Antioxidative and Chemopreventive Properties of Vernonia amygdalina and Garcinia biflavonoid
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Vernonia amygdalina (Asteraceae)
2.1. Botanical Classification
2.2. Compounds Isolated from Vernonia amygdalina
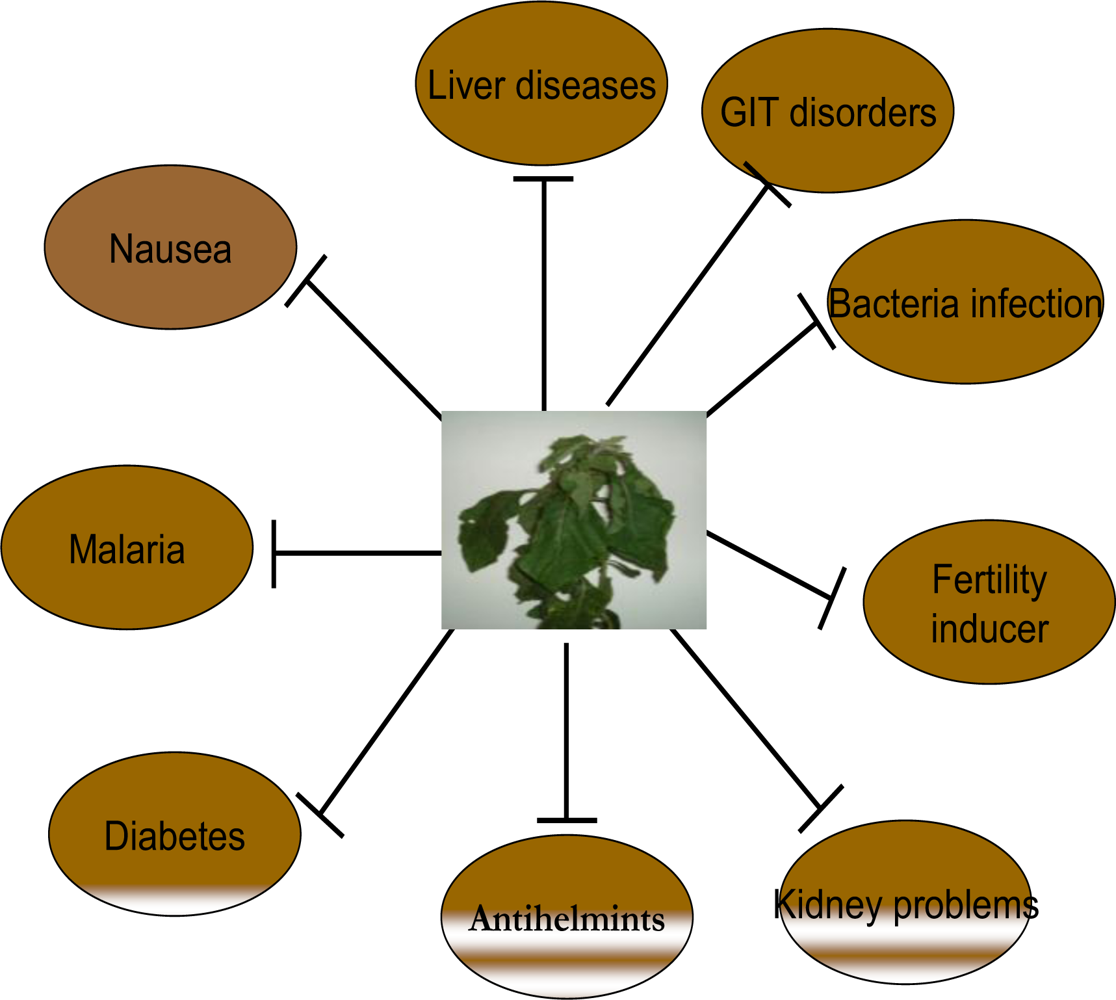
2.3. Traditional Uses of Vernonia amygdalina
2.4. Biological Activities of Vernonia amygdalina
2.4.1. Antioxidant Activity
2.4.2. Chemopreventive Properties of Vernonia amygdalina
3. Garcinia kola Heckel (Guttiferae)
3.1. Medicinal Uses of Garcinia kola
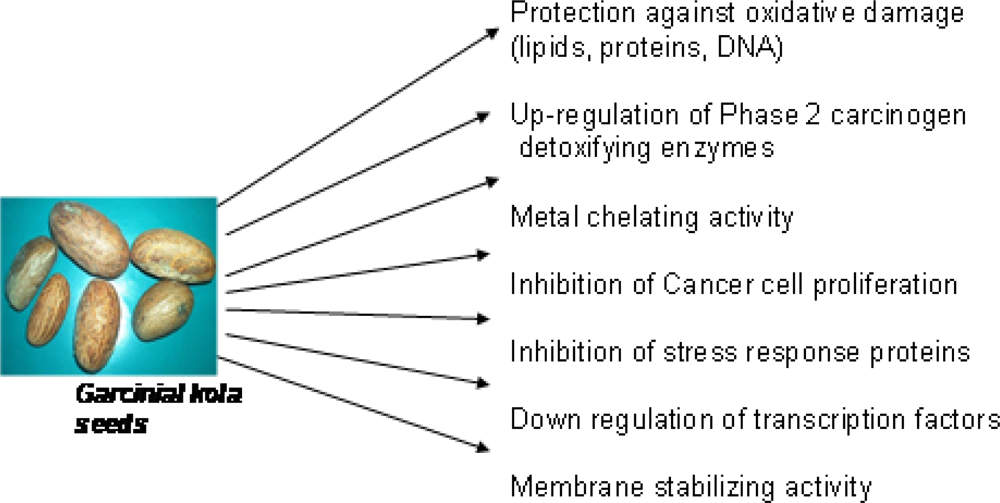
3.2. Biological Properties of Garcinia kola
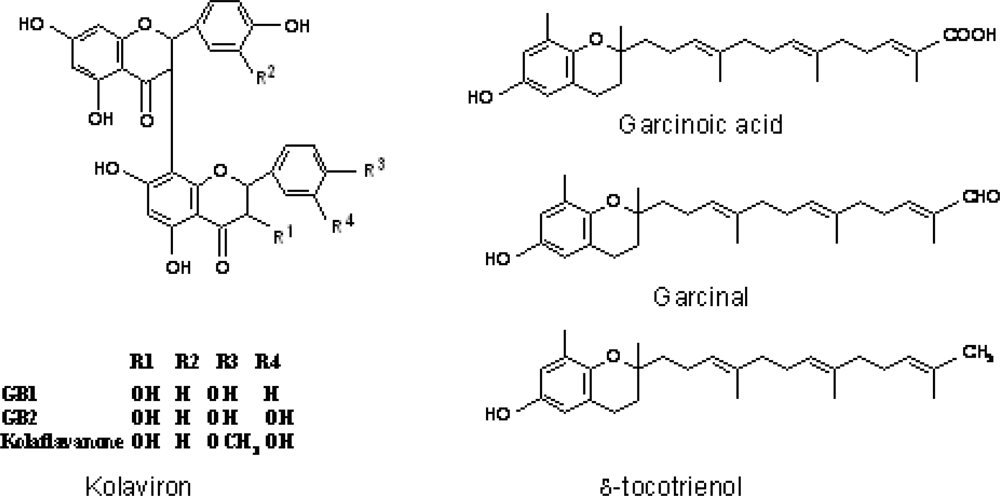
3.3. Chemical Composition of Garcinia kola
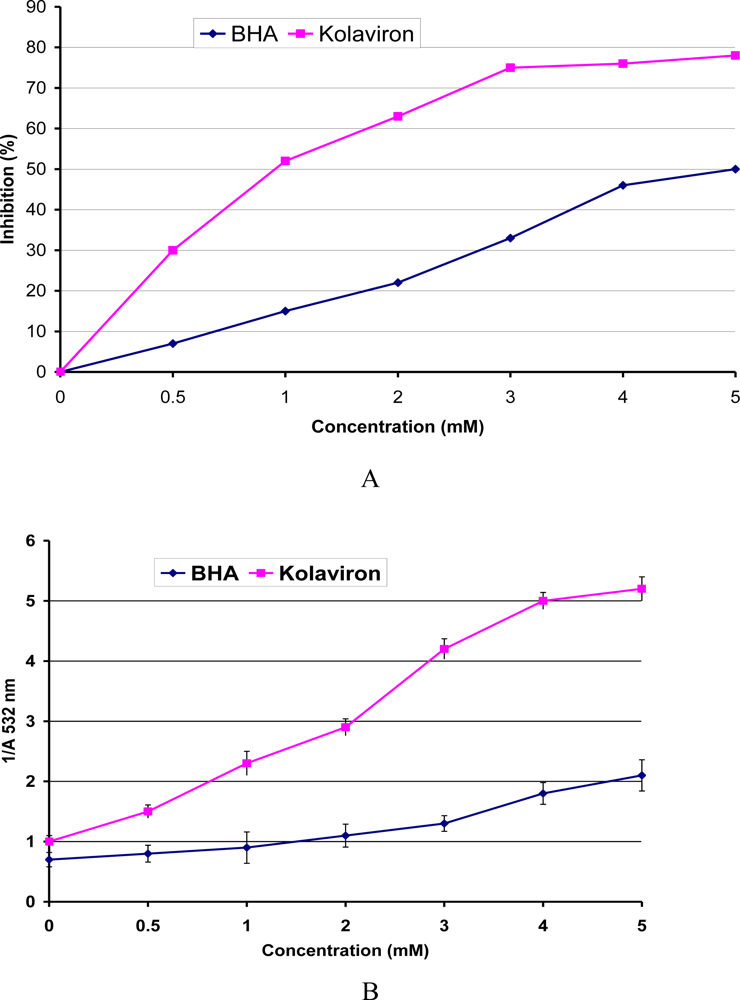
3.4. Antioxidant and Radical Scavenging Effects of Garcinia Biflavonoid (kolaviron)
3.4.1. Effects of Garcinia Biflavonoid on LDL Oxidation and Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress
3.4.2. Effects of Kolaviron on Oxidative DNA Damage
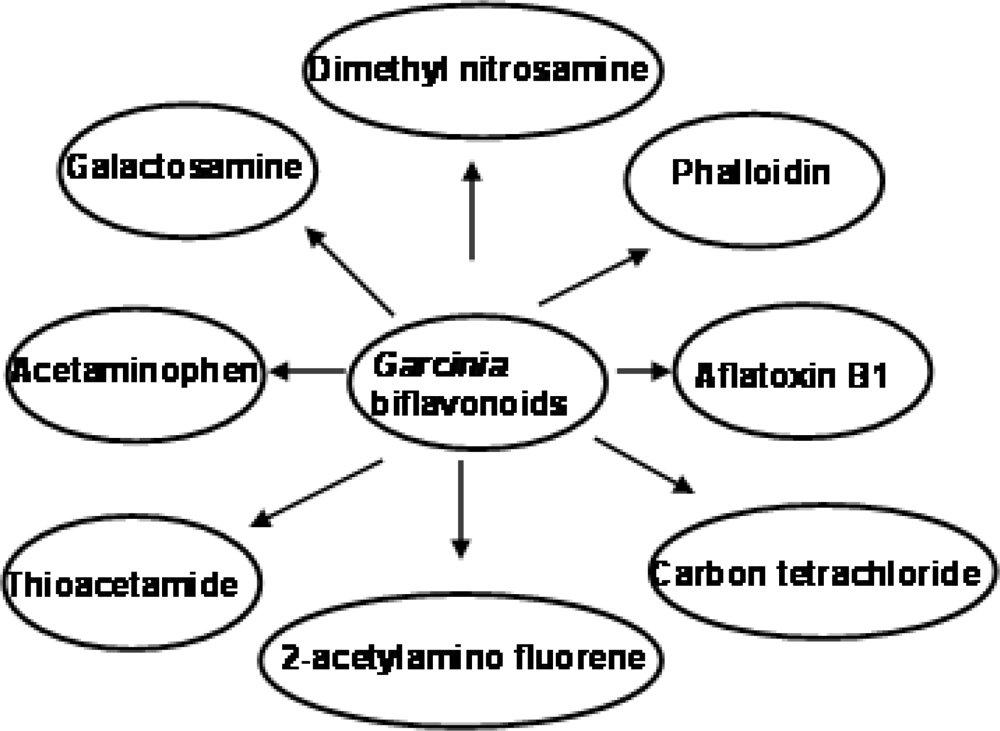
3.5. Chemopreventive Properties of Garcinia Biflavonoid
3.5.1. Antigenotoxic Effect of Garcinia Biflavonoid
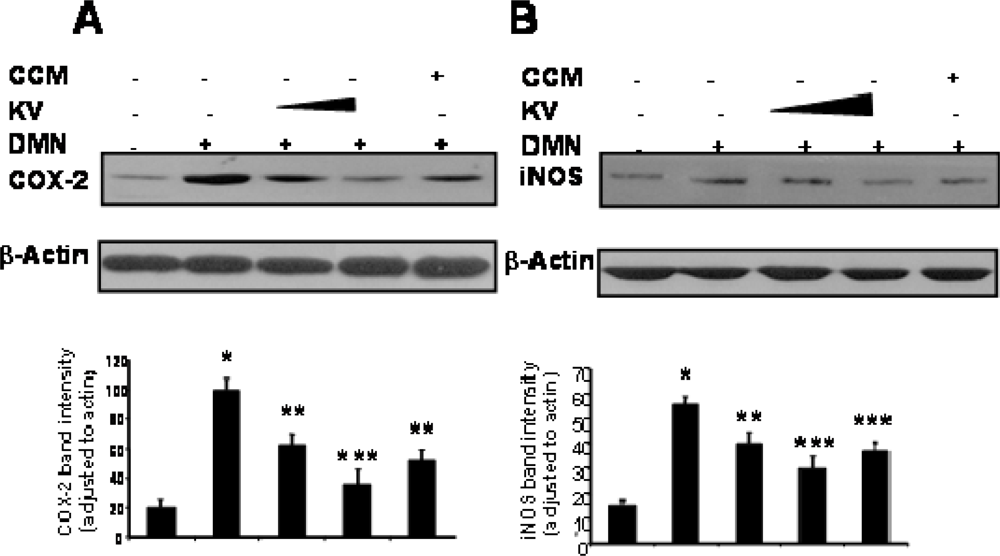
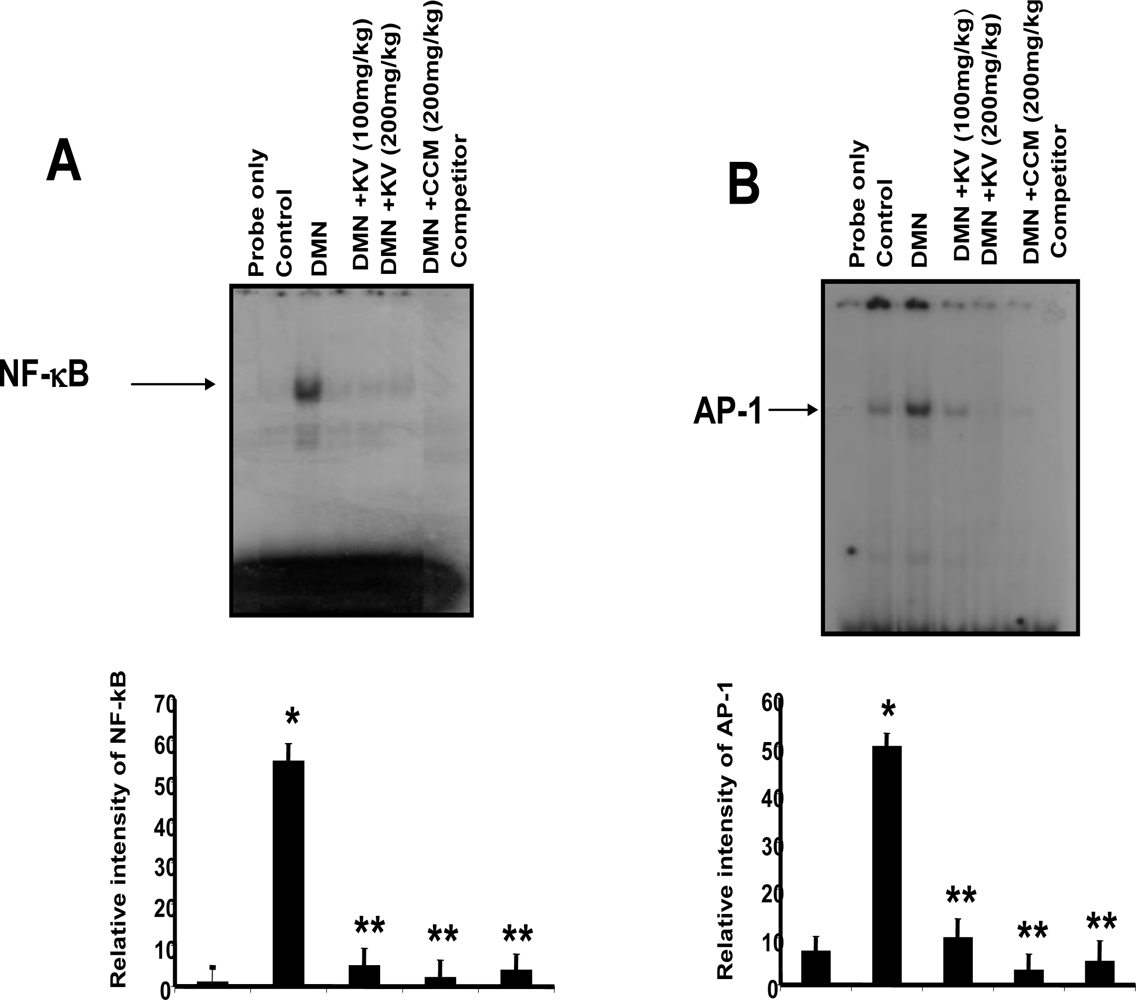
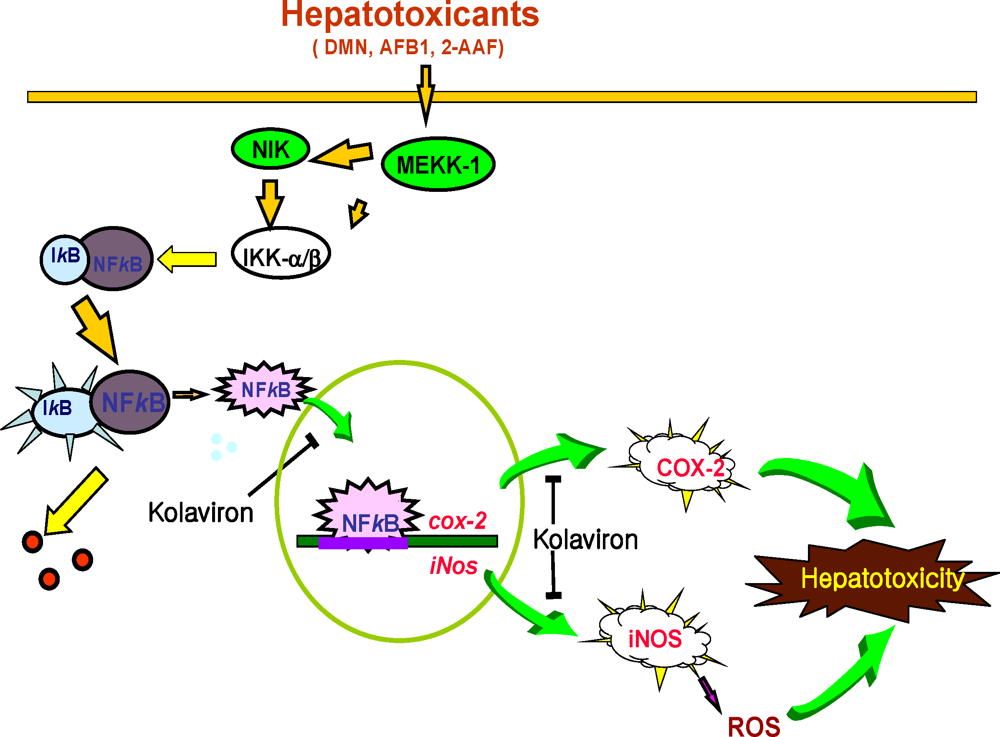
3.5.2. Effect of Garcinia Biflavonoid on Stress Response Proteins and Transcription Factors
3.5.3. Antiproliferative Potentials of Garcinia Biflavonoid
4. Conclusions and Future Direction
Acknowledgments
References
- Aruoma, OI; Sun, B; Fuji, H; Neergheen, VS; Bahorun, T; Kang, KS; Sung, MK. Low molecular proanthocyamidin dietary biofactor oligonol: Its modulation of oxidative stress, bioefficacy, neuroprotection, food application and chemoprevention potentials. Biofactors 2006, 27, 245–265. [Google Scholar]
- Seef, LB; Lindsay, KL; Bacon, BR; Kresina, TF; Hoofnagle, JH. Complementary and alternative medicine in chronic liver disease. Hepatology 2001, 34, 595–603. [Google Scholar]
- Winslow, LC; Krol, DJ. Herbs as medicines. Arch. Intern. Med 1998, 1258, 2192–2199. [Google Scholar]
- Kupchan, SM; Hemmnigway, RJ; Karim, A; Werner, D. Tumor inhibitors. XLVII Vernodalin and Vernomygdin. Two new cytotoxic sesquiterpene lactones from Vernonia amygdalina Del. J. Org. Chem 1969, 34, 3908–3911. [Google Scholar]
- Moundipa, FP; Kamini, G; Melanie, F; Bilong, FC; Bruchhaus, I. In vitro amoebic activity of some medicinal plants of the Bamun region (Cameroon). Afr. J. Tad. Cam 2000, 62, 113–121. [Google Scholar]
- Akah, PA; Ekekwe, RK. Ethnopharmacology of some of the asteraceae family used in the Nigerian traditional medicine. Fitoterapia 1995, 66, 352–355. [Google Scholar]
- Akinpelu, DA. Antimicrobial activity of Vernonia amygdalina leaves. Fitoterapia 1999, 70, 232–234. [Google Scholar]
- Hladik, C; Krief, S; Haxaire, C. Ethnomedicinal and bioactive properties of plants ingested by wild chimpanzees in Uganda. J. Ethnopharmacol 2005, 101, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Muraina, IA; Adaudi, AO; Mamman, M; Kazeem, HM; Picard, J; McGaw, LJ; Eloff, JN. Antimycoplasmal activity of some plant species from northern Nigeria compared to the currently used therapeutic agent. Pharm. Biol 2010, 48, 1103–1107. [Google Scholar]
- Cimanga, RK; Tona, L; Mesia, K; Musuamba, CT; De Bruyne, T; Apers, S; Hernan, N; Miert, VS; Pieters, L; Totte, J; Vlietink, AJ. In vitro antiplasmodia acivity of extravts and fractions of seven medicinal plants used in the democratic republic of Congo. J. Ethnopharmacol 2004, 93, 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Izevbigie, EB. Discovery of water-soluble anticancer Agents (Edotides) from a vegetable found in Benin City, Nigeria. Exp. Biol. Med 2003, 228, 293–298. [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson, J; Dalziel, JM. Flora of West Tropica Africa, 2nd ed; Royal Botanic Garden, Kew: London, UK, 1956; p. 295. [Google Scholar]
- Iwu, MM. Traditional Igbo Medicine; Institute of African studies, University of Nigeria: Nsukka, Nigeria, 1982; pp. 104–110. [Google Scholar]
- Igile, GO; Oleszek, W; Burda, S; Jurzysta, M. Nutritional assessment of Vernonia amygdalina leaves in growing mice. J. Agr. Food Chem 1995, 43, 2162–2166. [Google Scholar]
- Ojiako, OA; Nwajo, HU. Is Vernonia amygdalina hepatotoxic or hepatoprotective? Response from biochemical and toxicity studies in rats. Afr. J. Biotechnol 2005, 5, 1648–1651. [Google Scholar]
- Erasto, G; Grierson, DS; Afolayan, AJ. Bioactive sesquiterpene from leaves of Vernonia amygdalina. J. Ethnopharmacol 2006, 106, 117–129. [Google Scholar]
- Owoeye, O. Anticancer Activity of Vernonia amygdalina Del. Leaf Extract, its Antioxidant and Radioprotective Properties in the Brain of Rats, Ph. D Thesis; Department of Veterinary Medicine, University of Ibadan: Ibadan, Nigeria. 2010.
- Bonsi, MLK; Osuji, PO; Tuah, AK; Umunna, NN. Vernonia amygdalina as a supplement to teff straw (Eragrosis tef.) fed to Ethiopian Menz sheep. Agroforest. Syst 1995, 31, 229–241. [Google Scholar]
- Huffman, MA; Seifu, M. Observations on the illness and consumption of a possibly medicinal plant, Vernonia amygdalina (Del.), by a wild chimpanzee in the Mahale Mountains National Park, Tanzania. Primates 1989, 30, 51–63. [Google Scholar]
- Huffman, MA. Self-medicative behavior in the African great apes: An evolutionary perspective into the origins of human traditional medicine. BioScience 2001, 51, 651–661. [Google Scholar]
- Huffman, MA. Animal self-medication and ethno-medicine: Exploration and exploitation of the medicinal properties of plants. Proc. Nutr. Soc 2003, 62, 371–381. [Google Scholar]
- Argheore, EM; Makkar, HPS; Becker, K. Feed value of some browse plants from the central zone of Delta State Nigeria. Trop. Sci 1998, 38, 97–104. [Google Scholar]
- Ganjian, I; Kubo, I; Fludzinski, P. Insect antifeedant elemanolide lactones from Vernonia amygdalina. Phytochemistry 1983, 22, 2525–2526. [Google Scholar]
- Taiwo, O; Xu, H-X; Lee, SF. Antibacteria activities of extracts from Nigerian chewing sticks. Phytother. Res 1999, 13, 675–679. [Google Scholar]
- Abosi, AO; Raseroka, BH. In vivo antimalarial activity of Vernonia amygdalina. Br. J. Biomed. Sci 2003, 60, 89–91. [Google Scholar]
- Kambizi, L; Afolayan, AJ. An ethnobotanical study of plants used for the treatment of sexually transmitted diseases (njovhera) in Guruve District, Zimbabwe. J. Ethnopharmacol 2001, 77, 5–9. [Google Scholar]
- Alawa, CBI; Adamu, AM; Gefu, JO; Ajanusi, OJ; Abdu, PA; Chiezey, NP; Alawa, JN; Bowan, DD. In vitro screening of two Nigerian medicinal plants (Vernonia amygdalina and Annona sengalensis) for anthelmintic activity. Vet. Parasitol 2003, 113, 78–81. [Google Scholar]
- Izevbigie, EB; Bryant, JL; Walker, A. A novel natural inhibitor of extracellular signal-regulated kinases and human breast cancer cell growth. Exp. Biol. Med 2004, 229, 163–169. [Google Scholar]
- Awe, SO; Makinde, JM; Olaide, OA. Cathartic effect of the leaf extract of Vernonia amygdalina. Fitoterapia 1999, 70, 161–165. [Google Scholar]
- Alabi, DA; Onibudo, MZ; Amusa, NA. Chemicals and nutritional composition of four botanicals with fungitoxic properties. World J. Agr. Sci 2005, 1, 84–88. [Google Scholar]
- Regassa, A. The use of herbal preparation for tick control in Western Ethiopia. J. S. Afr. Vet. Assoc 2000, 71, 240–243. [Google Scholar]
- Amira, CA; Okubadejo, NU. Frequency of complementary and alternative medicine utilization in hypertensive patients attending an urban tertiary care centres in Nigeria. BMC Compl. Alternative Med 2007, 7, 30–48. [Google Scholar]
- Igile, GO; Oleszek, W; Jurzysta, M; Burda, S; Fafunso, M; Fasanmade, AA. Flavonoids from Vernonia amygdalina and their antioxidant activities. J. Agric. Food Chem 1994, 42, 2445–2448. [Google Scholar]
- Jisaka, M; Ohigashi, H; Takagaki, T; Nozaki, H; Tada, T; Hirota, M; Irie, R; Huffman, MA; Nishida, T; Kaji, M; Koshimizu, K. Bitter steroids glucosides, vernoniosides A1, A2, and A3 and related B1 from a possible medicinal plant, Vernonia amygdalina used by wild chimpanzees. Tetrahedron 1992, 48, 625–632. [Google Scholar]
- Jisaka, M; Ohigashi, H; Takegawa, K; Hirota, M; Irie, R; Huffman, MA; Koshimizu, K. Steroid glucosides from Vernonia amygdalina, a possible chimpanzee plant. Phytochemistry 1993, 34, 409–413. [Google Scholar]
- Ohigashi, H; Jisaka, M; Takagaki, T; Nozaki, H; Tada, T; Huffman, MA; Nishida, T; Kaji, M; Koshimizu, K. Bitter principle and a related steroid glucoside from Vernonia amygdalina, a possible medicinal plant for wild chimpanzees. Agr. Biol. Chem 1991, 55, 1201–1203. [Google Scholar]
- Owoeye, O; Yousuf, S; Akhtar, MN; Qamar, K; Dar, A; Farombi, EO; Onwuka, SK; Choudhary, MI. Another Anticancer Elemanolide from Vernonia amygdalina Del. Int. J. Biol. Chem. Sci 2010, 4, 226–234. [Google Scholar]
- Koul, JL; Koul, S; Singh, C; Taneja, SC; Shanmugavel, M; Kampasi, H; Saxena, AK; Qazi, GN. In vitro Cytotoxic Elemanolides from Vernonia lasiopus. Plant. Med 2003, 69, 164–166. [Google Scholar]
- Singha, SC. Medicinal Plants of Nigeria; Nigerian National Press: Lagos, Nigeria, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Dalziel, JM. The Useful Plants of West Tropical Africa; Crown Overseas Agents for the Colonies: London, UK, 1937; p. 65. [Google Scholar]
- Getahun, A. Some Common Medicinal and Poisonous Plants Used in Ethiopian Folk Medicine; Faculty of Science, Addis Ababa University: Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 1976; p. 63. [Google Scholar]
- Oliver, B. Medicinal Plants in Nigeria; Nigerian college of Arts, Science and Technology: Zaria, Nigeria, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Masaba, SC. The antimalaria activity of Vernonia amygdalina Del (Compositae). Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg 2000, 94, 694–695. [Google Scholar]
- Iwalewa, EO; Adewunmi, CO; Omisore, NOA; Adebanji, OA; Azike, CK; Adigun, AO; Adesina, OA; Olowoyo, OG. Pro- and anti-oxidant effects and cytoprotective potentials of nine edible vegetables in South West Nigeria. J. Med. Foods 2005, 8, 539–544. [Google Scholar]
- Iwalokun, BA; Efedede, BU; Alabi-Sofunde, JA; Oduala, T; Magbagbeola, OA; Akinwande, AI. Hepatoprotective and antioxidant activities of Vernonia amygdalina on acetaminophen-induced hepatic damage in mice. J. Med. Food 2006, 9, 524–530. [Google Scholar]
- Adesanoye, OA; Farombi, EO. Hepatoprotective effects of Vernonia amygdalina (astereaceae) in rats treated with carbon tetrachloride. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol 2010, 62, 197–206. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, NC; Samman, S. Flavonoids—Chemistry, metabolism, cardioprotective effects and dietary sources. J. Nutr. Biochem 1996, 7, 66–76. [Google Scholar]
- Markham, KR; Bloor, SJ. Analysis and identification of flavonoids in practice. In Flavonoids in Health and Disease; Rice-Evans, CA, Lester, P, Eds.; Marcel Dekker Inc: New York, NY, USA, 1998; pp. 1–32. [Google Scholar]
- Farombi, EO; Akanni, OO; Emerole, GO. Antioxidative and scavenging activities of kolaviron in vitro. Pharm. Biol 2002, 40, 107–116. [Google Scholar]
- Mathew, J; Latha, PG; George, V. Antioxidant flavonoids from Vitex peduncularis. J. Trop. Med. Plants 2004, 5, 217–221. [Google Scholar]
- Schuldt, EZ; Favias, MR; Ribeiro-do-Valle, RM; Ckless, K. Comparative study of radical scavenger activities of crude extract and fractions of Cuphea carthagenesis leaves. Phytomedicine 2004, 11, 523–529. [Google Scholar]
- Prabhakar, KR; Veeresh, VP; Vipan, K; Sudheer, M; Priyadarsini, KI; Satish, RBSS; Unnikrishnan, MK. Bioactivity guided fractionation of Coronopus didymus: A free radical scavenging perspective. Phytomedicine 2006, 13, 591–595. [Google Scholar]
- Youdim, KA; Dobbie, MS; Kuhnle, G; Proteggente, AR; Abbott, NJ; Rice-Evans, C. Interaction between flavonoids and the blood brain barrier: In vitro studies. Neurochemistry 2003, 85, 180–192. [Google Scholar]
- Owoeye, O; Farombi, EO; Onwuka, SK. Gross morphometric reduction of rats cerebellum by gamma irradiation was mitigated by pretreatment with Vernonia amygdalina leaf extract. Rom J Morphol Embryol 2011, (in press). [Google Scholar]
- Yedjou, C; Izevbigie, E; Tchounwou, P. Preclinical assessment of Vernonia amygdalina leaf extracts as DNA damaging anti-cancer agent in the management of breast cancer. IJERPH 2008, 5, 337–341. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, CB; Stevens, J; Izevbigie, EB; Walker, A; McDaniel, O. Time and dose-dependent modulation of phase 1 and phase 2 gene expression in response to treatment of MCF-7 cells with a natural anti-cancer agent. Cell Mol. Biol. (Noisy-le-grand) 2003, 49, 1057–1065. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez, E; Towers, GHN; Mitchell, JC. Biological activities of sesquiterpene lactones. Phytochemistry 1976, 15, 1573–1580. [Google Scholar]
- Sweeney, CJ; Mehrotra, S; Sadaria, MR; Kumar, S; Shortle, NH; Roman, Y; Sheridan, C; Campbell, RA; Murray, DJ; Badve, S; Nakshatri, H. The sesquiterpene lactone parthenolide in combination with docetaxel reduces metastasis and improves survival in a xenograft model of breast cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther 2005, 4, 1004–1012. [Google Scholar]
- Song, YJ; Lee, DY; Kim, SN; Lee, KR; Lee, HW; Han, JW; Kang, DW; Lee, HY; Kim, YK. Apoptotic potential of sesquiterpene lactone ergolide through the inhibition of NF-κB signaling pathway. J. Pharmacol 2005, 57, 1591–1597. [Google Scholar]
- Colditz, GA; Hankinson, SE; Hunter, DJ; Willett, WC; Manson, JE; Sampler, MJ; Henneckens, C; Rosner, B; Spiezer, FE. The use of estrogen and progestin and the risk of cancer in postmenopausal women. NEJM 2006, 332, 1589–1595. [Google Scholar]
- Blanco, JG; Gil, RR; Bocco, JL; Meragelman, TL; Genti-Raimondi, S; Flury, A. Aromatase inhibition by an 11,13-Dihydroderivative of a sesquiterpene lactone. J. Pharmacol. Expt. Therap 2001, 297, 1099–1105. [Google Scholar]
- Ayensu, ES. Medicinal Plants of West Africa; Reference publication Inc: Algonac, MI, USA, 1978; pp. 162–168. [Google Scholar]
- Braide, VB. Antihepatotoxic biochemical effects of kolaviron, a biflavonoid of Garcinia kola seeds. Phytother. Res 1991, 5, 35–37. [Google Scholar]
- Iwu, MM; Igboko, OA; Okunji, CO; Tempesta, MS. Antidiabetic and aldose reductase activities of biflavanones of Garcinia kola. J. Pharm. Pharmacol 1990, 42, 290–292. [Google Scholar]
- Crabbe, MJ; Goode, D. Aldose reductase: A window to the treatment of diabetic complications? Prog. Retin. Eye Res 1998, 17, 313–323. [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita, JH; Fukushi, S; Kador, P; Merola, LO. Aldose reductase in diabetic complications of the eye. Metabolism 1979, 28, 462–469. [Google Scholar]
- Iwu, M. Biflavanones of garcinia: Pharmacological and biological activities. In Plant Flavonoids and Medicine: Biochemical, Pharmacological and Structure Activity Relationships; Cody, V, Middleton, E, Eds.; Alan R. Liss Inc: New York, NY, USA, 1986; pp. 485–488. [Google Scholar]
- Farombi, EO; Tahnteng, JG; Agboola, O; Nwankwo, JO; Emerole, GO. Chemoprevention of 2-acetyl aminofluorene-induced hepatotoxicity and lipid peroxidation in rats by kolaviron—A Garcinia kola seed extract. Food Chem. Toxicol 2000, 38, 535–541. [Google Scholar]
- Farombi, EO. Mechanisms for the hepatoprotective action of kolaviron: Studies on hepatic enzymes, microsomal lipids and lipid peroxidation in carbon tetrachloride-treated rats. Pharmacol. Res 2000, 42, 75–80. [Google Scholar]
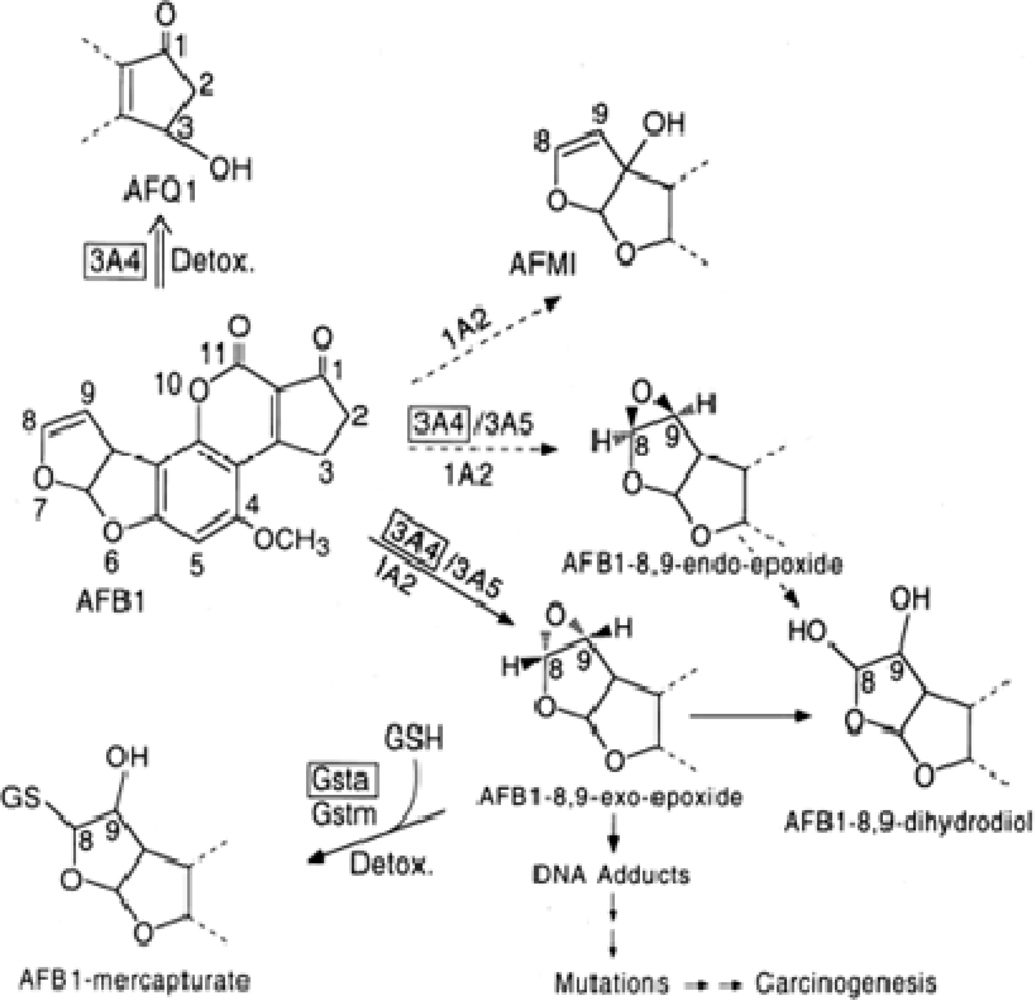
- Farombi, EO; Adepoju, BF; Ola-Davies, OE; Emerole, GO. Chemoprevention of aflatoxin B1-induced genotoxicity and hepatic oxidative damage in rats by Kolaviron, a natural biflavonoid of Garcinia kola seeds. Eur. J. Canc. Prev 2005, 14, 207–214. [Google Scholar]
- Farombi, EO; Shrotriya, S; Surh, YJ. Kolaviron inhibits Dimethyl Nitrosamine-induced hepatotoxicity by suppressing COX-2 and iNOS expression: NF-κB and AP-1 as potential molecular targets. Life Sci 2009, 84, 149–155. [Google Scholar]
- Aplin, RT; Blasdale, JKC; Halsall, TG; Hornby, GMJ. The isolation of cycloartenol and 24-methylenecycloartenol from false kola nuts (Garcinia kola Heckel). J Chem Soc 1967, C, 246–248. [Google Scholar]
- Cotterhill, PJ; Scheinmann, F; Stenhouse, TA. Extractives from Guttiferae: Kolaflavanone, a new biflavanone from the nuts of Garcinia kola. 1978, 532–538. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, RA; Owegby, AG; Parimoo, AG; Waterman, PG. Kolanone, a novel polyisoprenylated benzophenone with antimicrobial properties from the fruit of Garcinia kola. Plant. Med 1982, 44, 78–81. [Google Scholar]
- Iwu, MM. Antihepatotoxic constituents of Garcinia kola seeds. Experientia 1985, 41, 699–700. [Google Scholar]
- Terahima, K; Takaya, Y; Niwa, M. Powerful antioxidative agents based on Garcinoic acid from Garcinia kola. Biorg. Med. Chem 2002, 10, 1619–1625. [Google Scholar]
- Aruoma, OI. Free radicals and international nutrition. Asia Pacific J. Clin. Nutr 1999, 8, 53–63. [Google Scholar]
- Farombi, EO; Hansen, M; Ravn-Haren, G; Moller, P; Dragsted, LO. Commonly consumed and naturally occurring dietary substances affect biomarkers of oxidative stress and DNA damage in healthy rats. Food Chem. Toxicol 2004, 42, 1315–1322. [Google Scholar]
- Farombi, EO; Moller, P; Dragsted, LO. Ex-vivo and in vitro protective effects of kolaviron against oxygen-derived radical-induced DNA damage and oxidative stress in human lymphocytes and rat liver cells. Cell Biol. Toxicol 2004, 20, 71–82. [Google Scholar]
- Nwankwo, JO; Tanhnteng, JG; Emerole, GO. Inhibition of aflatoxin B1 genotoxicity in human liver-derived HepG2 cells by kolaviron biflavonoids and molecular mechanisms of action. Eur. J. Canc. Prev 2000, 9, 351–361. [Google Scholar]
- Eddy, EP; Howard, PC; McCoy, GD; Rosenkranz, HS. Mutagenicity, unscheduled DNA sysnthesis, and metabolism of 1-nitropyrene in the human hepatoma cell line HepG2. Canc. Res 1987, 47, 3163–3168. [Google Scholar]
- Farombi, EO; Nwaokeafor, IA. Anti-oxidant mechanisms of action of kolaviron: Studies on serum lipoprotein oxidation, metal chelation and oxidative microsomal membrane damage in rats. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Phys 2005, 32, 667–674. [Google Scholar]
- McKelvey-Martin, VJ; Green, MHL; Scmezer, P; Pool-Zobel, BL; DeMeo, MP. The single cell gel electrophoresis assay (comet assay): A European review. Mutat. Res 1993, 288, 47–63. [Google Scholar]
- Eaton, DL; Gallagher, EP. Mechanisms of aflatoxin carcinogenesis. Ann. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol 1994, 34, 135–172. [Google Scholar]
- IARC. Evaluation of carcinogenic risks to human. Some naturally occurring substances: Food items and constituents, heterocyclic aromatic amines and mycotoxins. IARC Monographs 1993, 56, 362–370. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, JS; Shen, X; He, X; Zhu, Y-R; Zhang, B-C; Wang, J-B; Quian, G-S; Kuang, S-Y; Zarba, A; Egner, PA; Jacobson, LP; Munoz, A; Helzlsouer, KJ; Groopman, JD; Kensler, TW. Protective alterations in phase 1 and 2 metabolism of aflatoxin B1 by oltipraz in residents of Qidong, Peoples Republic of China. J. Natl. Canc. Inst 1998, 91, 347–354. [Google Scholar]
- Dierickx, PJ. The influence of picolines on glutathione transferase activity and subunit composition in human liver derived HepG2 cells. Biochm. Pharamcol 1994, 48, 1976–1978. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, SO; Kundu, JK; Shin, YK; Park, JH; Cho, MH; Kim, TY; Surh, YJ. [6]-Gingerol inhibits COX-2 expression by blocking the activation of p38 MAP kinase and NF-kappaB in phorbol ester-stimulated mouse skin. Oncogene 2005, 24, 2558–2567. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, WY; Park, JH; Kim, MJ; Kim, HO; Hwang, JK; Lee, SK; Park, KK. Xanthorrhizol inhibits 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate-induced acute inflammation and two-stage mouse skin carcinogenesis by blocking the expression of ornithine decarboxylase, cyclooxygenase-2 and inducible nitric oxide synthase through mitogen-activated protein kinases and/or the nuclear factor-kappa B. Carcinogenesis 2007, 28, 1224–1231. [Google Scholar]
- Aggarwal, BB; Shishoda, S. Suppression of the nuclear factor (B activation pathway by spice-derived phytochemicals: Reasoning for the seasoning. Ann. NY Acad. Sci 2004, 1030, 434–441. [Google Scholar]
- Neergheen, VS; Bahorun, T; Taylor, EW; Jen, LS; Aruoma, OI. Targeting specific cell signaling transduction pathways by dietary and medicinal phytochemicals in cancer chemoprevention. Toxicology 2010, 278, 229–241. [Google Scholar]
- Nanji, AA; Jokelainen, K; Tipoe, GL; Rahemtulla, A; Thomas, P; Dannenberg, AJ. Curcumin prevents alcohol-induced liver disease in rats by inhibiting the expression of NF-kappa B-dependent genes. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol 2003, 284, G321–327. [Google Scholar]
- Fogh, J; Trempe, X. Human Tumor Cells in Vitro; Fogh, J, Ed.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1975; pp. 115–159. [Google Scholar]
- Farombi, EO. Kolaviron, a biflavonoid complex from the seed of Garcinia kola modulates cell growth in human HT29 colon adenocarcinoma cells and LT97 colon adenoma cells. Unpublished data, 2005.
- Veeriah, S; Hofmann, T; Glei, M; Dietrich, H; Will, F; Schreier, P; Knaup, B; Pool-Zobel, BL. Apple polyphenols and products formed in the gut differently inhibit survival of human cell lines derived from colon adenoma (LT97) and carcinoma (HT29). J. Agr. Food Chem 2007, 55, 2892–2900. [Google Scholar]
- Farombi, EO. Biochemical and molecular mechanisms of hepatoprotection by kolaviron, a natural antioxidant biflavonoid from Garcinia kola seed. In Nutritional Antioxidants in Cancer and Degenerative Diseases; Farombi, EO, Ed.; Transworld Research: Kerala, India, 2009; pp. 153–166. [Google Scholar]
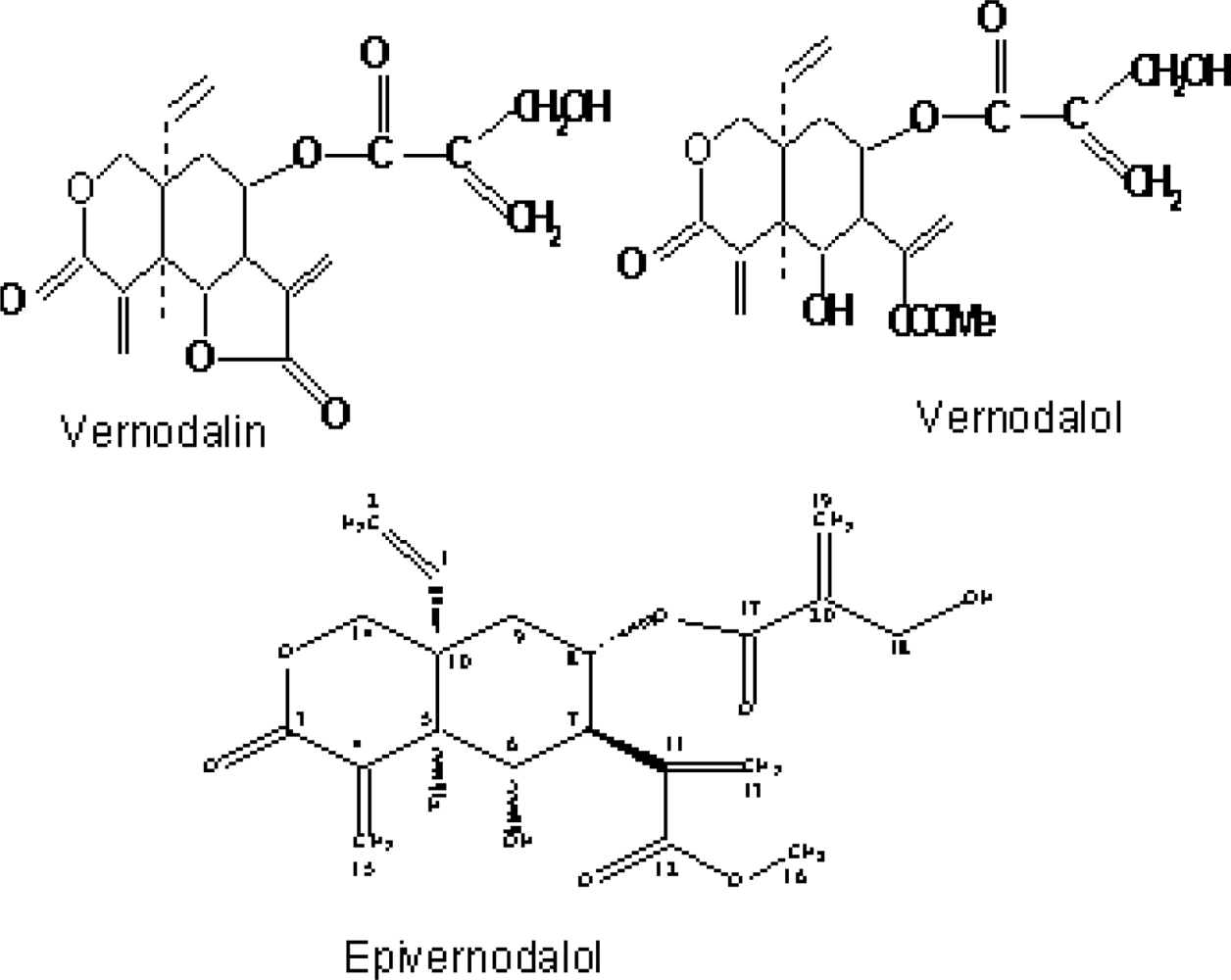
| Name of Compound | Class of Compound | Author (s) |
|---|---|---|
| Vernodalin | Sesquiterpene lactone | Kupchan et al. (1969) [4] |
| Vernomygdin | Sesquiterpene lactone | Kupchan et al. (1969) [4] |
| Vernoniosides A1, A2, A3, B1 | Steroid Glucosides | Jisaka et al. (1992) [34] |
| Vernoniosides A4, B2, B3 | Steroid Glucosides | Jisaka et al. (1993) [35] |
| Vernoniosides D and E | Steroid glycosides | Igile et al. (1995) [33] |
| Vernodalol | Sesquiterpene lactone | Ganjian et al. 1983 [23]; Erasto et al. 2006 [16] |
| Epivernodalol | Sesquiterpene lactone | Owoeye et al. (2010) [37] |
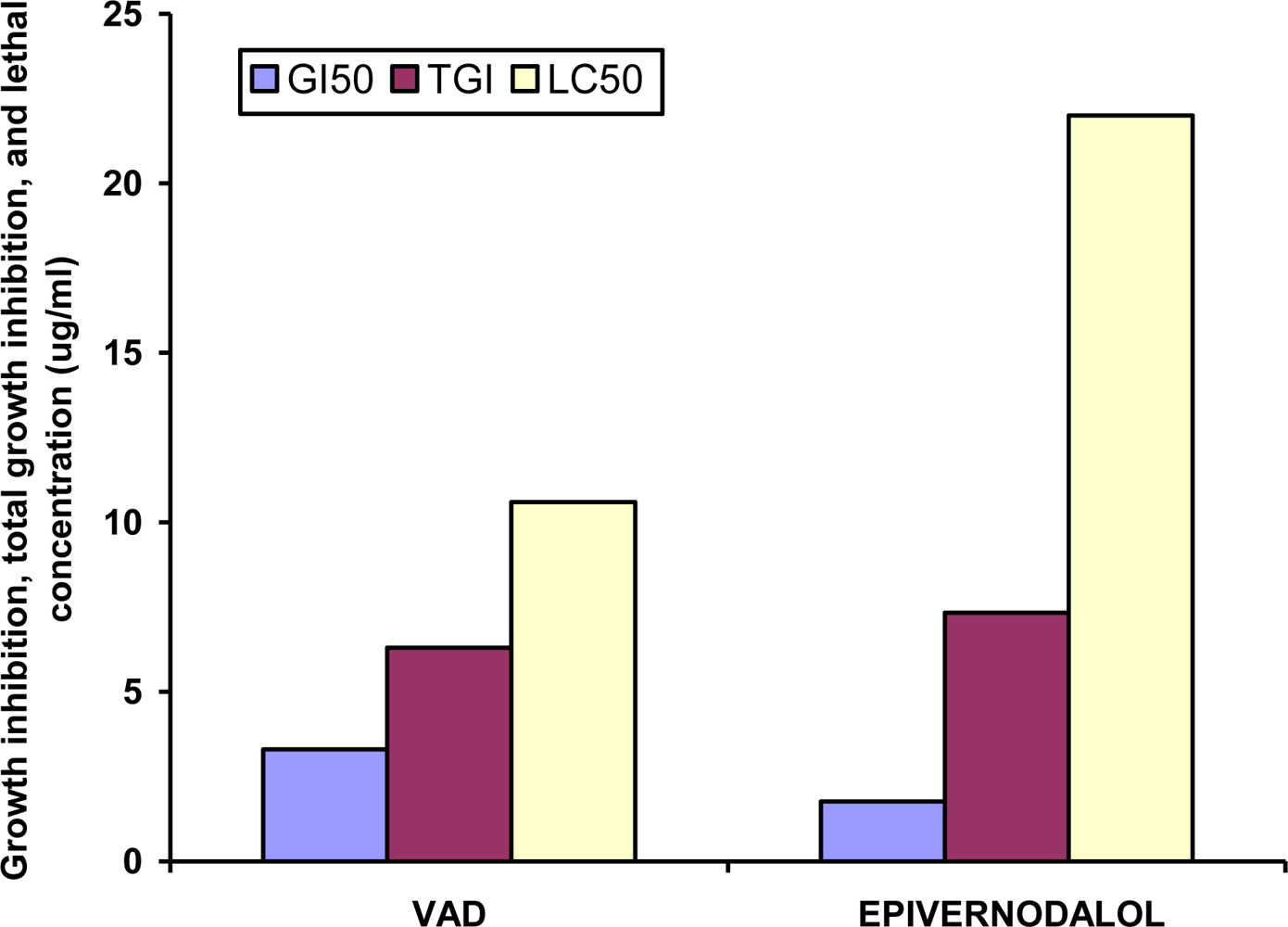
| Code | GI50 (μg/mL) | TGI (μg/mL) | LC50 (μg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MEVA (extract) | 86 ± 1.3 | 141.3 ± 4.7 | 199 ± 10.8 |
| VAD (fraction) | 3.3 ± 0.3** | 6.3 ± 0.3** | 10.6 ± 0.8** |
| VAP (fraction) | 9.7 ± 2.3* | 21.2 ± 5.4* | 37.7 ± 4.4* |
| Epivernodalol | 1.76 ± 0.3** | 7.33 ± 0.55** | 22 ± 1.2** |
| Doxorubicin | 0.01 ± 0 | 0.07 ± 0.03 | 0.48 ± 0.1 |
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Farombi, E.O.; Owoeye, O. Antioxidative and Chemopreventive Properties of Vernonia amygdalina and Garcinia biflavonoid. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2011, 8, 2533-2555. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph8062533
Farombi EO, Owoeye O. Antioxidative and Chemopreventive Properties of Vernonia amygdalina and Garcinia biflavonoid. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2011; 8(6):2533-2555. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph8062533
Chicago/Turabian StyleFarombi, Ebenezer O., and Olatunde Owoeye. 2011. "Antioxidative and Chemopreventive Properties of Vernonia amygdalina and Garcinia biflavonoid" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 8, no. 6: 2533-2555. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph8062533
APA StyleFarombi, E. O., & Owoeye, O. (2011). Antioxidative and Chemopreventive Properties of Vernonia amygdalina and Garcinia biflavonoid. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 8(6), 2533-2555. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph8062533




