Barriers and Facilitators of Ambient Assisted Living Systems: A Systematic Literature Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
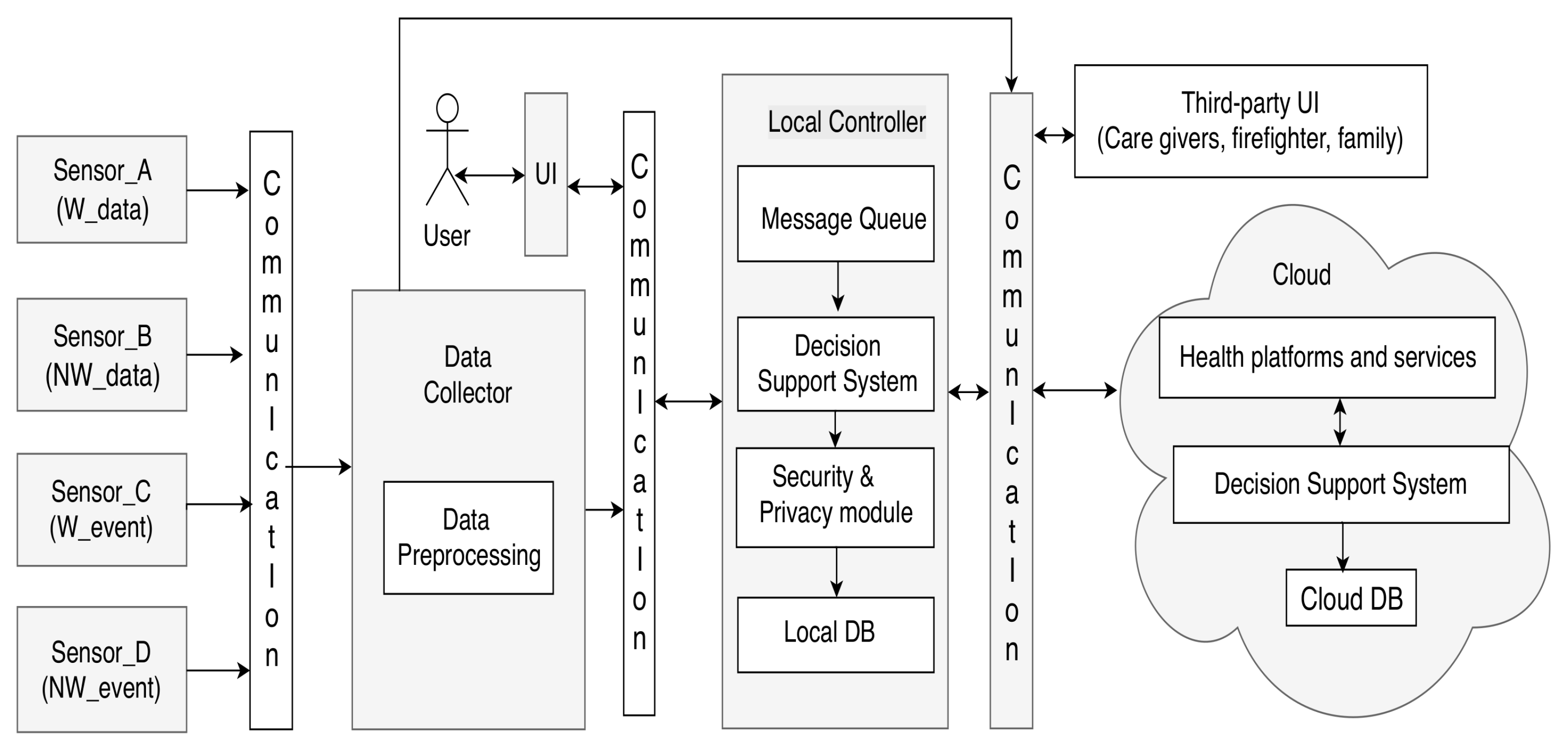
2. Ambient Assisted Living Systems
3. Related Work
4. Methods
- Which are the main operational barriers to AALSs?
- Which are the main operational facilitators to AALSs?
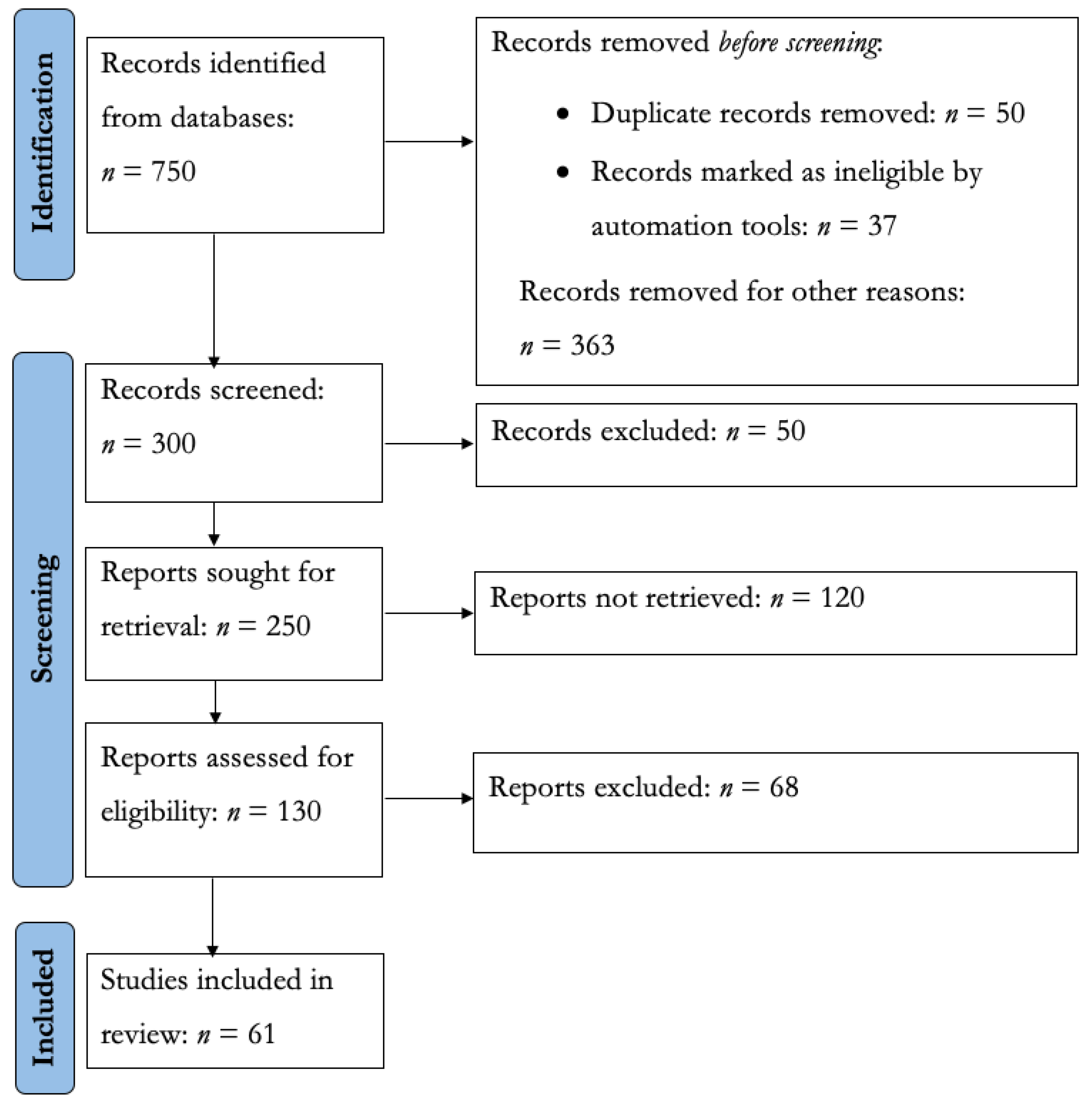
4.1. Identification
4.2. Screening
- Inclusion criteria
- –
- Papers must be related to health and AALSs.
- –
- Papers must be able to describe the results of their studies explicitly.
- –
- Papers must detail technological aspects of AALSs.
- –
- Papers discuss the advantages or disadvantages of AALSs.
- –
- Papers report, as far as possible, the experience of using AALSs.
- Exclusion criteria
- –
- The paper does not detail technical or methodological aspects of AALSs.
- –
- There is no evidence of the advantages or disadvantages of AALSs.
- –
- The paper does not describe the results of your research.
- –
- The paper is less than four pages long.
4.3. Included
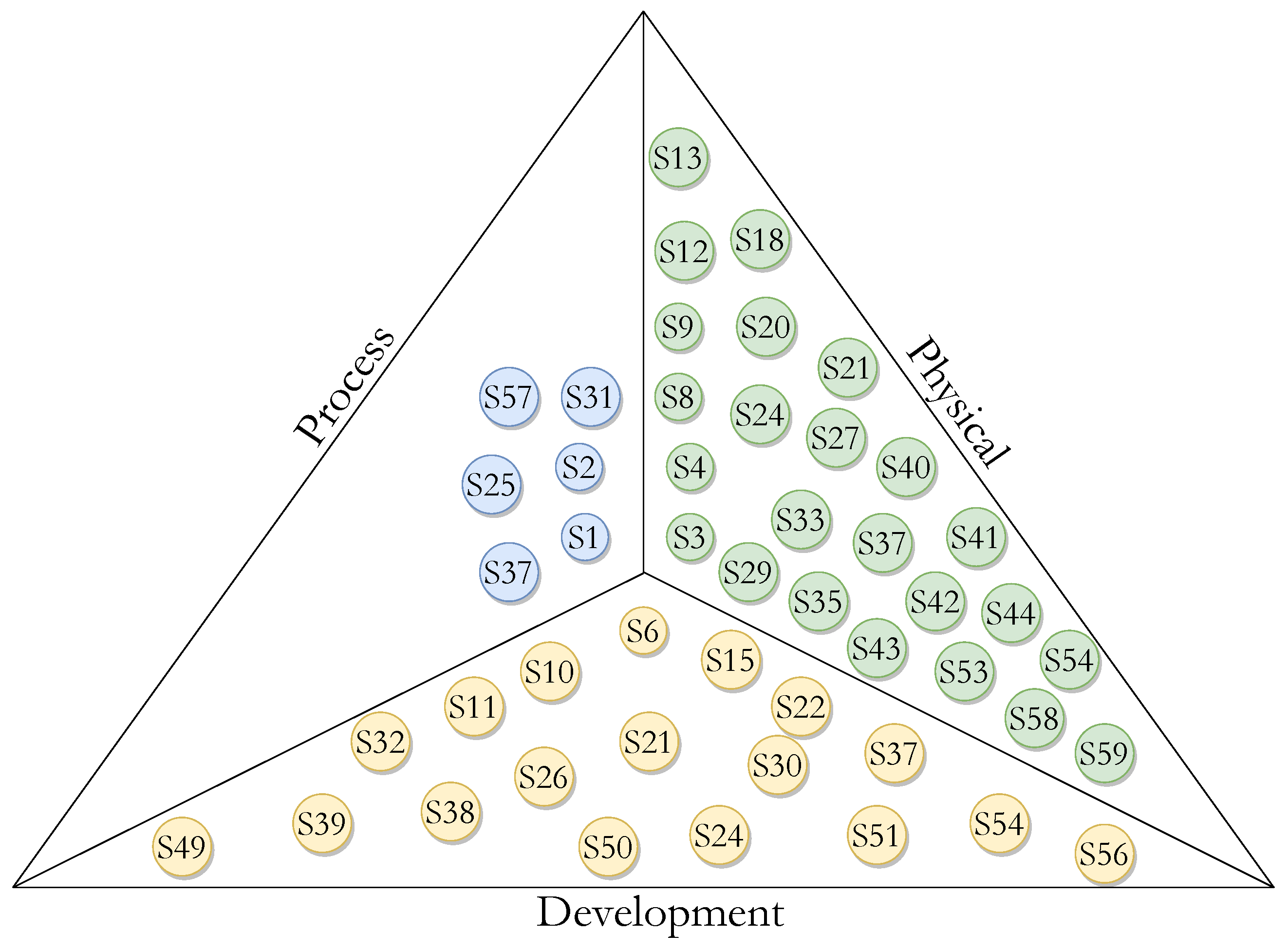
- Logical view: Describes the functionality that the system provides to end users. This represents what the system is supposed to do and the functions and services it offers.
- Development view: Details the system from a programming perspective and deals with the management of the software, i.e., it shows how the software system is divided into components and the dependencies between those components.
- Process view: Describes the processes in the system and how these processes communicate. In addition, from a system integrator’s perspective, it represents the step-by-step business and operational workflow of the components that make up the system.
- Physical view: Shows from a systems perspective all the physical components of the system as well as the physical connections between those components that integrate the solution (including services).
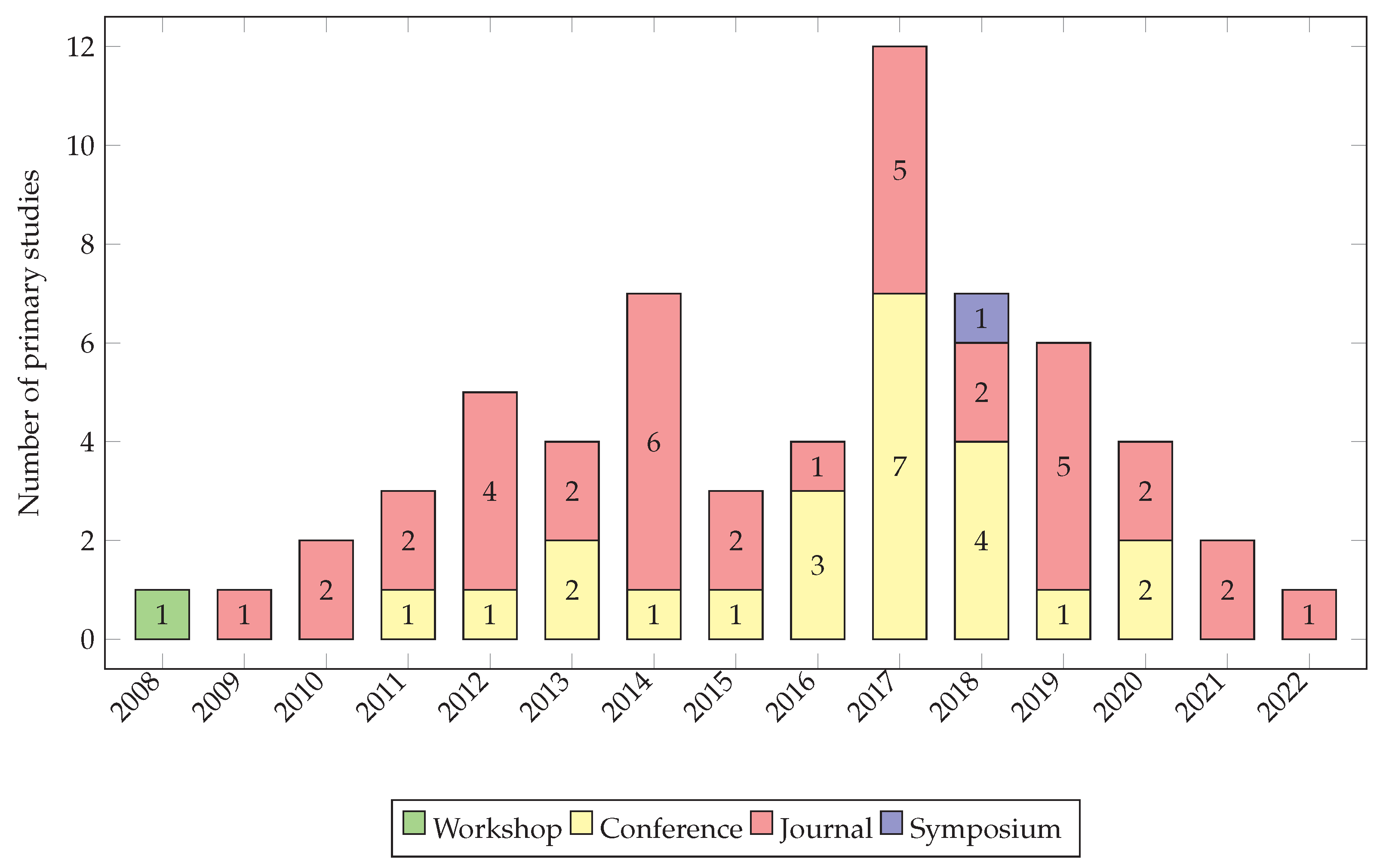
4.4. Replicability
5. Results
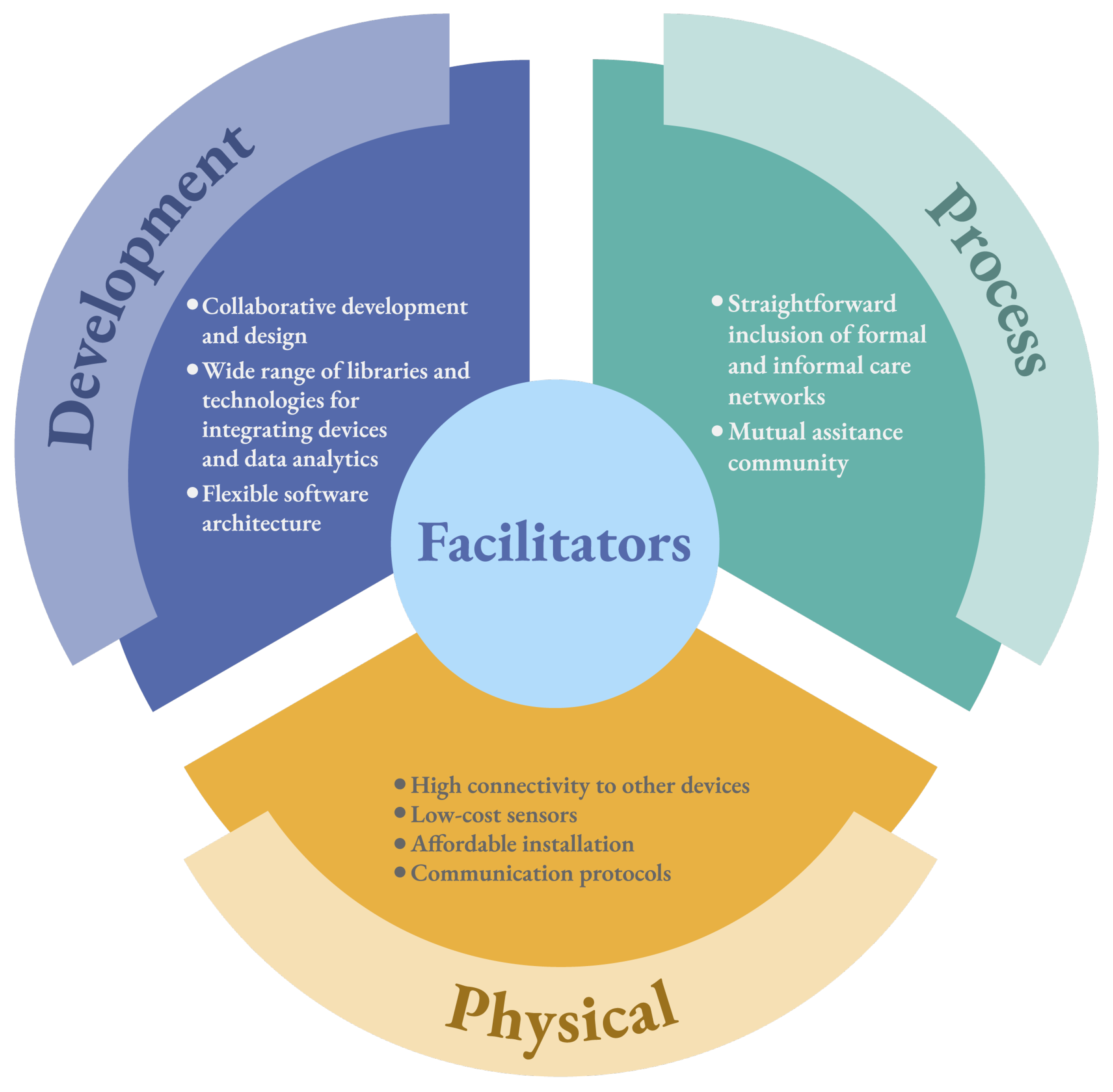
5.1. Facilitators
5.1.1. Development
5.1.2. Process
5.1.3. Physical
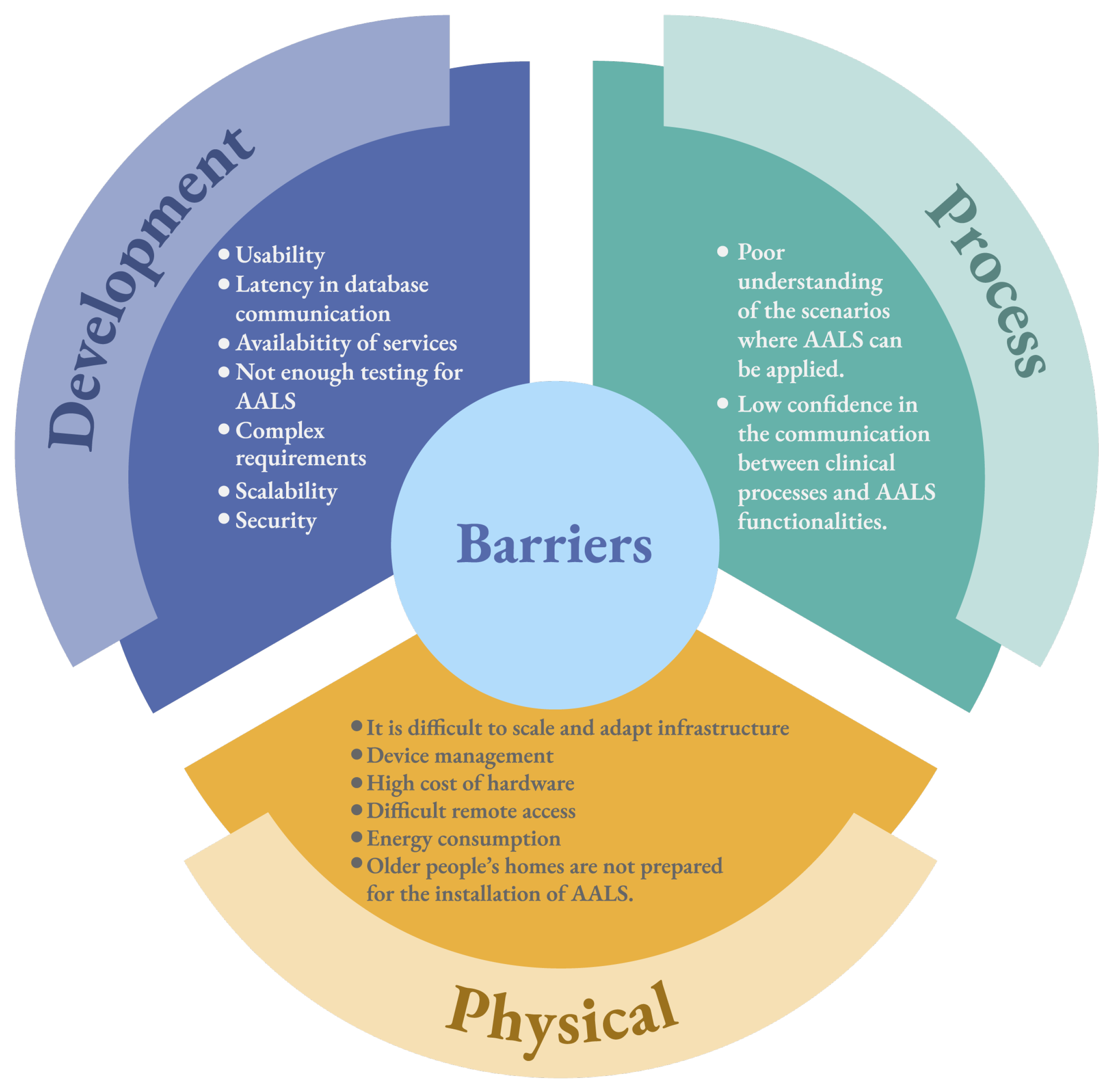
5.2. Barriers
5.2.1. Development
5.2.2. Process
5.2.3. Physical
6. Discussion
6.1. Implications for Researchers
6.2. Implications for Practitioners
7. Limitations
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AALSs | Ambient Assisted Living Systems |
Appendix A. Primary Studies
| ID | Name | Author(s) | Cite |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | Ambient Assisted Living: Elderly People’s Needs and How to Face Them | Fuchsberger, V. | [27] |
| S2 | Microsystem technology for ambient assisted living (AAL) | Weimar, U., Simpson, R., Barsan, N., Heine, T., Simmendinger, W., Malfatti, M., Margesin, B., Gonzo, L., Grassi, M., Lombardi, A., Malcovati, P., Leone, A., Diraco, P., Siciliano, P., Sicard, O. V., Pohle, R., Fleischer, M., Redaelli, A., Giacosi, A. and Bonassi, C. | [28] |
| S3 | Acoustic user interfaces for ambient-assisted living technologies | Goetze, S., Moritz, N., Appell, J.E., Meis, M., Bartsch, C., and Bitzer, J. | [29] |
| S4 | Towards evolutionary ambient assisted living systems | O’Grady, M.J., Muldoon, C., Dragone, M., Tynan, R., and O’Hare, G.M. | [30] |
| S5 | The architecture of ambient assisted living system | Reichman, A., and Zwiling, M. | [31] |
| S6 | Design and evaluation of an ambient assisted living system based on an argumentative multi-agent system | Muñoz, A., Augusto, J.C., Villa, A., and Botía, J.A. | [32] |
| S7 | A configurable sensor network applied to ambient assisted living | Villacorta, J.J., Jiménez, M.I., Val, L.D., and Izquierdo, A. | [33] |
| S8 | System services partitioning in ambient assisted living environment | Seguin, C., De Lamotte, F., and Philippe, J.L. | [34] |
| S9 | Data and information quality issues in ambient assisted living systems | McNaull, J., Augusto, J.C., Mulvenna, M., and McCullagh, P. | [35] |
| S10 | Ambient assisted living system for in-home monitoring of healthy independent elders | Botia, J.A., Villa, A., and Palma, J. | [5] |
| S11 | Enabling correct design and formal analysis of ambient assisted living systems | Benghazi, K., Hurtado, M.V., Hornos, M.J., Rodríguez, M.L., Rodríguez-Domínguez, C., Pelegrina, A.B., and Rodríguez-Fórtiz, M.J. | [36] |
| S12 | Semantic ambient media: From ambient advertising to ambient-assisted living | Pogorelc, B., Vatavu, R.D., Lugmayr, A., Stockleben, B., Risse, T., Kaario, J., Lomonaco, E.C. and Gams, M. | [37] |
| S13 | Living++ a platform for assisted living applications | Iqbal, M.U., Fet, N., Wagner, S., Handte, M., and Marrón, P.J. | [38] |
| S14 | Data-driven generation of rule-based behavior models for an ambient assisted living system | Rodner, T., and Litz, L. | [39] |
| S15 | Using temporal logic and model checking in automated recognition of human activities for ambient-assisted living | Magherini, T., Fantechi, A., Nugent, C.D., and Vicario, E. | [40] |
| S16 | Self-configuring agents for ambient assisted living applications | Ayala, I., Amor, M., and Fuentes, L. | [41] |
| S17 | A quality of context evaluating approach in an ambient assisted living e-Health system | Nazário, D.C., Todesco, J.L., Dantas, M.A.R., Tromel, I., and Neto, A. | [42] |
| S18 | Ambient assisted living system with capacitive occupancy sensor | Fernandez-Luque, F.J., Martínez, F.L., Domènech, G., Zapata, J., and Ruiz, R. | [43] |
| S19 | Care services provision in ambient assisted living | Camarinha-Matos, L.M., Ferrada, F., Oliveira, A.I., Rosas, J., and Monteiro, J. | [44] |
| S20 | An experimental characterization of reservoir computing in ambient assisted living applications | Bacciu, D., Barsocchi, P., Chessa, S., Gallicchio, C., and Micheli, A. | [45] |
| S21 | Disseminating ambient assisted living in rural areas | Leitner, G., Felfernig, A., Fercher, A.J., and Hitz, M. | [46] |
| S22 | A cloud-based Internet of Things platform for ambient assisted living | Cubo, J., Nieto, A., and Pimentel, E. | [47] |
| S23 | Active in-database processing to support ambient assisted living systems | De Morais, W.O., Lundström, J., and Wickström, N. | [48] |
| S24 | Authentication protocol for an ambient assisted living system | He, D., and Zeadally, S. | [49] |
| S25 | Challenges in designing and implementation of an effective ambient assisted living system | Koleva, P., Tonchev, K., Balabanov, G., Manolova, A., and Poulkov, V. | [50] |
| S26 | Data quality oriented taxonomy of ambient assisted living systems | Beevi, F.A., Wagner, S., Hallerstede, S., and Pedersen, C.F. | [51] |
| S27 | A new approach of facial expression recognition for ambient assisted living | Yaddaden, Y., Bouzouane, A., Adda, M., and Bouchard, B. | [52] |
| S28 | Expanding the Coverage of Ambient Assisted Living Systems | Bentes, J., Trevisan, D., and Viterbo, J. | [53] |
| S29 | Requirements and challenges in wireless network’s performance evaluation in ambient assisted living environments | Koren, A., and Šimunić, D. | [54] |
| S30 | Progress in ambient assisted systems for independent living by the elderly | Al-Shaqi, R., Mourshed, M., and Rezgui, Y. | [55] |
| S31 | Issues in the development of AAL systems: what experts think | Haslwanter, J.D.H., and Fitzpatrick, G. | [56] |
| S32 | Design tradeoffs for cloud-based ambient assisted living systems | Dong, Y., Wen, Y., Hu, H., Miao, C., and Leung, C. | [57] |
| S33 | Iot security (IoTsec) mechanisms for e-health and ambient assisted living applications | Minoli, D., Sohraby, K., and Occhiogrosso, B. | [8] |
| S34 | A novel integrated architecture for ambient assisted living systems | Kunnappilly, A., Sorici, A., Awada, I.A., Mocanu, I., Seceleanu, C., and Florea, A.M. | [58] |
| S35 | An ambient intelligence system for assisted living | De Paola, A., Ferraro, P., Gaglio, S., Re, G.L., Morana, M., Ortolani, M., and Peri, D. | [59] |
| S36 | An enhanced conceptual model for using ambient assisted living to provide a home proactive monitoring system for elderly Saudi Arabians | Alsulami, M.H., Atkins, A.S., Campion, R.J., and Alaboudi, A.A. | [60] |
| S37 | Crowd-based ambient assisted living to monitor the elderly’s health outdoors | Garcia, A.C.B., Vivacqua, A.S., Sánchez-Pi, N., Martí, L., and Molina, J.M. | [61] |
| S38 | Improving activity recognition accuracy in ambient-assisted living systems by automated feature engineering | Zdravevski, E., Lameski, P., Trajkovik, V., Kulakov, A., Chorbev, I., Goleva, R., Pombo, N. and Garcia, N. | [62] |
| S39 | Low-cost intelligent notification and alarming system for ambient assisted living applications | Žarić, N., and Djurišić, M.P. | [63] |
| S40 | A low-cost wireless acoustic sensor for ambient assisted living systems | Quintana-Suárez, M.A., Sánchez-Rodríguez, D., Alonso-González, I., and Alonso-Hernández, J.B. | [64] |
| S41 | A comprehensive and scalable middleware for ambient assisted living based on cloud computing and internet of things | Gomes, B.D.T.P., Muniz, L.C.M., da Silva e Silva, F.J., Ríos, L.E.T., and Endler, M. | [65] |
| S42 | Smart sensory furniture based on WSN for ambient assisted living | Bleda, A.L., Fernández-Luque, F.J., Rosa, A., Zapata, J., and Maestre, R. | [66] |
| S43 | A novel low-cost sensor prototype for nocturia monitoring in older people | Taramasco, C., Rodenas, T., Martinez, F., Fuentes, P., Munoz, R., Olivares, R., De Albuquerque, V.H. and Demongeot, J. | [11] |
| S44 | Failure Detector for Ambient Assisted Living | Junior, A.J., da Rocha, T., and Moreno, E.D. | [67] |
| S45 | Ambient Assisted Living Ecosystem for Supporting Senior Citizens’ Human System Interaction | Wagner, S., and Hunnerup, E. | [68] |
| S46 | BrainSmart: Ambient Assisted Living System Smartphone App Prototype for Parkinson’s Disease Patients | Ong, D.P., San Pedro, E.J.L., Valenzuela, M.E.M., and Tiglao, N.M.C. | [69] |
| S47 | Low-cost automatic ambient assisted living system | Malekmohamadi, H., Moemeni, A., Orun, A., and Purohit, J.K. | [70] |
| S48 | User Interface, Creation and Retrieval of User Health Information with Google Firebase, and Delivery of Automatic Emergency SMS for Ambient Assisted Living System: Monitoring of Elderly Condition Using Smart Devices | Pepita, A.G., and Juhana, T. | [71] |
| S49 | Incentive mechanism in participatory sensing for ambient assisted living | Yao, H., Muqing, W., and Tianze, L. | [72] |
| S50 | MiND: Mind Networked Device Architecture for Attention-Gated Ambient Assisted Living Systems | Mukherjee, A., Misra, S., and Atrish, A. | [73] |
| S51 | Air quality monitoring using assistive robots for ambient assisted living and enhanced living environments through internet of things | Marques, G., Pires, I.M., Miranda, N., and Pitarma, R. | [74] |
| S52 | An ambient assisted living system for dementia patients | Yilmaz, Ö. | [75] |
| S53 | Framework-oriented approach to ease the development of ambient assisted-living systems | Bellagente, P., Crema, C., Depari, A., Flammini, A., Lenzi, G., and Rinaldi, S. | [76] |
| S54 | ECASS: an encryption compression aggregation security scheme for secure data transmission in ambient assisted living systems | Mbarek, B., Jabeur, N., and Yasar, A.U.H. | [77] |
| S55 | Concept for the Large-Scale Deployment of Ambient Assisted Living Systems | Schiller, L., Wuehr, M., Poeschl, R., and Dorner, W. | [78] |
| S56 | Human Activity Recognition Using Smartphone Sensors and Beacon-based Indoor Localization for Ambient Assisted Living Systems | Vesa, A.V., Vlad, S., Rus, R., Antal, M., Pop, C., Anghel, I., Cioara, T. and Salomie, I. | [79] |
| S57 | AnAbEL: Towards empowering people living with dementia in ambient assisted living | Gimenez Manuel, J.G., Augusto, J.C., and Stewart, J. | [80] |
| S58 | Sensor failure detection in ambient assisted living using association rule mining | ElHady, N.E., Jonas, S., Provost, J., and Senner, V. | [81] |
| S59 | Deliberative Context-Aware Ambient Intelligence System for Assisted Living Homes | Babli, M., Rincon, J.A., Onaindia, E., Carrascosa, C., and Julian, V. | [82] |
| S60 | Evaluating the impact of different symmetrical models of ambient assisted living systems | Alosaimi, W., Ansari, M.T.J., Alharbi, A., Alyami, H., Seh, A.H., Pandey, A.K., Agrawal, A. and Khan, R.A. | [83] |
| S61 | FriendCare-AAL: a robust social IoT-based alert generation system for ambient assisted living | Gulati, N., and Kaur, P.D. | [84] |
References
- Rudnicka, E.; Napierała, P.; Podfigurna, A.; Męczekalski, B.; Smolarczyk, R.; Grymowicz, M. The World Health Organization (WHO) approach to healthy ageing. Maturitas 2020, 139, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Leeuwen, K.M.; Malley, J.; Bosmans, J.E.; Jansen, A.P.; Ostelo, R.W.; Van der Horst, H.E.; Netten, A. What can local authorities do to improve the social care-related quality of life of older adults living at home? Evidence from the Adult Social Care Survey. Health Place 2014, 29, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGilton, K.S.; Vellani, S.; Yeung, L.; Chishtie, J.; Commisso, E.; Ploeg, J.; Andrew, M.K.; Ayala, A.P.; Gray, M.; Morgan, D.; et al. Identifying and understanding the health and social care needs of older adults with multiple chronic conditions and their caregivers: A scoping review. BMC Geriatr. 2018, 18, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; De Florio, V.; Gui, N.; Blondia, C. Promises and challenges of ambient assisted living systems. In Proceedings of the 2009 Sixth International Conference on Information Technology: New Generations, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–29 April 2009; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 1201–1207. [Google Scholar]
- Botia, J.A.; Villa, A.; Palma, J. Ambient Assisted Living system for in-home monitoring of healthy independent elders. Expert Syst. Appl. 2012, 39, 8136–8148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcés, L.; Ampatzoglou, A.; Avgeriou, P.; Nakagawa, E.Y. Quality attributes and quality models for ambient assisted living software systems: A systematic mapping. Inf. Softw. Technol. 2017, 82, 121–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Murabet, A.; Abtoy, A.; Touhafi, A.; Tahiri, A. Ambient Assisted living system’s models and architectures: A survey of the state of the art. J. King Saud Univ. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2020, 32, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minoli, D.; Sohraby, K.; Occhiogrosso, B. Iot security (IoTsec) mechanisms for e-health and ambient assisted living applications. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Connected Health: Applications, Systems and Engineering Technologies (CHASE), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 17–19 July 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Ngankam, H.K.; Pigot, H.; Giroux, S. OntoDomus: A Semantic Model for Ambient Assisted Living System Based on Smart Homes. Electronics 2022, 11, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, M.A.; Qureshi, K.N.; Jeon, G.; Piccialli, F. Deep learning-based ambient assisted living for self-management of cardiovascular conditions. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 10449–10467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taramasco, C.; Rodenas, T.; Martinez, F.; Fuentes, P.; Munoz, R.; Olivares, R.; De Albuquerque, V.H.C.; Demongeot, J. A novel low-cost sensor prototype for nocturia monitoring in older people. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 52500–52509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Syst. Rev. 2021, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruchten, P.B. The 4+ 1 view model of architecture. IEEE Softw. 1995, 12, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrievski, A.; Zdravevski, E.; Lameski, P.; Trajkovik, V. A survey of Ambient Assisted Living systems: Challenges and opportunities. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 12th International Conference on Intelligent Computer Communication and Processing (ICCP), Cluj-Napoca, Romania, 8–10 September 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 49–53. [Google Scholar]
- Kunnappilly, A.; Marinescu, R.; Seceleanu, C. A model-checking-based framework for analyzing ambient assisted living solutions. Sensors 2019, 19, 5057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choukou, M.; Polyvyana, A.; Sakamoto, Y.; Osterreicher, A. Ambient assisted living technologies to support older adults’ health and wellness: A systematic mapping review. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 25, 4289–4307. [Google Scholar]
- Jovanovic, M.; Mitrov, G.; Zdravevski, E.; Lameski, P.; Colantonio, S.; Kampel, M.; Tellioglu, H.; Florez-Revuelta, F. Ambient Assisted Living: Scoping Review of Artificial Intelligence Models, Domains, Technology, and Concerns. J. Med. Internet Res. 2022, 24, e36553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicirelli, G.; Marani, R.; Petitti, A.; Milella, A.; D’Orazio, T. Ambient assisted living: A review of technologies, methodologies and future perspectives for healthy aging of population. Sensors 2021, 21, 3549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, K.; Vakkalanka, S.; Kuzniarz, L. Guidelines for conducting systematic mapping studies in software engineering: An update. Inf. Softw. Technol. 2015, 64, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohlin, C.; Runeson, P.; Höst, M.; Ohlsson, M.C.; Regnell, B.; Wesslén, A. Experimentation in Software Engineering; Springer Science and Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Marquez, G.; Taramasco, C. Barriers and Facilitators of Ambient-Assisted Living Systems: A Systematic Literature Review—Study Protocol. Zenodo. 2023. Available online: https://zenodo.org/record/7578848#.ZABnrx9ByUk (accessed on 25 February 2023).
- Jamil, M.A.; Arif, M.; Abubakar, N.S.A.; Ahmad, A. Software testing techniques: A literature review. In Proceedings of the 2016 6th International Conference on Information and Communication Technology for the Muslim World (ICT4M), Jakarta, Indonesia, 22–24 November 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 177–182. [Google Scholar]
- Bass, L.; Clements, P.; Kazman, R. Software Architecture in Practice; Addison-Wesley Professional: Boston, MA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Duo, W.; Zhou, M.; Abusorrah, A. A Survey of Cyber Attacks on Cyber Physical Systems: Recent Advances and Challenges. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2022, 9, 784–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownson, R.C.; Colditz, G.A.; Proctor, E.K. Dissemination and Implementation Research in Health: Translating Science to Practice; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Márquez, G.; Veloz, A.; Minonzio, J.G.; Reyes, C.; Calvo, E.; Taramasco, C. Using low-resolution non-invasive infrared sensors to classify activities and falls in older adults. Sensors 2022, 22, 2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchsberger, V. Ambient assisted living: Elderly people’s needs and how to face them. In Proceedings of the 1st ACM International Workshop on Semantic Ambient Media Experiences, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 31 October 2008; pp. 21–24. [Google Scholar]
- Weimar, U.; Simpson, R.; Barsan, N.; Heine, T.; Simmendinger, W.; Malfatti, M.; Margesin, B.; Gonzo, L.; Grassi, M.; Lombardi, A.; et al. Microsystem technology for ambient assisted living (AAL). Procedia Chem. 2009, 1, 710–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetze, S.; Moritz, N.; Appell, J.E.; Meis, M.; Bartsch, C.; Bitzer, J. Acoustic user interfaces for ambient-assisted living technologies. Inform. Health Soc. Care 2010, 35, 125–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Grady, M.J.; Muldoon, C.; Dragone, M.; Tynan, R.; O’Hare, G.M. Towards evolutionary ambient assisted living systems. J. Ambient Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2010, 1, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichman, A.; Zwiling, M. The architecture of ambient assisted living system. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Microwaves, Communications, Antennas and Electronic Systems (COMCAS 2011), Tel Aviv, Israel, 7–9 November 2011; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz, A.; Augusto, J.C.; Villa, A.; Botía, J.A. Design and evaluation of an ambient assisted living system based on an argumentative multi-agent system. Pers. Ubiquitous Comput. 2011, 15, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villacorta, J.J.; Jiménez, M.I.; Del Val, L.; Izquierdo, A. A configurable sensor network applied to ambient assisted living. Sensors 2011, 11, 10724–10737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seguin, C.; De Lamotte, F.; Philippe, J.L. System services partitioning in ambient assisted living environment. In Proceedings of the 2012 ACM Conference on Ubiquitous Computing, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 5–8 September 2012; pp. 778–781. [Google Scholar]
- McNaull, J.; Augusto, J.C.; Mulvenna, M.; McCullagh, P. Data and information quality issues in ambient assisted living systems. J. Data Inf. Qual. 2012, 4, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benghazi, K.; Hurtado, M.V.; Hornos, M.J.; Rodríguez, M.L.; Rodríguez-Domínguez, C.; Pelegrina, A.B.; Rodríguez-Fórtiz, M.J. Enabling correct design and formal analysis of Ambient Assisted Living systems. J. Syst. Softw. 2012, 85, 498–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogorelc, B.; Vatavu, R.D.; Lugmayr, A.; Stockleben, B.; Risse, T.; Kaario, J.; Lomonaco, E.C.; Gams, M. Semantic ambient media: From ambient advertising to ambient-assisted living. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2012, 58, 399–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.U.; Fet, N.; Wagner, S.; Handte, M.; Marrón, P.J. Living++ a platform for assisted living applications. In Proceedings of the 2013 ACM Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing Adjunct Publication, Zurich, Switzerland, 8–12 September 2013; pp. 853–860. [Google Scholar]
- Rodner, T.; Litz, L. Data-driven generation of rule-based behavior models for an ambient assisted living system. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Third International Conference on Consumer Electronics, Berlin (ICCE-Berlin), Berlin, Germany, 9–11 September 2013; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 35–38. [Google Scholar]
- Magherini, T.; Fantechi, A.; Nugent, C.D.; Vicario, E. Using temporal logic and model checking in automated recognition of human activities for ambient-assisted living. IEEE Trans. Hum.-Mach. Syst. 2013, 43, 509–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala, I.; Amor, M.; Fuentes, L. Self-configuring agents for ambient assisted living applications. Pers. Ubiquitous Comput. 2013, 17, 1159–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazário, D.C.; Todesco, J.L.; Dantas, M.A.R.; Tromel, I.; Neto, A. A quality of context evaluating approach in an ambient assisted living e-Health system. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE 16th International Conference on e-Health Networking, Applications and Services (Healthcom), Natal, Brazil, 15–18 October 2014; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 158–163. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Luque, F.J.; Martínez, F.L.; Domènech, G.; Zapata, J.; Ruiz, R. Ambient assisted living system with capacitive occupancy sensor. Expert Syst. 2014, 31, 378–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camarinha-Matos, L.; Ferrada, F.; Oliveira, A.; Rosas, J.; Monteiro, J. Care services provision in ambient assisted living. IRBM 2014, 35, 286–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacciu, D.; Barsocchi, P.; Chessa, S.; Gallicchio, C.; Micheli, A. An experimental characterization of reservoir computing in ambient assisted living applications. Neural Comput. Appl. 2014, 24, 1451–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitner, G.; Felfernig, A.; Fercher, A.J.; Hitz, M. Disseminating ambient assisted living in rural areas. Sensors 2014, 14, 13496–13531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cubo, J.; Nieto, A.; Pimentel, E. A cloud-based Internet of Things platform for ambient assisted living. Sensors 2014, 14, 14070–14105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Morais, W.O.; Lundström, J.; Wickström, N. Active in-database processing to support ambient assisted living systems. Sensors 2014, 14, 14765–14785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, D.; Zeadally, S. Authentication protocol for an ambient assisted living system. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2015, 53, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koleva, P.; Tonchev, K.; Balabanov, G.; Manolova, A.; Poulkov, V. Challenges in designing and implementation of an effective Ambient Assisted Living system. In Proceedings of the 2015 12th International Conference on Telecommunication in Modern Satellite, Cable and Broadcasting Services (TELSIKS), Nis, Serbia, 14–17 October 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 305–308. [Google Scholar]
- Beevi, F.A.; Wagner, S.; Hallerstede, S.; Pedersen, C. Data quality oriented taxonomy of ambient assisted living systems. In Proceedings of the IET International Conference on Technologies for Active and Assisted Living (TechAAL), London, UK, 5 November 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Yaddaden, Y.; Bouzouane, A.; Adda, M.; Bouchard, B. A new approach of facial expression recognition for ambient assisted living. In Proceedings of the 9th ACM International Conference on Pervasive Technologies Related to Assistive Environments, Corfu Island, Greece, 29 June–1 July 2016; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Bentes, J.; Trevisan, D.; Viterbo, J. Expanding the Coverage of Ambient Assisted Living Systems. In Proceedings of the 2016 49th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences (HICSS), Koloa, HI, USA, 5–8 January 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 3268–3277. [Google Scholar]
- Koren, A.; Šimunić, D. Requirements and challenges in wireless network’s performance evaluation in ambient assisted living environments. In Proceedings of the 2016 39th International Convention on Information and Communication Technology, Electronics and Microelectronics (MIPRO), Opatija, Croatia, 30 May–3 June 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 624–627. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Shaqi, R.; Mourshed, M.; Rezgui, Y. Progress in ambient assisted systems for independent living by the elderly. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haslwanter, J.D.H.; Fitzpatrick, G. Issues in the Development of AAL Systems: What experts think. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on PErvasive Technologies Related to Assistive Environments, Island of Rhodes, Greece, 21–23 June 2017; pp. 201–208. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Y.; Wen, Y.; Hu, H.; Miao, C.; Leung, C. Design tradeoffs for cloud-based ambient assisted living systems. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Crowd Science and Engineering, Beijing, China, 6–9 July 2017; pp. 144–151. [Google Scholar]
- Kunnappilly, A.; Sorici, A.; Awada, I.A.; Mocanu, I.; Seceleanu, C.; Florea, A.M. A novel integrated architecture for ambient assisted living systems. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 41st Annual Computer Software and Applications Conference (COMPSAC), Turin, Italy, 4–8 July 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; Volume 1, pp. 465–472. [Google Scholar]
- De Paola, A.; Ferraro, P.; Gaglio, S.; Re, G.L.; Morana, M.; Ortolani, M.; Peri, D. An ambient intelligence system for assisted living. In Proceedings of the 2017 AEIT International Annual Conference, Cagliari, Italy, 20–22 September 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Alsulami, M.H.; Atkins, A.S.; Campion, R.J.; Alaboudi, A.A. An enhanced conceptual model for using ambient assisted living to provide a home proactive monitoring system for elderly Saudi Arabians. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/ACS 14th International Conference on Computer Systems and Applications (AICCSA), Hammamet, Tunisia, 30 October–3 November 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1443–1449. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, A.C.B.; Vivacqua, A.S.; Sanchez-Pi, N.; Martí, L.; Molina, J.M. Crowd-based ambient assisted living to monitor the elderly’s health outdoors. IEEE Softw. 2017, 34, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdravevski, E.; Lameski, P.; Trajkovik, V.; Kulakov, A.; Chorbev, I.; Goleva, R.; Pombo, N.; Garcia, N. Improving activity recognition accuracy in ambient-assisted living systems by automated feature engineering. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 5262–5280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žarić, N.; Djurišić, M.P. Low cost intelligent notification and alarming system for ambient assisted living applications. In Proceedings of the 2017 40th International Conference on Telecommunications and Signal Processing (TSP), Barcelona, Spain, 5–7 July 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 259–262. [Google Scholar]
- Quintana-Suárez, M.A.; Sánchez-Rodríguez, D.; Alonso-González, I.; Alonso-Hernández, J.B. A low cost wireless acoustic sensor for ambient assisted living systems. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, B.d.T.P.; Muniz, L.C.M.; da Silva e Silva, F.J.; Ríos, L.E.T.; Endler, M. A comprehensive and scalable middleware for Ambient Assisted Living based on cloud computing and Internet of Things. Concurr. Comput. Pract. Exp. 2017, 29, e4043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleda, A.L.; Fernández-Luque, F.J.; Rosa, A.; Zapata, J.; Maestre, R. Smart sensory furniture based on WSN for ambient assisted living. IEEE Sensors J. 2017, 17, 5626–5636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junior, A.J.; da Rocha, T.; Moreno, E.D. A Failure Detector for Ambient Assisted Living. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Symposium on Computers and Communications (ISCC), Natal, Brazil, 25–28 June 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, S.; Hunnerup, E. Ambient Assisted Living Ecosystem for Supporting Senior Citizens’ Human System Interaction. In Proceedings of the 2018 11th International Conference on Human System Interaction (HSI), Gdansk, Poland, 4–6 July 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 221–225. [Google Scholar]
- Ong, D.P.; San Pedro, E.J.L.; Valenzuela, M.E.M.; Tiglao, N.M.C. BrainSmart: Ambient Assisted Living System Smartphone App Prototype for Parkinson’s Disease Patients. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Global Humanitarian Technology Conference (GHTC), San Jose, CA, USA, 18–21 October 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Malekmohamadi, H.; Moemeni, A.; Orun, A.; Purohit, J.K. Low-cost automatic ambient assisted living system. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications Workshops (PerCom Workshops), Athens, Greece, 19–23 March 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 693–697. [Google Scholar]
- Pepita, A.G.; Juhana, T. User interface, creation and retrieval of user health information with Google firebase, and delivery of automatic emergency SMS for ambient assisted living system: Monitoring of elderly condition using smart devices. In Proceedings of the 2018 4th International Conference on Wireless and Telematics (ICWT), Nusa Dua, Bali, Indonesia, 12–13 July 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, H.; Muqing, W.; Tianze, L. Incentive mechanism in participatory sensing for ambient assisted living. KSII Trans. Internet Inf. Syst. 2018, 12, 159–177. [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee, A.; Misra, S.; Atrish, A. MiND: Mind Networked Device Architecture for Attention-Gated Ambient Assisted Living Systems. IEEE Syst. J. 2019, 14, 1325–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, G.; Pires, I.M.; Miranda, N.; Pitarma, R. Air quality monitoring using assistive robots for ambient assisted living and enhanced living environments through internet of things. Electronics 2019, 8, 1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, Ö. An ambient assisted living system for dementia patients. Turk. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 2019, 27, 2361–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellagente, P.; Crema, C.; Depari, A.; Flammini, A.; Lenzi, G.; Rinaldi, S. Framework-oriented approach to ease the development of ambient assisted-living systems. IEEE Syst. J. 2019, 13, 4421–4432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbarek, B.; Jabeur, N.; Yasar, A.U.H. ECASS: An encryption compression aggregation security scheme for secure data transmission in ambient assisted living systems. Pers. Ubiquitous Comput. 2019, 23, 793–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiller, L.; Wuehr, M.; Poeschl, R.; Dorner, W. Concept for the Large Scale Deployment of Ambient Assisted Living Systems. In Proceedings of the 2020 10th International Conference on Advanced Computer Information Technologies (ACIT), Deggendorf, Germany, 16–18 September 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 288–292. [Google Scholar]
- Vesa, A.V.; Vlad, S.; Rus, R.; Antal, M.; Pop, C.; Anghel, I.; Cioara, T.; Salomie, I. Human activity recognition using smartphone sensors and beacon-based indoor localization for ambient assisted living systems. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 16th International Conference on Intelligent Computer Communication and Processing (ICCP), Cluj-Napoca, Romania, 3–5 September 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 205–212. [Google Scholar]
- Gimenez Manuel, J.G.; Augusto, J.C.; Stewart, J. AnAbEL: Towards empowering people living with dementia in ambient assisted living. Univers. Access Inf. Soc. 2020, 21, 457–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElHady, N.E.; Jonas, S.; Provost, J.; Senner, V. Sensor failure detection in ambient assisted living using association rule mining. Sensors 2020, 20, 6760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babli, M.; Rincón-Arango, J.A.; Onaindia De La Rivaherrera, E.; Carrascosa Casamayor, C.; Julian, V. Deliberative context-aware ambient intelligence system for assisted living homes. Hum.-Centric Comput. Inf. Sci. 2021, 11, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Alosaimi, W.; Ansari, M.T.J.; Alharbi, A.; Alyami, H.; Seh, A.H.; Pandey, A.K.; Agrawal, A.; Khan, R.A. Evaluating the impact of different symmetrical models of ambient assisted living systems. Symmetry 2021, 13, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulati, N.; Kaur, P.D. FriendCare-AAL: A robust social IoT based alert generation system for ambient assisted living. J. Ambient Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2022, 13, 1735–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Approach | Description | Keywords |
|---|---|---|
| Population | Papers related to AALSs and their derivatives | “ambient-assisted” OR “ambient assisted” OR “living” |
| Paper related to the types of technologies that support AALSs | “system*” OR “platform” OR “application” OR “software” OR “technology” | |
| Intervention | Papers related to health and care | “health” OR “care” OR “health care” |
| Output | Data regarding facilitators and barriers | “barrier” OR “disadvantage” OR “pitfall” OR “pain” OR “facilitator” OR “advantage” OR “gain” OR “benefit” |
| Data Item | Description |
|---|---|
| ID | This item describes a specific identification for each primary study |
| Name | Name of the study |
| Authors(s) | List of authors of the study |
| Year | Year of study publication |
| Venue | Description of where the study was published or presented |
| Facilitator | List of the facilitators described in the study |
| Barrier | List of barriers described in the study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Márquez, G.; Taramasco, C. Barriers and Facilitators of Ambient Assisted Living Systems: A Systematic Literature Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 5020. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20065020
Márquez G, Taramasco C. Barriers and Facilitators of Ambient Assisted Living Systems: A Systematic Literature Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023; 20(6):5020. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20065020
Chicago/Turabian StyleMárquez, Gastón, and Carla Taramasco. 2023. "Barriers and Facilitators of Ambient Assisted Living Systems: A Systematic Literature Review" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 20, no. 6: 5020. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20065020
APA StyleMárquez, G., & Taramasco, C. (2023). Barriers and Facilitators of Ambient Assisted Living Systems: A Systematic Literature Review. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(6), 5020. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20065020







