Analysis of the Spatial Relationship between Ecosystem Regulation Services and Rural Tourism
Abstract
:1. Introduction
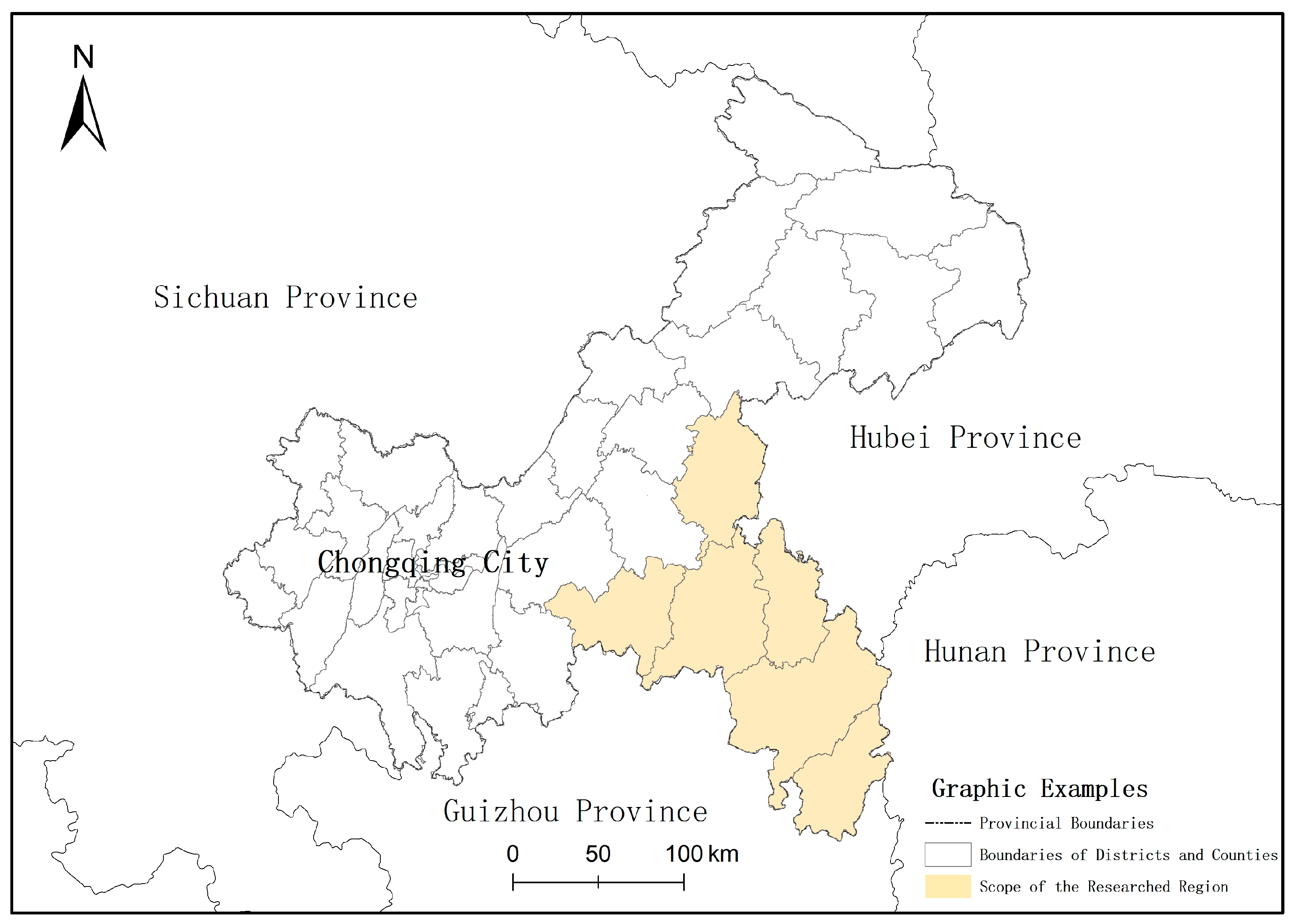
Overview of the Researched Areas
2. Data Source and Research Method
2.1. Data Source
2.2. Research Method
2.2.1. Analysis of Spatial Layout
- (1) The nearest neighbor index
- (2) Kernel density analysis
2.2.2. The Accounting of Ecosystem Regulation Services
2.2.3. Geographic Detector
3. Result Analysis
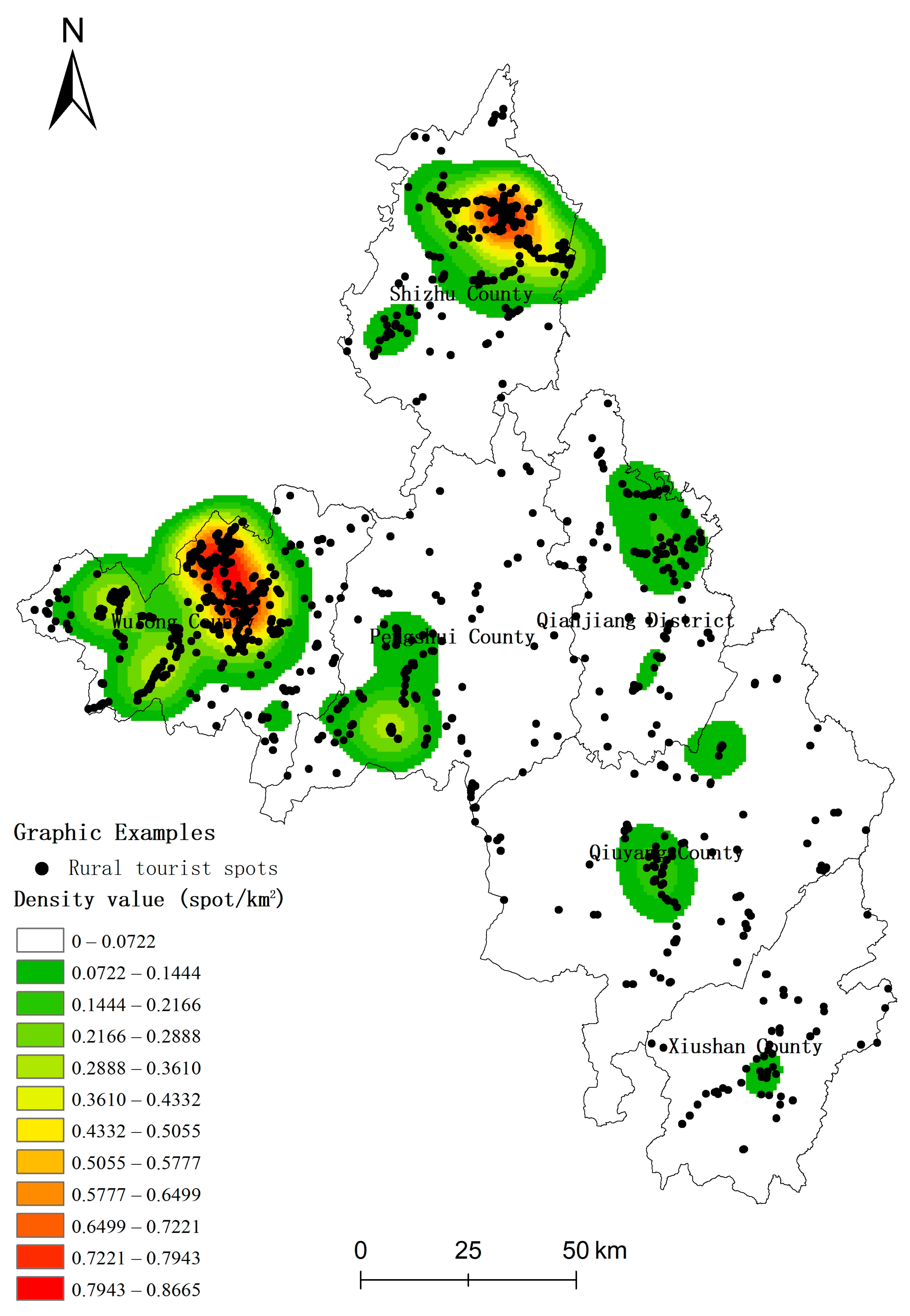
3.1. Spatial Layout of Rural Tourism
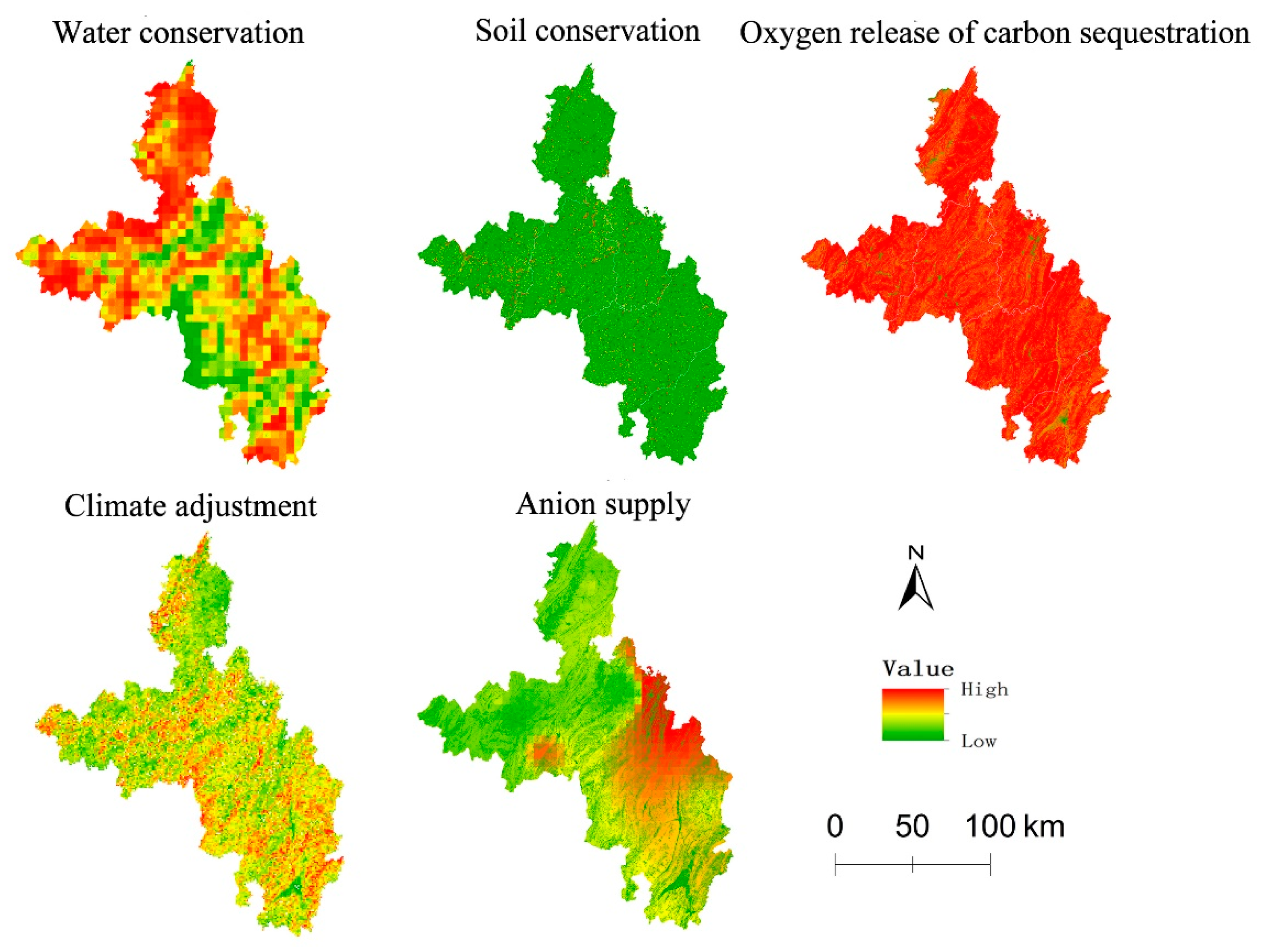
3.2. Spatial Layout of Ecosystem Regulation Services
3.3. Analysis of the Driving Effects of Space
3.3.1. Differentiation and Factor Detection (Single-Factor Analysis)
3.3.2. Detection of Interaction (Analysis of Combined Factors)
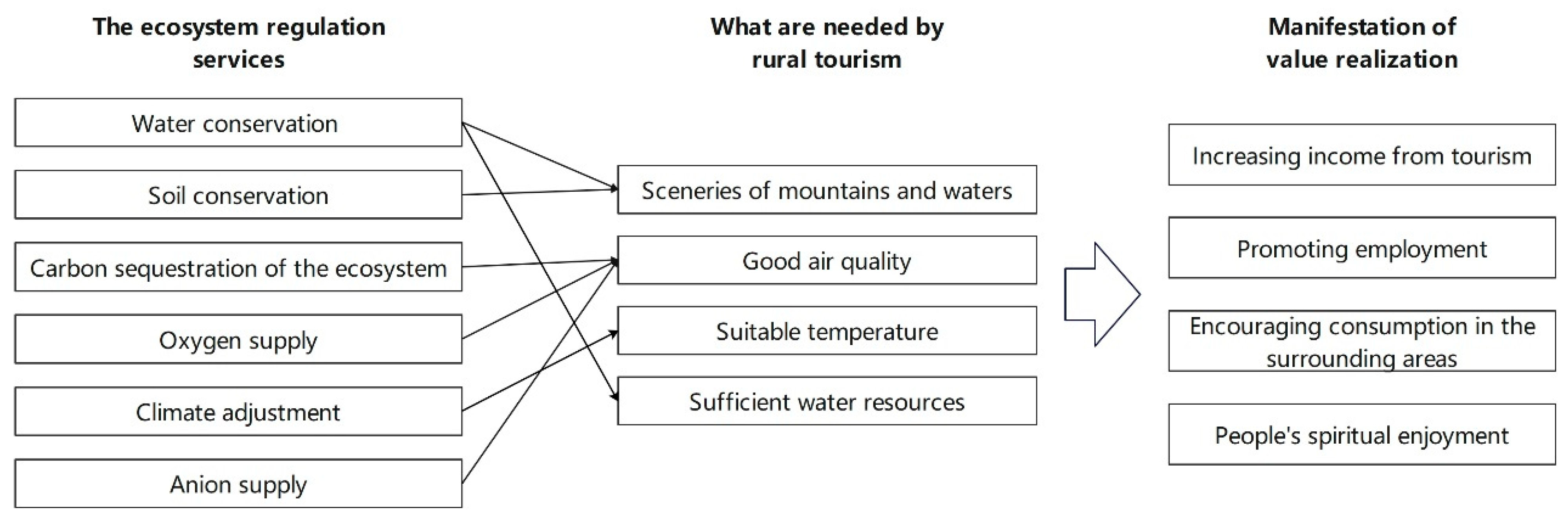
3.4. Analysis of the Development and Support Effects
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, Z.H.; Song, W.H.; Cheng, W.S.; Li, X.X. Have Leisure Agriculture and the Development of Rural Tourism Increased the Incomes of Farmers?—Evidence from Quasi-natural Experiments. Econ. Geogr. 2022, 42, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, L.H. The Effects of Rural Tourism on the Income Increase of Farmer Households Subject to Poverty Alleviation Programs on the Basis of Matching Multiplier Method. Resour. Sci. 2019, 41, 955–966. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.G.; Xi, J.C.; Kong, Q.Q. “Solid” and “Hollow”: Research on the “Polarization” of the Land Use Space of Rural Settlements in Tourist Destinations—Taking Two Villages in Yesanpo Tourist Area in Hebei Province. J. Nat. Resour. 2016, 12, 90–101. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.H. Research on the System-coupling Mechanism and Coordinated Development of Rural Revitalization-Rural Tourism—Taking Fenghuang County, Hunan Province as An Example. Geogr. Res. 2019, 38, 643–654. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, W.J.; Wang, C.S.; Zhang, Z. Research on the Time-space Coupling of Rural Revitalization and Rural Tourism in Shandong Province. Geogr. Sci. 2020, 40, 628–636. [Google Scholar]
- Sharpley, R.; Roberts, L. Rural tourism—10 years on. Int. J. Tour. Res. 2004, 6, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.L.; Cheng, Y.X.; Wang, L.W. Hot Spots of Researches on Rural Tourism Both at Home and Abroad—Review of Literature Published in the Recent 20 Years. Resour. Sci. 2014, 36, 200–205. [Google Scholar]
- Pop, C.; Cristina, B. Romanian Urban Tourism: A Survey of Accommodation Facilities; Studia Universitatis Babeş-Bolyai: Cluj Napoca, Romania, 2018; Volume 63, pp. 53–104. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, B.B.; Chen, X.P.; Ma, K.K.; Yang, M.; Zhai, F.; Li, Z.; Yao, H.; Li, H. Spatial Distribution, Types, Structures, and Influence Factors of Key Rural Tourist Spots in China. Econ. Geogr. 2020, 40, 190–199. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, L.; Hu, J.; Tian, X.B.; Xu, X. Space Aggregation, Evolution Pattern, and Influence Factors of Rural Tourism in Wuhan City. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2022, 31, 1234–1248. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, J.H.; Lv, J.F. Spatial Distribution Features and Accessibility of A-Level Scenic Spots in China. J. Nat. Resour. 2014, 29, 55–66. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, R.L.; Chen, H.Y.; Chen, G.P.; Ma, X.; Yang, Z. Spatial Distribution and Influence Factors of Rural Tourist Spots in Hubei Province—Taking Agritainment of High Star Levels as Examples. Econ. Geogr. 2018, 38, 210–217. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.Y.; Hou, J.J. Spatial Distribution and Influence Factors of Rural Tourist Spots in Shandong Province. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2016, 36, 1706–1714. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.B.; Song, Y.; Huang, S.; Chen, H.L.; Zhang, L.X. Research on Spatial Distribution and Influence Factors of Model Villages of Rural Tourism in Gansu Province. Chin. J. Agric. Resour. Reg. Plan. 2020, 41, 240–247. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.X.; Zhao, B.H.; Qin, A.C.; Zhu, K.X. Analysis of Sustainable-development Estimation and Influence Factors of Rural Tourism in Ecologically Vulnerable Areas—Taking Dongchuan District, Kunming as an Example. Ecol. Econ. 2022, 38, 157–163. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.J.; Sun, J.X. A Path of Popularization or An Invisible Door Threshold? The Exogenous Factors of Development Path for Rural Tourism Programs of Different Types. J. Nat. Resour. 2022, 37, 19. [Google Scholar]
- Kline, C.; Milburn, L. Ten Categories of Entrepreneurial Climate to Encourage Rural Tourism Development. Ann. Leis. Res. 2010, 13, 320–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, R.; Yan, J.J. Construction of the Application Framework for Embedding Landscape Management into the Research on the Man-land Relationship of Rural Tourism. Prog. Geogr. 2022, 41, 510–520. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, L.Q.; Yang, X.J.; Li, G. The Influence of Rural Tourism Development on Farmers’ Livelihood and Community Tourism Effects—Empirical Case Study from the Perspective of Tourism Development Pattern. Geogr. Res. 2017, 36, 1709–1724. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, P.; Xi, J.C. Research on the Time-space Evolution of the Industrial Clustering of Rural Settlements in Tourist Destinations and the Relevant Driving Mechanism—Empirical Case Study of Gougezhuang Village, Yesanpo Tourist Destination. Resour. Sci. 2017, 39, 1535–1544. [Google Scholar]
- Costanza, R.; d’Arge, R.; De Groot, R.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; O’Neill, R.V.; Paruelo, J.; et al. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature 1997, 387, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanza, R. Ecosystem services: Multiple classification systems are needed. Biol. Conserv. 2008, 141, 350–352. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, Z.Y.; Wang, X.K.; Hong, M. Initial Study on the Functions of Land-based Ecosystem Services and the Relevant Ecological Economic Values in China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 1998, 19, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, Z.Y.; Wang, R.S.; Zhao, J.Z. Appraisal of the Functions of Ecosystem Services and the Relevant Ecological Economic Values. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 1999, 10, 635–640. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, B.J.; Zhou, G.Y.; Bai, Y.F.; Song, C.C.; Liu, J.Y.; Zhang, H.Y.; Lv, Y.H.; Zheng, H.; Xie, G.D. The Functions and Ecological Safety of Main Land-based Ecosystem Services in China. Adv. Earth Sci. 2009, 6, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, B.; Zhang, L. Changes of Land Use and Ecosystem Services: Concept, Method, and Progression. Prog. Geogr. 2014, 33, 441–446. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, G.D.; Zhang, Y.L.; Lu, C.X.; Zheng, D.; Cheng, S.K. The Value of Ecosystem Services of Natural Grassland in China. J. Nat. Resour. 2001, 16, 47–53. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, G.D.; Zhen, L.; Lu, C.X.; Cao, S.Y.; Xiao, Y. The Supply, Consumption, and Value Realization of Ecosystem Services. Resour. Sci. 2008, 30, 93–99. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, X.Y.; Juha, M.; Jiang, B.; Wang, M.; Liu, W.J. Research on the Accounting System of Ecological Assets and Total Output Value of the Ecological System in Yunnan Province. J. Nat. Resour. 2017, 32, 1100–1112. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, Z.Y.; Lin, Y.Q.; Song, C.S. Research on the Accounting of Gross Ecosystem Product (GEP) of the Ecological System—Taking Lishui City, Zhejiang Province as an Example. Environ. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 45, 80–85. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Zou, Z.Y. Research on the Accounting of Gross Ecosystem Product (GEP) in the Basin of the Yarlung Zangbo River and the Relevant Applications. Ecol. Econ. 2022, 38, 167–172. [Google Scholar]
- Riegels, N.; Lynggaard-Jensen, A.; Jensen, J.K.; Gerner, N.V.; Anzaldua, G.; Mark, O.; Butts, M.; Birk, S. Making the ecosystem services approach operational: A case study application to the Aarhus River, Denmark. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 707, 135831–135836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wang, S.; Fu, B.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, Y. Land use optimization based on ecosystem service assessment: A case study in the Yanhe watershed. Land Use Policy Int. J. Cover. All Asp. Land Use 2018, 72, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Ren, B.N. The Application of the Accounting Theory of Gross Ecosystem Product (GEP) in the Appraisal of Ecological Civilization—Taking Wenmen Village of Sanya City as an Example. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2020, 40, 3236–3246. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.N.; Ma, G.X.; Wang, Z.K.; Wang, X.H.; Yu, F.; Liu, G.H.; Zhao, Y.H.; Yang, W.; Shi, M.J.; Deng, J.S. The Design and Application of the Framework for the Assessment of the Development of the Fourth Industry of Ecological Products. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2021, 31, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.H.; Hou, X.R.; Peng, M.X.; Cheng, M.; Xue, J.B.; Bao, H.J. The Appropriateness Appraisal and Pattern Partition of the Value Realization of Ecological Regulation Services and Products—Taking Lishui City, Zhejiang Province as an Example. China Land Sci. 2021, 35, 81–89. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, C.; Zeng, J.; Shen, Z.J.; Wang, Q.W. Layout Analysis and Spatial Control of Ecosystem Services During the Process of Rapid Urbanization—Taking Xiamen City as an Example. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 4379–4392. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.K.; Liu, D.F. Functional Partitioning of Ecosystem Services Based on the Scenario Simulation of Diversified National Land and Space Administration. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2021, 37, 262–270. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.Q.; Shi, X.Q.; Li, Y.H.; Li, Y.M.; Huang, P. The Time-space Layout and Functional Partitioning of Ecosystem Services in the Mountainous Areas of Karst Landform in Southeast Yunnan Province. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2022, 77, 736–756. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.L.; Lin, Y.Q.; Xu, W.H.; Ouyang, Z.Y. Progression of Researches on the Value Realization of Ecological Products. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2020, 40, 24–33. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, Y.M.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.H.; Wang, H.L. Multi-center Recognition of the Main Urban Districts of Chongqing City Based on POI Large Data. J. Nat. Resour. 2018, 33, 788–800. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Zhao, Q.; Yang, F. Quantitative Recognition of the Boundaries of Urban Agglomeration Based on POI and NPP/VIIRS Lamplight Data. Prog. Geogr. 2019, 38, 840–850. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, R.C.; Jiang, T.Q.; Li, H.H.; Li, S.Y.; Zhang, Y.L.; Fu, X. Analysis of the Service Radius of Green Spaces in the Urban Area of Beijing Based on the POI of Electronic Navigation Map. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 8536–8543. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, Z.Y.; Zhu, C.Q.; Yang, G.B.; Xu, W.H.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, Y. The Accounting of Gross Ecosystem Product (GEP): Concept, Accounting Method, and Case Study. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2013, 33, 6747–6761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.F.; Li, X.H.; Christakos, G.; Liao, Y.L.; Zhang, T.; Gu, X.; Zheng, X.Y. Geographical Detectors-Based Health Risk Assessment and its Application in the Neural Tube Defects Study of the Heshun Region, China. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2010, 24, 107–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.F.; Xu, C.D. Geographic Detector: Principles and Prospect. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2017, 72, 116–134. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, P.B.; Zhong, Y.P. The Mechanism and Empirical Analysis of the Promotion of Ecological Efficiency in Agriculture through the Integration of Agriculture and Tourism as Being Supported by the Government—Taking the Demonstration County of Leisure Agriculture and Rural Tourism as an Example. Chin. Rural. Econ. 2019, 12, 85–104. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.Q. Spatial Layout Features and Optimization Appraisal of Rural Tourism in Chongqing City. Chin. J. Agric. Resour. Reg. Plan. 2019, 40, 5. [Google Scholar]
| Index | Computing Method | Formula | Order Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water conservation | Equilibrium equation of water volume | (3) | |
| Soil conservation | Revised universal soil loss equation (RUSLE) | (4) | |
| Ecosystem carbon sequestration | Carbon sequestration velocity method | (5) | |
| Oxygen supply | Coefficient transformation method | (6) | |
| Climate regulation | Quantification through evapotranspiration | (7) | |
| Anion supply | Calculation of the number of anions | (8) |
| Judgment Basis | Interaction Type |
|---|---|
| q(Xi ∩ Xj) < Min(q(Xi), q(Xj)) | Nonlinear reduction |
| Min(q(Xi), q(Xj)) < q(Xi ∩ Xj) < Max(q(Xi), q(Xj)) | Single-factor nonlinear reduction |
| q(Xi ∩ Xj) > Max(q(Xi), q(Xj)) | Dual-factor enhancement |
| q(Xi ∩ Xj) > q(Xi) + q(Xj) | Nonlinear enhancement |
| q(Xi ∩ Xj) = q(Xi) + q(Xj) | Dual-driving factors independence |
| Driving Factor | Code | Factor Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Driving factors of ecosystem regulation services | Water conservation | X1 | The volume of water conservation in the unit area: to be calculated with Equation (3) |
| Soil conservation | X2 | The volume of water conservation in the unit area: to be calculated with Equation (4) | |
| Carbon sequestration of the ecosystem | X3 | The volume of carbon sequestration of the ecosystem in the unit area: to be calculated with Equation (5) | |
| Oxygen supply | X4 | The volume of oxygen supply in the unit area: to be calculated with Equation (6) | |
| Climate adjustment | X5 | The volume of climate adjustment in the unit area: to be calculated with Equation (7) | |
| Anion supply | X6 | The volume of anion supply in the unit area: to be calculated with Equation (8) |
| NNI | Z Value | p Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 667.37 | 2363.45 | 0.28 | −55.51 | 0.0000 |
| Driving Factor | Code | q | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Driving factors of ecosystem regulation services | Water conservation | X1 | 0.0628 | 0 |
| Soil conservation | X2 | 0.0063 | 0.7493 | |
| Carbon sequestration of the ecosystem | X3 | 0.0204 | 0.0255 | |
| Oxygen supply | X4 | 0.0204 | 0.0255 | |
| Climate adjustment | X5 | 0.0365 | 0 | |
| Anion supply | X6 | 0.0333 | 0 |
| X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | 0.0628 | |||||
| X2 | 0.1712 | 0.0063 | ||||
| X3 | 0.1150 | 0.0901 | 0.0204 | |||
| X4 | 0.1150 | 0.0901 | 0.0214 | 0.0204 | ||
| X5 | 0.1623 | 0.1257 | 0.1815 | 0.1815 | 0.0365 | |
| X6 | 0.1190 | 0.0806 | 0.0902 | 0.0902 | 0.1962 | 0.0333 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Han, G.; You, J.; Zhu, L.; Li, Y.; Zhou, X. Analysis of the Spatial Relationship between Ecosystem Regulation Services and Rural Tourism. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 3888. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20053888
Wang J, Han G, You J, Zhu L, Li Y, Zhou X. Analysis of the Spatial Relationship between Ecosystem Regulation Services and Rural Tourism. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023; 20(5):3888. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20053888
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Junying, Guifeng Han, Jing You, Liang Zhu, Yafei Li, and Xiang Zhou. 2023. "Analysis of the Spatial Relationship between Ecosystem Regulation Services and Rural Tourism" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 20, no. 5: 3888. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20053888
APA StyleWang, J., Han, G., You, J., Zhu, L., Li, Y., & Zhou, X. (2023). Analysis of the Spatial Relationship between Ecosystem Regulation Services and Rural Tourism. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(5), 3888. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20053888






