The Relationship between Nutritional Status and Body Composition with Clinical Parameters, Tumor Stage, CA19-9, CEA Levels in Patients with Pancreatic and Periampullary Tumors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Patients Characteristics
2.3. Nutritional Status and Anthropometric Measurements
2.3.1. Body Composition
2.3.2. Clinical Parameters
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient’s Characteristics and Differences between Resection and Non-Resection Groups
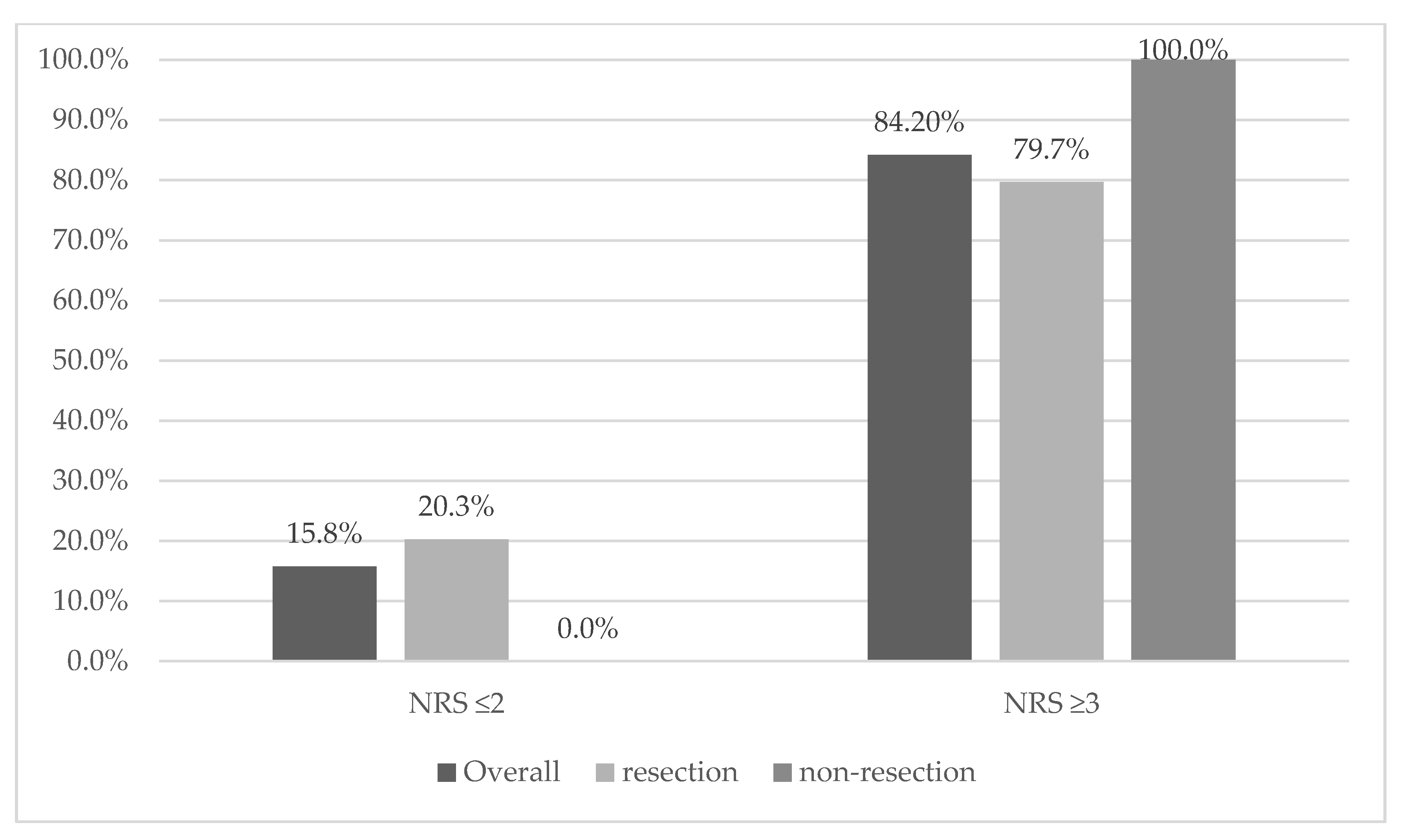
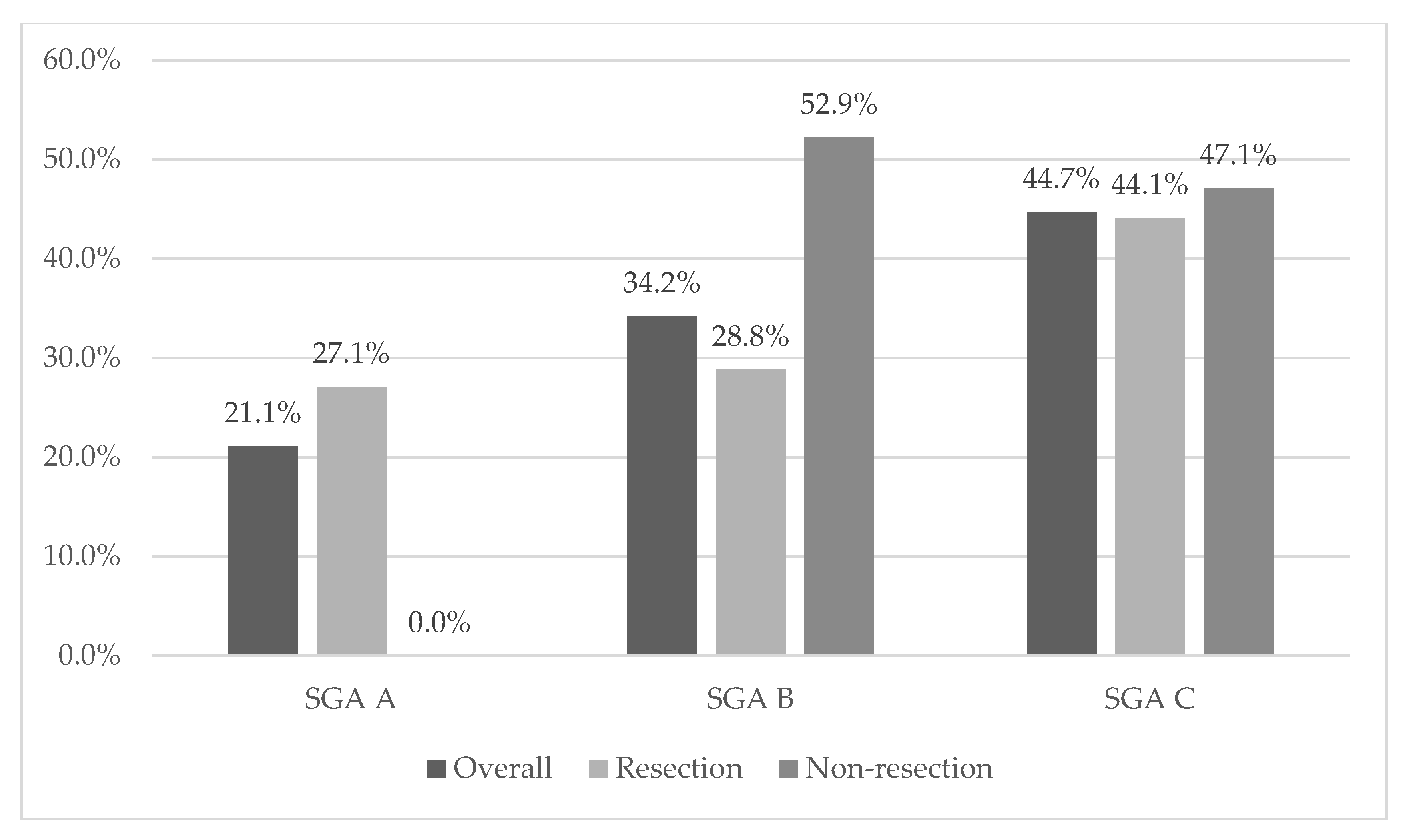
3.2. Nutritional Status
3.3. Body Composition
| Parameter | Overall n = 61 Mean (SD) | Resection n = 59 Mean (SD) | Non-Resection n = 17 Mean (SD) | p | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FFM [kg] | 48.61 | 11.04 | 49.06 | 11.61 | 46.80 | 8.56 | 0.530 |
| FFM [%] | 68.16 | 10.42 | 67.74 | 9.42 | 69.85 | 14.20 | 0.535 |
| FAT [kg] | 23.64 | 10.26 | 24.06 | 9.52 | 21.94 | 13.20 | 0.608 |
| FAT [%] | 31.85 | 10.22 | 32.33 | 9.27 | 29.92 | 13.74 | 0.468 |
| 50 Hz PhA | 7.64 | 1.52 | 7.67 | 1.49 | 7.55 | 1.68 | 0.809 |
| BCM [kg] | 26.23 | 5.95 | 26.45 | 6.26 | 25.33 | 4.62 | 0.565 |
| TBW [L] | 35.03 | 8.87 | 35.05 | 8.92 | 34.94 | 9.05 | 0.970 |
| ICW [kg] | 54.59 | 2.83 | 54.40 | 2.87 | 55.35 | 2.66 | 0.303 |
| ECW [kg] | 45.40 | 2.83 | 45.59 | 2.87 | 44.64 | 2.66 | 0.302 |
| ICW/ECW * | 0.83 | 0.10 | 0.84 | 0.10 | 0.80 | 0.09 | 0.062 |
| Muscle [kg] | 22.54 | 6.59 | 22.58 | 6.98 | 22.39 | 4.97 | 0.929 |
| Impedance 50 Hz | 541.79 | 93.95 | 537.65 | 96.52 | 558.67 | 84.31 | 0.492 |
3.4. Relationship between Nutritional Status, Body Composition, and Clinical Parameters
3.5. Relationship between Body Compositions with Tumor Stage, Karnofsky Performance, and Other Clinical Parameters
4. Discussion
4.1. Malnutrition, Weight Loss and BMI
4.2. Age
4.3. Albumin and Protein
4.4. CRP
4.5. CA19-9 and CEA
4.6. BIA Parameters
4.7. TNM
4.8. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- National Cancer Institute Surveillance. Epidemiology and End Results Program NCI SREER. Cancer Statistics Review 2011–2017. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/pancreas.html (accessed on 2 September 2021).
- Ray-Offor, E. Periampullary cancer and cancer in head of pancreas: What is the difference? Gastronterol. Hepatol. Endosc. 2012, 4, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Park, J.S.; Yoon, D.S.; Kim, W.J.; Chung, H.Y.; Lee, S.M.; Chang, N. A Study on the Dietary Intake and the Nutritional Status among the Pancreatic Cancer Surgical Patients. Clin. Nutr. Res. 2016, 5, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Chung, M.J.; Kim, B.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, H.J.; Heo, J.Y.; Kim, Y.J.; Park, J.Y.; Bang, S.; Park, S.W.; et al. The Significance of the Prognostic Nutritional Index for All Stages of Pancreatic Cancer. Nutr. Cancer 2016, 69, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bicakli, D.H.; Uslu, R.; Güney, S.C.; Coker, A. The Relationship Between Nutritional Status, Performance Status, and Survival Among Pancreatic Cancer Patients. Nutr. Cancer 2019, 72, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashi, P.; Popiel, B.; Lammersfeld, C.; Gupta, D. Outcomes of Systematic Nutritional Assessment and Medical Nutrition Therapy in Pancreatic Cancer. Pancreas 2015, 44, 750–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Kang, J.S.; Han, Y.; Kim, H.; Kwon, W.; Kim, J.R.; Kim, S.-W.; Jang, J.-Y. Influence of preoperative nutritional status on clinical outcomes after pancreatoduodenectomy. HPB 2018, 20, 1051–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, J.S.; Kim, H.-M.; Jeung, H.-C.; Kang, S.A. Association between early nutritional risk and overall survival in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer: A single-center retrospective study. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2019, 30, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Slee, A.; Birch, D.; Stokoe, D. A comparison of the malnutrition screening tools, MUST, MNA and bioelectrical impedance assessment in frail older hospital patients. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 34, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, D.; Lis, C.G.; Dahlk, S.L.; King, J.; Vashi, P.G.; Grutsch, J.F.; Lammersfeld, C.A. The relationship between bioelectrical impedance phase angle and subjective global assessment in advanced colorectal cancer. Nutr. J. 2008, 7, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- NCCN Guidelines for Patients. Available online: https://www.nccn.org/patients/guidelines/content/PDF/pancreatic-patient.pdf (accessed on 25 February 2021).
- Deng, G.C.; Yan, H.; Guo, Z.P.; Dai, G. Correlation Between Baseline Serum Tumor Markers and Clinical Characteristic Factors in Patients with Advanced Pancreatic Cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 11151–11163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, A.A.; Helzlsouer, K.J.; Kooperberg, C.; Shu, X.O.; Steplowski, E.; Bueno-de-Mesquita, H.B.; Fuchs, C.S.; Gross, M.D.; Jacobs, E.J.; Lacroix, A.Z.; et al. Anthropometric measures, body mass index, and pancreatic cancer: A pooled analysis from the Pancreatic Cancer Cohort Consortium (PanScan). Arch. Int. Med. 2010, 170, 791–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nemer, L.; Krishna, S.G.; Shah, Z.K.; Conwell, D.L.; Cruz-Monserrate, Z.; Dillhoff, M.; Guttridge, D.C.; Hinton, A.; Manilchuk, A.; Pawlik, T.M.; et al. Predictors of Pancreatic Cancer-Associated Weight Loss and Nutritional Interventions. Pancreas 2017, 46, 1152–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandona, M.; Linehan, D.; Hawkins, W.; Strasberg, S.; Gao, F.; Wang-Gillam, A. Influence of obesity and other risk factors on survival outcomes in patients undergoing pancreaticoduodenectomy for pancreatic cancer. Pancreas 2011, 40, 931–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrucci, L.M.; Bell, D.; Thornton, J.; Black, G.; McCorkle, R.; Heimburger, D.C.; Saif, M.W. Nutritional status of patients with locally advanced pancreatic cancer: A pilot study. Supportive Care Cancer 2010, 19, 1729–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seika, P.; Klein, F.; Pelzer, U.; Pratschke, J.; Bahra, M.; Malinka, T. Influence of the body mass index on postoperative outcome and long-term survival after pancreatic resections in patients with underlying malignancy. HepatoBiliary Surg. Nutr. 2019, 8, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Torre, M.; Ziparo, V.; Nigri, G.; Cavallini, M.; Balducci, G.; Ramacciato, G. Malnutrition and pancreatic surgery: Prevalence and outcomes. J. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 107, 702–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, S.; Choti, M.A.; Assumpcao, L.; Cameron, J.L.; Gleisner, A.L.; Herman, J.M.; Eckhauser, F.; Edil, B.H.; Schulick, R.D.; Wolfgang, C.L.; et al. Impact of Obesity on Perioperative Outcomes and Survival Following Pancreaticoduodenectomy for Pancreatic Cancer: A Large Single-Institution Study. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2010, 14, 1143–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendifar, A.; Osipov, A.; Khanuja, J.; Nissen, N.; Naziri, J.; Yang, W.; Li, Q.; Tuli, R. Influence of Body Mass Index and Albumin on Perioperative Morbidity and Clinical Outcomes in Resected Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzierżek, P.; Kurnol, K.; Hap, W.; Frejlich, E.; Diakun, A.; Karwowski, A.; Kotulski, K.; Rudno-Rudzińska, J.; Kielan, W. Assessment of changes in body composition measured with bioelectrical impedance in patients operated for pancreatic, gastric and colorectal cancer. Pol. Prz. Chir. 2020, 92, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikamori, M.; Miyamoto, A.; Asaoka, T.; Maeda, S.; Hama, N.; Yamamoto, K.; Hirao, M.; Ikeda, M.; Sekimoto, M.; Doki, Y.; et al. Postoperative Changes in Body Composition After Pancreaticoduodenectomy Using Multifrequency Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2015, 20, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundmann, O.; Yoon, S.L.; Williams, J.J. The value of bioelectrical impedance analysis and phase angle in the evaluation of malnutrition and quality of life in cancer patients--a comprehensive review. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 69, 1290–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gilliland, T.M.; Villafane-Ferriol, N.; Shah, K.P.; Shah, R.M.; Cao, H.S.T.; Massarweh, N.N.; Silberfein, E.J.; Choi, E.A.; Hsu, C.; McELHANY, A.L.; et al. Nutritional and Metabolic Derangements in Pancreatic Cancer and Pancreatic Resection. Nutrients 2017, 9, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tumas, J.; Tumiene, B.; Jurkeviciene, J.; Jasiunas, E.; Sileikis, A. Nutritional and immune impairments and their effects on outcomes in early pancreatic cancer patients undergoing pancreatoduodenectomy. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 3385–3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cresta Morgado, P.; Daud, M.; Carballido, M.; Méndez, G.; Iseas, S.; Lobbe, V.; De Simone, G.; Navigante, A. Relationship between skeletal muscle function, body composition, and weight loss in patients with advanced pancreatic and gastrointestinal cancers. Supportive Care Cancer 2019, 27, 1181–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, C.; Bao, Y.; Wu, C.; Kraft, P.; Ogino, S.; Ng, K.; Qian, Z.R.; Rubinson, D.A.; Stampfer, M.J.; Giovannucci, E.L.; et al. Prediagnostic body mass index and pancreatic cancer survival. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 4229–4234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milena, I.; Irena, I. Epidemiology of pancreatic cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 28, 9694–9705. [Google Scholar]
- Higuera, O.; Ghanem, I.; Nasimi, R.; Prieto, I.; Koren, L.; Feliu, J. Management of pancreatic cancer in the elderly. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 764–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aslani, A.; Gill, A.J.; Roach, P.J.; Allen, B.J.; Smith, R.C. Preoperative body composition is influenced by the stage of operable pancreatic adenocarcinoma but does not predict survival after Whipple’s procedure. HPB 2010, 12, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jabłońska, B.; Lampe, P.; Mrowiec, S. The influence of nutritional status on the incidence of postoperative complications in patients following distal pancreatectomy. Prz. Gastroenterol. 2020, 15, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecorelli, N.; Carrara, G.; De Cobelli, F.; Cristel, G.; Damascelli, A.; Balzano, G.; Beretta, L.; Braga, M. Effect of sarcopenia and visceral obesity on mortality and pancreatic fistula following pancreatic cancer surgery. Br. J. Surg. 2016, 103, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afaneh, C.; Gerszberg, D.; Slattery, E.; Seres, D.S.; Chabot, J.A.; Kluger, M.D. Pancreatic cancer surgery and nutrition management: A review of the current literature. Hepatobiliary Surg. Nutr. 2015, 4, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xiao, X.; Wang, T.; Li, L.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, H.; Chu, Y.; Jiao, F.; Cui, J.; Wang, L. A Survival Model in Locally Advanced and Metastatic Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. J. Cancer 2018, 9, 1301–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haas, M.; Heinemann, V.; Kullmann, F.; Laubender, R.P.; Klose, C.; Bruns, C.J.; Holdenrieder, S.; Modest, D.P.; Schulz, C.; Boeck, S. Prognostic value of CA 19-9, CEA, CRP, LDH and bilirubin levels in locally advanced and metastatic pancreatic cancer: Results from a multicenter, pooled analysis of patients receiving palliative chemotherapy. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 139, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozich, N.S.; Jones, C.E.; Morris, K.T. Malnutrition, frailty, and sarcopenia in pancreatic cancer patients: Assessments and interventions for the pancreatic surgeon. Ann. Pancreat. Cancer 2019, 2, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasenda, B.; Bass, A.; Koeberle, D.; Pestalozzi, B.; Borner, M.; Herrmann, R.; Jost, L.; Lohri, A.; Hess, V. Survival in overweight patients with advanced pancreatic carcinoma: A multicentre cohort study. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cai, Z.; Cai, D.; Yao, D.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, Y. Associations between body composition and nutritional assessments and biochemical markers in patients with chronic radiation enteritis: A case-control study. Nutr. J. 2016, 15, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beaudart, C.; Bruyère, O.; Geerinck, A.; Hajaoui, M.; Scafoglieri, A.; Perkisas, S.; Bautmans, I.; Gielen, E.; Reginster, J.Y.; Buckinx, F. Equation models developed with bioelectric impedance analysis tools to assess muscle mass: A systematic review. Belgian Aging Muscle Society (BAMS). Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2020, 35, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aleixo, G.; Shachar, S.S.; Nyrop, K.A.; Muss, H.B.; Battaglini, C.L.; Williams, G.R. Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis for the Assessment of Sarcopenia in Patients with Cancer: A Systematic Review. Oncologist 2020, 25, 170–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, M.Y.; Chok, K.S.H. Sarcopenia in pancreatic cancer—Effects on surgical outcomes and chemiotherapy. World J. Gastrointest. Ocol. 2019, 15, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ninomiya, G.; Fujii, T.; Yamada, S.; Yabusaki, N.; Suzuki, K.; Iwata, N.; Kanda, M.; Hayashi, M.; Tanaka, C.; Nakayama, G.; et al. Clinical impact of sarcopenia on prognosis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: A retrospective cohort study. Int. J. Surg. 2017, 39, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.; Lammersfeld, C.A.; Vashi, P.G.; King, J.; Dahlk, S.L.; Grutsch, J.F.; Lis, C.G. Bioelectrical impedance phase angle as a prognostic indicator in breast cancer. BMC Cancer 2008, 27, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maurício, S.F.; da Silva, J.B.; Bering, T.; Correia, M.I. Relationship between nutritional status and the Glasgow Prognostic Score in patients with colorectal cancer. Nutrition 2013, 29, 625–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gupta, D.; Lis, C.G.; Dahlk, S.L.; Vashi, P.G.; Grutsch, J.F.; Lammersfeld, C.A. Bioelectrical impedance phase angle as a prognostic indicator in advanced pancreatic cancer. Br. J. Nutr. 2004, 92, 957–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McSorley, S.T.; Black, D.H.; Horgan, P.G.; McMillan, D.C. The relationship between tumour stage, systemic inflammation, body composition and survival in patients with colorectal cancer. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 1279–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Poulia, K.A.; Yannakoulia, M.; Karageorgou, D.; Gamaletsou, M.; Panagiotakos, D.B.; Sipsas, N.V.; Zampelas, A. Evaluation of the efficacy of six nutritional screening tools to predict malnutrition in the elderly. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 31, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Parameter | p | Overall | Resection | Non-Resection | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 76 | n = 59 | n = 17 | |||||
| Age at diagnosis, mean (SD) [year] | 0.313 | 65.32 (9.65) | 64.71 (9.18) | 67.41 (11.17) | |||
| Gender | |||||||
| M n (%) | 0.312 | 41 53.9% | 30 | 50.80% | 11 | 64.70% | |
| F n (%) | 35 46.1% | 29 | 49.20% | 6 | 35.30% | ||
| BMI at diagnosis, mean (SD) [kg/m2] | 0.679 | 25.16 (4.59) | 25.28 (4.54) | 24.75 (4.85) | |||
| Usual BMI, mean (SD) [kg/m2] | 0.767 | 27.97 (4.83) | 27.88 (4.80) | 28.28 (5.08) | |||
| NRS 2002: [n, %] * | |||||||
| 2 | 0.024 | 12 | 15.80% | 12 | 20.30% | 0 | 0.00% |
| 3 | 18 | 23.70% | 15 | 25.40% | 3 | 17.60% | |
| 4 | 15 | 19.70% | 11 | 18.60% | 4 | 23.50% | |
| 5 | 23 | 30.30% | 18 | 30.50% | 5 | 29.40% | |
| 6 | 8 | 10.50% | 3 | 5.10% | 5 | 29.40% | |
| SGA [n, %] | 0.032 | ||||||
| A | 16 | 21.10% | 16 | 27.10% | 0 | 0.00% | |
| B | 26 | 34.20% | 17 | 28.80% | 9 | 52.90% | |
| C | 34 | 44.70% | 26 | 44.10% | 8 | 47.10% | |
| Weight loss at diagnosis, mean [kg] | 0.247 | 8.26 | 7.76 | 10 | |||
| Weight loss at diagnosis, mean [%] | 0.157 | 9.98 | 9.27 | 12.4 | |||
| ≤5% (n) [%] | 0.63 | 24 | 31.60% | 20 | 33.90% | 4 | 23.50% |
| >5% (n) [%] | 19 | 25.00% | 15 | 25.40% | 4 | 23.50% | |
| >10%(n) [%] | 33 | 43.40% | 24 | 40.70% | 9 | 52.90% | |
| Malnutrition risk NRS 2002 (≥3) n (%) * | 0.058 | 64 84.2% | 47 | 79.70% | 17 | 100.00% | |
| Malnutrition SGA n (%) | |||||||
| (stage B, C) n (%) * | 0.016 | 60 78.9% | 43 | 72.90% | 17 | 100% | |
| Diabetes mellites present at diagnosis, n (%) | 0.231 | 41 53.9% | 34 | 57.60% | 7 | 41.20% | |
| Serum albumin level [g/dL] mean | 0.389 | 3.74 | 3.79 | 3.6 | |||
| Total protein level [g/dL] mean | 0.767 | 6.52 | 6.53 | 6.47 | |||
| Glucose [mg/dL] mean * | 0.874 | 140.36 | 139.12 | 144.59 | |||
| Lipase [U/L] mean * | 0.316 | 121.36 | 122.02 | 119.06 | |||
| Amylase [U/L] mean * | 0.046 | 71.23 | 79.55 | 42.82 | |||
| Alt [U/L] mean * | 0.097 | 83.43 | 86.97 | 71.18 | |||
| Ast [U/L] mean * | 0.414 | 115.24 | 136.31 | 42.12 | |||
| WBC [G/L] mean * | 0.007 | 8.39 | 9.10 | 5.96 | |||
| HCT [%] mean | 0.093 | 38.13 | 38.6 | 36.52 | |||
| HGB [g/dL] mean * | 0.074 | 12.95 | 13.22 | 12.04 | |||
| RBC [T/L] mean * | 0.032 | 8.10 | 6.85 | 12.38 | |||
| CEA mean * | 0.068 | 6.46 | 4.13 | 15.6 | |||
| CA19-9 mean * | 0.526 | 548.27 | 621.39 | 275.28 | |||
| C-reactive protein (CRP 1) [mg/dL] mean * | 0.205 | 16.52 | 16.86 | 15.33 | |||
| Cachexia | 0.418 | 52 (68.4%) | 39 (66.1%) | 13 (76.5%) | |||
| Tumor size (n) [%] * | |||||||
| T1 | 0.836 | 1 | 1.30% | 1 | 1.70% | 0 | 0.00% |
| T2 | 15 | 19.70% | 13 | 22.00% | 2 | 11.80% | |
| T3 | 55 | 72.40% | 41 | 69.50% | 14 | 82.40% | |
| T4 | 5 | 6.60% | 4 | 6.80% | 1 | 5.90% | |
| Selected Clinical Parameters | b.Mass.% | b.Mass_Loss | NRS | ALB | TP | NRS ≥ 3 | SGA | Cachexia | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ffm_kg | −0.17 | 0.04 | −0.16 | 0.01 | −0.02 | −0.19 | −0.20 | 0.44 | |
| p | 0.182 | 0.78 | 0.228 | 0.935 | 0.896 | 0.847 | 0.135 | 0.66 | |
| Ffm % | 0.24 | 0.13 | 0.08 | −0.24 | −0.21 | 1.21 | 0.11 | 1.55 | |
| p | 0.062 | 0.303 | 0.546 | 0.069 | 0.111 | 0.231 | 0.41 | 0.125 | |
| fat_kg | −0.39 | −0.19 | −0.20 | 0.32 | 0.30 | −2.37 | −0.26 | −2.09 | |
| p | 0.002 | 0.146 | 0.128 | 0.014 | 0.026 | 0.021 | 0.049 | 0.041 | |
| fat% | −0.24 | −0.12 | −0.05 | 0.25 | 0.22 | −1.12 | −0.07 | −1.50 | |
| p | 0.065 | 0.342 | 0.683 | 0.057 | 0.098 | 0.268 | 0.572 | 0.14 | |
| 50 hz_pa | −0.22 | −0.2 | −0.17 | 0.17 | 0.05 | −0.52 | −0.15 | −0.63 | |
| p | 0.083 | 0.128 | 0.184 | 0.207 | 0.687 | 0.604 | 0.258 | 0.53 | |
| bcm_kg | −0.24 | −0.02 | −0.21 | 0.09 | 0.06 | −0.9 | −0.26 | −0.12 | |
| p | 0.07 | 0.864 | 0.106 | 0.486 | 0.666 | 0.372 | 0.043 | 0.908 | |
| tbw_lt | −0.26 | −0.03 | −0.15 | 0.08 | 0.06 | −0.65 | −0.22 | 0.05 | |
| p | 0.048 | 0.808 | 0.253 | 0.532 | 0.633 | 0.516 | 0.095 | 0.96 | |
| Icw % | 0.31 | 0.13 | 0.24 | −0.03 | 0.09 | 2.13 | 0.24 | 1.47 | |
| p | 0.017 | 0.323 | 0.063 | 0.83 | 0.508 | 0.037 | 0.062 | 0.147 | |
| Ecw % | −0.31 | −0.13 | −0.24 | 0.03 | −0.09 | −2.13 | −0.24 | −1.47 | |
| p | 0.017 | 0.324 | 0.063 | 0.833 | 0.502 | 0.037 | 0.063 | 0.148 | |
| ecw/icw * | −0.29 | −0.20 | −0.27 | 0.08 | 0.04 | −2.10 b | −0.25 | −1.56 | |
| p | 0.024 | 0.117 | 0.039 | 0.536 | 0.795 | 0.036 | 0.049 | 0.119 | |
| musle_kg | −0.06 | 0.11 | −0.03 | 0.08 | 0.11 | 1.03 | −0.08 | 1.22 | |
| p | 0.632 | 0.383 | 0.806 | 0.571 | 0.433 | 0.308 | 0.535 | 0.228 | |
| 50 hz_imp | 0.30 | 0.10 | 0.26 | −0.10 | 0.01 | 1.43 | 0.32 | 1.19 | |
| p | 0.018 | 0.433 | 0.044 | 0.47 | 0.972 | 0.159 | 0.012 | 0.237 | |
| Arm | −0.46 | −0.25 | −0.38 | 0.28 | 0.16 | −1.54 | −0.3 | −1.63 | |
| p | <0.001 | 0.058 | 0.003 | 0.04 | 0.255 | 0.129 | 0.022 | 0.11 | |
| Calf * | −0.38 | −0.26 | −0.4 | 0.13 | 0.01 | −1.31 | −0.33 | −1.38 | |
| p | 0.004 | 0.053 | 0.002 | 0.349 | 0.97 | 0.189 | 0.011 | 0.169 | |
| fold_tric * | −0.28 | −0.20 | −0.25 | 0.19 | 0 | −0.83 | −0.33 | −1.63 | |
| p | 0.055 | 0.17 | 0.081 | 0.192 | 1 | 0.405 | 0.022 | 0.104 | |
| bmi_usual | 0.17 | 0.37 | 0.19 | 0.13 | 0.08 | 1.19 | 0.11 | 1.19 | |
| p | 0.15 | 0.001 | 0.102 | 0.274 | 0.528 | 0.236 | 0.33 | 0.237 | |
| BMI | −0.36 | −0.13 | −0.19 | 0.32 | 0.19 | −1.07 | −0.27 | −1.98 | |
| p | 0.001 | 0.252 | 0.101 | 0.006 | 0.115 | 0.288 | 0.018 | 0.052 | |
| Karnofsky * | −0.45 | −0.38 | −0.52 | 0.41 | 0.27 | −3.51 b | −0.35 | −2.84 b | |
| p | <0.001 | 0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.024 | <0.001 | 0.002 | 0.005 | |
| tnm_t | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.13 | −0.04 | 0.07 | 0.64 | 0.15 | 0.55 | |
| p | 0.173 | 0.168 | 0.277 | 0.758 | 0.576 | 0.526 | 0.189 | 0.586 | |
| tnm_n | −1.29 | −1.45 | −1.34 | 0.31 | −0.03 | 0.73 | −1.48 | 0.03 | |
| p | 0.202 | 0.151 | 0.183 | 0.756 | 0.973 | 0.392 | 0.142 | 0.855 | |
| tnm_m | 0.05 | −0.03 | 0.24 | −0.1 | −0.07 | −1.37 | 0.16 | −0.76 | |
| p | 0.675 | 0.782 | 0.049 | 0.416 | 0.59 | 0.174 | 0.183 | 0.452 | |
| CA19−9 * | 0.16 | 0.17 | 0.15 | −0.23 | −0.09 | −2.20 a | 0.26 | −0.53 | |
| p | 0.181 | 0.153 | 0.215 | 0.061 | 0.478 | 0.028 | 0.026 | 0.597 | |
| Cea * | 0.16 | 0.21 | 0.25 | −0.13 | 0.01 | −0.91 | 0.13 | −0.13 | |
| p | 0.214 | 0.097 | 0.044 | 0.318 | 0.942 | 0.364 | 0.306 | 0.896 | |
| Rbc * | −0.25 | −0.23 | −0.34 | 0.37 | 0.36 | −1.97 b | −0.22 | −0.94 | |
| p | 0.03 | 0.047 | 0.003 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.049 | 0.06 | 0.349 | |
| Hgb * | −0.34 | −0.3 | −0.38 | 0.53 | 0.46 | −1.64 | −0.31 | −1.67 | |
| p | 0.002 | 0.009 | 0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.101 | 0.007 | 0.095 | |
| Hct | −0.25 | −0.21 | −0.26 | 0.47 | 0.43 | −0.82 | −0.22 | −0.84 | |
| p | 0.034 | 0.072 | 0.026 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.414 | 0.057 | 0.406 | |
| Crp * | 0.30 | 0.35 | 0.33 | −0.26 | −0.11 | −1.15 | 0.35 | −2.13 a | |
| p | 0.009 | 0.002 | 0.004 | 0.028 | 0.363 | 0.25 | 0.002 | 0.033 | |
| Age | 0.30 | 0.23 | 0.36 | −0.22 | −0.10 | −1.95 | 0.29 | 1.19 | |
| p | 0.008 | 0.041 | 0.001 | 0.06 | 0.408 | 0.055 | 0.01 | 0.236 |
| Selected Clinical Parameters | Ffm_kg | Ffm% | Fat_kg | Fat% | 50 hz_pa | Bcm_kg | Tbw_lt | Icw% | Ecw% | Ecw/Icw * | Musle_kg | 50 hz_imp | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| age | −0.31 | −0.06 | −0.07 | 0.06 | −0.39 | −0.36 | −0.31 | 0.05 | −0.05 | −0.03 | −0.25 | 0.07 | |
| p | 0.015 | 0.666 | 0.599 | 0.651 | 0.002 | 0.004 | 0.017 | 0.699 | 0.697 | 0.849 | 0.05 | 0.592 | |
| bmi | 0.31 | −0.74 | 0.93 | 0.76 | 0.32 | 0.36 | 0.44 | −0.35 | 0.35 | 0.35 | 0.19 | −0.52 | |
| p | 0.016 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.013 | 0.005 | <0.001 | 0.007 | 0.007 | 0.006 | 0.153 | <0.001 | |
| bmi_usual | 0.26 | −0.66 | 0.78 | 0.68 | 0.23 | 0.29 | 0.36 | −0.24 | 0.24 | 0.2 | 0.19 | −0.43 | |
| p | 0.042 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.078 | 0.026 | 0.005 | 0.069 | 0.07 | 0.131 | 0.154 | <0.001 | |
| Karnofsky * | 0.26 | −0.23 | 0.33 | 0.23 | 0.57 | 0.28 | 0.33 | −0.09 | 0.09 | 0.10 | 0.18 | −0.33 | |
| p | 0.044 | 0.07 | 0.01 | 0.071 | <0.001 | 0.029 | 0.009 | 0.496 | 0.496 | 0.454 | 0.158 | 0.008 | |
| arm | 0.53 | −0.47 | 0.74 | 0.49 | 0.18 | 0.54 | 0.59 | −0.38 | 0.38 | 0.41 | 0.39 | −0.49 | |
| p | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.17 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.004 | 0.004 | 0.002 | 0.003 | <0.001 | |
| Calf * | 0.38 | −0.40 | 0.63 | 0.40 | 0.18 | 0.39 | 0.44 | −0.44 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 0.30 | −0.47 | |
| p | 0.004 | 0.002 | <0.001 | 0.002 | 0.188 | 0.003 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.026 | <0.001 | |
| fold_tric * | 0.08 | −0.57 | 0.49 | 0.57 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.12 | −0.23 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0 | −0.11 | |
| p | 0.588 | <0.001 | 0.001 | <0.001 | 0.632 | 0.636 | 0.434 | 0.124 | 0.124 | 0.117 | 0.992 | 0.459 | |
| tnm_t | −0.06 | −0.10 | 0.11 | 0.06 | −0.01 | −0.04 | −0.03 | 0.20 | −0.20 | −0.25 | 0.03 | 0.09 | |
| p | 0.671 | 0.451 | 0.416 | 0.643 | 0.963 | 0.756 | 0.822 | 0.125 | 0.123 | 0.051 | 0.82 | 0.488 | |
| tnm_n | 0.59 | 0.79 | −0.93 | −0.19 | 0.4 | 0.35 | 0.33 | −1.16 | 1.18 | −1.51 | −0.09 | −0.72 | |
| p | 0.558 | 0.434 | 0.359 | 0.852 | 0.69 | 0.724 | 0.74 | 0.25 | 0.244 | 0.13 | 0.925 | 0.472 | |
| tnm_m | −0.20 | 0.10 | −0.18 | −0.10 | −0.09 | −0.23 | −0.19 | 0.14 | −0.14 | −0.20 | −0.16 | 0.31 | |
| p | 0.134 | 0.466 | 0.193 | 0.435 | 0.498 | 0.089 | 0.153 | 0.311 | 0.316 | 0.146 | 0.245 | 0.017 | |
| CA19−9 * | −0.24 | −0.22 | 0.05 | 0.19 | −0.07 | −0.23 | −0.25 | 0.08 | −0.08 | −0.12 | −0.22 | 0.09 | |
| p | 0.078 | 0.103 | 0.719 | 0.149 | 0.603 | 0.083 | 0.063 | 0.54 | 0.54 | 0.366 | 0.102 | 0.487 | |
| Cea * | −0.24 | −0.07 | 0.12 | 0.06 | −0.26 | −0.22 | −0.20 | −0.03 | 0.03 | −0.03 | −0.25 | 0.05 | |
| p | 0.10 | 0.634 | 0.409 | 0.679 | 0.068 | 0.117 | 0.164 | 0.861 | 0.861 | 0.813 | 0.08 | 0.725 | |
| Crp * | 0.17 | 0.06 | −0.01 | −0.04 | 0 | 0.11 | 0.17 | 0.07 | −0.07 | −0.07 | 0.19 | 0.02 | |
| p | 0.215 | 0.644 | 0.965 | 0.737 | 0.998 | 0.424 | 0.213 | 0.602 | 0.602 | 0.60 | 0.161 | 0.902 | |
| Rbc * | 0.17 | −0.18 | 0.31 | 0.20 | 0.26 | 0.20 | 0.16 | 0.15 | −0.15 | −0.13 | 0.15 | −0.06 | |
| p | 0.183 | 0.159 | 0.017 | 0.129 | 0.04 | 0.12 | 0.209 | 0.266 | 0.266 | 0.308 | 0.268 | 0.648 | |
| hct | 0.14 | −0.17 | 0.29 | 0.2 | 0.26 | 0.19 | 0.15 | 0.14 | −0.14 | −0.16 | 0.16 | −0.04 | |
| p | 0.278 | 0.182 | 0.026 | 0.12 | 0.046 | 0.142 | 0.247 | 0.275 | 0.275 | 0.219 | 0.226 | 0.733 | |
| Hgb * | 0.31 | −0.14 | 0.32 | 0.14 | 0.29 | 0.36 | 0.30 | 0.13 | −0.13 | −0.12 | 0.32 | −0.15 | |
| p | 0.018 | 0.285 | 0.014 | 0.274 | 0.023 | 0.005 | 0.021 | 0.328 | 0.328 | 0.356 | 0.012 | 0.241 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jachnis, A.; Słodkowski, M.T. The Relationship between Nutritional Status and Body Composition with Clinical Parameters, Tumor Stage, CA19-9, CEA Levels in Patients with Pancreatic and Periampullary Tumors. Curr. Oncol. 2021, 28, 4805-4820. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol28060406
Jachnis A, Słodkowski MT. The Relationship between Nutritional Status and Body Composition with Clinical Parameters, Tumor Stage, CA19-9, CEA Levels in Patients with Pancreatic and Periampullary Tumors. Current Oncology. 2021; 28(6):4805-4820. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol28060406
Chicago/Turabian StyleJachnis, Aneta, and Maciej Tomasz Słodkowski. 2021. "The Relationship between Nutritional Status and Body Composition with Clinical Parameters, Tumor Stage, CA19-9, CEA Levels in Patients with Pancreatic and Periampullary Tumors" Current Oncology 28, no. 6: 4805-4820. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol28060406
APA StyleJachnis, A., & Słodkowski, M. T. (2021). The Relationship between Nutritional Status and Body Composition with Clinical Parameters, Tumor Stage, CA19-9, CEA Levels in Patients with Pancreatic and Periampullary Tumors. Current Oncology, 28(6), 4805-4820. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol28060406




