Mécanismes Physiopathologiques de la Fibrillation Auriculaire
Abstract
Résumé
Introduction
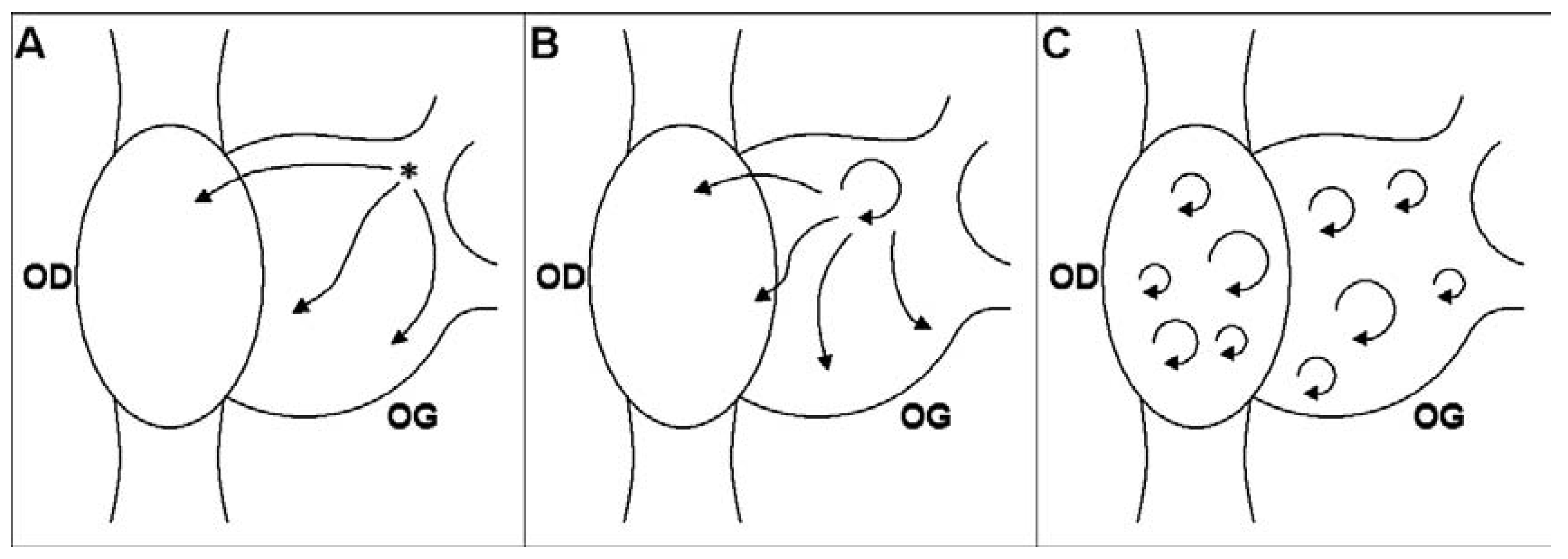
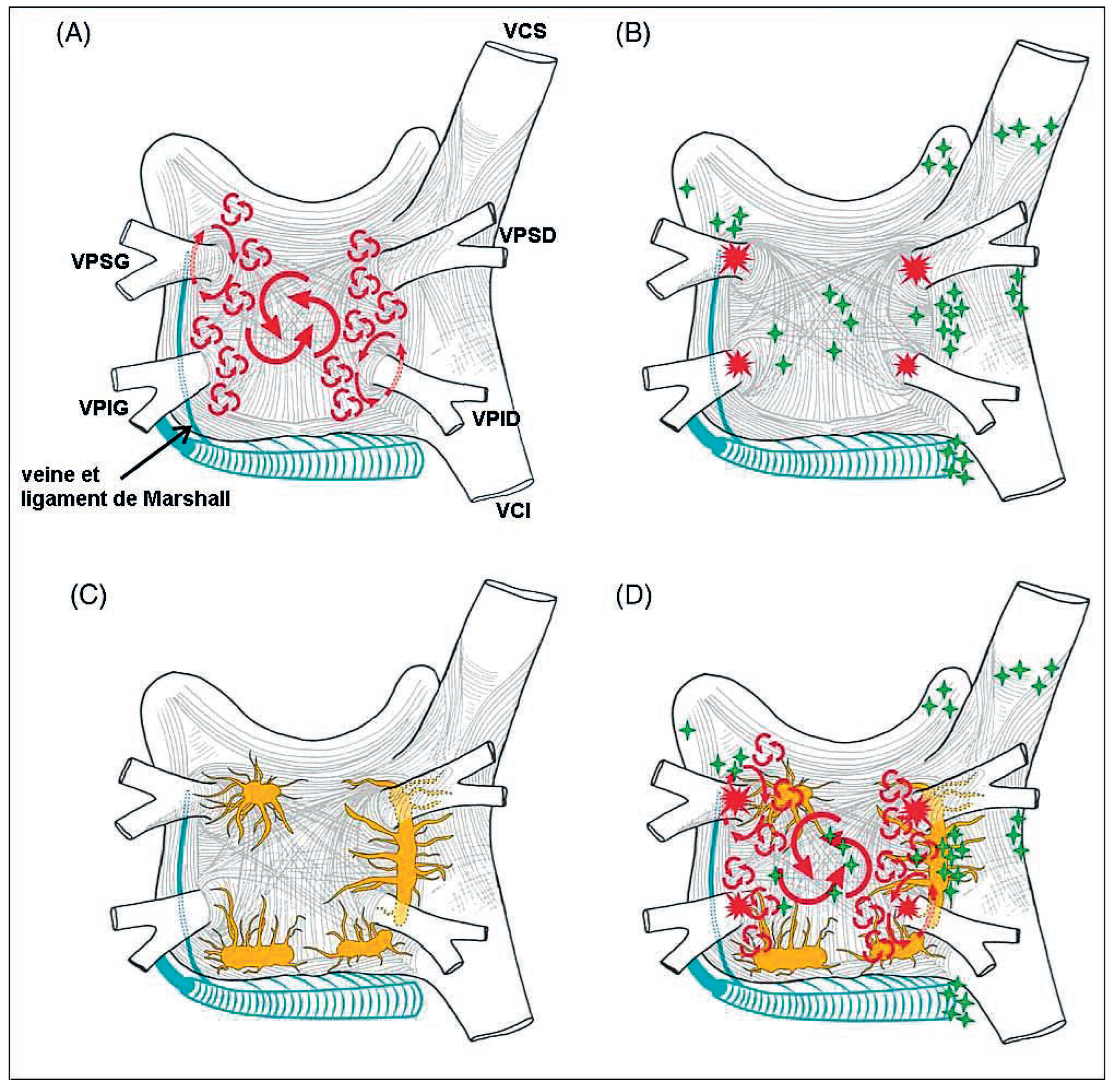
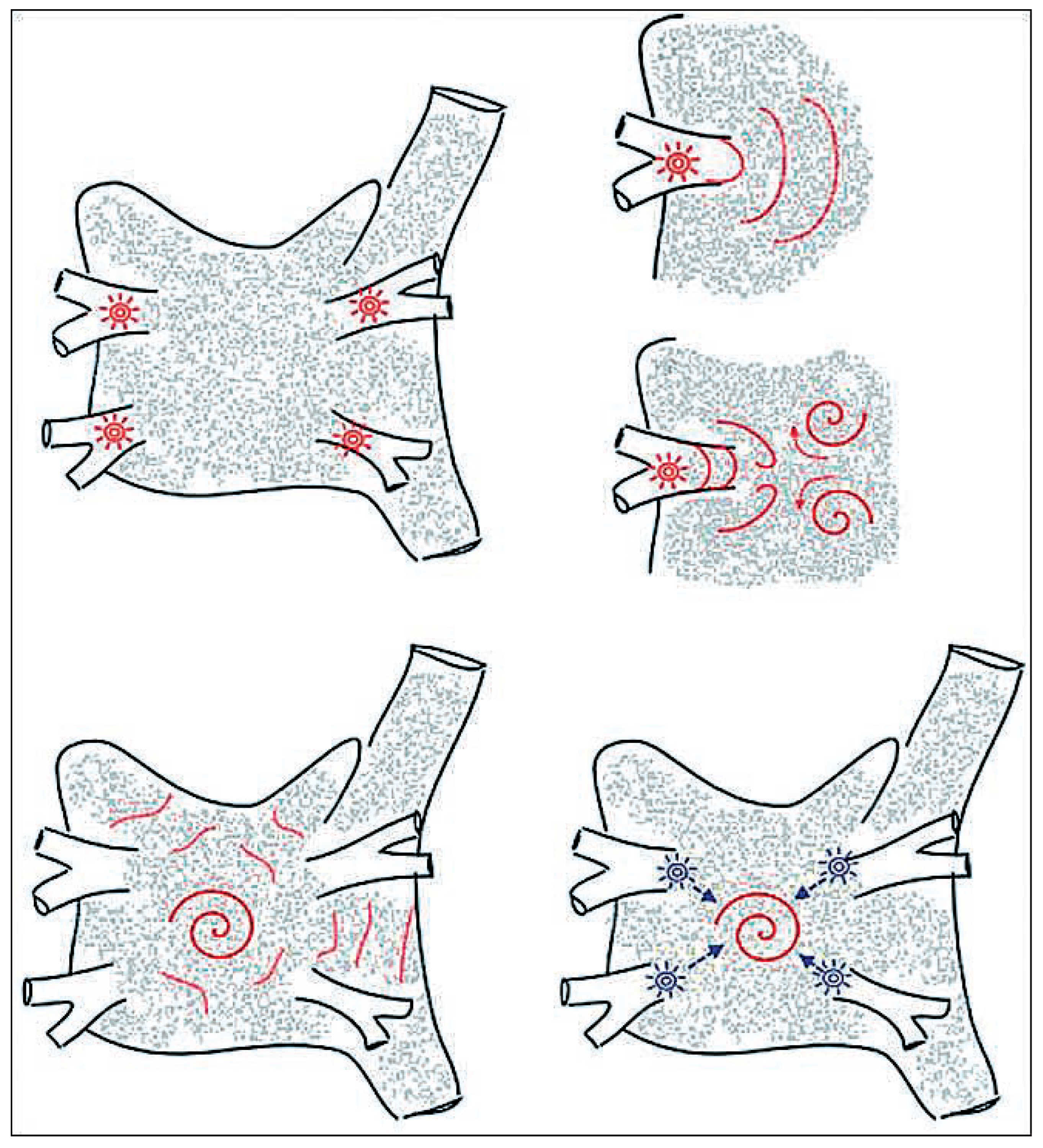
Mécanismes de la Fibrillation Auriculaire
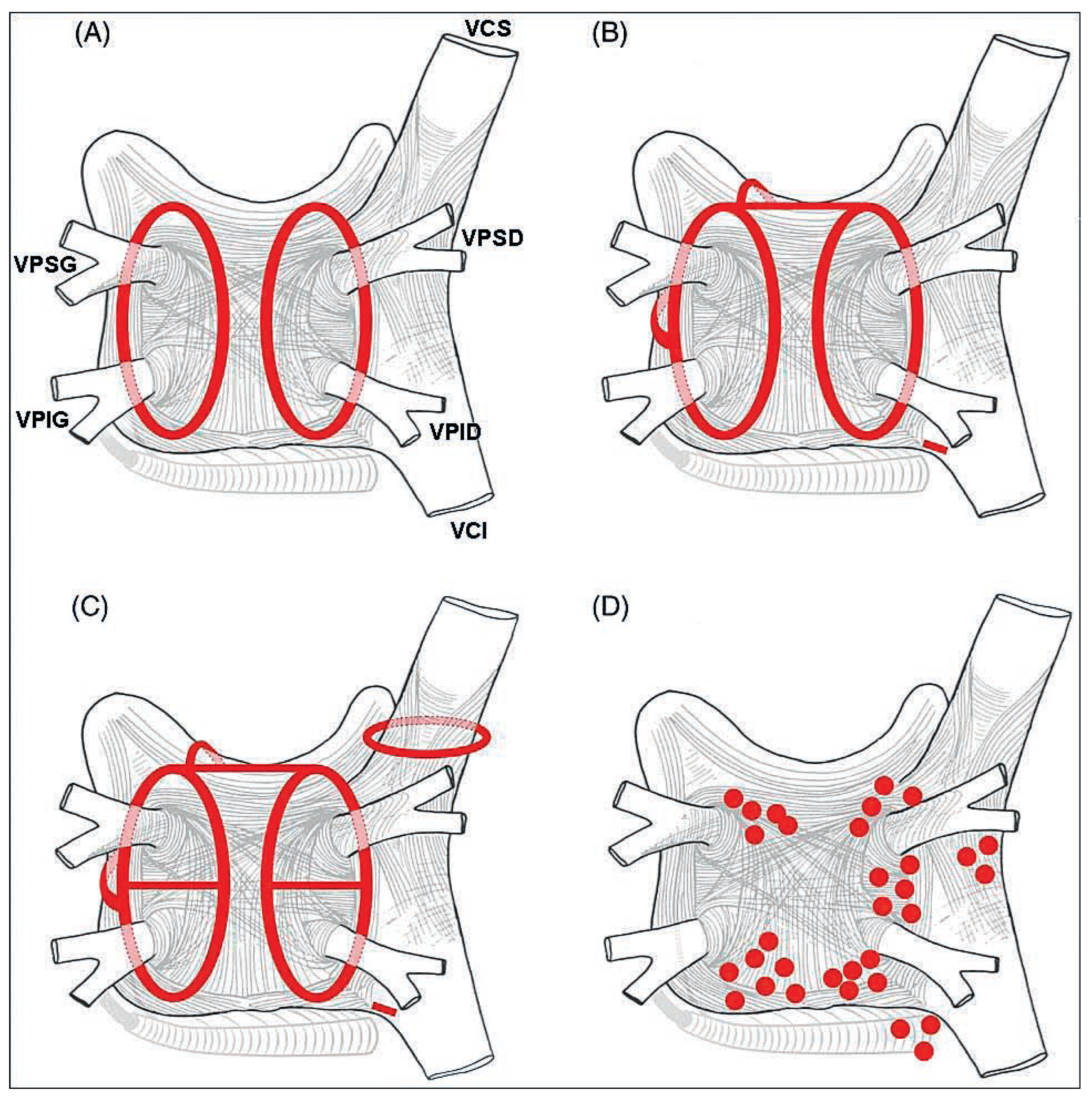
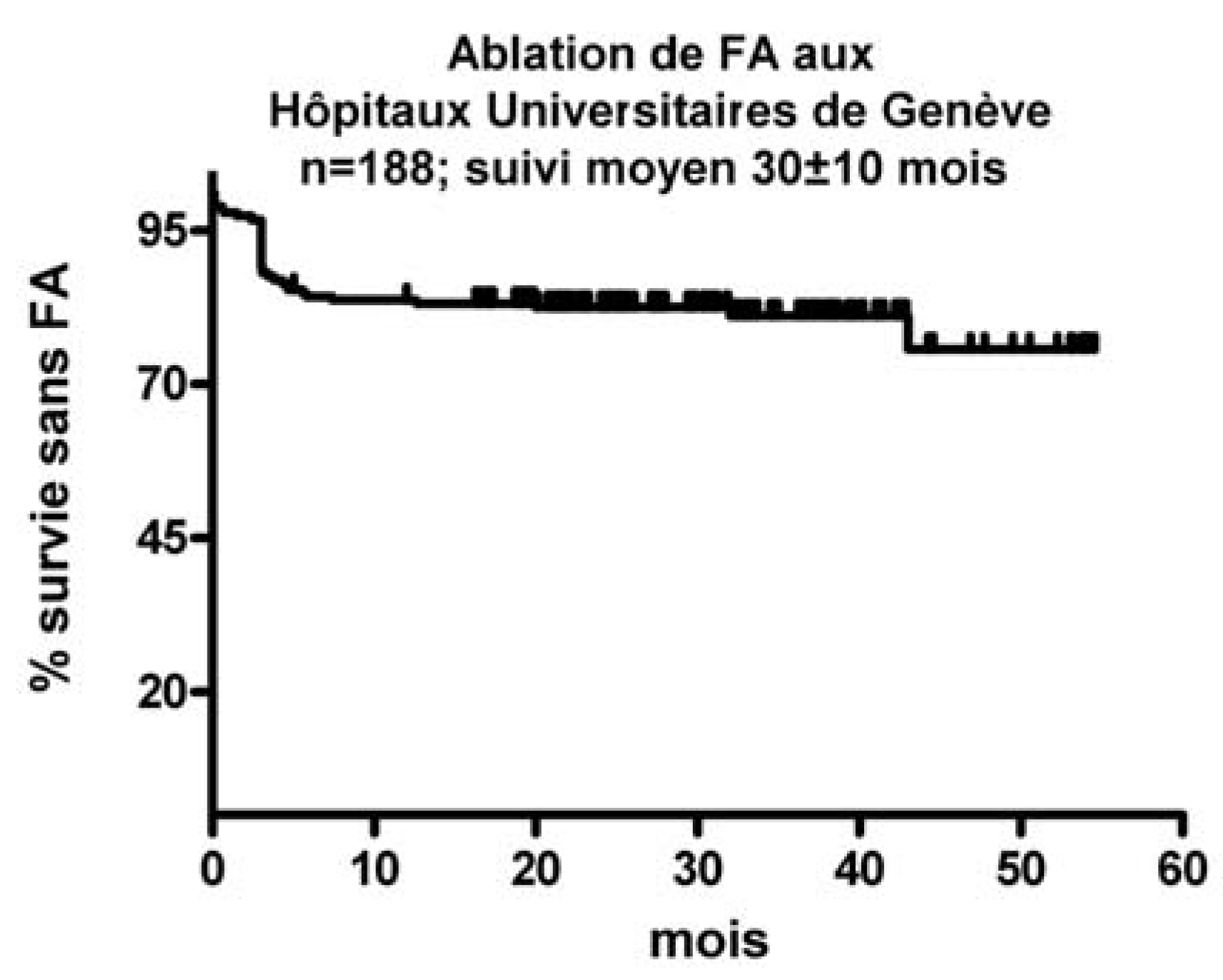
Aspects Thérapeutiques
Conclusions
References
- Fuster, V.; Rydén, L.E.; Cannom, D.S.; Crijns, H.J.; Curtis, A.B.; Ellenbogen, K.A.; et al. ACC/AHA/ESC 2006 Guidelines for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and the European Society of Cardiology Committee for Practice Guidelines (Writing Committee to Revise the 2001 Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Atrial Fibrillation). Circulation. 2006, 114, e257–e354. [Google Scholar]
- Calkins, H.; Brugada, J.; Packer, D.L.; Cappato, R.; Chen, S.A.; Crijns, H.J.; et al. HRS/EHRA/ECAS Expert Consensus Statement on Catheter and Surgical Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation: recommendations for personnel, policy, procedures and follow-up: a report of the Heart Rhythm Society (HRS) Task Force on Catheter and Surgical Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation Developed in partnership with the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) and the European Cardiac Arrhythmia Society (ECAS); in collaboration with the American College of Cardiology (ACC), American Heart Association (AHA), and the Society of Thoracic Surgeons (STS). Endorsed and Approved by the governing bodies of the American College of Cardiology, the American Heart Association, the European Cardiac Arrhythmia Society, the European Heart Rhythm Association, the Society of Thoracic Surgeons, and the Heart Rhythm Society. Europace. 2007, 9, 335–379. [Google Scholar]
- Lip, G.Y.; Beevers, D.G. ABC of atrial fibrillation. History, epidemiology, and importance of atrial fibrillation. BMJ. 1995, 311, 1361–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrey, W.E. Auricular fibrillation. Physiol Rev. 1924, 4, 215–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moe, G.K.; Rheinboldt, W.C.; Abildskov, J.A. A computer model of atrial fibrillation. Am Heart J. 1964, 67, 200–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allessie, M.A.; Lammers, W.J.E.P.; Bonke, F.I.M.; Hollen, J. Experimental evaluation of Moe’s multiple wavelet hypothesis of atrial fibrillation. In Cariac Arrhythmias; Zipes, D.P., Jalife, J., Eds.; Grune & Stratton: New York, NY, USA, 1985; pp. 265–276. [Google Scholar]
- Haissaguerre, M.; Marcus, F.I.; Fischer, B.; Clementy, J. Radiofrequency catheter ablation in unusual mechanisms of atrial fibrillation: report of three cases. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 1994, 5, 743–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jais, P.; Haissaguerre, M.; Shah, D.C.; Chouairi, S.; Gencel, L.; Hocini, M.; et al. A focal source of atrial fibrillation treated by discrete radiofrequency ablation. Circulation. 1997, 95, 572–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haissaguerre, M.; Jais, P.; Shah, D.C.; Takahashi, A.; Hocini, M.; Quiniou, G.; et al. Spontaneous initiation of atrial fibrillation by ectopic beats originating in the pulmonary veins. New Engl J Med. 1998, 339, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nattel, S.; Shiroshita-Takeshita, A.; Brundel, B.J.; Rivard, L. Mechanisms of atrial fibrillation: lessons from animal models. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2005, 48, 9–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, J.L.; Canavan, T.E.; Schuessler, R.B.; Cain, M.E.; Lindsay, B.D.; Stone, C.; et al. The surgical treatment of atrial fibrillation. II. Intraoperative electrophysiologic mapping and description of the electrophysiologic basis of atrial flutter and atrial fibrillation. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1991, 101, 406–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherf, D. Studies on auricular tachycardia caused by aconitine administration. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1947, 4, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.A.; Tai, C.T.; Yu, W.C.; et al. Right atrial focal atrial fibrillation: electrophysiologic characteristics and radiofrequency catheter ablation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 1999, 10, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.S.; Tai, C.T.; Hsieh, M.H.; et al. Catheter ablation of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation initiated by non-pulmonary vein ectopy. Circulation. 2003, 107, 3176–3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumagai, K.; Ogawa, M.; Noguchi, H.; Yasuda, T.; Nakashima, H.; Saku, K. Electrophysiologic properties of pulmonary veins assessed using a multielectrode basket catheter. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004, 43, 2281–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nattel, S. Basic electrophysiology of the pulmonary veins and their role in atrial fibrillation: precipitators, perpetuators, and perplexers. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2003, 14, 1372–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalife, J.; Berenfeld, O.; Mansour, M. Mother rotors and fibrillatory conduction: a mechanism of atrial fibrillation. Cardiovasc Res. 2002, 54, 204–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atienza, F.; Jalife, J. Reentry and atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm. 2007, 4, S13–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiroshita-Takeshita, A.; Brundel, B.J.; Nattel, S. Atrial fibrillation: basic mechanisms, remodeling and triggers. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2005, 13, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tieleman, R.G. The pathophysiology of maintenance of atrial fibrillation. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2003, 26, 1569–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijffels, M.C.; Kirchhof, C.J.; Dorland, R.; Allessie, M.A. Atrial fibrillation begets atrial fibrillation. A study in awake chronically instrumented goats. Circulation. 1995, 92, 1954–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allessie, M.; Ausma, J.; Schotten, U. Electrical, contractile and structural remodeling during atrial fibrillation. Cardiovasc Res. 2002, 54, 230–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Gaspo, R.; Leblanc, N.; Nattel, S. Cellular mechanisms of atrial contractile dysfunction caused by sustained atrial tachycardia. Circulation. 1998, 98, 719–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coumel, P. Autonomic influences in atrial tachyarrhythmias. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2005, 16, 1348–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bettoni, M.; Zimmermann, M. Autonomic tone variations before the onset of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 2002, 105, 2753–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schauerte, P.; Scherlag, B.J.; Pitha, J.; Scherlag, M.A.; Reynolds, D.; Lazzara, R.; et al. Catheter ablation of cardiac autonomic nerves for prevention of vagal atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 2000, 102, 2774–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvan, A.; Pride, H.P.; Eble, J.N.; Zipes, D.P. Radiofrequency catheter ablation of the atria reduces inducibility and duration of atrial fibrillation in dogs. Circulation. 1995, 91, 2235–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappone, C.; Santinelli, V.; Manguso, F.; Vicedomini, G.; Gugliotta, F.; Augello, G.; et al. Pulmonary vein denervation enhances longterm benefit after circumferential ablation for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 2004, 109, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frustaci, A.; Chimenti, C.; Bellocci, F.; Morgante, E.; Russo, M.A.; Maseri, A. Histological substrate of atrial biopsies in patients with lone atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 1997, 96, 1180–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, M.K.; Martin, D.O.; Sprecher, D.; Wazni, O.; Kanderian, A.; Carnes, C.A.; et al. C-reactive protein elevation in patients with atrial arrhythmias: inflammatory mechanisms and persistence of atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 2001, 104, 2886–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aviles, R.J.; Martin, D.O.; Apperson-Hansen, C.; Houghtaling, P.L.; Rautaharju, P.; Kronmal, R.A.; et al. Inflammation as a risk factor for atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 2003, 108, 3006–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allessie, M.A.; Boyden, P.A.; Camm, A.J.; Kléber, A.G.; Lab, M.J.; Legato, M.J.; et al. Pathophysiology and prevention of atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 2001, 103, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oral, H. Mechanisms of atrial fibrillation: lessons from studies in patients. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2005, 48, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wagoner, D.R. Recent insights into the pathophysiology of atrial fibrillation. Semin Thrac Cardiovasc Surg. 2007, 19, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damiano RJJr Gaynor, S.L.; Bailey, M.; Prasad, S.; Cox, J.L.; Boineau, J.P.; et al. The long-term outcome of patients with coronary disease and atrial fibrillation undergoing the Cox maze procedure. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2003, 126, 2016–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillinov, A.M.; McCarthy, P.M. Advances in the surgical treatment of atrial fibrillation. Cardiol Clin. 2004, 22, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Packer, D.L.; Asirvatham, S.; Munger, T.M. Progress in nonpharmacologic therapy of atrial fibrillation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2003, 14, S296–S309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nademanee, K.; McKenzie, J.; Kosar, E.; et al. A new approach for catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: mapping of the electrophysiologic substrate. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004, 43, 2044–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappato, R.; Calkins, H.; Chen, S.A.; Davies, W.; Iesaka, Y.; Kalman, J.; et al. Worldwide survey on the methods, efficacy, and safety of catheter ablation for human atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 2005, 111, 1100–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wazni, O.M.; Marrouche, N.F.; Martin, D.O.; Verma, A.; Bhargava, M.; Saliba, W.; et al. Radiofrequency ablation vs antiarrhythmic drugs as first-line treatment of symptomatic atrial fibrillation: a randomized trial. JAMA. 2005, 293, 2634–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stabile, G.; Bertaglia, E.; Senatore, G.; De, S.A.; Zoppo, F.; Donnici, G.; et al. Catheter ablation treatment in patients with drug-refractory atrial fibrillation: a prospective, multi-centre, randomized, controlled study (Catheter Ablation For The Cure Of Atrial Fibrillation Study). Eur Heart J. 2006, 27, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, D.C.; Sunthorn, H.; Burri, H.; Gentil-Baron, P. Evaluation of an individualized strategy of cavotricuspid isthmus ablation as an adjunct to atrial fibrillation ablation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2007, 9, 926–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
 |
 |
© 2008 by the author. Attribution - Non-Commercial - NoDerivatives 4.0.
Share and Cite
Fassa, A.-A.; Shah, D.C. Mécanismes Physiopathologiques de la Fibrillation Auriculaire. Cardiovasc. Med. 2008, 11, 265. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2008.01352
Fassa A-A, Shah DC. Mécanismes Physiopathologiques de la Fibrillation Auriculaire. Cardiovascular Medicine. 2008; 11(9):265. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2008.01352
Chicago/Turabian StyleFassa, Amir-Ali, and Dipen C. Shah. 2008. "Mécanismes Physiopathologiques de la Fibrillation Auriculaire" Cardiovascular Medicine 11, no. 9: 265. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2008.01352
APA StyleFassa, A.-A., & Shah, D. C. (2008). Mécanismes Physiopathologiques de la Fibrillation Auriculaire. Cardiovascular Medicine, 11(9), 265. https://doi.org/10.4414/cvm.2008.01352




