E-Cigarette or Vaping Product Use-Associated Lung Injury: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Provide a comprehensive overview of the epidemiology and public health impact of EVALI.
- Detail the current understanding of the pathogenesis of EVALI, including the role of various e-liquid components and device characteristics.
- Describe the clinical, radiological, and pathological features characteristic of EVALI.
- Summarize current diagnostic approaches and clinical management strategies.
- Discuss the known long-term consequences and ongoing research directions related to EVALI.
2. Epidemiology
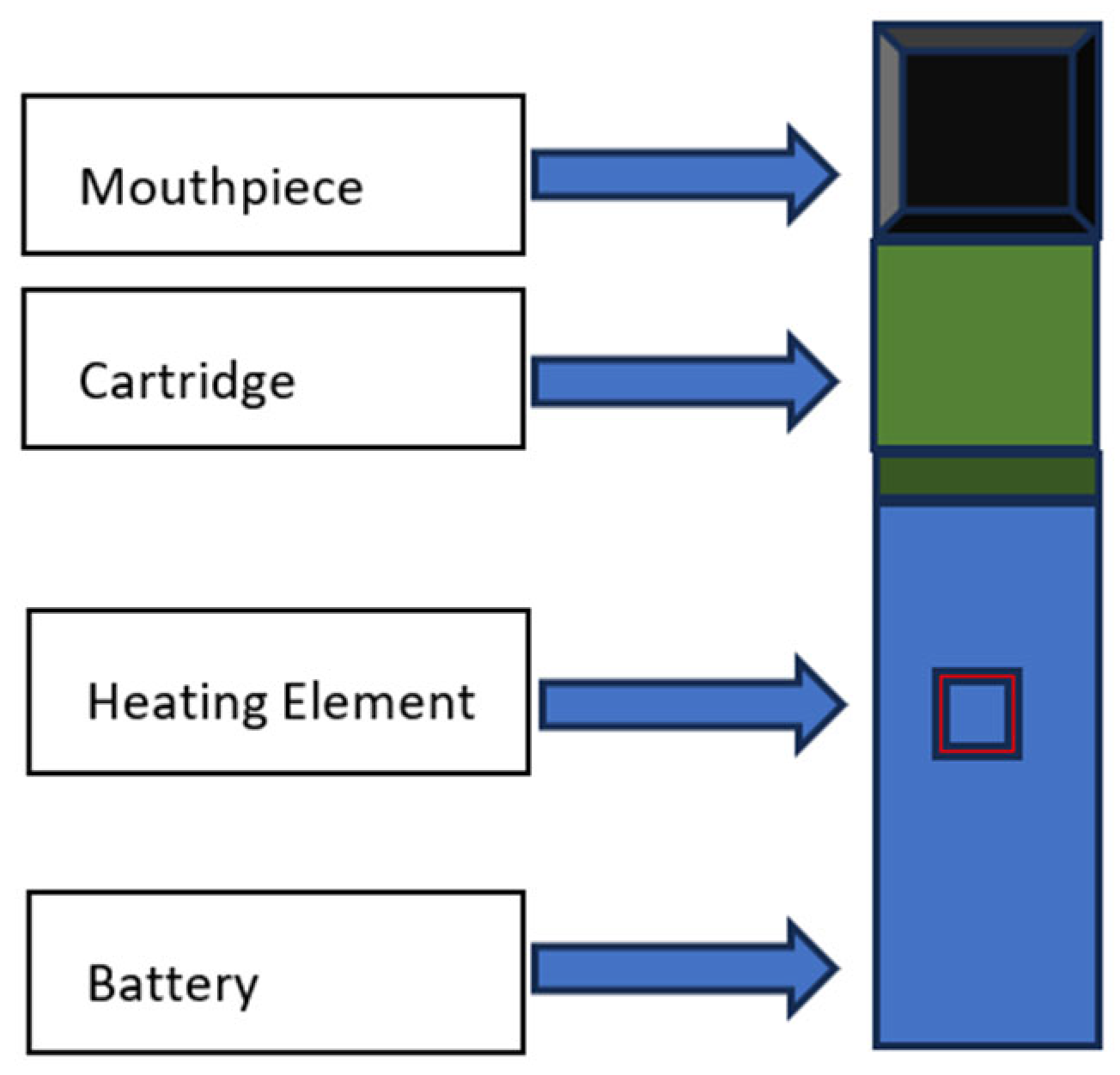
3. Structure of E-Cigarettes
4. E-Liquid Components
| Pathogenic Factor | Function | Mechanism of Action | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin E acetate (alpha-tocopherol acetate) | Thickening agent, particulary in cannabis-containing e-liquids | Disrupts surfactant function | [28,42] | |
| Flavoring Agents | Cinnamaldehyde | Provide flavor to e-liquids | Direct cellular toxicity Airway irritation Suppression of macrophage phagocytosis Decreased neutrophil oxidative burst | [43,44] |
| Vanillin | ||||
| Ethyl vanillin | ||||
| Menthol | ||||
| Heavy metals | Various (present as contaminants) | Increases oxidative stress | [10] | |
| Propylene glycol | Base of e-liquids, solvent | Direct cytotoxic Generates carcinogenic compounds | [45,46] | |
| Diacetyl | Flavoring agent (buttery flavor) | Airway inflammation Associated with bronchiolitis | [33] | |
| Vegetable glycerin (glycerol/glycerin) | Base of e-liquids | Increase mucin expression | [12,47] | |
5. Pathogenesis of Vaping-Induced Lung Injury
5.1. Direct Cellular Injury and Inflammation
5.2. Bronchiolitis Obliterans
5.3. Heavy Metal Toxicity
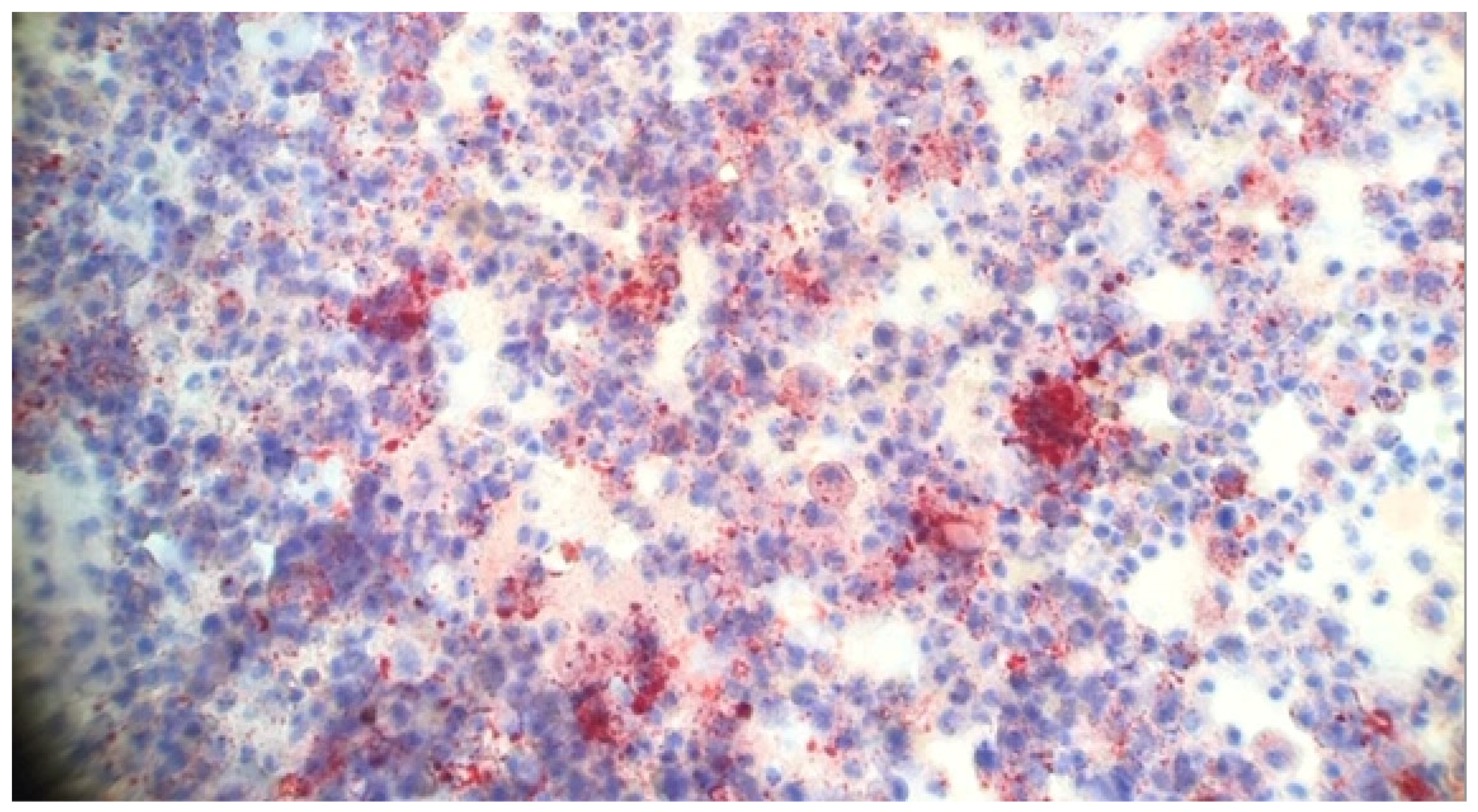
5.4. Lipid-Laden Alveolar Macrophages
5.5. Disruption of the Alveolar–Capillary Barrier
5.6. Vitamin E Acetate and Surfactant Dysfunction
5.7. Immune Dysregulation
6. Clinical Features
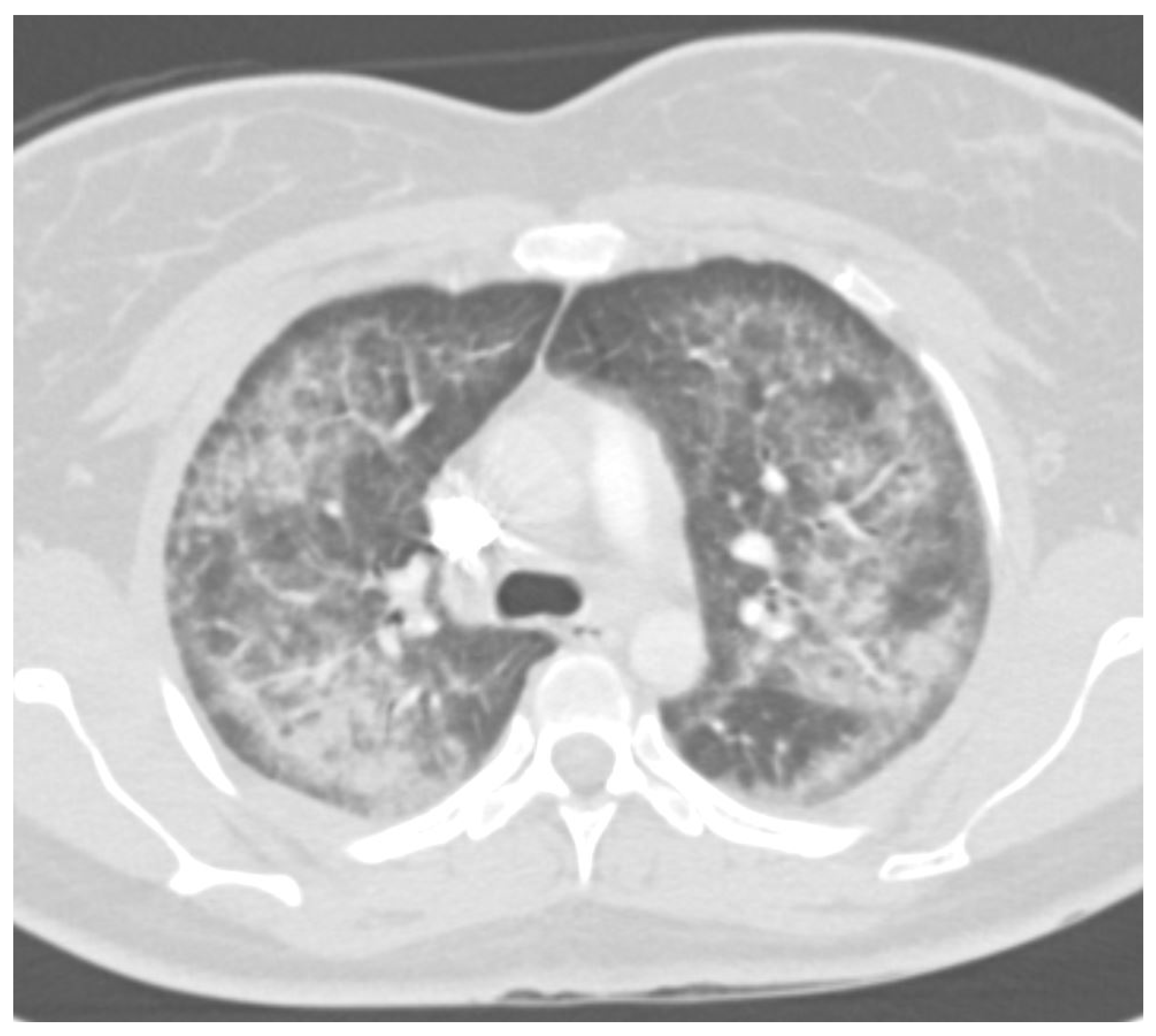
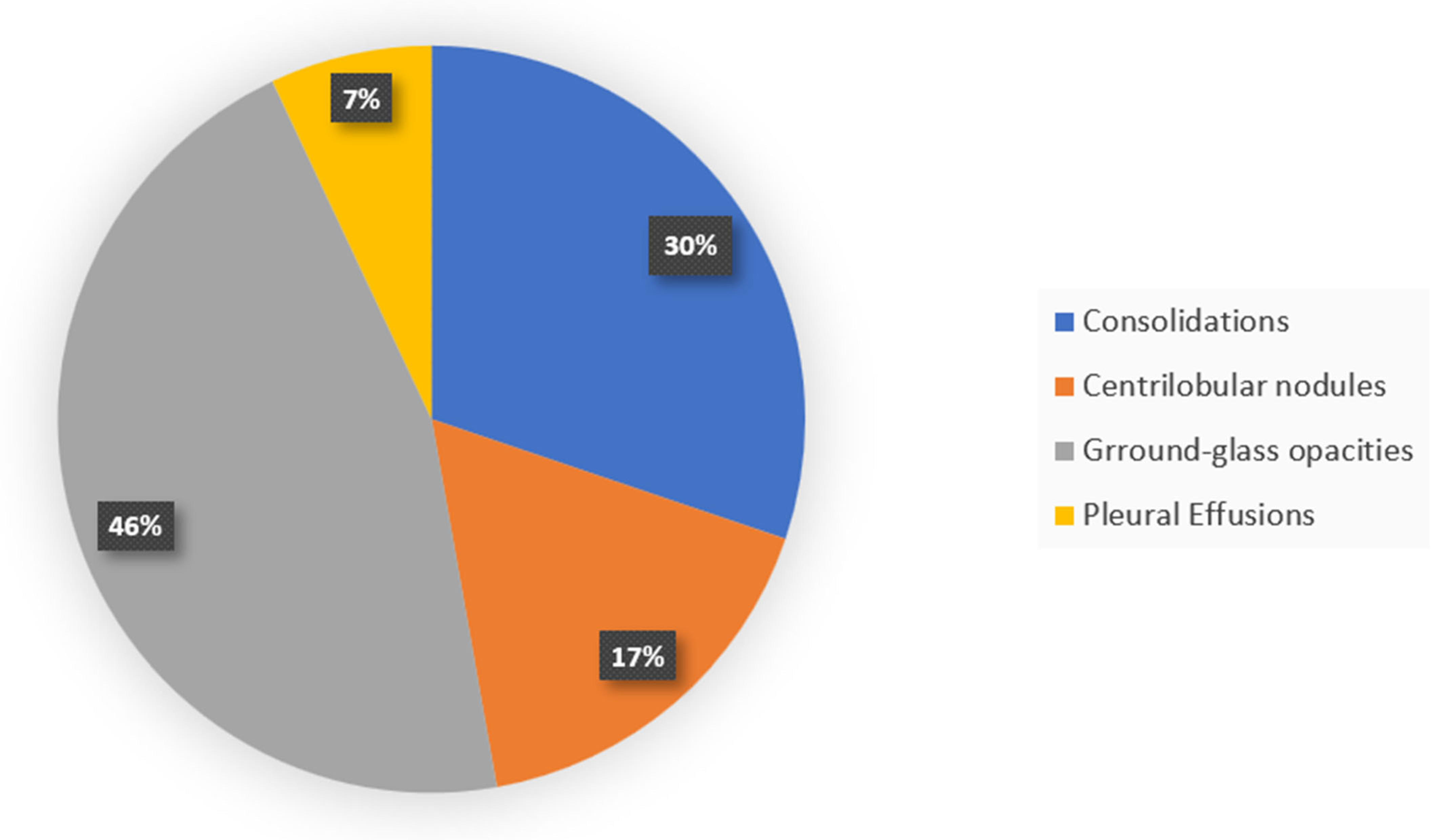
7. Radiology
8. Pathology
9. Diagnosis
10. Clinical Management
11. Public Health Interventions
12. Long-Term Consequences of EVALI
13. Ongoing Research Efforts
14. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ARDS | Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome |
| ATS | American Thoracic Society |
| BAL | Bronchoalveolar Lavage |
| CDC | Centers for Disease Control and Prevention |
| COPD | Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
| ECMO | Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation |
| ENDS | Electronic Nicotine Delivery Systems |
| EVALI | E-cigarette or Vaping Product Use-Associated Lung Injury |
| FDA | US Food and Drug Administration |
| GGOs | Ground-Glass Opacities |
| GI | Gastrointestinal |
| HRCT | High-Resolution Computed Tomography |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| NIV | Noninvasive Ventilation |
| OP | Organizing Pneumonia |
| PCR | Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| PET | Positron Emission Tomography |
| RB-ILD | Respiratory Bronchiolitis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| SpO2 | Oxygen Saturation |
| THC | Tetrahydrocannabinol |
References
- Dai, H.; Leventhal, A.M. Prevalence of E-Cigarette Use Among Adults in the United States, 2014–2018. JAMA 2019, 322, 1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullen, K.A.; Gentzke, A.S.; Sawdey, M.D.; Chang, J.T.; Anic, G.M.; Wang, T.W.; Creamer, M.R.; Jamal, A.; Ambrose, B.K.; King, B.A. E-Cigarette Use Among Youth in the United States, 2019. JAMA 2019, 322, 2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barker, C.K.; Ghera, P.; Hsu, B. The Evolution of a Pediatric Public Health Crisis: E-Cigarette or Vaping-Associated Lung Injury. Pediatrics 2024, 153, e2023063484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrine, C.G.; Pickens, C.M.; Boehmer, T.K.; King, B.A.; Jones, C.M.; DeSisto, C.L.; Duca, L.M.; Lekiachvili, A.; Kenemer, B.; Shamout, M.; et al. Characteristics of a Multistate Outbreak of Lung Injury Associated with E-Cigarette Use, or Vaping—United States, 2019. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2019, 68, 860–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebuli, M.E.; Rose, J.J.; Noël, A.; Croft, D.P.; Benowitz, N.L.; Cohen, A.H.; Goniewicz, M.L.; Larsen, B.T.; Leigh, N.; McGraw, M.D.; et al. The E-Cigarette or Vaping Product Use–Associated Lung Injury Epidemic: Pathogenesis, Management, and Future Directions: An Official American Thoracic Society Workshop Report. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2023, 20, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherian, S.V.; Kumar, A.; Estrada-Y-Martin, R.M. E-Cigarette or Vaping Product-Associated Lung Injury: A Review. Am. J. Med. 2020, 133, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, A.K.; Koumans, E.H.; Chatham-Stephens, K.; Salvatore, P.P.; Armatas, C.; Byers, P.; Clark, C.R.; Ghinai, I.; Holzbauer, S.M.; Navarette, K.; et al. Hospitalizations and Deaths Associated with EVALI. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1589–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatham-Stephens, K.; Roguski, K.; Jang, Y.; Cho, P.; Jatlaoui, T.C.; Kabbani, S.; Glidden, E.; Ussery, E.N.; Trivers, K.F.; Evans, M.E.; et al. Characteristics of Hospitalized and Nonhospitalized Patients in a Nationwide Outbreak of E-Cigarette, or Vaping, Product Use–Associated Lung Injury—United States, November 2019. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2019, 68, 1076–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soerianto, W.; Jaspers, I. E-cigarette, or Vaping, Product Use Associated Lung Injury: Epidemiology, Challenges, and Implications with COVID-19. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2025, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margham, J.; McAdam, K.; Cunningham, A.; Porter, A.; Fiebelkorn, S.; Mariner, D.; Digard, H.; Proctor, C. The Chemical Complexity of E-Cigarette Aerosols Compared with the Smoke from a Tobacco Burning Cigarette. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 743060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, S.E.; Scheman, A.; McGowan, M.A. Propylene Glycol. Dermatitis 2018, 29, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komura, M.; Sato, T.; Yoshikawa, H.; Nitta, N.A.; Suzuki, Y.; Koike, K.; Kodama, Y.; Seyama, K.; Takahashi, K. Propylene Glycol, a Component of Electronic Cigarette Liquid, Damages Epithelial Cells in Human Small Airways. Respir. Res. 2022, 23, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.D.; Chung, S.; Dennis, J.S.; Yoshida, M.; Aguiar, C.; Aller, S.P.; Mendes, E.S.; Schmid, A.; Sabater, J.; Baumlin, N.; et al. Vegetable Glycerin E-Cigarette Aerosols Cause Airway Inflammation and Ion Channel Dysfunction. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1012723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.B.; Olgin, J.E.; Nah, G.; Vittinghoff, E.; Cataldo, J.K.; Pletcher, M.J.; Marcus, G.M. Cigarette and E-Cigarette Dual Use and Risk of Cardiopulmonary Symptoms in the Health EHeart Study. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moheimani, R.S.; Bhetraratana, M.; Yin, F.; Peters, K.M.; Gornbein, J.; Araujo, J.A.; Middlekauff, H.R. Increased Cardiac Sympathetic Activity and Oxidative Stress in Habitual Electronic Cigarette Users. JAMA Cardiol. 2017, 2, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traboulsi, H.; Cherian, M.; Abou Rjeili, M.; Preteroti, M.; Bourbeau, J.; Smith, B.M.; Eidelman, D.H.; Baglole, C.J. Inhalation Toxicology of Vaping Products and Implications for Pulmonary Health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, T.-J.; Kim, S.A. Effect of Heating on Physicochemical Property of Aerosols during Vaping. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefaniak, A.B.; LeBouf, R.F.; Ranpara, A.C.; Leonard, S.S. Toxicology of Flavoring- and Cannabis-Containing e-Liquids Used in Electronic Delivery Systems. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 224, 107838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulmonary Disease Related to E-Cigarette Use. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 792–793. [CrossRef]
- Helfgott, D.; Capozzoli, G.; Madray, J.; Baig, A.; Uppaluri, L.; Gaur, S.; Simon, M.; Amorosa, J.; Ramagopal, M. E-cigarette or Vaping Product Use Associated Lung Injury (EVALI) in the Time of COVID-19: A Clinical Dilemma. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2022, 57, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreiss, K.; Gomaa, A.; Kullman, G.; Fedan, K.; Simoes, E.J.; Enright, P.L. Clinical Bronchiolitis Obliterans in Workers at a Microwave-Popcorn Plant. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harry-Hernandez, S.; Thiboutot, J.; Wahidi, M.M.; Giovacchini, C.X.; De Cardenas, J.; Meldrum, C.; Los, J.G.; Illei, P.B.; Shojaee, S.; Eissenberg, T.; et al. Bronchoalveolar Lavage (BAL) and Pathologic Assessment of Electronic Cigarette or Vaping Product Use-Associated Lung Injury (EVALI). J. Bronchol. Interv. Pulmonol. 2023, 30, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, A.; Ahmad, S.; Coakley, R.D.; Sassano, M.F.; Alexis, N.E.; Tarran, R. Lipid-Laden Macrophages Are Not Unique to Patients with E-Cigarette or Vaping Product Use–Associated Lung Injury. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 203, 1030–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddock, S.D.; Cirulis, M.M.; Callahan, S.J.; Keenan, L.M.; Pirozzi, C.S.; Raman, S.M.; Aberegg, S.K. Pulmonary Lipid-Laden Macrophages and Vaping. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1488–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthumalage, T.; Lamb, T.; Friedman, M.R.; Rahman, I. E-Cigarette Flavored Pods Induce Inflammation, Epithelial Barrier Dysfunction, and DNA Damage in Lung Epithelial Cells and Monocytes. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durrani, K.; El Din, S.-M.A.; Sun, Y.; Rule, A.M.; Bressler, J. Ethyl Maltol Enhances Copper Mediated Cytotoxicity in Lung Epithelial Cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2021, 410, 115354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massey, J.B.; She, H.S.; Pownall, H.J. Interaction of Vitamin E with Saturated Phospholipid Bilayers. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1982, 106, 842–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blount, B.C.; Karwowski, M.P.; Shields, P.G.; Morel-Espinosa, M.; Valentin-Blasini, L.; Gardner, M.; Braselton, M.; Brosius, C.R.; Caron, K.T.; Chambers, D.; et al. Vitamin E Acetate in Bronchoalveolar-Lavage Fluid Associated with EVALI. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layden, J.E.; Ghinai, I.; Pray, I.; Kimball, A.; Layer, M.; Tenforde, M.W.; Navon, L.; Hoots, B.; Salvatore, P.P.; Elderbrook, M.; et al. Pulmonary Illness Related to E-Cigarette Use in Illinois and Wisconsin—Final Report. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 903–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, Y.M.; Smith, M.L.; Tazelaar, H.D.; Vaszar, L.T.; Swanson, K.L.; Cecchini, M.J.; Boland, J.M.; Bois, M.C.; Boyum, J.H.; Froemming, A.T.; et al. Pathology of Vaping-Associated Lung Injury. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1780–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panse, P.M.; Feller, F.F.; Butt, Y.M.; Smith, M.L.; Larsen, B.T.; Tazelaar, H.D.; Harvin, H.J.; Gotway, M.B. Pulmonary Injury Resulting from Vaping or E-Cigarette Use: Imaging Appearances at Presentation and Follow-Up. Radiol. Cardiothorac. Imaging 2020, 2, e200081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cecchini, M.J.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Arrossi, A.V.; Beasley, M.B.; Butt, Y.M.; Jones, K.D.; Pambuccian, S.; Mehrad, M.; Monaco, S.E.; Saqi, A.; et al. E-Cigarette or Vaping Product Use-Associated Lung Injury: A Review for Pathologists. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2020, 144, 1490–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, A.V.; Wambui, D.W.; Pokhrel, L.R. Risk Assessment of Inhaled Diacetyl from Electronic Cigarette Use among Teens and Adults. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 772, 145486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickman, E.; Herrera, C.A.; Jaspers, I. Common E-Cigarette Flavoring Chemicals Impair Neutrophil Phagocytosis and Oxidative Burst. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2019, 32, 982–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winnicka, L.; Shenoy, M.A. EVALI and the Pulmonary Toxicity of Electronic Cigarettes: A Review. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2020, 35, 2130–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.; Byun, M.K.; Shin, J.; Crotty Alexander, L.E. Effects of E-cigarettes and Vaping Devices on Cardiac and Pulmonary Physiology. J. Physiol. 2020, 598, 5039–5062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonas, A. Impact of Vaping on Respiratory Health. BMJ 2022, 378, e065997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bavel, N.; Lai, P.; Amrein, M.; Prenner, E.J. Pulmonary Surfactant Function and Molecular Architecture Is Disrupted in the Presence of Vaping Additives. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2023, 222, 113132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnasamy, V.P.; Hallowell, B.D.; Ko, J.Y.; Board, A.; Hartnett, K.P.; Salvatore, P.P.; Danielson, M.; Kite-Powell, A.; Twentyman, E.; Kim, L.; et al. Update: Characteristics of a Nationwide Outbreak of E-Cigarette, or Vaping, Product Use–Associated Lung Injury—United States, August 2019–January 2020. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2020, 69, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navon, L.; Ghinai, I.; Layden, J. Notes from the Field: Characteristics of Tetrahydrocannabinol–Containing E-Cigarette, or Vaping, Products Used by Adults—Illinois, September–October 2019. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2020, 69, 973–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, W.; Gartner, C.; Bonevski, B. Lessons from the Public Health Responses to the US Outbreak of Vaping-related Lung Injury. Addiction 2021, 116, 985–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H. Vitamin E Acetate as Linactant in the Pathophysiology of EVALI. Med. Hypotheses 2020, 144, 110182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clapp, P.W.; Pawlak, E.A.; Lackey, J.T.; Keating, J.E.; Reeber, S.L.; Glish, G.L.; Jaspers, I. Flavored E-Cigarette Liquids and Cinnamaldehyde Impair Respiratory Innate Immune Cell Function. Am. J. Physiol.-Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2017, 313, L278–L292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.R.; Jarrell, Z.R.; Orr, M.; Liu, K.H.; Go, Y.-M.; Jones, D.P. Metabolome-Wide Association Study of Flavorant Vanillin Exposure in Bronchial Epithelial Cells Reveals Disease-Related Perturbations in Metabolism. Environ. Int. 2021, 147, 106323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrini, V.; Panettieri, R.A.; Gennaro, M.L. Lipid-Laden Macrophages as Biomarkers of Vaping-Associated Lung Injury. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, D.J.; Aldy, K.; Hsu, S.; McGetrick, M.; Verbeck, G.; De Silva, I.; Feng, S. Review of Health Consequences of Electronic Cigarettes and the Outbreak of Electronic Cigarette, or Vaping, Product Use-Associated Lung Injury. J. Med. Toxicol. 2020, 16, 295–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotts, J.E.; Jordt, S.-E.; McConnell, R.; Tarran, R. What Are the Respiratory Effects of E-Cigarettes? BMJ 2019, 366, l5275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroll, B.J.; Kim, M.; Hemyari, A.; Thakrar, P.; Kump, T.E.; Wade, T.; De Vela, G.; Hall, J.; Diaz, C.D.; D’Andrea, L.A. Impaired Lung Function Following E-cigarette or Vaping Product Use Associated Lung Injury in the First Cohort of Hospitalized Adolescents. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2020, 55, 1712–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracken-Clarke, D.; Kapoor, D.; Baird, A.M.; Buchanan, P.J.; Gately, K.; Cuffe, S.; Finn, S.P. Vaping and Lung Cancer—A Review of Current Data and Recommendations. Lung Cancer 2021, 153, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitzer, Z.T.; Goel, R.; Reilly, S.M.; Elias, R.J.; Silakov, A.; Foulds, J.; Muscat, J.; Richie, J.P. Effect of Flavoring Chemicals on Free Radical Formation in Electronic Cigarette Aerosols. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 120, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landman, S.T.; Dhaliwal, I.; Mackenzie, C.A.; Martinu, T.; Steel, A.; Bosma, K.J. Life-Threatening Bronchiolitis Related to Electronic Cigarette Use in a Canadian Youth. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2019, 191, E1321–E1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reagan-Steiner, S.; Gary, J.; Matkovic, E.; Ritter, J.M.; Shieh, W.-J.; Martines, R.B.; Werner, A.K.; Lynfield, R.; Holzbauer, S.; Bullock, H.; et al. Pathological Findings in Suspected Cases of E-Cigarette, or Vaping, Product Use-Associated Lung Injury (EVALI): A Case Series. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 1219–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonsalves, C.L.; Zhu, J.W.; Kam, A.J. Diagnosis and Acute Management of E-Cigarette or Vaping Product Use–Associated Lung Injury in the Pediatric Population: A Systematic Review. J. Pediatr. 2021, 228, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Arcos, I.; Geraghty, P.; Baumlin, N.; Campos, M.; Dabo, A.J.; Jundi, B.; Cummins, N.; Eden, E.; Grosche, A.; Salathe, M.; et al. Chronic Electronic Cigarette Exposure in Mice Induces Features of COPD in a Nicotine-Dependent Manner. Thorax 2016, 71, 1119–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jatlaoui, T.C.; Wiltz, J.L.; Kabbani, S.; Siegel, D.A.; Koppaka, R.; Montandon, M.; Adkins, S.H.; Weissman, D.N.; Koumans, E.H.; O’Hegarty, M.; et al. Update: Interim Guidance for Health Care Providers for Managing Patients with Suspected E-Cigarette, or Vaping, Product Use–Associated Lung Injury—United States, November 2019. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2019, 68, 1081–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blagev, D.P.; Callahan, S.J.; Harris, D.; Collingridge, D.S.; Hopkins, R.O.; Eve, J.R.; Waddoups, L.; Aston, V.; Brown, S.; Lanspa, M.J. Prospectively Assessed Long-Term Outcomes of Patients with E-Cigarette– or Vaping-Associated Lung Injury. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2022, 19, 1892–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratton, K.; Kwan, L.Y.; Eaton, D.L. (Eds.) Public Health Consequences of E-Cigarettes; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, V.; Tran, M.; Behar, R.Z.; Zhai, S.; Cui, X.; Phandthong, R.; Wang, Y.; Pan, S.; Luo, W.; Pankow, J.F.; et al. Menthol in Electronic Cigarettes: A Contributor to Respiratory Disease? Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2020, 407, 115238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, L.E.C.; Bellinghausen, A.L.; Eakin, M.N. What Are the Mechanisms Underlying Vaping-Induced Lung Injury? J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 2754–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodas, M.; Van Westphal, C.; Carpenter-Thompson, R.; Mohanty, D.K.; Vij, N. Nicotine Exposure Induces Bronchial Epithelial Cell Apoptosis and Senescence via ROS Mediated Autophagy-Impairment. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2016, 97, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Coakley, R.D.; Ghio, A.J.; Muhlebach, M.S.; Esther, C.R.; Alexis, N.E.; Tarran, R. Chronic E-Cigarette Use Increases Neutrophil Elastase and Matrix Metalloprotease Levels in the Lung. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 200, 1392–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Kong, J.; Yang, M.X.; Xie, W.P.; Wang, H.; Rong, R.; Kong, H. Analysis of Clinical Characteristics of 21 Cases of Acute Fibrinous and Organizing Pneumonia. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi 2020, 43, 670–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casals, C.; Cañadas, O. Role of Lipid Ordered/Disordered Phase Coexistence in Pulmonary Surfactant Function. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Biomembranes 2012, 1818, 2550–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kligerman, S.; Raptis, C.; Larsen, B.; Henry, T.S.; Caporale, A.; Tazelaar, H.; Schiebler, M.L.; Wehrli, F.W.; Klein, J.S.; Kanne, J. Radiologic, Pathologic, Clinical, and Physiologic Findings of Electronic Cigarette or Vaping Product Use–Associated Lung Injury (EVALI): Evolving Knowledge and Remaining Questions. Radiology 2020, 294, 491–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, D.A.; Jatlaoui, T.C.; Koumans, E.H.; Kiernan, E.A.; Layer, M.; Cates, J.E.; Kimball, A.; Weissman, D.N.; Petersen, E.E.; Reagan-Steiner, S.; et al. Update: Interim Guidance for Health Care Providers Evaluating and Caring for Patients with Suspected E-Cigarette, or Vaping, Product Use Associated Lung Injur—United States, October 2019. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2019, 68, 919–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, D.R.; Maple, K.L.; Dettori, A.; Afolabi, F.; Francis, J.K.R.; Artunduaga, M.; Lieu, T.J.; Aldy, K.; Cao, D.J.; Hsu, S.; et al. Clinical Features of E-Cigarette, or Vaping, Product Use–Associated Lung Injury in Teenagers. Pediatrics 2020, 146, e20194104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blagev, D.P.; Harris, D.; Dunn, A.C.; Guidry, D.W.; Grissom, C.K.; Lanspa, M.J. Clinical Presentation, Treatment, and Short-Term Outcomes of Lung Injury Associated with e-Cigarettes or Vaping: A Prospective Observational Cohort Study. Lancet 2019, 394, 2073–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, J.J.; Poulos, V.C.; Zhou, J.; Sharma, M.; Parraga, G.; McIntosh, M.J. Review of Quantitative and Functional Lung Imaging Evidence of Vaping-Related Lung Injury. Front. Med. 2024, 11, 1285361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artunduaga, M.; Rao, D.; Friedman, J.; Kwon, J.K.; Pfeifer, C.M.; Dettori, A.; Winant, A.J.; Lee, E.Y. Pediatric Chest Radiographic and CT Findings of Electronic Cigarette or Vaping Product Use–Associated Lung Injury (EVALI). Radiology 2020, 295, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajak, A.; Bascoy, S.; Li, J.C.; Benninghoff, M.; Deitchman, A. E-Cigarette or Vaping Product Use Associated Lung Injury Among Three Young Adults: A Retrospective Case Series From Delaware. Cureus 2020, 12, e11031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalininskiy, A.; Bach, C.T.; Nacca, N.E.; Ginsberg, G.; Marraffa, J.; Navarette, K.A.; McGraw, M.D.; Croft, D.P. E-Cigarette, or Vaping, Product Use Associated Lung Injury (EVALI): Case Series and Diagnostic Approach. Lancet Respir. Med. 2019, 7, 1017–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aberegg, S.K.; Cirulis, M.M.; Maddock, S.D.; Freeman, A.; Keenan, L.M.; Pirozzi, C.S.; Raman, S.M.; Schroeder, J.; Mann, H.; Callahan, S.J. Clinical, Bronchoscopic, and Imaging Findings of e-Cigarette, or Vaping, Product Use–Associated Lung Injury Among Patients Treated at an Academic Medical Center. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e2019176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyilas, S.; Bauman, G.; Korten, I.; Pusterla, O.; Singer, F.; Ith, M.; Groen, C.; Schoeni, A.; Heverhagen, J.T.; Christe, A.; et al. MRI Shows Lung Perfusion Changes after Vaping and Smoking. Radiology 2022, 304, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kizhakke Puliyakote, A.S.; Elliott, A.R.; Sá, R.C.; Anderson, K.M.; Crotty Alexander, L.E.; Hopkins, S.R. Vaping Disrupts Ventilation-Perfusion Matching in Asymptomatic Users. J. Appl. Physiol. 2021, 130, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eddy, R.L.; Serajeddini, H.; Knipping, D.; Landman, S.T.; Bosma, K.J.; Mackenzie, C.A.; Dhaliwal, I.; Parraga, G. Pulmonary Functional MRI and CT in a Survivor of Bronchiolitis and Respiratory Failure Caused by E-Cigarette Use. Chest 2020, 158, e147–e151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wetherill, R.R.; Doot, R.K.; Young, A.J.; Lee, H.; Schubert, E.K.; Wiers, C.E.; Leone, F.T.; Mach, R.H.; Kranzler, H.R.; Dubroff, J.G. Molecular Imaging of Pulmonary Inflammation in Users of Electronic and Combustible Cigarettes: A Pilot Study. J. Nucl. Med. 2023, 64, 797–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wall, A.; Roslin, S.; Borg, B.; McDermott, S.; Walele, T.; Nahde, T.; O’Connell, G.; Thompson, J.; Lubberink, M.; Antoni, G. E-Cigarette Aerosol Deposition and Disposition of [11C]Nicotine Using Positron Emission Tomography: A Comparison of Nicotine Uptake in Lungs and Brain Using Two Different Nicotine Formulations. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saqi, A.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Butt, Y.; Doxtader, E.; Heymann, J.J.; Larsen, B.T.; Moreira, A.L.; Patel, A.; Reynolds, J.P.; Sung, S.; et al. E-cigarette or Vaping Product Use–Associated Lung Injury: What Is the Role of Cytologic Assessment? Cancer Cytopathol. 2020, 128, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schier, J.G.; Meiman, J.G.; Layden, J.; Mikosz, C.A.; VanFrank, B.; King, B.A.; Salvatore, P.P.; Weissman, D.N.; Thomas, J.; Melstrom, P.C.; et al. Severe Pulmonary Disease Associated with Electronic-Cigarette–Product Use—Interim Guidance. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2019, 68, 787–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffer, S.; Strang, A.; Saul, D.; Krishnan, V.; Chidekel, A. Adolescent E-Cigarette or Vaping Use-Associated Lung Injury in the Delaware Valley: A Review of Hospital-Based Presentation, Management, and Outcomes. Cureus 2022, 14, e21988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triantafyllou, G.A.; Tiberio, P.J.; Zou, R.H.; Lynch, M.J.; Kreit, J.W.; McVerry, B.J.; Morris, A.; Rose, J.J. Long-Term Outcomes of EVALI: A 1-Year Retrospective Study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, e112–e113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kligerman, S.J.; Kay, F.U.; Raptis, C.A.; Henry, T.S.; Sechrist, J.W.; Walker, C.M.; Vargas, D.; Filev, P.D.; Chung, M.S.; Digumarthy, S.R.; et al. CT Findings and Patterns of E-Cigarette or Vaping Product Use-Associated Lung Injury. Chest 2021, 160, 1492–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Pulmonary Complication | Description | References |
|---|---|---|
| Lipoid Pneumonia | A condition caused by the accumulation of lipids (fats) in the lungs. | [6,19,20] |
| Hypersensitivity Pneumonia | An immune-mediated inflammatory lung disease caused by the inhalation of certain antigens. | [21,22,23] |
| Acute Eosinophilic Pneumonia | A rare disease characterized by the rapid accumulation of eosinophils in the lungs. | [5,24,25] |
| Respiratory Bronchiolitis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease (RB-ILD) | Lung disease primarily affects the small airways (bronchioles) and the surrounding lung tissue. | [26,27,28] |
| Acute Fibrinous Organizing Pneumonia | A pattern of lung injury characterized by intra-alveolar fibrin deposition and organizing pneumonia. | [6,28,29] |
| Organizing Pneumonia | A pattern of lung inflammation and fibrosis that can occur in response to various lung injuries. | [30,31,32] |
| EVALI | E-cigarette or Vaping Product Use-Associated Lung Injury; a serious condition characterized by respiratory symptoms and lung damage. | [4,5,6] |
| Pathophysiological Mechanism | Key Features | Adverse Effects | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Cellular Injury and Inflammation |
| General lung irritation, inflammation and increased risk of emphysema. | [48,49,50] |
| Bronchiolitis Obliterans |
| Severe and irreversible lung damage, difficulty breathing, coughing, wheezing. | [51,52,53] |
| Heavy Metal Toxicity |
| Increased risk of bronchitis, asthma, COPD, and lung cancer. | [16,54,55] |
| Lipid-Laden Alveolar Macrophages |
| Disrupted lung function and immune response, potential respiratory problems. | [22,45,56] |
| Disruption of the Alveolar-Capillary Barrier |
| Pulmonary edema (fluid in the lungs), respiratory distress, difficulty breathing. | [25,49,57] |
| Vitamin E Acetate and Surfactant Dysfunction |
| Alveolar collapse, inflammation, impaired lung function. | [6,26,58] |
| Immune Dysregulation |
| Weakened respiratory immune system, increased susceptibility to infections, increased risk of lung damage. | [3,43,44] |
| Feature | Confirmed Case of EVALI | Probable Case of EVALI |
|---|---|---|
| E-cigarette use | Used within 90 days before symptoms started | Used within 90 days before symptoms started |
| Lung abnormalities | Present (seen on chest X-ray or CT scan) | Present (seen on chest X-ray or CT scan) |
| Infection testing | No signs of lung infection after initial tests (must include negative respiratory viral panel, influenza test if needed, and any other relevant tests based on the situation) | An infection was found but does not fully explain the lung problems, or not enough infection testing is performed, and the doctors believe the infection is not the leading cause. |
| Other causes | No other likely explanations for the lung problems (like heart, autoimmune, or cancer-related issues) | No other likely explanations for the lung problems (like heart, autoimmune, or cancer-related issues) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amjad, M.A.; Ocazionez Trujillo, D.; Estrada-Y-Martin, R.M.; Cherian, S.V. E-Cigarette or Vaping Product Use-Associated Lung Injury: A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2025, 22, 792. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22050792
Amjad MA, Ocazionez Trujillo D, Estrada-Y-Martin RM, Cherian SV. E-Cigarette or Vaping Product Use-Associated Lung Injury: A Comprehensive Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2025; 22(5):792. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22050792
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmjad, Mohammad Asim, Daniel Ocazionez Trujillo, Rosa M. Estrada-Y-Martin, and Sujith V. Cherian. 2025. "E-Cigarette or Vaping Product Use-Associated Lung Injury: A Comprehensive Review" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 22, no. 5: 792. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22050792
APA StyleAmjad, M. A., Ocazionez Trujillo, D., Estrada-Y-Martin, R. M., & Cherian, S. V. (2025). E-Cigarette or Vaping Product Use-Associated Lung Injury: A Comprehensive Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 22(5), 792. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22050792







