Pathophysiological background
Introduction
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common sustained arrhythmia in adults affecting about 6% of the population over the age of 60 [1]. About 25% of ischaemic strokes result from cardiac emboli due to atrial fibrillation [2]. In addition, young patients and even teenagers may suffer from AF, which leads to exercise intolerance, palpitations and dyspnea. The pathophysiologic consequences of AF are a loss of rate adaptation, atrioventricular synchrony and irregular ventricular filling, which can cause a cardiomyopathy over time. Many theories have been proposed for the pathophysiological basis of AF [3], partly derived from computer models [4] and later demonstrated in vivo [5], involving multiple wavelets [6], rotors and a critical mass [7]. These models led to the development of the surgical MAZE operation [8]. However, this operation requires open heart surgery and did not gain widespread popularity for patients with lone atrial fibrillation. The greatest step towards a cure of AF came from an observation published by Haissaguerre et al. in their landmark publication in 1998 [9]. Paroxysmal AF turned out to be of focal origin, initiated by triggers in the pulmonary veins (PV’s), which could be successfully treated by delivery of radiofrequency energy (RF). The anatomical substrate of these triggers are PV fascicles, which are muscular sleeves extending from the left atrium (LA) around the PV’s in longitudinal and circular fashion (Figure 1) [10]. They exhibit distinct electrophysiological properties [11] allowing very rapid firing (pulmonary vein tachycardia [12]), which itself either leads to fibrillatory conduction into the LA or electrical remodelling facilitating sustained fibrillation [13]. Instead of targeting only active triggers inside the veins, the therapeutic strategy evolved to achieve a complete electrical isolation of all PV’s by means of ablation of all fascicles [14,15]. The pathophysiological basis and the evolution of current techniques are described in detail in the following section.
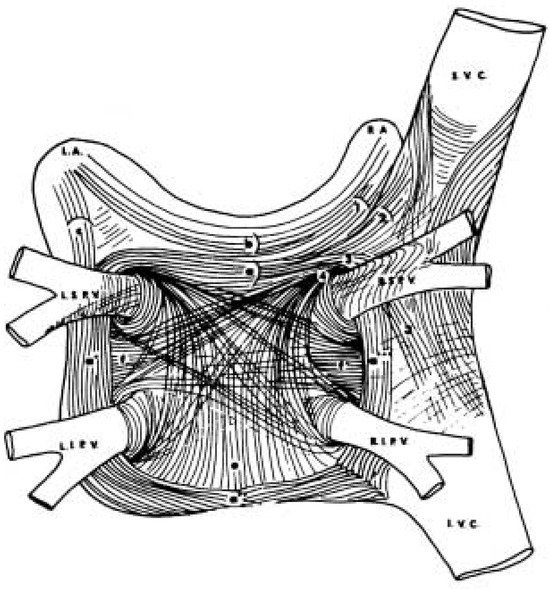
Figure 1.
Anatomy of muscle fibers in the left atrium and their extension into the pulmonary veins, where they form distinct muscular fascicles. Modified on [16].
The electrophysiology of the pulmonary veins
As opposed to smooth muscle, striated muscle in the PV’s (the same as in the atria) is known to be electrically active [17]. In the form of a muscular sleeve, this myocardium is proximally continuous with the LA and distally peters out within a couple of centimeters of the veno-atrial junction or in proximity to the first order branches. Accordingly, activation in sinus rhythm enters from the veno-atrial junction and dies out distally resembling a dead end (cul-de-sac) while during ectopy originating from a particular vein, venous activation precedes adjacent atrial activation. Changing fiber direction, fibrosis and the pathological effects of left heart disease result in delayed activation in this tissue [18]. The recent introduction of preshaped circular mapping catheters designed to sit at the ostia of the PV’s has shown that activation of the veins is asymmetrical rather than symmetrical. Specific segments of the circumference are therefore activated earlier followed by the rest of the tissue [19].
The electrophysiological properties of the PV myocardium have only recently begun to be studied. Decremental conduction in both directions has been demonstrated: From the LA to the veins as well as vice versa although the exact site of slow conduction has not yet been documented. Evidence of interconnected PV’s has recently been presented, suggesting an underlying variability that may be related to anatomy—a near common ostium or very close ostia [20]. There is evidence to suggest heterogeneity of refractoriness in the PV’s and shorter refractory periods distal to the venoatrial junction [11]. Whether this reflects accentuated electrophysiological remodeling or is a more causal element in arrhythmogenesis remains to be determined. These conditions make the veno-atrial junction a ripe substrate for reentry. Analysis of recordings from culprit PV’s during initiation of a paroxysm of AF suggest at least two distinct phases. The earliest activation is probably the result of abnormal impulse generation and repetitive activation in the same pattern can follow for a few more beats (at short intervals at about 200 ms) after which activation sequences become difficult or impossible to follow because of fractionation and continuous and / or changing activation. An intermediate phase is compatible with reentry within the PV which may then spread or move to the veno-atrial junction and then involve the LA. Non-pulmonary foci from other great veins or the atrial myocardium may play similar roles, particularly in patients with more persistent AF.
The above account describes the mechanism of AF as a reentrant maintenance mechanism coupled with a distinct initiator originating nearly always from the PV’s or their ostia. It is likely that the veno-atrial junction and the myocardium in the veins are also involved in the maintenance of AF [21].
The veno-atrial junction
Anatomically as well as histologically, the veno-atrial junction cannot be distinguished from surrounding myocardium—there is no demarcation of transition from the LA into the veins. Commonly, the change in diameter has been used to designate the veno-atrial junction.
The choice of the level of isolation of the PV myocardium has an impact on the amount of myocardium isolated from the LA and may affect success rates after catheter ablation. The level of ablation is commonly accepted to be the ostium of the PV’s, but has not been precisely defined.
Though the optimum level of PV isolation is not known, it is clear that in the presence of ectopy or nonsustained arrhythmias it should be proximal (on the LA side) to their earliest activation. In the absence of arrhythmias or with sustained AF, an arbitrary designation of the level of ablation such as diameter change has to be accepted. Some groups target the morphologic definition given above and supplement this by eliminating fractionated potentials in the vicinity. Though there is not much data available to decide the extent of isolation required, an analysis of surgical experience suggests that the best results in curing AF have been achieved using procedures which isolate all four PV’s together with a cuff of posterior LA tissue, with a fall off in cure rates when the PV’s are isolated two by two or individually [22,23].
Techniques and results of atrial fibrillation ablation
Mapping guided ablation of of the pulmonary veins
A minority of patients with AF has frequent nonsustained arrhythmias, such as isolated ectopy and runs of atrial tachycardia, which initiate short paroxysms of AF. The iterative and beat to beat reproducible activity characteristics of ectopy and atrial tachycardia allow to trace it back to its source [24]. Being typically located at or within the PV ostium, the precise site of origin can be targeted or a whole sleeve of myocardium (including the site of origin) can be isolated from the LA without having to perform detailed and delicate mapping. The latter procedure is called PV isolation. Lately, the practical difficulties of mapping the precise source within a PV have been bypassed by performing isolation of all four PV’s. This is facilitated by the fact that the myocardium within the veins serves no clinically discernible function and justified by the very frequent participation of multiple PV’s.
The asymmetrical activation of PV ostia allows sites of early activation (considered “inputs” into the PV) [19] to be preferentially targeted, eventually eliminating all PV activation distal to the level of ablation. A minority of PV’s exhibit evidence of more than two distinct zones of veno-atrial connections and in all about 50% of PV’s can be disconnected by ablation limited to half or less of their circumference, though this depends on the level of ablation (lesser ablation is required more distally—towards the lungs). This is important because the presently available technology allows the creation of larger or longer lesions only by the confluence of multiple small ones.
An alternative technique relies upon creating a circle of closely spaced ablation lesions anatomically around each PV orifice without reference to the sequence of electrical activation [25]. Specific technology permitting precise localisation of the catheter tip in 3 dimensions within the LA anatomy is required; in general more extensive and more atrial (proximal) ablations are produced compared to the electrophysiologically guided technique.
Complications of PV ablation
Thromboembolic events are common to ablation or catheter based interventions within the left heart and can be minimised by screening for pre-existing thrombi using transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) as well as proper anticoagulation before, during and after the procedure. On the other hand, PV stenosis is a complication specifically linked to ablation. As a result of their limited diameters, the tissue response to radiofrequency (RF) energy delivered on the PV wall can result in luminal encroachment with haemodynamic consequences. Segmental or unilateral pulmonary edema and even venous pulmonary infarction have been described as a result of severe PV stenosis or occlusion—frequently of more than one vein [26,27]. It’s well known, that heat fixing the coronary arteries produced an unacceptably high incidence of stenosis (restenosis, in fact), and though the venous structure is clearly distinct, experimental studies support the role of RF energy generated tissue heating being responsible for PV stenosis [28]. Serial angiographic follow-up suggests that mild to moderate (≤50%) stenosis frequently improves or disappears over a period of days. Such narrowing and subsequent improvement may reflect the impact of edema and inflammation, with more severe stenosis presumably caused by greater and irreversible tissue heating on vessel wall proteins, a “heat shrink” like effect [29]. In some cases, intermediate or long term progression of PV stenosis does occur. Higher RF power and more extensive ablation seem to favor stenosis. Distal ablation also seems to increase the risk of stenosis. One study also found a predominance of left inferior PV stenosis which may have been the result of unrecognized ablation distally within this vein [30].
In recent series, PV stenosis occurred in about 1.5% of patients [30,31], though earlier reports described a higher incidence (up to 40%). Diameter narrowing more than 50% and a mean gradient of more than 5 mm Hg may be considered significant; however it is the presence of effort dyspnea, pulmonary hypertension, haemoptysis, or symptoms at rest which should prompt consideration of relieving the stenosis. Balloon dilatation can provide some improvement, however, restenosis is likely. It is not clear whether stent implantation provides any additional benefit [31]. Surgical reimplantation of the PV’s may have to be considered in the event of restenosis or complete occlusion.
PV isolation may also create large zones of unexcitable tissue (ablated ostia) which could then serve as central obstacles for reentrant circuits. It follows, therefore, that larger obstacles favour more stable reentry by providing a longer conduction time around it; however, zones of slow conduction may stabilise even small reentrant circuits. In practice, 7–18% of patients undergoing catheter ablation for AF develop sustained monomorphic reentrant left atrial tachycardias requiring repeat ablation if other measures fail.
Results of mapping-guided PV isolation (and supplementary linear LA ablation in selected patients)
Presently, the overall results of catheter isolation of the PV’s are distinctly better for paroxysmal than for persistent or permanent AF. Surveys of various electrophysiology laboratories around the world suggest that the best results correlate with increasing experience and patient volumes. Different EP laboratories have evolved towards specific variations on the main theme of neutralizing PV arrhythmogenicity. At the University hospital in Geneva 143 patients have undergone curative catheter ablation for AF using this technique. The results of the first 83 patients who have been followed up for more than 6 months (at the time of writing) are presented below.
These patients all had AF resistant to multiple antiarrhythmic drugs. Their mean age was 55 ± 9 years, and 17 were female, 61 patients had paroxysmal and 22 had persistent or permanent AF. Only six had structural heart disease. Many patients had undergone external cardioversion and six patients had a history of an embolic cerebrovascular event.
All patients underwent isolation of all the PV’s using irrigated tip radiofrequency (RF) catheters and circumferential mapping. Supplementary ablation of the cavotricuspid isthmus was performed in patients with a history or evidence of typical atrial flutter. Patients with persistent AF or others in whom AF persisted despite successful and complete PV isolation underwent additional linear ablation (n = 21) in the LA performed as a series of lesions that joined the left PV ostia to the right PV ostia and from the left PV ostia down to the posterolateral mitral annulus. The electrophysiologic consequences of the linear lesion (the presence of complete conduction block) was assessed by double potential mapping, differential pacing as well as 3D electroanatomic mapping.
After 1.3 procedures per patient (for recurrences of AF as well as for ablation of macroreentry) and a follow-up of 15 ± 8 months (range 6–28 months), 88% of patients are in stable sinus rhythm without treatment with antiarrhythmic drugs. The mean procedure duration was 190 minutes (fluoroscopy: 57 minutes), and RF delivery time was 42 minutes. One patient developed tamponade after the procedure (drained percutaneously), another developed a reversible cerebrovascular embolic event, and 2 patients developed PV stenosis (no treatment required). The subset of patients with paroxysmal AF did better than those with persistent or permanent AF: 92% success for paroxysmal AF after 1.2 procedures per patient vs 82% for persistent AF (after 1.57 procedures per patient).
Circumferential left atrial ablation
Soon after the initial success with PV ablation, an anatomical LA ablation technique was developed [32]. Using a nonfluoroscopic navigation system (Carto®), a model of the LA is created and ablation lines drawn in circles around the PV’s [33] (Figure 2). The distance of 1–2 cm to the PV ostium should prevent post ablation PV narrowing, which can be asymptomatic and discrete, but has also been reported to be significant after ostial PV isolation [30]. In addition, the method has the advantage of including roughly 25% of LA surface within the circles thereby reducing the electric continuum of the atrial substrate [34].
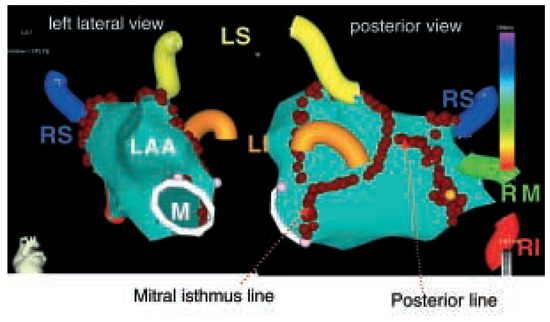
Figure 2.
Anatomical circumferential ablation around the pulmonary veins (PV’s) using a nonfluoroscopic navigation system. LS = left superior PV; RS = right superior PV; LI = left inferior PV; RI = right inferior PV; RM = right middle PV; LAA = left atrial appendage; M = mitral annulus.
To prevent potential proarrhythmic effects of the ablation circles, such as atrial flutter around the PV’s or the mitral valve, additional connecting lines are drawn along the posterior aspect of the roof and from the left inferior PV to the mitral isthmus. The success rate of this technique has been over 85% in paroxysmal AF [25] and has been shown to be superior to segmental isolation of the PV at the ostium itself in one study [35]. The greater success rate may be a result of a more extensive modification of the LA substrate [34] and incorporation of triggers outside the PV ostium into the ablation circles [36]. It should be kept in mind, however, that ablation procedures in the LA are an invasive therapy with potentially deleterious complications such as cardiac tamponade, stroke or even oesophageal fistula, which have been reported in 2 patients [37]. Therefore, the maximum power delivery at the posterior LA wall has to be reduced. The risk of thromboembolic events can be kept at an acceptable level (<1%) by full anticoagulation during and after the intervention. After all, as in all invasive procedures, complication rates depend on operator’s experience.
Results of circumferential left atrial ablation
At the University hospital in Zurich over 30 patients have been treated with circumferential left atrial ablation for AF since september 2003. Patients with paroxysmal (n = 17) as well as persistent AF (n = 13) and patients with structural heart disease (coronary artery disease [CAD, n = 2], restrictive cardiomyopathy [n = 1] and tachycardiomyopathy with ejection fraction ≤40% [n = 4]) were treated. The mean age was 55 ± 11 years (range 39–78). The mean total procedure time has been 2.5 ± 0.6 hours with a total fluoroscopy time of 20 ± 9 min. There were no procedure related complications. Follow-up over 3 months is available for 20 patients with a success rate of 77% in persistent and 85% in paroxysmal AF. Patients with symptomatic recurrence of AF undergo a redo procedure aimed at residual foci with use of Lasso technique. Residual triggers generating AF have been ablated at the PV ostia, at the mitral annulus and in the right atrium at the crista terminalis and in the superior vena cava.
Combined approaches
Generally, it can be said that techniques for AF ablation are increasingly merging towards a similar approach: the results of pulmonary vein ablation have been enhanced by linear ablations in the left atrium, between the veins and to the mitral annulus using the Carto® system [38]. Likewise, if the circumferential left atrial ablation does not eliminate all triggers of AF, an additional specific ablation for remaining fascicles using the Lasso technique (PV isolation) can be very effective to enhance the treatment success. A combination of different techniques specifically tailored to the different causes of AF in the individual patient may be the best way to cure this heterogeneous arrhythmia.
A combined approach has been used in Berne since 2001. To date, 45 patients have undergone curative catheter ablation of AF. In all patients, AF was highly symptomatic and in all but two patients resistant to multiple antiarrhythmic drug therapies. The patients mean age was 55.7 ± 9 (range 29–73) years. AF was paroxysmal in 33 patients (76%), persistent in 7 patients (15%) and permanent in 4 patients (9%). In all patients, TEE was performed immediately prior to ablation to rule out preexisting LA thrombus. Cavotricuspid ablation was done only in patients with documented typical atrial flutter. All patients were kept on anticoagulant therapy for at least 3 months after the procedure.
PV isolation was done in 33 patients and linear ablation with a nonfluoroscopic mapping system (Carto®) in 12 patients. In one patient, TEE prior to ablation detected a LA thrombus in the appendage despite correct therapeutic anticoagulant therapy. Catheter ablation was successfully done after 3 additional months of anticoagulation and exclusion of a LA thrombus by TEE. Over all, the success rate is 62% (34 out of 45 patients) with the longest freedom of AF for 41 months. One patient with very frequent paroxysms of AF and a history of recurrent syncope (documented sinus arrests lasting 5–22 seconds after spontaneous conversion of paroxysmal AF without any antiarrhythmic drug therapy) was withheld from pacemaker therapy, and ablated curatively, instead. After ablation, sinus node function improved dramatically. Another patient had been referred for AV-node ablation and pacing because of AF induced tachycardiomyopathy. He improved and returned to work after ablation of permanent AF. One patient experienced cardiac tamponade which could be successfully drained. In one patient, asymptomatic PV stenosis of less than 50% of diameter was found. We are not aware of any other procedure related complications.
Indications for radiofrequency ablation of atrial fibrillation
Currently accepted indications (demonstrated benefit in recent studies)
- -
- paroxysmal or persistent AF with symptoms (palpitations, fatigue, dyspnea, malaise) despite antiarrhythmic medication [14,15,39]
- -
- persistent or paroxysmal AF associated with heart failure [40], especially in patients with poor rate control or side effects on medication (i.e., hypotension)
- -
- patients with immediate recurrence of AF (IRAF) after cardioversion (indicates active triggers in the PV’s [41])
- -
- note: presence of structural heart disease such as CAD, hypertension, dilative cardiomyopathy or moderate LA dilatation does not preclude ablation of AF anymore [39,40]
Possible indications (risk/benefit ratio of ablation has to be weighted individually, no studies available yet)
- -
- paroxysmal AF in physically active or young patients who do not want to take medications (especially vagotonic AF with sinus bradycardia)
- -
- persistent AF in young patients
- -
- patients with severe dilatation of the LA
No indication
- -
- patients with AF caused by reversible diseases such as hyperthyroidism, pericarditis, postoperative AF or related to exacerbation of congestive heart failure
- -
- patients with significant mitral valve disease with indication for cardiac surgery (intraoperative ablation or MAZE should be considered)
- -
- patients with advanced age and indication for cardiac pacemaker (AV block); in these patients AV-nodal ablation would be a suitable alternative
Contra-indications for catheter-based ablation of atrial fibrillation
- -
- inability to tolerate intraand postprocedural anticoagulation
- -
- thrombus in the LA (at least 3 weeks anticoagulation and repeated TEE required)
- -
- inadequate anticoagulation in the last 3 weeks in persistent AF (in this case a thrombus has to be ruled out by TEE)
- -
- inability to perform transseptal puncture (i.e., closure device for patent foramen ovale)
- -
- pregnancy
- -
- contra-indications for venous access from the groin (current venous thrombosis, Greenfield filter, infections)
Management after the ablation procedure
Antiarrhythmic treatment and evaluation of success
During the past years, it has become apparent that the treatment effect of AF ablation can be delayed for several months (3 up to 12 months [34]). This implies that during the first months after ablation, recurrence of AF is common and not an indicator of poor long-term success [42]. This may be due to the reversal process of electrical and anatomical remodelling, decrease of LA size [30] and scarring effects of RF lesions. On the other hand, recurrence of conduction into previously isolated PV’s has been demonstrated in a considerable proportion of patients [43]. Therefore, the interpretation of the evolution since the procedure is critical to assess treatment success: A decrease in AF burden might indicate a delayed success whereas an increase might indicate recurrence of conduction. In order to facilitate the reversal of electric remodelling the continuation of a previously well tolerated antiarrhythmic is prescribed by some groups. Once the postinterventional period is over and the patient is weaned from antiarrhythmics, a longer ECG recording, preferably with an event recorder might be performed in order to detect episodes of silent AF. After extensive LA ablation and denervation, AF sometimes becomes asymptomatic though still present, which has important implications for anticoagulation.
Anticoagulation
During and after the procedure patients should be fully anticoagulated and given low molecular heparin until a therapeutic level of anticoagulation (INR >2) is reached. The latter has eliminated the occurrence of transient or persistent ischaemic cerebrovascular events in a cohort of patients [15,44] which result from the extensive surface of ablated tissue in contact with the systemic circulation. Once these lesions are endothelised and the patient is in stable sinus rhythm the question arises when to stop anticoagulation. For many patients the goal of the ablation procedure has also been to eliminate the need for long-term anticoagulation. Unfortunately, no prospective data have been published regarding this issue. Current practice is to continue anticoagulation for 3 to 6 months and then switch to aspirin in the absence of additional risk factors (hypertension, history of stroke, severe LA dilatation, age over 70). In the presence of risk factors, anticoagulation might only be stopped if evidence of effective atrial contraction is available on echocardiogram. As some patients might have recurrence of any other forms of atrial arrhythmias the continuation of aspirin is strongly recommended in all patients. It has to be emphasized that there is no gold-standard to assess freedom of AF. Numerous AF studies indicate that the incidence of “silent” episodes is up to 70% [45]. This might be one reason for an increased rate of stroke despite antiarrhythmic medication in recent multicenter trials [46,47]. On the other hand, the patients with symptomatic AF referred for ablation are usually very sensitive to their rhythm and silent AF has been found in only 2% after PV isolation [48]. Generally, patients should be treated according to the guidelines of the American and European Heart Associations [49,50].
Suggested follow-up after ablation of atrial fibrillation
The following suggestions are based on current practice. They vary from patient to patient and between centers.
Anticoagulation
- -
- keep anticoagulation therapeutic (INR >2) for at least 3 months in all patients
- -
- after 3 to 6 months an individualized approach depending on patient’s risk of stroke is recommended:
- -
- Low risk patients can be switched to aspirin if stable sinus rhythm is documented for one week on an event recorder or the patient can reliably tell the difference between sinus rhythm and AF and does not report any such symptoms.
- -
- Intermediate risk patients should be anticoagulated for at least 6 months. If stable sinus rhythm is documented on a seven-day event recorder and evidence of atrial contraction is present on echocardiogram, these patients may be switched to aspirin, but no prospective data have been published for these patients.
- -
- High risk patients should be kept on anticoagulation. It should be kept in mind that the ablation procedure has not been shown to prevent embolic events. Anticoagulation should be continued if a patient has silent (asymptomatic) AF.
The risk stratification for development of cardiac emboli due to AF after ablation is based on the guidelines for treatment of AF [49]:
Low risk: lone intermittent AF, age below 60, no hypertension, no diabetes, a normal atrial size, no history of an embolic event.
Intermediate risk: persistent AF, age below 60, normal sized atria.
High risk: enlarged atria, previous embolic event (ie transient ischaemic attack), persistent or silent AF, age over 60, hypertension or diabetes.
Antiarrhythmic drugs
In order to facilitate reversal of electric remodelling, previous effective antiarrhythmics have been advised for 1–2 months after the ablation procedure, perhaps depending on inducibility of AF at the end of the procedure. These recommendations have to be individualised. A beta-blocker is frequently prescribed to prevent the development of a rapid ventricular response in case of atrial flutter.
References
- Feinberg, W.M.; Blackshear, J.L.; Laupacis, A.; Kronmal, R.; Hart, R.G. Prevalence, age distribution, and gender of patients with atrial fibrillation. Analysis and implications. Arch Intern Med 1995, 155, 469–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, P.A.; Abbott, R.D.; Kannel, W.B. Atrial fibrillation as an independent risk factor for stroke: the Framingham Study. Stroke 1991, 22, 983–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquemet, V.; Virag, N.; Ihara, Z.; Dang, L.; Blanc, O.; Zozor, S.; et al. Study of unipolar electrogram morphology in a computer model of atrial fibrillation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 2003, 14, S172–S179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moe, G.K.; Rheinboldt, W.C.; Abildskov, J.A. A computer model of atrial fibrillation. Am Heart J 1964, 67, 200–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchhof, C.; Chorro, F.; Scheffer, G.J.; Brugada, J.; Konings, K.; Zetelaki, Z.; et al. Regional entrainment of atrial fibrillation studied by high-resolution mapping in open-chest dogs. Circulation 1993, 88, 736–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moe, G.K.A.J. Atrial fibrillation as a self sustaining arrhythmia independent of focal discharge. Am Heart Journal 1959, 59, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalife, J.; Berenfeld, O.; Mansour, M. Mother rotors and fibrillatory conduction: a mechanism of atrial fibrillation. Cardiovasc Res 2002, 54, 204–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, J.L.; Schuessler, R.B.; Boineau, J.P. The development of the Maze procedure for the treatment of atrial fibrillation. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2000, 12, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haissaguerre, M.; Jais, P.; Shah, D.C.; Takahashi, A.; Hocini, M.; Quiniou, G.; et al. Spontaneous initiation of atrial fibrillation by ectopic beats originating in the pulmonary veins. N Engl J Med 1998, 339, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.Y.; Cabrera, J.A.; Tran, V.H.; Farre, J.; Anderson, R.H.; Sanchez-Quintana, D. Architecture of the pulmonary veins: relevance to radiofrequency ablation. Heart 2001, 86, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jais, P.; Hocini, M.; Macle, L.; Choi, K.J.; Deisenhofer, I.; Weerasooriya, R.; et al. Distinctive electrophysiological properties of pulmonary veins in patients with atrial fibrillation. Circulation 2002, 106, 2479–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tada, H.; Ozaydin, M.; Oral, H.; Knight, B.P.; Chugh, A.; Scharf, C.; et al. Characteristics of rapid rhythms recorded within pulmonary veins during atrial fibrillation. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 2003, 26, 1342–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daoud, E.G.; Bogun, F.; Goyal, R.; Harvey, M.; Man, K.C.; Strickberger, S.A.; et al. Effect of atrial fibrillation on atrial refractoriness in humans. Circulation 1996, 94, 1600–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haissaguerre, M.; Jais, P.; Shah, D.C.; Garrigue, S.; Takahashi, A.; Lavergne, T.; et al. Electrophysiological end point for catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation initiated from multiple pulmonary venous foci. Circulation 2000, 101, 1409–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oral, H.; Knight, B.P.; Tada, H.; Ozaydin, M.; Chugh, A.; Hassan, S.; et al. Pulmonary vein isolation for paroxysmal and persistent atrial fibrillation. Circulation 2002, 105, 1077–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, H.; Eliakim, M. The junction between the left atrium and the pulmonary veins. An anatomic study of human hearts. Circulation 1966, 34, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Almeida, O.P.; Bohm, G.M.; Carvalho, M.P.; De Carvalho, A.P. The cardiac muscle in the pulmonary vein of the rat: a morphological and electrophysiological study. J Morph 1975, 145, 409–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hocini, M.; Ho, S.Y.; Kawara, T.; Linnenbank, A.C.; Potse, M.; Shah, D.; et al. Electrical conduction in canine pulmonary veins: electrophysiological and anatomic correlation. Circulation 2002, 105, 2442–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haissaguerre, M.; Shah, D.C.; Jais, P.; Hocini, M.; Yamane, T.; Deisenhofer, I.; et al. Electrophysiological breakthroughs from the left atrium to the pulmonary veins. Circulation 2000, 102, 2463–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, A.; Iesaka, Y.; Takahashi, Y.; Takahashi, R.; Kobayashi, K.; Takagi, K.; et al. Electrical connections between pulmonary veins: implication for ostial ablation of pulmonary veins in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Circulation 2002, 105, 2998–3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, D.C.; Haissaguerre, M.; Jais, P. Toward a mechanismbased understanding of atrial fibrillation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 2001, 12, 600–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sueda, T.; Nagata, H.; Orihashi, K.; Morita, S.; Okada, K.; Sueshiro, M.; et al. Efficacy of a simple left atrial procedure for chronic atrial fibrillation in mitral valve operations. Ann Thorac Surg 1997, 63, 1070–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, J.Q.; Neves, J.; Adragao, P.; Ribeiras, R.; Ferreira, M.M.; Bruges, L.; et al. When and how to report results of surgery on atrial fibrillation. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 1997, 12, 739–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jais, P.; Haissaguerre, M.; Shah, D.C.; Chouairi, S.; Gencel, L.; Hocini, M.; et al. A focal source of atrial fibrillation treated by discrete radiofrequency ablation. Circulation 1997, 95, 572–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappone, C.; Oreto, G.; Rosanio, S.; Vicedomini, G.; Tocchi, M.; Gugliotta, F.; et al. Atrial electroanatomic remodeling after circumferential radiofrequency pulmonary vein ablation: efficacy of an anatomic approach in a large cohort of patients with atrial fibrillation. Circulation 2001, 104, 2539–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbins, I.M.; Colvin, E.V.; Doyle, T.P.; Kemp, W.E.; Loyd, J.E.; McMahon, W.S.; et al. Pulmonary vein stenosis after catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. Circulation 1998, 98, 1769–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravenel, J.G.; McAdams, H.P. Pulmonary venous infarction after radiofrequency ablation for atrial fibrillation. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2002, 178, 664–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G.W.; Kay, G.N.; Zheng, X.; Bishop, S.; Ideker, R.E. Pathological effects of extensive radiofrequency energy applications in the pulmonary veins in dogs. Circulation 2000, 101, 1736–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kok, L.C.; Everett THt Akar, J.G.; Haines, D.E. Effect of heating on pulmonary veins: how to avoid pulmonary vein stenosis. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 2003, 14, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharf, C.; Sneider, M.; Case, I.; Chugh, A.; Lai, S.W.; Pelosi FJr et, a.l. Anatomy of the pulmonary veins in patients with atrial fibrillation and effects of segmental ostial ablation analyzed by computed tomography. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 2003, 14, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, E.B.; Rossillo, A.; Saad, C.P.; Martin, D.O.; Bhargava, M.; Erciyes, D.; et al. Pulmonary vein stenosis after radiofrequency ablation of atrial fibrillation: functional characterization, evolution, and influence of the ablation strategy. Circulation 2003, 108, 3102–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappone, C.; Oreto, G.; Lamberti, F.; Vicedomini, G.; Loricchio, M.L.; Shpun, S.; et al. Catheter ablation of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation using a 3D mapping system. Circulation 1999, 100, 1203–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappone, C.; Rosanio, S.; Oreto, G.; Tocchi, M.; Gugliotta, F.; Vicedomini, G.; et al. Circumferential radiofrequency ablation of pulmonary vein ostia: a new anatomic approach for curing atrial fibrillation. Circulation 2000, 102, 2619–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kottkamp, H.; Tanner, H.; Kobza, R.; Schirdewahn, P.; Dorszewski, A.; Gerds-Li, J.H.; et al. Time courses and quantitative analysis of atrial fibrillation episode number and duration after circular plus linear left atrial lesions: trigger elimination or substrate modification: early or delayed cure? J Am Coll Cardiol 2004, 44, 869–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oral, H.; Scharf, C.; Chugh, A.; Hall, B.; Cheung, P.; Good, E.; et al. Catheter ablation for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: segmental pulmonary vein ostial ablation versus left atrial ablation. Circulation 2003, 108, 2355–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharf, C.; Oral, H.; Chugh, A.; Hall, B.; Good, E.; Cheung, P.; et al. Acute effects of left atrial radiofrequency ablation on atrial fibrillation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 2004, 15, 1515–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappone, C.; Oral, H.; Santinelli, V.; Vicedomini, G.; Lang, C.C.; Manguso, F.; et al. Atrio-esophageal fistula as a complication of percutaneous transcatheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. Circulation 2004, 109, 2724–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jais, P.; Weerasooriya, R.; Shah, D.; Raybaud, F.; Scavee, C.; Macle, L.; et al. Left atrial isthmus ablation: technique and results in patients with atrial fibrillation. Circulation 2002, 106, II–501. [Google Scholar]
- Pappone, C.; Rosanio, S.; Augello, G.; Gallus, G.; Vicedomini, G.; Mazzone, P.; et al. Mortality, morbidity, and quality of life after circumferential pulmonary vein ablation for atrial fibrillation: outcomes from a controlled nonrandomized long-term study. J Am Coll Cardiol 2003, 42, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, L.F.; Jais, P.; Sanders, P.; Garrigue, S.; Hocini, M.; Sacher, F.; et al. Catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation in congestive heart failure. N Engl J Med 2004, 351, 2373–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chugh, A.; Ozaydin, M.; Scharf, C.; Lai, S.W.; Hall, B.; Cheung, P.; et al. Mechanism of immediate recurrences of atrial fibrillation after restoration of sinus rhythm. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 2004, 27, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oral, H.; Knight, B.P.; Ozaydin, M.; Tada, H.; Chugh, A.; Hassan, S.; et al. Clinical significance of early recurrences of atrial fibrillation after pulmonary vein isolation. J Am Coll Cardiol 2002, 40, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappato, R.; Negroni, S.; Pecora, D.; Bentivegna, S.; Lupo, P.P.; Carolei, A.; et al. Prospective assessment of late conduction recurrence across radiofrequency lesions producing electrical disconnection at the pulmonary vein ostium in patients with atrial fibrillation. Circulation 2003, 108, 1599–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oral, H.; Scharf, C.; Chugh, A.; Hall, B.; Cheung, P.; Good, E.; et al. Catheter ablation for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: segmental pulmonary vein ostial ablation vs. left atrial ablation. Submitted 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetsch, T.; Bauer, P.; Engberding, R.; Koch, H.P.; Lukl, J.; Meinertz, T.; et al. Prevention of atrial fibrillation after cardioversion: results of the PAFAC trial. Eur Heart J 2004, 25, 1385–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gelder, I.C.; Hagens, V.E.; Bosker, H.A.; Kingma, J.H.; Kamp, O.; Kingma, T.; et al. A comparison of rate control and rhythm control in patients with recurrent persistent atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med 2002, 347, 1834–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyse, D.G.; Waldo, A.L.; DiMarco, J.P.; Domanski, M.J.; Rosenberg, Y.; Schron, E.B.; et al. A comparison of rate control and rhythm control in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med 2002, 347, 1825–1833. [Google Scholar]
- Oral, H.; Veerareddy, S.; Good, E.; Hall, B.; Cheung, P.; Tamirisa, K.; et al. Prevalence of asymptomatic recurrences of atrial fibrillation after successful radiofrequency catheter ablation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 2004, 15, 920–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuster, V.; Ryden, L.E.; Asinger, R.W.; Cannom, D.S.; Crijns, H.J.; Frye, R.L.; et al. ACC/AHA/ESC guidelines for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation: executive summary. A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and the European Society of Cardiology Committee for Practice Guidelines and Policy Conferences (Committee to Develop Guidelines for the Management of Patients with Atrial Fibrillation): developed in collaboration with the North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology. J Am Coll Cardiol 2001, 38, 1231–1266. [Google Scholar]
- Fuster, V.; Ryden, L.E.; Asinger, R.W.; Cannom, D.S.; Crijns, H.J.; Frye, R.L.; et al. ACC/AHA/ESC guidelines for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation: executive summary. A report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and the European Society of Cardiology Committee for Practice Guidelines and Policy Conferences (Committee to Develop Guidelines for the Management of Patients with Atrial Fibrillation): developed in collaboration with the North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology. Circulation 2001, 104, 2118–2150. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2005 by the author. Attribution - Non-Commercial - NoDerivatives 4.0.