Summary
Purpose: We investigated whether the additional knowledge of lung uptake (lung-heart-ratio, LHR), transient ischaemic dilation (TID) and ungated left ventricular volumes (VOL) on top of perfusion defects (summed stress score [SSS]) derived from a single day rest-stress-technetium-99m SestaMIBI imaging protocol (sd-MPS) improves prediction of major cardiac events (MACE) in the long-term. SSS together with exercise SestaMIBI measurements provide important prognostic information. However, little is known about the incremental prognostic value of LHR, TID, and VOL. Methods: In a primary care outpatient setting, 519 patients underwent a supine bicycle electrocardiogram stress test (EST) as specified by an sd-MPS protocol. SSS, TID, and VOL were quantified wit hAutoQUANT (version 4.3). LHR was measured from a planar anterior image 4–6 minutes after peak exercise. The mean follow-up period was 6.1 ± 1.5 years. Results: The mean patient age was 59 ± 11 years. Of the 519 patients, 363 (70%) were male and 236 (45%) had known coronary artery disease. There were 44 major cardiac events, thereof 32 cardiac deaths and 12 nonfatal myocardial infarctions. Using Cox analysis for EST and scintigraphic variables, the independent predictors of MACE were male gender, the cardiac workload level reached during testing, and VOL. When a Cox-proportional Hazard model was used, LHR (X2 = 26.83, p = 0.04) and VOL (X2 = 69.55, p <0.001) showed a significant increase in the prognostic value over standard stress test and SSS measures. Conclusions: The strongest predictors of MACE were VOL. LHR, but not TID added incremental prognostic information to perfusion data.
Introduction
At present, there is evidence demonstrating a high prognostic value of myocardial perfusion SPECT (MPS), in particular summed stress scores (SSS) [1,2,3,4,5], and also the incremental value of post-stress ejection fraction and end-systolic volume [6]. However, longterm prognostic data is lacking with respect to the interrelationship of perfusion (expressed as SSS), lung uptake / lung-heart-ratio (LHR), transient ischaemic dilation ratio (TID), and left ventricular volumes (VOL) as assessed in patients undergoing one-day physical stress testing in accordance with a prescribed test protocol.
Two questions were addressed by the present study: (1.) to evaluate the contribution of perfusion (expressed as SSS), LHR, TID, and VOL to predict longterm prognosis with respect to MACE risk, and (2.) to analyse the results of a one-day rest/stress SestaMIBI myocardial perfusion SPECT protocol at a single European medical centre in all patients with known or suspected coronary artery disease (CAD) who were admitted to the centre over a randomly selected time period.
Methods
Study Population
In a retrospective analysis, 519 consecutive patients referred for the evaluation of suspected or known CAD to a private Radiology Centre between July 1994 through October 1996 with complete clinical, exercise and perfusion data were identified for this study. Not considered were patients imaged for a 2nd time as follow-up controls (n = 45), those with pharmacological stress tests (n = 68) or missing clinical (n = 40) or perfusion data (n = 166).
Follow-Up and End-Point Definitions
All identified patients were contacted 6.1 ± 1.5 years (range 5–9 years) after the examination by questionnaire or if necessary by phone calls. When no response was obtained, private physicians of the patients were interviewed and survival status ascertained through official death statistics of the local authorities. Thus, follow-up was completed in all patients regarding survival and 98% complete regarding other cardiac events. The primary endpoint was major adverse cardiac events (MACE); i.e., cardiac death or documented non-fatal myocardial infarction. Cardiac death was death due to myocardial infarction, congestive heart failure, cardiac interventions as well as witnessed or non-witnessed sudden cardiac death. Myocardial infarction had to be documented based on the basis of characteristic chest pain, ECG changes, or serum creatine kinase levels that were twice the upper limit of the normal value. The local ethical committee of the canton of Solothurn, Switzerland approved this study protocol.
Exercise Test Protocol
Patients performed a supine, symptom-limited exercise bicycle test (EST) with 25 W increments every 2 minutes, in which heart rate, blood pressure, and 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG) were monitored as previously described [7]. Whenever possible, anti-ischaemic drugs where withheld for at least 48 hours before the test. The ECG was considered positive if a horizontal or down-sloping ST segment depression of 1–2 mm at 0.08 second after the J point was observed whether accompanied by chest pain or not. The ECG was considered negative when the ST segment remained isoelectric. In all other cases, the ECG was considered non diagnostic in value.
Nuclear Cardiology Protocol
All patients were studied with a one-day, ungated, rest/stress study with at least four hours between rest and stress [7]. The rest SPECT studies were completed in the morning, one hour after an injection of the radiotracer [296–444 MBq (8–12 mCi) of 99mTc-SestaMIBI, depending on the weight of the patient followed by a symptom-limited EST with ECG monitoring in the afternoon. One minute before the completion of the exercise test, 814–962 MBq (22–26 mCi) of 99mTc-sestamibi (depending on patient weight) was injected. After a short cooldown period of 4–6 minutes, an anterior planar image of the chest was obtained, which contained a minimum of 1 million counts. Immediately thereafter, a 180° noncircular SPECT study was performed by using 16 stops at 45–60 seconds with a dual-head camera and 90° orientation (Vertex, ADAC) for a total of 32 image data sets. Image processing was performed in all patients by using a back-projection algorithm without scatter or attenuation correction and a Butterworth filter with a cut-off value of 0.4 and an order of 10.
Image interpretation was done visually and supported through the use of quantitative analysis software (AutoQUANT®, Version 4.3 [2]) by an operator blinded to the outcome data. SPECT images were quantified by using an automatically generated summed stress score that was corrected later in a few cases by visual analysis. The LHR was determined from an anterior, immediate post-stress planar image by using a nine-pixel rectangular region of interest placed over the maximal myocardial and left lung activity based on visual inspection. LHR was calculated as lung activity/heart activity.
The TID ratios and ungated post-stress left ventricular volumes (VOL) were derived from the same automated computer program (AutoQUANT®) by using ungated SPECT data. This computer program segments the left ventricle, estimates and displays the endocardial surface, the pericardial surface, and the valve plane for both the rest set and the stress set, calculates the left ventricular volumes (VOL) (bounded by the endocardial surface and the valve plane), and derives the TID ratio as VOL stress/VOL rest.
Statistical Analysis
All continuous variables were described as median and means ± SD. Receiver-operator characteristics (ROC) analyses were performed to define thresholds of abnormality for ungated left ventricular volumes; this provided optimal sensitivity and specificity in predicting MACE. Group comparisons were performed using analysis of variance (ANOVA) or chi-square testing. Kaplan-Meier cumulative event-free survival curves were used to compare the survival of different patient groups (logrank test). Univariate predictors of MACE were evaluated for their prognostic value by using a Cox-proportional hazards model. The association between the relevant variables and the risk of an adverse outcome was determined by using a multivariate Cox proportional hazards model. The selection of variables for inclusion in the model was based on univariate significance (age, gender, prior history of CAD, maximum cardiac workload level achieved, ischaemic ECG during stress testing, and the SSS, TID, LHR, and volume), A forward stepwise method was then applied by using a p value <0.05 for inclusion and a p-value >0.10 for exclusion in the model. The incremental value of variables was determined stepwise by calculating the change in global X2 with respect to prognosis after adding the nuclear variables to the pre-scan information (i.e., cardiac workload level achieved, the ECG response during stress). The analyses were performed by using the statistical package for social sciences (SPSS, version 12.0). A p-value <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Patient Characteristics
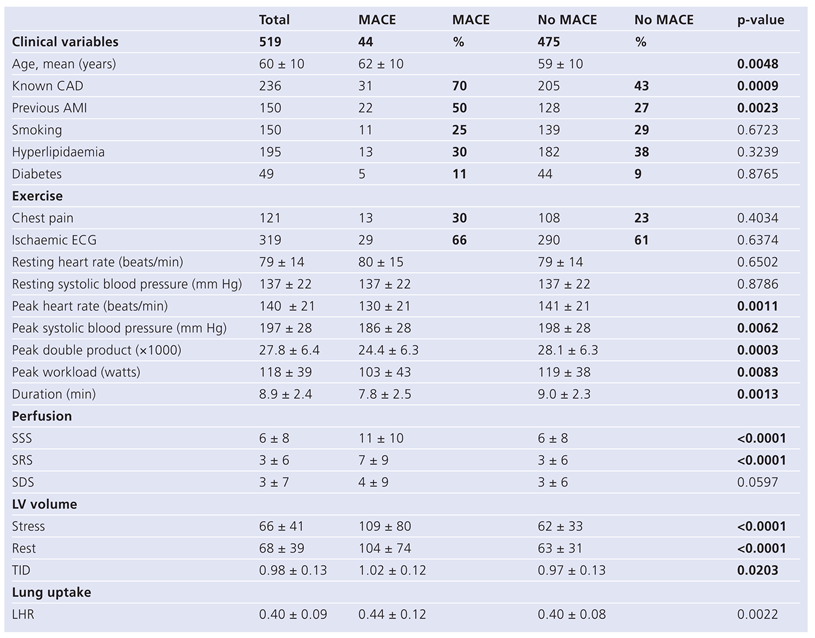
The majority of the patients were men (70%) with an age range between 27 and 86 years, mean age was 59 ± 11 years. More than half of the patients had no history of known CAD (55%) but the risk factor profile was comparable in those with versus without known CAD with respect to diabetes mellitus (10% vs 9%) and hypertension (51% vs 47%). However, in the CAD group higher frequencies were present for smoking (37% vs 22%, p = 0.0002), hyperlipidaemia (50% vs 27%, p <0.0001) and family history of CAD (22% vs 12%, p = 0.0048). Coronary revascularisation procedures had been performed using CABG in 14% and PTCA in 21% of the population under investigation. Patients with MACE were older than those without MACE during follow-up (62 ± 10 vs 59 ± 10, p = 0.0048), and had known CAD more often (31 vs 205, p = 0.0009, Table 1). Most MACE occurred in men (40 out of 44).

Table 1.
Baseline characteristics, exercise results, and scan findings in relation to the occurrence of MACE.
Table 1.
Baseline characteristics, exercise results, and scan findings in relation to the occurrence of MACE.
 |
Lung Uptake Measurements
LHR was measured after exercise using an anterior planar image with data acquisition 4–6 minutes after peak exercise. Mean LHR values stratified according to SSS severity (0, 1–3, 4–13, >13) showed mean values of 0.39 ± 0.08; 0.38 ± 0.07, p = ns; 0.39 ± 0.08, p = ns; and 0.45 ± 0.10, p <0.0001). Therefore, LHR increased abnormally only in the group of subjects with a SSS >13.
Event Rates for MACE in Relation to SSS, History of CAD and Peak Heart Rate Achieved
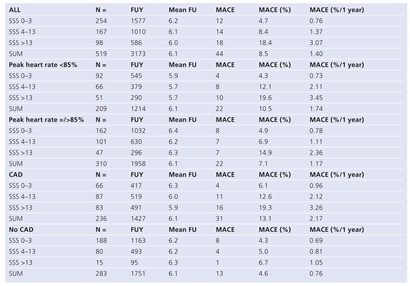
The annual event rate for MACE was 1.4% in the whole group, was 0.8% for subjects with no CAD and 2.2% for subjects with CAD. Subjects with no CAD and an SSS <4 had a very low MACE rate of 0.7%; subjects with CAD and an SSS <4 had a slightly higher event rate of 1.0% (Table 2). A history of CAD altered the risk of a high-risk perfusion defect (SSS >13) with respect to event rates: 3.3% in those with CAD versus 1.1% in those with no CAD.
The annual event rate was 0.7% in those patients having an SSS <4, whether a subject reached the predicted peak heart rate of >85% or not, However, in patients who did not reach a predicted heart rate level >85% and were judged at intermediate risk on the basis of the scan (SSS 4–13), the annual event rate for MACE was higher than in patients who reached the predicted heart rate (2.1% vs 1.1%, p = ns).
Survival Analysis
During a mean follow-up of 6.1 ± 1.5 years, the following events were observed: 32 cardiac deaths and 12 non-fatal myocardial infarctions.
Patients with versus without MACE are shown in Table 1. Patients without MACE reached a higher peak heart rate, a higher peak systolic blood pressure, higher peak double product, higher peak work load and higher duration of exercise.
Individuals with MACE had a higher mean LHR as compared to subjects without MACE (0.44 ± 0.12 vs 0.40 ± 0.08, p = 0.0022), had a higher ungated left ventricular volume after exercise (109 ± 80 ml vs 62 ± 33 ml, p <0.0001) and before exercise (104 ± 74 ml vs 63 ± 31, p <0.0001), but TID showed only marginal statistical significance (1.02 ± 0.12 vs 0.97 ± 0.13, p = 0.0203). Perfusion defect size after exercise as well as at rest were also significant predictors of MACE (SSS: 11 ± 10 vs 6 ± 8, p <0.0001 and SRS: 7 ± 9 vs 3 ± 6, p <0.0001), however, summed difference scores (SDS) reflecting exercise induced ischaemia were not significant (SDS: 4 ± 9 vs 3 ± 6, p = 0.0597).

Table 2.
Event rates for MACE in relation to SSS, peak heart rate, and history of coronary artery disease.
Table 2.
Event rates for MACE in relation to SSS, peak heart rate, and history of coronary artery disease.
 |
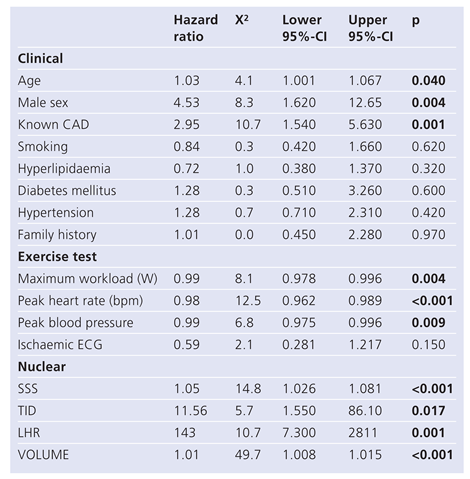
The hazard ratios (HR) for MACE (Table 3) were significant for age (1.03, p = 0.040), for gender (4.53, p = 0.004), for known CAD (2.95, p = 0.001), for maximum workload achieved in Watt (0.99, p = 0.004), for peak heart rate (0.98, p <0.001), for peak blood pressure (0.99, p = 0.009), for SSS (1.05, p <0.001), for TID (11.56, p = 0.017), for LHR (143, 0.001) and for ungated left ventricular volumes (1.01, p <0.001).

Table 3.
Univariate predictors of MACE based on hazard ratios.
Table 3.
Univariate predictors of MACE based on hazard ratios.
 |
Using ROC analysis (Table 4A), the highest areas under the curve for MACE were found for exercise double product (AUC 0.67), for SSS (AUC 0.68) and for ungated left ventricular volumes (0.68). Based on our previously published normal values for TID (cut-off defining abnormality: 1.17 [7]) and LHR (cut-off defining abnormality: 0.5) the sensitivity and specificity to detect MACE was 9% and 93% for TID and 25% and 91% for LHR (Table 4B). Cut-offs for SSS were based on the literature [1,2,3,4] and for VOL on a ROC analysis (ROC data not shown). SSS >14 had a sensitivity and specificity of 39% and 83% to detect MACE, respectively, and VOL ≥100 ml had a sensitivity and specificity of 34% and 93%, respectively.
The ROC curve for SSS and LHR is displayed in Figure 1. The contrast between the two tests was 9% (p = 0.086), therefore, based on ROC analysis in this patient group, LHR did not add significant diagnostic information over SSS.
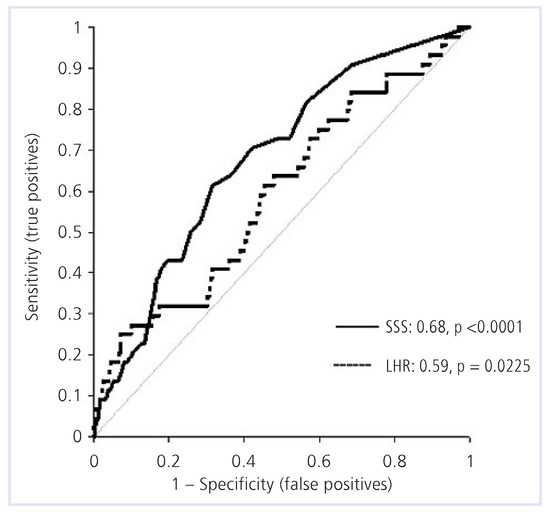
Figure 1.
ROC analysis for SSS and LHR for prediction of MACE. SSS = summed stress scores; LHR = lung-heart-ratio.
Cox analysis showed no significant predictive value of EST regarding MACE-free survival (p = 0.86). MACE-free survival was high with SSS <4 (95%) and significantly lower with SSS >13 (80%, p = 0.0001, Figure 2). Similarly, LHR risk stratified patients effectively. Patient with a LHR <0.5 and >0.5 had a survival of 92% and 79%, respectively (p = 0.0002, Figure 3). For a TID <0.98, survival was 94%; and for a TID >0.98, survival was 86% (p = 0.007). For VOL <100, survival was 93%; whereas for VOL ≥100, MACE-free survival was only 70% (p <0.001).
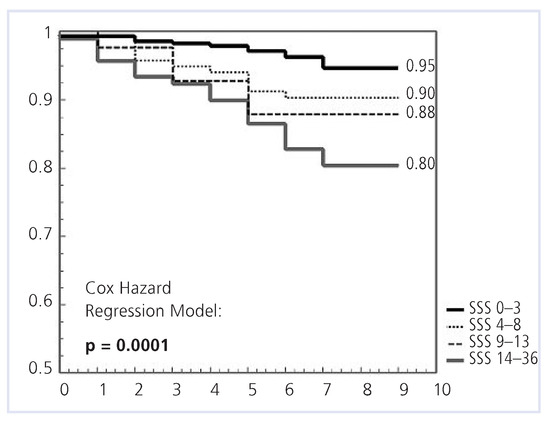
Figure 2.
Kaplan-Meier plots of event-free survival according to SSS categories. SSS = summed stress scores.
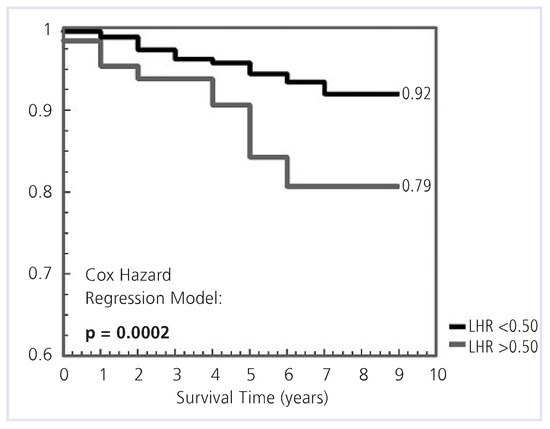
Figure 3.
Kaplan-Meier plots of event-free survival according to LHR above or below 0.5. LHR = lung-heart-ratio.

Table 4A.
Major variables predicting MACE in ROC analysis.
Table 4A.
Major variables predicting MACE in ROC analysis.
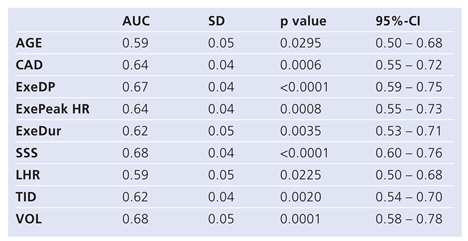 |

Table 4B.
Accuracies of LHR, SSS, VOL, TID, to detect MACE.
Table 4B.
Accuracies of LHR, SSS, VOL, TID, to detect MACE.
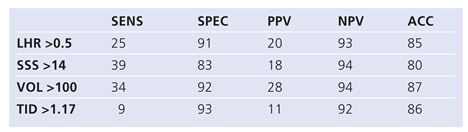 |
By including the information that was derived from baseline characteristics, EST, SSS, and LHR using Cox-multivariate predictors of MACE in the final model, only male gender, the cardiac workload level attained, and the SSS remained significant independent predictors for MACE (Table 5). When the new variable, VOL, was incorporated in the final model, male gender, the cardiac workload level attained, and VOL were identified as independent predictors of MACE (Table 6).

Table 5.
Final COX model with standard variables.
Table 5.
Final COX model with standard variables.
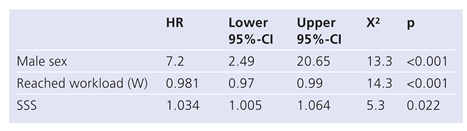 |

Table 6.
Final COX model that incorporates VOL.
Table 6.
Final COX model that incorporates VOL.
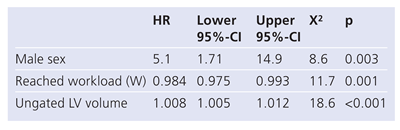 |
Incremental Value of LHR, TID, and SSS Over EST Data
By using a Cox-proportional hazard model, a significant increase of global X2 and thus incremental value of LHR and VOL over standard stress test and MPS variables have been demonstrated (Figure 4). The global Chi value for the exercise stress tests was 10.35, for SSS 22.18 (p = 0.004), for LHR 26.83 (p = 0.044) and for VOL 69.55 (p <0.001).
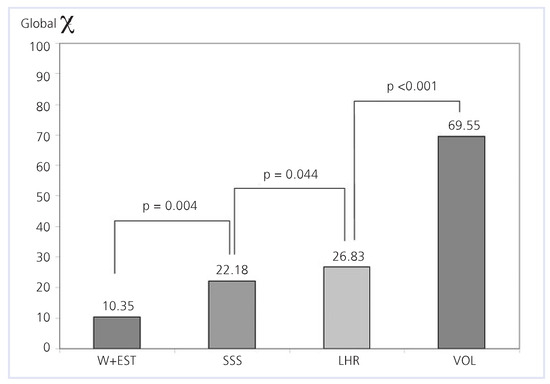
Figure 4.
Incremental value of nuclear variables over pre-scan information. W + EST = information from clinical and exercise test data; SSS = summed stress scores; LHR = lung-heart-ratio; VOL = left ventricular volume from ungated SPECT imaging.
Discussion
This study shows that LHR and VOL both add incremental value to clinical exercise test and scintigraphic perfusion data gathered under a one-day rest/stress 99mTc-SestaMIBI myocardial perfusion SPECT protocol.
Lung Uptake Measurements
LHR derived from 99mTc-SestaMIBI perfusion studies is an indirect measure of left ventricular dysfunction and generally becomes abnormal in patients with decreased ejection fraction induced by physical exercise [8,9]. The present study is the first long-term study on risk for MACE derived from an anterior planar chest image, from which our LHR measurements were obtained shortly after peak exercise. There have been conflicting results as to whether LHR has a diagnostic and prognostic impact using SestaMIBI perfusion tracers, especially if patients are imaged late (e.g., >30 minutes) after peak exercise [10] due to wash-in and wash-out problems over time both in the lungs and the heart [11,12]. In a study published from our institution, we could however demonstrate that LHR has a higher sensitivity than TID and perfusion defect size to detect subjects with severe and extensive CAD [7]. Interestingly, in a long-term prognostic study [13], LHR obtained late after peak exercise (e.g., 60 minutes) maintained a high and incremental prognostic value for MACE; however, absolute LHR were different in distribution: e.g., the upper tertile was 0.34 in that study [13], whereas in our study, an LHR of 0.34 corresponded to the 25th percentile. This difference in LHR distribution may therefore be influenced not only by differences in the study protocol, but also due to different wash-out kinetics of the lung over time [11,12]. However, since both early and delayed post-stress LHR had similar accuracy to predict MACE with the exception that in the study by Leslie [13] also non-cardiac mortality was included into “MACE”, it remains unclear, which timing to obtain LHR is more ideal to detect MACE. More studies are needed not only to elucidate the best timing for LHR measurements, but also to elucidate, whether automated LHR obtained from multiple SPECT images [13] is as accurate as LHR obtained from an anterior planar image 4–6 minutes after peak exercise.
Ungated Left Ventricular Volumes (VOL)
In this study, VOL provide a high level of prognostic value using a cut-off of 100 ml as determined by ROC analysis. Subjects with a VOL <100 ml had an annual MACE event rate of only 0.7% during the follow-up period. However, subjects with a VOL ≥100 ml had an annual MACE rate of 3.0% (p <0.001), regardless of the SSS values. As a preliminary finding at our institution, we found a relationship between VOL and left ventricular ejection fraction. The ROC analysis for VOL to detect left ventricular ejection fraction below 40% in 32 subjects determined by gated SPECT was 0.95 (p <0.0001, 95%-CI: 0.921–0.987) in 506 consecutive subjects (unpublished data). This indicates that ungated volumes are a good surrogate marker for left ventricular ejection fraction. This is in agreement with results from a previous study, where end-systolic volume (ESV) and left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) as measured by gated SPECT were significant predictors for MACE in addition to a history of AMI, a likelihood of CAD, the type of stress test used, and the SSS [6]. Therefore, our finding could be useful for evaluating risk in patients with gating artefacts, e.g., in patients with atrial fibrillation or other rhythm irregularities. However, we did not specifically address the question, whether VOL has an as high prognostic impact in patients where gating problems preclude the measure of left ventricular ejection fraction using SPECT as in those who present themselves with regular heart beats. Interestingly, the absolute difference of mean VOL values to detect subjects with and without MACE was comparable between the study by Leslie (122 ± 98 ml vs 70 ± 38 ml, p <0.00001, absolute difference 52 ml) [13] and our study (109 ± 80 ml, vs 62 ± 33, p <0.0001, absolute difference 47 ml) and VOL added high incremental value over clinical, exercise and perfusion data in the work by Leslie [13], confirmed by our data.
Summed Stress Scores
Another relevant finding is that an SSS <4 indicates an excellent prognosis both in subjects without known CAD (annualised MACE 0.6%) and in subjects with known CAD (annualised MACE 1.0%). A history of CAD identifies high-risk subjects, as expected; but a history of CAD also modifies the prognostic impact of SSS. In subjects with no CAD, an SSS >13 were found to be correlated with an intermediate risk for MACE (1.1%). In subjects with CAD, an SSS >13 were found to be correlated with a higher risk for MACE (3.3%).
Another important finding is the relationship of peak heart rate to MACE. Whether the predicted heart rate of >85% was achieved in subjects with a SSS <4 or not, the prognosis for the patients was excellent (MACE 0.7%). This underscores the fact, that myocardial perfusion SPECT also stratifies risk for patients who are not able to reach 85% of their maximum predicted heart rate during stress testing. This may not be the case in tests that rely on left ventricular function, such as stress-echocardiography, due to the ischaemic cascade. However, in patients with an intermediate-risk scan (defined as an SSS between 4 and 13) who do not achieve a peak heart rate >85%, the MACE risk is high (2.4%), although, the risk remains at an intermediate level in patients with an SSS between 4 and 13 who do reach a peak hear rate of >85% (1.2%).
Limitations
Because a substantial portion of our potentially eligible patients could not be included in this study because there was either no nuclear data available (n = 166) or no clinical data available (n = 40), some of our findings might have been different if we had been able to include them.
Conclusions
In a consecutive patient population with a considerable number of patients with known CAD (45%), a very low event rate for MACE has been demonstrated for patients with normal or near normal myocardial perfusion SPECT studies. In addition, we could show for the first time, that LHR derived from anterior planar images has an incremental prognostic value to predict MACE beyond and above clinical and perfusion data also for a single day rest/stress perfusion protocol. Not unexpectedly, a dilated left ventricle – as measured by ungated SPECT imaging of the heart – implies adverse cardiac outcome and may be used to substitute left ventricular function as an outcome marker in selected patients with arrhythmias. For refined risk stratification, we strongly advocate to incorporate early LHR measurements and VOL, a highly accurate surrogate marker for left ventricular function and dilation, where left ventricular ejection fraction cannot be obtained with gated SPECT imaging into routine SPECT perfusion imaging. The timing of LHR measurements, however, warrants further elucidation with respect to its ability to predict MACE.
Conflicts of Interest
There is no conflict of interest.
References
- Stratman, H.; William, G.; Wittry, M.; Chaitman, B.; Miller, D. Exercise Tc99m sestamibi tomography for cardiac risk stratification of patients with stable chest pain. Circulation. 1994, 89, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Germano, G.; Kavanagh, P.B.; Berman, D.S. An automatic approach to the analysis, quantitation and review of perfusion and function from myocardial perfusion SPECT images. Int J Card Imaging. 1997, 13, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanzetto, G.; Ormezzano, O.; Fagret, D.; Comet, M.; Denis, B.; Machecourt, J. Long-term additive prognostic value of thallium-201 myocardial perfusion imaging over clinical and exercise stress test in low to intermediate risk patients study in 1137 patients with 6-year follow-up. Circulation. 1999, 100, 1521–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hachamovitch, R.; Berman, D.S.; Shaw, L.J.; Kiat, H.; Cohen, I.; Cabico, J.A.; Friedman, J.; Diamond, G.A. Incremental prognostic value of myocardial perfusion single photon emission computed tomography for the prediction of cardiac death; differential stratification for risk of cardiac death and myocardial infarction. Circulation. 1998, 97, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marie, P.Y.; Danchin, N.; Durand, J.F.; Feldmann, L.; Grentzinger, A.; Olivier, P.; Karcher, G.; Juilliere, Y.; Virion, J.M.; Beurrier, D. Long term prediction of major ischaemic events by exercise thallium 201 single photon emission computed tomography: incremental prognostic value compared with clinical, exercise testing, catheterization and radio-nuclide angiographic data. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1995, 26, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharir, T.; Germano, G.; Kavanagh, P. , et al. Incremental prognostic value of post-stress left ventricular ejection fraction and volume by gated myocardial perfusion single photon emission computed tomography. Circulation. 1999, 100, 1035–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romanens, M.; Graedel Ch Saner, H.; Pfisterer, M. Comparison of 99mTcsestamibi lung/heart ratio, transient ischaemic dilation and perfusion defect size for the identification of severe and extensive coronary artery disease. Eur J Nucl Med. 2001, 28, 907–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giubbini, R.; Campini, R.; Milan, E. , et al. Evaluation of Tc-99m sestamibi lung uptake: correlation with left ventricular function. J Nucl Med. 1995, 36, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bacher-Stier, C.; Sharir, T.; Kavanagh, P.; Lewin, H.; Friedman, J.; Miranda, R.; Germano, G.; Berman, D. Postexercise lung uptake of 99mTc-sestamibi determined by a new automatic technique: validation and application in detection of severe and extensive coronary artery disease and reduced left ventricular dysfunction. J Nucl Med. 2000, 41, 1190–1197. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Saha, M.; Farrand, T.; Brown, K. Lung uptake of technetium 99m sestamibi: relation to clinical, exercise, hemodynamic, and left ventricular function variables. J Nucl Cardiol. 1994, 1, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, W.; Cordes, M.; Calder, D.; Eichstaedt, H.; Felix, R. Washout and redistribution between immediate and two-hour myocardial images using Tc-99m sestamibi. Eur J Nucl Med. 1995, 22, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurwitz, G.; Fox, S.; Driedger, A.; Willems, C.; Powe, J. Pulmonary uptake of sestamibi on early post-stress images: angiographic relationships, incidence and kinetics. Nucl Med Commun. 1993, 14, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leslie, W.; Tully, S.; Yogendran, M. , et al. Prognostic value of lung sestamibi uptake in myocardial perfusion imaging of patients with known or suspected coronary artery disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2005, 45, 1676–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2009 by the author. Attribution - Non-Commercial - NoDerivatives 4.0.