for Improved Breast Cancer Screening Strategies, Not only for Women with Dense Breasts. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2121492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhl, C.K.; Strobel, K.; Bieling, H.; Leutner, C.; Schild, H.H.; Schrading, S. Supplemental breast MR imaging screening of women with average risk of breast cancer. Radiology 2017, 283, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnuki, K.; Tohno, E.; Tsunoda, H.; Uematsu, T.; Nakajima, Y. Overall assessment system of combined mammography and ultrasound for breast cancer screening in Japan. Breast Cancer 2021, 28, 254–262, Erratum in Breast Cancer 2021, 28, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brem, R.F.; Tabár, L.; Duffy, S.W.; Inciardi, M.F.; Guingrich, J.A.; Hashimoto, B.E.; Lander, M.R.; Lapidus, R.L.; Peterson, M.K.; Rapelyea, J.A.; et al. Assessing improvement in detection of breast cancer with three-dimensional automated breast US in women with dense breast tissue: The somoinsight study. Radiology 2015, 274, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, K.M.; Dean, J.; Comulada, W.S.; Lee, S.J. Breast cancer detection using automated whole breast ultrasound and mammography in radiographically dense breasts. Eur. Radiol. 2010, 20, 734–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, W.A.; Vourtsis, A. Screening Breast Ultrasound Using Handheld or Automated Technique in Women with Dense Breasts. J. Breast Imaging 2019, 1, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Is Optimal Breast Cancer Screening Accessible in Your Province/Territory? Available online: https://mybreastscreening.ca (accessed on 12 March 2022).
- Dense Breast Info. State Legislation Map. Available online: https://densebreast-info.org/legislative-information/state-legislation-map/ (accessed on 12 March 2022).
- Dense Breast Info. European Screening Guidelines by Country. Available online: https://densebreast-info.org/europe/european-screening-guidelines/map-screening-guidelines/ (accessed on 12 March 2022).
- Niklason, L.T.; Christian, B.T.; Niklason, L.E.; Kopans, D.B.; Castleberry, D.E.; Opsahl-Ong, B.H.; Landberg, C.E.; Slanetz, P.J.; Giardino, A.A.; Moore, R.; et al. Digital tomosynthesis in breast imaging. Radiology 1997, 205, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skaane, P.; Bandos, A.I.; Eben, E.B.; Jebsen, I.N.; Krager, M.; Haakenaasen, U.; Ekseth, U.; Izadi, M.; Hofvind, S.; Gullien, R. Two-view digital breast tomosynthesis screening with synthetically reconstructed projection images: Comparison with digital breast tomosynthesis with full-field digital mammographic images. Radiology 2014, 271, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedewald, S.M.; Rafferty, E.A.; Rose, S.L.; Durand, M.A.; Plecha, D.M.; Greenberg, J.S.; Hayes, M.K.; Copit, D.S.; Carlson, K.L.; Cink, T.M.; et al. Breast cancer screening using tomosynthesis in combination with digital mammography. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2014, 311, 2499–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciatto, S.; Houssami, N.; Bernardi, D.; Caumo, F.; Pellegrini, M.; Brunelli, S.; Tuttobene, P.; Bricolo, P.; Fantò, C.; Valentini, M.; et al. Integration of 3D digital mammography with tomosynthesis for population breast-cancer screening (STORM): A prospective comparison study. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaane, P.; Bandos, A.I.; Niklason, L.T.; Sebuødegård, S.; Østerås, B.H.; Gullien, R.; Gur, D.; Hofvind, S. Digital mammography versus digital mammography plus tomosynthesis in breast cancer screening: The Oslo tomosynthesis screening trial. Radiology 2019, 291, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conant, E.F.; Zuckerman, S.P.; McDonald, E.S.; Weinstein, S.P.; Korhonen, K.E.; Birnbaum, J.A.; Tobey, J.D.; Schnall, M.D.; Hubbard, R.A. Five consecutive years of screening with digital breast tomosynthesis: Outcomes by screening year and round. Radiology 2020, 295, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partyka, L.; Lourenco, A.P.; Mainiero, M.B. Detection of mammographically occult architectural distortion on digital breast tomosynthesis screening: Initial clinical experience. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2014, 203, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafferty, E.A.; Park, J.M.; Philpotts, L.E.; Poplack, S.P.; Sumkin, J.H.; Halpern, E.F.; Niklason, L.T. Assessing Radiologist Performance Using Combined Digital Mammography and Breast Tomosynthesis Compared with Digital Mammography Alone: Results of a Multicenter, Multireader Trial 1. Radiology 2013, 266, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA. MQSA National Statistics. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/radiation-emitting-products/mqsa-insights/mqsa-national-statistics (accessed on 12 March 2022).
- Digital Tomosynthesis Mammography and Digital Mammography in Screening Patients for Breast Cancer. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03233191#contacts (accessed on 12 March 2022).
- Lee, C.; McCaskill-Stevens, W. Tomosynthesis mammographic Imaging Screening Trial (TMIST): An Invitation and Opportunity for the National Medical Association Community to Shape the Future of Precision Screening for Breast Cancer. J. Natl. Med. Assoc. 2020, 112, 613–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conant, E.F.; Beaber, E.F.; Sprague, B.L.; Herschorn, S.D.; Weaver, D.L.; Onega, T.; Tosteson, A.N.; McCarthy, A.M.; Poplack, S.P.; Haas, J.S.; et al. Breast cancer screening using tomosynthesis in combination with digital mammography compared to digital mammography alone: A cohort study within the PROSPR consortium. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2016, 156, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahl, M.; Gaffney, S.; McCarthy, A.M.; Lowry, K.P.; Dang, P.A.; Lehman, C.D. Breast cancer characteristics associated with 2D digital mammography versus digital breast tomosynthesis for screening-detected and interval cancers. Radiology 2018, 287, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafferty, E.A.; Durand, M.A.; Conant, E.F.; Copit, D.S.; Friedewald, S.M.; Plecha, D.M.; Miller, D.P. Breast Cancer Screening Using Tomosynthesis and Digital Mammography in Dense and Nondense Breasts. JAMA 2016, 315, 1784–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tagliafico, A.S.; Calabrese, M.; Mariscotti, G.; Durando, M.; Tosto, S.; Monetti, F.; Airaldi, S.; Bignotti, B.; Nori, J.; Bagni, A.; et al. Adjunct screening with tomosynthesis or ultrasound in women with mammography-negative dense breasts: Interim report of a prospective comparative trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 1882–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tagliafico, A.S.; Mariscotti, G.; Valdora, F.; Durando, M.; Nori, J.; La Forgia, D.; Rosenberg, I.; Caumo, F.; Gandolfo, N.; Sormani, M.P.; et al. A prospective comparative trial of adjunct screening with tomosynthesis or ultrasound in women with mammography-negative dense breasts (ASTOUND-2). Eur. J. Cancer 2018, 104, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancer Stat Facts: Cancer Disparities Reports on Cancer Annual Report to the Nation Cancer Stat Facts Breast (Female) Melanoma of the Skin Statistics at a Glance. Available online: https://seer.Cancer.gov/statistics/reports.html (accessed on 12 March 2022).
- Foy, K.C.; Fisher, J.L.; Lustberg, M.B.; Gray, D.M.; De Graffinreid, C.R.; Paskett, E.D. Disparities in breast cancer tumor characteristics, treatment, time to treatment, and survival probability among African American and white women. NPJ Breast Cancer 2018, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochman, S. Study Finds Black Women Have Denser Breast Tissue Than White Women. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2015, 107, djv296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dietze, E.C.; Sistrunk, C.; Miranda-Carboni, G.; O’regan, R.; Seewaldt, V.L. Triple-Negative Breast Cancer in African-American Women: Disparities Versus Biology. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 248–254. Available online: https://www.nature.com/reviews/cancer (accessed on 12 March 2022). [CrossRef]
- Berg, W.A. Tailored supplemental screening for breast cancer: What now and what next? Am. J. Roentgenol. 2009, 192, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhl, C.; Weigel, S.; Schrading, S.; Arand, B.; Bieling, H.; König, R.; Tombach, B.; Leutner, C.; Rieber-Brambs, A.; Nordhoff, D.; et al. Prospective multicenter cohort study to refine management recommendations for women at elevated familial risk of breast cancer: EVA Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 1450–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, G.W.; Gibby, W.A.; Tweedle, M.F. Comparison of Gd(DTPA-BMA) (Omniscan) versus Gd(HP-DO3A) (ProHance) relative to gadolinium retention in human bone tissue by inductively coupled plasma mass spectroscopy. Investig. Radiol. 2006, 41, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibby, W.A.; Gibby, K.A.; Gibby, W.A. Comparison of Gd DTPA-BMA (Omniscan) versus Gd HP-DO3A (ProHance) retention in human bone tissue by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy. Investig. Radiol. 2004, 39, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, D.R.; Lindhorst, S.M.; Welsh, C.T.; Maravilla, K.R.; Herring, M.N.; Braun, K.A.; Thiers, B.H.; Davis, W.C. High Levels of Gadolinium Deposition in the Skin of a Patient with Normal Renal Function. Investig. Radiol. 2016, 51, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, R.J.; McDonald, J.S.; Dai, D.; Schroeder, D.; Jentoft, M.E.; Murray, D.L.; Kadirvel, R.; Eckel, L.J.; Kallmes, D.F. Comparison of gadolinium concentrations within multiple rat organs after intravenous administration of linear versus macrocyclic gadolinium chelates. Radiology 2017, 285, 536–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, R.J.; McDonald, J.S.; Kallmes, D.F.; Jentoft, M.E.; Murray, D.L.; Thielen, K.R.; Williamson, E.E.; Eckel, L.J. Intracranial gadolinium deposition after contrast-enhanced MR imaging. Radiology 2015, 275, 772–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, C.H. Screening Breast MRI and Gadolinium Deposition: Cause for Concern? J. Breast Imaging 2022, 4, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheel, J.R.; Kim, E.; Partridge, S.C.; Lehman, C.D.; Rosen, M.A.; Bernreuter, W.K.; Pisano, E.D.; Marques, H.S.; Morris, E.A.; Weatherall, P.T.; et al. MRI, clinical examination, and mammography for preoperative assessment of residual disease and pathologic complete response after neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer: ACRIN 6657 trial. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2018, 210, 1376–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saslow, D.; Boetes, C.; Burke, W.; Harms, S.; Leach, M.O.; Lehman, C.D.; Morris, E.; Pisano, E.; Schnall, M.; Sener, S.; et al. American Cancer Society guidelines for breast screening with MRI as an adjunct to mammography. Cancer J. Clin. 2007, 57, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monticciolo, D.L.; Newell, M.S.; Moy, L.; Niell, B.; Monsees, B.; Sickles, E.A. Breast Cancer Screening in Women at Higher-Than-Average Risk: Recommendations From the ACR. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 2018, 15, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, M.F.; de Lange, S.V.; Pijnappel, R.M.; Mann, R.M.; Peeters, P.H.M.; Monninkhof, E.M.; Emaus, M.J.; Loo, C.E.; Bisschops, R.H.C.; Lobbes, M.B.I.; et al. Supplemental MRI Screening for Women with Extremely Dense Breast Tissue. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 2091–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mango, V.L.; Goel, A.; Mema, E.; Kwak, E.; Ha, R. Breast MRI screening for average-risk women: A monte carlo simulation cost–benefit analysis. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, 49, e216–e221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geuzinge, H.A.; Bakker, M.F.; Heijnsdijk, E.A.M.; Ravesteyn, N.T.; Veldhuis, W.B.; Pijnappel, R.M.; de Lange, S.V.; Emaus, M.J.; Mann, R.M.; Monninkhof, E.M.; et al. Cost-Effectiveness of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Screening for Women with Extremely Dense Breast Tissue. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2021, 113, 1476–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, R.M.; Athanasiou, A.; Baltzer, P.A.T.; Camps-Herrero, J.; Clauser, P.; Fallenberg, E.M.; Forrai, G.; Fuchsjäger, M.H.; Helbich, T.H.; Killburn-Toppin, F.; et al. Breast Cancer Screening in Women with Extremely Dense Breasts Recommendations of the European Society of Breast Imaging (EUSOBI). Eur. Radiol. 2022, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, W.A.; Blume, J.D.; Adams, A.M.; Jong, R.A.; Barr, R.G.; Lehrer, D.E.; Pisano, E.D.; Evans, W.P., 3rd; Mahoney, M.C.; Hovanessian Larsen, L.; et al. Reasons women at elevated risk of breast cancer refuse breast MR imaging screening: ACRIN 6666. Radiology 2010, 254, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, V.; Hatterman, V.; Preibsch, H.; Bahrs, S.D.; Hahn, M.; Nikolaou, K.; Wiesinger, B. Contrast-enhanced spectral mammography in patients with MRI contraindications. Acta Radiol. 2018, 59, 798–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghadimi, M.; Sapra, A. Magnetic Resonance Imaging Contraindications; StatPearls Publishing LLC: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhl, C.K.; Schrading, S.; Strobel, K.; Schild, H.H.; Hilgers, R.D.; Bieling, H.B. Abbreviated breast Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): First postcontrast subtracted images and maximum-intensity projection—A novel approach to breast cancer screening with MRI. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 2304–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhl, C.K. Abbreviated Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) for Breast Cancer Screening: Rationale, Concept, and Transfer to Clinical Practice. Annu. Rev. Med. 2019, 70, 501–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comstock, C.E.; Gatsonis, C.; Newstead, G.M.; Snyder, B.S.; Gareen, I.F.; Bergin, J.T.; Rahbar, H.; Sung, J.S.; Jacobs, C.; Harvey, J.A.; et al. Comparison of Abbreviated Breast MRI vs Digital Breast Tomosynthesis for Breast Cancer Detection among Women with Dense Breasts Undergoing Screening. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2020, 323, 746–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.; Heacock, L.; Gao, Y.; Elias, K.; Moy, L.; Heller, S. Advances in Abbreviated Breast MRI and Ultrafast Imaging. Semin. Roentgenol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Flynn, E.A.M.; Blackledge, M.; Collins, D.; Downey, K.; Doran, S.; Patel, H.; Dumonteil, S.; Mok, W.; Leach, M.O.; Koh, D.M. Evaluating the diagnostic sensitivity of computed diffusion-weighted MR imaging in the detection of breast cancer. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2016, 44, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amornsiripanitch, N.; Bickelhaupt, S.; Shin, H.J.; Dang, M.; Rahbar, H.; Pinker, K.; Partridge, S.C. Diffusion-weighted MRI for unenhanced breast cancer screening. Radiology 2019, 293, 504–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Hippe, D.S.; Rahbar, H.; Parsian, S.; Rendi, M.H.; Partridge, S.C. Diffusion tensor imaging for characterizing tumor microstructure and improving diagnostic performance on breast MRI: A prospective observational study. Breast Cancer Res. 2019, 21, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Panda, A.; Pahwa, S.; Hamilton, J.I.; Dastmalchian, S.; McGivney, D.F.; Ma, D.; Batesole, J.; Seiberlich, N.; Griswold, M.A.; et al. Three-dimensional MR fingerprinting for quantitative breast imaging. Radiology 2019, 290, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabouri, S.; Chang, S.D.; Goldenberg, S.L.; Savdie, R.; Jones, E.C.; Black, P.C.; Fazli, L.; Kozlowski, P. Comparing diagnostic accuracy of luminal water imaging with diffusion-weighted and dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI in prostate cancer: A quantitative MRI study. NMR Biomed. 2019, 32, e4048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Retter, A.; Gong, F.; Syer, T.; Singh, S.; Adeleke, S.; Punwani, S. Emerging methods for prostate cancer imaging: Evaluating cancer structure and metabolic alterations more clearly. Mol. Oncol. 2021, 15, 2565–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jochelson, M.S.; Lobbes, M.B.I. Contrast-enhanced Mammography: State of the art. Radiology 2021, 299, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kornecki, A. Current Status of Contrast Enhanced Mammography: A Comprehensive Review. Can. Assoc. Radiol. J. 2021, 73, 9047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francescone, M.A.; Jochelson, M.S.; Dershaw, D.D.; Sung, J.S.; Hughes, M.C.; Zheng, J.; Moskowitz, C.; Morris, E.A. Low energy mammogram obtained in contrast-enhanced digital mammography (CEDM) is comparable to routine full-field digital mammography (FFDM). Eur. J. Radiol. 2014, 83, 1350–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 1Konstantopoulos, C.; Mehta, T.S.; Brook, A.; Dialani, V.; Mehta, R.; Fein-Zachary, V.; Phillips, J. Cancer Conspicuity on Low-energy Images of Contrast-enhanced Mammography Compared With 2D Mammography. J. Breast Imaging 2022, 4, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sogani, J.; Mango, V.L.; Keating, D.; Sung, J.S.; Jochelson, M.S. Contrast-enhanced mammography: Past, present, and future. Clin. Imaging 2021, 69, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 1Amir, T.; Hogan, M.P.; Jacobs, S.; Sevilimedu, V.; Sung, J.; Jochelson, M.S. Comparison of False-Positive Versus True-Positive Findings on Contrast-Enhanced Digital Mammography. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2022, 218, 797–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, Y.C.; Lin, Y.C.; Wan, Y.L.; Yeow, K.M.; Huang, P.C.; Lo, Y.F.; Tsai, H.P.; Ueng, S.H.; Chang, C.J. Diagnostic performance of dual-energy contrast-enhanced subtracted mammography in dense breasts compared to mammography alone: Interobserver blind-reading analysis. Eur. Radiol. 2014, 24, 2394–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fallenberg, E.M.; Dromain, C.; Diekmann, F.; Engelken, F.; Krohn, M.; Singh, J.M.; Ingold-Heppner, B.; Winzer, K.J.; Bick, U.; Renz, D.M. Contrast-enhanced spectral mammography versus MRI: Initial results in the detection of breast cancer and assessment of tumour size. Eur. Radiol. 2014, 24, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, J.R.; Pavlicek, W.; Hanson, J.A.; Boltz, T.F.; Patel, B.K. Breast radiation dose with CESM compared with 2D FFDM and 3D tomosynthesis mammography. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2017, 208, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, J.; Mihai, G.; Hassonjee, S.E.; Raj, S.D.; Palmer, M.R.; Brook, A.; Zhang, D. Comparative Dose of Contrast-Enhanced Spectral Mammography (CESM), digital mammography, and digital breast tomosynthesis. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2018, 211, 839–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, R.; Raiano, N.; Raiano, C.; Maio, F.; Vallone, P.; Mattace Raso, M.; Setola, S.V.; Granata, V.; Rubulotta, M.R.; Barretta, M.L.; et al. Evaluation of average glandular dose and investigation of the relationship with compressed breast thickness in dual energy contrast enhanced digital mammography and digital breast tomosynthesis. Eur. J. Radiol. 2020, 126, 108912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanardo, M.; Cozzi, A.; Trimboli, R.M.; Labaj, O.; Monti, C.B.; Schiaffino, S.; Carbonaro, L.A.; Sardanelli, F. Technique, protocols and adverse reactions for contrast-enhanced spectral mammography (CESM): A systematic review. Insights Imaging 2019, 10, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobbes, M.B.I.; Smidt, M.L.; Houwers, J.; Tjan-Heijnen, V.C.; Wildberger, J.E. Contrast enhanced mammography: Techniques, current results, and potential indications. Clin. Radiol. 2013, 68, 935–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jochelson, M.S.; Pinker, K.; Dershaw, D.D.; Hughes, M.; Gibbons, G.F.; Rahbar, K.; Robson, M.E.; Mangino, D.A.; Goldman, D.; Moskowitz, C.S.; et al. Comparison of screening CEDM and MRI for women at increased risk for breast cancer: A pilot study. Eur. J. Radiol. 2017, 97, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCCN Guidelines Version 1. 2021 Breast Cancer Screening and Diagnosis. Available online: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/breast-screening.pdf (accessed on 16 April 2022).
- Sung, J.S.; Lebron, L.; Keating, D.; D’Alessio, D.; Comstock, C.E.; Lee, C.H.; Pike, M.C.; Ayhan, M.; Moskowitz, C.S.; Morris, E.A.; et al. Performance of dual-energy contrast-enhanced digital mammography for screening women at increased risk of breast cancer. Radiology 2019, 293, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klang, E.; Krosser, A.; Amitai, M.M.; Sorin, V.; Halshtok Neiman, O.; Shalmon, A.; Gotlieb, M.; Sklair-Levy, M. Utility of routine use of breast ultrasound following contrast-enhanced spectral mammography. Clin. Radiol. 2018, 73, 908.e11–908.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorin, V.; Yagil, Y.; Yosepovich, A.; Shalmon, A.; Gotlieb, M.; Neiman, O.H.; Sklair-Levy, M. Contrast-enhanced spectral mammography in women with intermediate breast cancer risk and dense breasts. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2018, 211, W267–W274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Health Canada, F. Active Licence Search Results. 2017. Available online: https://health-products.canada.ca/mdall-limh/ (accessed on 12 March 2022).
- GE Press Release. GE Healthcare Receives FDA Clearance of the Industry’s First Contrast-Enhanced Mammography Solution for Biopsy. Available online: https://health-products.canada.ca/mdall-limh/dispatch-repartition.do?type=active. Health Canada Approval (accessed on 12 March 2022).
- FDA. FDA Approval Letter. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/cdrh_docs/pdf19/K193334.pdf (accessed on 12 March 2022).
- Houben, I.P.L.; van de Voorde, P.; Jeukens, C.R.L.P.N.; Wildberger, J.E.; Kooreman, L.F.; Smidt, M.L.; Lobbes, M.B.I. Contrast-enhanced spectral mammography as work-up tool in patients recalled from breast cancer screening has low risks and might hold clinical benefits. Eur. J. Radiol. 2017, 94, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ACR announcement. CMIST Clinical Trial. Available online: https://www.acr.org/-/media/ACR/Files/Breast-Imaging-Resources/GEHC_CMIST_2020_01_113019---Post-Card.pdf (accessed on 12 March 2022).
- Contrast Enhanced Mammography (CEM) (A Supplement to ACR BI-RADS® Mammography 2013). Available online: https://www.acr.org/-/media/ACR/Files/RADS/BI-RADS/BIRADS_CEM_2022.pdf (accessed on 16 April 2022).
- Hruska, C.B. Molecular breast imaging for screening in dense breasts: State of the art and future directions. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2017, 208, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, W.A.; Rafferty, E.A.; Friedewald, S.M.; Hruska, C.B.; Rahbar, H. Screening algorithms in dense breasts: AJR expert panel narrative review. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2021, 216, 275–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, W.A. Nuclear breast imaging: Clinical results and future directions. J. Nucl. Med. 2016, 57, 46S–52S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, D.J.; Hruska, C.B.; Conners, A.L.; Tortorelli, C.L.; Maxwell, R.W.; Jones, K.N.; Toledano, A.Y.; O’Connor, M.K. Molecular breast imaging at reduced radiation dose for supplemental screening in mammographically dense breasts. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2015, 204, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shermis, R.B.; Wilson, K.D.; Doyle, M.T.; Martin, T.S.; Merryman, D.; Kudrolli, H.; Brenner, R.J. Supplemental breast cancer screening with molecular breast imaging for women with dense breast tissue. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2016, 207, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, D.; Hunt, K.; Conners, A.; Zingula, S.; Whaley, D.; Ellis, R.; Gasal Spilde, J.; Mehta, R.; Polley, M.-Y.; O’Connor, M.; et al. Abstract PD4-05: Molecular breast imaging and tomosynthesis to eliminate the reservoir of undetected cancer in dense breasts: The Density MATTERS trial. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, PD4-05. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hruska, C.B. Let’s Get Real about Molecular Breast Imaging and Radiation Risk. Radiol. Imaging Cancer 2019, 1, e190070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, M.; Covington, M.F. Comparative Benefit-to-Radiation Risk Ratio of Molecular Breast Imaging, Two-Dimensional Full-Field Digital Mammography with and without Tomosynthesis, and Synthetic Mammography with Tomosynthesis. Radiol. Imaging Cancer 2019, 1, e190005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendrick, R.E.; Tredennick, T. Benefit to radiation risk of breast-specific gamma imaging compared with mammography in screening asymptomatic women with dense breasts. Radiology 2016, 281, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Initial Certification for Diagnostic Radiology Certification Requirements. Available online: https://www.theabr.org/diagnostic-radiology/initial-certification/core-exam (accessed on 12 March 2022).
- Romero-Martín, S.; Elías-Cabot, E.; Raya-Povedano, J.L.; Gubern-Mérida, A.; Rodríguez-Ruiz, A.; Álvarez-Benito, M. Stand-Alone Use of Artificial Intelligence for Digital Mammography and Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Screening: A Retrospective Evaluation. Radiology 2021, 302, 211590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoshan, Y.; Bakalo, R.; Gilboa-Solomon, F.; Ratner, V.; Barkan, E.; Ozery-Flato, M.; Amit, M.; Khapun, D.; Ambinder, E.B.; Oluyemi, E.T.; et al. Artificial Intelligence for Reducing Workload in Breast Cancer Screening with Digital Breast Tomosynthesis. Radiology 2022, 303, 211105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philpotts, L.E. Advancing Artificial Intelligence to Meet Breast Imaging Needs. Radiology 2022, 303, 78–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Shamout, F.E.; Oliver, J.R.; Witowski, J.; Kannan, K.; Park, J.; Wu, N.; Huddleston, C.; Wolfson, S.; Millet, A.; et al. Artificial intelligence system reduces false-positive findings in the interpretation of breast ultrasound exams. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchsjäger, M.H.; Adelsmayr, G. Artificial Intelligence as an Assistant in Breast Cancer Screening. Radiology 2021, 302, 212675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mango, V.L.; Sun, M.; Wynn, R.T.; Ha, R. Should we ignore, follow, or biopsy? Impact of artificial intelligence decision support on breast ultrasound lesion assessment. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2020, 214, 1445–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanders, A.J.T.; Mees, W.; Bun, P.A.M.; Janssen, N.; Rodríguez-Ruiz, A.; Dalmış, M.U.; Karssemeijer, N.; van Gils, C.H.; Sechopoulos, I.; Mann, R.M.; et al. Interval Cancer Detection Using a Neural Network and Breast Density in Women with Negative Screening Mammograms. Radiology 2022, 303, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organisation for Economic Co-Operation and Development (OECD) Data on MRI Units. Available online: https://data.oecd.org/healtheqt/magnetic-resonance-imaging-mri-units.htm (accessed on 16 April 2022).
- Cancer Detection by Screening Method. Available online: https://densebreast-info.org/screening-technologies/cancer-detection-by-screening-method/ (accessed on 15 April 2022).
- Klarenbach, S.; Sims-Jones, N.; Lewin, G.; Singh, H.; Thériault, G.; Tonelli, M.; Doull, M.; Courage, S.; Garcia, A.J.; Thombs, B.D.; et al. Recommendations on screening for breast cancer in women aged 40-74 years who are not at increased risk for breast cancer. CMAJ 2018, 190, E1441–E1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siu, A.L. Screening for breast cancer: U.S. Preventive services task force recommendation statement. Ann. Intern. Med. 2016, 164, 279–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
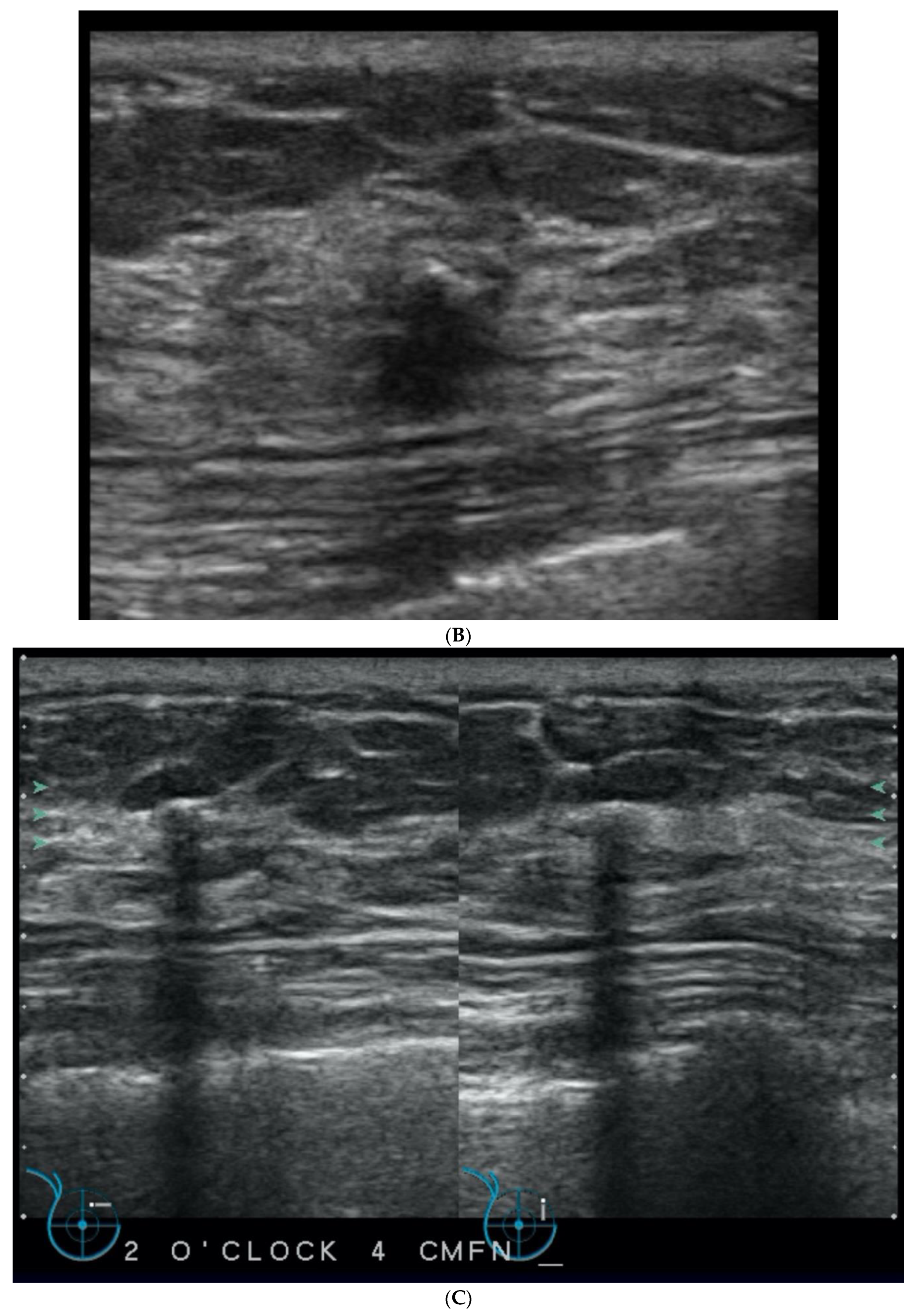
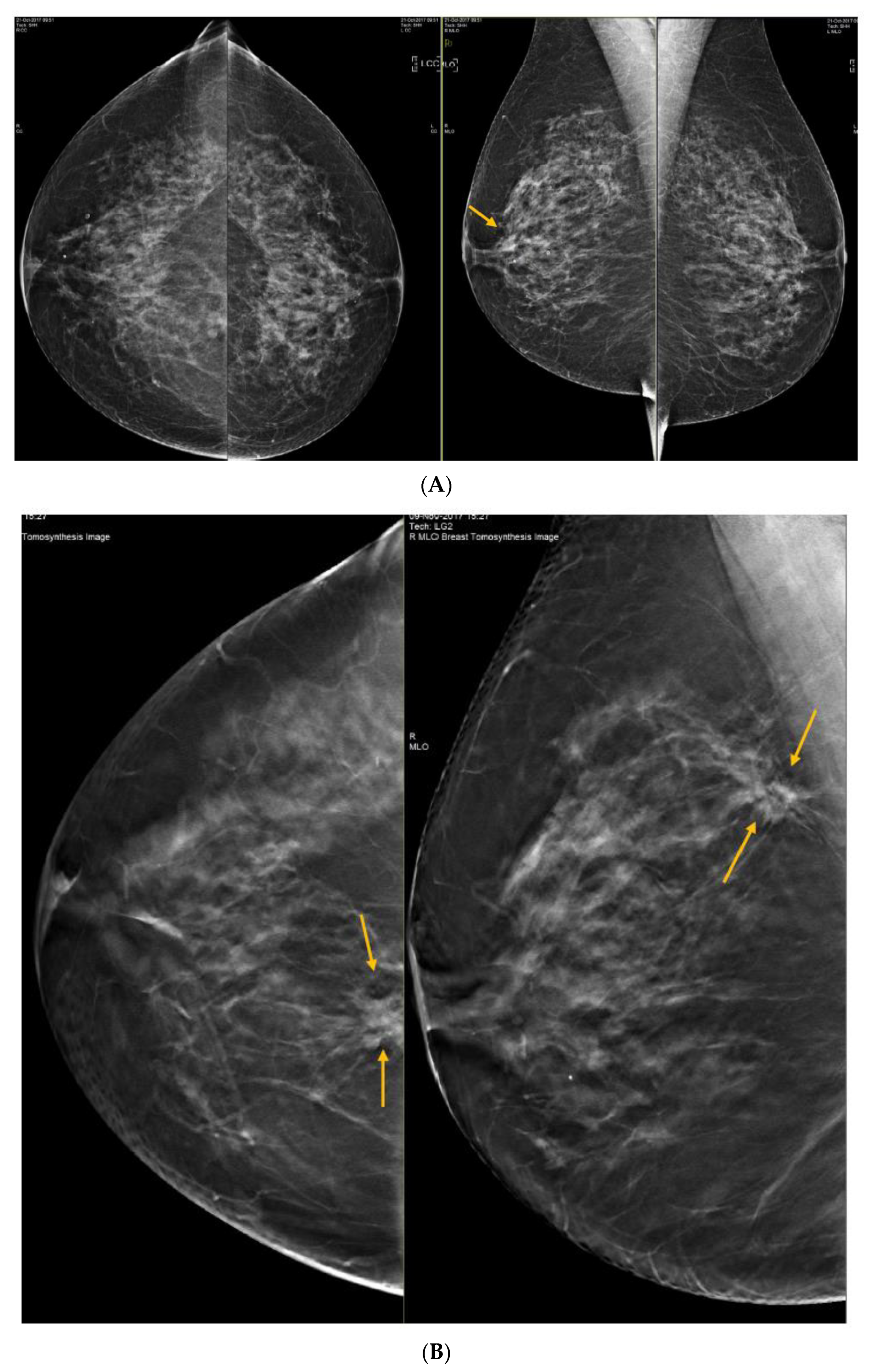
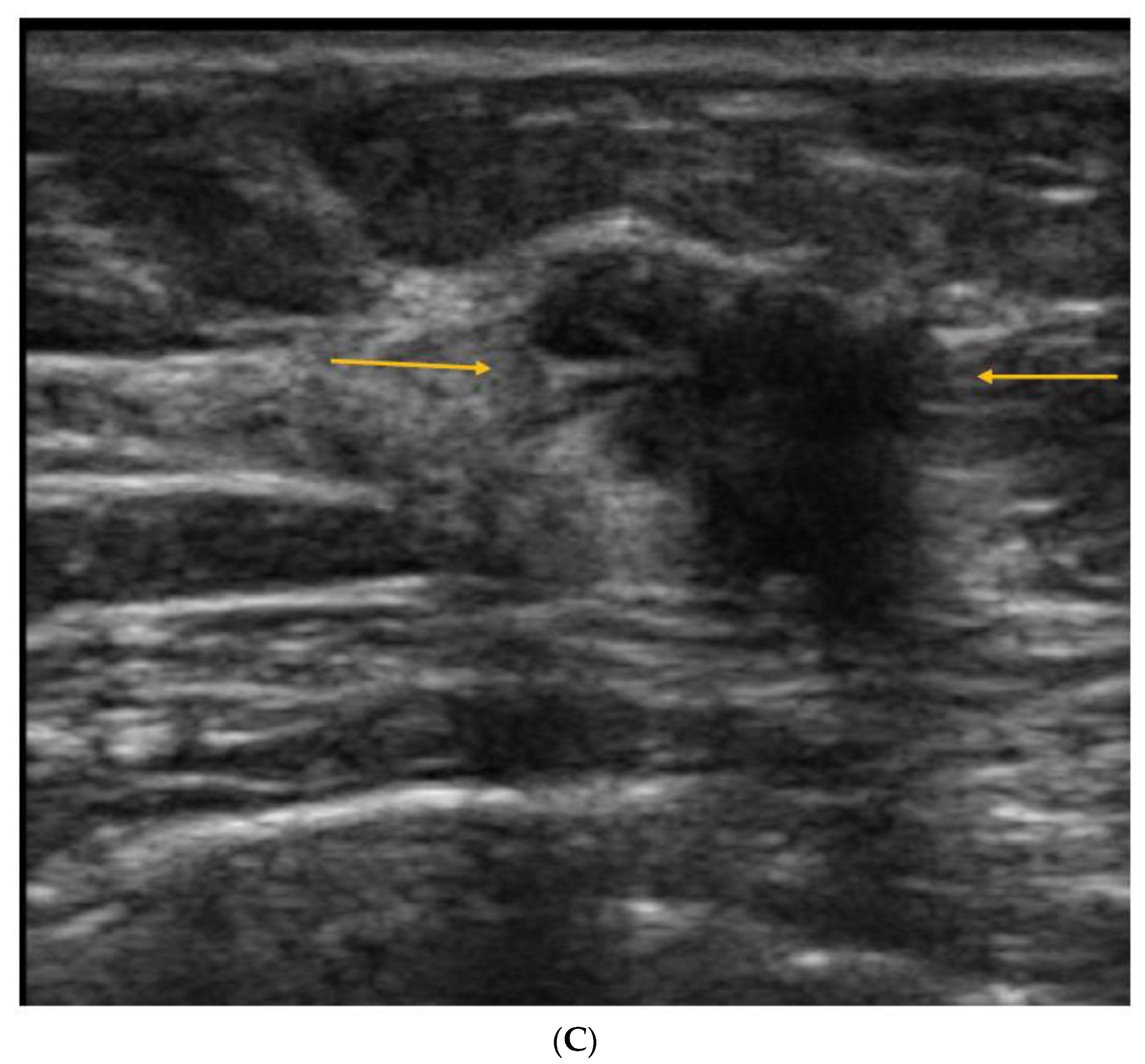
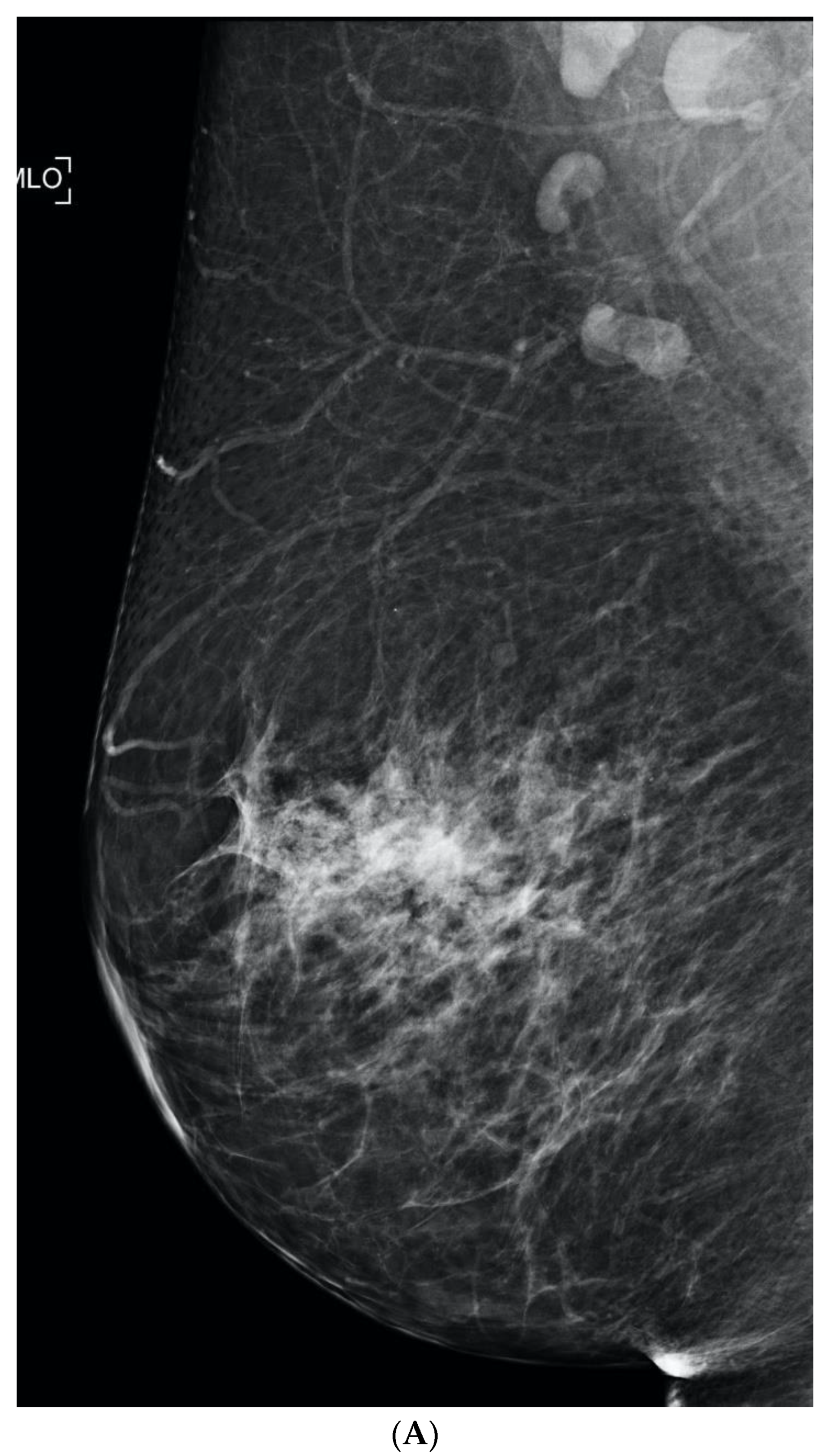
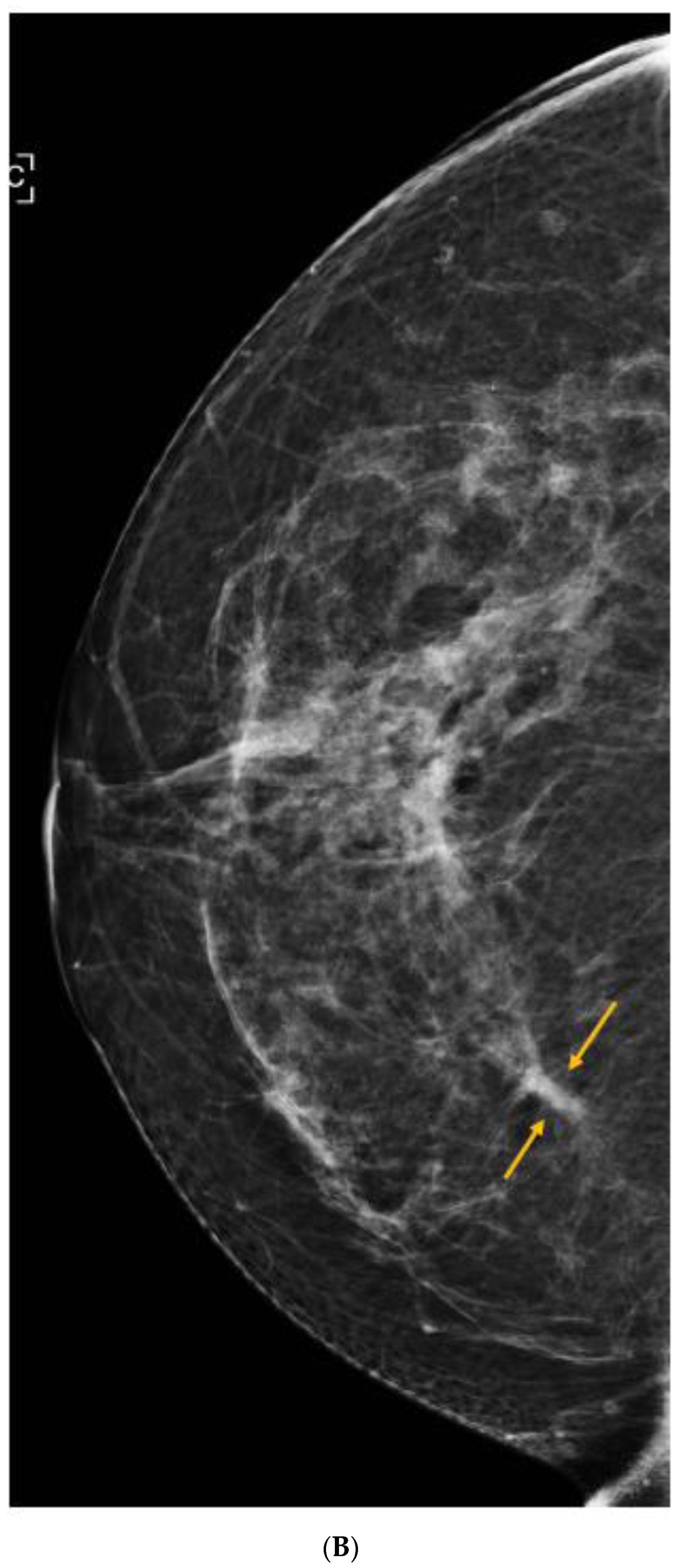
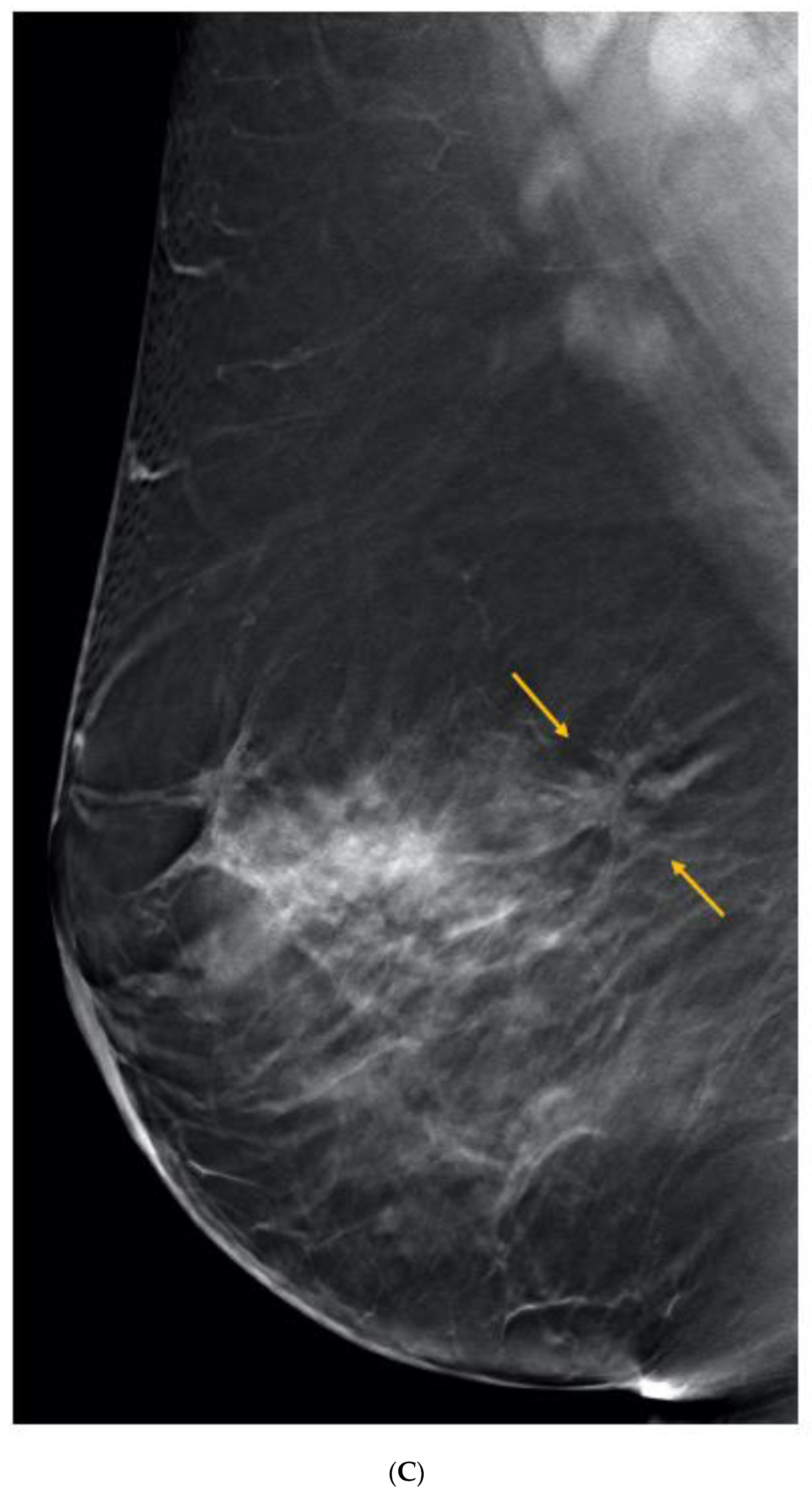
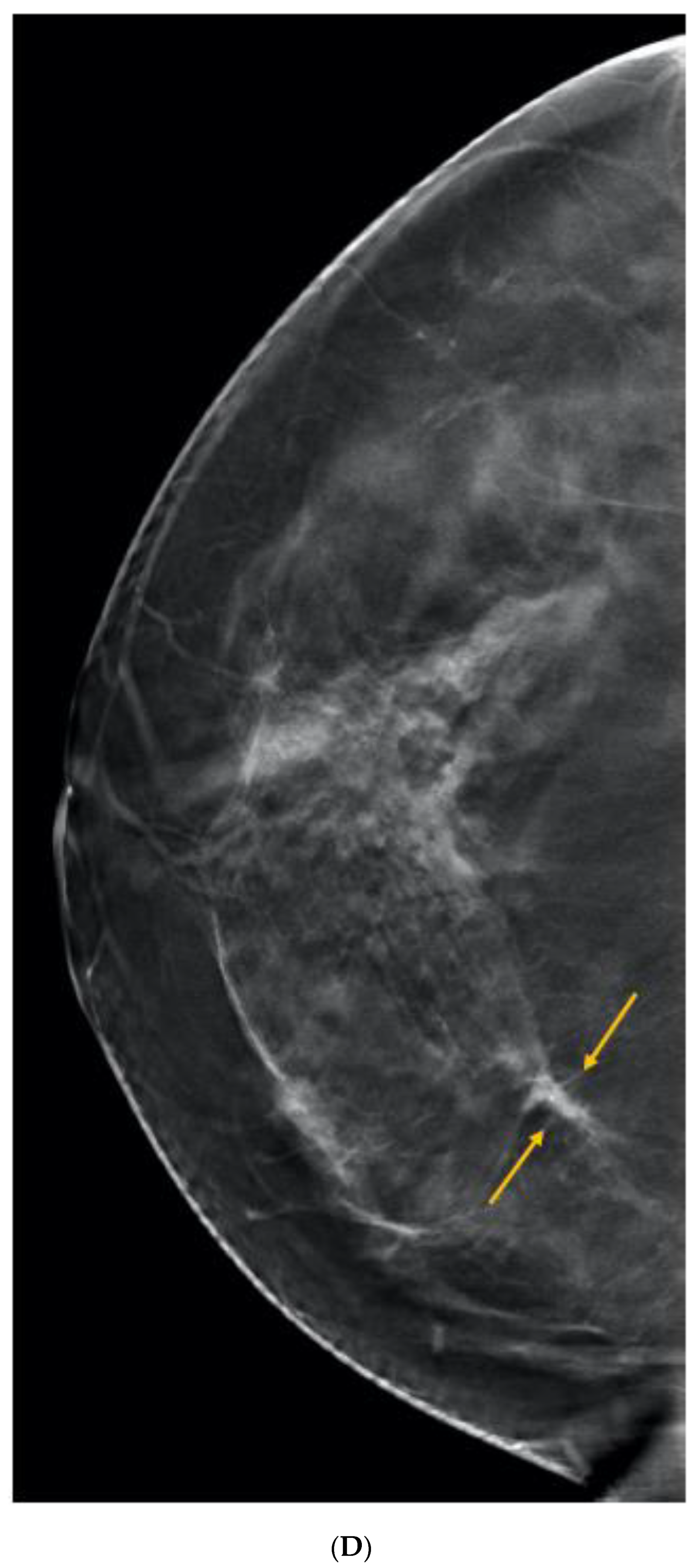
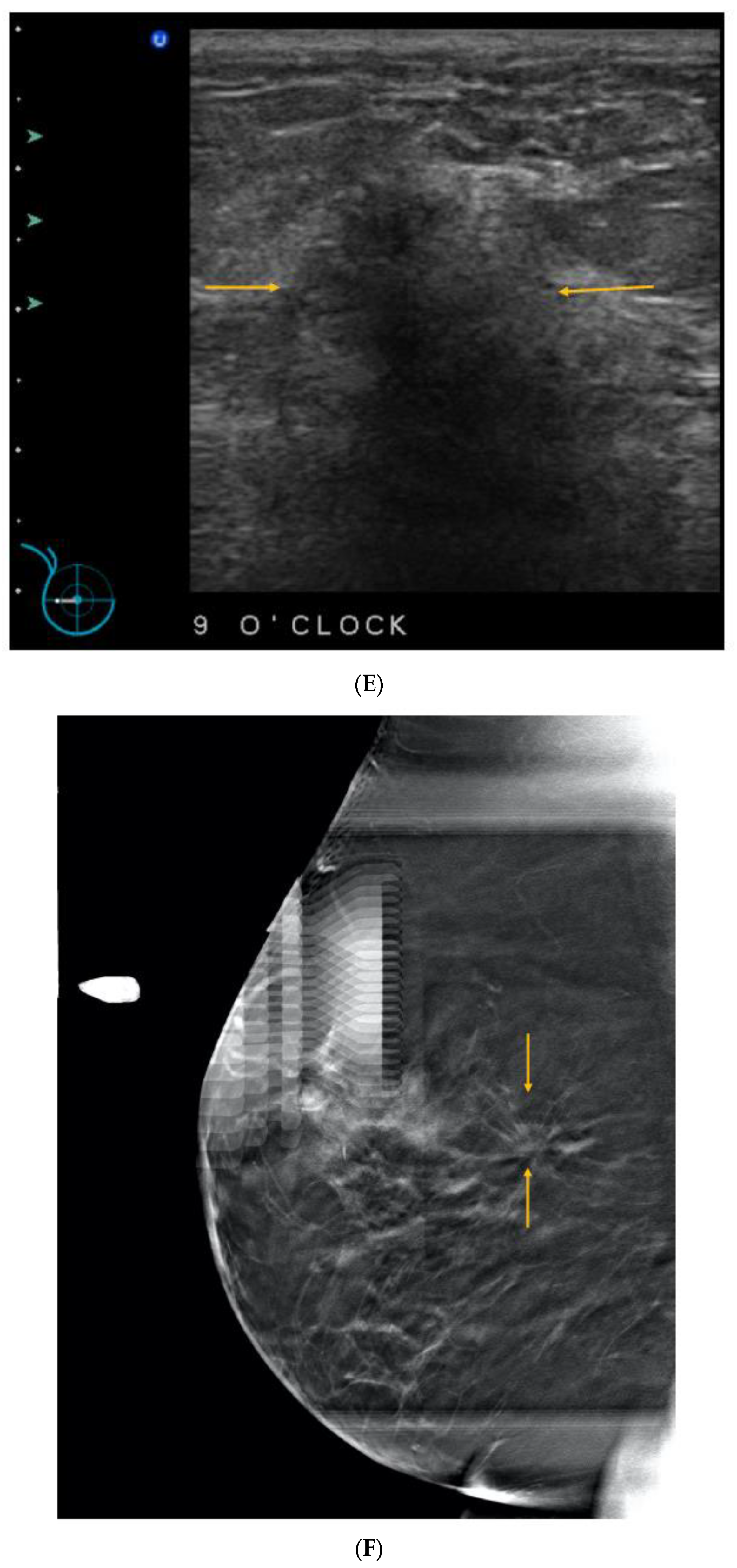
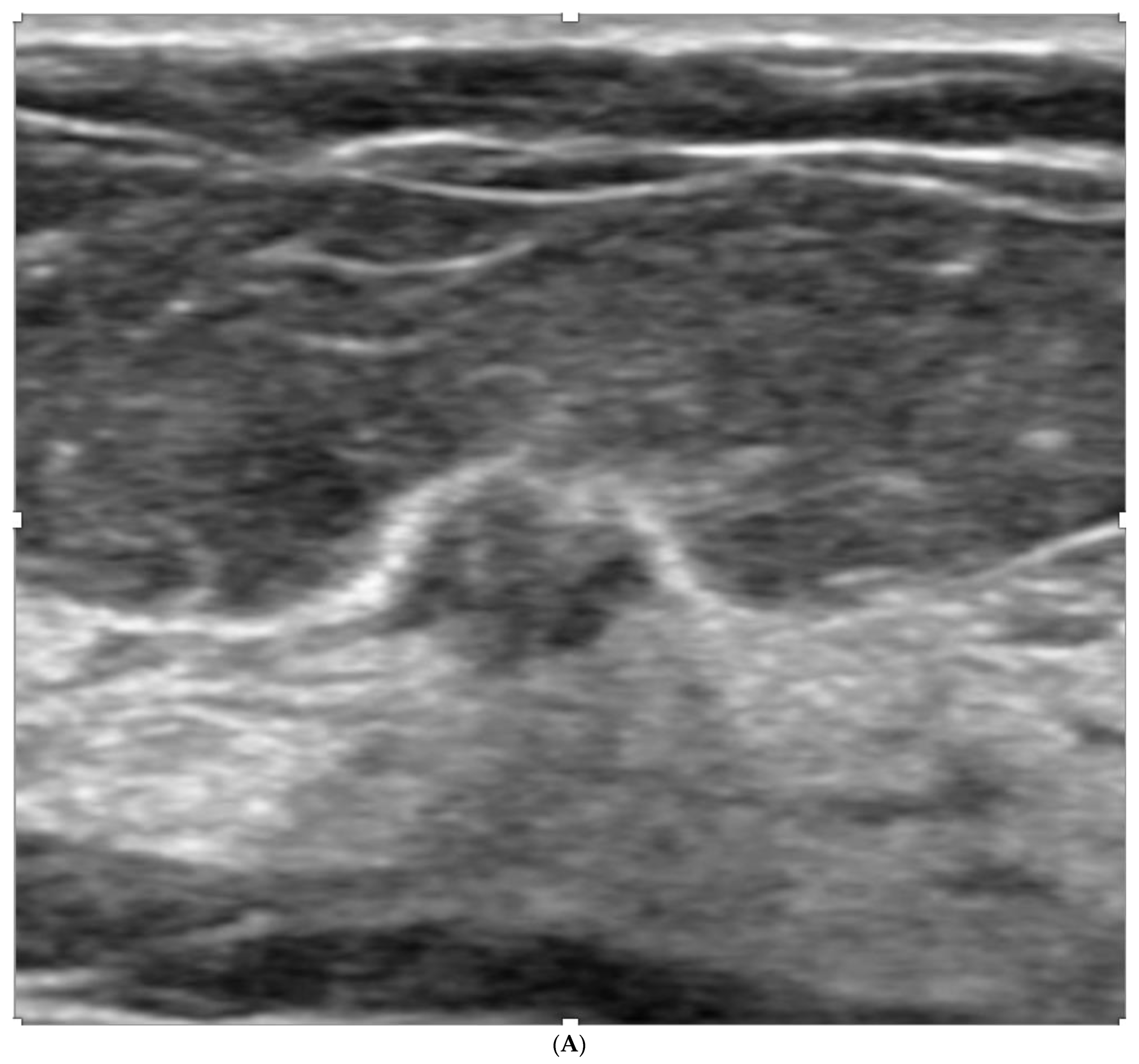
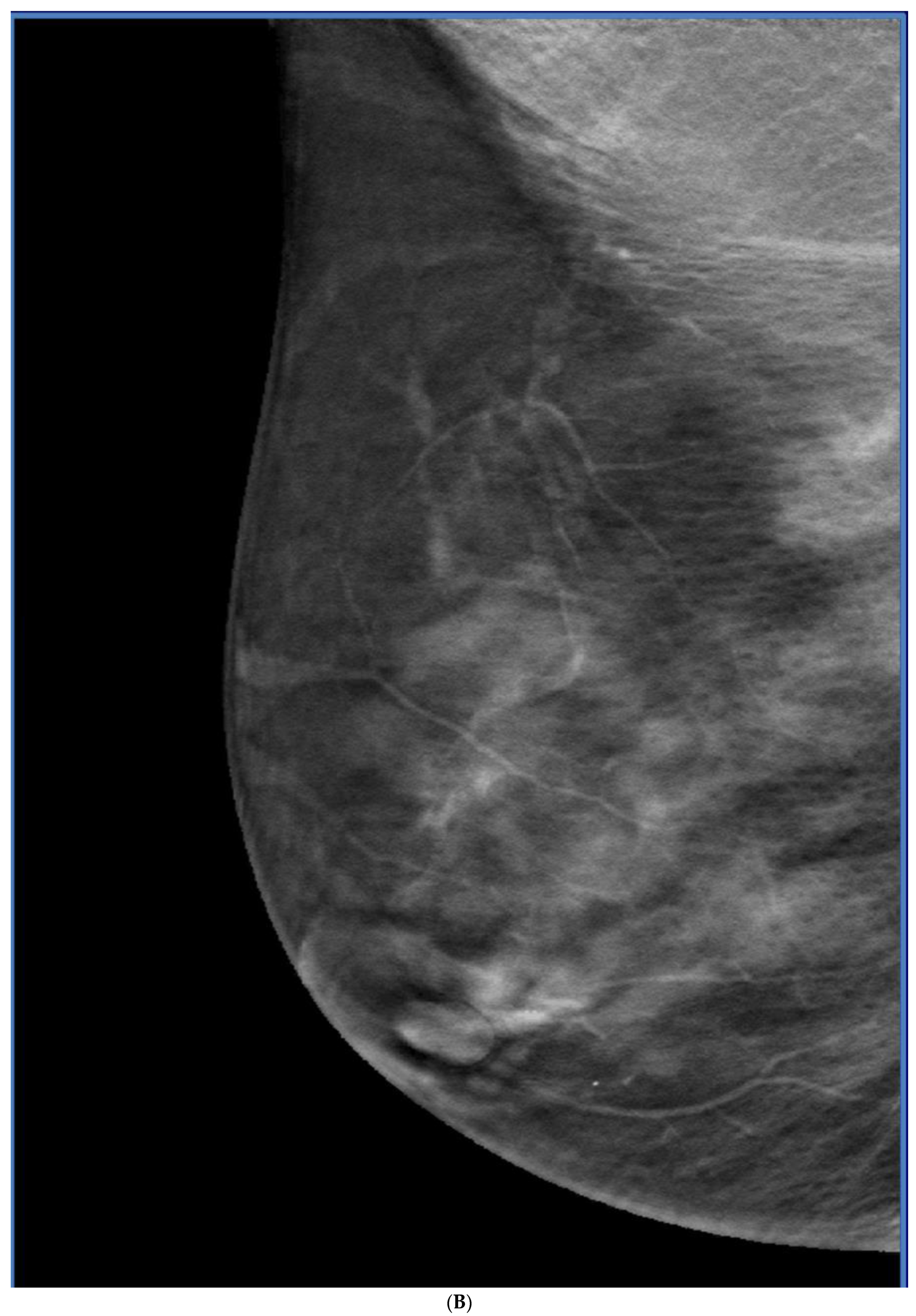
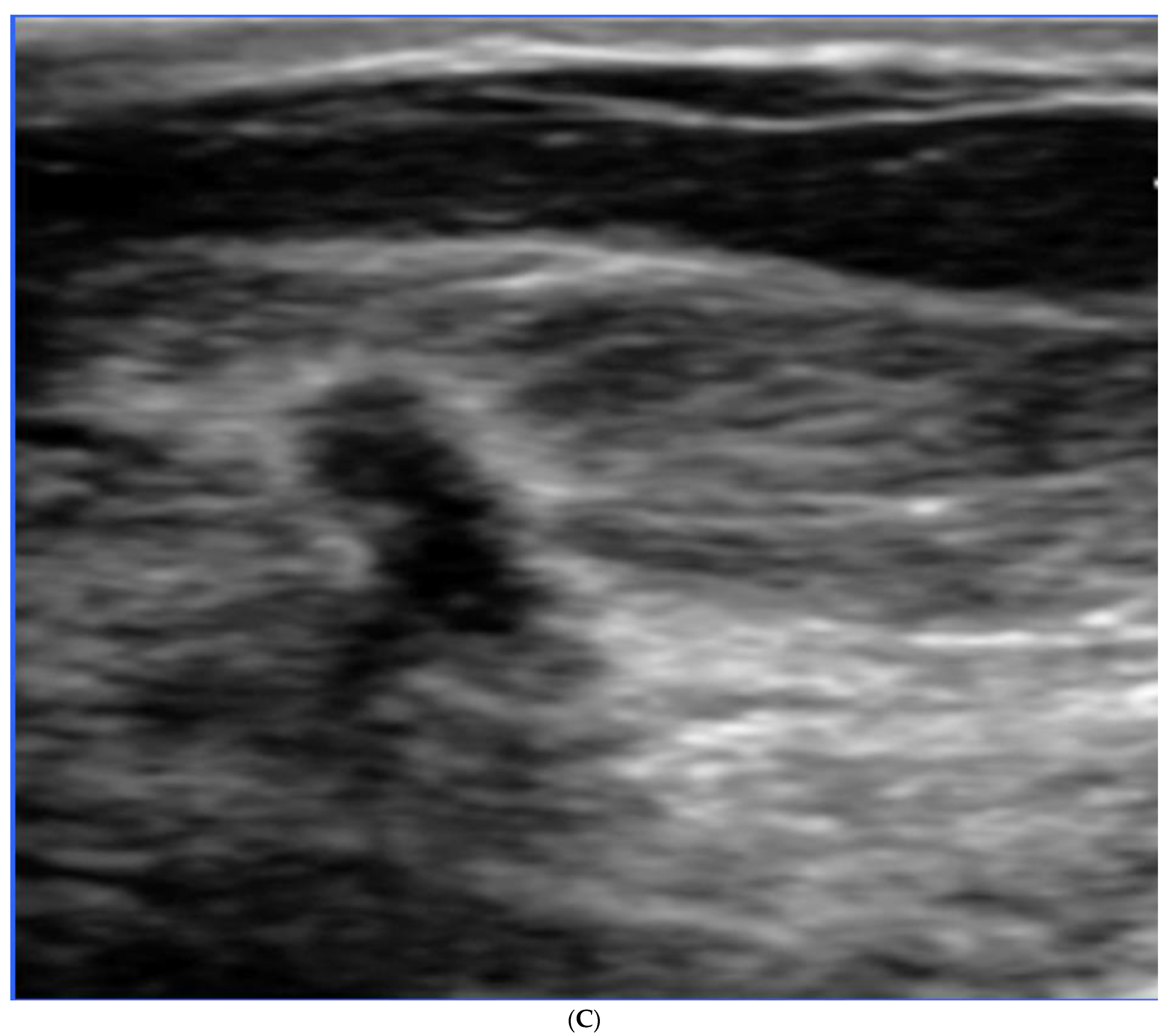

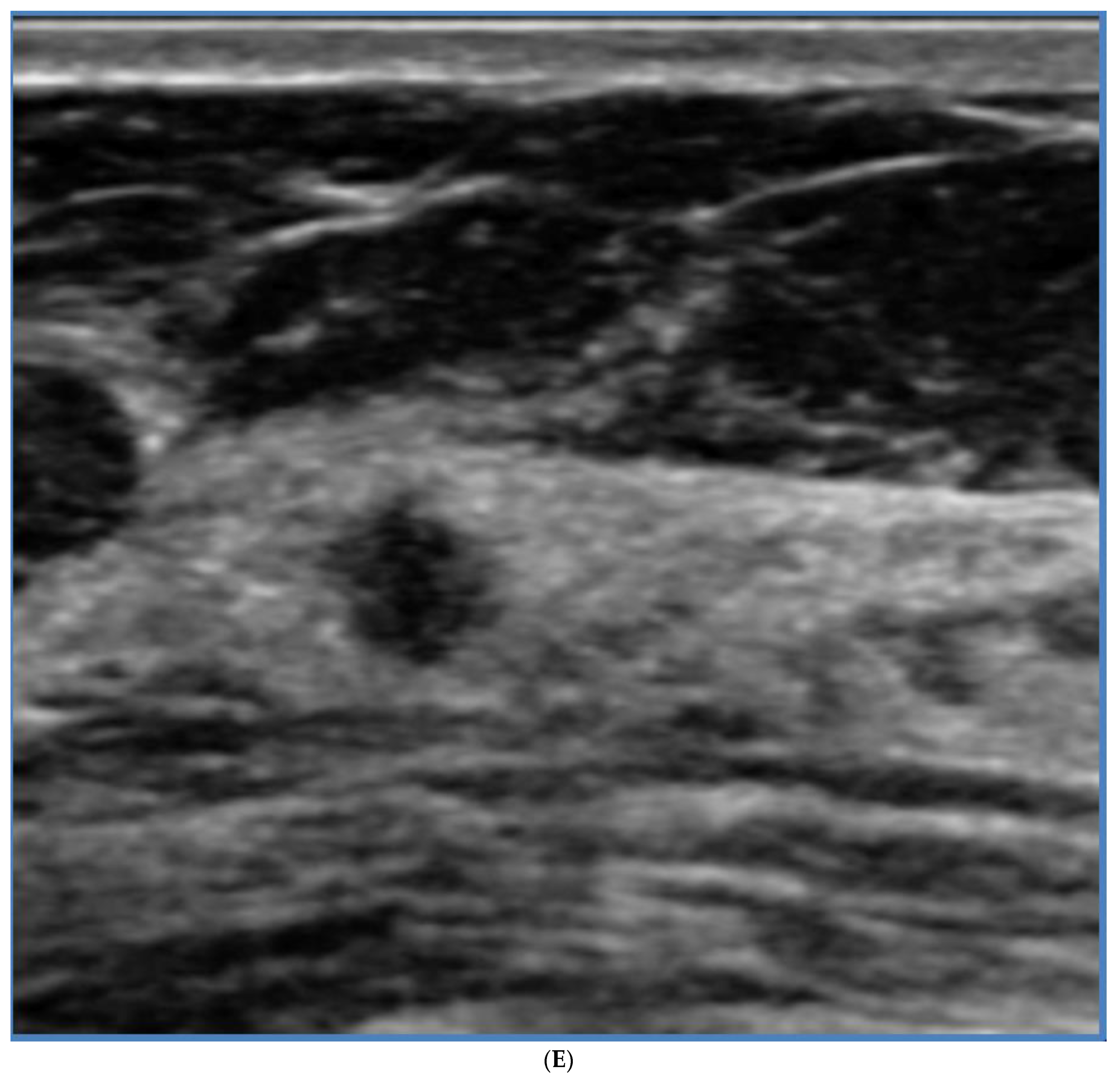

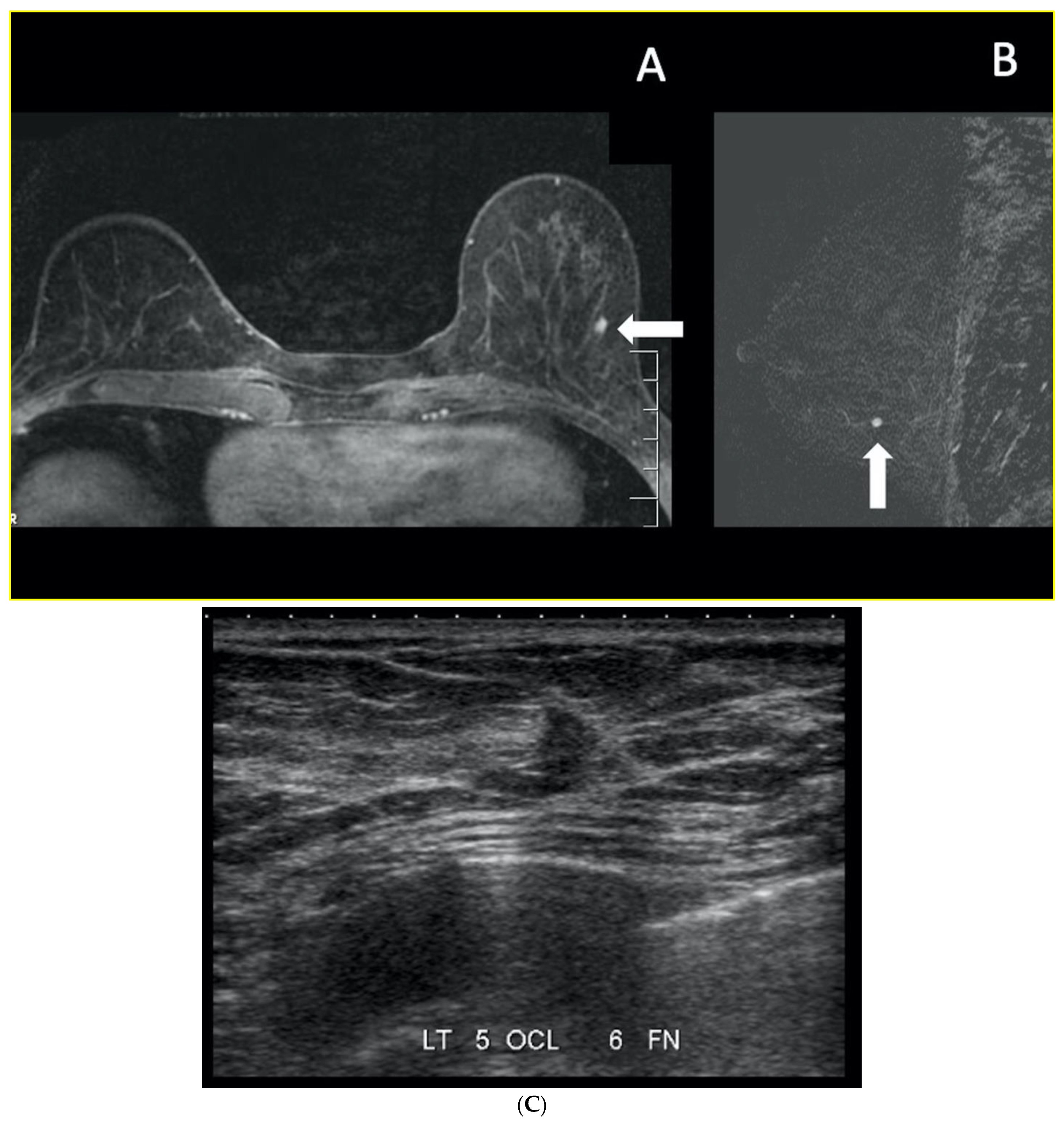
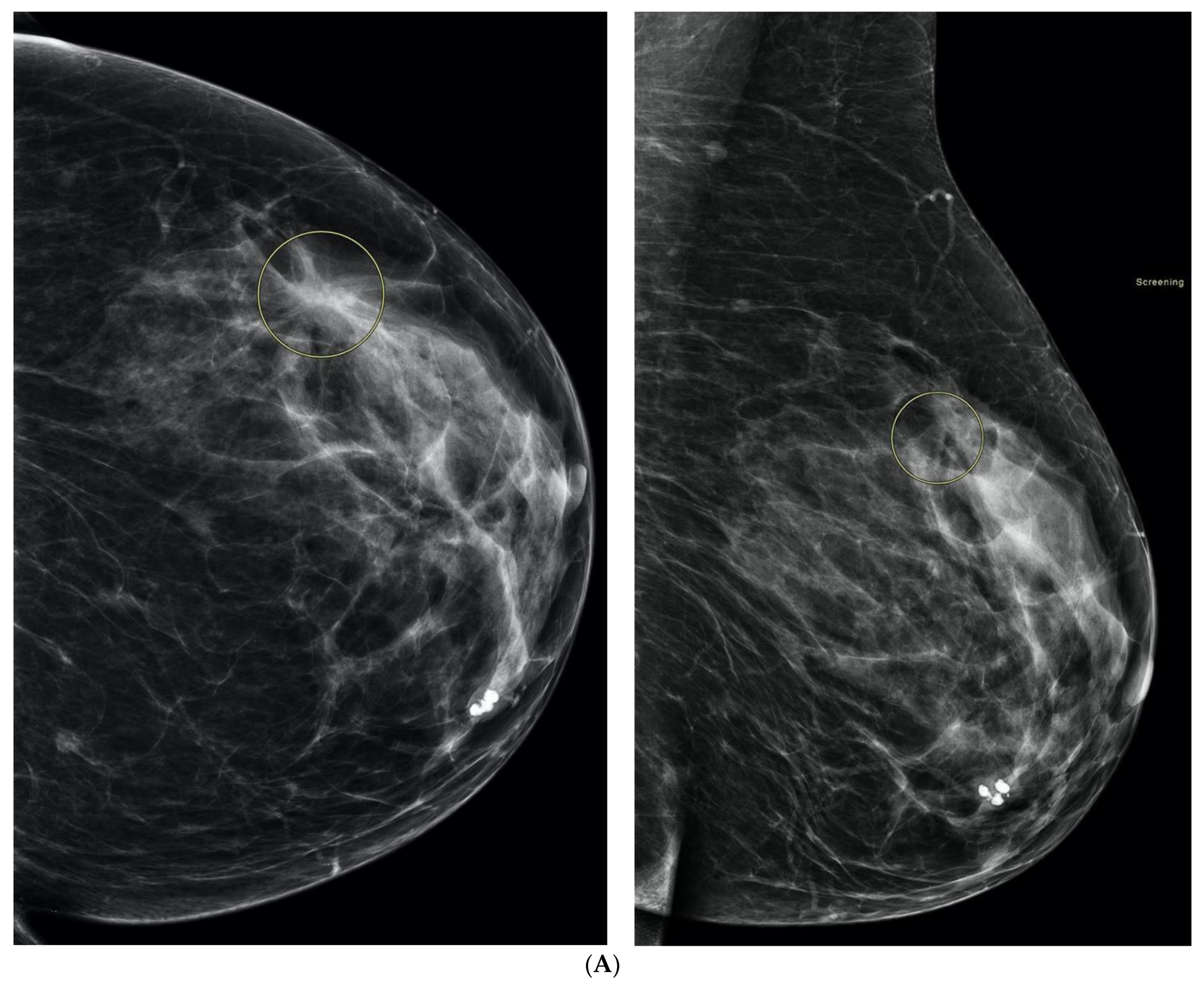
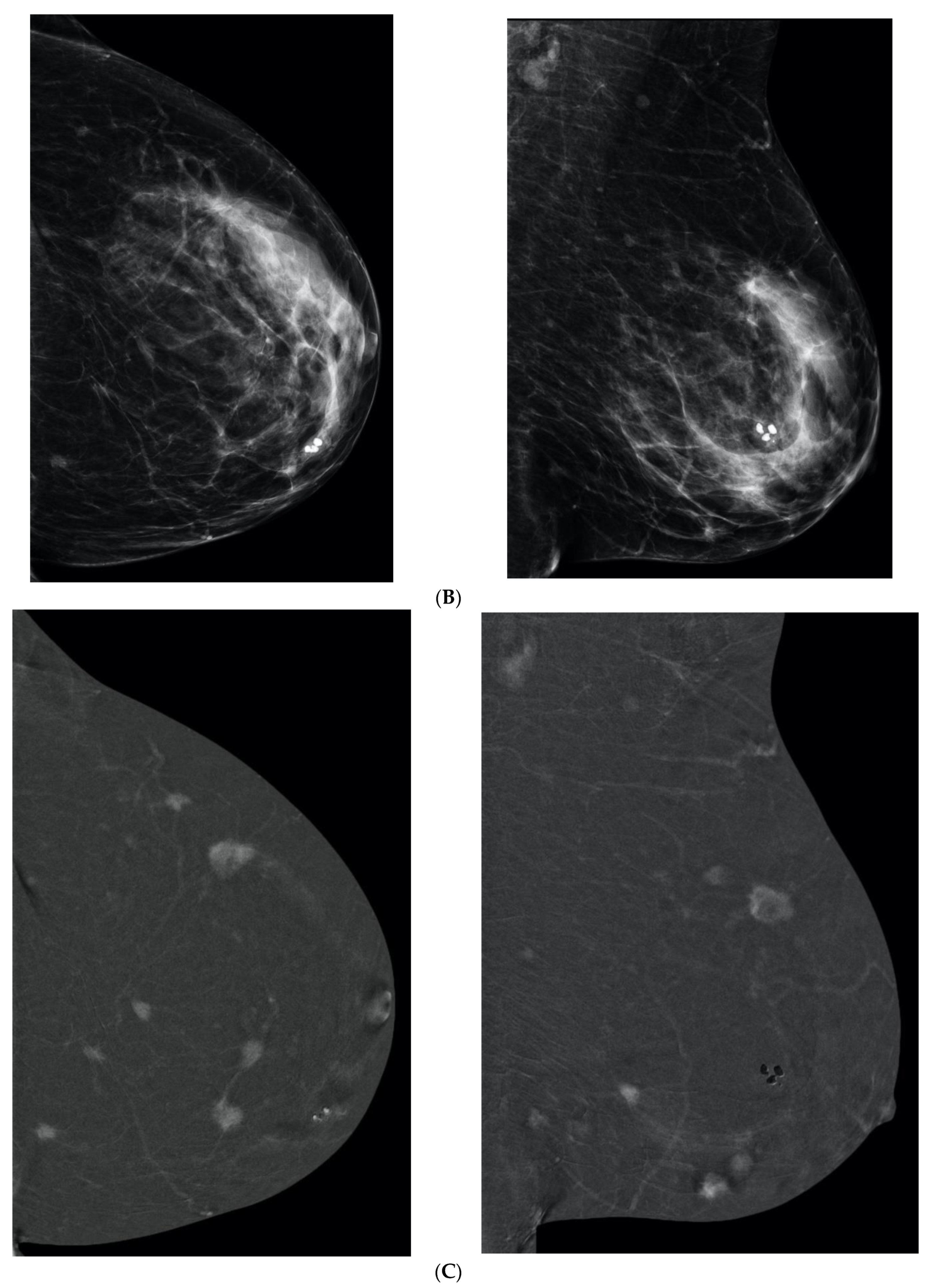
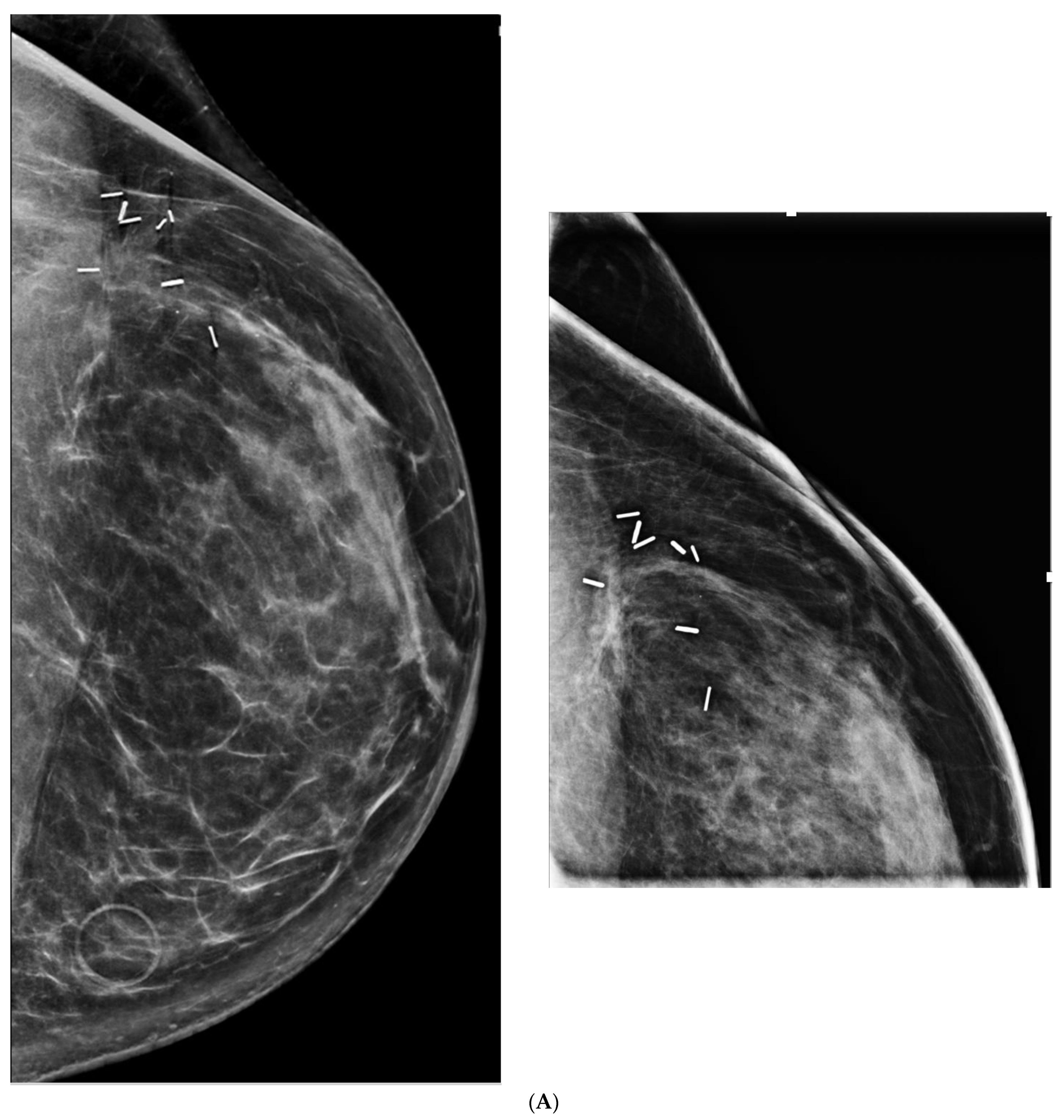
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gordon, P.B. The Impact of Dense Breasts on the Stage of Breast Cancer at Diagnosis: A Review and Options for Supplemental Screening. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 3595-3636. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29050291
Gordon PB. The Impact of Dense Breasts on the Stage of Breast Cancer at Diagnosis: A Review and Options for Supplemental Screening. Current Oncology. 2022; 29(5):3595-3636. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29050291
Chicago/Turabian StyleGordon, Paula B. 2022. "The Impact of Dense Breasts on the Stage of Breast Cancer at Diagnosis: A Review and Options for Supplemental Screening" Current Oncology 29, no. 5: 3595-3636. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29050291
APA StyleGordon, P. B. (2022). The Impact of Dense Breasts on the Stage of Breast Cancer at Diagnosis: A Review and Options for Supplemental Screening. Current Oncology, 29(5), 3595-3636. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29050291




