Abstract
Sorafenib, an oral multi-tyrosine kinase inhibitor, has been the first-line therapy for the treatment of patients with advanced HCC, providing a survival benefit of only three months in approximately 30% of patients. Cancer stem cells (CSCs) are a rare tumour subpopulation with self-renewal and differentiation capabilities, and have been implicated in tumour growth, recurrence and drug resistance. The process of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) contributes to the generation and maintenance of the CSC population, resulting in immune evasion and therapy resistance in several cancers, including HCC. The aim of this study is to target the chemoresistant CSC population in HCC by assessing the effectiveness of a combination treatment approach with Sorafenib, an EMT inhibitor and an immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI). A stem-cell-conditioned serum-free medium was utilised to enrich the CSC population from the human HCC cell lines Hep3B, PLC/PRF/5 and HepG2. The anchorage independent spheres were characterised for CSC features. The human HCC-derived spheres were assessed for EMT status and expression of immune checkpoint molecules. The effect of combination treatment with SB431542, an EMT inhibitor, and siRNA-mediated knockdown of programmed cell death protein ligand-1 (PD-L1) or CD73 along with Sorafenib on human HCC-derived CSCs was examined with cell viability and apoptosis assays. The three-dimensional spheres enriched from human HCC cell lines demonstrated CSC-like features. The human HCC-derived CSCs also exhibited the EMT phenotype along with the upregulation of immune checkpoint molecules. The combined treatment with SB431542 and siRNA-mediated PD-L1 or CD73 knockdown effectively enhanced the cytotoxicity of Sorafenib against the CSC population compared to Sorafenib alone, as evidenced by the reduced size and proliferation of spheres. Furthermore, the combination treatment of Sorafenib with SB431542 and PD-L1 or CD73 siRNA resulted in an increased proportion of an apoptotic population, as evidenced by flow cytometry analysis. In conclusion, the combined targeting of EMT and immune checkpoint molecules with Sorafenib can effectively target the CSC tumour subpopulation.
1. Introduction
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a major global health problem with increasing incidence and poor survival rates [1,2]. Curative treatments for HCC patients are only feasible at early stages, with limited treatment modalities for advanced HCC [3,4,5]. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved Sorafenib as the first drug for the treatment of unresectable advanced HCC [6].
The potential survival benefit with Sorafenib is minimal with an extension in the survival time of only three months in patients with HCC [6,7,8]. Furthermore, only one-third of advanced HCC patients respond to Sorafenib treatment due to the development of Sorafenib resistance [6,9,10]. Effective treatment alternatives for patients with HCC resistant to Sorafenib are still lacking. Elucidating the mechanisms of Sorafenib resistance and exploring better treatment strategies to improve therapeutic outcomes in HCC is warranted. Studies have proposed several mechanisms of Sorafenib resistance. Primary or intrinsic resistance to Sorafenib in HCC patients mostly results from genetic heterogeneity, while secondary or acquired resistance to Sorafenib treatment results from several resistance factors [11]. The commonly reported mechanisms attributed to Sorafenib resistance are epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) [12,13,14], cancer stem cells (CSCs) [15,16], autophagy [17,18], hypoxia [19,20] and deregulated signal transduction including EGFR activation [21,22], c-Jun activation [23,24,25] and Akt activation [26,27].
EMT, a major reversible cellular process allowing cells to transform from epithelial to motile phenotypes, is well known for its role in embryonic development processes, organ fibrosis and the progression and metastasis of many cancers, including HCC [28,29,30]. The process of EMT has been implicated in tumour cells acquiring resistance to chemo and radiotherapies [28]. Studies have revealed a significant link between EMT and Sorafenib resistance in HCC [28,31,32,33,34]. Similarly, studies have demonstrated that EMT also contributes to the generation and maintenance of the CSC population in cancers, including HCC [32,35,36,37].
CSCs are a tumour-initiating subset of tumour cells with stem-cell-like properties for self-renewal, proliferation, production of heterogeneous progeny, metastasis and chemotherapy resistance [38,39,40]. Hepatic CSCs have been isolated and characterised using multiple cell surface markers, including CD133, CD44, EpCAM, CD90, CD13 and others [38,41]. Despite accounting for only a small portion of a tumour, CSCs are a chemoresistant subpopulation contributing to therapy failure in most cancers, including HCC [42,43].
Upon undergoing EMT, cells are reported to possess CSC-like features and vice versa as a result of crosstalk between EMT and CSCs [39]. Studies have demonstrated that EMT is activated in Sorafenib-resistant cells along with an enrichment of the CSCs [12,44]. However, specific studies on the modulation of EMT, CSC and Sorafenib resistance in HCC are still lacking.
Recently, the FDA has approved immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), Nivolumab and Pembrolizumab, against programmed cell death protein-1 (PD-1), for treatment of HCC patients previously treated with Sorafenib [45,46]. Furthermore, several combination approaches with ICIs, such as Nivolumab combined with Ipilimumab (anti-cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein-4 (CTLA-4)) and Atezolizumab (anti-PD-L1) combined with Bevacizumab, have been approved to improve therapeutic efficacy in HCC patients [47,48]. CSCs and EMT have been closely linked with the development of immune evasion in cancers [49,50,51]. However, little is known about the Sorafenib–EMT–CSC–ICI axis.
In this study, we utilised a sphere-forming assay to enrich CSCs from human HCC cell lines based on the initial protocol established by Reynolds and Weiss to generate neurospheres from adult brain [52]. The sphere-forming assay for CSC enrichment uses a serum-free medium supplemented with appropriate mitogens such as epidermal growth factor (EGF), basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF), b27 and N2 supplements in a low adherence system to form tumour spheres that exhibit self-renewal and tumourigenicity [53]. The culture medium conditions used for this assay provide an appropriate niche environment required for forming spheres and maintaining the stemness of CSCs [53]. For instance, EGF maintains pluripotency in neuroglioma stem cells, whereas bFGF is critical for the formation of tumour spheres [54]. Similarly, b27 is vital in sphere formation and maintaining characteristics of CSCs, and N2 supplement supports the proliferation of tumour spheres [54,55]. The CSCs enriched by this method are capable of forming three-dimensional spheroids with a heterogeneous population of progenitor cells that can differentiate into multiple cell phenotypes [56]. Notably, the sphere-forming culture method is based on the ability of CSCs to grow as anchorage-independent three-dimensional spheres and is not dependent on CSC marker expression [57]. The sphere-forming assay has been increasingly utilised in various tumours, including HCC for isolating, enriching, maintaining or expanding the potential CSC subpopulations [53,55,57,58,59].
In this study, the sphere-forming assay was used to examine the stemness and chemoresistance properties with several in vitro assays. Furthermore, we evaluated the relationship between EMT and immune checkpoint molecule expression in the CSC population. We also demonstrated that human HCC-derived CSCs exhibit mesenchymal traits with increased expression of immune checkpoints. Thus, we utilized the combined targeting of EMT and immune checkpoints to enhance the cytotoxicity of Sorafenib against resistant HCC-derived CSCs.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Reagents
The human HCC cell lines PLC/PRF/5 (85061113) and HepG2 (85011430) were purchased from CellBank Australia. The human HCC cell line Hep3B was kindly provided by Prof. V. Nathan Subramaniam, The Queensland University of Technology, Australia. All cell lines were mycoplasma-tested using the MycoAlert test (Abm, Richmond, BC, Canada) and cultured in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) (Thermofisher, Victoria, Australia) with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Gibco, Victoria, Australia) and 1% penicillin/streptomycin (P/S) (Thermofisher, Victoria, Australia) and incubated in a humidified atmosphere with 5% CO2 at 37 °C [57]. Sorafenib was procured from Selleckchem.com, Australia. The TGF-β receptor kinase inhibitor, SB431542 (Sigma, New South Wales, Australia), was used at a concentration of 2 µM.
2.2. Three-Dimensional Sphere Enrichment Assay
A serum-free stem-cell-conditioned medium was prepared with 1:1 mixture of DMEM/HAM’s F-12 (Thermofisher, Victoria, Australia) supplemented with 1% pencillin/streptomycin (P/S) (Thermofisher, Victoria, Australia), 10 ng/mL human recombinant basic fibroblast growth factor (hrbFGF) (Peprotech, Lonza, Victoria, Australia), 20 ng/mL human recombinant epidermal growth factor (hrEGF) (Peprotech, Lonza, Victoria, Australia), 2% B27 supplement without vitamin A (Thermofisher, Victoria, Australia) and 1% N2 supplement (Thermofisher, Victoria, Australia) [58]. The parental adherent cells were dissociated with Trypsin-EDTA (Thermofisher, Australia) and the detached cells were washed three times with 1XPBS to remove serum. Approximately 5000 cells/well were seeded in a 6-well ultra-low attachment plate and cultured with serum-free stem-cell-conditioned medium at 37 °C under a humidified atmosphere with 5% CO2 in air [57]. The spheres were photographed under an inverted microscope equipped with a digital camera (Olympus DP21, Tokyo, Japan) and collected after 5 days [57].
2.3. Colony-Forming Assay
Both adherent cells and spheres were enzymatically dissociated with Trypsin-EDTA and stained with Trypan Blue dye (Thermofisher, Australia) to determine cell viability and cell count. Approximately 100 cells were seeded in 6-well plates with DMEM medium. After 7 days, the colony-forming ability was assessed after staining with Crystal Violet (Sigma, Australia). Representative views were photographed under an inverted microscope equipped with a digital camera (Olympus DP21, Japan).
2.4. RNA Extract and cDNA Synthesis
RNA was isolated as previously described using an Isolate II Bioline RNA synthesis kit (Bioline, New South Wales, Australia) as per the manufacturer’s protocol [57]. Nanodrop 2000c (Thermofisher, Australia) was used to confirm the quantity and purity of RNA. cDNA was synthesised by reverse transcribing 1 µg RNA using a Bioline SensiFAST cDNA synthesis kit (Bioline, Australia).
2.5. Quantitative Reverse Transcription-PCR (qRT-PCR)
qRT-PCR was performed using Lo-ROX SYBR Green (Bioline, Australia) on a ViiA7 Applied Biosystems Real-Time PCR system as previously described [57]. Beta-Actin (ActB) was used as an internal control. The primer sequences were previously reported [60] and listed in Table 1. Expression levels are presented as copies of the target gene per 10,000 copies of ActB. The 2ΔΔCt method was used for data analysis, where ActB was assigned as the housekeeping gene. In this 2ΔΔCt method, target gene expression was normalised to ActB expression and data are presented as copies of the target gene per 10,000 copies of ActB.

Table 1.
List of primers for qRT-PCR.
2.6. Western Blot Analysis
This method was performed as previously described [60]. Briefly, cells cultured and treated in 6-well plates. Cells were lysed using RIPA buffer (Thermofisher, Victoria, Australia) with Complete (Roche, New South Wales, Australia) and phosSTOP (Roche, New South Wales, Australia) protease and phosphatase inhibitors at 4 °C to extract the total protein. The total protein was quantified with a Pierce BCA protein assay kit (Thermofisher, Victoria, Australia). A total of 10 µg of protein was used for separation by electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) in a polyacrylamide gel in the presence of sodium dodecyl sulphate (SDS) and transferred to a polyvinylidene difluoride film (PVDF) membrane. Following blocking with 5% skim milk in Tris-buffered saline containing 0.1% Tween 20 (TBS-T), the membranes were exposed to primary antibodies at 4 °C overnight. Next, the membranes were incubated with HRP-conjugated secondary antibodies and SuperSignal West Femto Maximum Sensitivity Substrate (Thermofisher, Victoria, Australia) was used to detect the protein adhered to the membrane. Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) and Beta-Actin were used as the housekeeping controls. Image Quant LAS 500 was used to capture images and Image Studio Lite Ver 5.2 software (VWR, International, Radnor, PA, USA) was used for quantification. The antibodies used were previously reported [60] and are listed in Table 2.

Table 2.
List of antibodies.
2.7. Transwell Migration Assay
Migration assay was performed with transwell chambers (8 µm pore size, Corning, Australia). Cells grown as spheres and monolayer were enzymatically dissociated to single cells with Trypsin-EDTA treatment. Trypan Blue dye (Thermofisher, Australia) staining was performed to determine cell viability and cell count. 1 × 105 of harvested cells from sphere or monolayer culture were plated into the upper chamber in a serum-free DMEM culture medium. A total of 500 µL of DMEM culture medium with 10% FBS was added into the lower chamber as the chemoattractant. Following 24 h of incubation at 37 °C, cells were treated with 4% paraformaldehyde (Fisher Scientific, Victoria, Australia) for 15 min for fixation. Next, cells were stained with 0.1% Crystal Violet (Sigma-Aldrich, New South Wales, Australia). The cells were removed from the upper chamber. Cells migrated onto the lower chamber were photographed under an inverted Olympus DP21 microscope equipped with a digital camera. For the quantification of cell migration, the Crystal Violet staining on the transwell membrane was extracted using 5% SDS and a 570 nm wavelength was used to measure absorbance [61].
2.8. Proliferation Assay
1 × 103 cells were seeded in 96-well plates and treated as indicated. Cell proliferation was quantified with the CellTitre 96 Aqueous one solution cell proliferation assay (MTS) from Promega, Australia according to the manufacturer’s protocol.
2.9. siRNA Transfection
Cells were transfected at 50% confluency for transient siRNA transfection with Lipofectamine RNAiMAX (Invitrogen, Victoria, Australia) and 10 nM final concentration of a control siRNA (4390843) (Thermofisher, Australia) and two distinct silencer select siRNAs targeting PD-L1 (s26547 and s26548) (Thermofisher, Victoria, Australia) and CD73 (s9735 and s9734) (Thermofisher, Victoria, Australia) according to manufacturer’s protocol. Cells were incubated with siRNA complex for 72 h and then collected for further experiments.
2.10. Flow Cytometry
Cells were plated and treated as indicated. Cells grown as spheres and monolayer were enzymatically dissociated to single cells with Trypsin-EDTA. Harvested cells were then washed in cold 1XPBS. The apoptosis induced by different treatment approaches was demonstrated using FITC Annexin V/Dead Cell Apoptosis Kit (Invitrogen, Victoria, Australia). The Annexin V is used for detecting cellular apoptosis, and propidium iodide (PI) is used for detecting necrotic or late apoptotic cells. For this assay, the 1× PBS washed cells were resuspended in 100 µL of 1× annexin-binding buffer per assay at density of approximately 1 × 106 followed by addition of 5 µL of FITC annexin V and 1 µL of 100 μg/mL PI. After the incubation period of 15 min at room temperature, 400 µL of 1× annexin-binding buffer was gently mixed and the samples were kept on ice. The cells were analysed using flow cytometry (Fortessa X-20, BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA, USA). BD FACSDiva software was used for data acquisition and FlowJo software was used for data analysis. The data obtained were plotted in two-dimensional dot plots where PI on the y-axis was plotted against Annexin V-FITC on the x-axis. These plots were divided in four quadrants. The quadrant Q1 represents apoptotic cells that were PI positive and Annexin V negative, the quadrant Q2 represents late apoptotic cells that were PI and Annexin V positive, the quadrant Q3 represents apoptotic cells that were PI negative and Annexin V positive and the quadrant Q4 represents viable cells that were negative for both Annexin V and PI.
2.11. Statistical Analysis
Prism software version 8.00 (GraphPad Software Inc., San Diego, CA, USA) was used for statistical analyses. Gene expression differences between control and Sorafenib-treated cells were analysed using Student’s t-test. For multiple comparisons, one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Sidak’s multiple comparisons test was used. Two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test was performed for statistical analysis for cell viability assay. All experiments were repeated at least three times and representative results are presented. The results are presented as mean ± standard error of mean. Statistical significance was set at p < 0.05. Error bars indicate standard error of the mean (SEM).
3. Results
3.1. Human HCC-Derived Spheres Exhibit Stem-Cell-Like Features
Human HCC cell lines, Hep3B, PLC/PRF/5 and HepG2 were used for the sphere-forming assay to enrich CSCs from adherent parental cells. All three cell lines formed anchorage-independent three-dimensional spheres free of any adherent cells when cultured in serum-free stem-cell-conditioned medium by Day 5 (Figure 1A). HCC parental cells termed adherent were cultured as conventional 2D monolayers without growth factor supplements. As previously reported, adherent cells were used for control and compared with spheres in the following experiments [57,62,63,64].
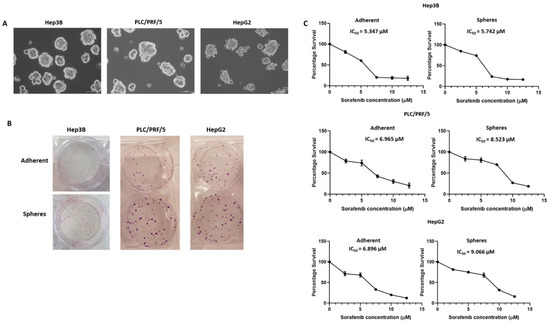
Figure 1.
Enrichment of human HCC-derived spheres. (A) Human HCC cell lines Hep3B, PLC/PRF/5 and HepG2-derived anchorage independent spheres in stem-cell-conditioned culture medium (scale bar = 100 µm). (B) Colony-forming assay revealed a higher number of colonies formed from HCC-derived spheres compared to parental cells. (C) Cell viability assay demonstrated the increased Sorafenib resistance of HCC-derived spheres with higher IC50 values compared to parental cells after 72 h of increasing doses of Sorafenib treatment.
To examine the self-renewal and proliferative abilities of human HCC-derived spheres, we utilised a colony-forming assay to compare the colony-forming ability between adherent cells and spheres. We demonstrated that spheres proliferated rapidly with a higher number of colonies in comparison to parental adherent cells for all three cell lines (Figure 1B), indicating that three-dimensional spheres are more proliferative and could be vital in the maintenance of tumour growth.
Furthermore, proliferation assay was used to determine the chemoresistant property of anchorage-independent spheres. The sensitivity of three-dimensional spheres versus parental adherent cells to Sorafenib were examined and IC50 values calculated. Notably, the spheres showed higher resistance to Sorafenib compared to adherent cells with higher IC50 values for all cell lines examined (Figure 1C). The IC50 values for Hep3B adherent cells and spheres were 5.347 and 5.742 µM, respectively, whereas IC50 values for PLC/PRF/5 adherent and spheres were 6.965 and 8.523 µM, respectively. Similarly, the IC50 values for HepG2 adherent cells and spheres were 6.896 and 9.066 µM, respectively. Based on these findings, we refer to HCC-derived CSCs as Sorafenib-resistant CSCs.
To further characterise the enriched spheres, we assessed the putative stem-cell-associated marker expression. An equal number of cells was plated for adherent and sphere cultures. The cells were collected at Day 5 for RNA and protein extraction. As demonstrated by qRT-PCR, stem-cell-associated genes CD133, KLF-4, SOX-2, OCT-4, NANOG and BMI were elevated in Hep3B-derived spheres compared to adherent cells (Figure 2A). Similarly, we observed higher expression of CD44, KLF-4 and BMI in PLC/PRF/5-derived spheres compared to adherent cells (Figure 2B) and increased expression of CD133, KLF-4, OCT-4 and NANOG in HepG2-derived spheres compared to adherent cells (Figure 2C). The upregulation of putative CSC marker CD133 in spheres compared to adherent cells was further confirmed by Western blot analysis in Hep3B and HepG2 cells. Similarly, upregulation of CD44 was observed in spheres derived from PLC/PRF/5 compared to parental adherent cells (Figure 2D). These results support the enrichment of the CSC population with sphere-forming assay.
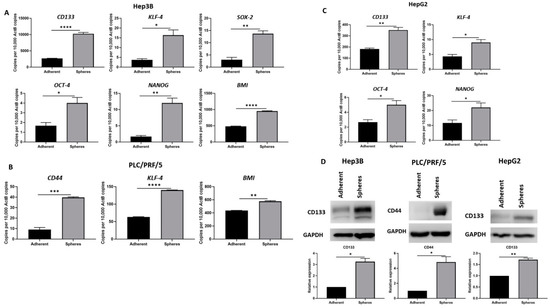
Figure 2.
Human HCC-derived spheres exhibit stem-cell-like features. (A) qRT-PCR demonstrated upregulation of stem cell markers CD133, KLF-4, SOX-2, OCT-4, NANOG, and BMI in Hep3B-derived spheres compared to adherent Hep3B cells. (B) PLC/PRF/5-derived spheres exhibited increased expression of CD44, KLF-4 and BMI compared to adherent cells as shown by qRT-PCR. (C) qRT-PCR revealed higher expression of CD133, KLF-4, OCT-4 and NANOG in HepG2-derived spheres compared to parental cells. (D) Increased CD133 expression in Hep3B and HepG2-derived spheres and upregulation of CD44 in PLC/PRF/5-derived spheres compared to adherent cells. GAPDH was the loading control. Detailed information about Western Blot can be found at Supplementary Materials. (n = 3, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.005, **** p < 0.001).
3.2. Anchorage-Independent Spheres Exhibit Mesenchymal Phenotype
To explore the relationship between EMT and CSCs, we examined the EMT features related to HCC-derived CSCs. The epithelial markers E-cadherin and Occludin showed decreased expression, whereas the mesenchymal markers N-cadherin, Vimentin, Snai1 and Snai2 showed increased expression in Hep3B-derived CSCs compared to adherent cells (Figure 3A), as demonstrated by qRT-PCR. Similarly, we observed a decrease in E-cadherin and Occludin expression along with an increase in N-cadherin, Vimentin and Snai1 expression in PLC/PRF/5-derived CSCs compared to adherent cells (Figure 3B). In addition, HepG2-derived CSCs also demonstrated reduced expression of epithelial markers E-cadherin and Occludin with an elevated expression of mesenchymal markers N-cadherin, Snai1 and Snai2 (Figure 3C).

Figure 3.
Human HCC-derived spheres exhibit mesenchymal phenotype. qRT-PCR demonstrated (A) a decrease in epithelial markers E-cadherin and Occludin and an increase in mesenchymal markers N-cadherin, Vimentin, Snai1 and Snai2 expression in Hep3B-derived spheres compared to adherent cells, (B) a reduction in E-cadherin and Occludin expression and an elevation in N-cadherin, Vimentin and Snai1 expression in PLC/PRF/5-derived spheres compared to adherent cells, and (C) downregulation of E-cadherin and Occludin and upregulation of N-cadherin, Snai1 and Snai2 in HepG2-derived spheres compared to adherent cells. (n = 3, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.005, **** p < 0.001, ns: not significant).
This association of stem cell phenotype with EMT phenotype was further confirmed by Western blot analysis wherein epithelial markers were downregulated and mesenchymal markers were upregulated in CSCs compared to adherent cells in Hep3B (Figure 4A), PLC/PRF/5 (Figure 4B) and HepG2 (Figure 4C).
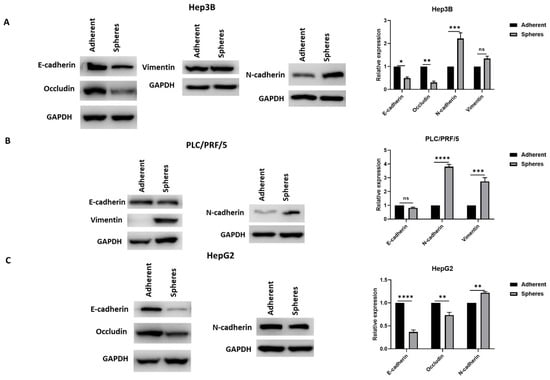
Figure 4.
Human HCC-derived spheres exhibit mesenchymal phenotype. Western blot analysis revealed (A) a decrease in E-cadherin and Occludin expression and an increase in N-cadherin and Vimentin expression in Hep3B-derived spheres compared to adherent cells, (B) reduced expression of E-cadherin and elevated expression of N-cadherin and Vimentin in PLC/PRF/5-derived spheres compared to adherent cells, and (C) reduced expression of E-cadherin and Occludin and elevated expression of N-cadherin in HepG2-derived spheres compared to adherent cells. Detailed information about Western Blot can be found at Supplementary Materials. (n = 3, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.005, **** p < 0.001, ns: not significant).
To further confirm EMT activation in CSCs, we assessed the activation of transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1, a potent inducer of EMT. We observed elevated expression of TGF-β1 in Hep3B and PLC/PRF/5-derived CSCs compared to adherent cells, as demonstrated by qRT-PCR. However, no upregulation of TGF-β1 was observed in HepG2 spheres (Figure 5A). The activation of TGF-β1 signalling in CSCs was further confirmed by the phosphorylation of Smad2/3 using Western blot analysis (Figure 5B). These findings suggest the activation of Smad-dependent TGF-β1 signalling in HCC-derived CSCs.
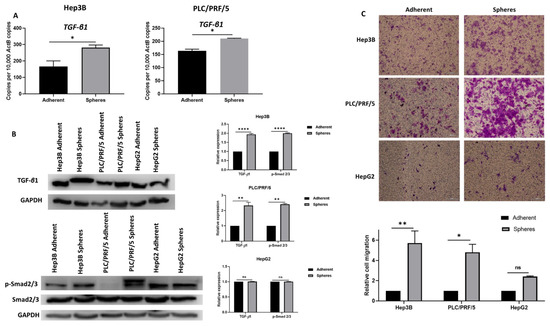
Figure 5.
Human HCC-derived spheres exhibit mesenchymal phenotype. (A) qRT-PCR demonstrated an upregulation of TGF-β1 in Hep3B and PLC/PRF/5-derived spheres compared to adherent cells. (B) Western blot analysis revealed an upregulation of TGF-β1 and p-Smad2/3 in Hep3B and PLC/PRF/5-derived spheres compared to adherent cells and no upregulation of TGF-β1 and p-Smad2/3 in HepG2-derived spheres compared to adherent cells. GAPDH was the loading control. Detailed information about Western Blot can be found at Supplementary Materials. (C) Transwell migration assay demonstrated higher motility of human HCC-derived spheres compared to adherent cells (scale bar = 500 µm). The number of motile cells on the transwell membrane was quantified by measuring the absorbance of Crystal Violet staining. (n = 3, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, **** p < 0.001, ns: not significant).
We utilised transwell migration assay to examine the migratory ability of HCC-derived CSCs compared to adherent cells. We observed that HCC-derived CSCs exhibited higher migratory ability (Figure 5C). Together, these findings suggest that anchorage-independent spheres exhibit the mesenchymal phenotype and may be modulated by EMT, particularly by the activation of Smad-dependent TGF-β1 signalling.
3.3. Inhibition of EMT with SB431542 Can Enhance Cytotoxicity of SORAFENIB
Given our observation that HCC-derived CSCs exhibit a mesenchymal phenotype and have a close association with EMT during the activation of TGF-β1 signalling in Hep3B and PLC/PRF/5-derived spheres, we hypothesise that EMT may be responsible for maintaining tumour growth and therapy resistance in Hep3B and PLC/PRF/5-derived CSCs. Thus, we utilised SB431542, a specific inhibitor of TGF-β receptor kinase, to treat Hep3B and PLC/PRF/5-derived CSCs with a concentration of 2 µM for a period of 72 h to assess the variation in cytotoxic effects of Sorafenib alone versus in combination with SB431542 (inhibition of TGF-β1-induced EMT). The proliferation assay demonstrated that the cytotoxic effects of Sorafenib in HCC-derived CSCs was enhanced when combined with SB431542 in comparison to Sorafenib alone (Figure 6A,B), suggesting better therapeutic efficacy of Sorafenib when combined with an EMT inhibitor.
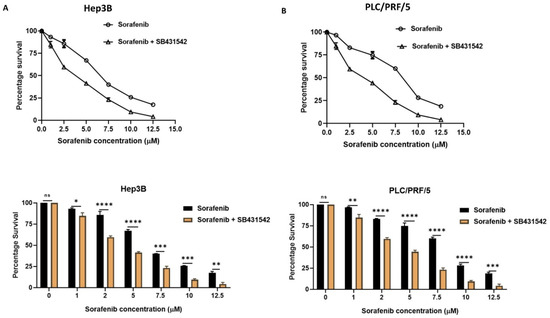
Figure 6.
EMT inhibition with SB431542 enhanced the cytotoxic effects of Sorafenib. Cell viability assay revealed increased cytotoxicity of Sorafenib when combined with SB431542 in comparison to Sorafenib alone in (A) Hep3B-derived spheres and (B) PLC/PRF/5-derived spheres. (n = 3, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.005, **** p < 0.001, ns: not significant).
3.4. CSCs Overexpress Immune Checkpoint Molecules
To gain a better understanding of the role of the immune checkpoint in the Sorafenib resistance mechanism in HCC, we evaluated the expression of immune checkpoint molecules in HCC-derived CSCs by qRT-PCR and Western blot analysis. In particular, we sought to analyse the expression of ICIs in CSCs that were associated with poor HCC patient prognosis, as reported in our previous studies [60,65]. Higher expression of PD-L1, PD-L2, CD73 and B7-H3 was observed in Hep3B-derived CSCs compared to adherent cells (Figure 7A). Similarly, PLC/PRF/5-derived CSCs exhibited an increase in PD-L1, CD73 and B7-H3 expression compared to adherent cells (Figure 7B), whereas HepG2-derived CSCs exhibited increased expression of PD-L1, PD-L2 and CD73 compared to adherent cells (Figure 7C). The increase in the expression of immune checkpoint molecules, PD-L1 and CD73 in CSCs was further confirmed by Western blot analysis in all cell lines examined (Figure 7D).
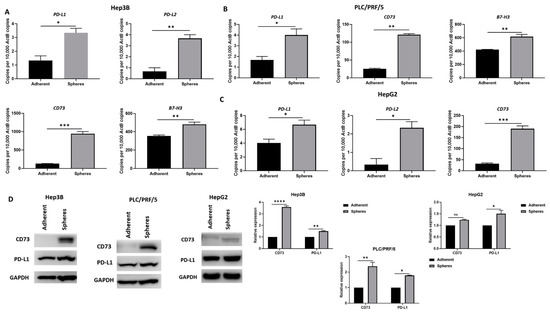
Figure 7.
Human HCC-derived spheres overexpress immune checkpoint molecules. (A) qRT-PCR demonstrated upregulation of PD-L1, PD-L2, CD73 and B7-H3 in Hep3B-derived spheres compared to adherent cells. (B) PLC/PRF/5-derived spheres overexpress PD-L1, CD73 and B7-H3 compared to adherent cells, and (C) HepG2-derived spheres exhibited increased expression of PD-L1, PD-L2 and CD73 compared to adherent cells, as revealed by qRT-PCR. (D) Western blot analysis demonstrated an increase in CD73 and PD-L1 expression in Hep3B, PLC/PRF/5 and HepG2-derived spheres compared to adherent cells. GAPDH was the loading control. Detailed information about Western Blot can be found at Supplementary Materials. (n = 3, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.005, **** p < 0.001, ns: not significant).
3.5. Combination of Immune Checkpoint and EMT Inhibition Can Sensitise Human HCC-Derived CSCs to Sorafenib Treatment
As the inhibition of EMT enhances the cytotoxic effects of Sorafenib, resulting in the re-sensitising of CSCs to Sorafenib, we further evaluated the combined effects of EMT inhibition along with immune checkpoint inhibition on the therapy resistance of CSCs to Sorafenib. The expression of immune checkpoint molecules PD-L1 and CD73 were depleted with RNA interference. We demonstrated knockdown of PD-L1 using two different siRNAs in our previous study [61]. In this study, we also observed the effective knockdown of CD73 with two siRNA targeting CD73 in both Hep3B and PLC/PRF/5 cells as confirmed by qRT-PCR and Western blot analysis (Figure S1A,B).
Further, we assessed the effects of EMT inhibitor, SB431542, alone and in combination with either PD-L1 or CD73 knockdown on the cytotoxicity of Sorafenib. The proliferation assay demonstrated that the number and size of spheres formed at Day 5 were significantly reduced when Sorafenib was combined with SB431542 and/or PD-L1 or CD73 siRNA in Hep3B (Figure 8A,B). Similarly, we noted that the reduction in the number and size of spheres when combined with Sorafenib was combined with SB431542 and/or PD-L1 siRNA or CD73 siRNA in PLC/PRF/5 (Figure 8C,D). We also observed better therapeutic effects of CD73 knockdown on Sorafenib and SB431542 in comparison to PD-L1 knockdown.
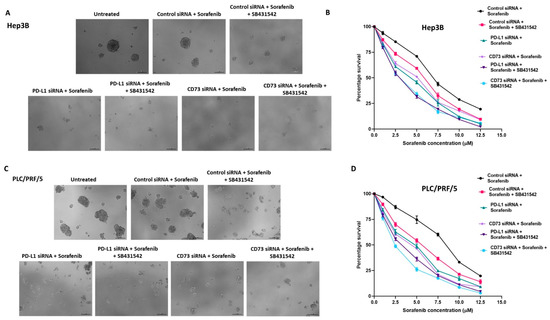
Figure 8.
Combined targeting of EMT and immune checkpoint molecules enhanced the cytotoxicity of Sorafenib against human HCC-derived spheres. (A) Day 5 images of Hep3B-derived spheres revealed a decreased sphere size as a result of increased cytotoxicity of Sorafenib when combined with SB431542 and PD-L1 or CD73 siRNA compared to Sorafenib alone (scale bar = 200 µm). (B) Cell viability assay revealed reduced viability of Hep3B-derived spheres following combination treatment of Sorafenib with SB431542 and PD-L1 siRNA or CD73 siRNA compared to Sorafenib alone. (C) Day 5 images of PLC/PRF/5-derived spheres demonstrated increased cytotoxicity of Sorafenib when combined with SB431542 and PD-L1 siRNA or CD73 siRNA compared to Sorafenib alone with decreased sphere size (scale bar = 200 µm). (D) Cell viability assay revealed reduced viability of PLC/PRF/5-derived spheres following combination treatment of Sorafenib with SB431542 and PD-L1 siRNA or CD73 siRNA compared to Sorafenib alone.
Next, we examined whether the treatment of HCC spheres with Sorafenib or SB431542 affected the expression of stemness markers and immune checkpoint molecules. We observed downregulation of stemness markers CD133, KLF-4, SOX2, OCT-4, NANOG and BMI and immune checkpoint molecules CD73 and PD-L1 in Hep3B-derived spheres treated with Sorafenib compared with untreated Hep3B-derived spheres (Figure S2A,B). PLC/PRF/5-derived spheres showed downregulation of CD44 and BMI along with upregulation of CD73 and PD-L1 upon Sorafenib treatment (Figure S3A,B). SB431542-treated Hep3B spheres showed downregulation of stemness markers CD133, KLF-4, SOX2, OCT-4, NANOG and BMI and immune checkpoint molecules CD73 and PD-L1 (Figure S4A,B). SB431542-treated PLC/PRF/5-derived spheres downregulated the expression of stemness markers CD44 and BMI with upregulated expression of KLF-4 along with upregulation of CD73 and PD-L1 compared with untreated spheres (Figure S5A,B). Knockdown of either CD73 or PD-L1 in Hep3B spheres decreased the expression of stemness markers CD133, KLF4, SOX2, OCT-4, NANOG and BMI compared with control siRNA-treated spheres (Figure S6). Similarly, treatment of PLCPRF5-derived spheres with either CD73 or PD-L1 siRNA resulted in the downregulation of stemness markers CD44 and BMI (Figure S7).
To further validate the increased cytotoxic effects of Sorafenib on HCC-derived CSCs with combined targeting of EMT and immune checkpoint molecules, we used flow cytometry analysis to examine apoptosis induced by Sorafenib alone versus combination with EMT inhibitor and/or immune checkpoint inhibitors. We observed that the percentage of apoptotic spheres increased with a combination therapy of SB431542 and immune checkpoint inhibitors (PD-L1 siRNA or CD73 siRNA) with Sorafenib compared to Sorafenib alone in both Hep3B (Figure 9A) and PLC/PRF/5-derived (Figure 9B) CSCs. These findings suggest that the combined targeting of EMT and immune checkpoint molecules can enhance the cytotoxic effects of Sorafenib or overcome the resistance of HCC-derived CSCs to Sorafenib, resulting in effective chemotherapeutic outcome in HCC.
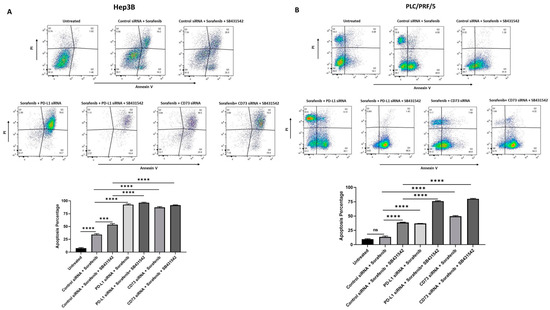
Figure 9.
Combined targeting of EMT and immune checkpoint molecules enhanced Sorafenib-induced apoptosis in human HCC-derived spheres. Flow cytometric analysis of Annexin V/Propidium Iodide staining revealed increased percentage of apoptotic cells following combination treatment of Sorafenib with SB431542 and PD-L1 or CD73 siRNA compared to Sorafenib alone in (A) Hep3B-derived spheres and (B) PLC/PRF/5-derived spheres. (n = 3, *** p < 0.005, **** p < 0.001, ns: not significant).
4. Discussion
The therapeutic benefit of Sorafenib, the standard clinical treatment for patients with unresectable advanced HCC, is limited primarily due to the acquisition of resistance to Sorafenib [6,7,8]. Thus, there is a pressing need to identify important mechanisms responsible for Sorafenib resistance in HCC and to develop better treatment alternatives to improve the efficacy of Sorafenib and overcome Sorafenib resistance. Herein, we report that CSCs, the chemoresistant subpopulation of HCC tumour are closely associated with EMT and overexpress immune checkpoint molecules. This study suggests a critical role of EMT, immune checkpoint molecules and CSCs together in orchestrating Sorafenib resistance. We thus utilised combined therapeutic approach to inhibit TGF-β1-induced EMT with SB431542 and immune checkpoint inhibition with PD-L1 and CD73 knockdown to improve the therapeutic effectiveness of Sorafenib and to overcome Sorafenib resistance in HCC-derived CSC subpopulation.
CSCs contribute to the development, recurrence, metastasis and maintenance of HCC [38,41,66]. Studies have identified several factors that contribute to Sorafenib resistance in HCC, and CSCs are one of the clinical factors closely associated with drug resistance [11,15,16]. Studies have revealed that the HCC tumour sub-populations that are highly resistant to cancer therapies possess more CSCs [66,67]. Thus, targeting CSCs is key to improving therapeutic outcome in cancer treatment. Initially, CSCs were isolated and identified based on the side population method by flow cytometry using DNA-intercalating dye Hoechst 33342 or the magnetic activated cell sorting (MACS) and fluorescence activated cell sorting (FACS) based on cell surface markers [68,69,70]. In the present study, we have utilised a sphere-forming assay for enriching the cancer stem cell population in serum-free culture medium that provides the appropriate niche environment required for the maintenance of the stemness of CSCs without the pre-selection of specific cell surface markers [53]. Previous studies have demonstrated that the sphere-forming assay can enrich CSCs by evaluating a combination of CSC marker expression and assessing the self-renewing and proliferative abilities of CSCs using limited dilution and expansion assays [53]. The present study revealed that spheres enriched for CSCs possess stem-cell-like features with higher proliferation and chemoresistant abilities consistent with findings from other studies [53,55,58].
EMT is another factor contributing to therapy resistance in several cancers, including HCC [28,32,34,71]. Studies have also revealed that EMT plays an important role in the generation and maintenance of CSC population in cancers, including HCC [32,35,36,37]. Moreover, EMT and CSCs are reported to be mechanistically linked and contribute to the development of Sorafenib resistance [12,32]. Our study demonstrated that human HCC-derived CSCs exhibit a mesenchymal phenotype. Similarly, many studies have reported that EMT activation is closely associated with the gain of stem-cell-like features [35,72,73,74]. A study by Jing et al. utilised the Oncomine database to demonstrate the correlation between EMT and CSC markers in HCC [72]. The study also revealed that HIF-1α-driven EMT mediated the acquisition of stem-cell-like features such as expression of CSC markers, stronger colony-forming ability and sphere formation ability in human HCC cells [72]. We have previously shown a similar association between the expression of EMT markers and CSCs in murine HCC and normal hepatocyte cell lines [57].
CSCs are known to possess immune-evasive properties through a reduction in major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC I) and molecules for antigen presentation in cancers such as colon cancer [75], melanoma [76] and breast cancer [77]. The association between immune suppression and CSC is well studied in glioblastoma, where studies have demonstrated an important role of CSCs in the initiation of immune suppression with interplay between CSCs and immune cells changing from stimulatory to inhibitory status throughout tumourigenesis [78,79,80]. Another study by Ozawa et al. revealed that glioma stem cells exhibit higher indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO-1) expression, resulting in immunosuppression and therapy resistance [81]. Furthermore, studies have demonstrated that enrichment of PD-L1 expression in CSCs facilitates immune evasion in lung [82,83] and head and neck cancer [83]. This association between CSCs and immune evasion is not extensively studied in HCC. Nishida et al. revealed that the expression of stem cell markers CK19 and SALL4 was positively correlated with the expression of PD-L1 in HCC patients [84]. In addition to the well-documented role of PD-L1 in suppressing the anti-tumour immune response by interacting with PD1 receptor on T-cells and subsequently inactivating T-cells, recent studies have reported a distinct tumour-intrinsic role for PD-L1 in regulating CSCs, EMT, motility, metastasis and drug resistance, including resistance to Sorafenib [61,85]. Studies have been conducted on tumour cells in the absence of T-cells to evaluate the intrinsic functions of immune checkpoints. Immune-independent studies of PD-L1 in breast cancer, melanoma and ovarian cancer facilitate the generation of CSCs [86,87]. Similarly, immune-independent studies of CD73 have reported that it promoted HCC progression and metastasis by activating the transcription of SOX9 and also increases its protein stability in an AKT/glycogen synthase kinase (GSK)3β-dependent manner, which sustained the stemness of HCC cells [88,89].
Our study is the first to report a higher expression of immune checkpoints in enriched HCC-derived CSCs compared to adherent cells. Given the increased expression of several immune checkpoint molecules such as PD-L1, CD73, B7-H3 and others in HCC-derived CSCs, it is conceivable that CSCs exhibit immune-evasive features that may contribute to Sorafenib resistance. Further studies using RNA sequencing technology to profile HCC-derived CSCs and to identify novel immune regulatory molecules expressed on these CSCs will be more informative.
Our study demonstrated a significant association between CSCs and EMT along with immune checkpoint molecules. These findings suggest that HCC-derived CSCs exhibit Sorafenib resistance by immune evasion through enhanced expression of immune checkpoints such as PD-L1 and CD73 following the induction of EMT. Whilst we observed elevated expression and activation of TGF-β1 in Hep3B and PLC/PRF/5-derived CSCs, no upregulation of TGF-β1 was observed in HepG2 spheres. Although all three cell lines had similar E-cad levels and expression of stemness markers, the differences in TGF-β expression among Hep3b, PLC/PRF/5 and HepG2 spheres may be due to the intrinsic property of the cell lines. Frequent aberrations in TGF-β superfamily at both the transcriptomic level and the genomic level have been reported to occur in HCC leading to either activation or inactivation of TGF-β signalling [90]. This study implicates several genetic mutations or expression levels of different genes, such as SIRT1-6 and SPTBN1, that may contribute to alterations in TGF-β signalling [90]. Further studies are needed to examine the specific reason for differences in TGF-β signalling across the three HCC-derived spheres in this study.
We have previously reported that cytokine-driven EMT in HCC cells can regulate the expression of immune checkpoints, including PD-L1 and CD73 [60]. The present study further demonstrates acquisition of Sorafenib resistance following activation of EMT which results in the regulation of immune checkpoint molecules and the maintenance of the CSC population. Thus, we hypothesised that targeting EMT and immune checkpoint molecules can be a better therapeutic alternative to effectively target the therapy-resistant CSC population, resulting in the effective elimination of HCC tumour bulk. Consequently, we utilised SB431542 to inhibit TGF-β1-induced EMT and siRNA against PD-L1 and CD73 for immune checkpoint inhibition as combination therapy to overcome resistance to Sorafenib in the CSC population. The present study reported the effective targeting of CSCs with reduced proliferation and increased apoptosis following combination treatment via the enhanced cytotoxicity of Sorafenib. We noted that SB431542 treatment induced a pronounced early-stage apoptosis in PLC/PRF/5 cells when compared with Hep3B cells. We speculate that these differences may be attributed to the intrinsic difference of the cell line itself. This heterogeneity noted in cell lines often mirrors heterogeneity observed across HCC patients. Further investigation into whether the EMT inhibitor-, ICIs- and Sorafenib-induced apoptosis is mediated via either the intrinsic pathway by the mitochondrial cascade involving Bcl-2/Bax family proteins, active caspases, and Akt signalling or the extrinsic pathway by the expression of surface death receptors will be pivotal to understand the mechanisms of actions employed by these agents [91].
Our study is the first to demonstrate the combined targeting of EMT and immune checkpoint molecules as an effective therapeutic treatment to overcome Sorafenib resistance. Furthermore, either monoclonal antibodies or siRNAs directed against immune checkpoints can be used for targeting CSCs. Whilst monoclonal antibodies can block immune checkpoint interaction, we sought to examine if the loss of expression of immune checkpoints with siRNA can reveal insights into molecular mechanisms such as EMT and TGF-β signal transduction. Further studies with monoclonal antibodies targeting CD73 and PD-L1 can be tested to corroborate the findings from this study with siRNAs.
Monotherapy treatment of Hep3B-derived spheres with Sorafenib or SB431542 decreased the expression of stemness markers and CD73 and PD-L1, while the same treatment of PLC/PRF/5-derived spheres showed downregulation of stemness markers CD44 and BMI with elevated expression of KLF-4, CD73 and PD-L1. These differences observed may be attributed to cell-line-specific effects, and heterogeneity noticed among cell lines is a feature commonly recapitulated in HCC patients. Importantly, treatment with Sorafenib causes cell death and the residual CSCs can be targeted with immune checkpoint inhibitors as CSCs still have expression of PD-L1, CD73 and CSC markers, regardless of overexpression or downregulation. Furthermore, it is plausible that these treatments as monotherapies may not be effective in eliminating CSCs, and the application of combination therapies, including the immune checkpoint inhibitors, is essential for targeting these CSCs.
In HCC, a study demonstrated that targeting tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) can overcome Sorafenib resistance [92]. Another study reported the enrichment of PD-L1 in breast cancer CSCs through TGF-β-driven EMT [93]. In addition, the study also suggested that more PD-L1 expression is enriched by EMT in CSCs compared to non-CSCs [93]. However, there are very limited studies investigating the role of EMT, immune checkpoint molecules and therapy resistance in HCC. The limitation of this study is the application of established human HCC cell lines for the enrichment of CSCs that may not be conducive for long-term expansion in culture. Using HCC patient tumour-derived primary cells for spheroid culture may closely recapitulate the status of the primary tumour. Furthermore, organoid cultures from fresh HCC patient tissue samples have been demonstrated to be better preclinical models for propagating 3D spheres with CSC traits, especially in long-term cultures for up to 5 months [94]. As organoid cultures are promising disease models for testing drug efficacy in vitro, the effectiveness of combination therapy for targeting CSC can be tested in this system before moving to animal models. Further studies in animal models to validate the findings from this study are warranted.
5. Conclusions
The combination treatment approach with the blockade of EMT and immune checkpoint molecules along with Sorafenib can be an effective treatment modality to target an aggressive and chemoresistant HCC-derived CSC subpopulation. However, further validation of this novel combination approach in in vivo animal model is warranted.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/curroncol28030200/s1, Figure S1: Silencing of CD73 in human HCC-derived spheres, Figure S2: Hep3B derived spheres treatment with Sorafenib, Figure S3: PLC/PRF/5 derived spheres treatment with Sorafenib, Figure S4: Hep3B derived spheres treatment with SB431542, Figure S5: PLC/PRF/5 derived spheres treatment with SB431542, Figure S6: Silencing of PD-L1 and CD73 in Hep3B derived spheres, Figure S7: Silencing of PD-L1 and CD73 in PLC/PRF/5 derived spheres, Figure S8–S12: Uncropped Western Blot figures.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.S. and A.J.; Data curation, R.S.; Formal analysis, R.S. and A.J.; Investigation, R.S.; Methodology, R.S. and A.J.; Resources, K.R.B. and D.H.G.C.; Supervision, D.H.G.C. and A.J.; Validation, A.J.; Writing—original draft, R.S.; Writing—review and editing, K.R.B., L.C., D.H.G.C. and A.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The study was funded by Gallipoli Medical Research Institute and the University of Queensland.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chacko, S.; Samanta, S. Hepatocellular carcinoma: A life-threatening disease. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 84, 1679–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 7–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruix, J.; da Fonseca, L.G.; Reig, M. Insights into the success and failure of systemic therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 617–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daher, S.; Massarwa, M.; Benson, A.A.; Khoury, T. Current and Future Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: An Updated Comprehensive Review. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2018, 6, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.D.; Hainaut, P.; Gores, G.J.; Amadou, A.; Plymoth, A.; Roberts, L.R. A global view of hepatocellular carcinoma: Trends, risk, prevention and management. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 589–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Tan, X.; Luo, J.; Yao, H.; Si, Z.; Tong, J.S. The miR-30a-5p/CLCF1 axis regulates sorafenib resistance and aerobic glycolysis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, A.L.; Kang, Y.K.; Chen, Z.; Tsao, C.J.; Qin, S.; Kim, J.S.; Luo, R.; Feng, J.; Ye, S.; Yang, T.S.; et al. Efficacy and safety of sorafenib in patients in the Asia-Pacific region with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: A phase III randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J.M.; Ricci, S.; Mazzaferro, V.; Hilgard, P.; Gane, E.; Blanc, J.F.; de Oliveira, A.C.; Santoro, A.; Raoul, J.L.; Forner, A.; et al. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 378–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Méndez-Blanco, C.; Fondevila, F.; García-Palomo, A.; González-Gallego, J.; Mauriz, J.L. Sorafenib resistance in hepatocarcinoma: Role of hypoxia-inducible factors. Exp. Mol. Med. 2018, 50, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.J.; Zheng, B.; Wang, H.Y.; Chen, L. New knowledge of the mechanisms of sorafenib resistance in liver cancer. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2017, 38, 614–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, L.; Liu, L.; Yang, S.; Ren, J.; Lai, P.B.S.; Chen, G.G. New insights into sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma: Responsible mechanisms and promising strategies. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2017, 1868, 564–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, A.K.; Ng, L.; Lam, C.S.; Wong, S.K.; Wan, T.M.; Cheng, N.S.; Yau, T.C.; Poon, R.T.; Pang, R.W. The Enhanced metastatic potential of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells with sorafenib resistance. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Malenstein, H.; Dekervel, J.; Verslype, C.; Van Cutsem, E.; Windmolders, P.; Nevens, F.; van Pelt, J. Long-term exposure to sorafenib of liver cancer cells induces resistance with epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, increased invasion and risk of rebound growth. Cancer Lett. 2013, 329, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Zijl, F.; Mall, S.; Machat, G.; Pirker, C.; Zeillinger, R.; Weinhaeusel, A.; Bilban, M.; Berger, W.; Mikulits, W. A human model of epithelial to mesenchymal transition to monitor drug efficacy in hepatocellular carcinoma progression. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2011, 10, 850–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernando, J.; Malfettone, A.; Cepeda, E.B.; Vilarrasa-Blasi, R.; Bertran, E.; Raimondi, G.; Fabra, À.; Alvarez-Barrientos, A.; Fernández-Salguero, P.; Fernández-Rodríguez, C.M.; et al. A mesenchymal-like phenotype and expression of CD44 predict lack of apoptotic response to sorafenib in liver tumor cells. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, E161–E172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.L.; Fu, D.; Ma, Y.; Shen, X.Z. The power and the promise of liver cancer stem cell markers. Stem. Cells Dev. 2011, 20, 2023–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guidetti, A.; Carlo-Stella, C.; Locatelli, S.L.; Malorni, W.; Pierdominici, M.; Barbati, C.; Mortarini, R.; Devizzi, L.; Matteucci, P.; Marchianò, A.; et al. Phase II study of sorafenib in patients with relapsed or refractory lymphoma. Br. J. Haematol. 2012, 158, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, W.T.; Shiau, C.W.; Chen, H.L.; Liu, C.Y.; Lin, C.S.; Cheng, A.L.; Chen, P.J.; Chen, K.F. Mcl-1-dependent activation of Beclin 1 mediates autophagic cell death induced by sorafenib and SC-59 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cell Death. Dis. 2013, 4, e485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Zheng, T.; Song, R.; Wang, J.; Yin, D.; Wang, L.; Liu, H.; Tian, L.; Fang, X.; Meng, X.; et al. Hypoxia-mediated sorafenib resistance can be overcome by EF24 through Von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor-dependent HIF-1α inhibition in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2013, 57, 1847–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Zhai, B.; He, C.; Tan, G.; Jiang, X.; Pan, S.; Dong, X.; Wei, Z.; Ma, L.; Qiao, H.; et al. Upregulation of HIF-2α induced by sorafenib contributes to the resistance by activating the TGF-α/EGFR pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cell. Signal 2014, 26, 1030–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blivet-Van Eggelpoël, M.J.; Chettouh, H.; Fartoux, L.; Aoudjehane, L.; Barbu, V.; Rey, C.; Priam, S.; Housset, C.; Rosmorduc, O.; Desbois-Mouthon, C. Epidermal growth factor receptor and HER-3 restrict cell response to sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J. Hepatol. 2012, 57, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezzoukhry, Z.; Louandre, C.; Trécherel, E.; Godin, C.; Chauffert, B.; Dupont, S.; Diouf, M.; Barbare, J.C.; Mazière, J.C.; Galmiche, A. EGFR activation is a potential determinant of primary resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma cells to sorafenib. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 131, 2961–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Xiao, W.; Zhang, K.; Yin, X.; Lai, J.; Liang, L.; Chen, D. Activation of c-Jun predicts a poor response to sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma: Preliminary Clinical Evidence. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haga, Y.; Kanda, T.; Nakamura, M.; Nakamoto, S.; Sasaki, R.; Takahashi, K.; Wu, S.; Yokosuka, O. Overexpression of c-Jun contributes to sorafenib resistance in human hepatoma cell lines. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagiwara, S.; Kudo, M.; Nagai, T.; Inoue, T.; Ueshima, K.; Nishida, N.; Watanabe, T.; Sakurai, T. Activation of JNK and high expression level of CD133 predict a poor response to sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 106, 1997–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gedaly, R.; Angulo, P.; Hundley, J.; Daily, M.F.; Chen, C.; Koch, A.; Evers, B.M. PI-103 and sorafenib inhibit hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation by blocking Ras/Raf/MAPK and PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathways. Anticancer Res. 2010, 30, 4951–4958. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Ge, C.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Yao, M.; Li, J. NRBP2 Overexpression Increases the Chemosensitivity of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells via Akt Signaling. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 7059–7071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Jin, R.; Zhao, J.; Liu, J.; Ying, H.; Yan, H.; Zhou, S.; Liang, Y.; Huang, D.; Liang, X.; et al. Potential molecular, cellular and microenvironmental mechanism of sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2015, 367, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R.; Weinberg, R.A. The basics of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 1420–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiery, J.P.; Acloque, H.; Huang, R.Y.; Nieto, M.A. Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease. Cell 2009, 139, 871–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.Y.; Ke, A.W.; Shi, G.M.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, C.; Shi, Y.H.; Wang, X.Y.; Ding, Z.B.; Xiao, Y.S.; Yan, J.; et al. αB-crystallin complexes with 14-3-3ζ to induce epithelial-mesenchymal transition and resistance to sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2013, 57, 2235–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mir, N.; Jayachandran, A.; Dhungel, B.; Shrestha, R.; Steel, J.C. Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition: A Mediator of Sorafenib Resistance in Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2017, 17, 698–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.X.; Wang, X.Q.; Chok, S.H.; Man, K.; Tsang, S.H.Y.; Chan, A.C.Y.; Ma, K.W.; Xia, W.; Cheung, T.T. Blocking CDK1/PDK1/β-Catenin signaling by CDK1 inhibitor RO3306 increased the efficacy of sorafenib treatment by targeting cancer stem cells in a preclinical model of hepatocellular carcinoma. Theranostics 2018, 8, 3737–3750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.F.; Li, K.S.; Shen, Y.H.; Gao, P.T.; Dong, Z.R.; Cai, J.B.; Zhang, C.; Huang, X.Y.; Tian, M.X.; Hu, Z.Q.; et al. Galectin-1 induces hepatocellular carcinoma EMT and sorafenib resistance by activating FAK/PI3K/AKT signaling. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, S.A.; Guo, W.; Liao, M.J.; Eaton, E.N.; Ayyanan, A.; Zhou, A.Y.; Brooks, M.; Reinhard, F.; Zhang, C.C.; Shipitsin, M.; et al. The epithelial-mesenchymal transition generates cells with properties of stem cells. Cell 2008, 133, 704–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, A.; Satelli, A.; Xia, X.; Cutrera, J.; Mishra, L.; Li, S. Cell-surface Vimentin: A mislocalized protein for isolating csVimentin(+) CD133(-) novel stem-like hepatocellular carcinoma cells expressing EMT markers. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 137, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheel, C.; Weinberg, R.A. Phenotypic plasticity and epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in cancer and normal stem cells? Int. J. Cancer 2011, 129, 2310–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oishi, N.; Wang, X.W. Novel therapeutic strategies for targeting liver cancer stem cells. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2011, 7, 517–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Settleman, J. EMT, cancer stem cells and drug resistance: An emerging axis of evil in the war on cancer. Oncogene 2010, 29, 4741–4751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Mu, D.; Feng, K. Hierarchical potential differentiation of liver cancer stem cells. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2017, 26, 1137–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayachandran, A.; Dhungel, B.; Steel, J.C. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal plasticity of cancer stem cells: Therapeutic targets in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2016, 9, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capper, D.; Gaiser, T.; Hartmann, C.; Habel, A.; Mueller, W.; Herold-Mende, C.; von Deimling, A.; Siegelin, M.D. Stem-cell-like glioma cells are resistant to TRAIL/Apo2L and exhibit down-regulation of caspase-8 by promoter methylation. Acta Neuropathol. 2009, 117, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, H.W.; Ambe, C.M.; Hari, D.M.; Wiegand, G.W.; Miller, T.C.; Chen, J.Q.; Anderson, A.J.; Ray, S.; Mullinax, J.E.; Koizumi, T.; et al. Label-retaining liver cancer cells are relatively resistant to sorafenib. Gut 2013, 62, 1777–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Lingala, S.; Khoobyari, S.; Nolta, J.; Zern, M.A.; Wu, J. Epithelial mesenchymal transition and hedgehog signaling activation are associated with chemoresistance and invasion of hepatoma subpopulations. J. Hepatol. 2011, 55, 838–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Khoueiry, A.B.; Sangro, B.; Yau, T.; Crocenzi, T.S.; Kudo, M.; Hsu, C.; Kim, T.Y.; Choo, S.P.; Trojan, J.; Welling, T.H.; et al. Nivolumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (CheckMate 040): An open-label, non-comparative, phase 1/2 dose escalation and expansion trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 2492–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, A.X.; Finn, R.S.; Edeline, J.; Cattan, S.; Ogasawara, S.; Palmer, D.; Verslype, C.; Zagonel, V.; Fartoux, L.; Vogel, A.; et al. Pembrolizumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma previously treated with sorafenib (KEYNOTE-224): A non-randomised, open-label phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 940–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, A.L.; Qin, S.; Ikeda, M.; Galle, P.; Ducreux, M.; Zhu, A.; Kim, T.Y.; Kudo, M.; Breder, V.; Merle, P.; et al. IMbrave150: Efficacy and safety results from a ph III study evaluating atezolizumab (atezo) 1 bevacizumab (bev) vs sorafenib (Sor) as first treatment (tx) for patients (pts) with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yau, T.; Kang, Y.K.; Kim, T.Y.; El-Khoueiry, A.B.; Santoro, A.; Sangro, B.; Melero, I.; Kudo, M.; Hou, M.M.; Matilla, A.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Nivolumab Plus Ipilimumab in Patients with Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma Previously Treated with Sorafenib: The CheckMate 040 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhan, H. Communication between EMT and PD-L1 signaling: New insights into tumor immune evasion. Cancer Lett. 2020, 468, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soundararajan, R.; Fradette, J.J.; Konen, J.M.; Moulder, S.; Zhang, X.; Gibbons, D.L.; Varadarajan, N.; Wistuba, I.I.; Tripathy, D.; Bernatchez, C.; et al. Targeting the Interplay between Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal-Transition and the Immune System for Effective Immunotherapy. Cancers 2019, 11, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, M.; Coyle, K.M.; Vidovic, D.; Thomas, M.L.; Gujar, S.; Marcato, P. Hide-and-seek: The interplay between cancer stem cells and the immune system. Carcinogenesis 2017, 38, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, B.A.; Weiss, S. Generation of neurons and astrocytes from isolated cells of the adult mammalian central nervous system. Science 1992, 255, 1707–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Yu, Y.; Wang, J.; Yan, Z.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Ding, M.; Cui, L.; Wu, M.; Jiang, X.; et al. Establishment of a novel system for the culture and expansion of hepatic stem-like cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2015, 360, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, S.O.; Lee, S.W.; Bak, S.Y.; Kim, K.S. Ideal sphere-forming culture conditions to maintain pluripotency in a hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Cell Int. 2015, 15, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, N.; Tsunedomi, R.; Yoshimura, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Hazama, S.; Oka, M. Cancer stem-like sphere cells induced from de-differentiated hepatocellular carcinoma-derived cell lines possess the resistance to anti-cancer drugs. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores-Téllez, T.N.; Villa-Treviño, S.; Piña-Vázquez, C. Road to stemness in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 6750–6776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayachandran, A.; Shrestha, R.; Dhungel, B.; Huang, I.T.; Vasconcelos, M.Y.K.; Morrison, B.J.; Ramlogan-Steel, C.A.; Steel, J.C. Murine hepatocellular carcinoma derived stem cells reveal epithelial-to-mesenchymal plasticity. World J. Stem. Cells 2017, 9, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhai, B.; Liao, J.; Xu, W.; Zhang, R.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.; Qian, H.; et al. Sphere-forming cell subpopulations with cancer stem cell properties in human hepatoma cell lines. BMC Gastroenterol. 2011, 11, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.C.; Bose, S.K.; Steele, R.; Meyer, K.; Di Bisceglie, A.M.; Ray, R.B.; Ray, R. Promotion of Cancer Stem-Like Cell Properties in Hepatitis C Virus-Infected Hepatocytes. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 11549–11556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, R.; Bridle, K.R.; Crawford, D.H.G.; Jayachandran, A. TNF-α-mediated epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition regulates expression of immune checkpoint molecules in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 21, 1849–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, R.; Prithviraj, P.; Bridle, K.R.; Crawford, D.H.G.; Jayachandran, A. Combined Inhibition of TGF-β1-Induced EMT and PD-L1 Silencing Re-Sensitizes Hepatocellular Carcinoma to Sorafenib Treatment. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.; Fu, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; You, F. Transferrin receptor regulates malignancies and the stemness of hepatocellular carcinoma-derived cancer stem-like cells by affecting iron accumulation. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0243812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomizawa, M.; Shinozaki, F.; Motoyoshi, Y.; Sugiyama, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Ishige, N. Proliferation of sphere-forming hepatocellular carcinoma cells is suppressed in a medium without glucose and arginine, but with galactose and ornithine. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 1264–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Huang, W.C.; Tung, S.L.; Chen, Y.L.; Chen, P.M.; Chu, P.Y. IFI44L is a novel tumor suppressor in human hepatocellular carcinoma affecting cancer stemness, metastasis, and drug resistance via regulating met/Src signaling pathway. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, R.; Prithviraj, P.; Anaka, M.; Bridle, K.R.; Crawford, D.H.G.; Dhungel, B.; Steel, J.C.; Jayachandran, A. Monitoring Immune Checkpoint Regulators as Predictive Biomarkers in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, T.; Wang, X.W. Cancer stem cells in the development of liver cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 1911–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, G.; Han, Z.; Cheng, H.; Qiao, L. IL-6/STAT3 Signaling Contributes to Sorafenib Resistance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Through Targeting Cancer Stem Cells. Onco Targets Ther. 2020, 13, 9721–9730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, B.J.; Steel, J.C.; Morris, J.C. Sphere culture of murine lung cancer cell lines are enriched with cancer initiating cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.M.; Xu, Y.; Fan, J.; Zhou, J.; Yang, X.R.; Qiu, S.J.; Liao, Y.; Wu, W.Z.; Ji, Y.; Ke, A.W.; et al. Identification of side population cells in human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines with stepwise metastatic potentials. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 134, 1155–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, G.S.; Hu, Z.; Duan, W.; Tian, A.; Wang, X.M.; McLeod, D.; Lam, V.; George, J.; Qiao, L. Efficacy of using cancer stem cell markers in isolating and characterizing liver cancer stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2013, 22, 2655–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dazert, E.; Colombi, M.; Boldanova, T.; Moes, S.; Adametz, D.; Quagliata, L.; Roth, V.; Terracciano, L.; Heim, M.H.; Jenoe, P.; et al. Quantitative proteomics and phosphoproteomics on serial tumor biopsies from a sorafenib-treated HCC patient. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 1381–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, L.; Ruan, Z.; Sun, H.; Li, Q.; Han, L.; Huang, L.; Yu, S.; Wang, Y.; Guo, H.; Jiao, M. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition induced cancer-stem-cell-like characteristics in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 18448–18458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, X.; Zhang, B.H.; Zheng, S.S.; Gao, D.M.; Qiu, S.J.; Wu, W.Z.; Ren, Z.G. Coexpression of gene Oct4 and Nanog initiates stem cell characteristics in hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition through activation of Stat3/Snail signaling. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2015, 8, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Li, B.; Liu, F.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Yao, Y.; Li, D. The epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) and cancer stem cells: Implication for treatment resistance in pancreatic cancer. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tallerico, R.; Todaro, M.; Di Franco, S.; Maccalli, C.; Garofalo, C.; Sottile, R.; Palmieri, C.; Tirinato, L.; Pangigadde, P.N.; La Rocca, R.; et al. Human NK cells selective targeting of colon cancer-initiating cells: A role for natural cytotoxicity receptors and MHC class I molecules. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 2381–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schatton, T.; Frank, M.H. Cancer stem cells and human malignant melanoma. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2008, 21, 39–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tallerico, R.; Conti, L.; Lanzardo, S.; Sottile, R.; Garofalo, C.; Wagner, A.K.; Johansson, M.H.; Cristiani, C.M.; Kärre, K.; Carbone, E.; et al. NK cells control breast cancer and related cancer stem cell hematological spread. Oncoimmunology 2017, 6, e1284718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado, A.G.; Thiagarajan, P.S.; Mulkearns-Hubert, E.E.; Silver, D.J.; Hale, J.S.; Alban, T.J.; Turaga, S.M.; Jarrar, A.; Reizes, O.; Longworth, M.S.; et al. Glioblastoma Cancer Stem Cells Evade Innate Immune Suppression of Self-Renewal through Reduced TLR4 Expression. Cell Stem Cell 2017, 20, 450–461.e454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.; Wei, J.; Kong, L.Y.; Wang, Y.; Priebe, W.; Qiao, W.; Sawaya, R.; Heimberger, A.B. Glioma cancer stem cells induce immunosuppressive macrophages/microglia. Neuro Oncol. 2010, 12, 1113–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Li, G.; Li, R.; Chang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Wang, D.; Wu, F.; Zhang, W. Single-Cell RNA-Sequencing Shift in the Interaction Pattern Between Glioma Stem Cells and Immune Cells During Tumorigenesis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 581209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozawa, Y.; Yamamuro, S.; Sano, E.; Tatsuoka, J.; Hanashima, Y.; Yoshimura, S.; Sumi, K.; Hara, H.; Nakayama, T.; Suzuki, Y.; et al. Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 is highly expressed in glioma stem cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 524, 723–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Fillmore, C.M.; Koyama, S.; Wu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, Z.; Herter-Sprie, G.S.; Akbay, E.A.; Tchaicha, J.H.; Altabef, A.; et al. Loss of Lkb1 and Pten leads to lung squamous cell carcinoma with elevated PD-L1 expression. Cancer Cell 2014, 25, 590–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Shin, J.H.; Longmire, M.; Wang, H.; Kohrt, H.E.; Chang, H.Y.; Sunwoo, J.B. CD44+ Cells in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Suppress T-Cell-Mediated Immunity by Selective Constitutive and Inducible Expression of PD-L1. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 3571–3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishida, N.; Sakai, K.; Morita, M.; Aoki, T.; Takita, M.; Hagiwara, S.; Komeda, Y.; Takenaka, M.; Minami, Y.; Ida, H.; et al. Association between Genetic and Immunological Background of Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Expression of Programmed Cell Death-1. Liver Cancer 2020, 9, 426–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, P.; Xiong, Y.; Yue, J.; Hanley, S.J.B.; Watari, H. Tumor-Intrinsic PD-L1 Signaling in Cancer Initiation, Development and Treatment: Beyond Immune Evasion. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almozyan, S.; Colak, D.; Mansour, F.; Alaiya, A.; Al-Harazi, O.; Qattan, A.; Al-Mohanna, F.; Al-Alwan, M.; Ghebeh, H. PD-L1 promotes OCT4 and Nanog expression in breast cancer stem cells by sustaining PI3K/AKT pathway activation. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 141, 1402–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, H.B.; Clark, C.A.; Yuan, B.; Sareddy, G.; Pandeswara, S.; Padron, A.S.; Hurez, V.; Conejo-Garcia, J.; Vadlamudi, R.; Li, R.; et al. Tumor cell-intrinsic PD-L1 promotes tumor-initiating cell generation and functions in melanoma and ovarian cancer. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 2016, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.L.; Shen, M.N.; Hu, B.; Wang, B.L.; Yang, W.J.; Lv, L.H.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Jin, A.L.; Sun, Y.F.; et al. CD73 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression and metastasis via activating PI3K/AKT signaling by inducing Rap1-mediated membrane localization of P110β and predicts poor prognosis. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.L.; Hu, B.; Tang, W.G.; Xie, S.H.; Ren, N.; Guo, L.; Lu, R.Q. CD73 sustained cancer-stem-cell traits by promoting SOX9 expression and stability in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zaidi, S.; Rao, S.; Chen, J.S.; Phan, L.; Farci, P.; Su, X.; Shetty, K.; White, J.; Zamboni, F.; et al. Analysis of Genomes and Transcriptomes of Hepatocellular Carcinomas Identifies Mutations and Gene Expression Changes in the Transforming Growth Factor-β Pathway. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcante, G.C.; Schaan, A.P.; Cabral, G.F.; Santana-da-Silva, M.N.; Pinto, P.; Vidal, A.F.; Ribeiro-Dos-Santos, Â. A Cell’s Fate: An Overview of the Molecular Biology and Genetics of Apoptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, W.; Luo, X.; Li, W.; Zhong, J.; Cao, J.; Zhu, S.; Chen, X.; Zhou, R.; Shang, C.; Chen, Y. TNF-α is a potential therapeutic target to overcome sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma. EBioMedicine 2019, 40, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, J.M.; Xia, W.; Hsu, Y.H.; Chan, L.C.; Yu, W.H.; Cha, J.H.; Chen, C.T.; Liao, H.W.; Kuo, C.W.; Khoo, K.H.; et al. STT3-dependent PD-L1 accumulation on cancer stem cells promotes immune evasion. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broutier, L.; Mastrogiovanni, G.; Verstegen, M.M.; Francies, H.E.; Gavarró, L.M.; Bradshaw, C.R.; Allen, G.E.; Arnes-Benito, R.; Sidorova, O.; Gaspersz, M.P.; et al. Human primary liver cancer-derived organoid cultures for disease modeling and drug screening. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 1424–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).