Abstract
Mutations in proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) were first described in 2003 as a cause of autosomal dominant hypercholesterolaemia. Moreover, genetic studies have indicated that some PCSK9 loss-of-function mutations are associated with a markedly reduced risk of coronary artery disease (CAD), suggesting that PCSK9 represents a promising novel target for the prevention and management of CAD. Already, PCSK9 inhibition using monoclonal antibodies is entering the clinical management of familial hypercholesterolaemia and large-scale clinical outcome programmes have been started to evaluate the impact of PCSK9 inhibition on cardiovascular events in high-risk patients. Both the refinement of monoclonal antibody-based therapies and the identification of this novel target represent an impressive example of the rapid translation of research to prevention of coronary disease, and may allow further reduction in low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels to decrease progression or even reverse atherosclerosis.
Introduction
Dyslipidaemia and, in particular, increased low density lipoprotein-cholesterol (LDL-C) levels represent one of the most important modifiable risk factors for cardiovascular disease (CVD) [1,2].
The introduction of statin therapy for treatment of dyslipidaemia was a pivotal step for effective prevention of CVD. Statins reduce LDL-C levels and result in a significant reduction of cardiovascular events and mortality in patients with hypercholesterolaemia, coronary disease or diabetes. The meta-analysis published by the Cholesterol Treatment Trialists’ (CTT) Collaboration in 2005 analysed data from 90 056 individuals enrolled in 14 randomised trials with statins. In this prospective meta-analysis a 10% proportional reduction in all-cause mortality and a 20% proportional reduction in coronary artery disease (CAD) deaths per 1.0 mmol/l LDL-C reduction by statin therapy was observed. The risk for major coronary events was reduced by 23% and the risk for stroke was diminished by 17% per mmol/l LDL-C reduction [3]. In a further meta-analysis of 170 000 participants it was shown that highintensity statin regimens can more effectively reduce cardiovascular events as compared with low-intensity statin therapy [4].
As such the current clinical practice guidelines of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Atherosclerosis Society (EAS) recommend prescribing a statin up to the highest dose or highest tolerable dose to reach the target level for LDL-C [5].
Concerning statin therapy, two important points should be underlined: first, a substantial “residual cardiovascular risk” is observed in patients on statin treatment; second, despite treatment with statins numerous patients with a high CVD risk and around 80% of those with heterozygous familiar hypercholesterolaemia do not achieve optimal levels of LDL-C [6,7].
Excessively high basal levels of LDL-C before treatment initiation, inadequate statin dosing, adverse effects under the required dose, statin resistance, or insufficient adherence should be taken into account as possible reasons for both observations. Last but not least there is a considerable number of patients who do not tolerate statins because of side effects [8].
Therefore, additional pharmacological strategies to treat dyslipidaemia are needed. In recent years, novel genes and proteins that may be pharmacologicaly targeted to improve lipoprotein profiles have been identified in biological and large-scale genetic research. This review focuses on proprotein convertase subtilisin/ kexin type 9 (PCSK9), its role in lipid metabolism and its inhibition as a novel therapeutic approach for patients with dyslipidaemia.
Physiological role of PCSK9 in lipid homeostasis
PCSK9 belongs to the proprotein convertase family, composed of proteins that cleave protein precursors of growth factors, hormones, receptors and transmembrane transcription factors passing through the secretory pathway.
PCSK9 has the unique characteristics of enhancing both endosomal and lysosomal degradation of cell surface receptors that regulate lipid metabolism in a non-enzymatic fashion (Figure 1) [9,10]. PCSK9 binds to LDL receptors (LDL-Rs) and targets them for degradation rather than for recycling to the cell surface, thereby decreasing LDLR-mediated uptake of LDL into the liver and ultimately increasing levels of plasma LDL cholesterol.
PCSK9 is expressed mainly in the liver, small intestine, kidney and central nervous system and was first identified in cells undergoing apoptosis induced by serum deprivation and called neural apoptosis-regulated convertase 1 (NARC-1) [11]. The author noticed a co-localisation of NARC-1 (1p33–34.3) with a major locus for autosomal dominant hypercholesterolaemia located at 1p34.1–p32. As this locus is associated with an increase in the hepatic secretion of LDL-C the author supposed this protein to play a role in familial hypercholesterolaemia. At the same time, Abifadel and co-workers [12] described two mutations in the PCSK9 gene co-segregating with autosomal dominant hypercholesterolaemia in two families without mutations in the candidate genes encoding the LDL-R and apolipoprotein-B (apoB), and two years later Cohen et al. [13,14] found that PCSK9 mutations were associated with low LDL-C levels and dramatically reduced cardiovascular risk. Subsequent in-vitro and animal work revealed that the mutations with gain of function to PCSK9 cause hypercholesterolaemia, whereas mutations with loss-of-function of PCSK9 lower plasma cholesterol levels.
These findings suggested a causal role of PCSK9 gene variations in the regulation of cholesterol homeostasis and in the determination of CVD risk. Based on these interesting findings inhibition of PCSK9 was considered a promising target for the development of new treatment strategies for hypercholesterolaemia and CVD prevention.
The major part of circulating LDL-C is removed from the plasma by hepatic uptake [15]. Transmembrane LDL-Rs internalise bound LDL particles by means of endocytosis. Traditionally it was thought that after internalisation LDL particles and LDL-Rs are separated in endosomes so that LDL particles are targeted to lysosomes for degradation, whereas the LDL-R is recycled to the cell surface. Of note, the fate of the LDL-R is altered by the presence of PCSK9: upon binding of secreted extracellular PCSK9 and internalisation, the LDL-R is no longer recycled from early endosomes but targeted together with LDL particles to late endosomes and ultimately lysosomes for degradation (Figure 1). Interestingly, activation of the longevity gene Sirt1 by its activator SRT3025 provides atheroprotection in apolipoprotein E-deficient (ApoE–/–) mice by reducing hepatic PCSK9 secretion and enhancing LDL-R expression [16,17]. Moreover, human intestinal cells also expressed PCSK9, suggesting a further role for this protein in the regulation of lipid absorption [18].
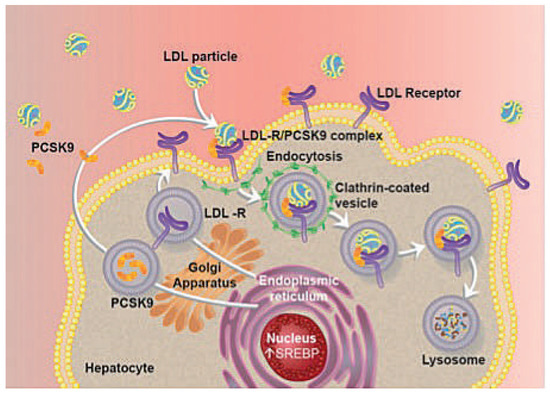
Figure 1.
The role of PCSK9 in the regulation of LDL-receptor expression. LDL = low density lipoprotein; LDL-R = low density lipoprotein receptor; PCSK9 = proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9; SREBP = sterol regulator element-binding protein.
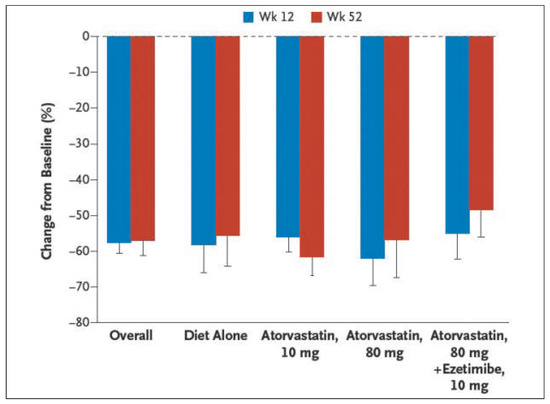
Figure 2.
Percent reduction from baseline in low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol levels in the evolocumab group, as compared with the placebo group, at week 52, according to background lipid-lowering therapy. Values are means with lower 95% confidence limits (as indicated by T bars) in the active-treatment groups after taking into account the values in the placebo group. LDL cholesterol was measured by means of ultracentrifugation separation. Modified with permission from Blom DJ, et al. N Engl J Med. 2014;370:1809-19 [37].
PCSK9 and atherosclerosis: more than just LDL increase?
A recent study by Denis et al. evaluated the effect of inactivation of PCSK9 versus its overexpression in the liver on the development of atherosclerosis in animal models such as wild type mice under high-fat high-cholesterol diet and ApoE–/– mice. The study showed that gene inactivation of PCSK9 protects wild-type and ApoE–/– from atherosclerosis, whereas PCSK9 overexpression results in stronger atherosclerotic phenotypes [17].
The possible role of PSCK9 in the development of atherosclerosis was also examined in humans. An in-vitro study by Italian researchers showed that PCSK9 is expressed in smooth muscle cells but not in endothelial cells, macrophages and monocytes. The PCSK9 secreted by vascular smooth muscle cells was found to be functionally active and able to affect LDL-R expression and function [19].
PCSK9 was also detectable in human atherosclerotic plaques, and the results of this study suggested a possible role of PCSK9 in the cholesterol uptake by macrophages in atherosclerotic plaque and potentially in the foam cell formation [19].
In human endothelial cells, oxidized LDL-induced apoptosis was associated with increased expression of PCSK9 [20].
Moreover, many other experimental studies have identified additional mechanisms by which PCSK9 might affect vascular biology such as pro-inflammatory effect, promotion of blood pressure increase, glucose intolerance and adipogenesis [21].
PCSK9 and its inhibition: preclinical data
PCSK9 knockout mice have decreased plasma cholesterol levels owing to increased LDL-R protein in the liver and statin administration to these mice lacking PCSK9 enhances LDL-C clearance from plasma [22].
The first study evaluating the impact of the absence or overexpression of PCSK9 on atherosclerosis in mouse models was performed by Denis and colleagues [17]. The results of this study nicely showed that gene inactivation of PCSK9 markedly reduced atherosclerosis in mice, by a process mediated through action on LDL-R. As previously shown by Sun et al. [23] and Levy et al. [18], Tavori and co-workers [24] confirmed that overexpression of PCSK9 increases serum LDL-C and its triglyceride-rich lipoprotein precursors, probably by increasing both the hepatic and intestinal synthesis of apoB. Moreover, the authors performed a series of elegant in-vitro and in-vivo studies in different mouse models (wild type, LDL-R knockout, human(h) PCSK9 and hLDL-R transgenic mice) aimed at better understanding of the serum levels, tissue distribution and activity of PCSK9.
Experiments in transgenic mice expressing human PCSK9 (hPCSK9) showed that endogenous mouse PCSK9 (mPCSK9) was expressed mainly in liver, small intestine and kidney [24]. Expression of hPCSK9 was highest in the kidney, LDL-R reduction was strongest in liver and kidney while no effect of hPCSK9 expression on LDL-R levels was observed in the adrenals. Human PCSK9 expression did not alter the pattern of tissue mPCSK9 and LDL-R expression. Moreover, this study showed that the clearance of serum PCSK9 is due predominantly to LDL-R-mediated uptake, that PCSK9 increases serum cholesterol levels via both LDL-R-dependent and LDL-R-independent pathways and that serum PCSK9 associates with LDL in a way that can affect peripheral or hepatic PCSK9 action.
Following these physiological studies several monoclonal antibodies neutralising PCSK9 have been tested in preclinical studies on the inhibition of the interaction between PCSK9 and LDL-R and its effect on lipids in mice and primates [25,26], as well as in diet-induced hypercholesterolaemia in monkeys [27] or the effect of the inhibition of PCSK9 internalisation [28].

Table 1.
PCSK9 Inhibitors in development.
Table 1.
PCSK9 Inhibitors in development.
| Company | Name of agent | Type of agent | Stage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sanofi/Regeneron | Alirocumab | mAb | Phase III |
| Amgen | mAb1 (AMG-145) evolocumab | mAb | Phase III |
| Pfizer | PF-04950615 (RN316) | mAb | Phase III |
| Roche/Genentech | MPSK-3169A (RG7652) | mAb | Phase II |
| Alnylam | ALN-PCS | ASO | Preclinical |
| BMS-Adnexus | PCSK9 Adnectin | Adnectin | Preclinical |
| BMS-Isis | BMS-PCSK9Rx2 | ASO | Preclinical |
| Merck | 1D05 | mAb | Preclinical |
| Nativis | PCSK9 siRNA drug signal | RNAi | Preclinical |
| Novartis | NVP-LGT209 | mAb | Terminated? |
| Santaris | SPC5001 | ASO | Terminated? |
mAb = monoclonal antibody; ASO = antisense oligonucleotide; RNAi = interfering RNA.
Inhibition of PCSK9: clinical data
Many monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) to PCSK9 have been developed for use in humans. Data been published from clinical studies with three of these mAbs only: alirocumab (SAR236553/REGN727, Sanofi/Regeneron), evolocumab (Amgen, AMG145) and in abstract form with bococizumab (RN316/PF04950615, Pfizer/ Rinat).
Phase I and II showed that therapy with alirocumab and evolocumab leads to a significant reduction in LDL-C in patients with familial hypercholesterolaemia as well as in high-risk patients and confirmed that these drugs are very well tolerated. The efficacy results of these studies are summarised in Table 2 and Table 3.

Table 2.
PHASE I Study with PCSK9 Inhibitors.

Table 3.
PHASE II Study with PCSK9 Inhibitors.
This review will focus on the published phase III studies. SAR236553/REGN727 or alirocumab is an investigational, fully human monoclonal antibody that is highly specific for human PCSK9 and blocks its interaction with the LDL-R.
The efficacy and safety of alirocumab in reducing LDL-C and cardiovascular events in patients with hypercholesterolaemia is being evaluated in the large multicenter ODYSSEY clinical trial programme (Clinical Trial.gov Identifiers NCT01663402, NCT01644175, NCT01507831, NCT01617655, NCT01709513). Exciting are the results of the ODYSSEY COMBO I and II [29,30], OPTIONS I and II [31], FH I and II and HIGH FH [32], as well as of the ODYSSEY ALTERNATIVE [33] and preliminary data from the ODYSSEY LONG TERM, which were presented at the ESC and AHA 2014 meetings and recently published [34].
The ODYSSEY COMBO I and II, the ODYSSEY Options I and II and the ODYSSEY LONG TERM included patients with high or very high cardiovascular risk.
The ODYSSEY COMBO I and II [29,30] included patients with high cardiovascular risk unable to achieve targets with maximal statin use.
In the ODYSSEY COMBO II trials [29,30] a treat-to-target approach with alirocumab was tested: the patients treated with alirocumab achieved significantly greater (~30% absolute) reductions in LDL-C vs ezetimibe after 24 and 52 weeks of treatment. At Week 24, >75% of alirocumab-treated patients achieved LDL-C <1.81 mmol/l (<70 mg/dl). Similar results were observed in the ODYSSEY COMBO I, which showed that 75/150 mg Q2W alirocumab treatment induced a significant reduction of LDL-C from baseline at week 24 (48 vs 2% placebo; p <0.0001) which was maintained through 52 weeks. The safety profile of alirocumab in the ODYSSEY COMBO I and II was comparable to the one in placebo arm [29,30].
ODYSSEY OPTION I and II [31] included patients with very high or high cardiovascular risk not achieving LDL-C levels (<70 or <100 mg/dl) under statin.
In ODYSSEY OPTION I [31] alirocumab was administered as add-on to either atorvastatin 20 or 40 mg or rosuvastatin 10 or 20 mg and compared with the combination of statin + ezetrol, the doubling of statin dose or the switch from atorvastatin to rosuvastatin. Alirocumab significantly reduced LDL-C when added to atorvastatin 20 or 40 mg and rosuvastatin 10 mg as compared with adding ezetimibe or doubling the dose of statin, the effect with alirocumab + rosuvastatin 20 mg was similar to the reduction obtained by doubling the dose of rosuvastatin.
The ODYSSEY FH I and II and HIGH FH trials enrolled patients with familial hypercholesterolaemia [32].
In the FH I and II, self-administered alirocumab (75/150 mg Q2W) was associated with a significantly greater LDL-C reduction versus placebo at week 24 and a better achievement of target LDL-C (72% of alirocumab patients in FH I and 81% in FH II study) [32].
The ODYSSEY HIGH FH study focused on patients with familial hypercholesterolaemia and high baseline levels of LDL-C despite maximally tolerated statin (with or without other lipid-lowering drugs). Even with baseline LDL-C >190 mg/dl, 57 and 32% of alirocumab patients reached LDL-C <100 mg/dl and <70 mg/dl, respectively, at week 24. In patients with familial hypercholesterolaemia alirocumab was as safe as placebo. The ODYSSEY ALTERNATIVE trial (2014 AHA Meeting, Chicago) evaluated patients with a history of intolerance to two or more statins, who were randomised to receive alirocumab, ezetimibe or atorvastatin 20 mg. The primary efficacy endpoint was the percent reduction from baseline in LDL-C within 24 weeks treatment, with alirocumab compared with ezetimibe. Alirocumab induced a 45% LDL-C reduction versus a 15% reduction in the ezetimibe arm (p = 0.0001). The adverse events and the discontinuation rates were similar in the three arms.
Recently, the phase III trials ODYSSEY (CHOICE I and II) trials were completed and met their primary efficacy endpoints – alirocumab, administered for the first time in these trials every 4 weeks, significantly reduced LDL-C at 24 weeks versus placebo in 803 patients with hypercholesterolaemia at moderate to high cardiovascular risk (CHOICE I) and in 233 patients with hypercholesterolaemia with high cardiovascular risk and/or a history of intolerance to two or more statins (CHOICE II) (Stroes E et al., ACC Meeting in San Diego 2015).
The ODYSSEY LONG TERM [35] evaluated the safety, tolerability and efficacy of alirocumab in high cardiovascular risk patients treated with a maximal tolerated dose of statin with or without other lipid-lowering drugs. Eighteen months of double blind treatment with alirocumab (n = 1 553) or placebo (n = 788) was planned, the primary efficacy endpoint was the reduction of LDL-C at week 24, and the analysis of results at 52 weeks in term of safety and efficacy was prespecified. The reduction of LDL-C (mean –62% at 24 weeks and –61% at 52 weeks vs placebo) and the proportion of patients reaching the target LDL-C value were significantly higher in the alirocumab group as compared with placebo at week 24, both in total and across all subgroups evaluated.
A post-hoc adjudicated cardiovascular events analysis obtained by pooling all phase III placebo-controlled trials with alirocumab (LONG TERM + HIGH FH and COMBO I + FH I + FH II) suggests a trend towards reduction in cardiovascular events (Figure 3) [35].
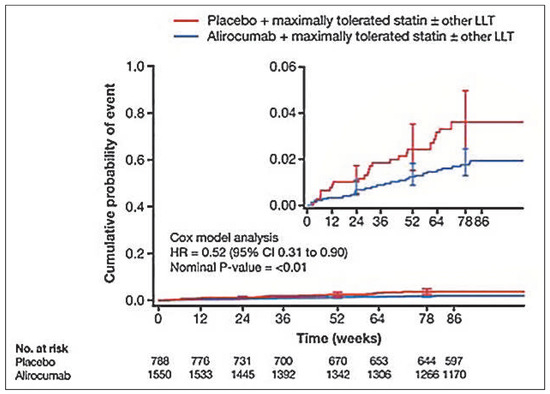
Figure 3.
Post-hoc analysis of a subgroup of adjudicated major adverse cardiovascular events (ODYSSEY OUTCOMES endpoint). Kaplan-Meier Estimates for Time to First Positively Adjudicated Cardiovascular Event During the TEAE Period. Modified with permission from Figure S5 Supplement to: Robinson JG, Farnier M, Krempf M, et al. Efficacy and safety of alirocumab in reducing lipids and cardiovascular events. N Engl J Med. 2015;372:1489-99.
The results of a large-scale clinical outcome study (NCT01663402) are expected for March 2018.
AMG145 or evolocumab is a fully human monoclonal antibody (immunoglobulin G2) that binds specifically to human PCSK9.
The first large long-term evaluation of efficacy and safety of evolocumab (52 weeks) was recently published [36]. A total of 1 104 patients enrolled in the four evolocumab phase II parent studies were included in the Open-Label Study of Long-term Evaluation Against LDL-C (OSLER) study. Regardless of their treatment assignment in the previous studies, patients were randomized 2:1 to receive either open-label subcutaneous evolocumab 420 mg Q4W with standard of care (SOC) (evolocumab + SOC, n = 736) or SOC alone (n = 368). At 12 weeks, the larger LDL-C reduction was observed in the patients who received evolocumab for the first time in the OSLER Study and this reduction was maintained during the 52-week follow-up (–51.8% at 12 weeks, –52.3% at 52 weeks). Patients who continued to be treated with evolocumab in the OSLER Study had persistent reductions in LDL-C (–52.1% at 52 weeks). Moreover, the majority of patients treated with evolocumab achieved LDL-C levels significantly below current guidelines.
Patients who were treated with evolocumab in the previous study and randomised to SOC in the OSLER Study came back to baseline values without a rebound phenomenon. At 52 weeks apoB, lipoprotein(a) (Lp(a)) and triglyceride were significant reduced, high-density lipoprotein (HDL) and apolipoprotein A1 (apoA1) significantly increased in patients treated with evolocumab [36].
Adverse events were similar in patients treated with evolocumab and SOC and a small percentage of patients (3.7%) discontinued the study drug because of any adverse event suggesting long-term safety and good tolerance of the parenteral therapy [36].
Similarly, the 52-week phase III DESCARTES Study [37] showed that evolocumab (420 mg/every 4 weeks) significantly reduced LDL-C (as a mean 57% vs placebo) in patients with cardiovascular risk treated on top of riskbased lipid-lowering therapies (diet alone, atorvastatin 10 or 80 mg and ezetimibe).
In a prespecified, but exploratory, analysis a year of therapy with evolocumab was also shown to reduce the incidence of cardiovascular events [38].
The efficacy of evolocumab on outcomes will be evaluated in the Further Cardiovascular Outcomes Research With PCSK9 Inhibition in Subjects With Elevated Risk (FOURIER) (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT01764633) and the results are expected to be available by the beginning of 2018.
RN316/PF04950615 or bococizumab is a humanised monoclonal antibody-binding PCSK9, which was developed to have a longer serum half-life and duration of LDL-C decrease in mice and monkeys [39]. The results of three phase I and two phase II studies were presented at the American Heart Association scientific sessions in November 2012 and some of these results were recently published in an extended form [40].
Bococizumab lowered LDL-C in patients with hypercholesterolaemia both as monotherapy (subcutaneously or intravenously) and when added to atorvastatin, without similar safety. In phase II trials, LDL-C levels were significantly reduced by bococizumab (3.0 or 6.0 mg/kg i.v.) in addition to high or maximal dosage statin treatment [39]. New phase III studies are currently recruiting patients, including two outcome trials, which aim to evaluate the effect of bococizumab on cardiovascular events, i.e., SPIRE-1 and SPIRE-2 (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifiers: NCT01968980, NCT01968954, NCT01968967, NCT01975389, NCT01975376).
Alternative approaches to the monoclonal antibodies for the inhibition of PCSK9 synthesis is the use of RNA interference drugs such as exogenous small interfering RNA (siRNA) [41].
A recent safety study published in The Lancet [41] showed that ALN-PCS (Alnylam Pharmaceuticals), an siRNA drug designed to inhibit the synthesis of the PCSK9 transcript and thus reduce plasma PCSK9, was well tolerated and significantly lowered PCSK9 and LDL-C after a single intravenous dose in healthy volunteers with raised cholesterol and without lipid-lowering treatment.
Thirty-two patients were randomised to receive single dose of intravenous ALN-PCS (n = 24, doses ranging from 0.015 to 0.150 mg/kg – n = 3 patients in each dosegroup – or 0.250/0.400 mg/kg, n = 6 in each group) or placebo (n = 8).
The study showed that ALN-PCS was safe and well tolerated and no drug-related serious adverse events were observed. One patient (treated with 0.045 mg/kg) was diagnosed with bilateral pulmonary emboli and a deep vein thrombosis on day 3 of the study. This event was considered by the investigator and safety review committee to be unrelated to study drug [41]. A mild macular erythematous rash was described in patients treated with ALN-PCS as well as with placebo.
Although this was a small Phase I study that was not powered to detect changes in PCSK9 or LDL-C, a significant lowering of plasma PCSK9 and serum LDL-C in the higher dose groups (0.250 and 0.400 mg/kg) was found.
Conclusion and future prospects
The currently available evidence from completed clinical trials suggests that PCSK9 inhibition by mAbs is a new therapeutical option to modify the lipid profile towards a non-atherogenic pattern. Inhibition of PCSK9 is very effective in lowering LDL-C, non-HDL-C and apoB levels, with concomitant reduction of Lp(a) and increase of HDL-C and apoA1. The efficacy of mAbs to PCSK9 has been demonstrated in healthy volunteers, in hypercholesterolaemic patients with or without familial hypercholesterolaemia as monotherapy or added to statins and/or ezetimibe, and in patients intolerant to statin therapy.
The mAbs tested so far have been largely well tolerated, apart from mild injection site reactions in short- (12 weeks) and long-term (52 weeks) studies.
A number of questions remain still open. Extended data about long-term safety, tolerability and efficacy of PCSK9 inhibitors are needed. The results from the ODYSSEY LONG TERM [34] as well as the DESCARTES [37] and OSLER [38] studies are promising with respect to safety and persistent LDL-C lowering and two largescale long-term phase III trials are ongoing. Moreover, outcome data are needed to demonstrate reduction of cardiovascular events in relation to the amount of LDL-C lowering and cost-effectiveness analysis should be provided. Great optimism has been generated by the outcome of the Improve-It trial in which for the first time additional lowering of LDL-C with a non-statin drug, namely ezetimibe, produced additional clinical benefit [51]. Optimism is also generated by the post-hoc analyses of the long-term trials of alirocumab [36] and evolocumab [52], as well as the meta-analysis [53] of all phase II trials that indicate reduced cardiovascular event rates.
Such trials will also provide the opportunity to assess the long-term safety of very low LDL-C levels, the physiological role of PCSK9 and the consequences of PCSK9 inhibition in a variety of patient populations including mixed hyperlipidaemia, metabolic syndrome, diabetes and chronic kidney disease.
PCSK9 inhibition generates new hope for all patients currently not reaching the target LDL-C level because of severe hypercholesterolaemia or intolerance to the current therapies, and a new approach to modifying lipoproteins to anti-atherogenic levels in high-risk patients. Indeed, a large number of patients do not reach recommended LDL-C targets, especially high-risk patients. In this regard, an increase in PCSK9 levels during statin therapy could be considered as a potential mechanism of statin resistance. PCSK9 inhibitors might be a good therapeutical option for these patients and their approval for the treatment of familial hypercholesterolaemia and for patients with statin intolerance may be a reality in a very near future.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors report having received grant/research support and/or honoraria/consultant fees from Novartis, Pfizer, Amgen, Roche, Sanofi-Aventis, Astra Zeneca, Merck Sharp and Dohme.
References
- Yusuf, S.; Hawken, S.; Ounpuu, S.; Dans, T.; Avezum, A.; Lanas, F.; et al. Effect of potentially modifiable risk factors associated with myocardial infarction in 52 countries (the INTERHEART study): Case-control study. Lancet 2004, 364, 937–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, M.; Townsend, N.; Scarborough, P.; Rayner, M. Trends in age-specific coronary heart disease mortality in the European Union over three decades: 1980–2009. Eur Heart J. 2013, 34, 3017–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baigent, C.; Keech, A.; Kearney, P.M.; Blackwell, L.; Buck, G.; Pollicino, C.; et al. Efficacy and safety of cholesterollowering treatment: Prospective meta-analysis of data from 90,056 participants in 14 randomised trials of statins. Lancet 2005, 366, 1267–1278. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cholesterol Treatment Trialists Baigent, C.C.; Blackwell, L.; Emberson, J.; Holland, L.E.; Reith, C.; et al. Efficacy and safety of more intensive lowering of LDL cholesterol: A metaanalysis of data from 170,000 participants in 26 randomised trials. Lancet 2010, 376, 1670–1681. [Google Scholar]
- European Association for Cardiovascular, P.; Rehabilitation Reiner, Z.; Catapano, A.L.; de Backer, G.; Graham, L.; et al. ESC/EAS Guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias: The Task Force for the management of dyslipidaemias of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Atherosclerosis Society (EAS). Eur Heart J. 2011, 32, 1769–1818. [Google Scholar]
- Pearson, T.A.; Laurora, I.; Chu, H.; Kafonek, S. The lipid treatment assessment project (L-TAP): A multicenter survey to evaluate the percentages of dyslipidemic patients receiving lipid-lowering therapy and achieving low-density lipoprotein cholesterol goals. Arch Intern Med. 2000, 160, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gitt, A.K.; Drexel, H.; Feely, J.; Ferrieres, J.; Gonzalez-Juanatey, J.R.; Thomsen, K.K.; et al. Persistent lipid abnormalities in statintreated patients and predictors of LDL-cholesterol goal achievement in clinical practice in Europe and Canada. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2012, 19, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Plutzky, J.; Skentzos, S.; Morrison, F.; Mar, P.; Shubina, M.; et al. Discontinuation of statins in routine care settings: A cohort study. Ann Intern Med. 2013, 158, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seidah, N.G.; Z Awan, M. Chretien, and M. Mbikay, PCSK9: A key modulator of cardiovascular health. Circ Res 2014, 114, 1022–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abifadel, M.; Varret, M.; Rabes, J.P.; Allard, D.; Ouguerram, K.; Devillers, M.; et al. Mutations in PCSK9 cause autosomal dominant hypercholesterolemia. Nat Genet. 2003, 34, 154–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidah, N.G.; Benjannet, S.; Wickham, L.; Marcinkiewicz, J.; Jasmin, S.B.; Stifani, S.; et al. The secretory proprotein convertase neural apoptosis-regulated convertase 1 (NARC-1): Liver regeneration and neuronal differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2003, 100, 928–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awan, Z.; Delvin, E.E.; Levy, E.; Genest, J.; Davignon, J.; Seidah, N.G.; et al. Regional distribution and metabolic effect of PCSK9 insLEU and R46L gene mutations and apoE genotype. Can J Cardiol. 2013, 29, 927–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doblinger, A.; Becker, A.; Seidah, N.G.; Laslop, A. Proteolytic processing of chromogranin A by the prohormone convertase PC2. Regul Pept. 2003, 111, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalus, I.; Schnegelsberg, B.; Seidah, N.G.; Kleene, R.; Schachner, M. The proprotein convertase PC5A and a metalloprotease are involved in the proteolytic processing of the neural adhesion molecule L1. J Biol Chem. 2003, 278, 10381–10388. [Google Scholar]
- Dietschy, J.M.; Turley, S.D.; Spady, D.K. Role of liver in the maintenance of cholesterol and low density lipoprotein homeostasis in different animal species, including humans. J Lipid Res. 1993, 34, 1637–1659. [Google Scholar]
- Miranda, M.X.; van Tits, L.J.; Lohmann, C.; Arsiwala, T.; Winnik, S.; Tailleux, A.; et al. The Sirt1 activator SRT3025 provides atheroprotection in Apoe-/- mice by reducing hepatic Pcsk9 secretion and enhancing Ldlr expression. Eur Heart J. 2015, 36, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denis, M.; Marcinkiewicz, J.; Zaid, A.; Gauthier, D.; Poirier, S.; Lazure, C.; et al. Gene inactivation of proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 reduces atherosclerosis in mice. Circulatio 2012, 125, 894–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, E.; Ben Djoudi Ouadda, A.; Spahis, S.; Sane, A.T.; Garofalo, S.; Grenier, E.; et al. PCSK9 plays a significant role in cholesterol homeostasis and lipid transport in intestinal epithelial cells. Atherosclerosis 2013, 227, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferri, N. Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9: From the Discovery to the Development of New Therapies for Cardiovascular Diseases. Scientifica (Cairo) 2012, 2012, 927352. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.Y.; Tang, Z.H.; Jiang, L.; Li, X.F.; Jiang, Z.S.; Liu, L.S. PCSK9 siRNA inhibits HUVEC apoptosis induced by ox-LDL via Bcl/Bax-caspase9-caspase3 pathway. Mol Cell Biochem. 2012, 359, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urban, D.; Poss, J.; Bohm, M.; Laufs, U. Targeting the proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 for the treatment of dyslipidemia and atherosclerosis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013, 62, 1401–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, S.; Curtis, D.E.; Garuti, R.; Anderson, N.N.; Bashmakov, Y.; Ho, Y.K.; et al. Decreased plasma cholesterol and hypersensitivity to statins in mice lacking Pcsk9. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005, 102, 5374–5379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Samarghandi, A.; Zhang, N.; Yao, Z.; Xiong, M.M.; Teng, B.B. Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 interacts with apolipoprotein B and prevents its intracellular degradation, irrespective of the low–density lipoprotein receptor. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2012, 32, 1585–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavori, H.; Fan, D.; Blakemore, J.L.; Yancey, P.G.; Ding, L.; Linton, M.F.; et al. Serum proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 and cell surface low-density lipoprotein receptor: Evidence for a reciprocal regulation. Circulation 2013, 127, 2403–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.C.; Piper, D.E.; Cao, Q.; Liu, D.; King, C.; Wang, W.; et al. A proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 neutralizing antibody reduces serum cholesterol in mice and nonhuman primates. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009, 106, 9820–9825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.G.; Di Marco, S.; Condra, J.H.; Peterson, L.B.; Wang, W.; Wang, F.; et al. A PCSK9-binding antibody that structurally mimics the EGF(A) domain of LDL-receptor reduces LDL cholesterol in vivo. J Lipid Res. 2011, 52, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, H.; Chaparro-Riggers, J.; Strop, P.; Geng, T.; Sutton, J.E.; Tsai, D.; et al. Proprotein convertase substilisin/kexin type 9 antagonism reduces low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in statin-treated hypercholesterolemic nonhuman primates. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2012, 340, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, Y.G.; Condra, J.H.; Orsatti, L.; Shen, X.; Di Marco, S.; Pandit, S.; et al. A proprotein convertase subtilisin-like/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) C-terminal domain antibody antigen-binding fragment inhibits PCSK9 internalization and restores low density lipoprotein uptake. J Biol Chem. 2010, 285, 12882–12891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colhoun, H.M.; Robinson, J.G.; Farnier, M.; Cariou, B.; Blom, D.; Kereiakes, D.J.; et al. Efficacy and safety of alirocumab, a fully human PCSK9 monoclonal antibody, in high cardiovascular risk patients with poorly controlled hypercholesterolemia on maximally tolerated doses of statins: Rationale and design of the ODYSSEY COMBO I and II trials. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2014, 14, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, C.P.; Cariou, B.; Blom, D.; McKenney, J.M.; Lorenzato, C.; Pordy, R.; et al. Efficacy and safety of alirocumab in high cardiovascular risk patients with inadequately controlled hypercholesterolaemia on maximally tolerated doses of statins: The ODYSSEY COMBO II randomized controlled trial. Eur Heart J. 2015, 36, 1186–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, J.G.; Colhoun, H.M.; Bays, H.E.; Jones, P.H.; Du, Y.; Hanotin, C.; et al. Efficacy and safety of alirocumab as add-on therapy in high-cardiovascular-risk patients with hypercholesterolemia not adequately controlled with atorvastatin (20 or 40 mg) or rosuvastatin (10 or 20 mg): Design and rationale of the ODYSSEY OPTIONS Studies. Clin Cardiol. 2014, 37, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastelein, J.J.; Robinson, J.G.; Farnier, M.; Krempf, M.; Langslet, G.; Lorenzato, C.; et al. Efficacy and safety of alirocumab in patients with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia not adequately controlled with current lipid-lowering therapy: Design and rationale of the ODYSSEY FH studies. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2014, 28, 281–289. [Google Scholar]
- Moriarty, P.M.; Jacobson, T.A.; Bruckert, E.; Thompson, P.D.; Guyton, J.R.; Baccara-Dinet, M.T.; et al. Efficacy and safety of alirocumab, a monoclonal antibody to PCSK9, in statin-intolerant patients: Design and rationale of ODYSSEY ALTERNATIVE, a randomized phase 3 trial. J Clin Lipidol. 2014, 8, 554–561. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, J.G.; Farnier, M.; Krempf, M.; Bergeron, J.; Luc, G.; Averna, M.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Alirocumab in Reducing Lipids and Cardiovascular Events. N Engl J Med. 2015, 372, 1489–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, J.G.; Nedergaard, B.S.; Rogers, W.J.; Fialkow, J.; Neutel, J.M.; Ramstad, D.; et al. Effect of evolocumab or ezetimibe added to moderate- or high-intensity statin therapy on LDL-C lowering in patients with hypercholesterolemia: The LAPLACE-2 randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2014, 311, 1870–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koren, M.J.; Giugliano, R.P.; Raal, F.J.; Sullivan, D.; Bolognese, M.; Langslet, G.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Longer-Term Administration of Evolocumab (AMG 145) in Patients With Hypercholesterolemia: 52-Week Results From the Open-Label Study of Long-Term Evaluation Against LDL-C (OSLER) Randomized Trial. Circulation 2014, 129, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blom, D.J.; Hala, T.; Bolognese, M.; Lillestol, M.J.; Toth, P.D.; Burgess, L.; et al. A 52-week placebo-controlled trial of evolocumab in hyperlipidemia. N Engl J Med. 2014, 370, 1809–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabatine, M.S.; Giugliano, R.P.; Wiviott, S.D.; Raal, F.J.; Blom, D.J.; Robinson, J.; et al. Efficacy and safety of evolocumab in reducing lipids and cardiovascular events. N Engl J Med. 2015, 372, 1500–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farnier, M. PCSK9 inhibitors. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2013, 24, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballantyne, C.M.; Neutel, J.; Cropp, A.; Duggan, W.; Wang, E.Q.; Plowchalk, D.; et al. Results of bococizumab, a monoclonal antibody against proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9, from a randomized, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging study in statin-treated subjects with hypercholesterolemia. Am J Cardiol. 2015, 115, 1212–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, K.; Frank-Kamenetsky, M.; Shulga-Morskaya, S.; Liebow, A.; Bettencourt, B.R.; Sutherland, J.E.; et al. Effect of an RNA interference drug on the synthesis of proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) and the concentration of serum LDL cholesterol in healthy volunteers: A randomised, single-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 1 trial. Lancet 2014, 383, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, E.A.; Gipe, D.; Bergeron, J.; Gaudet, D.; Weiss, R.; Dufour, R.; et al. Effect of a monoclonal antibody to PCSK9, REGN727/SAR236553, to reduce low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in patients with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolaemia on stable statin dose with or without ezetimibe therapy: A phase 2 randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2012, 380, 29–36. [Google Scholar]
- Stein, E.A.; Mellis, S.; Yancopoulos, G.D.; Stahl, N.; Logan, D.; Smith, W.B.; et al. Effect of a monoclonal antibody to PCSK9 on LDL cholesterol. N Engl J Med. 2012, 366, 1108–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, C.S.; Shaywitz, A.J.; Wasserman, S.M.; Smith, B.P.; Gao, B.; Stolman, D.S.; et al. Effects of AMG 145 on low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels: Results from 2 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, ascending-dose phase 1 studies in healthy volunteers and hypercholesterolemic subjects on statins. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012, 60, 1888–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenney, J.M.; Koren, M.J.; Kereiakes, D.J.; Hanotin, C.; Ferrand, A.C.; Stein, E.A. Safety and efficacy of a monoclonal antibody to proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 serine protease, SAR236553/REGN727, in patients with primary hypercholesterolemia receiving ongoing stable atorvastatin therapy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012, 59, 2344–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, E.M.; Diller, P. Alirocumab for hyperlipidemia: Physiology of PCSK9 inhibition, pharmacodynamics and Phase I and II clinical trial results of a PCSK9 monoclonal antibody. Future Cardiol. 2014, 10, 183–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, E.A.; Giugliano, R.P.; Koren, M.J.; Raal, F.J.; Roth, E.M.; Weiss, R.; et al. Efficacy and safety of evolocumab (AMG 145), a fully human monoclonal antibody to PCSK9, in hyperlipidaemic patients on various background lipid therapies: Pooled analysis of 1359 patients in four phase 2 trials. Eur Heart J. 2014, 35, 2249–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giugliano, R.; Desai, N.R.; Kohli, P.; Rogers, W.J.; Somaratne, R.; Huang, F.; et al. Efficacy, safety, and tolerability of a monoclonal antibody to proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 in combination with a statin in patients with hypercholesterolaemia (LAPLACE-TIMI 57): A randomised, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging, phase 2 study. Lancet 2012, 380, 2007–2017. [Google Scholar]
- Koren, M.J.; Scott, R.; Kim, J.B.; Knusel, B.; Liu, T.; Lei, L.; et al. Efficacy, safety, and tolerability of a monoclonal antibody to proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 as monotherapy in patients with hypercholesterolaemia (MENDEL): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 study. Lancet. 2012, 380, 1995–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, M.J.; Sanchez, A.J.; Erickson, B.R.; Basak, A.; Chretien, M.; Seidah, N.G.; et al. Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus glycoprotein proteolytic processing by subtilase SKI-1. J Virol. 2003, 77, 8640–8649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroes, E.; Colquhoun, D.; Sullivan, D.; Civeira, F.; Rosenson, R.S.; Watts, G.F.; et al. Anti-PCSK9 Antibody Effectively Lowers Cholesterol in Patients With Statin Intolerance: The GAUSS-2 Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Phase 3 Clinical Trial of Evolocumab. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014, 63, 2541–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabatine, M.S.; Giugliano, R.P.; Wiviott, S.D.; Raal, F.J.; Blom, D.J.; Robinson, J.; et al. Efficacy and safety of evolocumab in reducing lipids and cardiovascular events. N Engl J Med. 2015, 372, 1500–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarese, E.P.; Kolodziejczak, M.; Schulze, V.; Gurbel, P.A.; Tantry, U.; Lin, Y.; et al. Effects of Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9 Antibodies in Adults With Hypercholesterolemia: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 2015, 163, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).