Carotid Artery Dissection and Sports
Summary
Introduction
Epidemiology
Pathogenesis
- − Compression or stretching, due to the enlarged artery or aneurysm, causes local symptoms such as pain, Horner’s syndrome and cranial nerve palsies.
- − Retinal or focal cerebral ischaemia caused by embolisation of thrombus overlying the dissection to the retinal artery or the intracranial vessels. Less frequently, if the collateral circulation is insufficient, hypoperfusion may lead to haemodynamically induced infarction.
- − Subadventitial rupture of the dissected artery (only in intracranial dissections) can cause subarachnoid haemorrhage. This may be because the wall of the intracranial segment is thinner than that of the extracranial arteries.
Aetiology of traumatic carotid dissection
Aetiology of spontaneous carotid artery dissection
Clinical manifestations
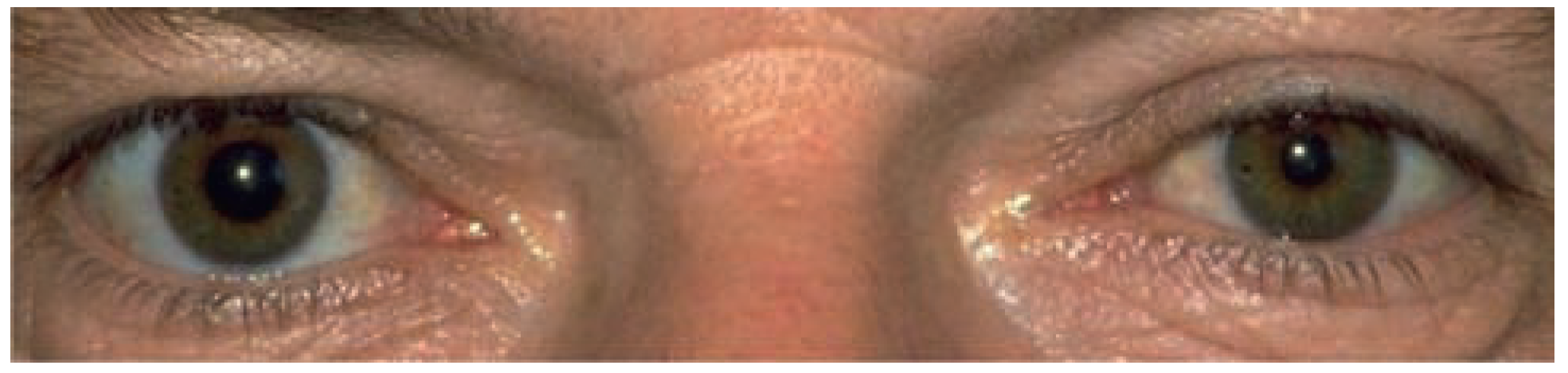
Local symptoms and signs
Retinal and cerebral ischaemia
Diagnosis
Treatment
Prognosis
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Davis, J.W.; Holbrook, T.L.; Hoyt, D.B.; Mackersie, R.C.; Field, T.O.J.; Shackford, S.R. Blunt carotid artery dissection: Incidence, associated injuries, screening, and treatment. J. Trauma. 1990, 30, 1514–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedeltchev, K.; Auf der Maur, T.; Georgiadis, D.; Arnold, M.; Caso, V.; Mattle, H.P.; et al. Ischaemic stroke in young adults: predictors of outcome and recurrence. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2005, 76, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giroud, M.; Fayolle, H.; Andre, N.; Dumas, R.; Becker, F.; Martin, D.; et al. Incidence of internal carotid artery dissection in the community of Dijon. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1995, 57, 1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schievink, W.I.; Mokri, B.; Whisnant, J.P. Internal carotid artery dissection in a community. Rochester, Minnesota, 1987–1992. Stroke 1993, 24, 1678–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, M.; Kappeler, L.; Georgiadis, D.; Berthet, K.; Keserue, B.; Bousser, M.G.; et al. Gender differences in spontaneous cervical artery dissection. Neurology 2006, 67, 1050–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajewski, L.P.; Hertzer, N.R. Blunt carotid artery trauma: Report of two cases and review of the literature. Ann. Surg. 1980, 191, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabian, T.C.; Patton, J.H.J.; Croce, M.A.; Minard, G.; Kudsk, K.A.; Pritchard, F.E. Blunt carotid injury: Importance of early diagnosis and anticoagulant therapy. Ann. Surg. 1996, 223, 513–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laitt, R.D.; Lewis, T.T.; Bradshaw, J.R. Blunt carotid arterial trauma. Clin. Radiol. 1996, 51, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biffl, W.L.; Moore, E.E.; Ryu, R.K.; Offner, P.J.; Novak, Z.; Coldwell, D.M.; et al. The unrecognized epidemic of blunt carotid arterial injuries: Early diagnosis improves neurologic outcome. Ann. Surg. 1998, 228, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, K.M.; Collier, B.; Greene, K.A.; Kurek, S. Traumatic carotid artery dissection: A significant incidental finding. Am. Surg. 2000, 66, 1023–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crissey, M.M.; Bernstein, E.F. Delayed presentation of carotid intimal tear following blunt craniocervical trauma. Surgery 1974, 75, 543–549. [Google Scholar]
- Biffl, W.L.; Moore, E.E.; Offner, P.J.; Burch, J.M. Blunt carotid and vertebral arterial injuries. World J. Surg. 2001, 25, 1036–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, D.A.; Mehelas, T.J.; Savolaine, E.R.; Dougherty, L.S. Basal skull fracture with traumatic polycranial neuropathy and occluded left carotid artery: Significance of fractures along the course of the carotid artery. J. Trauma. 1998, 44, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resnick, D.K.; Subach, B.R.; Marion, D.W. The significance of carotid canal involvement in basilar cranial fracture. Neurosurgery 1997, 40, 1177–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, R.R.; Bergstein, J.M.; DeBord, J.R. Diagnosis, treatment, and outcome of blunt carotid arterial injuries. Am. J. Surg. 1999, 178, 190–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lascelles, K.; Hewes, D.; Ganesan, V. An unexpected consequence of a roller coaster ride. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry. 2001, 71, 704–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mourad, J.J.; Girerd, X.; Safar, M. Carotid-artery dissection after a prolonged telephone call. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997, 336, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, T.; Orberk, E.; Weber, R.; Werner, I.; Busse, O.; Muller, B.T.; et al. Pathogenesis of cervical artery dissections: association with connective tissue abnormalities. Neurology 2001, 57, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grond-Ginsbach, D.; Weber, R.; Haas, J.; et al. Mutations in COL5A1 coding sequence are not common in patients with spontaneous cervical artery dissection. Stroke 1999, 30, 1887–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grau, A.J.; Brandt, T.; Buggle, F.; Orberk, E.; Mytilineos, J.; Werle, E.; et al. Association of cervical artery dissection with recent infection. Arch. Neurol. 1999, 56, 851–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schievink, W.I. Spontaneous dissection of the carotid and vertebral arteries. New Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 899–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biousse, V.; D’Anglejan-Chatillon, J.; Massiou, H.; Bousser, M.G. Head pain in non-traumatic carotid artery dissection: a series of 65 patients. Cephalalgia 1994, 14, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biousse, V.; Touboul, P.J.; D’Anglejan-Chatillon, J.; Levy, C.; Schaison, M.; Bousser, M.G. Ophthalmological manifestations of internal carotid artery dissection. Am. J. Ophtalm. 1998, 26, 565–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumgartner, R.W.; Arnold, M.; Baumgartner, I.; Mosso, M.; Goenner, F.; Studer, A.; et al. Carotid dissection with and without ischemic events: local symptoms and cerebral artery findings. Neurology 2001, 57, 827–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo, E.H.; Osborne, D.L.; Spain, D.A.; Miller, F.B.; Senler, S.O.; Richardson, J.D. Blunt carotid artery injuries: Difficulties with the diagnosis prior to neurologic event. J. Trauma. 1999, 46, 1120–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, M.; Baumgartner, R.W.; Stapf, C.; Nedeltchev, K.; Buffon, F.; Benninger, D.; et al. Ultrasound diagnosis of spontaneous carotid dissection with isolated Horner syndrome. Stroke. 2008, 39, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, C.; Moulin, T.; Deplanque, D.; Tatu, L.; Chavot, D. Stroke patterns of internal carotid artery dissection in 40 patients. Stroke 1998, 29, 2646–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benninger, D.H.; Georgiadis, D.; Kremer, C.; Studer, A.; Nedeltchev, K.; Baumgartner, R.W. Mechanism of ischemic infarct in spontaneous carotid dissection. Stroke 2004, 35, 482–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyrer, P.; Engelter, S. Antithrombotic drugs for carotid artery dissection. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2003, CD000255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, M.; Nedeltchev, K.; Sturzenegger, M.; Schroth, G.; Loher, T.J.; Stepper, F.; et al. Thrombolysis in Patients with Acute Stroke Caused by Cervical Artery Dissection. Analysis of 9 Patients and Review of the Literature. Arch. Neurol. 2002, 59, 549–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, B.T.; Luther, B.; Hort, W.; Neumann-Haefelin, T.; Aulich, A.; Sandmann, W. Surgical treatment of 50 carotid dissections: Indications and results. J. Vasc. Surg. 2000, 31, 980–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokri, B. Traumatic and spontaneous extracranial internal carotid a rtery dissections. J. Neurology. 1990, 237, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremer, C.; Mosso, M.; Georgiadis, D.; Stockli, E.; Benninger, D.; Arnold, M.; et al. Carotid dissection with permanent and transient occlusion or severe stenosis: Long-term outcome. Neurology. 2003, 60, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touze, E.; Gauvrit, J.Y.; Moulin, T.; Meder, J.F.; Bracard, S.; Mas, J.L. Risk of stroke and recurrent dissection after a cervical artery dissection: a multicenter study. Neurology 2003, 61, 1347–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schievink, W.I.; Mokri, B.; O’Fallon, W.M. Recurrent spontaneous cervicalartery dissection. N. Engl. J. Med. 1994, 330, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dittrich, R.; Nassenstein, J.; Bachmann, R.; Maintz, D.; Nabavi, D.G.; Heindel, W. Polyarterial clustered recurrence of cervical artery dissection seems to be the rule. Neurology 2007, 69, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelkonen, O.; Tikkakoski, T.; Leinonen, S.; Pyhtinen, J.; Lepojarvi, M.; Sotaniemi, K. Extracranial internal carotid and vertebral artery dissections: angiographic spectrum, course and prognosis. Neuroradiology 2003, 45, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


 |
 |
© 2009 by the author. Attribution-Non-Commercial-NoDerivatives 4.0.
Share and Cite
Arnold, M.; Fischer, U.; Nedeltchev, K. Carotid Artery Dissection and Sports. Cardiovasc. Med. 2009, 12, 209. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2009.01439
Arnold M, Fischer U, Nedeltchev K. Carotid Artery Dissection and Sports. Cardiovascular Medicine. 2009; 12(7):209. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2009.01439
Chicago/Turabian StyleArnold, Marcel, Urs Fischer, and Krassen Nedeltchev. 2009. "Carotid Artery Dissection and Sports" Cardiovascular Medicine 12, no. 7: 209. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2009.01439
APA StyleArnold, M., Fischer, U., & Nedeltchev, K. (2009). Carotid Artery Dissection and Sports. Cardiovascular Medicine, 12(7), 209. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2009.01439




