Acclimation to Low Level Exposure of Copper in Bufo arenarum Embryos: Linkage of Effects to Tissue Residues
Abstract
:Introduction
Material and Methods
Statistical Analysis
Solutions and Reagents
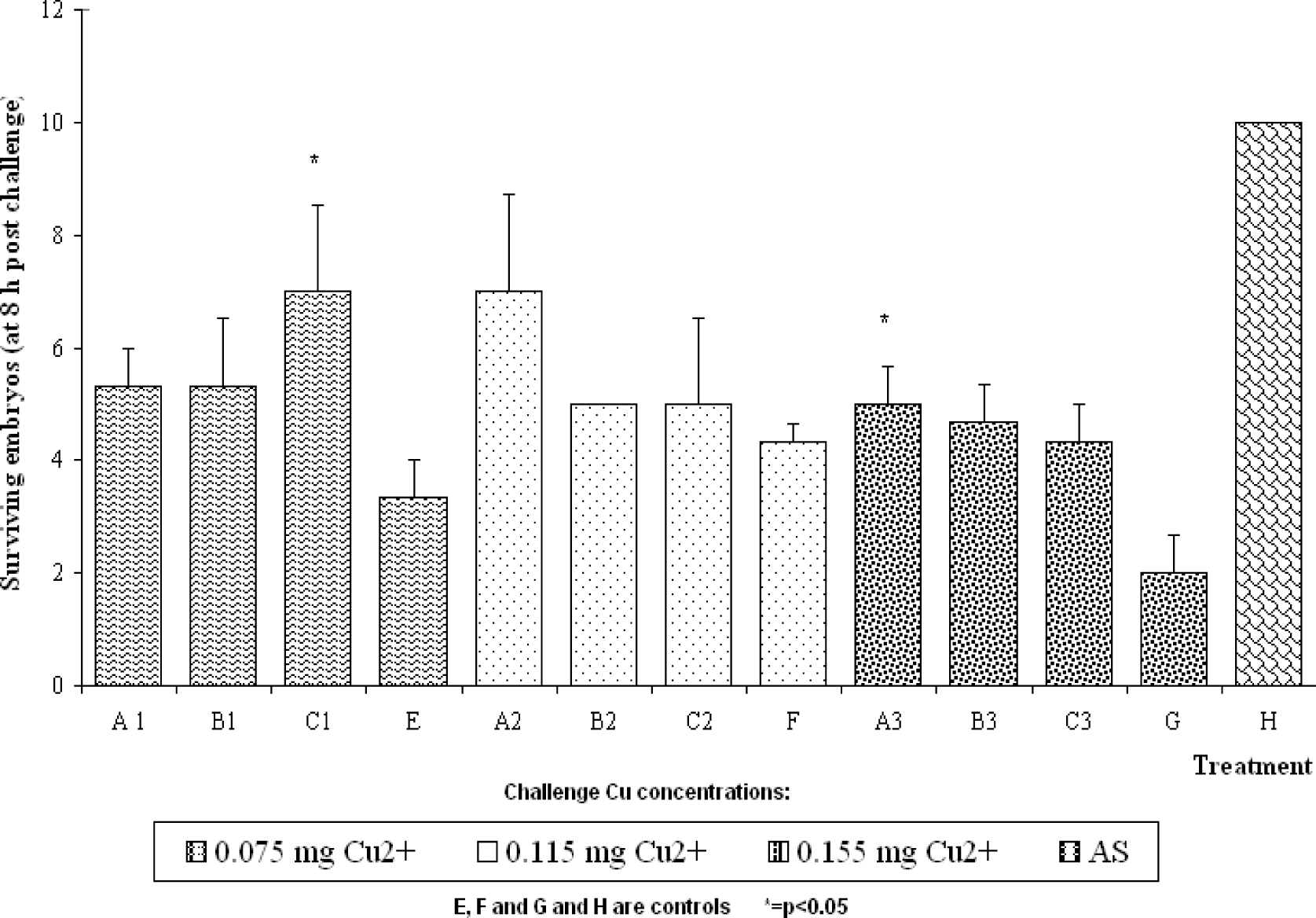
Results
Discussion
| Ranges of Cu concentration during the acclimation protocols (ng.L−1) | μg Cu/g wet weight (a) | μg Zn/g wet weight (a) |
|---|---|---|
| Control | 1.035 (0.09) | 17.92 (0.42) |
| 40 – 270 | 0.785 (0.02)* | 17.42 (0.84) |
| 115 – 350 | 0.800 (0,03)* | 17.93 (0.92) |
| 190 – 420 | 0.805 (0.04)* | 17.44 (0.71) |
Acknowledgments
References
- Weis, P; Weis, JS. Cadmium acclimation and hormesis in Fundulus heteroclitus during fin regeneration. Environ. Res. 1986, 39(2), 356–363. [Google Scholar]
- van Straalen, NM; Vaal, MA. Physiological mechanism underlying adaptation to environmental stress. Sci. Total Environ. (Supp.) 1993, 1783–1787. [Google Scholar]
- Herkovits, J; Pérez-Coll, CS. Increased resistance against cadmium toxicity by means of pretreatment with low cadmium/zinc concentrations in Bufo arenarum embryos. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 1995, 49, 171–175. [Google Scholar]
- Calabrese, EJ; Baldwin, LA. Hormesis as a biological hypothesis. Environ. Health Perspect. 1998, 106 Suppl. 1, 357–362. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, JM; Farland, WH. Biological effects of low level exposures: A perspective from U.S. EPA Scientist. Environ. Health Perspect. 1998, 106 Suppl. 1, 379–381. [Google Scholar]
- IPCS Environmental Health Criteria 200. Copper; Geneva; WHO, International Programme on Chemical Safety, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Linder, MC; Hazegh-Azam, M. Copper biochemistry and molecular biology. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1996, 63, 797–811. [Google Scholar]
- Nriagu, JO. Global inventory of natural and anthropogenic emissions of trace metals to the atmosphere. Nature (Lond) 1979, 279, 409–411. [Google Scholar]
- Alt, ER; Sternlieb, I; Goldfisher, S. The cytopathology of metal overload. Int. Rev. Exp. Pathol. 1990, 31, 165–188. [Google Scholar]
- Noel-Lambot, F; Bouquegneau, JM; Frankenne, F; Dieteche, A. Cadmium, zinc and copper accumulation in limpets (Patella vulgata) from the Bristol Channel with special reference to metallotioneins. Mar. Ecol. Pro. Ser. 1980, 2, 81–89. [Google Scholar]
- Coimbra, J; Carraça, S. Accumulation of Fe, Zn, Cu and Cd during the different stages of the reproductive cycle in Mytilus edulis. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 1990, 95C, 265–270. [Google Scholar]
- Kannan, K; Yasunaga, Y; Iwata, H; Ichihashi, H; Tanabe, S; Tatsukawa, R. Concentrations of heavy metals, organochlorines and organotins in horseshoe crab Tachypleus tridentatus, from Japanese coastal waters. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1995, 28, 40–47. [Google Scholar]
- Favero, N; Cattalini, F; Bertaggia, D; Albergoni, V. Metal accumulation in a biological indicator (Ulva rigida) from the lagoon of Venice (Italy). Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1996, 31, 9–18. [Google Scholar]
- Gale, SA; Smith, SV; Lim, RP; Jeffree, RA; Petocz, P. Insights into the mechanisms of copper tolerance of a population of black-banded rainbow fish (Melanotaenia nigrans) (Richardson) exposed to mine leachate, using64/67Cu. Aquat. Toxicol. 2003, 62, 135–153. [Google Scholar]
- Jarvinen, AW; Ankley, GT. Linkage of effects to tissue residues: Development of a comprehensive database for aquatic organisms exposed to inorganic and organic chemicals. In SETAC Technical Publications Series; SETAC Press, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Herkovits, J; Cardellini, P; Pavanati, C; Pérez-Coll, CS. Cadmium uptake and bioaccumulation in Xenopus laevis embryos at different developmental stages. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 1998, 39, 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Ashida, J. Adaptation of fungi to metal toxicants. Annu. Rev. Phytopatol. 1965, 3, 153–174. [Google Scholar]
- Chopra, I. Decreased uptake of cadmium by a resistant strain of Staphylococcus aureus. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1971, 63, 265–267. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, AJM. Metal Tolerance. N. Phytol 1987, 106, S93–S111. [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchiya, N; Ochi, T. Mechanisms for the decrease in the accumulation of cadmium (Cd) in Cd-resistant Chinese hamster V79 cells. Arch. Toxicol. 1994, 68, 325–331. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, L; Klerks, PL. Changes in cadmium accumulation as a mechanism for cadmium resistance in the least killifish Heterandria formosa. Aquatic. Toxicol. 2004, 66, 73–81. [Google Scholar]
- Naab, F; Volcominsky, M; Burlón, A; Caraballo, ME; Debray, M; Kesque, JM; Kreiner, AJ; Ozafrán, MJ; Schuff, JA; Stoliar, P; Vázquez, ME; Davidson, J; Davidson, M; Fonovich de Schroeder, TM. Metabolic alterations without metal accumulation in the ovary of adult Bufo arenarum females, observed after long-term exposure to Zn2+, followed by toxicity to embryos. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2001, 41, 201–207. [Google Scholar]
- Van Tilborg, WJM; Van Assche, F. Risk assessment of essential elements: proposal for a fundamentally new approach. SETAC NEWS 1996, 16, 28–29. [Google Scholar]
- Cousins, RJ; Hempe, JM. Brown, ML, Ed.; Washington, DC, 1990; pp. 251–260.
- Bertazzo, A; Costa, C; Biasiolo, M; Allegri, G; Cirrincione, G; Presti, G. Determination of copper and zinc levels in human hair. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 1996, 52, 37–53. [Google Scholar]
- Herkovits, J; Helguero, LA. Copper toxicity and copper-zinc interactions in amphibian embryos. Sci. Total Environ 1998, 221, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Herkovits, J; Pérez-Coll, CS; Dominguez, O. Cu-Zn antagonism in Bufo arenarum embryos: the time thresholds for Zn to protect against lethality exerted by copper. SETAC 21st Annual Meeting, Abstract Book 2000, 273. [Google Scholar]
- Gachot, B; Poujeol, P. Effects of cadmium and copper on Zn transport kinetics by isolated renal proximal cells. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 1992, 35, 93–103. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Copper. In Trace elements in human nutrition and health; Geneva; World Health Organization, 1996; chapter 7; pp. 123–143. [Google Scholar]
- Salim, S; Farquharson, J; Arneil, GC; Cockburn, F; Forbes, GI; Logan, RW; Sherloc, JC; Wilson, TS. Dietary copper intake in artificially fed infants. Arch. Dis. Chil. 1986, 61(11), 1068–1075. [Google Scholar]
- August, D; Janghorbani, M; Young, VR. Determination of zinc and copper absorption at three dietary Zn-Cu ratios by using stable isotope methods in young adult and elderly subjects. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1989, 50, 1457–1463. [Google Scholar]
- Muller, JP; Wouters-Tyrou, D; Erraiss, N; Vedel, M; Touzet, N; Mesnard, J; Sautiere, P; Wegnez, M. Molecular cloning and expression of a metallothionein mRNA inXenopus laevis. DNA and Cell. Biol. 1993, 12(4), 341–349. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Coll, CS; Herkovits, J; Fridman, O; D′Eramo, JL; Corró, L. Acclimation of Bufo arenarum embryos to copper: effects on survival and the induction of metallothioneins. 21st SETAC Annual Meeting; Abstract Book. 2000. PWP140. p. 274. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y; Liu, J; Iszard, MB; Andrews, GK; Palmiteer, RD; Klaassen, CD. Transgenic mice that over-express metallothionein-I are protected from cadmium lethality and toxicity. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1995, 13, 222–228. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Coll, CS; Herkovits, J. Stage dependent uptake of cadmium in Bufo arenarum embryos. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1996, 56(4), 663–669. [Google Scholar]
- McCarty, LS. The relationship between aquatic toxicity QSARs and bioconcentration for some organic chemicals. Environ. Toxicol. Chem., 1986, 5, 1071–1080. [Google Scholar]
- McCarty, LS. Toxicant body residues: Implications for aquatic bioassays with some organic chemicals. Aquat. Toxicol. 1991, 14, 183–192. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, PM; Erickson, RJ; Spehar, L; Bradbury, SP; Ankley, GT. Interim report on data and methods for assessment of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin risk to aquatic life and associated wildlife; Duluth MN; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency; EPA-600/R-93/055; 1993. [Google Scholar]
- McCarty, LS; Mackay, D. Enhancing ecotoxicological modeling and assessment: body residues and modes of toxic action. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1993, 27, 1719–1728. [Google Scholar]
- Herkovits, J; Pérez-Coll, CS; Herkovits, FD. Ecotoxicological studies of environmental samples from Buenos Aires area using standardized amphibian embryo toxicity test (AMPHITOX). Environ. Poll. 2002, 116, 177–183. [Google Scholar]
- Zang, L; Wang, W. Alteration of dissolved cadmium and zinc uptake kinetics by metal pre- exposure in the Black Sea bream (Acanthopagrus schlegeli). Environm. Toxicol. Chem. 2006, 25, 1312–1321. [Google Scholar]
- Blaustein, AR; Wake, DB; Sousa, WP. Amphibian declines: judging stability, persistence and susceptibility of populations to local and global extinctions. Conserv. Biol. 1994, 8, 60–71. [Google Scholar]
- Boyer, R; Grue, CE. The need for water quality criteria for frogs. Environ. Health Perspect. 1995, 103, 352–355. [Google Scholar]
- Besser, JM; Dwyer, FJ; Ingersoll, CG; Wang, N. Early Life-stage toxicity of copper to endangered and surrogate fish species; Washington, DC; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency; EPA/600/R-01/051; 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Herkovits, J; Pérez-Coll, CS; Herkovits, FD. Ecotoxicity in Reconquista River (Province of Buenos Aires, Argentina): A preliminary study. Environ. Health Perspect. 1996, 104(2), 186–189. [Google Scholar]
- Burkhart, JG; Ankley, G; Bell, H; Carpenter, H; Fort, D; Gardner, D; Gardner, H; Hale, R; Helgen, JC; Jepson, P; Johnson, D; Lannoo, M; Lee, D; Lary, J; Levey, R; Magner, J; Meteyer, C; Shelby, MD; Lucier, G. Strategies for assessing the implications of malformed frogs for environmental health. Environ. Health Perspect. 2000, 108(1), 83–90. [Google Scholar]
- Tietge, JE; Ankley, GT; DeFoe, DL; Holcombe, GW; Jensen, KM. Effects of water quality on development of Xenopus laevis: a frog embryo teratogenesis assay-Xenopus assessment of surface water associated with malformations in native anurans. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2000, 19, 2114–2121. [Google Scholar]
- Herkovits, J; Pérez-Coll, CS. AMPHITOX: A customized set of toxicity tests employing amphibian embryos. “Symposium on multiple stressor effects in relation to declining amphibian populations”. In “Multiple Stressor Effects in Relation to Declining Amphibian Populations” ASTM International STP 1443; Linder, GL, Krest, S, Sparling, D, Little, EE, Eds.; USA, 2003; pp. 46–60. [Google Scholar]
- Del Conte, E; Sirlin, L. The first stages of Bufo arenarum development. Acta Zool. Lilloana 1951, 12, 495–499. [Google Scholar]
- Herkovits, J; Pérez-Coll, CS. Dose-response relationship within the potentized microdoses phenomenon. Complementary Therapies in Medicine 1993, 1, 7–9. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Coll, CS; Herkovits, J; Fridman, O; Daniel, P; D′Eramo, JL. Metallothionein induction and cadmium uptake in Bufo arenarum embryos following an acclimation protocol. Environ. Poll 1999, 106, 443–448. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, T; Nordberg, GF. Cadmium toxicity in kidney cells. Resistance induced by short-term pretreatment in vitro and in vivo. Acta Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1986, 58, 137–143. [Google Scholar]
- Sanders, BM. Stress proteins, potential as multitiered biomarkers. In Biomarkers of Environmental Contamination; Lewis: Chelsea, MI, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Schelesinger, MJ. Heat shock proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 1986, 265, 12111–12114. [Google Scholar]
- Kägi, JHR. Evolution, structure and chemical activity of class I metallothioneins: An overview. In Metallothionein III: Biological Roles and Medical Implications; Suzuki, KT, Imura, N, Kimura, M, Eds.; Berlin; Birkhauser Verlag, 1993; pp. 29–56. [Google Scholar]
- Clements, FE. Plant succession: An analysis of the development of vegetation; Publication 42; Carnegie Institute: Washington DC, USA, 1916. [Google Scholar]
- Brandon, RN. Adaptation and environment; Princeton University Press: Princeton, New Jersey, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Postma, JF; Groenendijk, D. Adaptation to metals in the midge Chironomus riparius: a case study in the river Dommel. In Genetics and Ecotoxicology; Forbes, VE, Ed.; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 1999; pp. 79–101. [Google Scholar]
- Herkovits, J. Paleoecotoxicology: The impact of chemical and physical stress in the evolutionary process. Environ. Health Perspect. 2001, 109(12), 564–566. [Google Scholar]
- Groenendijk, D; Lucker, SMG; Plans, M; Kraak, MHS; Admiraal, W. Dynamics of metal adaptation in riverine chironomids. Environ. Poll 2002, 117, 101–109. [Google Scholar]
- Herkovits, J. Evoecotoxicology: environmental changes and life features development during the evolutionary process – the record of the past at developmental stages of living organisms. Environ. Health Perspect. 2006, 114, 1139–1142. [Google Scholar]
© 2007 MDPI All rights reserved.
Share and Cite
Herkovits, J.; Pérez-Coll, C.S. Acclimation to Low Level Exposure of Copper in Bufo arenarum Embryos: Linkage of Effects to Tissue Residues. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2007, 4, 166-172. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph2007040012
Herkovits J, Pérez-Coll CS. Acclimation to Low Level Exposure of Copper in Bufo arenarum Embryos: Linkage of Effects to Tissue Residues. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2007; 4(2):166-172. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph2007040012
Chicago/Turabian StyleHerkovits, Jorge, and Cristina Silvia Pérez-Coll. 2007. "Acclimation to Low Level Exposure of Copper in Bufo arenarum Embryos: Linkage of Effects to Tissue Residues" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 4, no. 2: 166-172. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph2007040012
APA StyleHerkovits, J., & Pérez-Coll, C. S. (2007). Acclimation to Low Level Exposure of Copper in Bufo arenarum Embryos: Linkage of Effects to Tissue Residues. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 4(2), 166-172. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph2007040012




