Coronary Revascularisation in Diabetics: Surgical Aspects
Summary
Zusammenfassung
Introduction
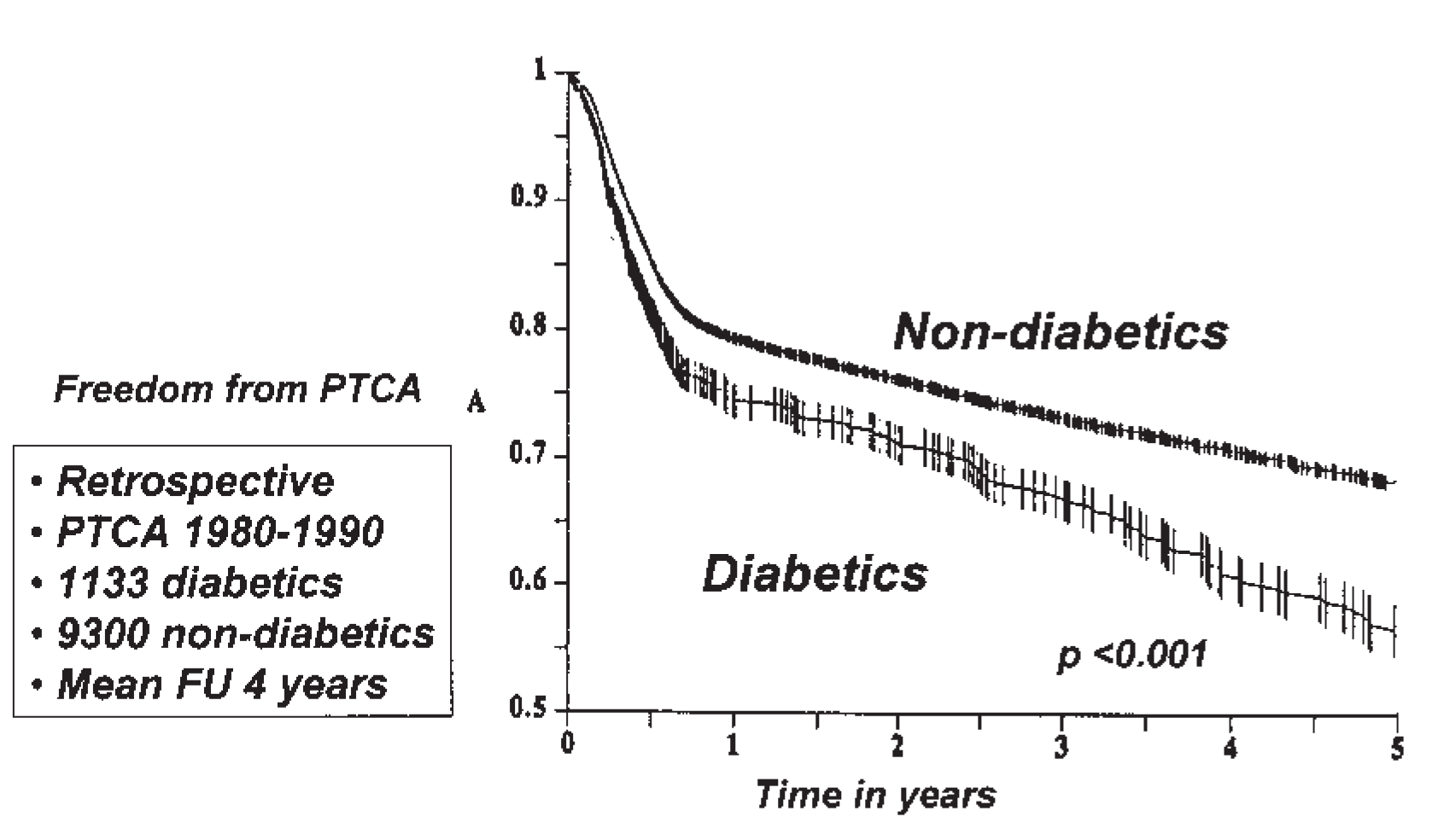
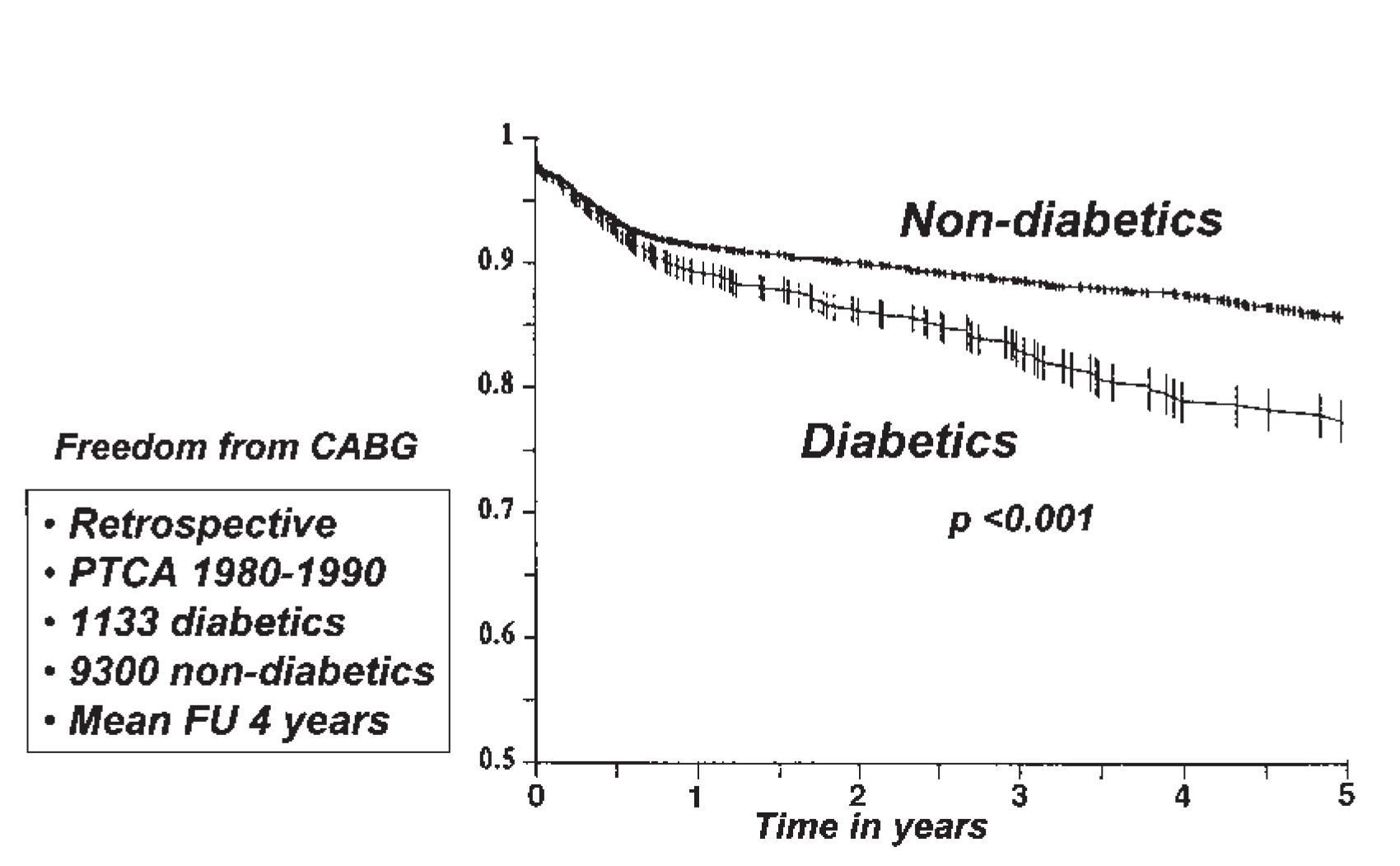
Characteristics of coronary heart disease (CHD) in diabetic patients
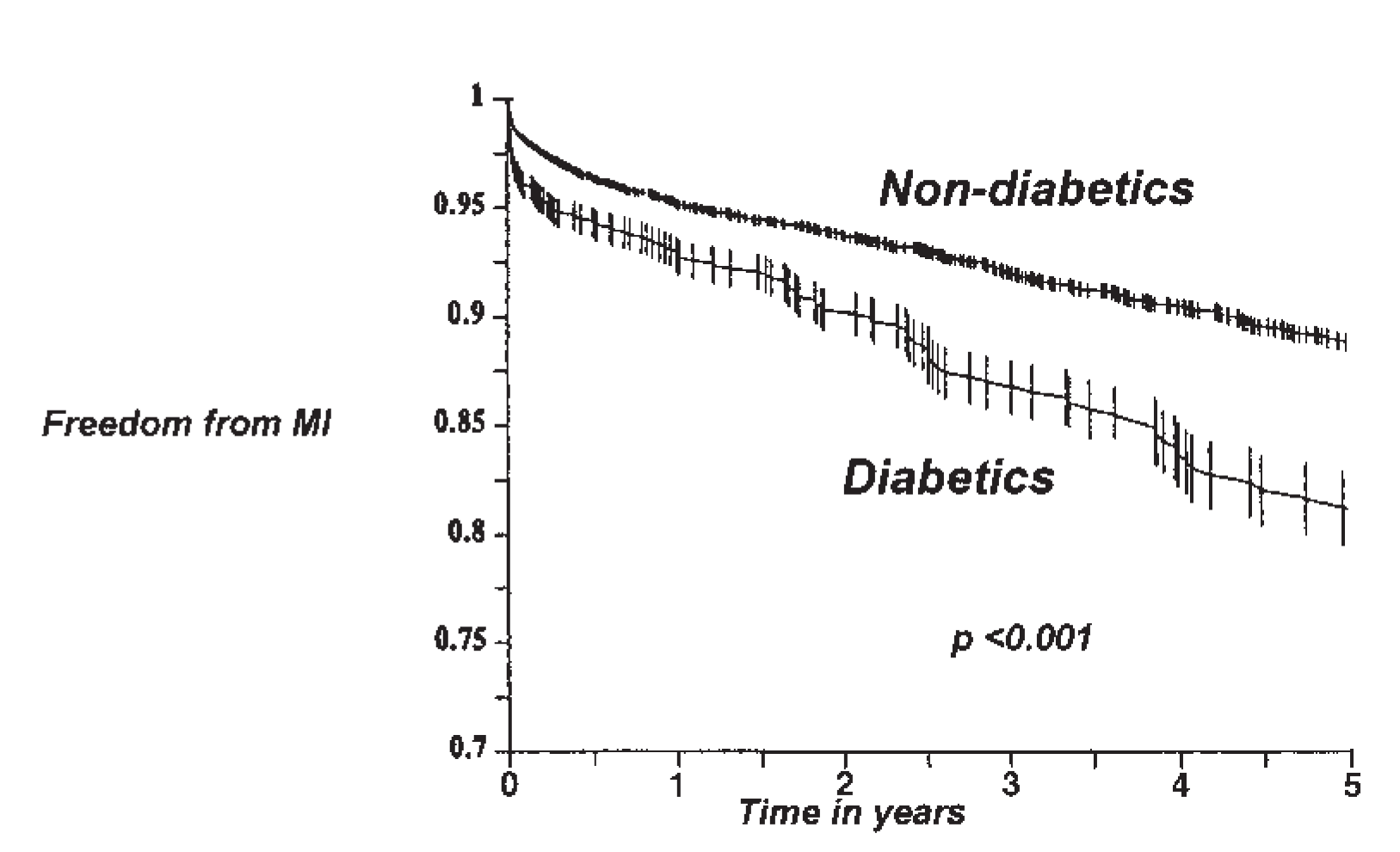
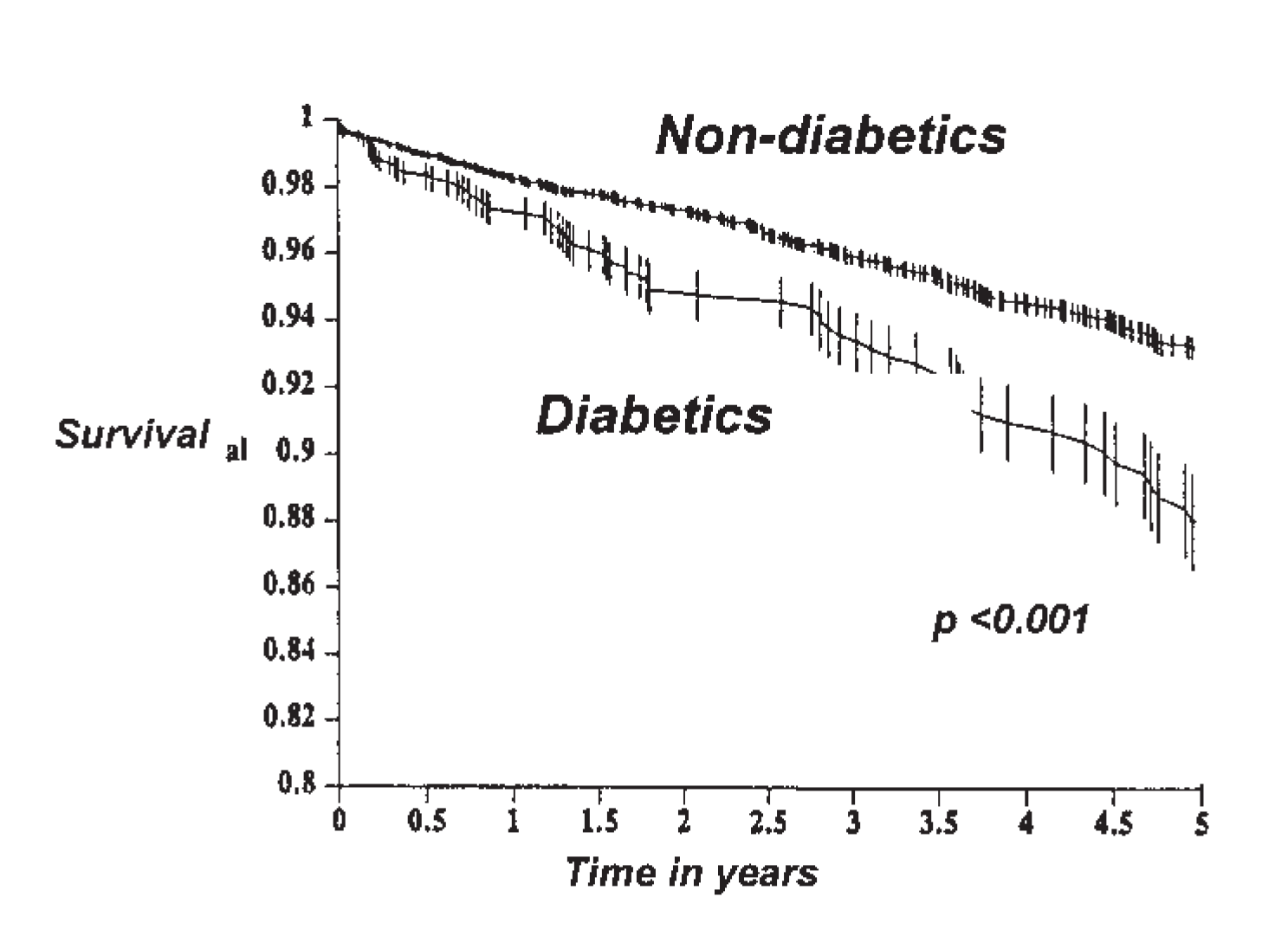
Options for myocardial revascularisation
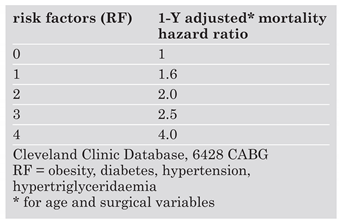
Special surgical aspects
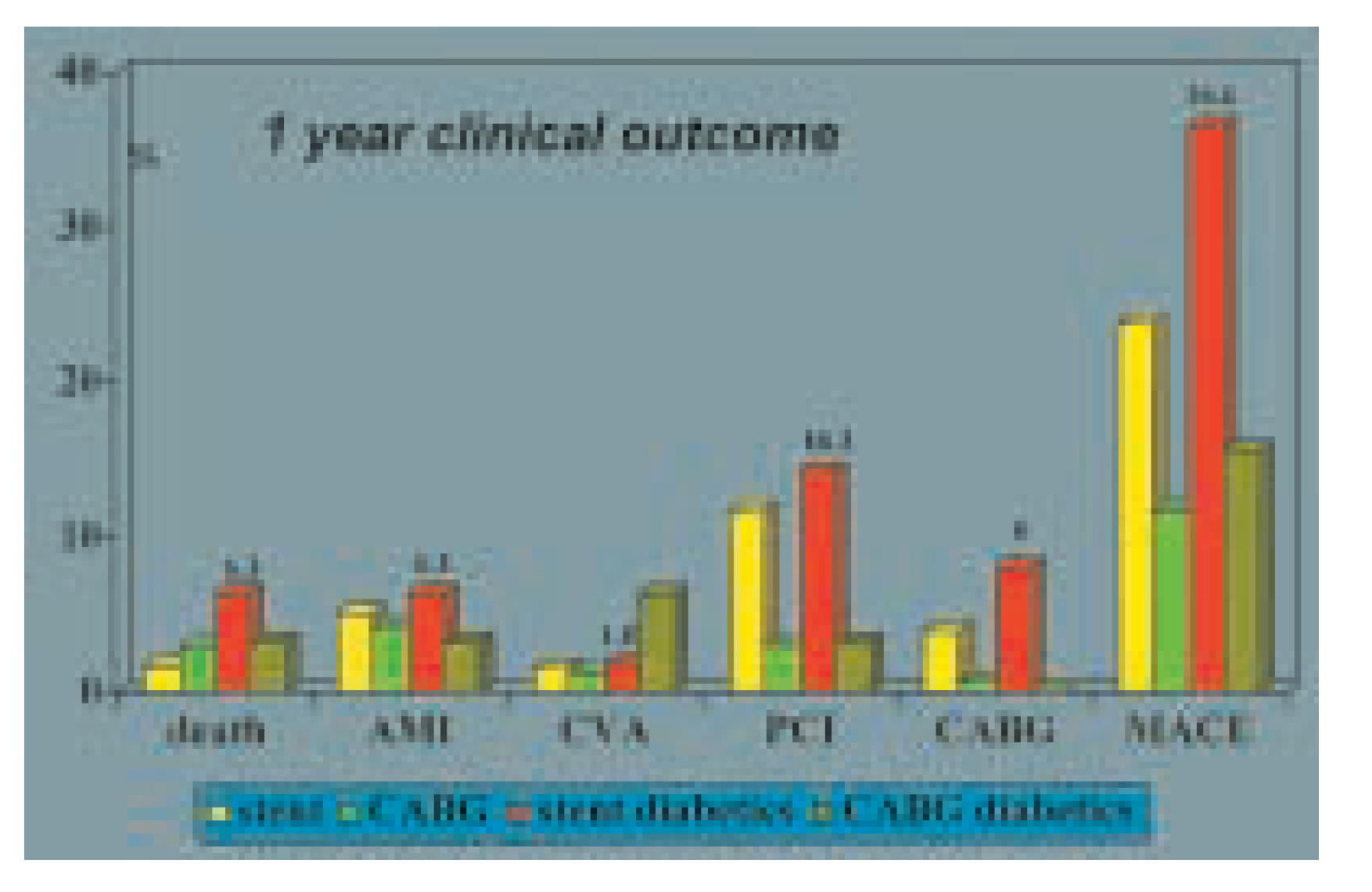
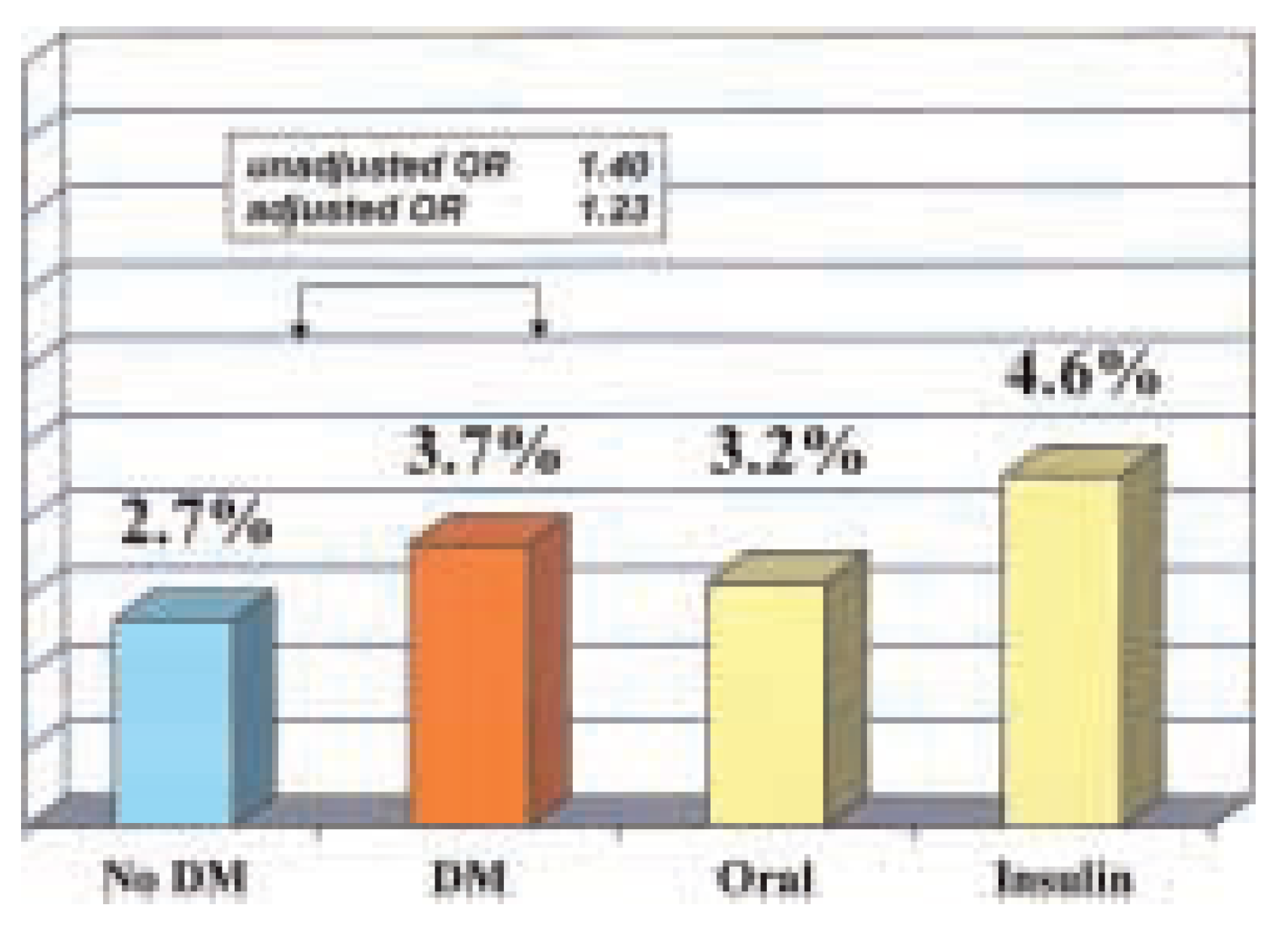
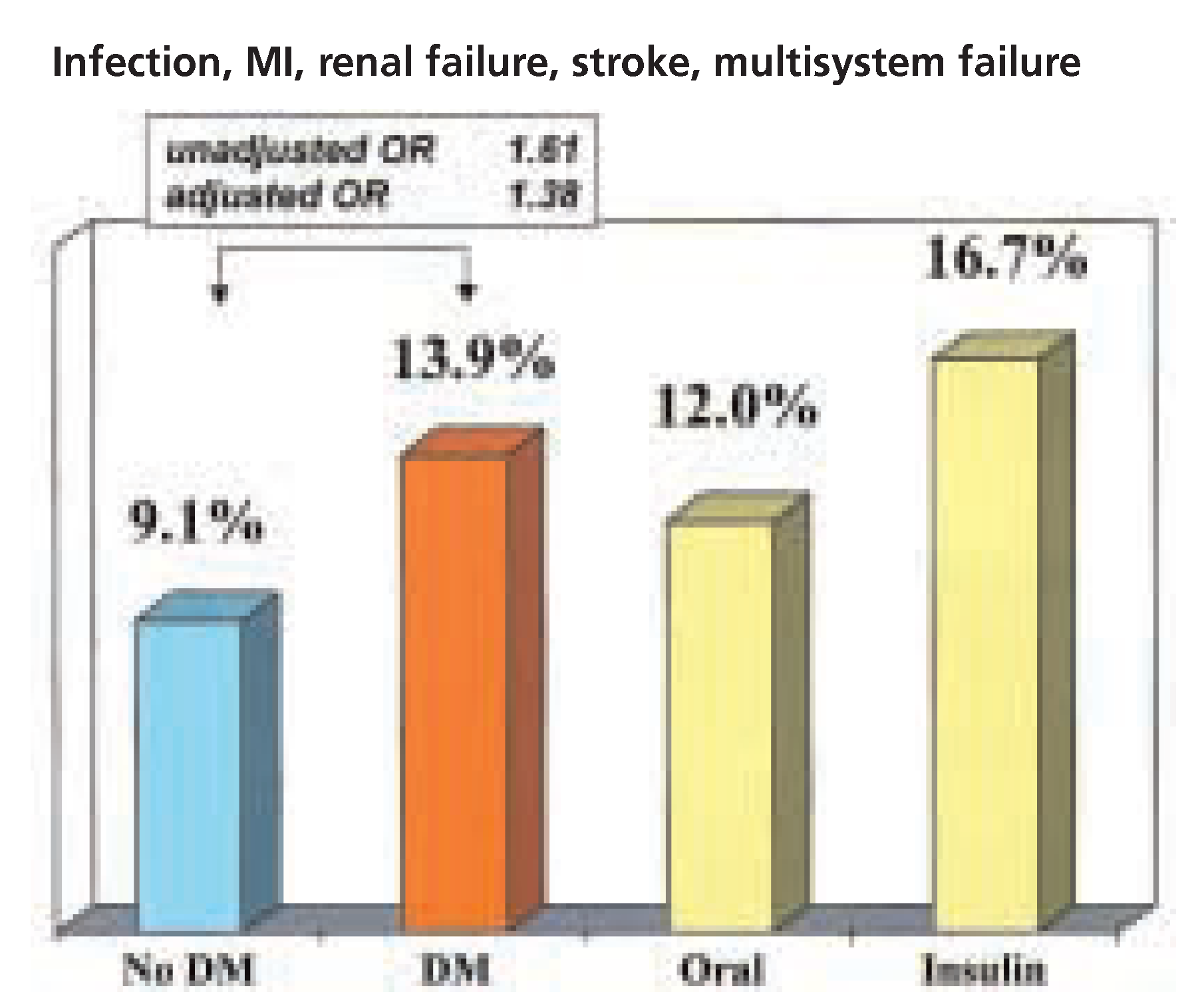
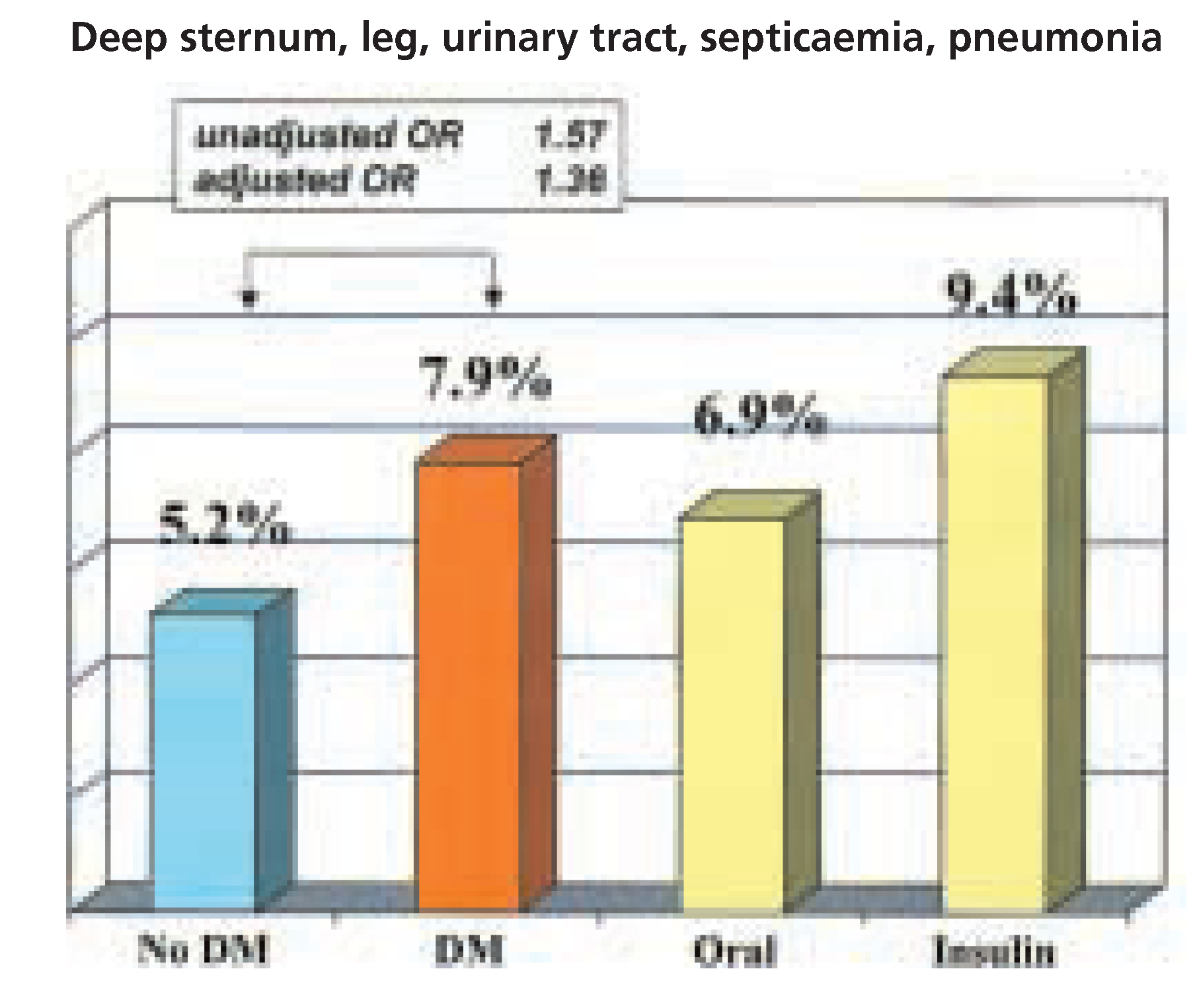
Postoperative care and long-term follow-up
Conclusions
References
- Serruys, P.W.; Unger, F.; Sousa, J.E.D.; et al. Comparison of coronary artery bypass surgery and stenting for the treatment of multivessel disease. N Engl J Med 2001, 344, 1117–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Bypass Angioplasty Revascularization Investigation (BARI) Investigators. Comparison of bypass surgery with angioplasty in patients with multivessel disease. N Engl J Med 1996, 335, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morice, M.C.; Serruys, P.W.; Sousa, J.E.D.; et al. for the RAVEL study group. A randomized comparison of sirolimus-eluting stent with a standard stent for coronary revascularization. N Engl J Med 2002, 346, 1773–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regar, E.; Morice, M.C.; Sousa, J.E.D.; et al. Can sirolimuseluting stents prevent restenosis in diabetic patients? A subanalysis of the randomized multicenter RAVEL trial. Eur Heart J 2002, 23 (Suppl. S142), 4. [Google Scholar]
- Stamler, J.; Vaccaro, O.; Neaton, J.D.; Wentworth, D. Diabetes, other risk factors and 12-year cardiovascular mortality for men screened in the multiple risk factor intervention trial. Diabetes Care 1993, 16, 434–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, L.P.; Liu, K.; Greenland, O.; Metzger, B.E.; Dyer, A.R.; Stamler, J. Diabetes, asymptomatic hyperglycemia and 22-year mortality in black and white men. Diabetes Care 1997, 20, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, M.I.; Hadden, W.C.; Knowler, W.E.; Bennet, P.H. Prevalence of diabetes and impaired glucose tolerance and plasma glucose levels in US population aged 20–74 years. Diabetes 1987, 36, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, Y.; Raz, I.; Merin, G.; Mozes, B. Comparison of factors associated with 30-day mortality after coronary artery bypass grafting in patients with versus without diabetes mellitus. Am J Cardiol 1998, 81, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, J.J.; Smith, L.R.; Jones, R.H.; et al. Influence of diabetes and mammary artery grafting on survival after coronary bypass. Circulation 1991, 84, 275–284. [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub, W.S.; Wenger, N.K.; Jones, E.L.; Craver, J.M.; Guyton, R.A. Changing clinical characteristics of coronary artery surgery patients. Differences between men and women. Circulation 1993, 88, 79–86. [Google Scholar]
- Jacoby, R.M.; Nesto, R.W. Acute myocardial infarction in the diabetic patient: pathophysiology, clinical course and prognosis. J Am Coll Cardiol 1992, 20, 736–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlson, B.W.; Herlitz, J.; Hjalmarson, A. Prognosis of acute myocardial infarction in diabetic and non-diabetic patients. Diabetes Med 1993, 10, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarich, S.; Waxman, S.; Freeman, R.T.; Mittleman, M.; Hegarty, P.; Nesto, R.W. Effect of autonomic nervous system dysfunction on the circadian pattern of myocardial ischemia in diabetes mellitus. J Am Coll Cardiol 1994, 24, 956–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasher, P.J.; Brown, R.E.; Oskarsoson, H.; Winniford, M.D.; Rossen, J.D. Maximal coronary flow reserve and metabolic coronary vasodilatation in patients with diabetes mellitus. Circulation 1995, 91, 635–640. [Google Scholar]
- Nitenberg, A.; Valensi, P.; Sachs, R.; Dali, M.; Aptecar, E.; Attali, J.R. Impairment of coronary vascular reserve and Ach-induced coronary vasodilatation in diabetic patients with angiographically normal coronary arteries and normal left ventricular systolic function. Diabetes 1993, 42, 1017–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayan, H.G. Impairment of endothelium-dependent dilatation of cerebral arterioles during diabetes mellitus. Am J Physiol 1989, 256, 621–625. [Google Scholar]
- Huszka, M.; Kaplar, M.; Rejto, L.; et al. The association of reduced endothelium-derived relaxing factor-NO production with endothelial damage and increased in-vivo platelet activation in patients with diabetes mellitus. Thromb Res 1997, 86, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diederich, D.; Skopec, J.; Diederich, A.; Dai, F.X. Endothelial dysfunction in mesenteric resistance arteries of diabetic rats: role of free radicals. Am J Physiol 1994, 266, 1153–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesfamarian, B.; Jakubowski, J.A.; Cohen, R.A. Contraction of diabetic rabbit aorta caused by endothelium-derived PGH2TXA2. Am J Physiol 1989, 257, 1327–1333. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, T.S.; McGregor, L.C.; Fluharty, S.J.; King, G.L. Differential regulation of protein kinase C and (Na,K)-adenosine triphosphatase activities by elevated glucose levels in retinal capillary endothelial cells. J Clin Invest 1989, 83, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawler, D.; Milligan, G.; Spiegel, A.M.; Unson, C.G.; Houslay, M.D. Abolition of the expression of inhibitory guanine necleotide regulatory protein G1 activity in diabetes. Nature 1987, 327, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abaci, A.; Oguzhan, A.; Kahraman, S.; et al. Effect of diabetes on formation of coronary collateral vessels. Circulation 1999, 99, 2239–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Bypass Angioplasty Revascularization Investigation (BARI) Investigators. Influence of diabetes on 5-year mortality and morbidity in a randomized trial comparing CABG and PTCA in patients with multivessel disease: the Bypass Angioplasty Revascularization Investigation. Circulation 1997, 96, 1761–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abizaid, A.; Kornowski, R.; Mintz, G.; et al. The influence of diabetes mellitus on acute and late clinical outcomes following coronary stent implantation. J Am Coll Cardiol 1998, 32, 584–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, B.; Weintraub, W.S.; Gebhart, S.; et al. Influence of diabetes mellitus on early and late outcome after percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty. Circulation 1995, 91, 979–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thourani, V.H.; Weintraub, W.S.; Stein, B.; et al. Influence of diabetes mellitus on early and late outcome after coronary artery bypass grafting. Ann Thorac Surg 1999, 67, 1045–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brener, S.J.; Lytle, B.W.; Casserly, I.P.; et al. Propensity analysis of long-term survival after surgical or percutaneous revascularization in patients with multivessel coronary artery disease and high-risk features. Circulation 2004, 109, 2290–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, M.M.; Jones, R.H.; Bach, R.G.; et al. Predictors of mortality and morbidity from cardiac causes in the Bypass Angioplasty Revascularization Investigation (BARI) randomized trial and registry. Circulation 2000, 101, 2682–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Bypass Angioplasty Revascularization Investigation (BARI) Investigators. Seven-year outcome in the Bypass Angioplasty Revascularization Investigation (BARI) by treatment and diabetic status. J Am Coll Cardiol 2000, 35, 1130–1133. [Google Scholar]
- Abizaid, A.; Costa, M.A.; Centemero, M.; et al. Clinical and economic impact of diabetes mellitus on percutaneous and surgical treatment of multivessel coronary disease patients. Insights from the Arterial Revascularization Therapy Study (ARTS) trial. Circulation 2001, 104, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marso, S.P.; Lincoff, A.M.; Ellis, S.G.; et al. for the EPISTENT investigators. Optimizing the percutaneous interventional outcomes for patients with diabetes mellitus. Results of the EPISTENT diabetic substudy. Circulation 1999, 100, 2477–2484. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kuntz, R.E. Importance of considering atherosclerosis progression when choosing a coronary revascularization strategy: the diabetes-percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty dilemma. Circulation 1999, 99, 847–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carson, J.L.; Scholz, P.M.; Chen, A.Y.; Peterson, E.D.; Gold, J.; Schneider, S.H. Diabetes mellitus increases short-term mortality and morbidity in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass graft surgery. J Am Coll Cardiol 2002, 40, 418–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprecher, D.L.; Pearce, G.L. How deadly is the “deadly quartett”? A post-CABG evaluation. J Am Coll Cardiol 2000, 36, 1159–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lytle, B.W.; Blackstone, E.H.; Sabik, J.F.; Houghtaling, P.; Loop, F.D.; Cosgroive, D.M. The effects of bilateral internal thoracic artery grafting on survival during 20 postoperative years. Ann Thorac Surg 2004, 78, 2005–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detre, K.M.; Lombardero, M.S.; Brooks, M.M.; et al. The effect of previous coronary artery bypass surgery on the prognosis of patients with diabetes mellitus who have acute myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med 2000, 342, 989–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossi, E.A.; Esposito, R.; Harris, L.J.; et al. Sternal wound infections and use of internal mammary artery grafts. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1991, 102, 342–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.W.; Ryan, W.H.; Acuff, T.E.; et al. Risk factors for operative mortality and sternal wound infection in bilateral mammary artery grafting. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1994, 107, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calafiore, A.M.; Vitolla, G.; Iaco, A.L.; et al. Bilateral internal mammary artery grafting: midterm results of pedicled versus skeletonized conduits. Ann Thorac Surg 1999, 67, 1637–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borger, M.A.; Cohen, G.; Buth, K.J.; et al. Multiple arterial grafts. Radial versus right internal thoracic arteries. Circulation 1999, 98, 117–123. [Google Scholar]
- Roach, G.W.; Kanchuger, M.; Magano, C.M.; et al. Adverse cerebral outcome after coronary bypass surgery. N Engl J Med 1996, 335, 1857–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, M.F.; Wolman, R.; Kanchuger, M.; et al. Multicenter preoperative stroke risk index for patients undergoing coronary artery bypass graft surgery. Multicenter Study of Perioperative Ischemia (McSPI) Research Group. Circulation 1996, 94, II74–II80. [Google Scholar]
- Mangos, G.J.; Brown, M.A.; Chan, W.Y.; Horton, D.; Trew, P.; Withworth, J.A. Acute renal failure following cardiac surgery: incidence, outcome and risk factors. Aust N Z J Med 1995, 25, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furnary, A.P.; Zehr, K.J.; Grunkemeier, G.L.; Starr, A. Continuous intravenous insulin infusion reduces the incidence of deep sternal wound infection in diabetic patients after cardiac surgical procedures. Ann Thorac Surg 1999, 67, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauruschkat, A.H.; Ennker, J. Diabetes mellitus in coronary artery surgery. Therapeutic strategies in the light of recent studies. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2004, 52, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedlis, S.P.; Morrison, D.A.; Lorin, J.D.; et al. Percutaneous coronary intervention versus coronary artery bypass graft for diabetic patients with unstable angina and risk factors for adverse outcome with bypass: outcome of diabetic patients in the AWESOME randomized trial and registry. J Am Coll Cardiol 2002, 40, 1555–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Brandt, M.J.; Rensing, B.J.; Morel, M.A.; et al. The effect of completness on event-free survival at one year in the ARTS trial. J Am Coll Cardiol 2002, 39, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, S.N.; TenBrook, J.A.; Wolf, M.P.; Pauker, S.G.; Salem, D.N.; Wong, J.B. A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials comparing coronary artery bypass graft with percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty: one- to eight-year outcomes. J Am Coll Cardiol 2003, 41, 1293–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feit, F.; Brooks, M.M.; Sopko, G.; Keller, N.M.; Rosen, A.; Krone, R.; et al. Long-term clinical outcome in the Bypass Angioplasty Revascularization Investigation Registry: comparison with the randomized trial. BARI Investigators. Circulation. 2000, 101, 2795–2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheridan, P.; Crossman, D. Coronary revascularization: chronic stable angina. In The Evidence for Cardiothoracic Surgery; Treasure, T., Hunt, I., Keogh, B., Pagano, D., Eds.; Tfm Publishing ltd: Shrewsbury, 2005; pp. 165–178. [Google Scholar]
- Roffi, M.; Moliterno, D.J.; Meier, B.; Powers, E.R.; Grines, C.L.; Di Battiste, P.M.; et al. Impact of different platelet glycoprotein Iib/IIIa receptor inhibitors among diabetic patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention: do Tirofibran and ReoPro give similar efficacy outcomes trial (TARGET) 1-year follow-up. Circulation 2002, 105, 2730–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
 |
© 2005 by the author. Attribution - Non-Commercial - NoDerivatives 4.0.
Share and Cite
Carrel, T.; Englberger, L. Coronary Revascularisation in Diabetics: Surgical Aspects. Cardiovasc. Med. 2005, 8, 172. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2005.01100
Carrel T, Englberger L. Coronary Revascularisation in Diabetics: Surgical Aspects. Cardiovascular Medicine. 2005; 8(5):172. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2005.01100
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarrel, Thierry, and Lars Englberger. 2005. "Coronary Revascularisation in Diabetics: Surgical Aspects" Cardiovascular Medicine 8, no. 5: 172. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2005.01100
APA StyleCarrel, T., & Englberger, L. (2005). Coronary Revascularisation in Diabetics: Surgical Aspects. Cardiovascular Medicine, 8(5), 172. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2005.01100




