Antibody-Negative Paraneoplastic Autoimmune Multiorgan Syndrome (PAMS) in a Patient with Follicular Lymphoma Accompanied by an Excess of Peripheral Blood CD8+ Lymphocytes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
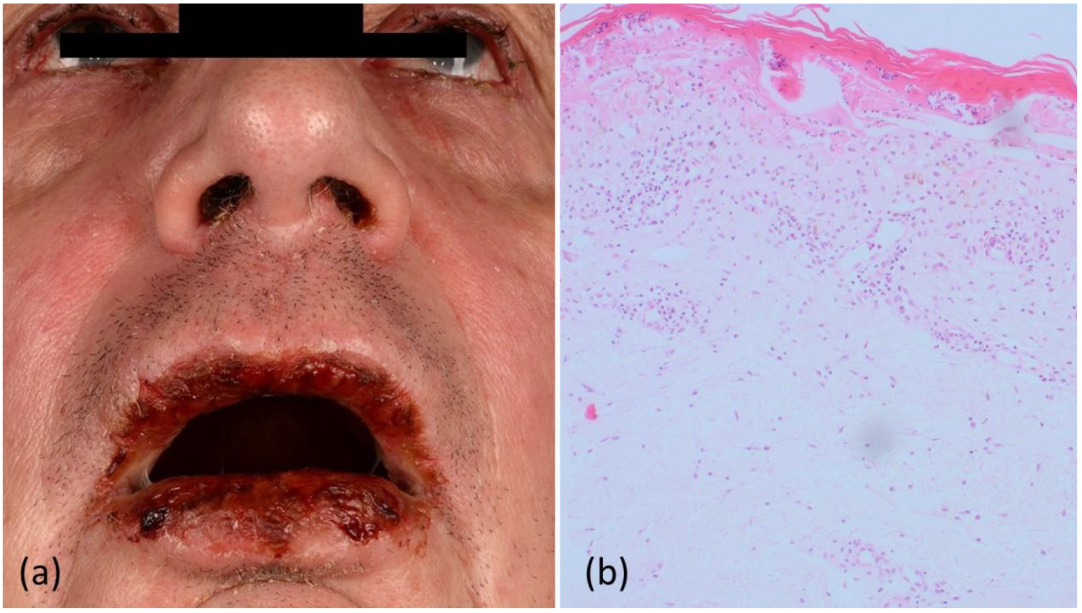
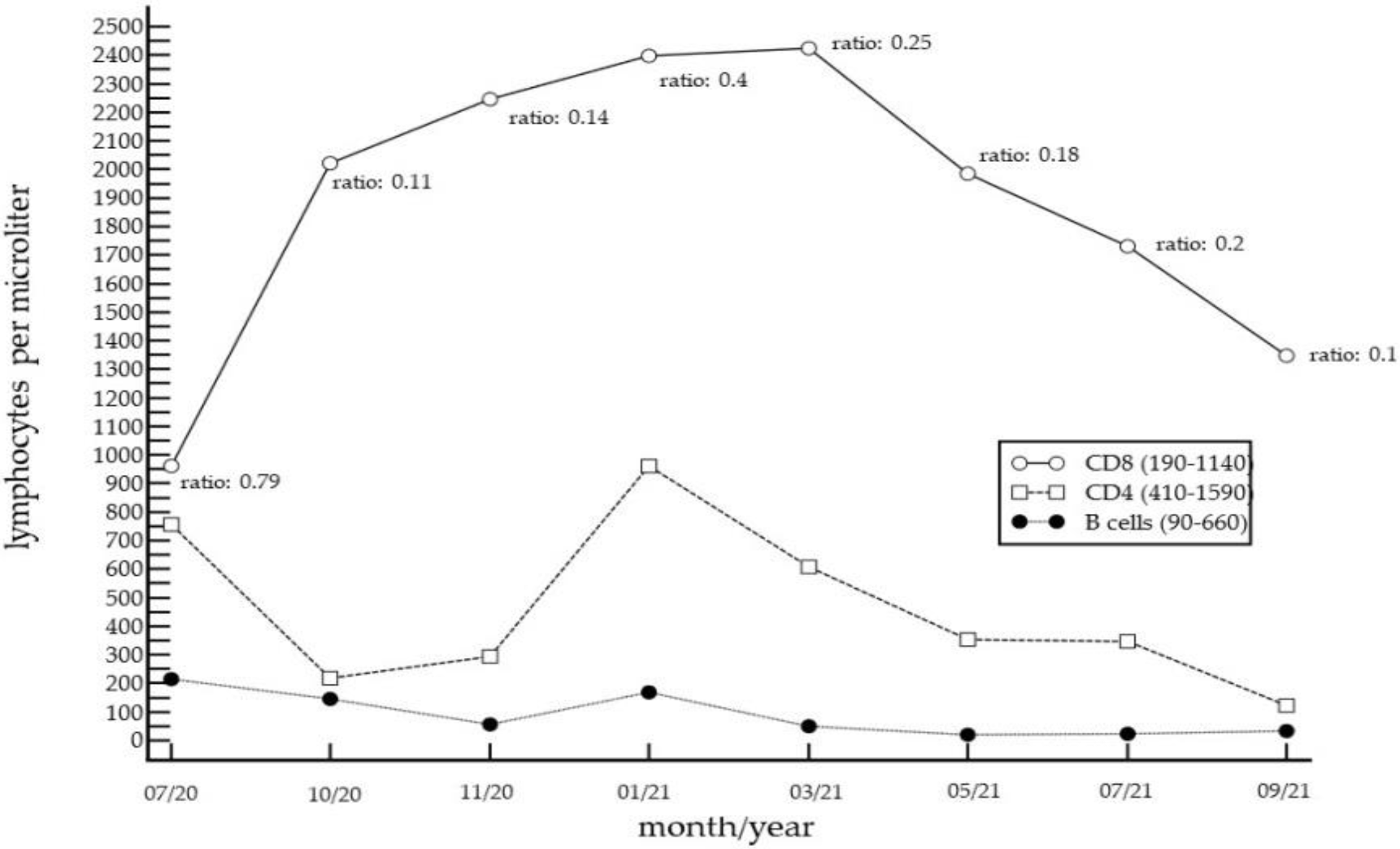
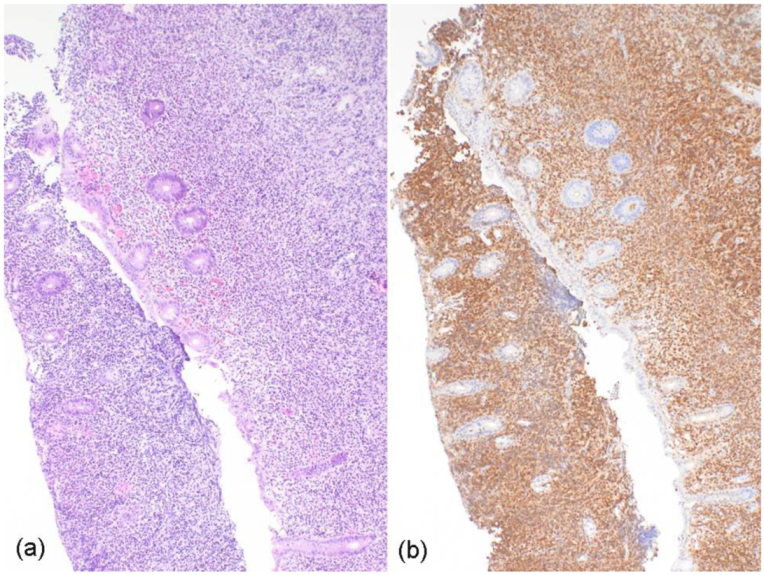
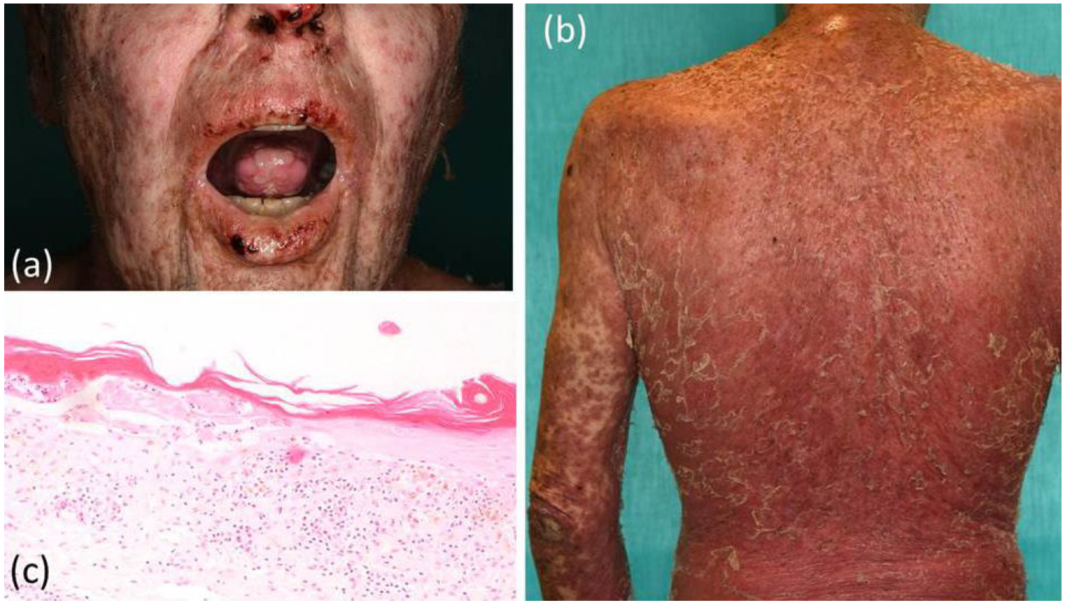
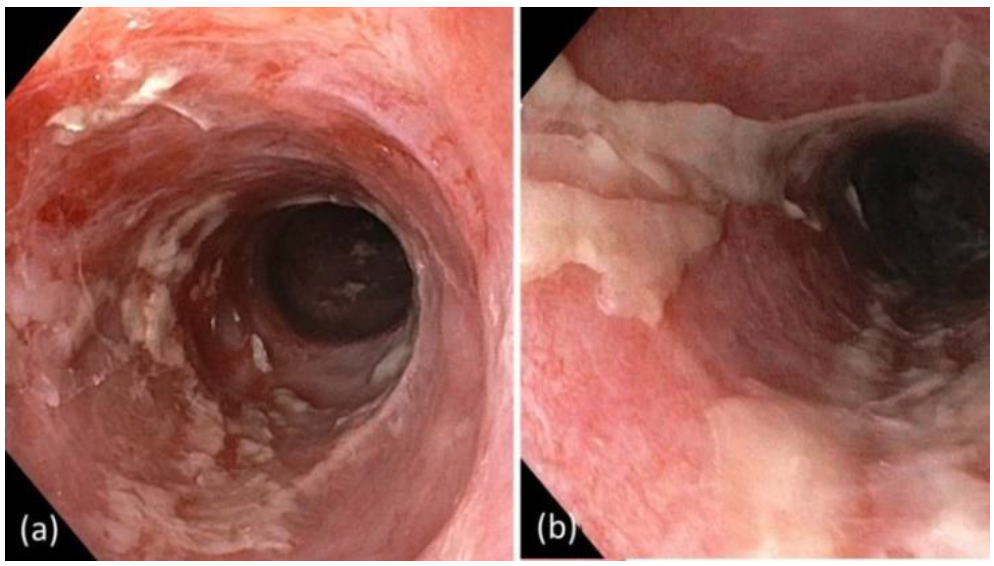
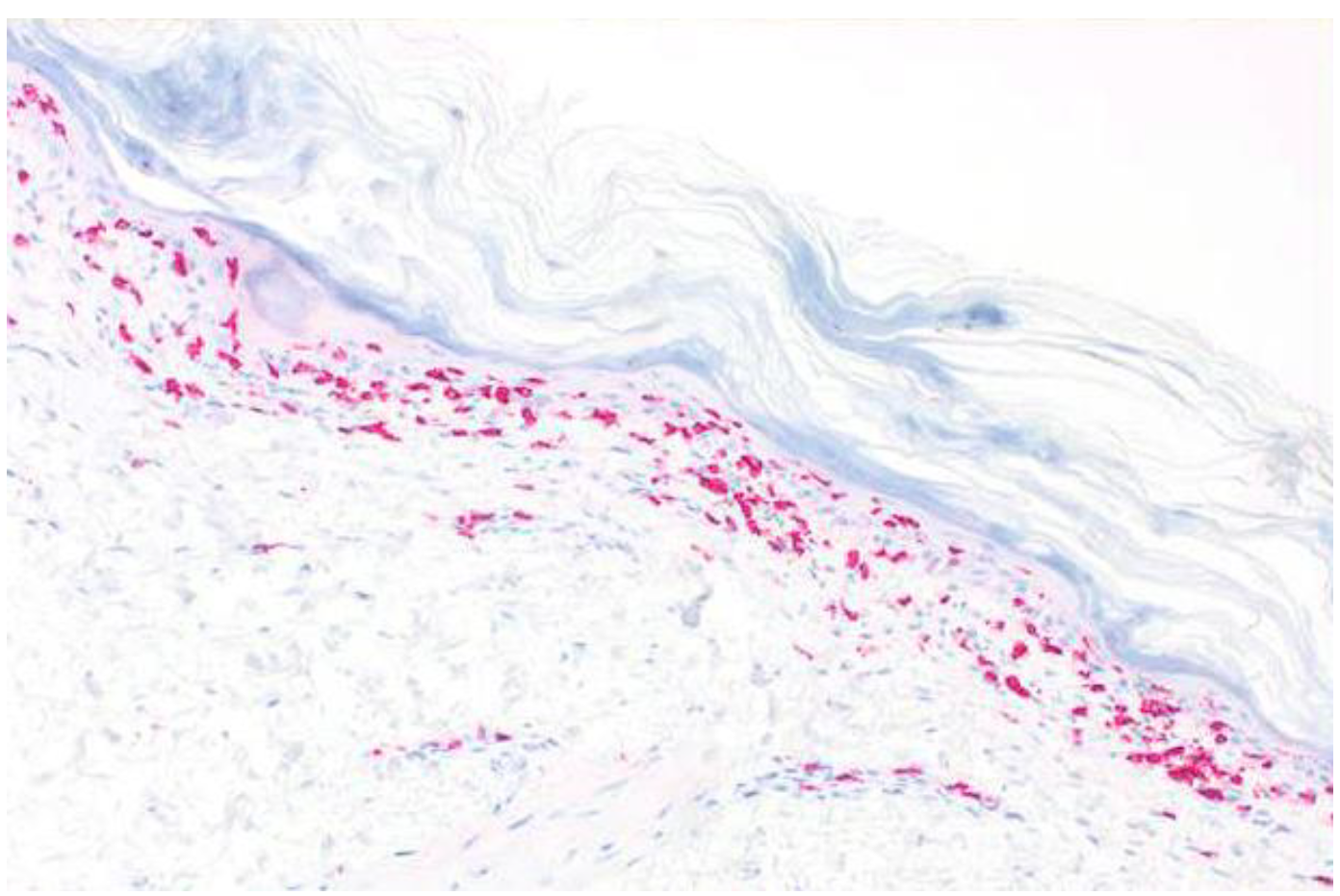
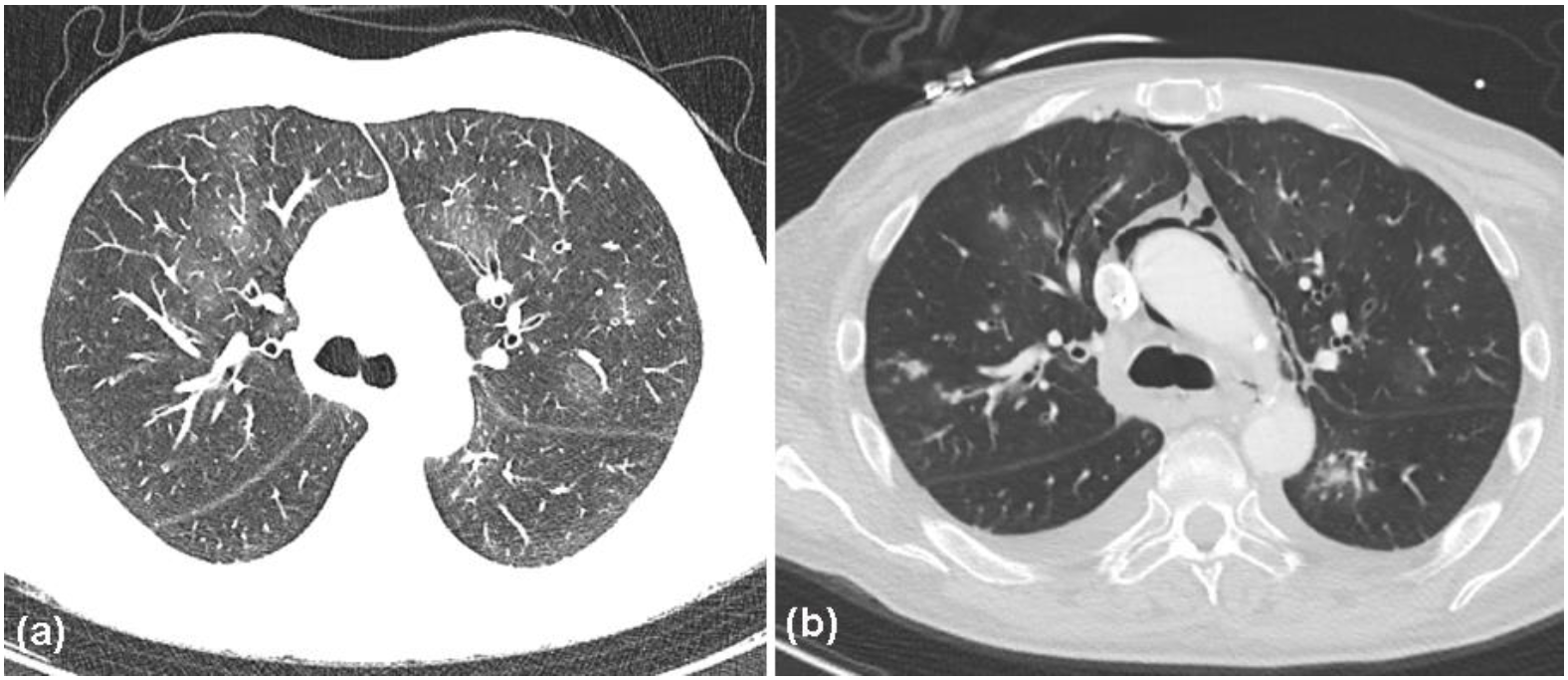
2. Case Report
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anhalt, G.J.; Kim, S.C.; Stanley, J.R.; Korman, N.J.; Jabs, D.A.; Kory, M.; Izumi, H.; Ratrie, H., III; Mutasim, D.; Ariss-Abdo, L.; et al. Paraneoplastic pemphigus. An autoimmune mucocutaneous disease associated with neoplasia. N. Engl. J. Med. 1990, 323, 1729–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, V.T.; Ndoye, A.; Bassler, K.D.; Shultz, L.D.; Shields, M.C.; Ruben, B.S.; Webber, R.J.; Pittelkow, M.R.; Lynch, P.J.; Grando, S.A. Classification, clinical manifestations, and immunopathological mechanisms of the epithelial variant of paraneoplastic autoimmune multiorgan syndrome: A reappraisal of paraneoplastic pemphigus. Arch. Dermatol. 2001, 137, 193–206. [Google Scholar]
- Amber, K.T.; Valdebran, M.; Grando, S.A. Paraneoplastic autoimmune multiorgan syndrome (PAMS): Beyond the single phenotype of paraneoplastic pemphigus. Autoimmun. Rev. 2018, 17, 1002–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kappius, R.H.; Ufkes, N.A.; Thiers, B.H. Paraneoplastic Pemphigus. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Didona, D.; DIZenzo, G.; Joly, P. Paraneoplastic autoimmune multiorgan syndrome. Ital. J. Dermatol. Venereol. 2021, 156, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svoboda, S.A.; Huang, S.; Liu, X.; Hsu, S.; Motaparthi, K. Paraneoplastic pemphigus: Revised diagnostic criteria based on literature analysis. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2021, 48, 1133–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuriyama, K.; Kitamura, Y.; Tsuji, T.; Nishikawa, R.; Nagata, H.; Ohshiro, M.; Sugitani, M.; Hirakawa, Y.; Matsumoto, Y.; Iwai, T.; et al. Successful treatment of paraneoplastic pemphigus and bronchiolitis obliterans associated with follicular lymphoma with obinutuzumab and bendamustine. Curr. Probl. Cancer 2021, 46, 100813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Gao, D.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, P.; Wang, Y.; Wang, N.; Xu, J.; Yu, G. Follicular lymphoma with paraneoplastic pemphigus as the first symptom: A case report and review of the literature. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2020, 13, 1915–1923. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, J.M.; Kim, J.H.; Hashimoto, T.; Kim, S.-C. Lichenoid paraneoplastic pemphigus associated with follicular lymphoma without detectable autoantibodies. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2018, 43, 613–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, T.; Higuchi, Y.; Yuki, H.; Hirata, S.; Nosaka, K.; Ishii, N.; Hashimoto, T.; Mitsuya, H.; Okuno, Y. Rituximab Monotherapy and Rituximab-Containing Chemotherapy Were Effective for Paraneoplastic Pemphigus Accompanying Follicular Lymphoma, but not for Subsequent Bronchiolitis Obliterans. J. Clin. Exp. Hematop. 2015, 55, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morikawa, K.; Tsuji, T.; Yamasaki, H.; Egashira, S.; Kaguchi, A.; Kido, M.; Tsuda, H. Paraneoplastic Pemphigus Occurs Most Commonly in Indolent B Cell Lymphoma. Acta Haematol. 2014, 132, 73–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, S.-C. Paraneoplastic Pemphigus: Paraneoplastic Autoimmune Disease of the Skin and Mucosa. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Labib, A.; Milroy, C. Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hafsi, W.; Badri, T. Erythema Multiforme. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tong, J.; Chan, J. Case Report: Stevens-Johnson Syndrome Due to Influenza Vaccination. Cureus 2020, 12, e9405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yalcin, B.; Alli, N. Pemphigus vulgaris following antirabies vaccination. J. Dermatol. 2007, 34, 734–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokubu, H.; Nishikawa, J.; Kato, T.; Mukaisho, K.; Hayashi, D.; Tateishi, C.; Tsuruta, D.; Hashimoto, T.; Tanaka, T.; Fujimoto, N. Paraneoplastic Pemphigus Mimicking Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis Associated with Follicular Lymphoma: Possible Pathological Role of CD8 T Cells. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2020, 100, adv00204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, D., Jr.; Harhay, M.O.; Nicol, K.K.; Liyanage, N.P.M.; Keller, B.C.; Robinson, R.T. Lung T-Cell Profile Alterations are Associated with Bronchiolitis Obliterans Syndrome in Cystic Fibrosis Lung Transplant Recipients. Lung 2020, 198, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodge, G.; Hodge, S.; Yeo, A.; Nguyen, P.; Hopkins, E.; Holmes-Liew, C.-L.; Reynolds, P.N.; Holmes, M. BOS Is Associated With Increased Cytotoxic Proinflammatory CD8 T, NKT-Like, and NK Cells in the Small Airways. Transplantation 2017, 101, 2469–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, E.E.; Lavoie, T.L.; Orens, J.B.; Chen, E.S.; Ye, S.Q.; Finkelman, F.D.; Garcia, J.G.N.; McDyer, J.F. Pluripotent Allospecific CD8+Effector T Cells Traffic to Lung in Murine Obliterative Airway Disease. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2006, 34, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hata, T.; Nishimoto, S.; Nagao, K.; Takahashi, H.; Yoshida, K.; Ohyama, M.; Yamada, T.; Asano, K.; Amagai, M. Ectopic Expression of Epidermal Antigens Renders the Lung a Target Organ in Paraneoplastic Pemphigus. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoffman, M.A.; Qiao, X.; Anhalt, G.J. CD8+ T Lymphocytes in Bronchiolitis Obliterans, Paraneoplastic Pemphigus, and Solitary Castleman’s Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 407–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giurdanella, F.; Fania, L.; Gnarra, M.; Toto, P.; Di Rollo, D.; Sauder, D.N.; Feliciani, C. A Possible Role for CD8+ T Lymphocytes in the Cell-Mediated Pathogenesis of Pemphigus Vulgaris. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 764290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gill, H.; Trendell-Smith, N.J.; Loong, F.; Yeung, C.-K.; Kwong, Y.-L. Paraneoplastic pemphigus due to CD8-positive cytotoxic T-cell lymphoma. Br. J. Haematol. 2010, 149, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwatra, S.G.; Boozalis, E.; Pasieka, H.; Anhalt, G.J. Decreased recognition of paraneoplastic pemphigus in patients previously treated with anti- CD 20 monoclonal antibodies. Br. J. Dermatol. 2019, 180, 1238–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummins, D.L.; Mimouni, D.; Tzu, J.; Owens, N.; Anhalt, G.J.; Meyerle, J.H. Lichenoid paraneoplastic pemphigus in the absence of detectable antibodies. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2007, 56, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Artero, E.; Querol-Cisneros, E.; Rodríguez-Garijo, N.; Tomás-Velázquez, A.; Idoate, M.A.; Ishii, N.; Hashimoto, T.; España, A. Paraneoplastic pemphigus without detectable anti-plakin antibodies in a patient with non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Ann. Hematol. 2018, 97, 543–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flood, K.; Stroud, C.; Lazarov, Z.; Vigneswaran, N.; Hsu, S. Paraneoplastic pemphigus without antibodies to desmoglein 1 and 3. Dermatol. Online J. 2018, 24, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, M.H.; Sa, Y.J.; Cho, K.D.; Jo, K.H.; Lee, S.H.; Sim, S.B. Thoracic Air-leak Syndromes In Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Recipients with Graft-versus-Host Disease: A Possible Sign for Poor Response to Treatment and Poor Prognosis. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2010, 25, 658–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Tefferi, A. Spontaneous pneumomediastinum and subcutaneous emphysema complicating bronchiolitis obliterans after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation—Case report and review of literature. Ann. Hematol. 2001, 80, 430–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, M.; Murayama, S.; Gibo, M.; Akamine, T.; Nagata, O. Frequent cause of the Macklin effect in spontaneous pneumomediastinum: Demonstration by multidetector-row computed tomography. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2006, 30, 92–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odani, K.; Itoh, A.; Yanagita, S.; Kaneko, Y.; Tachibana, M.; Hashimoto, T.; Tsutsumi, Y. Paraneoplastic Pemphigus Involving the Respiratory and Gastrointestinal Mucosae. Case Rep. Pathol. 2020, 2020, 7350759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | 18 July 2020 | 11 February 2021 | 9 September 2021 | 14 October 2021 | 29 October 2021 * | 5 November 2021 ** |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leukocytes (4600–9500/µL) | 9770 ↑ | 10,330 ↑ | 15,950 ↑ | 4530 ↓ | 3030 ↓ | 3670 ↓ |
| Erythrocytes (4.6–6.2 Mio/µL) | 4.1 ↓ | 5.21 | 5.1 | 4.25 ↓ | 4.19 ↓ | 3.44 ↓ |
| Hemoglobin (14–18 g/dL) | 12.1 ↓ | 15.6 | 15 | 12.2 ↓ | 12.1 ↓ | 9.8 ↓ |
| Thrombocytes (150,000–40,000/µL) | 269,000 | 217,000 | 216,000 | 195,000 | 76,000 ↓ | 21,000 ↓ |
| Lymphocytes (1000–4050/µL) | 2240 | 3320 | 4090 | 330 ↓ | 250 ↓ | 140 ↓ |
| Neutrophils (1800–7200/µL) | 6410 | 5710 | 8530 ↑ | 2898 | 2550 | 3400 |
| Eosinophils (40–360/µL) | 30 ↓ | 250 | 1600 ↑ | 70 | 10 ↓ | 20↓ |
| INR (0.8–1.1) | 1.13 ↑ | 1.14 ↑ | 1.21 ↑ | 1.21 ↑ | 1.35 ↑ | 1.4 ↑ |
| Lactate dehydrogenase (135–225 U/L) | 184 | 164 | 141 | 208 | 220 | 254 ↑ |
| GOT (10–50 U/L) | 16 | 19 | 18 | 18 | 16 | 17 |
| GPT (10–50 U/L) | 26 | 15 | 23 | 18 | 16 | 13 |
| Serum creatinine (0.7–1.2 mg/dL) | 0.92 | 1.1 | 1.0 | 0.84 | 0.73 | 1.0 |
| C-reactive protein (<5 mg/L) | 13.9 ↑ | <5 | 7.3 ↑ | 9.1 ↑ | 111.3 ↑ | 81.5 ↑ |
| Procalcitonin (<0.5 ng/mL) | - | - | - | - | <2 | 0.68 ↑ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gambichler, T.; Lee, Y.-P.; Oschlies, I.; Scheel, C.H.; Klapper, W.; Nowack, N.; Doerler, M.; Stücker, M.; Abolmaali, N.; Susok, L. Antibody-Negative Paraneoplastic Autoimmune Multiorgan Syndrome (PAMS) in a Patient with Follicular Lymphoma Accompanied by an Excess of Peripheral Blood CD8+ Lymphocytes. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 2395-2405. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29040194
Gambichler T, Lee Y-P, Oschlies I, Scheel CH, Klapper W, Nowack N, Doerler M, Stücker M, Abolmaali N, Susok L. Antibody-Negative Paraneoplastic Autoimmune Multiorgan Syndrome (PAMS) in a Patient with Follicular Lymphoma Accompanied by an Excess of Peripheral Blood CD8+ Lymphocytes. Current Oncology. 2022; 29(4):2395-2405. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29040194
Chicago/Turabian StyleGambichler, Thilo, Yi-Pei Lee, Ilske Oschlies, Christina H. Scheel, Wolfram Klapper, Nico Nowack, Martin Doerler, Markus Stücker, Nasreddin Abolmaali, and Laura Susok. 2022. "Antibody-Negative Paraneoplastic Autoimmune Multiorgan Syndrome (PAMS) in a Patient with Follicular Lymphoma Accompanied by an Excess of Peripheral Blood CD8+ Lymphocytes" Current Oncology 29, no. 4: 2395-2405. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29040194
APA StyleGambichler, T., Lee, Y.-P., Oschlies, I., Scheel, C. H., Klapper, W., Nowack, N., Doerler, M., Stücker, M., Abolmaali, N., & Susok, L. (2022). Antibody-Negative Paraneoplastic Autoimmune Multiorgan Syndrome (PAMS) in a Patient with Follicular Lymphoma Accompanied by an Excess of Peripheral Blood CD8+ Lymphocytes. Current Oncology, 29(4), 2395-2405. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29040194







