Lifelong Specialised Care of Adults with Congenital Heart Disease a Luxury or State of the Art?
Abstract
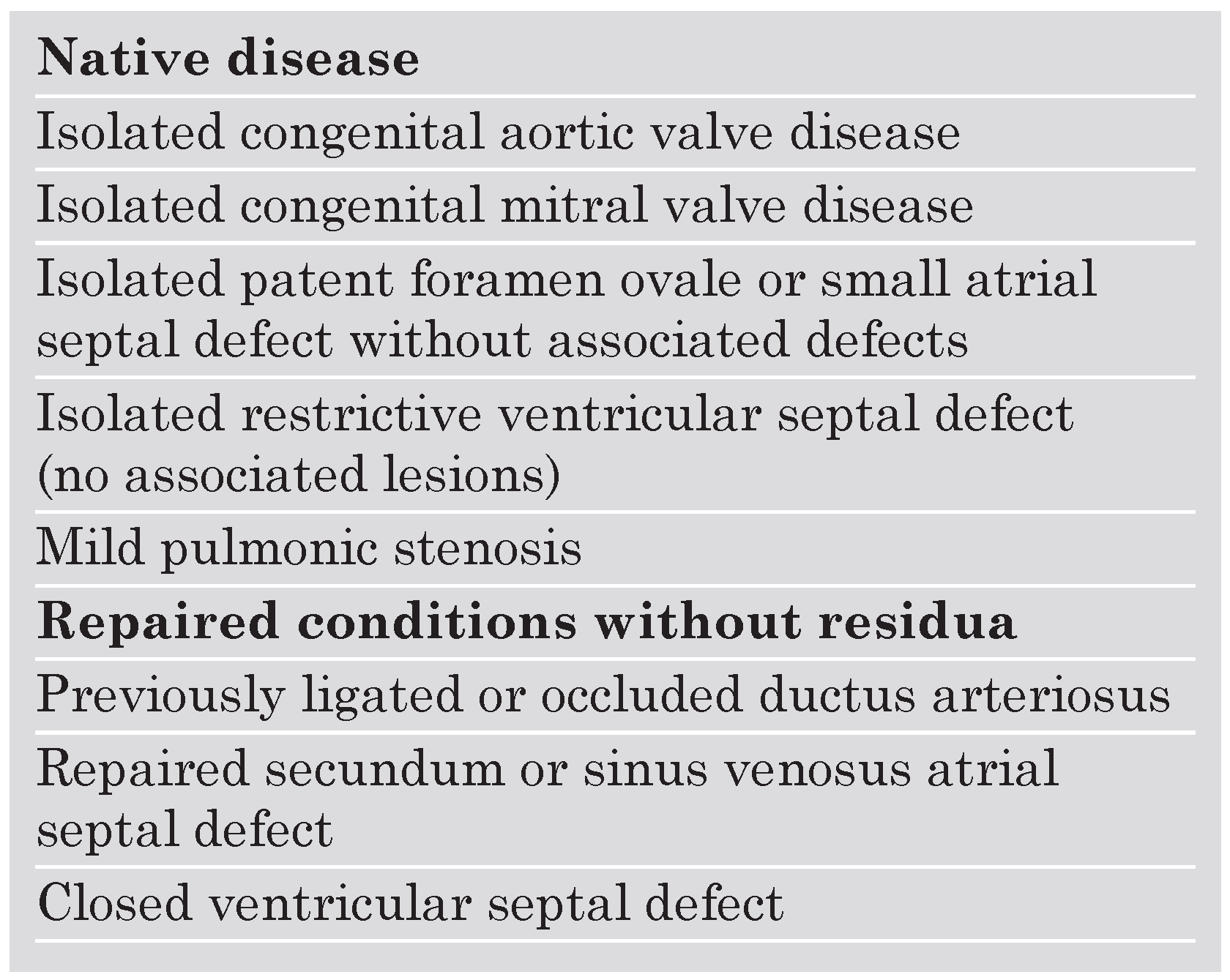
Introduction
Profile of Adult Patients with Congenital Heart Disease
Tetralogy of Fallot
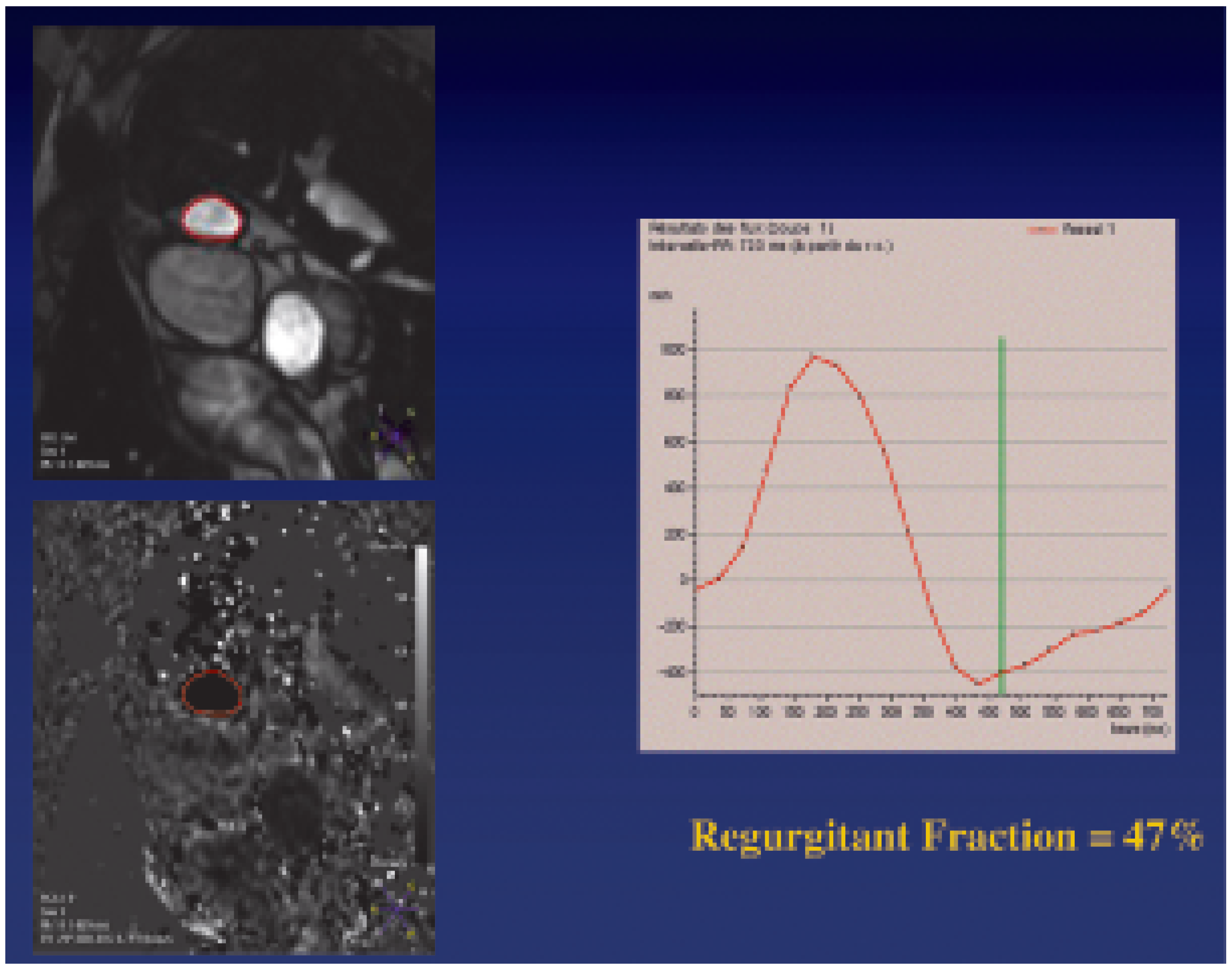
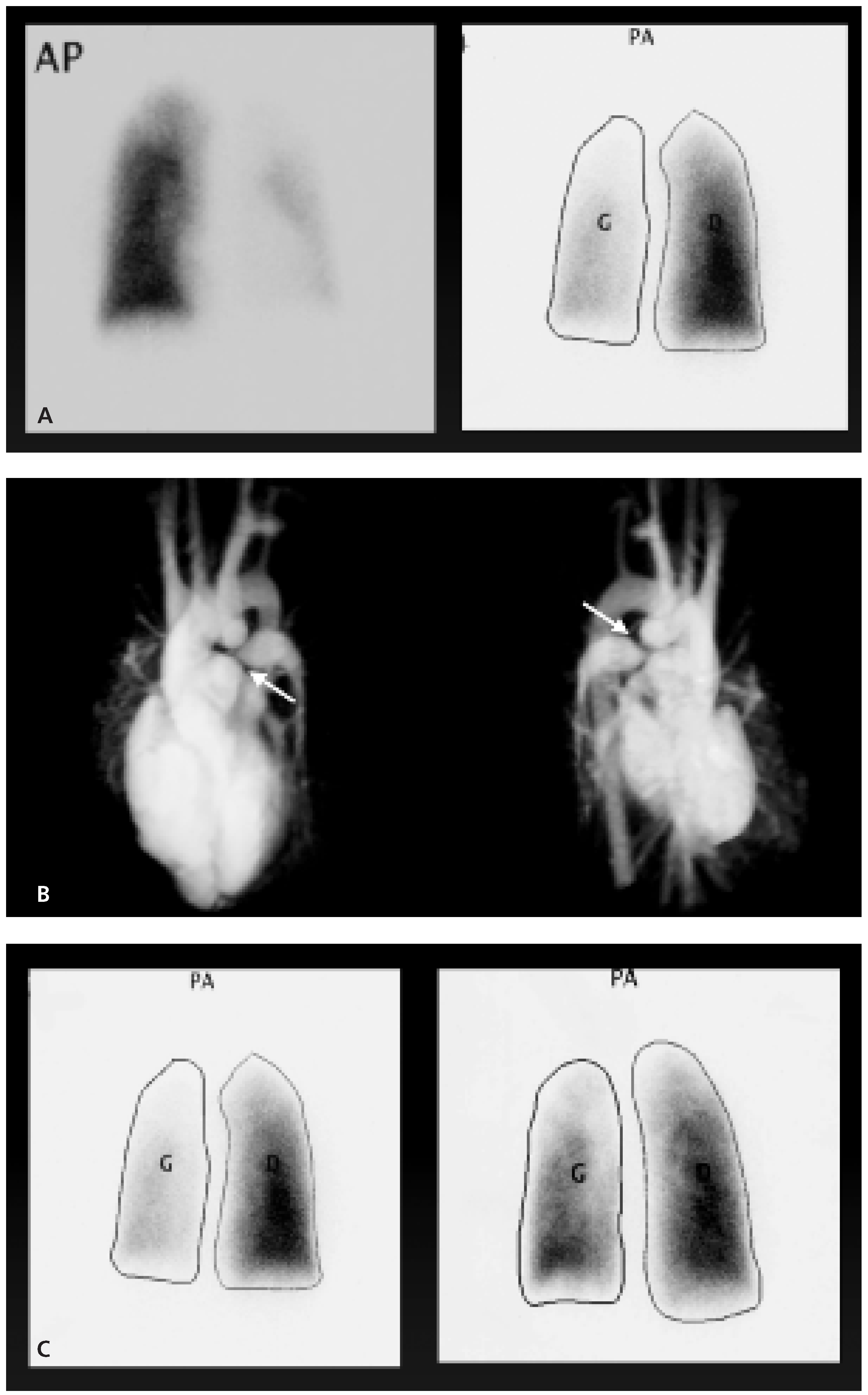
- Pulmonary regurgitation
- Pulmonary stenosis
- Arrhythmias
- Left ventricular dysfunction
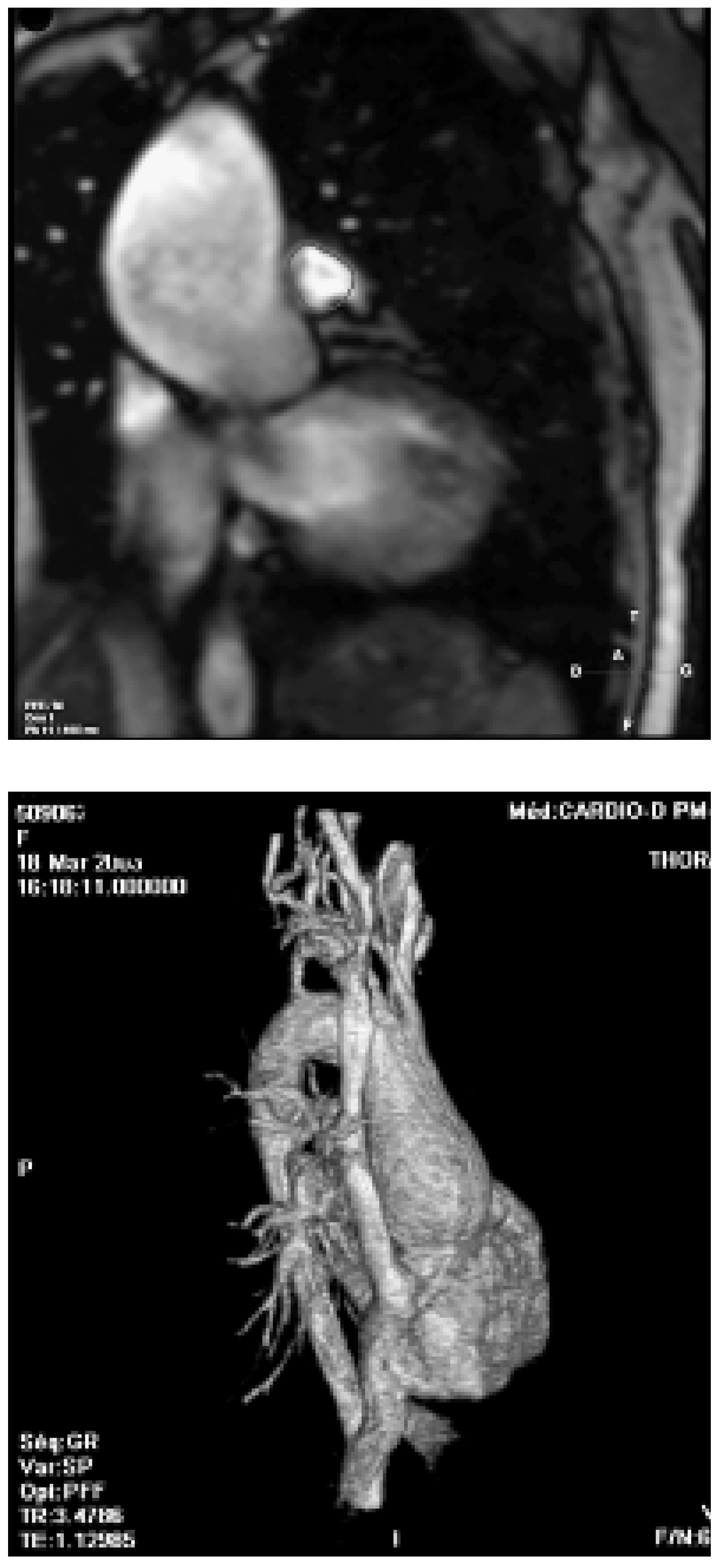
- Aortic root dilatation
Conclusions
References
- Moller, J.H.; Taubert, K.A.; Allen, H.D.; et al. Cardiovascular health and disease in children: Current status. Circulation 1994, 89, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warnes, C.A.; Liberthson, R.; et al. 32nd Bethesda Conference: Task Force 1: The changing profile of congenital heart disease in adult life. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2001, 37, 1170–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warnes, C.A. The adult with congenital heart disease. Born to be bad? 2005, 46, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Connelly, M.S.; Webb, G.D.; Somerville, J.; et al. Canadian Consensus Conference on adult congenital heart disease 1996. Can J Cardiol. 1998, 14, 395–452. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Therrien, J.; Dore, A.; Gersony, W.; et al. CCS Consensus Conference 2001 update: Recommendations for the management of adults with congenital heart disease. Part I. Can J Cardiol. 2001, 17, 940–959. [Google Scholar]
- Webb, G.D. Care of adults with congenital heart disease—A challenge for the new millennium. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2001, 49, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaemmerer, H.; Breithard, G. Clin Res Cardiol. 2006, 95 (Suppl. 4), 76–84, In process citation. [CrossRef]
- Oechslin, E.N.; Harrison, D.A.; Connelly, M.S.; et al. Mode of death in adults with congenital heart disease. Am J Cardiol. 2000, 86, 1111–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatzoulis, M.A.; Hechter, S.; Siu, S.C.; et al. Outpatient clinics for adults with congenital heart disease: Increasing workload and evolving patterns of referral. Heart 1999, 81, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, J.G.; Gersh, B.J.; Mair, D.D.; et al. Long-term outcome in patients undergoing surgical repair of tetralogy of Fallot. N Engl J Med. 1993, 329, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nollert, G.; Fischlein, T.; Boutewerk, D.M.D.; et al. Long-term survival in patients with repair of tetralogy of Fallot: 36-year follow-up of 490 survivors of the first year after surgical repair. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1997, 30, 1374–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, J.S.; Shinebourne, E.A.; Busst, C.; et al. Exercise capacity after complete repair of tetralogy of Fallot: Deleterious effects of residual pulmonary regurgitation. Heart 1992, 67, 470–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatzoulis, M.A.; Balaji, S.; Webber, S.A.; et al. Risk factors for arrhythmia and sudden cardiac death late after repair of tetralogy of Fallot: A multicentre study. Lancet 2000, 356, 975–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yemets, I.M.; Williams, W.G.; Webb, G.D.; et al. Pulmonary valve replacement late after repair of tetralogy of Fallot. Ann Thorac Surg. 1997, 64, 526–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warner, K.G.; O’Brien, P.K.; Rhodes, J.; et al. Expanding the indications for pulmonary valve replacement after repair of tetralogy of Fallot. Ann Thorac Surg. 2003, 76, 1066–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Therrien, J.; Siu, S.; McLaughlin, P.R.; et al. Pulmonary valve replacement in adults late after repair of tetralogy of Fallot: Are we operating too late? J Am Coll Cardiol. 2000, 36, 1670–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oechslin, E.N.; Harrison, D.A.; Harris, L.; et al. Re-operation in adults with repair of tetralogy of Fallot: Indications and outcomes. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1999, 118, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vliegen, H.W.; van Straten, A.; de Roos, A.; et al. Magnetic resonance imaging to assess the hemodynamic effects of pulmonary valve replacement in adults late after repair of tetralogy of Fallot. Circulation 2002, 106, 1703–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Therrien, J.; et al. Optimal timing for pulmonary valve replacement in adults after tetralogy of Fallot repair. Am J Cardiol. 2005, 95, 779–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roos-Hesselink, J.; Perlroth, M.J.; McGhie, J.; et al. Atrial arrythmias in adults after repair of tetralogy of Fallot: Correlation with clinical, exercise and echocardiographic findings. Circulation 1995, 91, 2214–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatzoulis, M.A.; Till, J.A.; Somerville, J.; et al. Mechano-electrical interaction in tetralogy of Fallot: QRS prolongation relates to right ventricular size and predicts malignant ventricular arrhythmias and sudden death. Circulation 1995, 92, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairy, P.; Landzberg, M.J.; Gatzoulis, M.A.; et al. Value of programmed ventricular stimulation after tetralogy of Fallot repair: A multicenter study. Circulation 2004, 109, 1994–2000. [Google Scholar]
- Babu-Narayan, S.V.; Kilner, P.J.; Li, W.; et al. Ventricular fibrosis suggested by cardiovascular magnetic resonance in adults with repaired tetralogy of Fallot and its relationship to adverse markers of clinical outcome. Circulation 2006, 113, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davlouros, P.A.; Kilner, P.J.; Hornung, T.S.; et al. Right ventricular function in adults with repaired tetralogy of Fallot assessed with cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging: Detrimental role of right ventricular outflow aneurysms or akinesia and adverse right-to-left ventricular interaction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2002, 40, 2044–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geva, T.; Sandweiss, B.M.; Gauvreau, K.; et al. Factors associated with impaired clinical status in long-term survivors of tetralogy of Fallot repair evaluated by magnetic resonance imaging. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004, 43, 1068–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghai, A.; Silversides, C.; Harris, L.; et al. Left ventricular dysfunction is a risk factor for sudden cardiac death in adults late after repair of tetralogy of Fallot. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2002, 40, 1675–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niwa, K.; Siu, S.C.; Webb, G.D.; et al. Progressive aortic root dilatation in adults late after repair of of tetralogy of Fallot. Circulation 2002, 106, 1374–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodds, G.A.; Warnes, C.A.; Danielson, G.K. Aortic valve replacement after repair of pulmonary atresia and ventricular septal defect of tetralogy of Fallot. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1997, 113, 736–741. [Google Scholar]
- Oosterhof, T.; Nollen, G.J.; van der Wall, E.E.; et al. Comparison of aortic stiffness in patients with juvenile forms of ascending aorta dilation with-vs-without the Marfan syndrome. Am J Cardiol. 2005, 95, 75–77. [Google Scholar]
 |
 |
 |
 |
© 2006 by the author. Attribution - Non-Commercial - NoDerivatives 4.0.
Share and Cite
Trindade, P.T. Lifelong Specialised Care of Adults with Congenital Heart Disease a Luxury or State of the Art? Cardiovasc. Med. 2006, 9, 376. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2006.01207
Trindade PT. Lifelong Specialised Care of Adults with Congenital Heart Disease a Luxury or State of the Art? Cardiovascular Medicine. 2006; 9(11):376. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2006.01207
Chicago/Turabian StyleTrindade, Pedro Trigo. 2006. "Lifelong Specialised Care of Adults with Congenital Heart Disease a Luxury or State of the Art?" Cardiovascular Medicine 9, no. 11: 376. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2006.01207
APA StyleTrindade, P. T. (2006). Lifelong Specialised Care of Adults with Congenital Heart Disease a Luxury or State of the Art? Cardiovascular Medicine, 9(11), 376. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2006.01207




