Summary
Why do we need a review specifically addressing arterial hypertension in elderly patients? First, arterial hypertension prevalence increases with age and, therefore, a large proportion of hypertensive patients are elderly patients. Despite this fact, the specific issues of arterial hypertension in elderly patients are only marginally debated in current guidelines. Second, there are physiological changes (e.g., increasing arterial stiffness, reduced body water content, decreased function of several organ systems) and pathophysiological changes (e.g., increasing prevalence of comorbidities) with increasing age, making diagnosis and therapy of arterial hypertension in elderly patients more demanding. Third, for some recommendations (e.g., appropriate target blood pressure) levels of evidence are lower than in younger hypertensive patients, leading to conflicting recommendations between guidelines. This review intends to discuss some of the specific issues in elderly patients with arterial hypertension.
Introduction
Several guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension have been published in recent years, the most important being the 2013 guideline of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) in Europe [1], the 2003 guideline of the Joint National Committee (JNC) in the United States [2], and the 2011 guideline of the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) in the United Kingdom [3]. So far, there is no guideline specifically addressing hypertension in elderly patients. However, several international societies elaborated an expert consensus document on hypertension in the elderly in 2011 [4]. In Switzerland, the Swiss Society of Hypertension (SSH) regularly publishes leaflets containing condensed and practical guidelines [5].
Diagnosis
Measurement of blood pressure in elderly patients
For the measurement of blood pressure (BP) in elderly patients, the same devices as for younger patients may be used and the measurement is as well performed in the sitting position. As in the younger age group, BP measurement is initially performed on both upper arms and the arm with the higher BP value is chosen for the subsequent BP measurements. Inter-arm differences (defined as difference >20 mm Hg between right and left arm) are more frequent among elderly patients (prevalence approximately 20%). In contrast to younger patients, additional BP measurements in the standing position are mandatory to exclude orthostatic hypotension (best performed 1 and 3 minutes after standing up, see below). Of note, the oscillometric method may fail in patients with atrial fibrillation, a frequent problem in elderly hypertensive patients.
Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring (ABPM) should be generously used in elderly patients, because indications for ABPM are encountered more frequently. For example, white-coat hypertension is more frequent among elderly patients (prevalence approximately 15%–25%) [4]. The opposite of white-coat hypertension, masked hypertension (i.e. higher BP at home than in the clinic), is also a frequent phenomenon in elderly patients with an estimated prevalence of 21%–45% [6]. Furthermore, BP values more frequently vary between measurements and elderly patients more frequently have resistant hypertension.
There are two important pitfalls while interpreting BP values: pseudohypo- and pseudohypertension. Pseudohypotension means the measurement of false low BP values distal to a stenosis that do not correspond to the relevant central BP. These patients are at risk of being undertreated. Pseudohypertension means the measurement of false high BP values – a phenomenon which occurs if the brachial artery is stiffened and the cuff is not capable of completely compressing the vessel. This results in persisting Korotkoff sounds though the cuff pressure exceeds the intravascular pressure. According to different studies, the prevalence of pseudohypertension in elderly patients ranges from 2% to 70%. These patients are at risk of being overtreated. The treating physician should always consider the presence of pseudohypertension if there are only few signs of end organ damage despite the high BP values or if the patient does not well tolerate antihypertensive treatment. However, it is difficult to prove pseudohypertension without invasive BP measurement. Recently, novel devices capable of noninvasively measuring central BP have become available. Whether or not these devices help to diagnose pseudohypo- and pseudohypertension is still an open question.
Diagnosis of arterial hypertension in elderly patients
The criteria for the diagnosis of arterial hypertension in elderly patients are identical across guidelines and identical to the criteria in use for younger patients. Arterial hypertension is diagnosed if a mean systolic BP >140 mm Hg OR a mean diastolic BP >90 mm Hg from at least three measurements on different days is found [5]. The “OR” is important in elderly patients: the criteria are met if only systolic BP is elevated. Although most young hypertensive patients also have elevated diastolic BP, most elderly hypertensive patients have elevated systolic and normal diastolic BP (i.e. isolated systolic hypertension, ISH). Figure 1 displays the prevalence of ISH according to age (data from reference [7]). The increasing ISH prevalence with age results from the loss of vessel elasticity with progressing atherosclerosis. The elasticity loss increases pulse wave velocity and consequently BP during late systole. Therefore, systolic BP increases during life, while diastolic BP tends to decrease after the age of 60. As a consequence of increasing systolic BP during life, prevalence of arterial hypertension increases with age (Figure 2) [8]. After the age of 70, arterial hypertension is the most frequent cardiovascular risk factor. One might argue that criteria for arterial hypertension are too strict in elderly patients. However, it is appropriate to use the same criteria for hypertension diagnosis in young and old patients, because the occurrence of dangerous cardiovascular events in elderly patients depends on BP similarly to young patients [9].
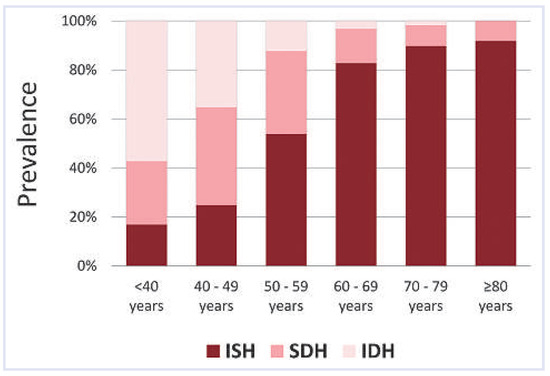
Figure 1.
Prevalence of isolated systolic hypertension (ISH) according to age (data from reference [7]). SDH = combined systolic-diastolic hypertension; IDH = isolated diastolic hypertension.
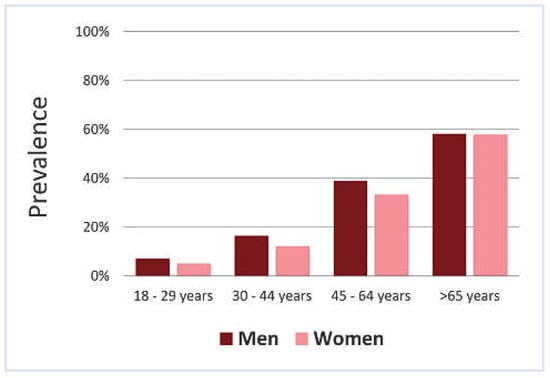
Figure 2.
Prevalence of arterial hypertension according to age and sex (data from reference [8]).
Searching for secondary forms of hypertension
In general, the recommendations for searching for secondary forms of hypertension in elderly patients are similar to young patients. However, the treating physician has to be aware that some aetiologies of secondary hypertension are more frequent in elderly patients (e.g., renal artery stenosis, sleep apnoea), whereas others are less common (e.g., primary aldosteronism). The question always arises as to whether or not to search for secondary forms of hypertension. This decision should be made individually. In general, it is recommended to search for secondary hypertension forms at the latest, if BP treatment targets are not achieved despite three antihypertensive drugs.
Searching for organ damage in elderly patients
Organ damage, caused by atherosclerosis in large and small arteries, is more frequent in elderly than in young patients. Usually, in newly diagnosed hypertensive patients organ damage is searched for in the most vital and most frequently affected organs: heart, kidney and eyes. An electrocardiogram (ECG), urinalysis including albuminuria/microalbuminuria, and fundoscopy should be performed in all patients. In particular, albuminuria/microalbuminuria and fundoscopy point to damage in small vessels. In elderly hypertensive patients, two further organs should be checked: brain and blood vessels. As hypertension is an important risk factor of cognitive decline, cognitive function should be assessed in elderly hypertensive patients with the use of a suitable instrument (e.g., Mini Mental State Examination). The assessment of cognitive function before therapy initiation is particularly valuable to detect cognitive decline after therapy initiation. Though white matter lesions are frequently seen during magnetic resonance imaging studies of elderly hypertensive patients, imaging studies are not generally recommended because of the costs of these examinations and the lack of consequences. Regarding blood vessels, the 2013 ESH/ESC guideline is the first to recommend the measurement of pulse wave velocity to determine the degree of vessel stiffness. With the recent advent of simple devices for its measurement, pulse wave velocity might become more important for estimating cardiovascular risk and effects of antihypertensive therapy in the future, but more studies are needed in this regard.
Treatment
Evidence for treating hypertension in elderly patients
For patients aged 70 to 79 years, the beneficial effects of antihypertensive drug therapy have been evident for many years [10]. Up until 2008, for patients aged 80 years and older, only subgroup analyses from large trials were available [11]. These subgroup analyses suggested beneficial effects of antihypertensive drug therapy on important nonfatal cardiovascular events, but also a possible increase of all-cause mortality. The 2008 HYVET study clarified the situation in patients aged 80 years and older: BP lowering with the use of antihypertensive drugs reduces all-cause mortality as well as nonfatal cardiovascular events [12]. However, as a limitation of this study, it has to be noted that the study participants were healthier than normal for this age, as shown by low numbers of cardiovascular risk factors and comorbidities. There are further studies showing that antihypertensive drug therapy reduces the occurrence of dementia [13]. It has to be recognised that all the trials showing the beneficial effects of antihypertensive drug therapy in elderly patients have been conducted in patients with systolic BP ≥160 mm Hg (grade 2 and 3 hypertension). Thus, trials do not resolve the question as to whether or not to treat grade 1 hypertension (systolic BP 140–159 mm Hg, diastolic BP 90–99 mm Hg) in elderly patients. Due to this uncertainty, guidelines are inconsistent regarding recommendations for treating grade 1 hypertension in elderly patients. The 2011 NICE guideline is the most restrictive and recommends drug therapy of grade 1 hypertension only in patients below the age of 80 years [3]. In patients aged 80 years and older, initiation of drug therapy is only recommended for grade 2 and 3 hypertension. The 2013 ESH/ESC guideline is less restrictive and says that antihypertensive drug treatment may be considered for grade 1 hypertension [1]. The most relevant document regarding treatment of hypertension in elderly, the 2011 expert consensus, clearly recommends initiation of treatment in grade 1 hypertension irrespective of age [4]. Thus, in conclusion, the opinions whether or not to treat grade 1 hypertension in patients aged 80 years and older differ considerably. Probably, in this group of patients, treatment decisions should also take into consideration overall cardiovascular risk.
Two interesting secondary findings from clinical trials
First, the efficacy of antihypertensive drug therapy is generally higher in elderly than in younger patients: numbers needed to treat are lower, because the rate of cardiovascular events is higher in elderly patients and an effective therapy will therefore lead to a higher absolute risk reduction than in young patients with low event rate. Second, the reduction of nonfatal events is more pronounced than the reduction of mortality. Consequently, antihypertensive drug therapy not only prolongs life, but also improves quality of life, because the sequelae of nonfatal events (e.g., paresis after stroke, heart failure after myocardial infarction) lead to disability and a decrease in quality of life.
Recommendations for lifestyle and drugs
Lifestyle measures are effective in elderly hypertensive patients. Salt restriction seems to be particularly effective, but the difficulties of salt restriction in daily life are well known [14]. Weight reduction may be recommended for elderly physically active patients. In patients unable to train their muscles, weight reduction should not be recommended because these patients will lose muscle mass which may promote disability. Though lifestyle measures are effective, it has to be realised that most elderly patients have high cardiovascular risk and therefore qualify for early initiation of drug therapy. Generally speaking, antihypertensive drug therapy should be started earlier in elderly than in young patients. The 2013 ESH/ESC guideline also recommends considering early initiation of two-drug combinations in patients with marked BP elevation and/or high cardiovascular risk, which often applies to elderly patients.
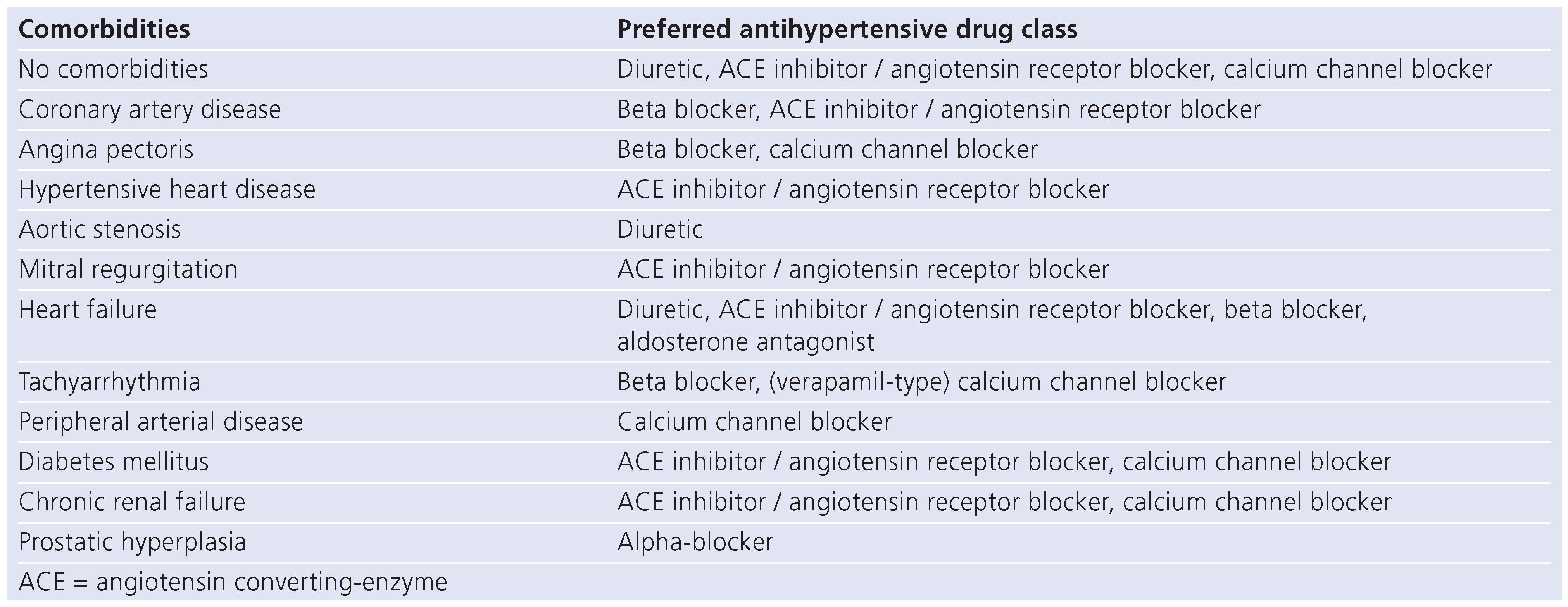
The choice of the antihypertensive drug class depends on comorbidities. As the prevalence of comorbidities increases with age, comorbidities more frequently influence the choice of drug class in elderly patients (Table 1). Treating physicians have to be aware that beta blockers may increase the incidence of depression, diabetes or relevant bradycardia. Diuretics and calcium channel blockers are often a good choice. It is important to know that calcium channel blockers may cause ankle oedema and that it is wrong to escalate drug therapy by adding a diuretic to treat the ankle oedema. In such a situation, the calcium channel blocker should be replaced by a calcium channel blocker less likely to cause ankle oedema or by another drug class. Initiating drug therapy with half of the usual dose (in accordance with “start low, go slow”) is appropriate in many elderly patients. However, it is important to increase to the usual dose if BP treatment targets are not achieved.

Table 1.
Preferred antihypertensive drug class according to comorbidities.
BP treatment targets in elderly patients
BP treatment targets in elderly patients are controversial (similar to the BP levels giving rise to the initiation of antihypertensive treatment, see above), which is the consequence of a lack of clear evidence from clinical trials. As denoted above, all clinical trials were conducted in patients with systolic BP ≥160 mm Hg before therapy initiation. In most trials, the mean BP reduction during treatment was in a range of 10 to 20 mm Hg. Therefore, it is unclear whether systolic BP should be reduced below 140 mm Hg in all elderly patients. The restrictive 2011 NICE guideline recommends a BP treatment target of <150/90 mm Hg in patients aged 80 years and older and <140/90 mm Hg in patients younger than 80 years [3]. The 2011 expert consensus documents generally recommends a BP treatment target <140/90 mm Hg irrespective of age, but adds that a BP of 140 to 145 mm Hg may be acceptable in some patients after the age of 80 [4]. The 2013 ESH/ESC guideline generally recommends reducing systolic BP to between 140 and 150 mm Hg in patients aged less than 80 years, but also states that systolic BP <140 mm Hg may be considered in fit elderly patients aged less than 80 years [1]. For patients older than 80 years, the 2013 ESH/ESC guideline recommends reducing systolic BP to between 140 and 150 mm Hg provided they are in good physical and mental conditions.
The problem of critical organ perfusion
Is there a rationale to recommend different BP treatment targets for young and elderly patients? Yes, there is. As atherosclerosis progresses during aging, stenoses may develop in large and small vessels. If the central BP is reduced by antihypertensive treatment, organ perfusion may become critical distal to the stenosis. Critical organ perfusion may have serious consequences in three organs, the heart, the kidneys and the brain. In the heart, myocardial ischaemia may be the result and is probably the main reason for the observed increase in mortality if BP is reduced below 130/65 mm Hg (J-curve phenomenon). The 2011 expert consensus document therefore recommends not to lower BP <130/65 mm Hg after the age of 80 [4]. Thus, a diastolic BP <65 mm Hg, renal failure and/or a decline of cognitive function may be adequate reasons why in some patients a systolic target BP >140 mm Hg has to be accepted. Regarding kidneys, physicians generally are trained to check the renal function 1 to 3 weeks after an intensification of antihypertensive treatment, in particular after the initiation of a drug treatment with angiotensin converting-enzyme (ACE) inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers. Regarding brain, physicians should increase their awareness of assessing cognitive function before and after initiation of antihypertensive treatment.
The problem of orthostatic hypotension
Orthostatic hypotension is defined as a decrease of systolic BP ≥20 mm Hg and/or diastolic BP ≥10 mm Hg on standing. The risk of orthostatic hypotension is increased in elderly hypertensive patients (prevalence approximately 5%–10%), in particular after the initiation of antihypertensive treatment. The increased risk is a consequence of stiffer vessel walls, a decreased intravascular blood volume and autonomic dysfunction in older age. Therefore, additional BP measurements in the standing position before as well as during therapy are mandatory in elderly patients to exclude orthostatic hypotension. The measurements are best performed 1 and 3 minutes after standing up. The presence of orthostatic hypotension may have two consequences: first, a reduced adherence to the prescribed drug regimen; second, an increased risk of falls. As falls may have serious consequences in elderly patients, orthostatic hypotension may be an adequate reason why in some patients a systolic target BP >140 mm Hg has to be accepted.
The problem of reduced life expectancy
There is general agreement that the decision whether or not to treat hypertension with drugs should also consider remaining life expectancy. It is commonly accepted not to treat arterial hypertension in patients with markedly reduced life expectancy (below 1 to 2 years), but such decisions should be made individually and take into consideration potential benefits and risks.
Why multidimensional geriatric assessment is important
Geriatric assessment is a multidimensional and interdisciplinary diagnostic process to determine an elderly person’s medical, psychosocial, and functional capacity and problems with the objective of developing an overall plan for treatment and follow-up. Geriatric assessment includes usual patient history, usual diagnostic tests (such as laboratory findings) as well as specific tests for the evaluation of cognition, mobility, risk of falls, nutrition, emotional status and other domains. Most of these domains are very relevant in elderly hypertensive patients. The assessment of cognition in elderly hypertensive patients is relevant mainly for two reasons: first, cognition may deteriorate during antihypertensive treatment and the treating physician should recognise such a deterioration; second, patients with cognitive limitations, in particular patients with nonobvious, only moderate cognitive limitations, are prone to nonadherence and the treating physician should be aware of this circumstance to ensure adherence to antihypertensive drugs. The assessment of mobility and risk of falls is important, because antihypertensive drugs, in particular diuretics, may increase risk of falls [15]. As some antihypertensive drugs also may have effects on nutrition and emotional status, these two domains should also be assessed before and during antihypertensive treatment. Furthermore, mobility and nutritional assessment may help the treating physician to decide whether lifestyle recommendations such as weight reduction or physical activity are feasible.
Final remarks
It is important to realise that differences in biological age increase with increasing chronological age. Therefore, chronological age is, in general, not a good marker on which decisions should be based. Nevertheless, many guidelines use chronological age to distinguish recommendations. This is problematic. There are healthy and less healthy elderly people. Probably antihypertensive treatment should be identical to that of young patients in healthy elderly people, irrespective of chronological age, whereas for less healthy elderly people different recommendations may be justified. Furthermore, many of the guideline recommendations differing between young and elderly patients are not supported by scientific evidence. The differing recommendations are only the result of a scientific black hole. Hopefully, future research will help to answer the open questions. Last but not least, antihypertensive treatment does not only prolong life. It is one of the most effective measures to improve quality of life and to reduce disability and nursing home admissions in elderly patients. Nevertheless, BP is currently brought to recommended target levels in less than one-half of patients. Let us hope that this proportion may be increased in the near future!
Funding / potential competing interests
No financial support and no other potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
References
- Mancia, G.; Fagard, R.; Narkiewicz, K.; Redón, J.; Zanchetti, A.; Böhm, M.; et al. 2013 ESH/ESC Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: The Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). J Hypertens. 2013, 31, 1281–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chobanian, A.V.; Bakris, G.L.; Black, H.R.; Cushman, W.C.; Green, L.A.; Izzo JLJr et, a.l. The Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure: the JNC 7 report. JAMA. 2003, 289, 2560–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence. Hypertension: clinical management of primary hypertension in adults. NICE clinical guideline 127. 24. August 2011. Available online: www.nice.org.uk/guidance/CG127.
- Aronow, W.S.; Fleg, J.L.; Pepine, C.J.; Artinian, N.T.; Bakris, G.; Brown, A.S.; et al. ACCF/AHA 2011 expert consensus document on hypertension in the elderly: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation Task Force on Clinical Expert Consensus documents developed in collaboration with the American Academy of Neurology, American Geriatrics Society, American Society for Preventive Cardiology, American Society of Hypertension, American Society of Nephrology, Association of Black Cardiologists, and European Society of Hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011, 57, 2037–2114. [Google Scholar]
- Swiss Society of Hypertension (SSH). Available at: www.swisshypertension.ch.
- Wing, L.M.; Brown, M.A.; Beilin, L.J.; Ryan, P.; Reid, C.M.; ANBP2 Management Committee and Investigators. Second Autralian National Blood Pressure Study. “Reverse white-coat hypertension” in older hypertensives. J Hypertens. 2002, 20, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franklin, S.S.; Jacobs, M.J.; Wong, N.D.; et al. Predominance of isolated systolic hypertension among middle-aged and elderly US hypertensives: analysis based on National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) III. Hypertension. 2001, 37, 869–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf-Maier, K.; Cooper, R.S.; Banegas, J.R.; et al. Hypertension prevalence and blood pressure levels in 6 European countries, Canada, and the United States. JAMA. 2003, 289, 2363–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewington, S.; Clarke, R.; Qizilbash, N.; Peto, R.; Collins, R.; Prospective Studies Collaboration. Age-specific relevance of usual blood pressure to vascular mortality: a meta-analysis of individual data for one million adults in 61 prospective studies. Lancet 2002, 360, 1903–1913. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Staessen, J.A.; Gasowski, J.; Wang, J.G.; et al. Risks of untreated and treated isolated systolic hypertension in the elderly: meta-analysis of outcome trials. Lancet. 2000, 355, 865–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gueyffier, F.; Bulpitt, C.; Boissel, J.P.; et al. Antihypertensive drugs in very old people: a subgroup meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. INDANA Group. Lancet. 1999, 353, 793–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beckett, N.S.; Peters, R.; Fletcher, A.E.; et al. Treatment of hypertension in patients 80 years of age or older. N Engl J Med. 2008, 358, 1887–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forette, F.; Seux, M.L.; Staessen, J.A.; et al. Prevention of dementia in randomised double-blind placebo-controlled Systolic Hypertension in Europe (Syst-Eur) trial. Lancet. 1998, 352, 1347–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinberger, M.H.; Fineberg, N.S. Sodium and volume sensitivity of blood pressure. Age and pressure change over time. Hypertension. 1991, 18, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leipzig, R.M.; Cumming, R.G.; Tinetti, M.E. Drugs and falls in older people: a systematic review and meta-analysis: II. Cardiac and analgesic drugs. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1999, 47, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2014 by the author. Attribution - Non-Commercial - NoDerivatives 4.0.