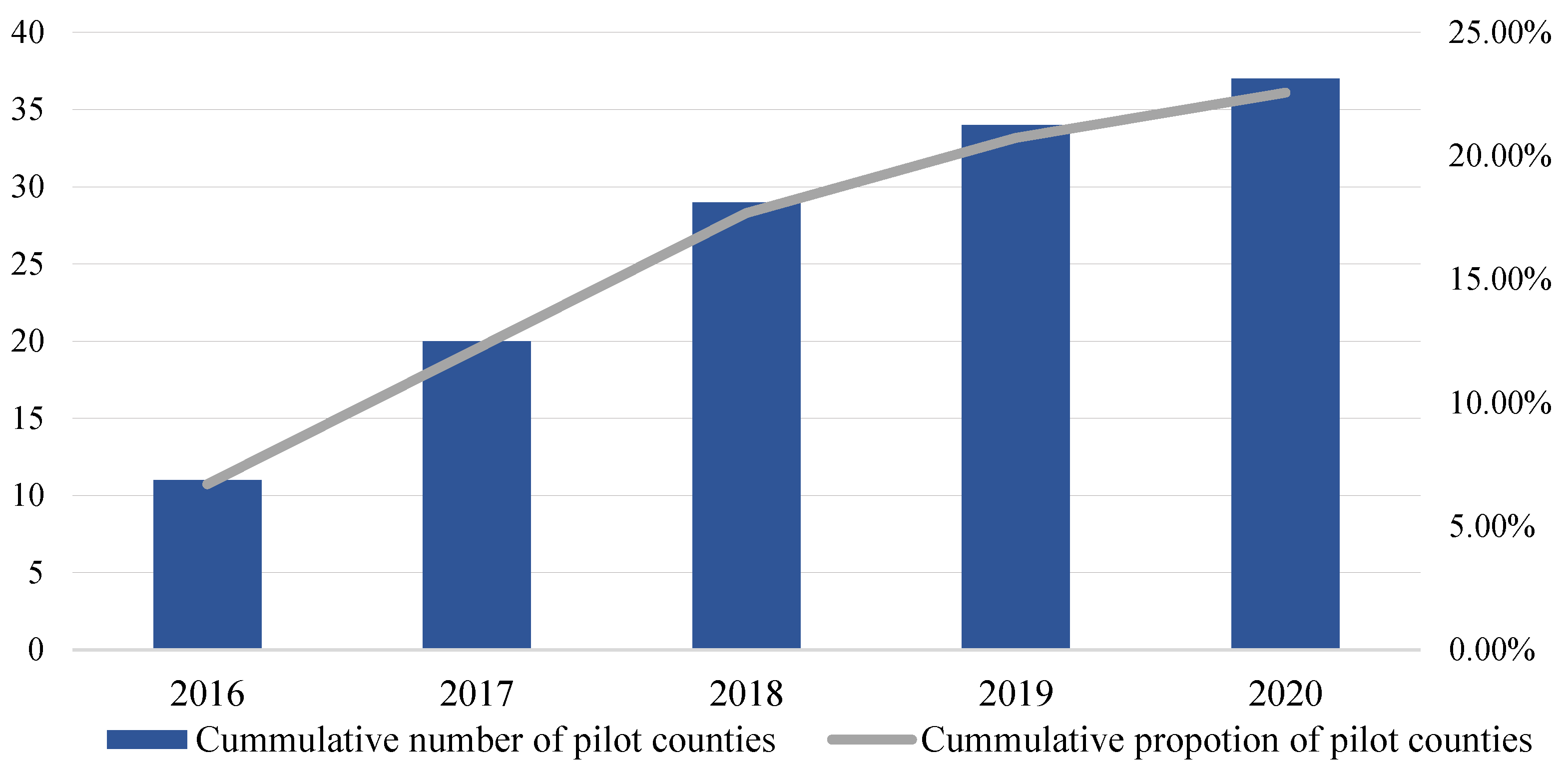1. Introduction
Crop straw is generated massively in the agricultural sector, and traditionally, it was disposed of by directly burning in the open air, leading to various environmental issues, mainly atmospheric pollutions and greenhouse gas emissions [
1,
2]. To mitigate the negative impacts of open-air burning of crop straw on the environment, various pathways for utilizing crop straw are proposed and practiced, and they can be used as renewable resources for improving soil fertility, producing livestock feed, and generating renewable energy if used effectively [
3]. In China, the effective utilization of crop straw can not only solve the tricky problems of disposing of crop straw, but also improve environmental quality, bring economic benefits, and create job opportunities, contributing to China’s Rural Revitalization Strategy [
4]. As a large agricultural country, China produced more than 819 million tons of crop residuals in 2021, including the residuals of rice, wheat, corn, potato, cassava, peanut, rape, soybean, cotton, sugarcane, etc., and the straw yield is still growing slowly but steadily. Due to the policy of prohibiting burning crop straw in the open air since early this century, various pathways for realizing crop straw resource utilization (CSRU) have been proposed, and the ratio of CSRU has kept rising, even exceeding 90% in recent years. In fact, the National Development and Reform Commission and the Ministry of Agriculture of China compiled The Catalogue of Straw Resource Utilization Technology in 2014, which proposed five technological pathways for realizing CSRU in rural China [
5]. With the proposal of carbon peak and neutralization, CSRU has become a major part of the national efforts in reducing carbon emissions and improving environmental sustainability [
6].
To drive the reduction of carbon emissions and the diffusion of renewable energy technologies, various policies and measures, such as the banning order for open-air burning of crop straw, have been developed and implemented [
7,
8]. In fact, the present supporting policies in China mainly focus on technical processes, project subsidies, and the establishment of residual collection, storage, and transportation systems [
4]. For instance, gasification is a promising technology that can be used for large-scale utilization of crop straw, so some scholars have focused on the policy that is aimed at promoting the commercialized utilization of crop straw with modern industrial technologies [
9]. The subsidy policy has also been greatly emphasized in many studies. Sun et al. (2019) empirically examined the effect of the public policy on crop straw utilization in the case of the Jiangsu Province of China and stated that the present subsidy policy played an insignificant role as the subsidy was low and not directly delivered to farmers [
7]. It is believed that the production operations, equipment purchase, storage, and transportation of CSRU should be established with the public subsidies [
4]. To improve the efficiency of CSRU in China, the Chinese government has adopted a pilot policy of rewards and subsidies for CSRU.
Many studies have recently been conducted to investigate the CSRU pilot policy and its diffusions, and they can be summarized as the streams shown in
Figure 1.
A pilot policy is like a form of experiment to “discover” new innovative objects, and then spread them to other places [
10]. It is believed that the pilot works aim to mobilize and manage ambiguity and conflicts related to specific policy objectives, and explore new policy tools through policy innovation [
11,
12]. One purpose of a pilot policy is to generate practical, replicable, and scalable policy tools through the bottom-up governance model in the process of policy innovation [
13], and different pilot policies have different influencing factors at different development stages [
14]. Usually, the phenomenon of “pilot diffusion” can be explained by the diffusion of innovation theory (DIT) [
15,
16]. Walker (1969) believed that innovation diffusion is not to conceive or develop new ideas or plans. On the contrary, it is the condition in which decision makers are most likely to adopt new plans [
17]. The diffusion of innovation policy refers to the development process in which the government knowledge at one department or level is applied to the governance of other departments or levels [
18]. Policy innovation is the basis of policy diffusion, and the objects of policy diffusion are innovative policies or projects [
19]. The exchange and interaction of innovation policies are emphasized, and policy innovation plays a significant role in the exchange activities [
20,
21].
From the numerous model construction studies, four basic diffusion models are summarized: national interaction model, regional diffusion model, leadership follow-up model, and vertical influence model [
22,
23,
24]. Presently, the research on the diffusion of energy policy is more focused on internal policy diffusion, with the country as the basic unit [
22,
23,
24], and different political systems and culture lead to different influencing mechanisms of policy diffusion [
23]. Based on different policy cases in China, scholars have put forward the diffusion of innovation theory with Chinese characteristics. For instance, Zhang and Xiao (2020) believed that China’s policies are vertically diffused from top to bottom, mainly in the form of experimental governance [
25]. The CSRU policy diffusion model in China conforms to the top-down diffusion characteristic, which is also the further excavation of the diffusion policy theory.
The trace of policy diffusion can be analyzed to identify the spatiotemporal distribution characteristics of the diffusion process. The S-shaped curve of the diffusion trace with “slow start-up period–accelerated mature period–slow and stable period” is recognized as the most common spatiotemporal distribution characteristic of policy diffusion [
26]. In addition, three other characteristics of policy diffusion have also been identified: R-shaped, steep S-shaped, and ladder-shaped [
27,
28]. In terms of spatial distribution, government departments are more inclined to learn the advanced experience and imitate the successful policies of the adjacent areas due to the similarity of environmental conditions and availability of resources and experience [
19]. Due to the influence of geographical and weather conditions on crops planting, some geographical characteristics and regional similarities can be witnessed, which may impact on the spatial distribution of CSRU policy diffusion within a region. Therefore, it is necessary to analyze the spatiotemporal distribution of the diffusion effects of the CSRU pilot policy.
In addition, scholars have paid great attention to the investigation of the influencing factors in the process of policy diffusion [
29,
30]. In fact, plenty of factors have been involved in policy diffusion, and most of them are multi-dimensional and comprehensive elements. Weiner (2002) summarized the influencing factors of policy diffusion as characteristic of innovation, innovators, and environmental background, which has been widely recognized by scholars [
31]. Some other factors are also thought to have impacts on the diffusion of policy. For example, Walker (1969) proposed that economic strength has a significant impact on policy diffusion [
17]; Volden (2006) believed that policy diffusion was closely related to the characteristics of states, population distribution, and financial situation [
32]. Abel (2019) proposed that, in addition to geographical proximity and party channels, cross-regional networks are also a predictor of the diffusion process of climate policies [
24]; Dagar et al. investigated the variations in technical efficiency of farmers with distinct land size across agro-climatic zones, implying the possible effect of difference in land size and agro-climatic zone on the adoption of CSRU [
33]. The different institutional basis of intergovernmental relations between China and Western countries is also believed to result in the obviously different influencing factors and specific paths of policy diffusion [
19]. Zhang and Xiao (2020) proposed that the pilot diffusion of innovative cities in the Chinese context would be affected by the experimental environment, basic conditions, and pilot proportion [
25]. Li and Gu (2020) found that, in a pressure government system similar to the Chinese governance, the adoption of local government policies should be based on the implementation of superior orders on the one hand, and horizontal competition and response to people’s needs on the other hand [
34]. Therefore, in the study of policy diffusion in China, in addition to considering the internal environment and its own resource conditions, the relationship between vertical management institutions and horizontal competition institutions should also be considered.
The pilot policy for CSRU promotion in China has been intensively discussed by scholars. For instance, He et al. (2018) analyzed the individual factors of farmers affecting their willingness to accept energy utilization of crop straw by using nonparametric estimation results [
35]; Zhang et al. (2019) analyzed the problems existing in the implementation of the pilot project of CSRU in Huaibin County of China and put forward corresponding solutions [
36]; Wang et al. (2022) discussed the hot areas, objects, and methods of CSRU pilot policy in China through text analysis [
4]; Li et al. (2022), and Del Valle and Jiang (2022) summarized the factors affecting farmers’ willingness and behavior in comprehensive straw utilization [
37,
38]. Despite this, very few studies have been conducted to discuss the diffusion of the CSRU pilot policy. In fact, the diffusion effect of the pilot policy is particularly important for achieving and improving CSRU.
Thus, this study tries to answer the following questions:
During the diffusion process of the CSRU pilot policy, what are the temporal and spatial characteristics of the current diffusion effect?
What elements and factors should be considered when selecting or formulating the pilots to achieve the diffusion effect?
How can we use the diffusion effect of the pilot policy to improve the CSRU efficiency?
The objective of this study is to explore the potential factors that may affect the diffusion process of the CSRU policy in China and identify the diffusion effects in the CSRU policy. The potential contribution of this study lies in the following points: (1) it tries to establish the pilot policy diffusion model of CSRU in China; (2) it summarizes the factors affecting CSRU policy diffusion from three aspects; (3) the effects of these influencing factors are tested to identify the important ones on CSRU policy diffusion.
The rest of this work is organized as follows:
Section 2 presents the introduction and evolution of the CSRU pilot policy in China;
Section 3 summarizes the various factors that affect the adoption and diffusion of the CSRU pilot policy in China and develops the research hypothesis;
Section 4 describes the research sample, variable measurement, and model specification;
Section 5 depicts the results of this study; and, finally, the conclusions and discussions are presented in
Section 6.
2. Pilot Policies for CSRU Promotion in China
Crop straw was utilized as the major energy source for cooking and heating in rural China up until the 1980s [
39]. However, with the improvement of rural living conditions, the massively generated crop straw has gradually been abandoned and directly burned in the fields. Due to the rapidly deteriorating air environment, the improper disposal of crop straw has been brought to the public’s attention, and the burning of crop straw in the open air has been prohibited nationwide. Instead, more attention has been paid to the utilization and valorization of rural crop straw.
According to China’s policy and practice in CSRU promotion, this paper summarizes the introduction and evolution of the CSRU pilot policy in China with three stages. (1) Project experiment and demonstration stage. In 2009, the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs (MARA) of China launched 16 large- and medium-sized pilot biogas projects with crop straw as the base material in 14 provinces, which initiated the large-scale promotion of CSRU in China. (2) Provincial pilot stage. In 2011, the National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC), MARA and Ministry of Finance (MOF) of China jointly issued the Implementation Plan for CSRU during the 12th Five Year Plan, which proposed the implement of the CSRU pilot policy and technology. In 2016, the MARA and MOF issued the Notice on Carrying out CSRU Pilot Policy to Promote the Improvement of Cultivated Land Quality, and invested CNY one billion to select ten provinces and autonomous regions as pilots for practicing CSRU, which is the first time the CSRU pilot policy was put forward at the central government level in China. (3) County pilot stage. Since 2017, the CSRU promotion has been implemented at the county level, and various supporting policies and efforts have been introduced intensively in the following years, as presented in
Table 1. Since then, the county has been acknowledged as the basic unit for implementing the pilot policy of CSRU promotion. Apparently, the Chinese government is increasing its efforts in implementing the CSRU pilot policy, and the ultimate goal is to improve the utilization of rural solid waste and build a green and low-carbon environment in rural areas.
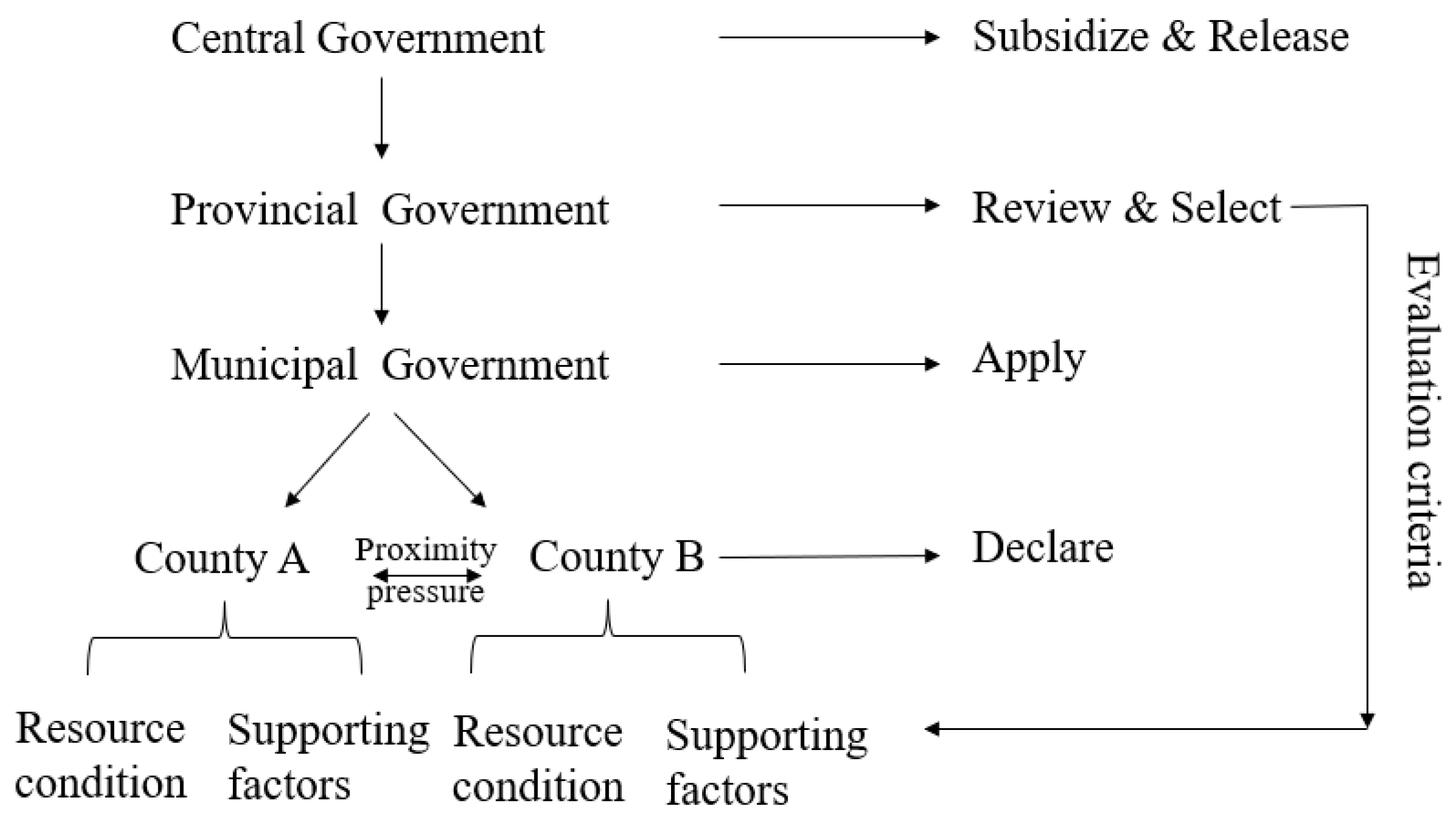
Presently, China uses the CSRU pilot policy of substituting subsidies with rewards. Under this subsidy policy, the local governments, mainly county and district governments, play a critical role in the last cycle in the implementation of CSRU, as they are the basic units of the subsidy distribution. The pilot selection process of the Chinese government includes initiative application of local government, national assessment and approval, etc., which reflects the combination of the central guidance and local initiative experiments [
25]. Under this CSRU pilot policy with the form of replacing subsidies with rewards, the MARA and MOF of China take the lead in providing the financial subsidy funds. After the procedures of a county-level declaration, municipal recommendation, and review, the provincial governments determine the lists of CSRU pilot counties and submit them to the MARA. The approved pilot counties and districts take the lead in using the subsidy funds granted by the MOF to support a number of market players to develop CSRU projects. In practice, county governments are encouraged to submit pilot applications, then the municipal governments transfer the application to the provincial government, who determines the list of selected pilot counties after careful evaluation, mainly supporting areas with large amounts of crop straw, the heavy task of prohibition of burning, and great CSRU potentials. Finally, this list is provided to the MOF and MARA, who determine the final list of CSRU pilot counties and arrange the financial support. This whole schedule is shown in
Figure 2.
By doing this, the Chinese government is aiming to promote the CSRU policy gradually by selecting a number of counties as pilots, which is called the CSRU pilot policy. By putting forward and implementing this pilot policy with rewards and subsidies for CSRU, China is aiming to establish a green and low-carbon oriented mechanism for realizing ecological utilization of crop straw.
Now it is still at the promotion stage of regional planning in CSRU promotion under the background of the Rural Revitalization Strategy [
40], and the Chinese government has adopted the pilot policy for promoting CSRU, which aims to improve CSRU efficiency and the quality of China’s rural ecological environment by using the diffusion effect of policy innovation. Apparently, China has adopted a set of policies for promoting CSRU concentrated on pilots and demonstration. By clarifying the trace and identifying the characteristics of the diffusion of the CSRU pilot policy, this study can help decision-makers to formulate better policies to facilitate CSRU and improve CSRU efficiency around the country.
4. Data and Methods
By taking 164 counties in Hebei Province as the research sample, this study introduced EHA to establish the methodological model of binary logistic regression, and investigate the effects of various factors on the diffusion of the CSRU pilot policy in China.
4.1. Data
Hebei Province, located in North China, with a temperate continental monsoon climate, is a major grain and cotton producing area of China. Hebei Province has a huge amount of crop straw with a high CSRU rate and high willingness to respond to the CSRU pilot policy of the central government. In 2020, the collectable amount of crop straw within this province reached 58.4 million tons, and about 97% of this, namely 56.6 million tons of crop straw, has been utilized as useful resources. By July 2022, more than 30% of the total amount of counties in Hebei Province were selected as CSRU pilots. Therefore, we took Hebei Province as the research area to map the temporal and spatial trace and characteristics in the diffusion of the CSRU pilot policy, and investigate the factors affecting the diffusion and adoption of this pilot policy in China.
For the statistical model, this study used the time-series cross-sectional data at the county level covering CSRU pilot adoption in Hebei province between 2016 and 2020. In order to maintain the integrity of the data, this paper selected 164 counties in Hebei Province with complete data for each year within the observation period. The adoption year of the pilot policy for each county was determined based on the official document of the pilot policy issued by the provincial government, with the adoption year of the local government as the observation end point. According to the EHA method, the year adopted by the local government was taken as the observation end point, and the data of subsequent years were eliminated. Finally, after data screening and sorting, 726 “county-year” observation points were obtained as the data sample of this study.
4.2. Methods
This study adopted the logistic regression model and EHA to explore the factors affecting the diffusion and adoption of the CSRU pilot policy. The logistic regression model can help explain why counties were selected as CSRU pilots. However, it could not explain when the counties adopted the pilot policies [
51]. To help understand the timing of policy adoption and the diffusion mechanisms, we adopted the EHA, which used a dichotomous dependent variable to describe the adoption of the CSRU pilot policy [
60]. EHA is a method that has been widely used in the study of policy innovation diffusion [
23,
29]. It is capable of explaining and modeling the diffusion effects of the behavior of individuals, and the rules and policies of organizations or governments, and is thus considered an ideal methodology for the study of policy diffusion.
According to EHA, the discrete-time model is usually used when the time unit is a year. The explained variable in the model is the risk rate or occurrence rate, which refers to the probability of a certain event for a specific person at a specific time. However, the occurrence ratio cannot be directly observed, so the binary logistic regression model is generally used for analysis. The model of pilot policy diffusion of CSRU is set as shown in Equation (1) [
61]:
where,
is the probability that the county will become the pilot of CSRU in year
t,
is the basic risk rate over time,
is the odds ratio, and
is the regression coefficient of independent variable
.
4.3. Variable Measurement
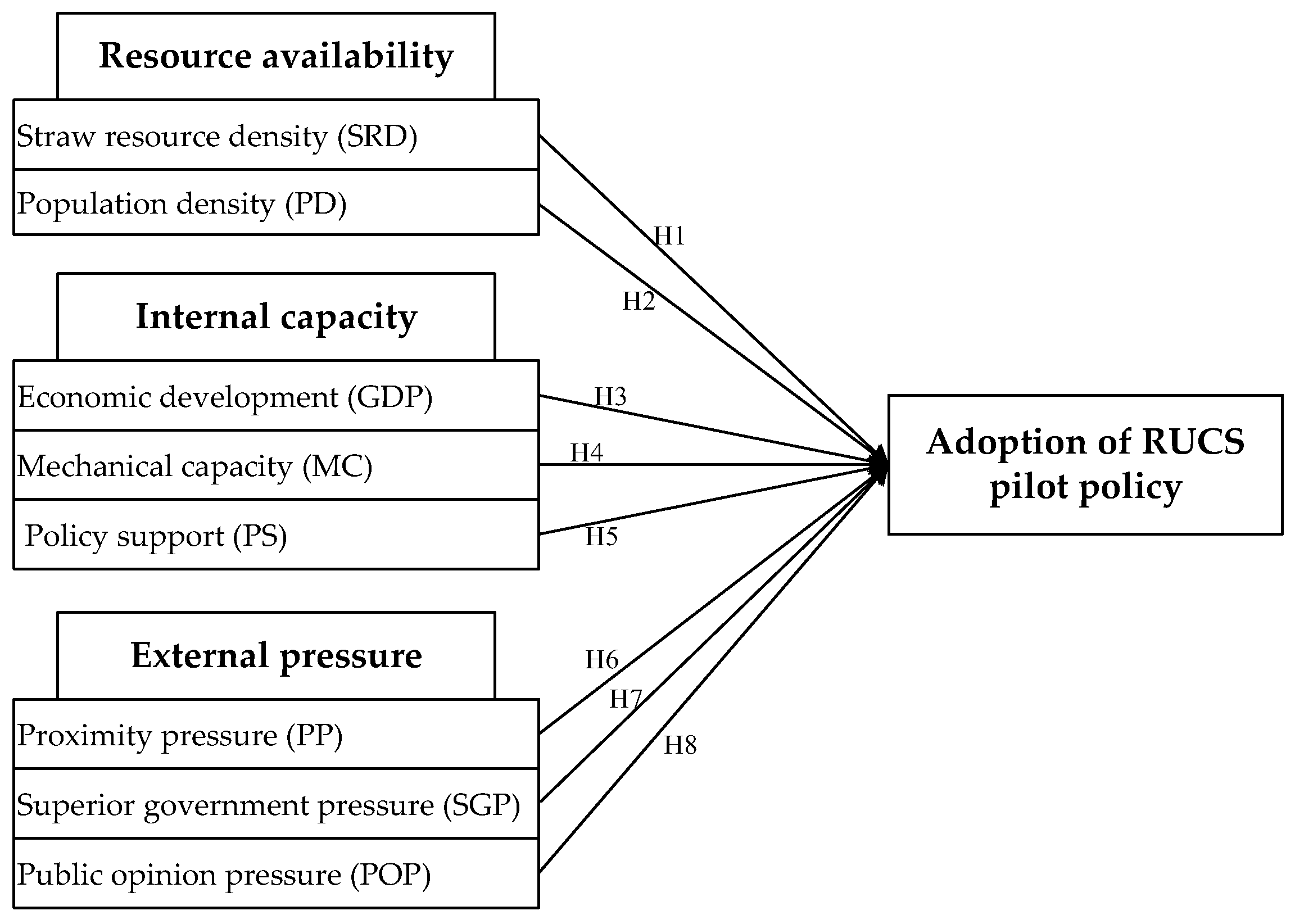
The dependent and independent variables as well as the relationship model among them is displayed in
Figure 3.
(1) Dependent Variable
The dependent variable of the binary logistic regression model is the possibility or probability of a county being selected as a CSRU pilot county or adopting the CSRU pilot policy. According to the discrete-time model of EHA, this is a dummy variable. If county i was selected as the CSRU pilot county in year t, it takes the value of 1 at year t, then the values before year t are all recorded as 0, and the data with respect to this county after year t are all deleted. The dependent variable data come from the documents published by the MARA of China and the Department of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of Hebei Province.
(2) Independent Variable
In terms of resource availability, crop straw resources are measured by straw resource density (SRD), and the population size is measured by population density (PD). The straw resource density of County
i in year
t-1 is used to measure the amount of straw resources in year
t, which is recorded as SRD
i,t [
62]. The amount of straw resources here mainly refers to the amount of collectable straw from grain crops. It is calculated by the author according to the grass–grain ratio, collection coefficient of crop straw, and the yields of various grains provided by the MARA of China [
63]. Similarly, the population size of County
i in year
t is measured by the population density at the end of year
t-1, which is recorded as PD
i,t [
64], and
log(PD
i,t) is taken to eliminate heteroscedasticity and avoid abnormal data fluctuations.
Among the internal capacity factors, the economic development in Country i is measured by the GDP at the end of year t-1, which is recorded as GDPi,t, and log(GDPi,t) is used to eliminate heteroscedasticity and avoid abnormal data fluctuations. The mechanical capacity (MC) is measured by the total power of agricultural machinery and the proportion of grain sown area in County i, which is recorded as MCi,t. The policy support (PS) is measured by the existence of CSRU relevant policies issued by local government of County i in year t-1, which is recorded as PSi,t, and it is also a dummy variable. If County i has issued CSRU relevant policies in year t-1, it will be recorded as 1; if not, it will be recorded as 0. The above data are from the Rural Statistical Yearbook of Hebei Province and the official website of local governments.
Among the external pressure factors, the proximity pressure (PP) of County
i is measured by the proportion of the number of counties that are selected as CSRU pilot counties among all counties in the prefecture level city in year
t, which is recorded as PP
i,t, and the proximity pressure of counties directly under the governance of the central government is 0 [
34]. The superior government pressure (SGP) of County
i is measured by the existence of CSRU policies launched by the prefecture level city government in year
t, which is recorded as SGP
i,t. If the prefecture level cities have issued relevant policies, this variable takes the value of 1, otherwise it is 0. The superior government pressure of the counties directly under the central government is determined based on the existence of CSRU policies issued by the provincial government. The above data come from PKULAW.com. The pressure of public opinions (POP) is measured by the number of CSRU-related reports. The news information and papers about the selected counties were obtained by using COOC V9.94 software to search the database of the China Knowledge Network (CNKI).
Based on the above variable specifications and measurements,
Table 2 presents all the variables as well as their measurements and data sources. According to Equation (1), the methodological model of this study is expressed as Equation (2):
6. Conclusions and Policy Implications
By taking Hebei Province as an example, this study mapped the temporal and spatial characteristics of the diffusion of the CSRU pilot policy among the counties in this province, and conducted an EHA by establishing a binary logistic regression model to identify the specific factors that determine the diffusion of the CSRU pilot policy in China. The conclusions can be drawn as follows:
- (1)
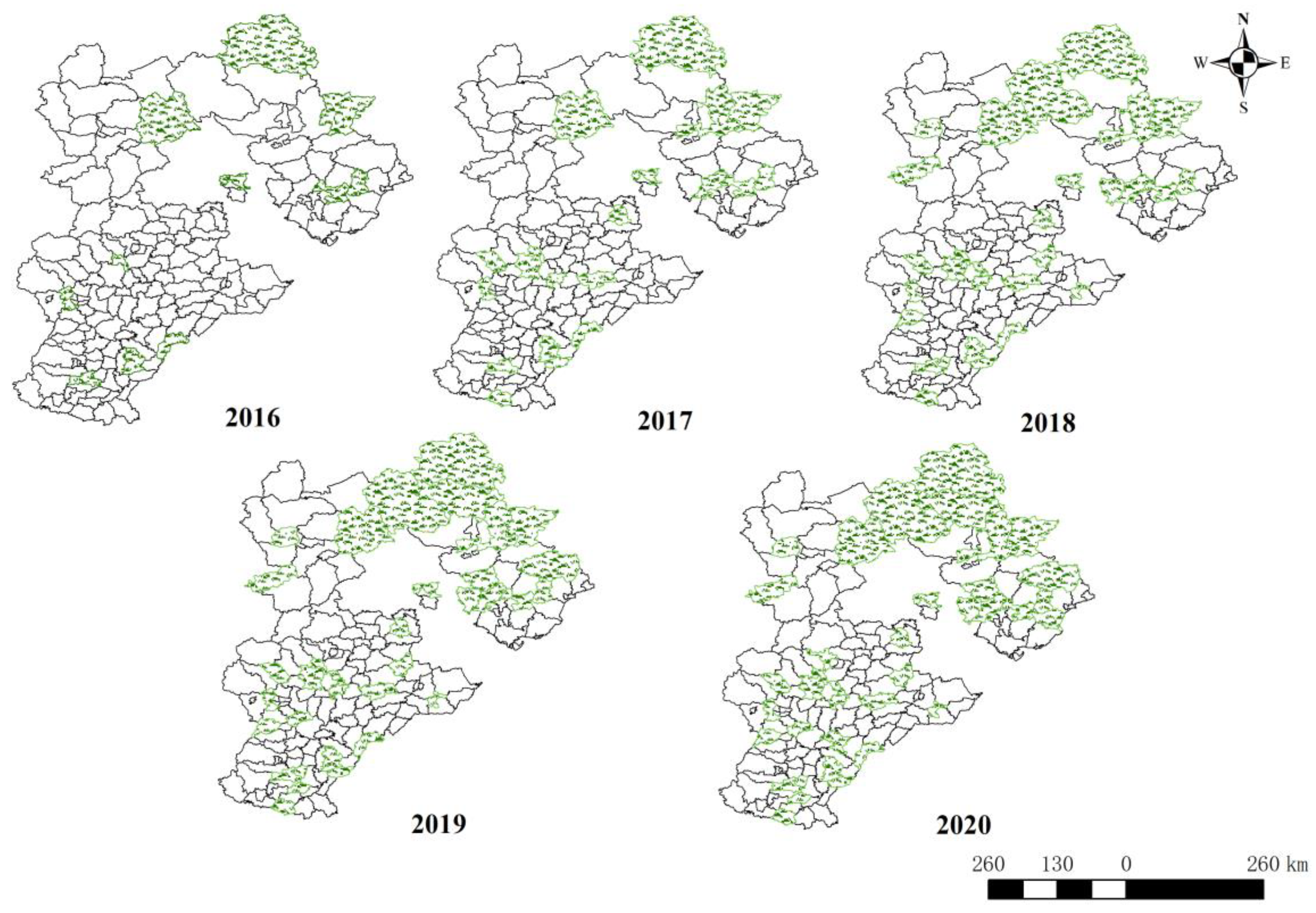
The CSRU pilot policy diffuses rapidly in Hebei Province, and a gradual diffusion from the northeast and southwest to the other parts has been presented. As a pilot policy of replacing subsidies with awards, the CSRU pilot quota is a kind of scare resource. However, about one fourth of the total number of counties in Hebei Province have been selected as CSRU pilot counties within the last five years, indicating the fast diffusion of this pilot policy in this province, considering this diffusion process is still at the initial rising stage of the S-shaped curve. In addition, a trend of gradual diffusion from the northeast and southwest to the central parts is also displayed, and great competition in pilot selecting can be witnessed among different prefecture level cities.
- (2)
Resource availability, namely straw resource density and population density, are proved to have significant effects on the diffusion of the CSRU pilot policy. To be specific, straw resource density has a positive effect on the diffusion of the CSRU pilot policy, as the abundant straw resources provide the physical basis for CSRU promotion. Population density has shown to have a negative effect on the diffusion of the CSRU pilot policy. A lower population density means more arable land per capita, which is more conducive to the utilization of crop straw, and this can increase the possibility of being selected as a CSRU pilot.
- (3)
Among the internal capacity factors, the policy support of local government is conducive to the diffusion of pilot policies. The counties with favorable and supporting CSRU policies indicates the willingness and actions of local government in CSRU promotion, which can attract enterprises and farmers to participate in CSRU and form a good industrial basis for the large-scale utilization of crop straw. By doing this, it can help the local government to win the reward of being selected as a CSRU pilot and receive more financial subsidies to promote the further development of CSRU.
- (4)
The proximity pressure from neighboring counties can have a positive effect on the diffusion of the CSRU pilot policy. Due to the similar geographical and climate conditions within a region, a county being selected as a CSRU pilot can generate pressure on other counties within this region that have failed to be selected as pilots. This pressure will push them to improve their CSRU performance, which then increases the possibility of them being selected as CSRU pilots.
To promote CSRU in China, the following policy implications are provided:
Firstly, in addition to considering the availability of crop straw, the attitude of stakeholders, especially the willingness of local governments, can play a vital role in CSRU promotion. In fact, CSRU promotion led by the government is more conducive to the participation of other stakeholders and the creation of a favorable market that can facilitate CSRU. Therefore, the CSRU pilot policy in China gives full play to the role of the county government. These three elements (local government, enterprises and farmers) are indispensable in CSRU promotion, and they form a solid three-element diffusion mechanism.
Secondly, it is important to collect information such as the availability of crop straw and the attitudes and supporting policy of local government, which is the foundation for the further diffusion of the CSRU pilot policy. In recent years, the MARA of China has gradually strengthened the establishment of crop straw accounts (including data on CSRU rates and the amount of crop straw that has been utilized by different technological pathways in each county, which have not yet been released to the public). At the same time, it is more important to implement supporting policies to promote CSRU by local government, so as to increase the probability of success in CSRU pilot selection and obtain the pilot subsidies to establish the industrial chain for realizing CSRU and activate the CSRU market.
In addition, a complete industrial chain of straw resource utilization needs to be established. Actually, the ultimate goal of “promoting CSRU in the whole county” is to form an independent and complete market industrial chain. The industrial chain will not be limited to a specific county, but will attract the stakeholders in neighboring counties. Therefore, local county governments should use this opportunity to attract straw utilization companies, and stimulate the willingness of farmers and self-employed households to establish a complete industrial chain for realizing CSRU, and maximize economic, social, and environmental benefits.