Leadless Cardiac Stimulation: Ready to Take Centre Stage?
Abstract
Introduction
Characteristics of the Different Leadless Pacing Systems
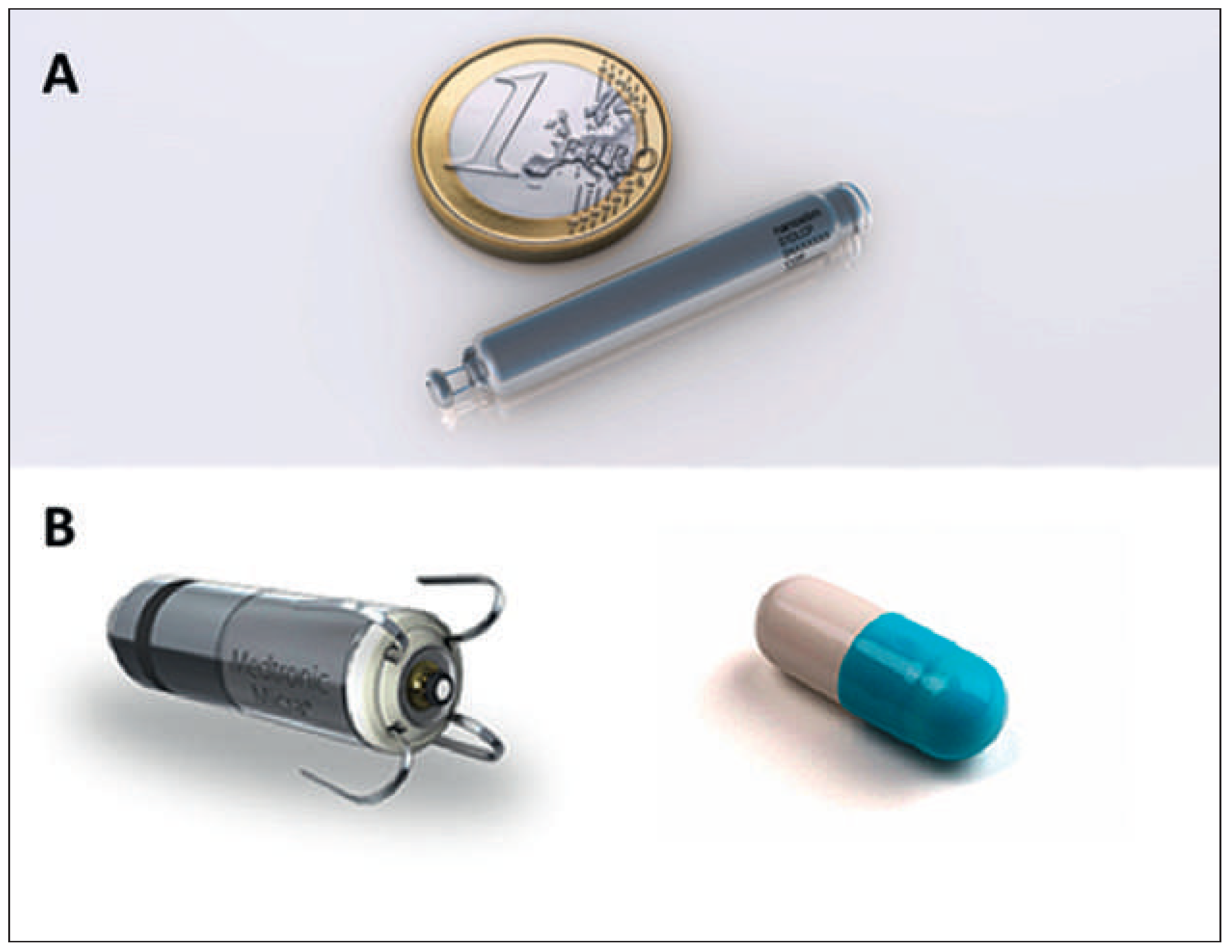
Right Ventricular Pacing Devices
Left Ventricular Pacing System
Implantation Procedures of Leadless Devices
Right Ventricular Pacing Systems
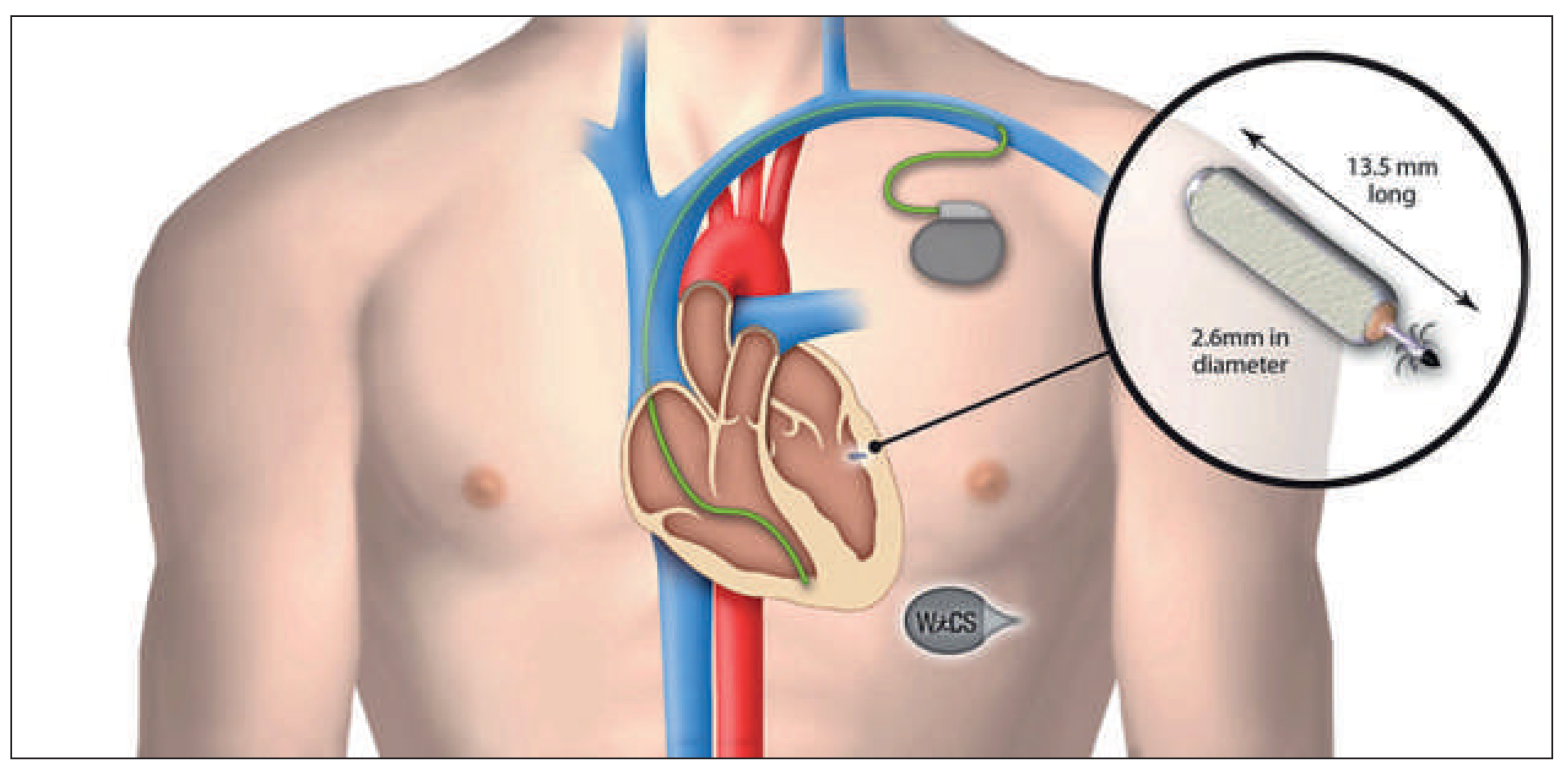
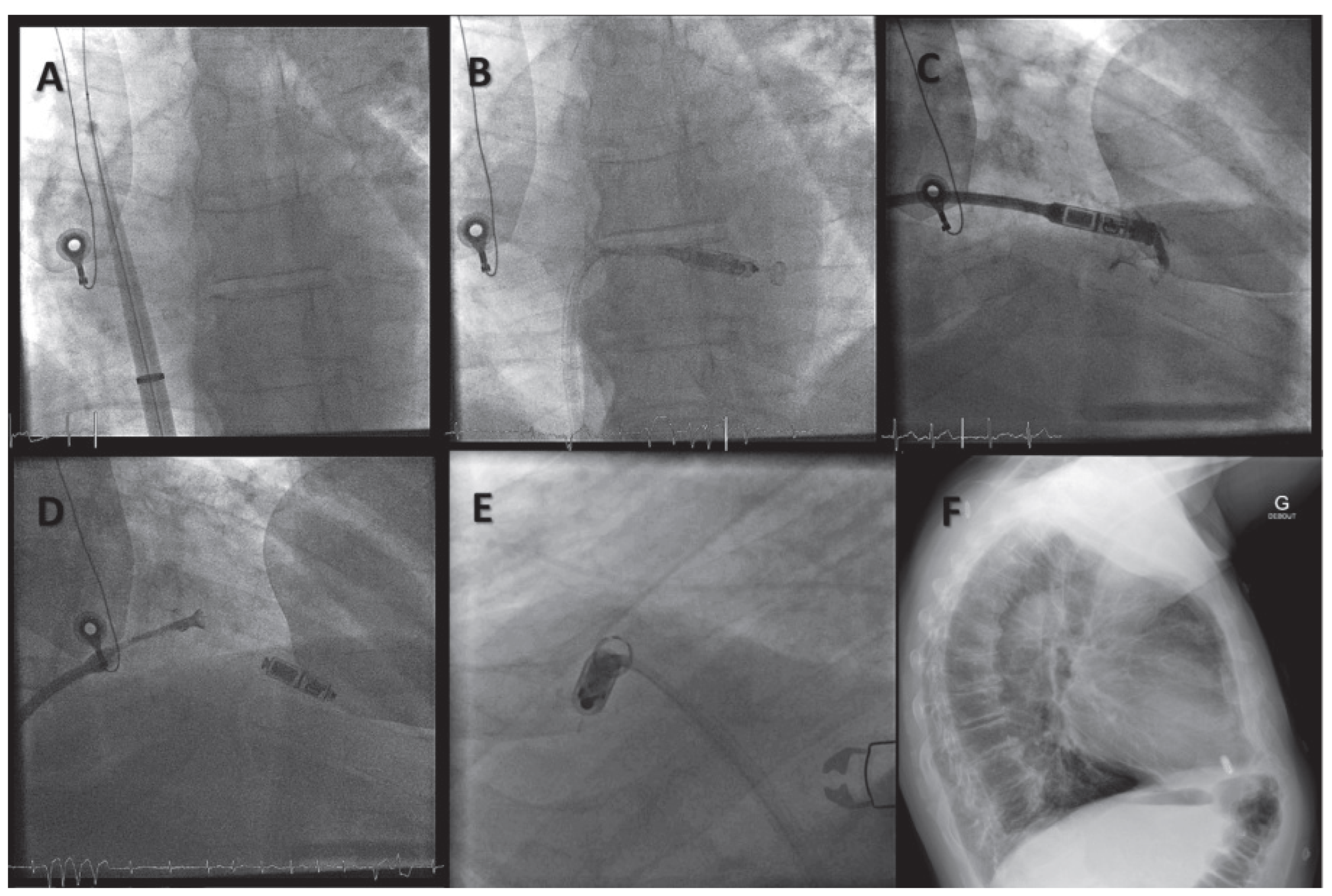
Wireless Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy System
Current Scientific Evidence Regarding Leadless Pacing Technology
Micra™ Transcatheter Pacing System
Nanostim™ Leadless Cardiac Pacemaker
Wireless Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy System
Remaining Questions
Leadless Right Ventricular Pacing
Leadless Endocardial Left Ventricular Pacing
Future Directions
Conclusions
Dislosure Statement
References
- Hyman, A. Resuscitation of the stopped heart by intracardial ther apy – II. Experimental use of an artificial pacemaker. Arch Intern Med. 1932, 50, 283–05. [Google Scholar]
- Larsson, B.; Elmqvist, H.; Ryden, L.; Schuller, H. Lessons from the first patient with an implanted pacemaker: 1958–2001. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2003, 26, 114–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furman, S.; Schwedel, J.B. An intracardiac pacemaker for Stokes Adams seizures. N Engl J Med. 1959, 261, 943–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagergren, H.; Johansson, L. Intracardiac stimulation for complete heart block. Acta Chir Scand. 1963, 125, 562–6. [Google Scholar]
- Kirkfeldt, R.E.; Johansen, J.B.; Nohr, E.A.; Jorgensen, O.D.; Nielsen, J.C. Complications aher cardiac implantable electronic device implanta tions: an analysis of a complete, nationwide cohort in Denmark. Eur Heart J. 2014, 35, 1186–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udo, E.O.; Zuithoff, N.P.; van Hemel, N.M.; de Cock, C.C.; Hendriks, T.; Doevendans, P.A.; et al. Incidence and predictors of short and long term complications in pacemaker therapy: the FOLLOWPACE study. Heart Rhythm. 2012, 9, 728–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spickler, J.W.; Rasor, N.S.; Kezdi, P.; Misra, S.N.; Robins, K.E.; LeBoeuf, C. Totally self contained intracardiac pacemaker. J Electrocardiol. 1970, 3, 325–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardas, P.P.E.; Manios, E.; Parthenakis, F.; Tsagarakis, C. A miniature pacemaker introduced intravenously and implanted endocardi ally. Preliminary findings from an experimental study. Eur J Card Pacing Electrophysiol. 1991, 1, 27–30. [Google Scholar]
- Echt, D.S.; Cowan, M.W.; Riley, R.E.; Brisken, A.F. Feasibility and safety of a novel technology for pacing without leads. Heart Rhythm. 2006, 3, 1202–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.L.; Lau, C.P.; Tse, H.F.; Echt, D.S.; Heaven, D.; Smith, W.; et al. First hu man demonstration of cardiac stimulation with transcutaneous ultrasound energy delivery: implications for wireless pacing with implantable devices. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007, 50, 877–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.L.; Tse, H.F.; Echt, D.S.; Lau, C.P. Temporary leadless pacing in heart failure patients with ultrasound mediated stimulation energy and effects on the acoustic window. Heart Rhythm. 2009, 6, 742–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieneke, H.; Konorza, T.; Erbel, R.; Kisker, E. Leadless pacing of the heart using induction technology: a feasibility study. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2009, 32, 177–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rademakers, L.M.; van Gelder, B.M.; Scheffer, M.G.; Bracke, F.A. Mid term follow up of thromboembolic complications in leh ventricular endocardial cardiac resynchronization therapy. Heart Rhythm. 2014, 11, 609–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, V.Y.; Knops, R.E.; Sperzel, J.; Miller, M.A.; Petru, J.; Simon, J.; et al. Permanent leadless cardiac pacing: results of the LEADLESS trial. Circulation. 2014, 129, 1466–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auricchio, A.; Delnoy, P.P.; Butter, C.; Brachmann, J.; Van Erven, L.; Spitzer, S.; et al. Feasibility, safety, and short term outcome of leadless ultrasound based endocardial leh ventricular resynchronization in heart failure patients: results of the wireless stimulation endo cardially for CRT (WiSE CRT) study. Europace. 2014, 16, 681–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonner, M.; Eggen, M.; Haddad, T.; Sheldon, T.; Williams, E. Early Perfor mance and Safety of the Micra Transcatheter Pacemaker in Pigs. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritter, P.; Duray, G.Z.; Steinwender, C.; Soejima, K.; Omar, R.; Mont, L.; et al. Early performance of a miniaturized leadless cardiac pacemaker: the Micra Transcatheter Pacing Study. Eur Heart J. 2015, 36, 2510–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, D.; Duray, G.Z.; Omar, R.; Soejima, K.; Neuzil, P.; Zhang, S.; et al. A Leadless Intracardiac Transcatheter Pacing System. N Engl J Med. 2015. [CrossRef]
- Mont, L.; et al. Micra Transcatheter Pacing System: early perfor mance assessment to demonstrate safety for pacemaker depend ent patients. 2015, 17 (Suppl. 3): (abstr) 1311. Europace. 2015, 17 (Suppl. 3):(abstr 1311).
- Bonner, M.; et al. Micra delivery system perforation risk assess ment. Europace. 2015, 17 (Suppl. 3), abstr 1312. [Google Scholar]
- Sperzel, J.; Burri, H.; Gras, D.; Tjong, F.V.; Knops, R.E.; Hindricks, G.; et al. State of the art of leadless pacing. Europace. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.A.; Neuzil, P.; Dukkipati, S.R.; Reddy, V.Y. Leadless Cardiac Pace makers: Back to the Future. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015, 66, 1179–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knops, R.E.; Tjong, F.V.; Neuzil, P.; Sperzel, J.; Miller, M.A.; Petru, J.; et al. Chronic performance of a leadless cardiac pacemaker: 1 year fol low up of the LEADLESS trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015, 65, 1497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, V.Y.; Exner, D.V.; Cantillon, D.J.; Doshi, R.; Bunch, T.J.; Tomassoni, G.F.; et al. Percutaneous Implantation of an Entirely Intracardiac Lead less Pacemaker. N Engl J Med. 2015, 373, 1125–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, V.Y. Wireless LV endocardial stimulation for CRT: Primary results of the Safety and Performance of Electrodes implanted in the Leh Ventricle (SELECT LV) Study. Presented at HRS 2015, Late Breaking clinical trials. 2015.
- Sperzel, J.K.A.; Ligon, D.; Zaltsberg, S. Feasibility, efficacy and safety of percutaneous retrieval of a leadless cardiac pacemaker in an in vivo bovine model. Europace. 2013, 15, 859. [Google Scholar]
- Bonner, M.N.N.; Byrd, C.; Schaerf, R.; Goode, L. Extraction of the Micra transcatheter pacemaker system (abstract). Heart Rhythm. 2014, 11, S342. [Google Scholar]
- Soejima, K. RF Heating of Micra: Can Patients with the Trans catheter Pacemaker Safely Undergo MRI? Heart Rhythm. 2015, 12, abstrAB06–5. [Google Scholar]
- Crossley, G.H.; Chen, J.; Choucair, W.; Cohen, T.J.; Gohn, D.C.; Johnson, W.B.; et al. Clinical benefits of remote versus transtelephonic monitor ing of implanted pacemakers. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009, 54, 2012–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2016 by the author. Attribution - Non-Commercial - NoDerivatives 4.0.
Share and Cite
Dayal, N.B.; Burri, H. Leadless Cardiac Stimulation: Ready to Take Centre Stage? Cardiovasc. Med. 2016, 19, 83. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2016.00397
Dayal NB, Burri H. Leadless Cardiac Stimulation: Ready to Take Centre Stage? Cardiovascular Medicine. 2016; 19(3):83. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2016.00397
Chicago/Turabian StyleDayal, Nicolas B., and Haran Burri. 2016. "Leadless Cardiac Stimulation: Ready to Take Centre Stage?" Cardiovascular Medicine 19, no. 3: 83. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2016.00397
APA StyleDayal, N. B., & Burri, H. (2016). Leadless Cardiac Stimulation: Ready to Take Centre Stage? Cardiovascular Medicine, 19(3), 83. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2016.00397



