Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors: 10-Year Experience in Cancer Center—The Ottawa Hospital (TOH)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Sites
3.3. Clinical Presentation
3.4. Pathology Data
3.5. Risk Assessment
3.6. Molecular Data
3.7. Management Data and TKI Use
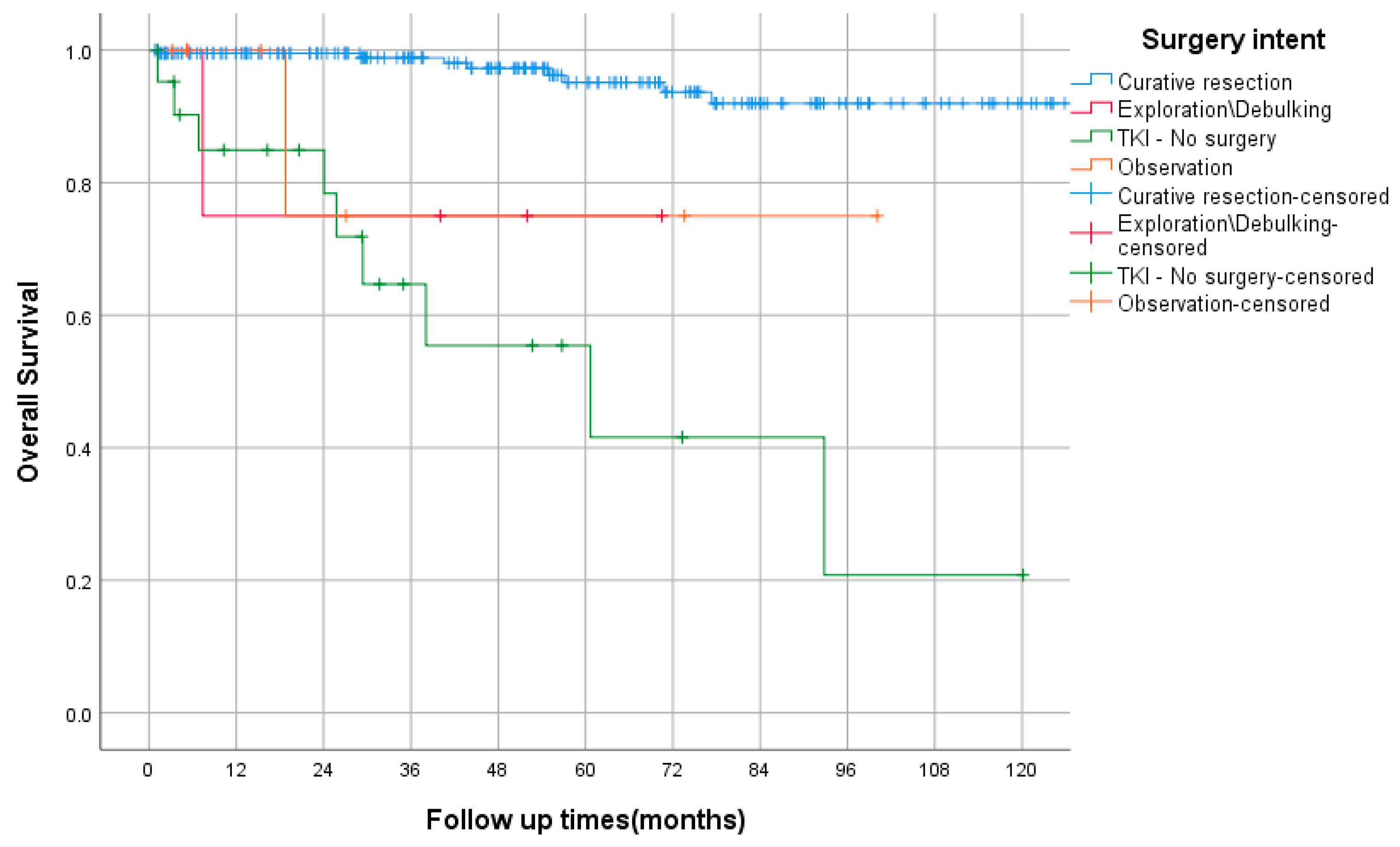
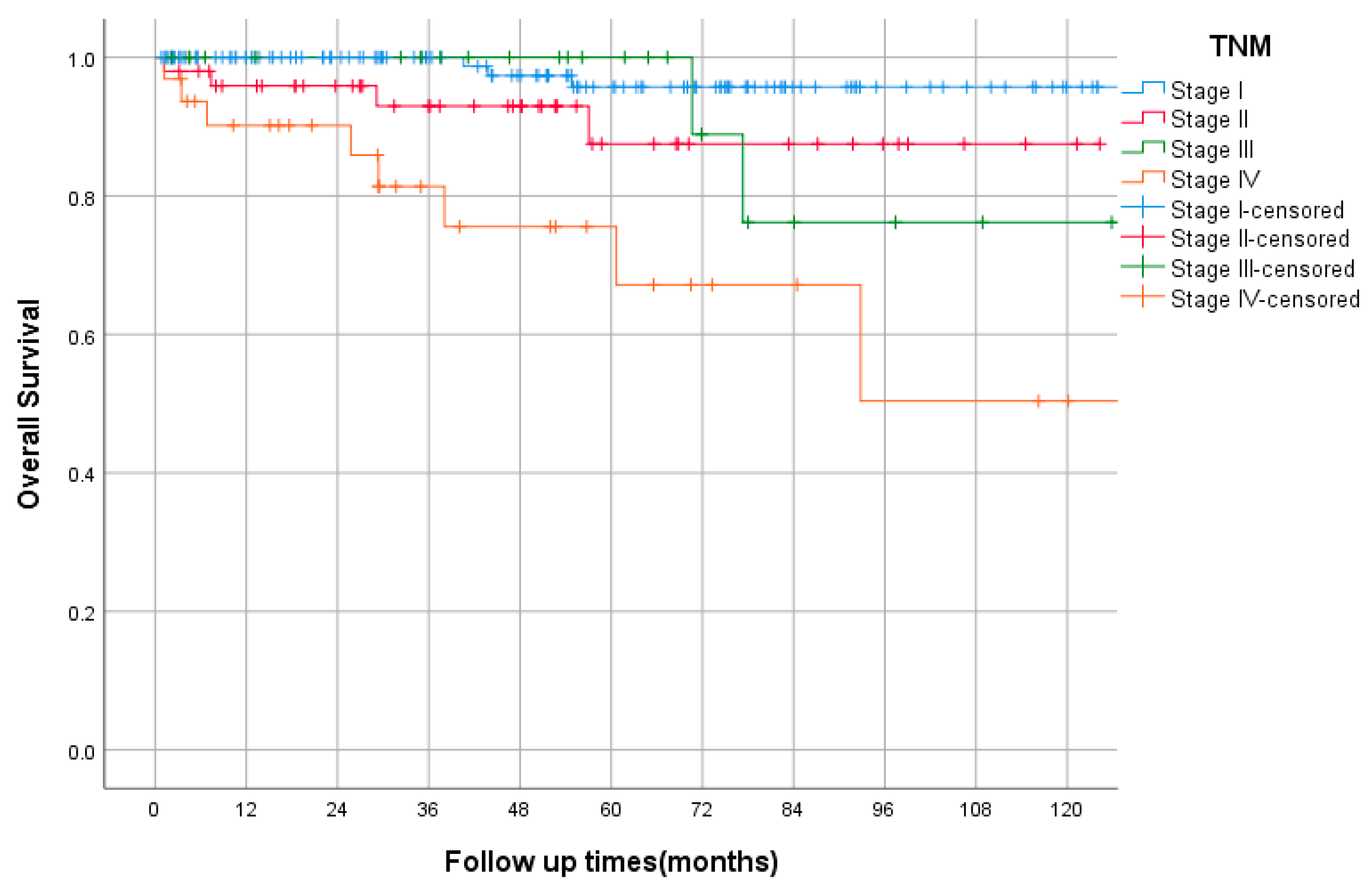
3.8. Survival
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sircar, K.; Hewlett, B.R.; Huizinga, J.D.; Chorneyko, K.; Berezin, I.; Riddell, R.H. Interstitial Cells of Cajal as Precursors of Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1999, 23, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corless, C.L.; Barnett, C.M.; Heinrich, M. Gastrointestinal stromal tumours: Origin and molecular oncology. Nat. Cancer 2011, 11, 865–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazur, M.T.; Clark, H.B. Gastric stromal tumors Reappraisal of histogenesis. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1983, 7, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirota, S.; Isozaki, K.; Moriyama, Y.; Hashimoto, K.; Nishida, T.; Ishiguro, S.; Kawano, K.; Hanada, M.; Kurata, A.; Takeda, M.; et al. Gain-of-Function Mutations of c-kit in Human Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors. Science 1998, 279, 577–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miettinen, M.; Lasota, J. Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors: Review on Morphology, Molecular Pathology, Prognosis, and Differential Diagnosis. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2006, 130, 1466–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichardt, P.; Blay, J.-Y.; Boukovinas, I.; Brodowicz, T.; Broto, J.M.; Casali, P.G.; Decatris, M.; Eriksson, M.; Gelderblom, H.; Kosmidis, P.; et al. Adjuvant therapy in primary GIST: State-of-the-art. Ann. Oncol. 2012, 23, 2776–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joensuu, H.; Eriksson, M.; Hall, K.S.; Reichardt, A.; Hermes, B.; Schütte, J.; Cameron, S.; Hohenberger, P.; Jost, P.J.; Al-Batran, S.-E.; et al. Survival Outcomes Associated with 3 Years vs 1 Year of Adjuvant Imatinib for Patients with High-Risk Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors. JAMA Oncol. 2020, 6, 1241–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joensuu, H.; Wardelmann, E.; Sihto, H.; Eriksson, M.; Hall, K.S.; Reichardt, A.; Hartmann, J.T.; Pink, D.; Cameron, S.; Hohenberger, P.; et al. Effect of KIT and PDGFRA Mutations on Survival in Patients with Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors Treated with Adjuvant Imatinib: An Exploratory Analysis of a Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanke, C.D.; Rankin, C.; Demetri, G.D.; Ryan, C.W.; von Mehren, M.; Benjamin, R.S.; Raymond, A.K.; Bramwell, V.H.; Baker, L.H.; Maki, R.G.; et al. Phase III Randomized, Intergroup Trial Assessing Imatinib Mesylate at Two Dose Levels in Patients with Unresectable or Metastatic Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors Expressing the Kit Receptor Tyrosine Kinase: S0033. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 626–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goettsch, W.G.; Bos, S.; Breekveldt-Postma, N.; Casparie, M.; Herings, R.M.; Hogendoorn, P. Incidence of gastrointestinal stromal tumours is underestimated: Results of a nation-wide study. Eur. J. Cancer 2005, 41, 2868–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demetri, G.D.; van Oosterom, A.T.; Garrett, C.R.; Blackstein, M.E.; Shah, M.H.; Verweij, J.; McArthur, G.; Judson, I.R.; Heinrich, M.C.; Morgan, J.A.; et al. Efficacy and safety of sunitinib in patients with advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumour after failure of imatinib: A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2006, 368, 1329–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demetri, G.D.; Reichardt, P.; Kang, Y.-K.; Blay, J.-Y.; Rutkowski, P.; Gelderblom, H.; Hohenberger, P.; Leahy, M.; Von Mehren, M.; Joensuu, H.; et al. Efficacy and safety of regorafenib for advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumours after failure of imatinib and sunitinib (GRID): An international, multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2013, 381, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Mehren, M.; Serrano, C.; Bauer, S.; Gelderblom, H.; George, S.; Heinrich, M.; Schöffski, P.; Zalcberg, J.; Chi, P.; Jones, R.L.; et al. INVICTUS: A phase III, interventional, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to assess the safety and efficacy of ripretinib as fourth-line therapy in advanced GIST who have received treatment with prior anticancer therapies (NCT03353753). Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2019, 30, v925–v926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montemurro, M.; Schöffski, P.; Reichardt, P.; Gelderblom, H.; Schütte, J.; Hartmann, J.; von Moos, R.; Seddon, B.; Joensuu, H.; Wendtner, C.; et al. Nilotinib in the treatment of advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumours resistant to both imatinib and sunitinib. Eur. J. Cancer 2009, 45, 2293–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montemurro, M.; Gelderblom, H.; Bitz, U.; Schütte, J.; Blay, J.; Joensuu, H.; Trent, J.; Bauer, S.; Rutkowski, P.; Duffaud, F.; et al. Sorafenib as third- or fourth-line treatment of advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumour and pretreatment including both imatinib and sunitinib, and nilotinib: A retrospective analysis. Eur. J. Cancer 2013, 49, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atiq, M.A.; Davis, J.L.; Hornick, J.L.; Dickson, B.C.; Fletcher, C.D.M.; Fletcher, J.A.; Folpe, A.L.; Mariño-Enríquez, A. Mesenchymal tumors of the gastrointestinal tract with NTRK rearrangements: A clinicopathological, immunophenotypic, and molecular study of eight cases, emphasizing their distinction from gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST). Mod. Pathol. 2020, 34, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, C.M.; Sainz, L.G.; Chi, P. The management of metastatic GIST: Current standard and investigational therapeutics. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mucciarini, C.; Rossi, G.; Bertolini, F.; Valli, R.; Cirilli, C.; Rashid, I.; Marcheselli, L.; Luppi, G.; Federico, M. Incidence and clinicopathologic features of gastrointestinal stromal tumors. A population-based study. BMC Cancer 2007, 7, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-H.; Shi, Y.-H.; Song, X.-Y.; Wang, H.; Li, M.-Z.; Yang, X.-F.; Wang, T.-Q.; Zhao, Q.-J.; Xu, W.-J.; Dong, P.-D.; et al. Multicenter analysis of gastrointestinal stromal tumors in inner Mongolia of China: A study of 804 cases. Asian J. Surg. 2021, 45, 718–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, T.; Chai, J.; Li, H.; de Bruyns, A.; Cleversey, C.; Lee, C.-H.; Yip, S.; Simmons, C.; Hart, J.; Pollock, P.; et al. Utilization of Mutational Analysis (MA) in Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor (GIST) Management in British Columbia (BC) Between January 2008 to December 2017: A Retrospective Population-Based Study. J. Gastrointest. Cancer 2021, 53, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joensuu, H. Risk stratification of patients diagnosed with gastrointestinal stromal tumor. Hum. Pathol. 2008, 39, 1411–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verschoor, A.J.; The PALGA group; Bovée, J.V.M.G.; Overbeek, L.I.H.; Hogendoorn, P.C.W.; Gelderblom, H. The incidence, mutational status, risk classification and referral pattern of gastro-intestinal stromal tumours in the Netherlands: A nationwide pathology registry (PALGA) study. Virchows Arch. 2018, 472, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Tu, L.; Qiu, W.-Q.; Wang, C.-J.; Shen, Y.-Y.; Liu, Q.; Cao, H. Gastrointestinal stromal tumor: 15-years’ experience in a single center. BMC Surg. 2014, 14, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMatteo, R.P.; Lewis, J.J.; Leung, D.H.Y.; Mudan, S.S.; Woodruff, J.M.; Brennan, M. Two Hundred Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors. Ann. Surg. 2000, 231, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joensuu, H.; Eriksson, M.; Hall, K.S.; Hartmann, J.T.; Pink, D.; Schütte, J.; Ramadori, G.; Hohenberger, P.; Duyster, J.; Al-Batran, S.-E.; et al. One vs Three Years of Adjuvant Imatinib for Operable Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor. JAMA 2012, 307, 1265–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joensuu, H.; Eriksson, M.; Hall, K.S.; Reichardt, A.; Hartmann, J.T.; Pink, D.; Ramadori, G.; Hohenberger, P.; Al-Batran, S.-E.; Schlemmer, M.; et al. Adjuvant Imatinib for High-Risk GI Stromal Tumor: Analysis of a Randomized Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 34, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanke, C.D.; Demetri, G.D.; von Mehren, M.; Heinrich, M.C.; Eisenberg, B.; Fletcher, J.A.; Corless, C.L.; Fletcher, C.D.; Roberts, P.J.; Heinz, D.; et al. Long-Term Results from a Randomized Phase II Trial of Standard-Versus Higher-Dose Imatinib Mesylate for Patients with Unresectable or Metastatic Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors Expressing KIT. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 620–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; Yang, Y.; Liao, W.; Li, Q. Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor: A Systematic Review. Front. Public Health 2022, 9, 2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Total n = 248 (Percentage %) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | Median | 64 (Range 28–90) | |
| Gender | Male | 124 | 50% |
| Female | 124 | 50% | |
| Comorbidities | HTN | 103 | 41.5% |
| DM | 49 | 19.8% | |
| DLP | 75 | 30.2% | |
| GERD | 25 | 10% | |
| IHD | 28 | 11.3% | |
| Neurofibromatosis | 4 | 1.6% | |
| Other | 104 | 42% | |
| Clinical presentation | Incidental | 87 * | 35% |
| Abdominal pain | 84 | 34% | |
| GI bleeding | 59 | 24% | |
| Anemia | 48 | 19% | |
| Bowel obstruction | 7 | 2.8% | |
| Perforation | 3 | 1.2% | |
| Other | 56 | 23% | |
| Duration of symptom ** | <14 days | 41 | 16.5% |
| >14 day | 32 | 12.9% | |
| >2 months | 38 | 15.3% | |
| >6 months | 32 | 12.9% | |
| NA | 24 | 9.7% | |
| ECOG | 0 | 100 | 40.3% |
| 1 | 77 | 31% | |
| 2 | 7 | 2.8% | |
| 3 | 4 | 1.6% | |
| NA | 22 | 8.9% | |
| Mode of initial diagnosis | CT | 123 | 49.5% |
| Endoscopy | 63 | 25% | |
| Surgical exploration | 14 | 5.6% | |
| EUS | 13 | 5.2% | |
| MRI | 10 | 4% | |
| Other | 11 | 4% | |
| Curative surgical resection | 213 | 85.9% | |
| Total n = 248 (Percentage %) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Site | Esophagus | 1 | 0.4% |
| Stomach | 156 | 62.9% | |
| Small bowel | 73 | 29.4% | |
| Duodenum | 19 | 7.7% | |
| Jejunum | 19 | 7.7% | |
| Ileum | 13 | 5.2% | |
| Unspecified | 22 | 8.9% | |
| Appendix | 1 | 0.4% | |
| Colon | 2 | 0.8% | |
| Rectum | 5 | 2% | |
| Diffuse/overlapping | 8 | 3.2% | |
| Mesentery | 2 | 0.8% | |
| Miettinenrisk class | None | 23 | 11% |
| None–rare ** | 5 | 2% | |
| Very low | 44 | 22% | |
| Low | 68 | 33% | |
| Moderate | 39 | 19% | |
| High | 24 | 12% | |
| Modified NIH risk class | Very low | 29 | 14% |
| Not defined ** | 5 | 2% | |
| Low | 78 | 38% | |
| Intermediate | 48 | 24% | |
| High | 42 | 21% | |
| Histology | Spindle cell | 159 | 64.1% |
| Epithelioid | 18 | 7.3% | |
| Mixed | 39 | 15.7% | |
| NA * | 32 | 12.9% | |
| Size | <2 cm | 37 | 14.9% |
| 2–5 | 91 | 36.7% | |
| 5–10 | 70 | 28.2% | |
| >10 | 31 | 12.5% | |
| NA | 19 | 7.7% | |
| Mitosis | ≤5 hpf | 177 | 71.4% |
| >5 hpf | 45 | 18.1% | |
| NA | 26 | 10.5% | |
| Grade | 1 | 159 | 64.1% |
| 2 | 36 | 14.5% | |
| 3 | 5 | 2% | |
| Unknown | 48 | 19.4% | |
| Mutation | No study | 237 | 95.6% |
| Study | 11 | 4.4% | |
| KIT Exon 11 | 3 | 1.2% | |
| PDGFR Exon 18 | 4 | 1.6% | |
| PDGFR c.2525A | 1 | 0.4% | |
| SDHB | 2 | 0.8% | |
| Other | 1 | 0.4% | |
| TNM stage | I | 131 | 52.8% |
| II | 50 | 20.2% | |
| III | 25 | 10.1% | |
| IV | 32 | 12.9% | |
| NA | 10 | 4% | |
| Total n = 248 (Percentage %) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Adjuvant Imatinib | 49 * | 19.8 | |
| Neoadjuvant Imatinib | 13 | 5.2% | |
| Palliative TKI | Imatinib | 41 | 16.5% |
| Sunitinib | 13 | 5.2% | |
| Regorafenib | 7 | 2.8% | |
| Ripertinib | 3 | 1.2% | |
| TKI alone (no surgery) | 22 | 8.9% | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alfagih, A.; AlJassim, A.; Alshamsan, B.; Alqahtani, N.; Asmis, T. Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors: 10-Year Experience in Cancer Center—The Ottawa Hospital (TOH). Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 7148-7157. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29100562
Alfagih A, AlJassim A, Alshamsan B, Alqahtani N, Asmis T. Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors: 10-Year Experience in Cancer Center—The Ottawa Hospital (TOH). Current Oncology. 2022; 29(10):7148-7157. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29100562
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlfagih, Abdulhameed, Abdulaziz AlJassim, Bader Alshamsan, Nasser Alqahtani, and Timothy Asmis. 2022. "Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors: 10-Year Experience in Cancer Center—The Ottawa Hospital (TOH)" Current Oncology 29, no. 10: 7148-7157. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29100562
APA StyleAlfagih, A., AlJassim, A., Alshamsan, B., Alqahtani, N., & Asmis, T. (2022). Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors: 10-Year Experience in Cancer Center—The Ottawa Hospital (TOH). Current Oncology, 29(10), 7148-7157. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29100562






