Ein Fast Normales EKG
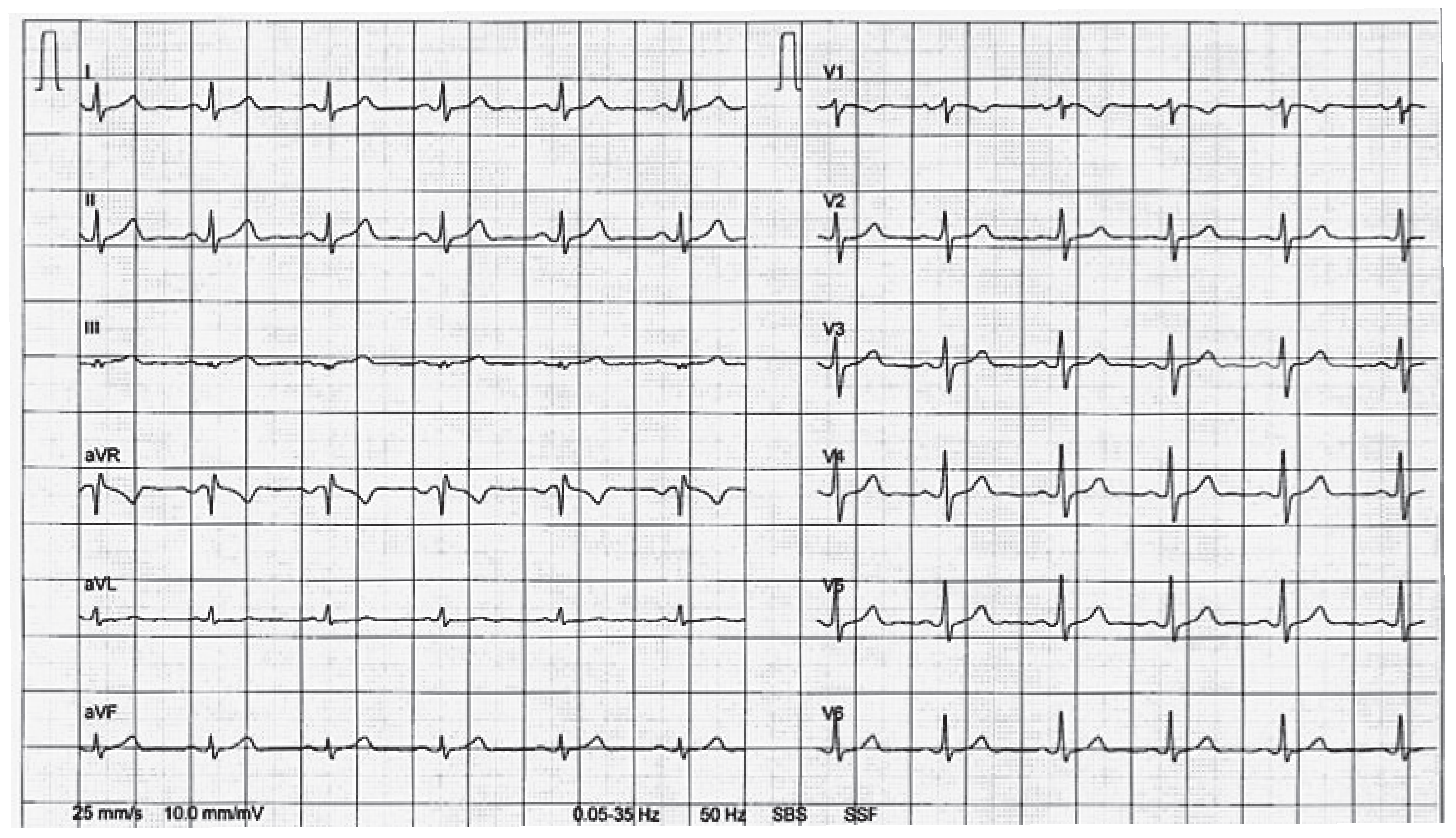
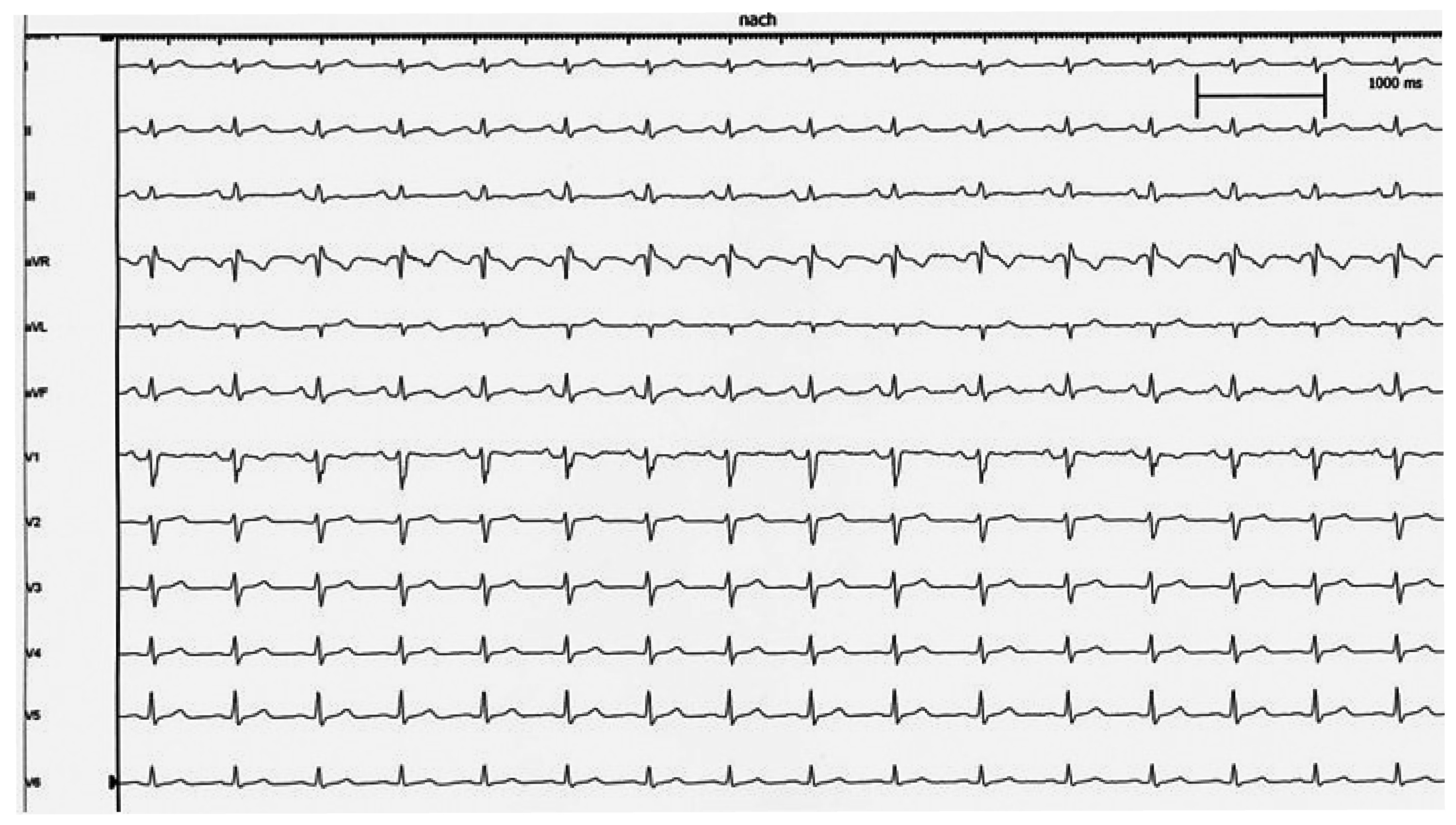
Wie beurteilen Sie das Ruhe EKG (Abb. 1)?
- A
- Kurze PQ-Zeit, keine Deltawelle.
- B
- NormalePQ-ZeitundDeltawelle.
- C
- KurzePQ-ZeitundDeltawelle.
Kommentar
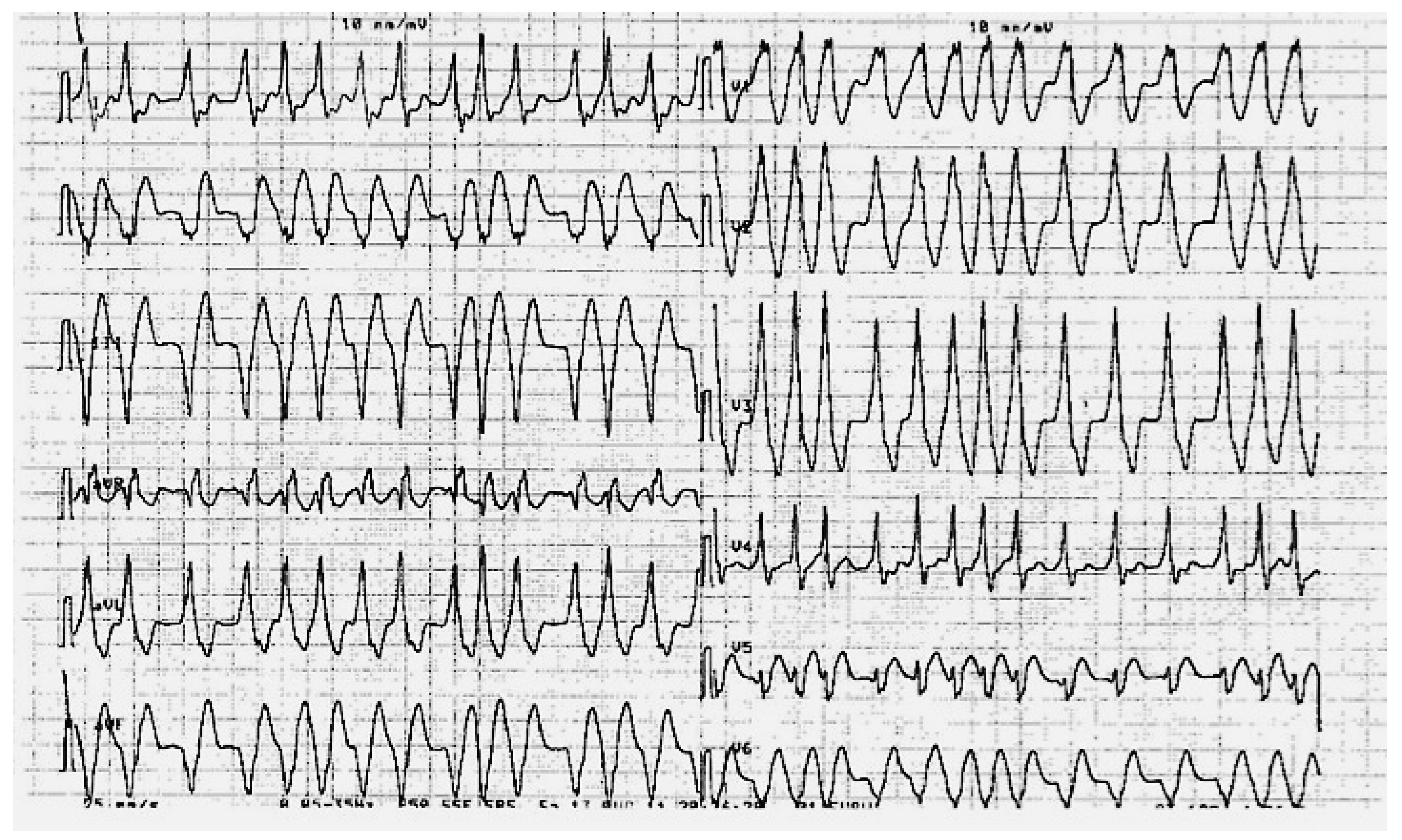
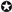 Adenosin blockiert nun den AV-Knoten, so dass das ventrikuläre Myokard nur noch über die akzessorische Bahn depolarisiert wird, was im EKG zu einer vollen Präexzitation, in unserem Fall mit deutlich positiver Deltawelle in V1, führt.
Adenosin blockiert nun den AV-Knoten, so dass das ventrikuläre Myokard nur noch über die akzessorische Bahn depolarisiert wird, was im EKG zu einer vollen Präexzitation, in unserem Fall mit deutlich positiver Deltawelle in V1, führt.
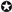 Adenosin blockiert nun den AV-Knoten, so dass das ventrikuläre Myokard nur noch über die akzessorische Bahn depolarisiert wird, was im EKG zu einer vollen Präexzitation, in unserem Fall mit deutlich positiver Deltawelle in V1, führt.
Adenosin blockiert nun den AV-Knoten, so dass das ventrikuläre Myokard nur noch über die akzessorische Bahn depolarisiert wird, was im EKG zu einer vollen Präexzitation, in unserem Fall mit deutlich positiver Deltawelle in V1, führt.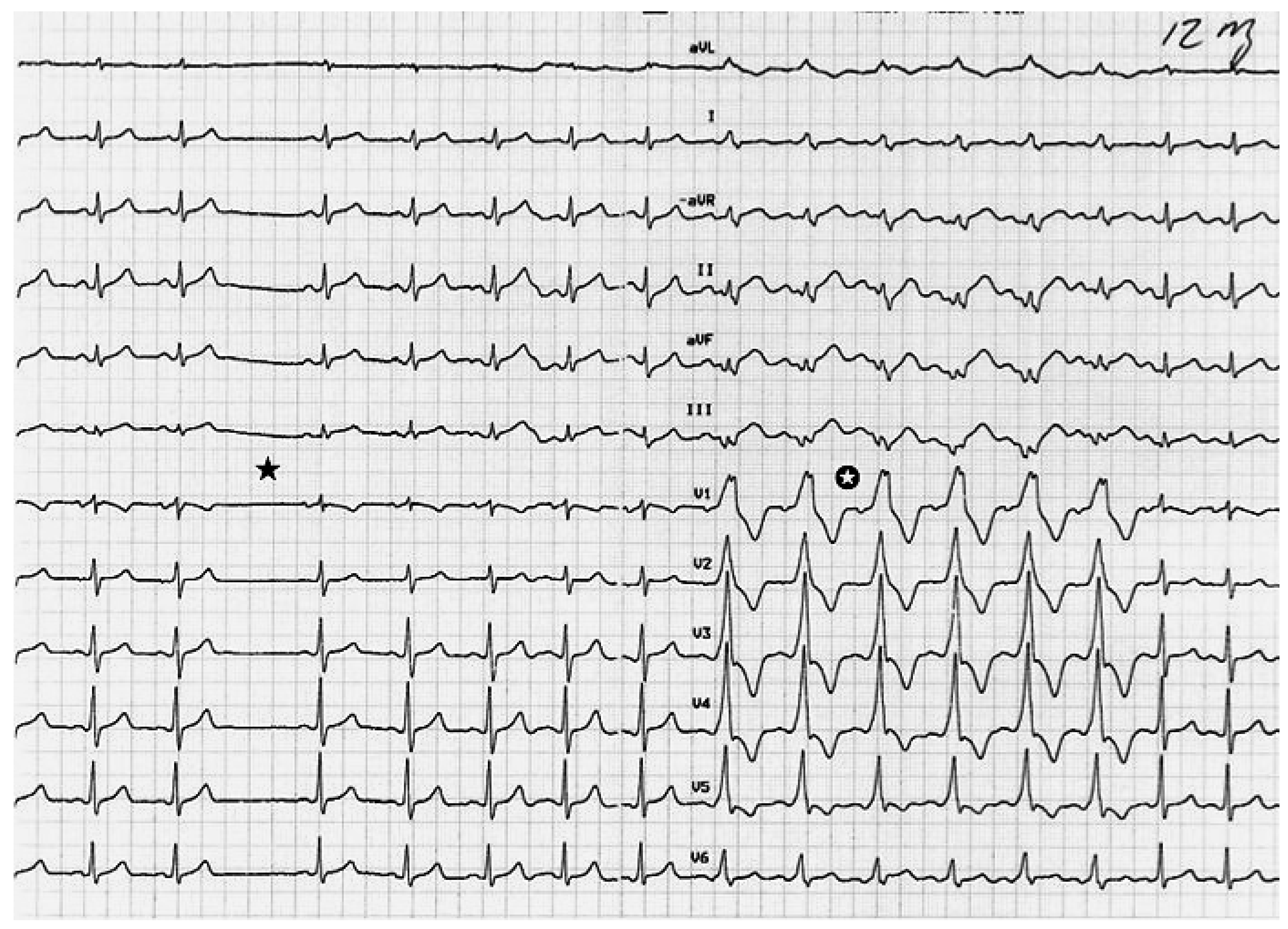
Funding/potential competing interests
© 2012 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Altmanna, D.; Kühnea, M.; Ammann, P. Ein Fast Normales EKG. Cardiovasc. Med. 2012, 15, 233. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2012.01679
Altmanna D, Kühnea M, Ammann P. Ein Fast Normales EKG. Cardiovascular Medicine. 2012; 15(7):233. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2012.01679
Chicago/Turabian StyleAltmanna, David, Michael Kühnea, and Peter Ammann. 2012. "Ein Fast Normales EKG" Cardiovascular Medicine 15, no. 7: 233. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2012.01679
APA StyleAltmanna, D., Kühnea, M., & Ammann, P. (2012). Ein Fast Normales EKG. Cardiovascular Medicine, 15(7), 233. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2012.01679



