Evaluation of Ki-67 as a Prognostic Marker in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma—A Single-Center Retrospective Cohort Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Histopathologic Evaluation
2.3. Parameters
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Patient Population
3.1.1. Ki-67 and IPI
3.1.2. Ki-67 and Response
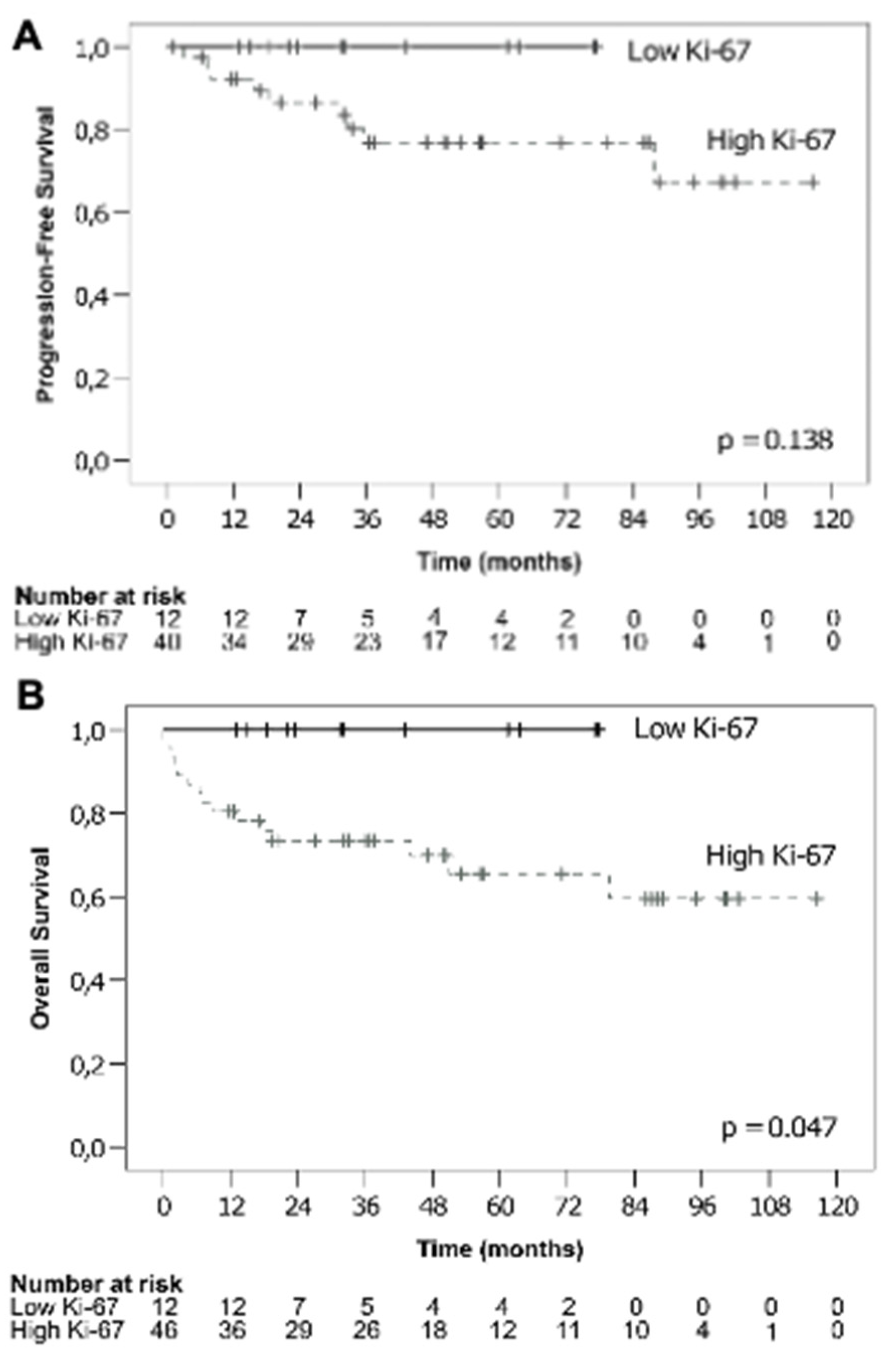
3.1.3. Ki-67 and Survival
3.2. Multivariate Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gascoyne, R.D.; Chan, J.K.C.; Campo, E.; Rosenwald, A.; Jaffe, E.S.; Stein, H.; Chan, W.C.; Swerdlow, S.H. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. In WHO Classification of Tumors of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues, 4th ed.; Swerdlow, S.H., Campo, E., Harris, N.L., Jaffe, E.S., Pileri, S.A., Stein, H., Thiele, J., Eds.; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2017; Volume 2, pp. 291–297. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Barta, S.K. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: 2019 update on diagnosis, risk stratification, and treatment. Am. J. Hematol. 2019, 94, 604–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tilly, H.; da Silva, M.G.; Vitolo, U.; Jack, A.; Meignan, M.; Lopez-Guillermo, A.; Walewski, J.; André, M.; Johnson, P.; Pfreundschuh, M.; et al. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL): ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, v116–v125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Chen, Z.; Fu, T.; Jin, X.; Yu, T.; Liang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Huang, L. Ki-67 is a valuable prognostic predictor of lymphoma but its utility varies in lymphoma subtypes: Evidence from a systematic meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, M.-K.; Chung, J.-S.; Lee, J.-J.; Yang, D.-H.; Kim, I.-S.; Shin, D.-H.; Shin, H.-J. High Ki-67 expression in involved bone marrow predicts worse clinical outcome in diffuse large B cell lymphoma patients treated with R-CHOP therapy. Int. J. Hematol. 2014, 101, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.-M.; Huang, J.-J.; Xia, Y.; Zhu, Y.-J.; Zhao, W.; Wei, W.-X.; Jiang, W.-Q.; Lin, T.-Y.; Huang, H.-Q.; Guan, Z.-Z. High Ki-67 expression in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients with non-germinal center subtype indicates limited survival benefit from R-CHOP therapy. Eur. J. Haematol. 2012, 88, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaudio, F.; Giordano, A.; Perrone, T.; Pastore, D.; Curci, P.; Delia, M.; Napoli, A.; Risi, C.D.; Spina, A.; Ricco, R.; et al. High Ki67 Index and Bulky Disease Remain Significant Adverse Prognostic Factors in Patients with Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma before and after the Introduction of Rituximab. Acta Haematol. 2011, 126, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, D.H.; Choi, D.R.; Ahn, H.J.; Kim, S.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, S.-W.; Park, B.H.; Yoon, S.O.; Huh, J.; Lee, S.-W.; et al. Ki-67 expression as a prognostic factor in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients treated with rituximab plus CHOP. Eur. J. Haematol. 2010, 85, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pătraşcu, A.M.; Rotaru, I.; Olar, L.; Pătraşcu, Ş.; Ghiluşi, M.C.; Neamţu, S.D.; Nacea, J.G.; Gluhovschi, A. The prognostic role of Bcl-2, Ki67, c-MYC and p53 in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Romanian J. Morphol. Embryol. = Revue Roumaine de Morphologie et Embryologie 2017, 58, 837–843. [Google Scholar]
- Abdulla, M.; Laszlo, S.; Triumf, J.; Hedström, G.; Berglund, M.; Enblad, G.; Amini, R.-M. A population-based study of cellular markers in R-CHOP treated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients. Acta Oncol. 2016, 55, 1126–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chabot-Richards, D.S.; Martin, D.R.; Myers, O.; Czuchlewski, D.R.; E Hunt, K. Quantitative image analysis in the assessment of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Mod. Pathol. 2011, 24, 1598–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ott, G.; Ziepert, M.; Klapper, W.; Horn, H.; Szczepanowski, M.; Bernd, H.-W.; Thorns, C.; Feller, A.C.; Lenze, D.; Hummel, M.; et al. Immunoblastic morphology but not the immunohistochemical GCB/nonGCB classifier predicts outcome in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in the RICOVER-60 trial of the DSHNHL. Blood 2010, 116, 4916–4925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hasselblom, S.; Ridell, B.; Sigurdardottir, M.; Hansson, U.; Nilsson-Ehle, H.; Andersson, P.-O. Low rather than high Ki-67 protein expression is an adverse prognostic factor in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Leuk. Lymphoma 2008, 49, 1501–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broyde, A.; Boycov, O.; Strenov, Y.; Okon, E.; Shpilberg, O.; Bairey, O. Role and prognostic significance of the Ki-67 index in non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Am. J. Hematol. 2009, 84, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, Y.W.; Hwang, H.S.; Park, C.-S.; Yoon, D.H.; Suh, C.; Huh, J. Prognostic effect of Ki-67 expression in rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine and prednisone-treated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma is limited to non-germinal center B-cell-like subtype in late-elderly patients. Leuk. Lymphoma 2015, 56, 2630–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashmi, A.A.; Iftikhar, S.N.; Nargus, G.; Ahmed, O.; Asghar, I.A.; Shirazi, U.A.; Afzal, A.; Irfan, M.; Ali, J. Ki67 Proliferation Index in Germinal and Non-Germinal Subtypes of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Cureus 2021, 13, e13120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salles, G.; De Jong, D.; Xie, W.; Rosenwald, A.; Chhanabhai, M.; Gaulard, P.; Klapper, W.; Calaminici, M.; Sander, B.; Thorns, C.; et al. Prognostic significance of immunohistochemical biomarkers in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: A study from the Lunenburg Lymphoma Biomarker Consortium. Blood 2011, 117, 7070–7078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.-L.; Zhou, Y.; Cheng, L.-L.; Su, Y.-Z.; Wang, C.-B. BCL2/Ki-67 index predict survival in germinal center B-cell-like diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 3767–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Patient Characteristics | Ki-67 | p-Value | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low (≤70%) (N = 12) | High (>70%) (N = 46) | |||||||||
| N (%) | Min. | Median | Max. | N (%) | Min. | Median | Max. | |||
| Gender | female | 6 (50.0%) | 17 (37.0%) | 0.513 | ||||||
| male | 6 (50.0%) | 29 (63.0%) | ||||||||
| Age (years) | 25 | 59 | 82 | 18 | 68 | 88 | 0.161 | |||
| BMI | 23.1 | 27.7 | 32.7 | 17.9 | 25.4 | 42.7 | 0.146 | |||
| Ann nmslyyds Arbor | I | 1 (8.3%) | 8 (17.4%) | 0.405 | ||||||
| II | 8 (66.7%) | 17 (37.0%) | ||||||||
| III | 1 (8.3%) | 6 (13.0%) | ||||||||
| IV | 2 (16.7%) | 15 (32.6%) | ||||||||
| B symptoms | no | 9 (75.0%) | 33 (71.7%) | 1.000 | ||||||
| yes | 3 (25.0%) | 13 (28.3%) | ||||||||
| Extranodal sites | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 5 | 0.124 | |||
| ECOG | 0 | 7 (58.3%) | 15 (41.7%) | |||||||
| 1 | 3 (25.0%) | 10 (27.8%) | 0.857 | |||||||
| 2 | 2 (16.7%) | 7 (19.4%) | ||||||||
| 3 | 0 (0.0%) | 3 (8.3%) | ||||||||
| 4 | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (2.8%) | ||||||||
| LDH (U/l) | 130 | 216 | 812 | 110 | 270 | 3108 | 0.437 | |||
| Bulk | No | 5 (41.7%) | 36 (78.3%) | 0.028 | ||||||
| Yes | 7 (58.3%) | 10 (21.7%) | ||||||||
| Maintenance therapy | No | 11 (91.7%) | 36 (78.3%) | 0.429 | ||||||
| Yes | 1 (8.3%) | 10 (21.7%) | ||||||||
| 2nd line | No | 12 (100.0%) | 40 (87.0%) | 0.328 | ||||||
| Yes | 0 (0.0%) | 6 (13.0%) | ||||||||
| 3rd line | No | 12 (100.0%) | 44 (95.7%) | 1.000 | ||||||
| Yes | 0 (0.0%) | 2 (4.3%) | ||||||||
| Transplant | No | 12 (100.0%) | 45 (97.8%) | 1.000 | ||||||
| Yes | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (2.2%) | ||||||||
| Radiotherapy | No | 7 (58.3%) | 32 (69.6%) | 0.360 | ||||||
| Initial | 5 (41.7%) | 11 (23.9%) | ||||||||
| Relapse | 0 (0.0%) | 3 (6.5%) | ||||||||
| Ki-67 | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low (≤70%) | High (>70%) | |||
| N (%) | N (%) | |||
| IPI Group | low | 7 (58.3%) | 19 (50.0%) | 0.148 |
| intermediate-low | 4 (33.3%) | 4 (10.5%) | ||
| intermediate-high | 0 (0.0%) | 4 (10.5%) | ||
| high | 1 (8.3%) | 11 (28.9%) | ||
| Response | CR | 12 (100.0%) | 34 (73.9%) | 0.373 |
| PR | 0 (0.0%) | 5 (10.9%) | ||
| SD | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (2.2%) | ||
| PD | 0 (0.0%) | 6 (13.0%) | ||
| Factors | Unstandardized Coefficients Beta | 95.0% CI | p-Value | Adjusted R2 | F Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Bound | Upper Bound | |||||
| Gender | −4.435 | −22.681 | 13.811 | 0.627 | 0.057 | 1.737 |
| Ki-67 ≤ 70% or > 70% | 10.788 | −10.244 | 31.820 | 0.307 | ||
| IPI | −6.477 | −12.530 | −0.424 | 0.037 | ||
| Presence of B symptoms | −5.252 | −26.679 | 16.175 | 0.624 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huber, F.; Zwickl-Traxler, E.; Pecherstorfer, M.; Singer, J. Evaluation of Ki-67 as a Prognostic Marker in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma—A Single-Center Retrospective Cohort Study. Curr. Oncol. 2021, 28, 4521-4529. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol28060383
Huber F, Zwickl-Traxler E, Pecherstorfer M, Singer J. Evaluation of Ki-67 as a Prognostic Marker in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma—A Single-Center Retrospective Cohort Study. Current Oncology. 2021; 28(6):4521-4529. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol28060383
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuber, Fabian, Elisabeth Zwickl-Traxler, Martin Pecherstorfer, and Josef Singer. 2021. "Evaluation of Ki-67 as a Prognostic Marker in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma—A Single-Center Retrospective Cohort Study" Current Oncology 28, no. 6: 4521-4529. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol28060383
APA StyleHuber, F., Zwickl-Traxler, E., Pecherstorfer, M., & Singer, J. (2021). Evaluation of Ki-67 as a Prognostic Marker in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma—A Single-Center Retrospective Cohort Study. Current Oncology, 28(6), 4521-4529. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol28060383





