Concomitant Renal Cell Carcinoma and Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia: Use of a Targeted Approach
Abstract
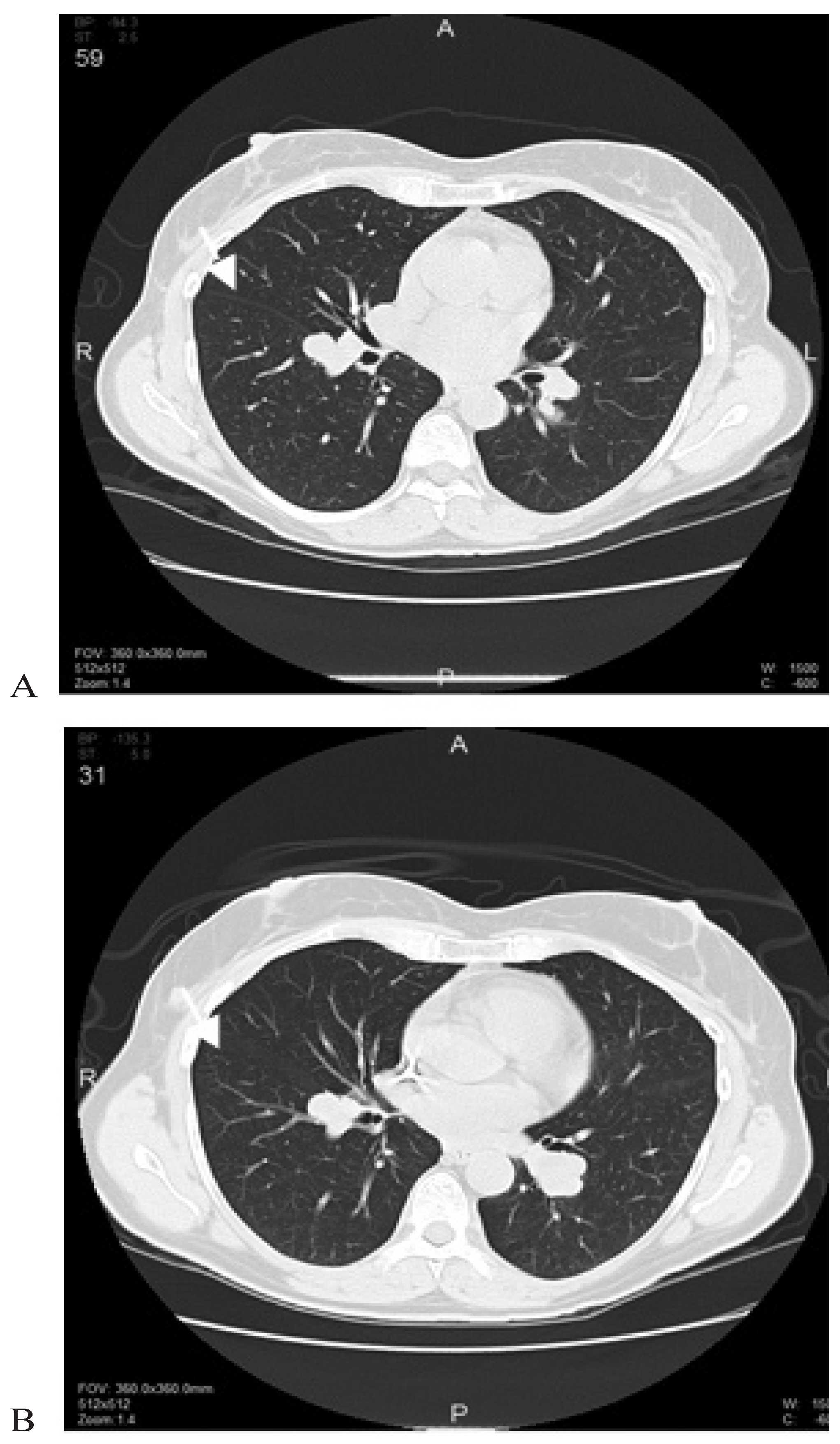
:1. CASE PRESENTATION
2. DISCUSSION
2.1. Targeted Therapy for mRCC and CML
2.2. Rationale for the Combination of Bevacizumab and Imatinib
3. CONCLUSION
4. RESEARCH SUPPORT AND DISCLAIMERS
References
- Druker, B.J.; Guilhot, F.; O’Brien, SG.; et al. on behalf of the IRIS Investigators. Five-year follow-up of patients receiving imatinib for chronic myeloid leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 2408–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talpaz, M.; Shah, N.P.; Kantarjian, H.; et al. Dasatinib in imatinib-resistant Philadelphia chromosome–positive leukemias. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 2531–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kantarjian, H.; Giles, F.; Wunderle, L.; et al. Nilotinib in imatinib-resistant CML and Philadelphia chromosome–positive ALL. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 2542–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motzer, R.J.; Bacik, J.; Murphy, B.A.; Russo, P.; Mazumdar, M. Interferon-alfa as a comparative treatment for clinical trials of new therapies against advanced renal cell carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 20, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izzedine, H.; Buhaescu, I.; Rixe, O.; Deray, G. Sunitinib malate. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2007, 60, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motzer, R.J.; Hutson, T.E.; Tomczak, P.; et al. Sunitinib versus interferon alfa in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escudier, B.; Eisen, T.; Stadler, W.M.; et al. on behalf of the TARGET Study Group. Sorafenib in advanced clear-cell renal-cell car- cinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudes, G.; Carducci, M.; Tomczak, P.; et al. on behalf of the Global ARCC Trial. Temsirolimus, interferon alfa, or both for advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 2271–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escudier, B.; Koralewski, P.; Pluzanska, A.; et al. on behalf of the Avoren investigators. A randomized, controlled, double-blind phase III study (Avoren) of bevacizumab/interferon-α2a vs placebo/ interferon-α2a as first-line therapy in metastatic renal cell carci- noma [abstract 3]. Proc. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. [Available online at: www.asco.org/ASCO/Abstracts+%26+Virtual+Meeting/ Abstracts?&vmview=abst_detail_view&confID=47&abstractID= 30355; cited January 29, 2009]. 2007, 25. [Google Scholar]
- Bukowski, R.M.; Kabbinavar, F.F.; Figlin, R.A.; et al. Randomized phase II study of erlotinib combined with bevacizumab com- pared with bevacizumab alone in metastatic renal cell cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 4536–4541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hainsworth, J.D.; Spigel, D.R.; Sosman, J.A.; et al. Treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma with the combination beva- cizumab/erlotinib/imatinib: a phase I/II trial. Clin. Genitourin Cancer 2007, 5, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tawfik, O.W.; Kramer, B.; Shideler, B.; Danley, M.; Kimler, B.F.; Holz-beierlein, J. Prognostic significance of CD44, platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha, and cyclooxygenase 2 expression in renal cell carcinoma. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2007, 131, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Tong, R.; Cochran, D.M.; Jain, R.K. Blocking platelet-derived growth factor-D/platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta signaling inhibits human renal cell carcinoma progression in an orthotopic mouse model. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 5711–5719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.J.; Li, B.; Winer, J.; et al. Inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor–induced angiogenesis suppresses tumour growth in vivo. Nature 1993, 362, 841–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, R.K. Normalization of tumor vasculature: an emerging concept in antiangiogenic therapy. Science 2005, 307, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Servidei, T.; Riccardi, A.; Sanguinetti, M.; Dominici, C.; Riccardi, R. Increased sensitivity to the platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) receptor inhibitor STI571 in chemoresistant glioma cells is associated with enhanced PDGF-BB-mediated signaling and STI571-induced Akt inactivation. J. Cell Physiol. 2006, 208, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buck, E.; Eyzaguirre, A.; Haley, J.D.; Gibson, N.W.; Cagnoni, P.; Iwata, K.K. Inactivation of Akt by the epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor erlotinib is mediated by HER-3 in pancreatic and colorectal tumor cell lines and contributes to erlotinib sensitivity. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2006, 5, 2051–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2009 by the author. Multimed Inc.
Share and Cite
Pal, S.K.; Gupta, R.K.; Dosik, G.; Figlin, R.A. Concomitant Renal Cell Carcinoma and Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia: Use of a Targeted Approach. Curr. Oncol. 2009, 16, 44-47. https://doi.org/10.3747/co.v16i2.301
Pal SK, Gupta RK, Dosik G, Figlin RA. Concomitant Renal Cell Carcinoma and Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia: Use of a Targeted Approach. Current Oncology. 2009; 16(2):44-47. https://doi.org/10.3747/co.v16i2.301
Chicago/Turabian StylePal, S. K., R. K. Gupta, G. Dosik, and R. A. Figlin. 2009. "Concomitant Renal Cell Carcinoma and Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia: Use of a Targeted Approach" Current Oncology 16, no. 2: 44-47. https://doi.org/10.3747/co.v16i2.301
APA StylePal, S. K., Gupta, R. K., Dosik, G., & Figlin, R. A. (2009). Concomitant Renal Cell Carcinoma and Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia: Use of a Targeted Approach. Current Oncology, 16(2), 44-47. https://doi.org/10.3747/co.v16i2.301



