Meta-Analysis of the Gut Microbiome: An African American Representation
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. The Global Microbiome
1.2. The Gut Microbiome
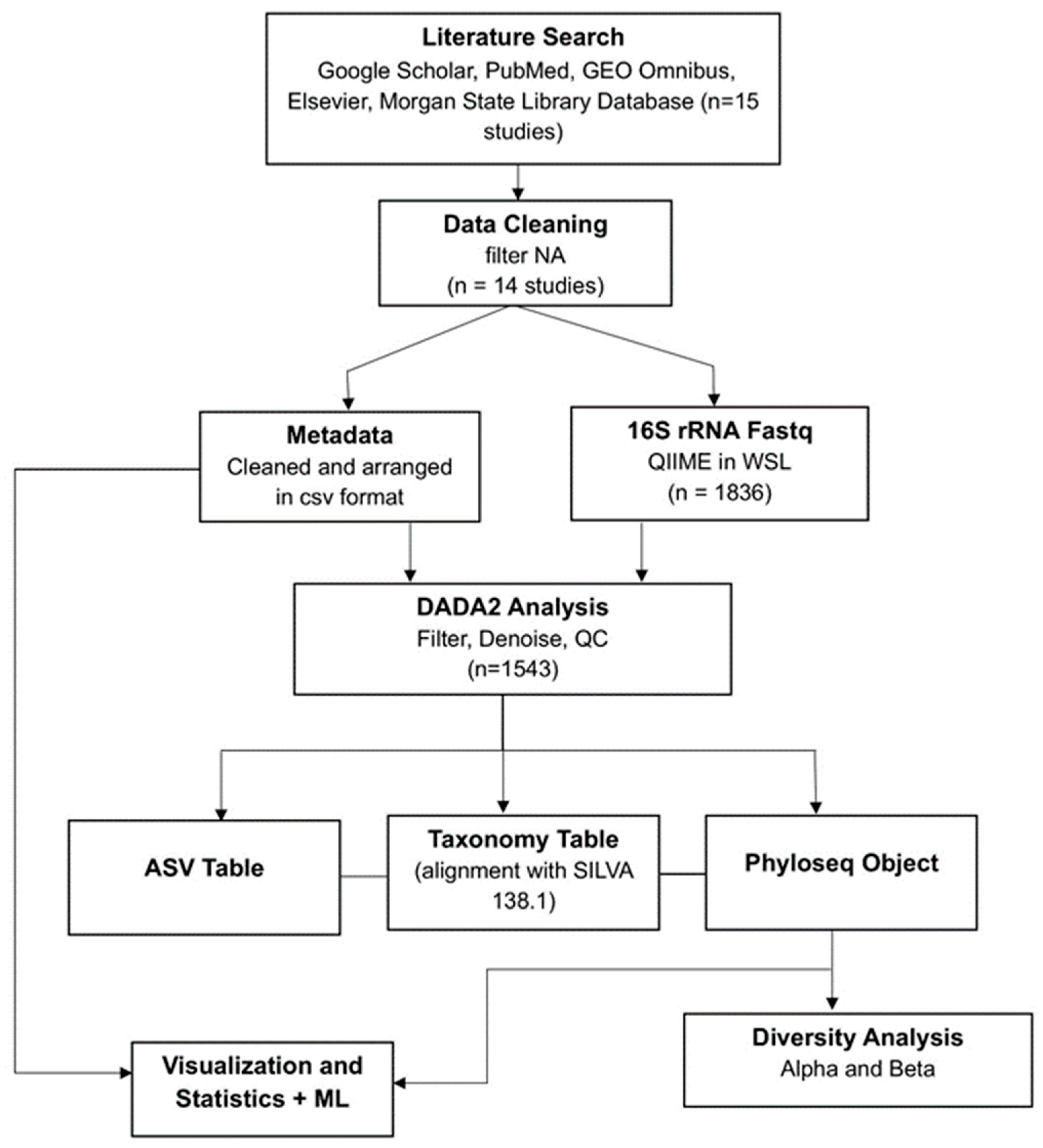
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population and Data Collection
2.2. Data Processing and Quality Control
2.2.1. Metadata Coercion
2.2.2. DADA2
2.2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.2.4. Preliminary Machine Learning Application for Ethnicity Prediction
3. Results
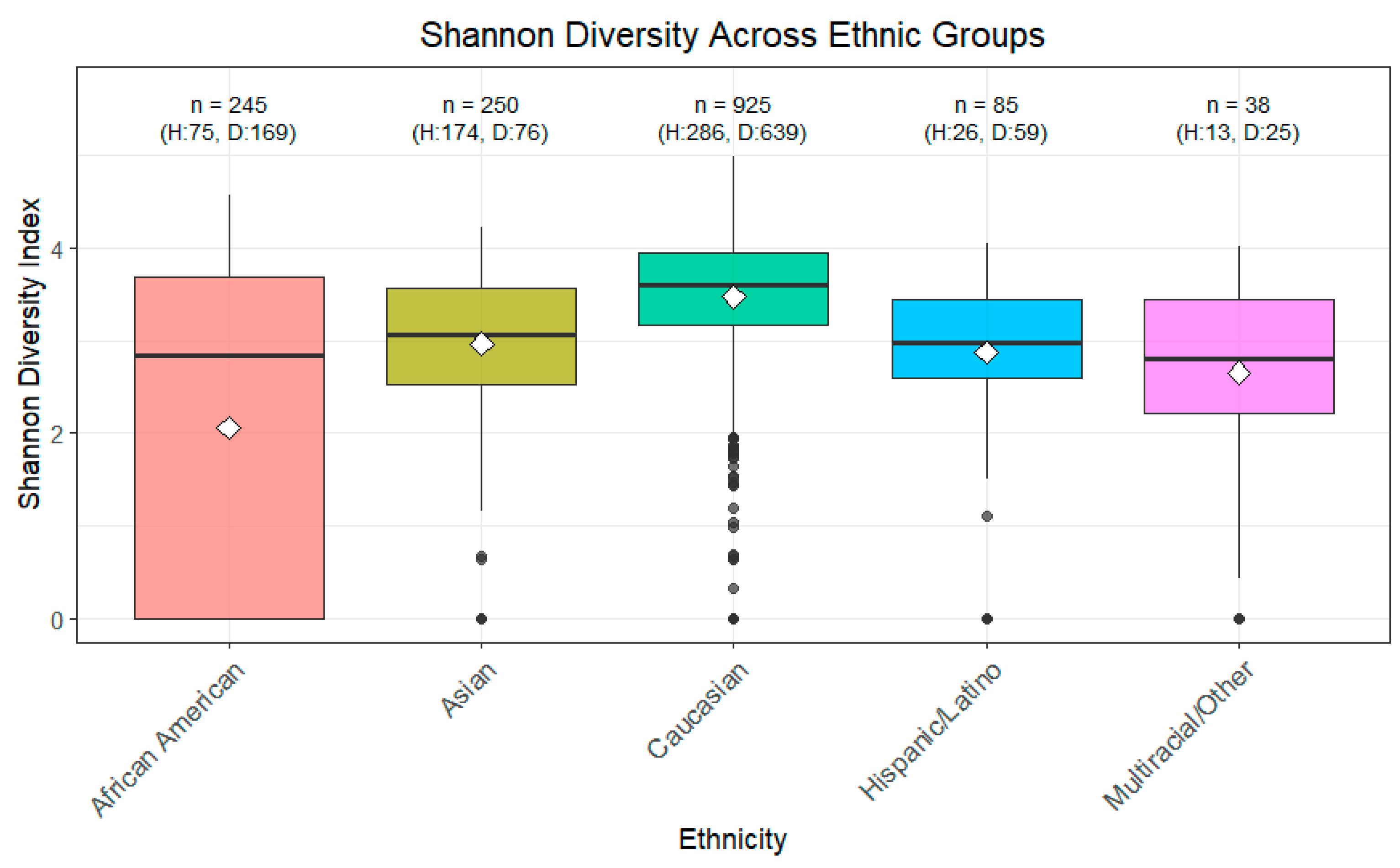
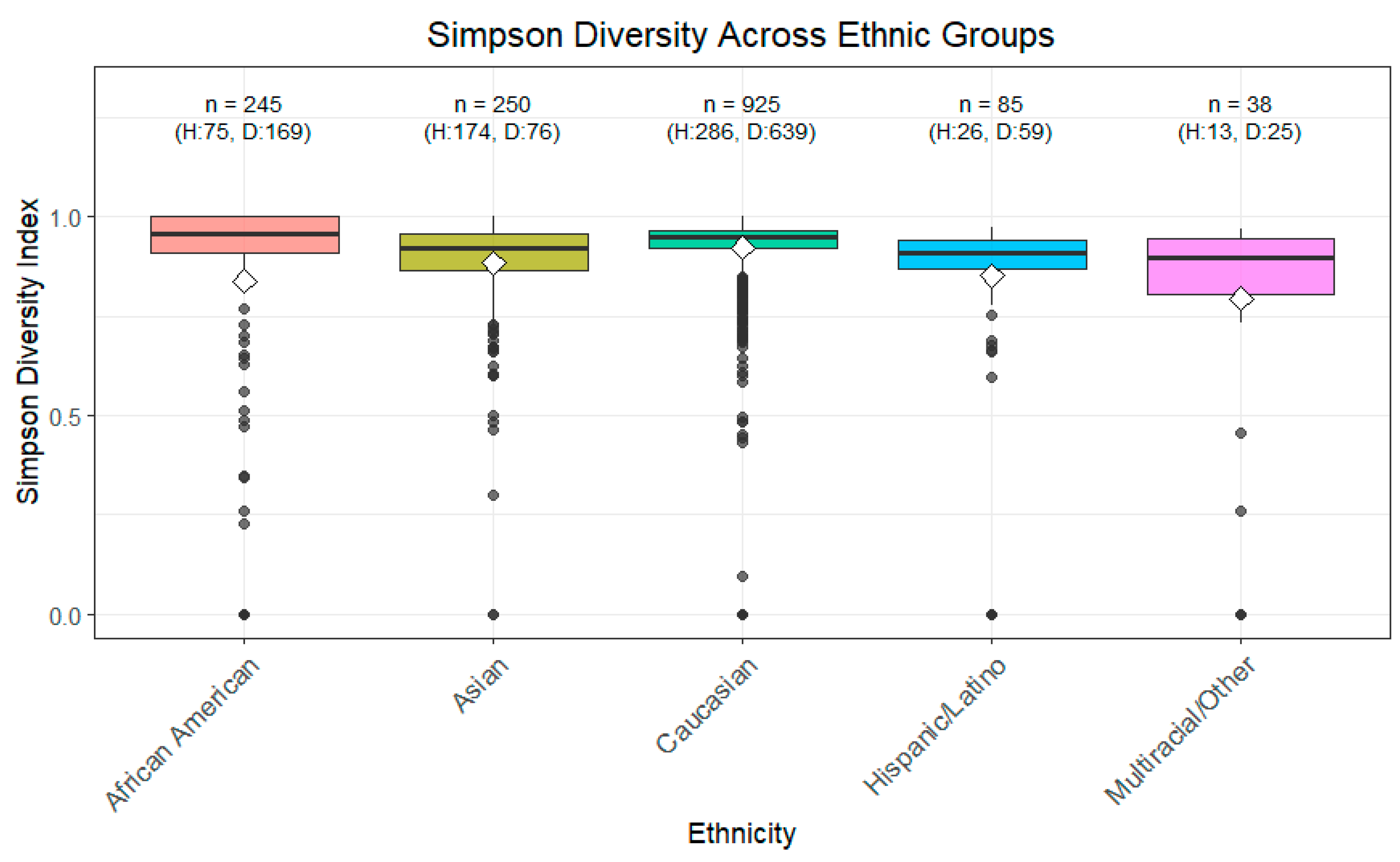
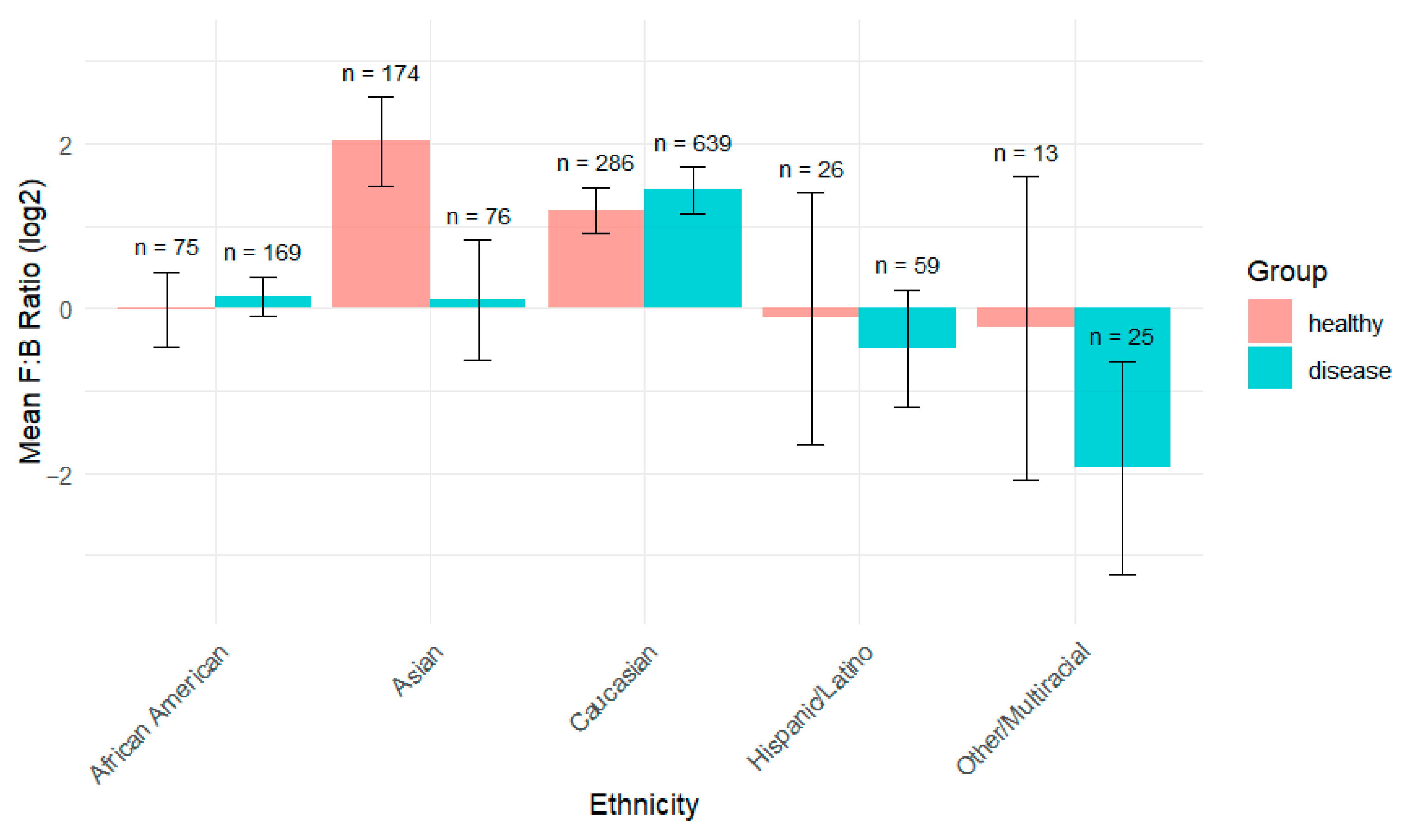
3.1. Alpha Diversity
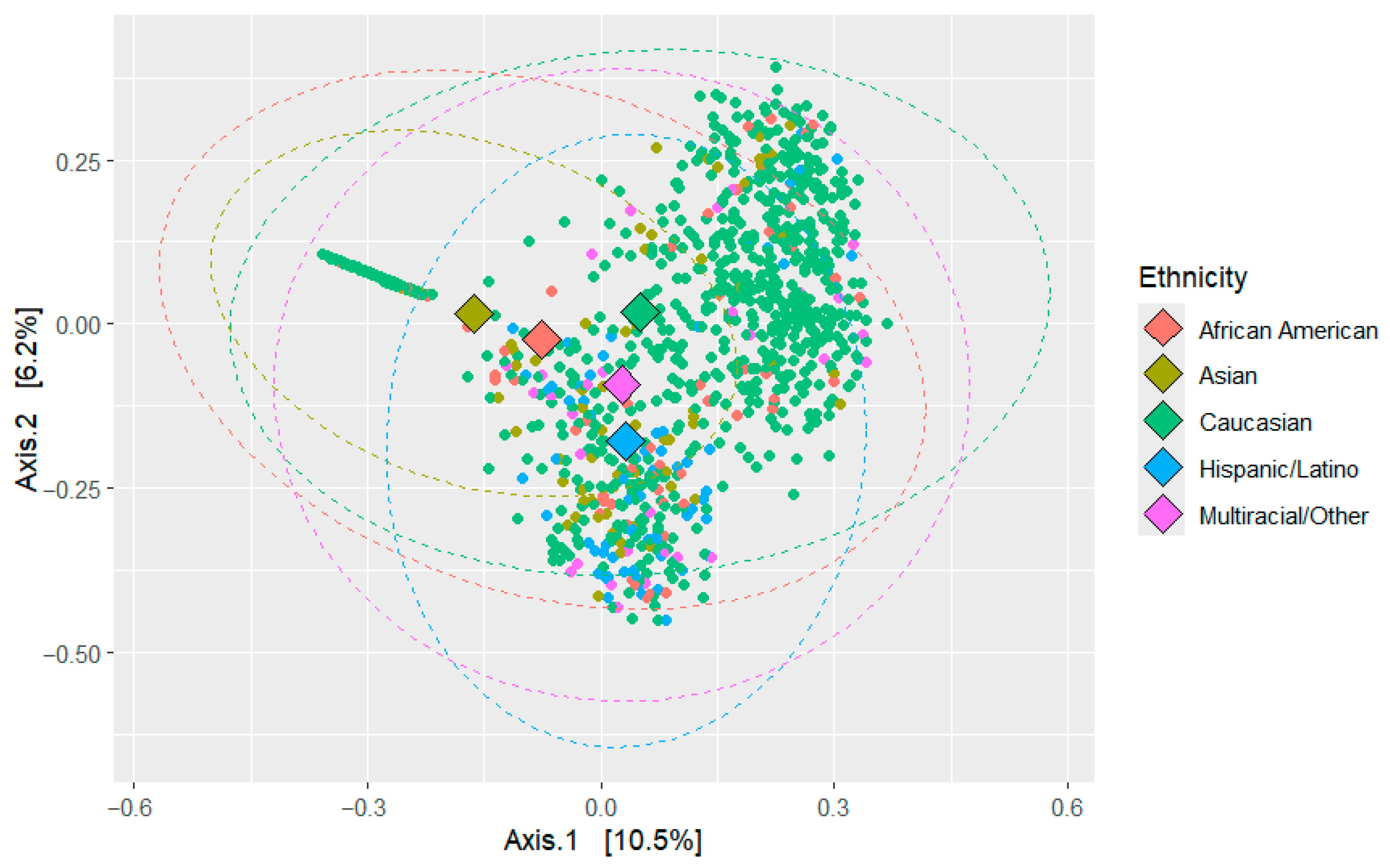
3.2. Beta Diversity
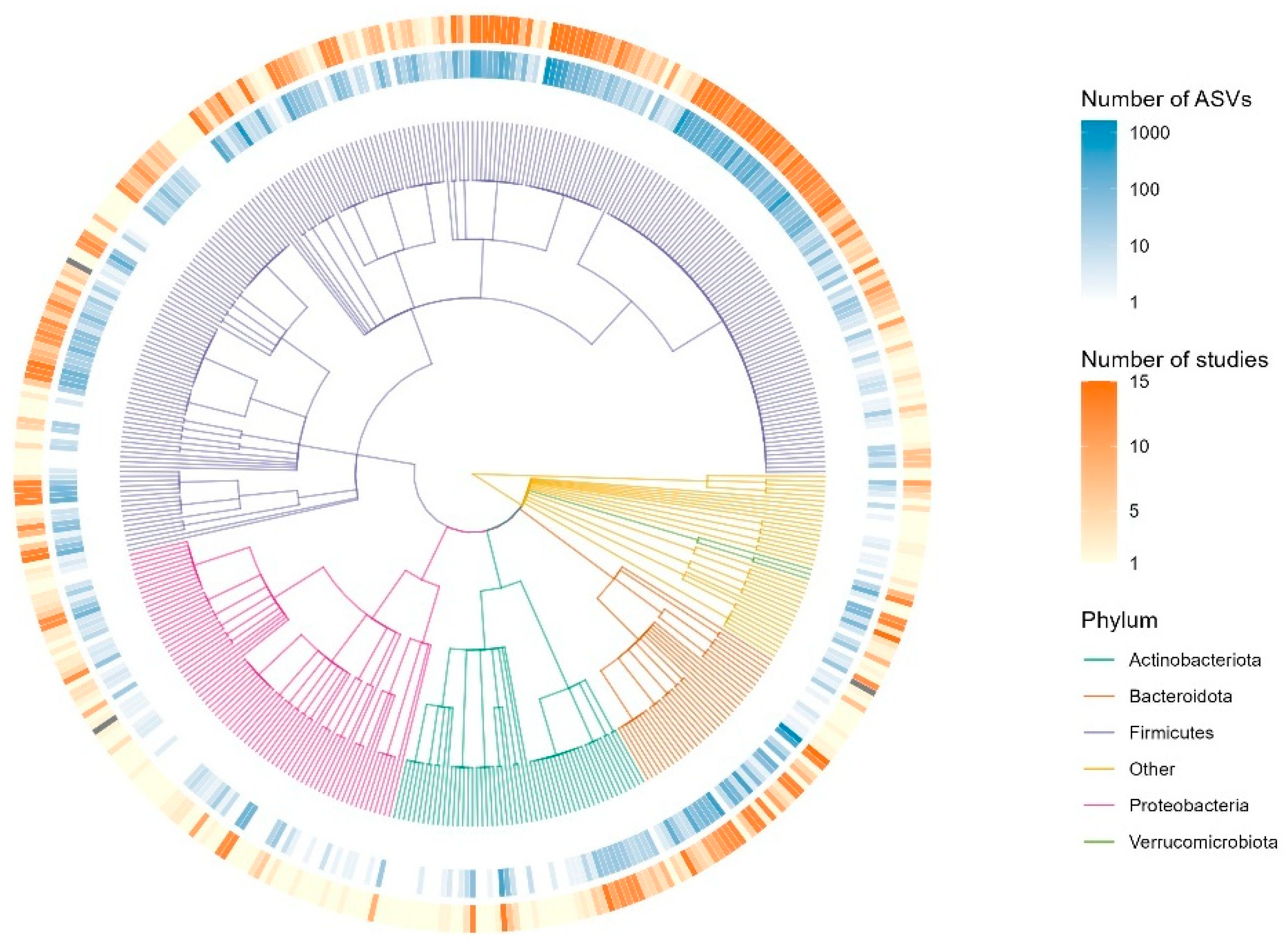
3.3. Microbial Composition
3.4. ANCOM-BC
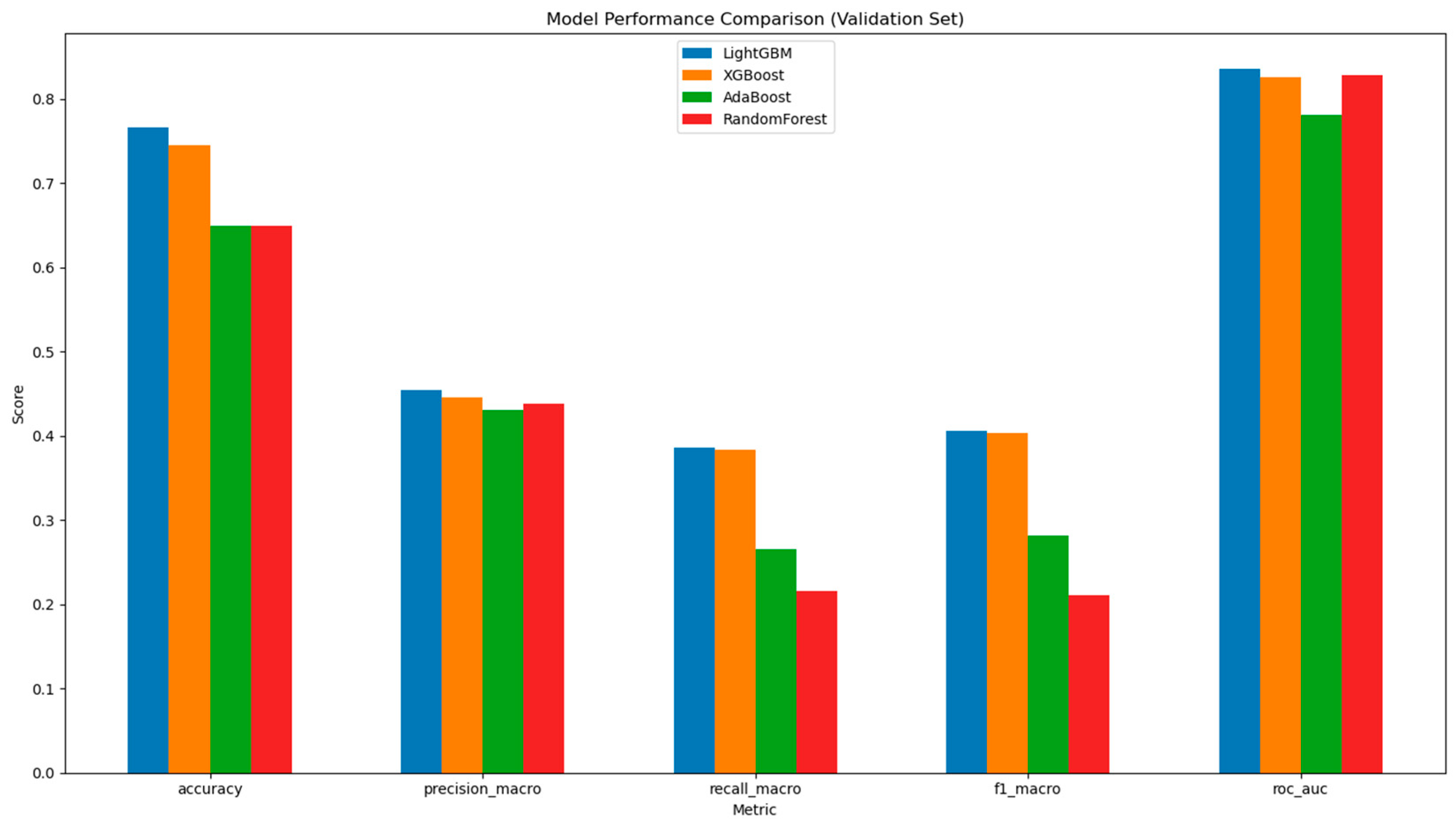
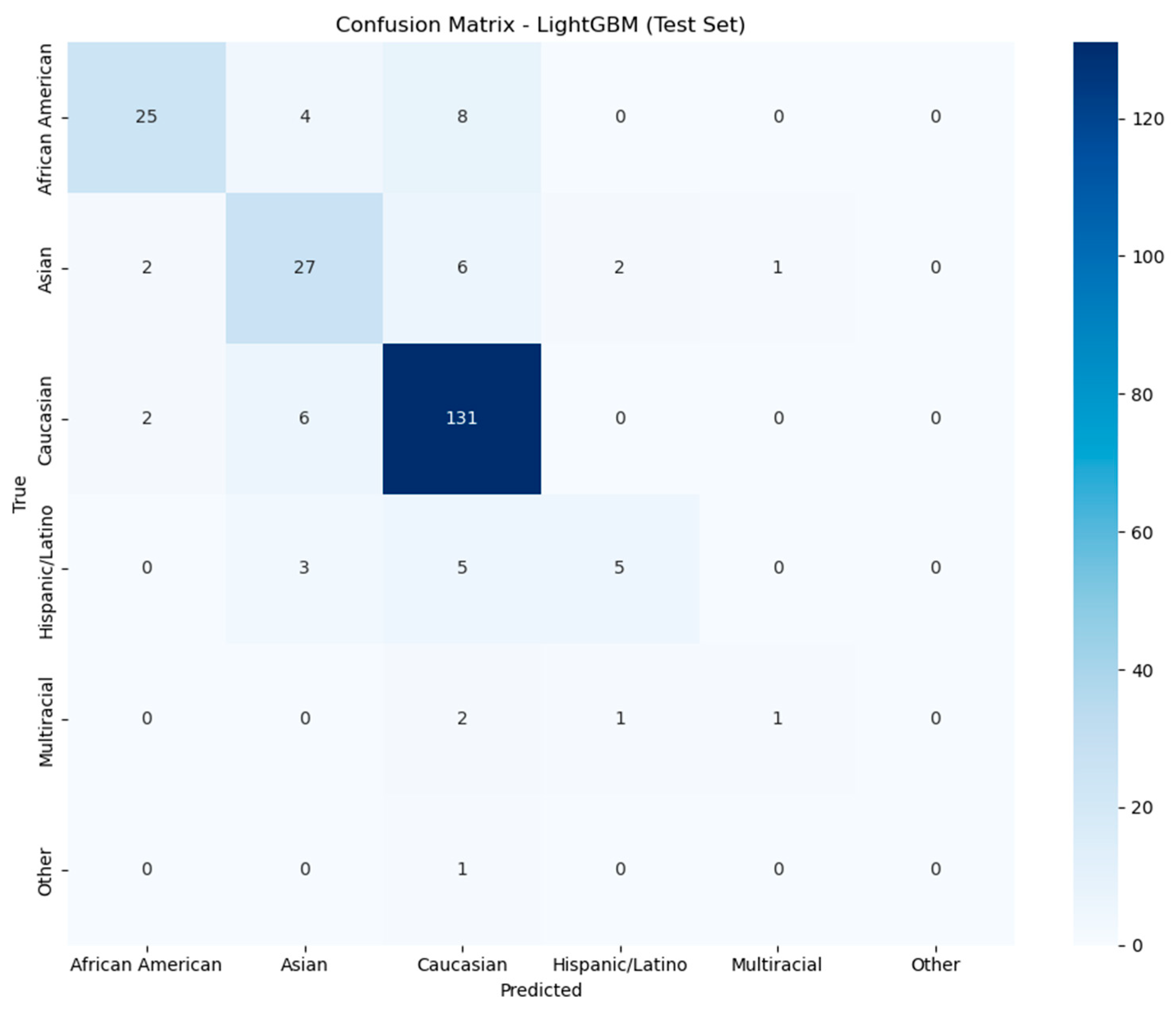
3.5. Machine Learning for Ethnicity Prediction
4. Discussion
5. Limitations of the Study
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leonard, J.M.; Toro, D.D. Defining the Microbiome Components (Bacteria, Viruses, Fungi) and Microbiome Geodiversity. Surg. Infect. 2023, 24, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-J.; Li, S.; Gan, R.-Y.; Zhou, T.; Xu, D.-P.; Li, H.-B. Impacts of Gut Bacteria on Human Health and Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 7493–7519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chi, Y.; Song, S. Important Soil Microbiota’s Effects on Plants and Soils: A Comprehensive 30-Year Systematic Literature Review. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1347745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkowski, P.G.; Fenchel, T.; Delong, E.F. The Microbial Engines That Drive Earth’s Biogeochemical Cycles. Science 2008, 320, 1034–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferranti, E.P.; Dunbar, S.B.; Dunlop, A.L.; Corwin, E.J. 20 Things You Didn’t Know About the Human Gut Microbiome. J. Cardiovasc. Nurs. 2014, 29, 479–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee-Sarwar, K.A.; Lasky-Su, J.; Kelly, R.S.; Litonjua, A.A.; Weiss, S.T. Metabolome–Microbiome Crosstalk and Human Disease. Metabolites 2020, 10, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Cao, L.; Ning, K. Microbiome Big-Data Mining and Applications Using Single-Cell Technologies and Metagenomics Approaches Toward Precision Medicine. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewandowska-Pietruszka, Z.; Figlerowicz, M.; Mazur-Melewska, K. The History of the Intestinal Microbiota and the Gut-Brain Axis. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shondelmyer, K.; Knight, R.; Sanivarapu, A.; Ogino, S. Ancient Thali Diet: Gut Microbiota, Immunity, and Health. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2018, 91, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Avuthu, N.; Guda, C. Meta-Analysis of Altered Gut Microbiota Reveals Microbial and Metabolic Biomarkers for Colorectal Cancer. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e00013-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, A.W.; Priya, S.; Blekhman, R.; Bordenstein, S.R. Gut Microbiota Diversity across Ethnicities in the United States. PLoS Biol. 2018, 16, e2006842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandoni, G.; D’Amico, F.; Fabbrini, M.; Mariani, L.; Sieri, S.; Casirati, A.; Di Guardo, L.; Del Vecchio, M.; Anichini, A.; Mortarini, R.; et al. Gut Microbiota, Metabolome, and Body Composition Signatures of Response to Therapy in Patients with Advanced Melanoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-Resolution Sample Inference from Illumina Amplicon Data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittaker, R.H. Evolution and Measurement of Species Diversity. Taxon 1972, 21, 213–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C.E. A Mathematical Theory of Communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SIMPSON, E.H. Measurement of Diversity. Nature 1949, 163, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Methodol. 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, J.R.; Curtis, J.T. An Ordination of the Upland Forest Communities of Southern Wisconsin. Ecol. Monogr. 1957, 27, 325–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulson, J.N.; Stine, O.C.; Bravo, H.C.; Pop, M. Differential Abundance Analysis for Microbial Marker-Gene Surveys. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 1200–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J. A New Method for Non-Parametric Multivariate Analysis of Variance. Austral Ecol. 2001, 26, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-G.; Lam, T.T.-Y.; Xu, S.; Dai, Z.; Zhou, L.; Feng, T.; Guo, P.; Dunn, C.W.; Jones, B.R.; Bradley, T.; et al. Treeio: An R Package for Phylogenetic Tree Input and Output with Richly Annotated and Associated Data. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 599–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Smith, D.K.; Zhu, H.; Guan, Y.; Lam, T.T. ggtree: An r Package for Visualization and Annotation of Phylogenetic Trees with Their Covariates and Other Associated Data. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2017, 8, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Peddada, S.D. Analysis of Microbial Compositions: A Review of Normalization and Differential Abundance Analysis. Npj Biofilms Microbiomes 2020, 6, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández Medina, R.; Kutuzova, S.; Nielsen, K.N.; Johansen, J.; Hansen, L.H.; Nielsen, M.; Rasmussen, S. Machine Learning and Deep Learning Applications in Microbiome Research. ISME Commun. 2022, 2, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, J.H. Greedy Function Approximation: A Gradient Boosting Machine. Ann. Stat. 2001, 29, 1189–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freund, Y.; Schapire, R.E. A Decision-Theoretic Generalization of On-Line Learning and an Application to Boosting. J. Comput. Syst. Sci. 1997, 55, 119–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. XGBoost: A Scalable Tree Boosting System. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, G.; Meng, Q.; Finley, T.; Wang, T.; Chen, W.; Ma, W.; Ye, Q.; Liu, T.-Y. LightGBM: A Highly Efficient Gradient Boosting Decision Tree. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Guyon, I., Luxburg, U.V., Bengio, S., Wallach, H., Fergus, R., Vishwanathan, S., Garnett, R., Eds.; Curran Associates, Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Bisong, E. Google Colaboratory. In Building Machine Learning and Deep Learning Models on Google Cloud Platform: A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners; Apress: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2019; pp. 59–64. ISBN 978-1-4842-4470-8. [Google Scholar]
- Carcy, S.; Ostner, J.; Tran, V.; Menden, M.; Müller, C.L. MetaIBS—Large-Scale Amplicon-Based Meta Analysis of Irritable Bowel Syndrome 2024. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magne, F.; Gotteland, M.; Gauthier, L.; Zazueta, A.; Pesoa, S.; Navarrete, P.; Balamurugan, R. The Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes Ratio: A Relevant Marker of Gut Dysbiosis in Obese Patients? Nutrients 2020, 12, 1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliphant, K.; Allen-Vercoe, E. Macronutrient Metabolism by the Human Gut Microbiome: Major Fermentation by-Products and Their Impact on Host Health. Microbiome 2019, 7, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickard, J.M.; Zeng, M.Y.; Caruso, R.; Núñez, G. Gut Microbiota: Role in Pathogen Colonization, Immune Responses, and Inflammatory Disease. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 279, 70–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Den Abbeele, P.; Belzer, C.; Goossens, M.; Kleerebezem, M.; De Vos, W.M.; Thas, O.; De Weirdt, R.; Kerckhof, F.-M.; Van De Wiele, T. Butyrate-Producing Clostridium Cluster XIVa Species Specifically Colonize Mucins in an in Vitro Gut Model. ISME J. 2013, 7, 949–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, E.; Algavi, Y.M.; Borenstein, E. The Gut Microbiome-Metabolome Dataset Collection: A Curated Resource for Integrative Meta-Analysis. Npj Biofilms Microbiomes 2022, 8, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.-J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhan, P.-C.; Lv, A.-P.; Li, P.-P.; Liu, L.; Li, W.-J.; Yang, L.-L.; Zhi, X.-Y. Comparative Genomic Analysis and Proposal of Clostridium yunnanense Sp. Nov., Clostridium rhizosphaerae Sp. Nov., and Clostridium paridis Sp. Nov., Three Novel Clostridium Sensu Stricto Endophytes with Diverse Capabilities of Acetic Acid and Ethanol Production. Anaerobe 2023, 79, 102686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Pan, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Ruan, B. Altered Gut Bacterial–Fungal Interkingdom Networks in Patients with Current Depressive Episode. Brain Behav. 2020, 10, e01677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelbary, M.M.H.; Hatting, M.; Bott, A.; Dahlhausen, A.; Keller, D.; Trautwein, C.; Conrads, G. The Oral-Gut Axis: Salivary and Fecal Microbiome Dysbiosis in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 1010853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadkhah, E.; Sikaroodi, M.; Korman, L.; Hardi, R.; Baybick, J.; Hanzel, D.; Kuehn, G.; Kuehn, T.; Gillevet, P.M. Gut Microbiome Identifies Risk for Colorectal Polyps. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2019, 6, e000297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, L.M.; Schafer, M.J.; Sohn, J.; Vincentini, J.; Weiner, H.L.; Ginsberg, S.D.; Blaser, M.J. Calorie Restriction Slows Age-Related Microbiota Changes in an Alzheimer’s Disease Model in Female Mice. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wexler, H.M. Bacteroides: The Good, the Bad, and the Nitty-Gritty. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2007, 20, 593–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Zhan, L.; Ye, T.; Xie, H.; Chen, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cai, X.; Yang, W.; Liao, X.; Liu, J.; et al. Gut Commensal Agathobacter Rectalis Alleviates Microglia-Mediated Neuroinflammation against Pathogenesis of Alzheimer Disease. iScience 2024, 27, 111116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiyrlykyzy, A.; Kozhakhmetov, S.; Babenko, D.; Zholdasbekova, G.; Alzhanova, D.; Olzhayev, F.; Baibulatova, A.; Kushugulova, A.R.; Askarova, S. Study of Gut Microbiota Alterations in Alzheimer’s Dementia Patients from Kazakhstan. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 15115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-García, A.; Arroyo, A.; García-Vicente, R.; Morales, M.L.; Gómez-Gordo, R.; Justo, P.; Cuéllar, C.; Sánchez-Pina, J.; López, N.; Alonso, R.; et al. Short-Chain Fatty Acid Production by Gut Microbiota Predicts Treatment Response in Multiple Myeloma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 30, 904–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakozaki, T.; Richard, C.; Elkrief, A.; Hosomi, Y.; Benlaïfaoui, M.; Mimpen, I.; Terrisse, S.; Derosa, L.; Zitvogel, L.; Routy, B.; et al. The Gut Microbiome Associates with Immune Checkpoint Inhibition Outcomes in Patients with Advanced Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2020, 8, 1243–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, S.G.; Goldenthal, A.R.; Uhlemann, A.-C.; Mann, J.J.; Miller, J.M.; Sublette, M.E. Systematic Review of Gut Microbiota and Major Depression. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valles-Colomer, M.; Falony, G.; Darzi, Y.; Tigchelaar, E.F.; Wang, J.; Tito, R.Y.; Schiweck, C.; Kurilshikov, A.; Joossens, M.; Wijmenga, C.; et al. The Neuroactive Potential of the Human Gut Microbiota in Quality of Life and Depression. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Ma, X.; Zhao, J.; Wang, X.; Gao, C. Succinate Metabolism and Its Regulation of Host-Microbe Interactions. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2190300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacca, M.; Celano, G.; Calabrese, F.M.; Portincasa, P.; Gobbetti, M.; De Angelis, M. The Controversial Role of Human Gut Lachnospiraceae. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, C.A.; Jospin, G.; Brownell, K.; Eisen, J.A.; Laraia, B.; Epel, E.S. Differences in Gut Microbiome by Insulin Sensitivity Status in Black and White Women of the National Growth and Health Study (NGHS): A Pilot Study. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0259889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, T.L.; Wang, F.; Cui, X.; Jackson, B.E.; Van Der Pol, W.J.; Lefkowitz, E.J.; Morrow, C.; Baskin, M.L. Associations Between Race, Perceived Psychological Stress, and the Gut Microbiota in a Sample of Generally Healthy Black and White Women: A Pilot Study on the Role of Race and Perceived Psychological Stress. Psychosom. Med. 2018, 80, 640–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cussotto, S.; Colle, R.; Voican, C.S.; Ciocan, D.M.; Trainel, N.; Bottemanne, H.; Pelloux, Y.; David, D.J.; Cassard, A.; Perlemuter, G.; et al. The Gut Microbiota Is Altered in Antidepressant-Free Depressed Patients and Is Associated with Depression Severity. J. Neurochem. 2025, 169, e70173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Callaghan, A.; Van Sinderen, D. Bifidobacteria and Their Role as Members of the Human Gut Microbiota. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vital, M.; Karch, A.; Pieper, D.H. Colonic Butyrate-Producing Communities in Humans: An Overview Using Omics Data. mSystems 2017, 2, e00130-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Lee, G.; Son, H.; Koh, H.; Kim, E.S.; Unno, T.; Shin, J.-H. Butyrate Producers, “The Sentinel of Gut”: Their Intestinal Significance with and beyond Butyrate, and Prospective Use as Microbial Therapeutics. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1103836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Pramanik, J.; Goyal, N.; Chauhan, D.; Sivamaruthi, B.S.; Prajapati, B.G.; Chaiyasut, C. Gut Microbiota in Anxiety and Depression: Unveiling the Relationships and Management Options. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, Y.; Nguyen, T.T.T.; Fujimura, Y.; Kameya, N.; Nakamura, S.; Arakawa, K.; Morita, H. Fecal Metabolite of a Gnotobiotic Mouse Transplanted with Gut Microbiota from a Patient with Alzheimer’s Disease. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2019, 83, 2144–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Taxon (Phylum) | AA | C | A | Coeff. * | p val ** | Comparison |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Firmicutes | 82.95 | 99.02 | 94.78 | 20.72 | 9.18705 × 10−18 | C vs. AA |
| Bacteroidota | 84.09 | 96.31 | 90.76 | 4.93 | 2.053122 × 10−8 | C vs. AA |
| Actinobacteriota | 78.41 | 92.4 | 87.15 | 3.34 | 2.426465 × 10−7 | C vs. AA |
| Proteobacteria | 80.11 | 88.93 | 75.9 | 0.39 | 7.817304 × 10−7 | A vs. C |
| Verrucomicrobiota | 43.75 | 62 | 24.1 | 0.19 | 6.707755 × 10−27 | A vs. C |
| Kingdom | Phylum | Class | Order | Family | Genus | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASV1575 | Bacteria | Firmicutes | Clostridia | Lachnospirales | Lachnospiraceae | Lachnoclostridium |
| ASV1451 | Bacteria | Bacteroidota | Bacteroidia | Bacteroidales | Bacteroidaceae | Bacteroides |
| ASV1514 | Bacteria | Bacteroidota | Bacteroidia | Bacteroidales | Bacteroidaceae | Bacteroides |
| ASV1450 | Bacteria | Firmicutes | Bacilli | RF39 | NA | NA |
| ASV7189 | Bacteria | Bacteroidota | Bacteroidia | Bacteroidales | Bacteroidaceae | Bacteroides |
| ASV9672 | Bacteria | Firmicutes | Clostridia | Lachnospirales | Lachnospiraceae | Blautia |
| ASV1449 | Bacteria | Firmicutes | Clostridia | Lachnospirales | Lachnospiraceae | Blautia |
| ASV1531 | Bacteria | Bacteroidota | Bacteroidia | Bacteroidales | Rikenellaceae | Alistipes |
| ASV12682 | Bacteria | Firmicutes | Clostridia | Oscillospirales | Ruminococcaceae | UBA1819 |
| ASV18151 | Bacteria | Bacteroidota | Bacteroidia | Bacteroidales | Bacteroidaceae | Bacteroides |
| ASV1454 | Bacteria | Firmicutes | Clostridia | Oscillospirales | Ruminococcaceae | Subdoligranulum |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
KC, A.; Paudel, R. Meta-Analysis of the Gut Microbiome: An African American Representation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2025, 22, 1591. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22101591
KC A, Paudel R. Meta-Analysis of the Gut Microbiome: An African American Representation. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2025; 22(10):1591. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22101591
Chicago/Turabian StyleKC, Anushka, and Roshan Paudel. 2025. "Meta-Analysis of the Gut Microbiome: An African American Representation" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 22, no. 10: 1591. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22101591
APA StyleKC, A., & Paudel, R. (2025). Meta-Analysis of the Gut Microbiome: An African American Representation. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 22(10), 1591. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22101591







