Research on Rural Population/Arable Land/Rural Settlements Association Model and Coordinated Development Path: A Case Analysis of the Yellow River Basin (Henan Section)
Abstract
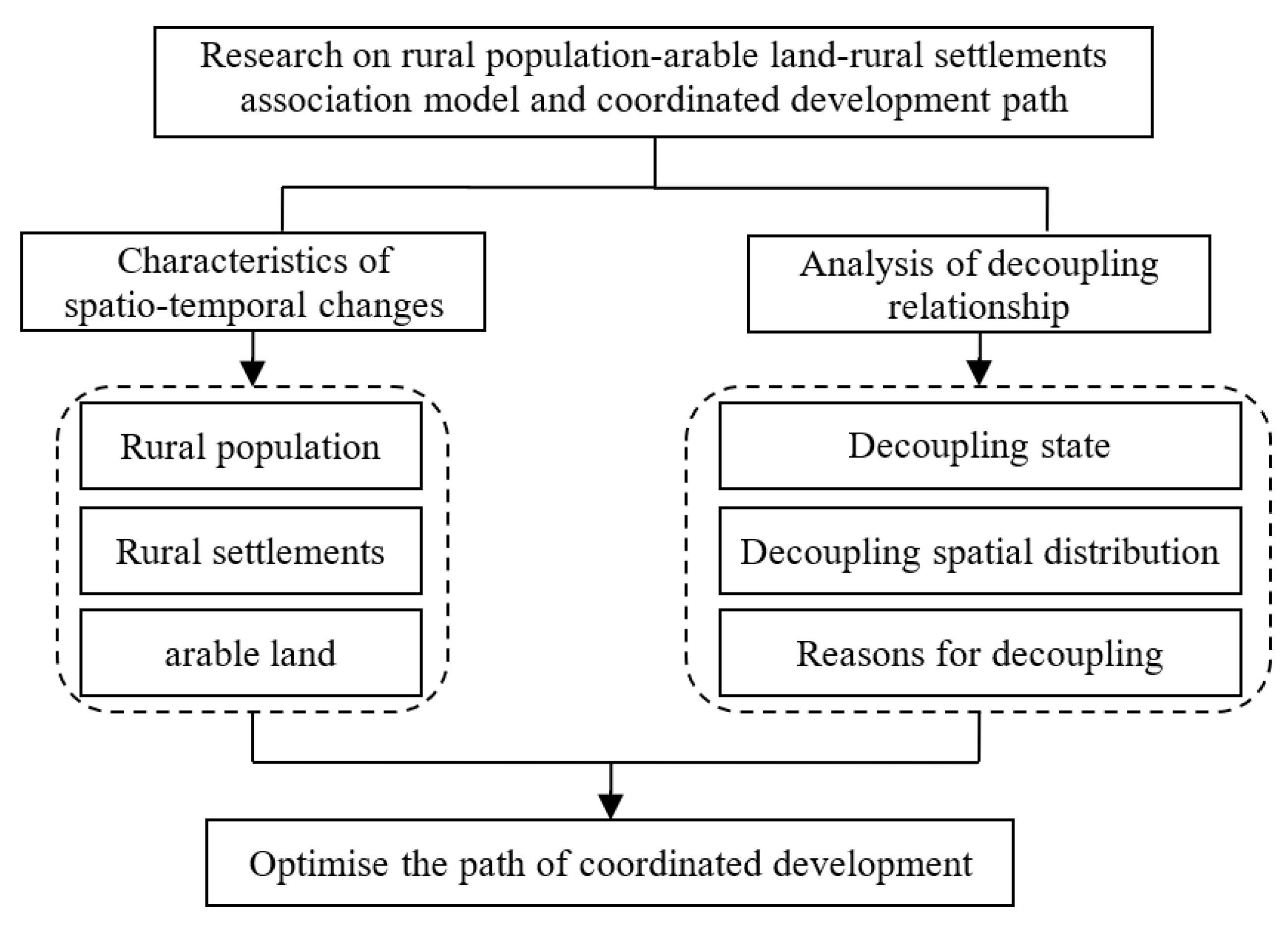
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
2.2. Date Source
2.3. Research Methods
3. Results
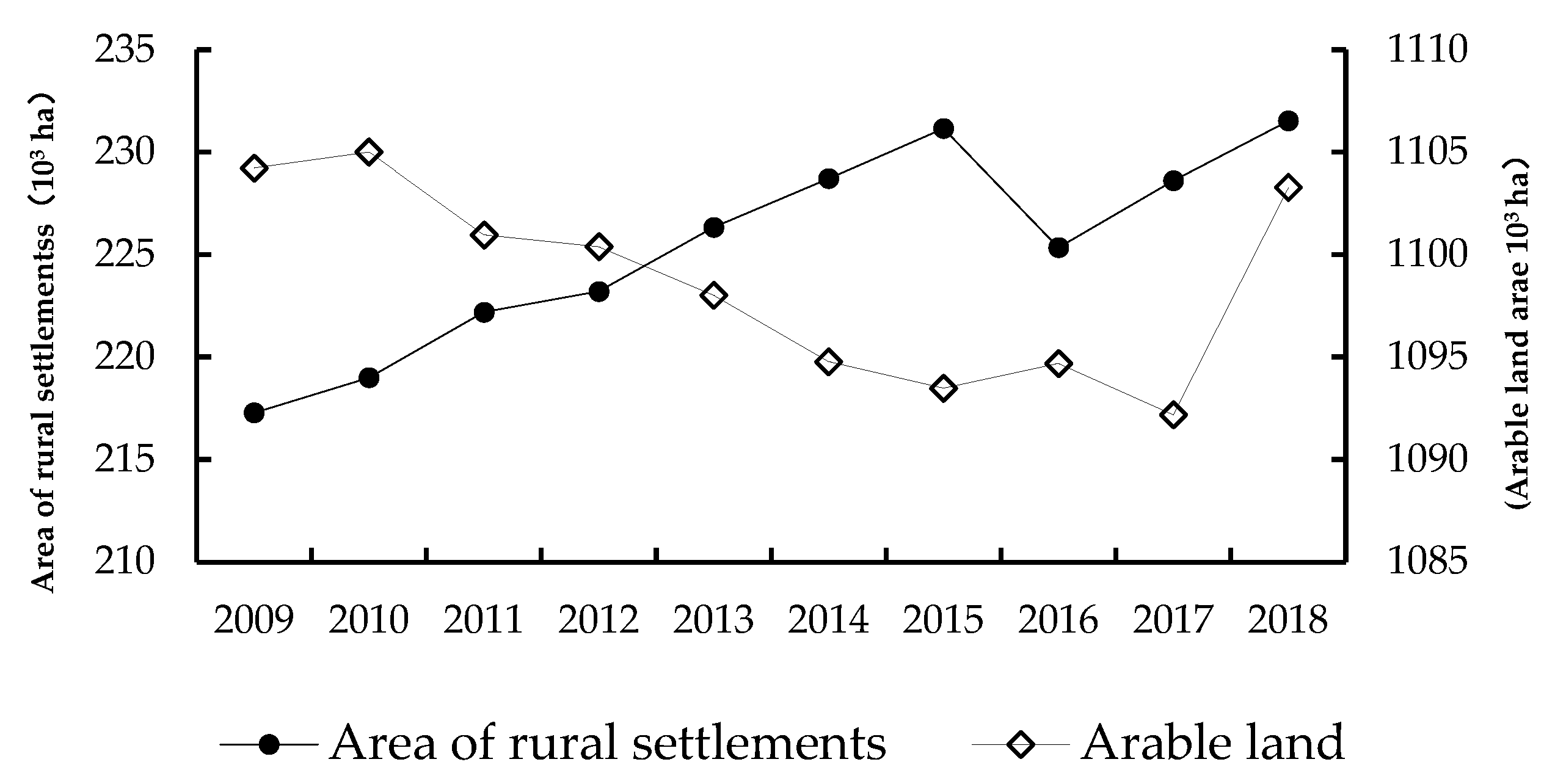
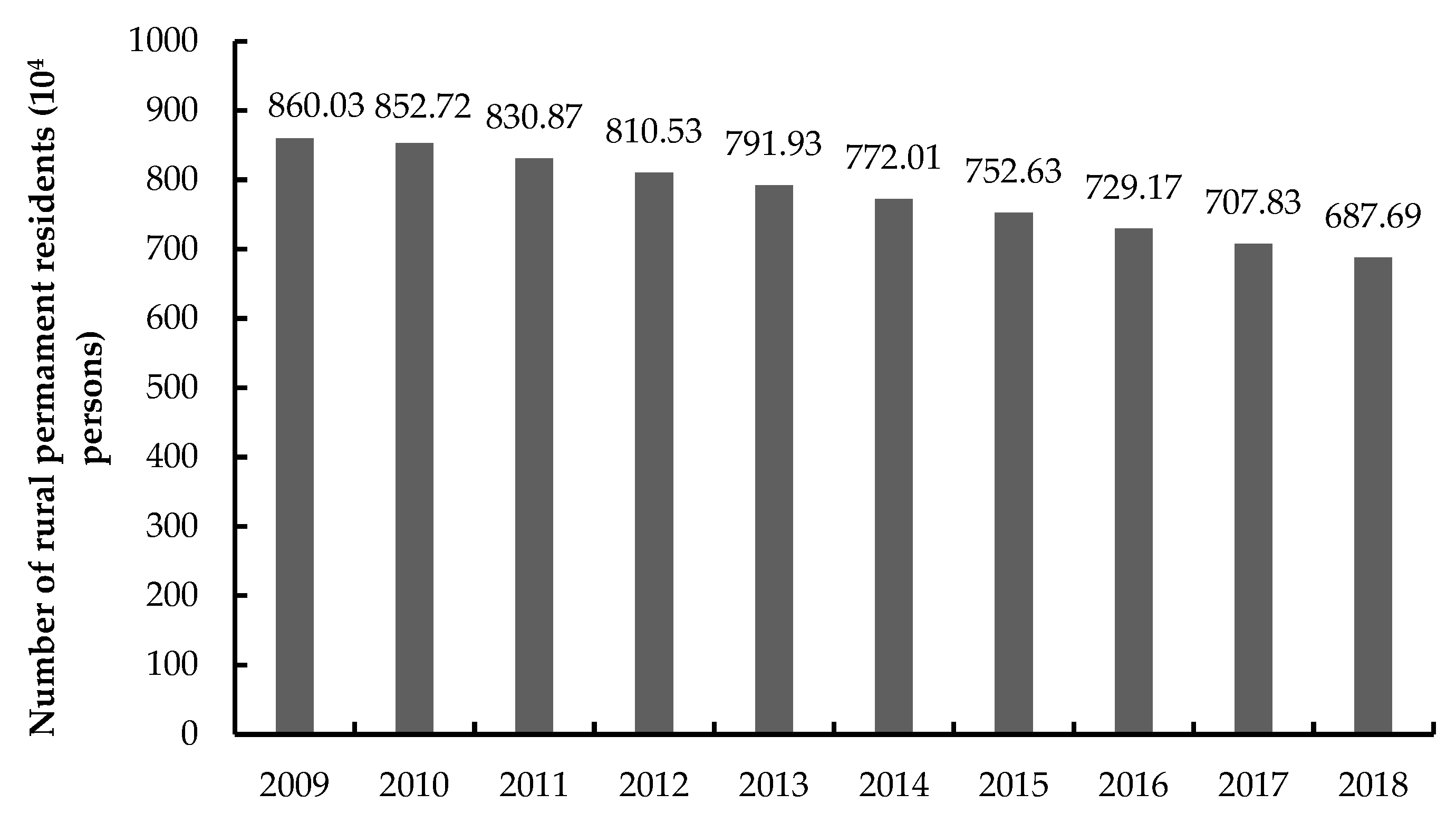
3.1. Changes of the Rural Population/Arable Land/Rural Settlements
3.2. The Decoupling State of Rural Population/Arable Land and Rural Population/Rural Settlements
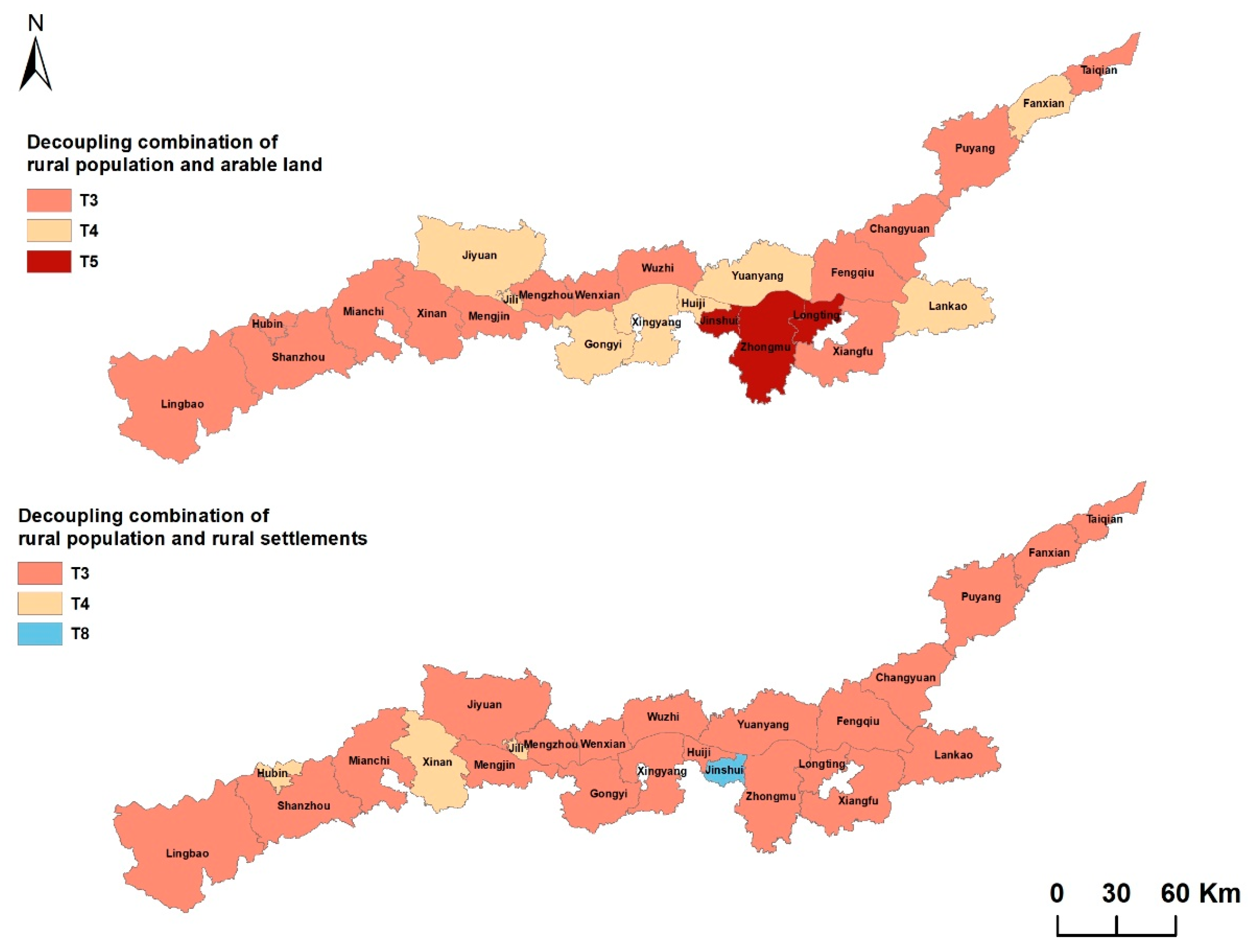
3.3. Decoupling Combinationof Rural Population/Arable Land/Rural Settlements
4. Discussion
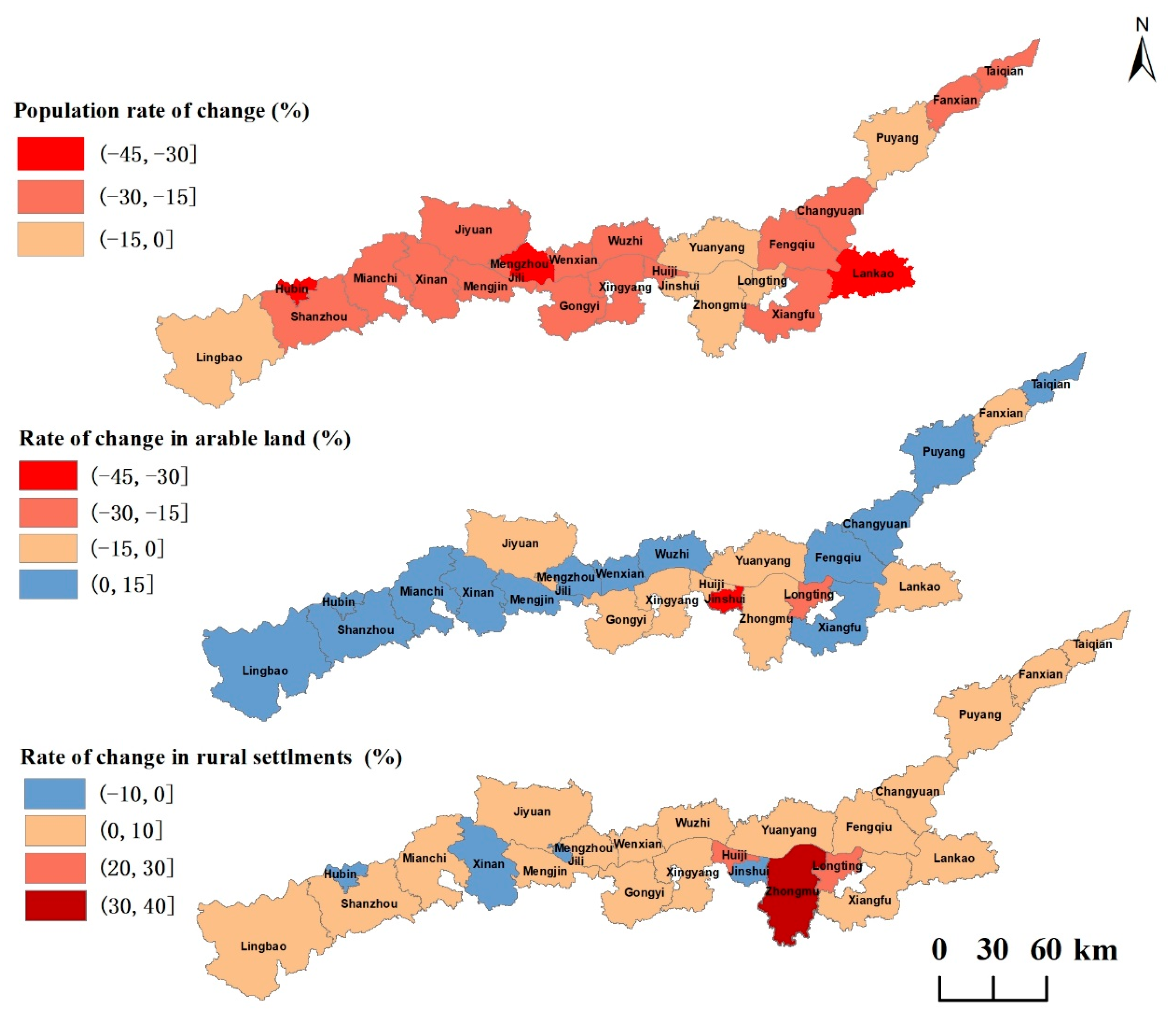
4.1. Spatial and Temporal Patterns of Rural Population/Arable Land/Rural Settlements
4.2. Uncoordinated Change of Rural Population/Arable Land/Rural Settlements
4.3. Driving Mechanism of Uncoordinated Development of Rural Population/Arable Land/Rural Settlements
4.4. Optimization Path for Coordinated Development of Rural Population/Arable Land/Rural Settlements
4.4.1. Optimization Path of Arable Land Reduction Decoupling Combination Area
4.4.2. Optimization Path for Development of Rural Population Reduction and Combined Decoupling and Regional Development
5. Conclusions and Prospects
5.1. Conclusions
5.2. Limitations and Prospects of the Study
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fang, C.; Cui, X.; Li, G.; Bao, C.; Wang, Z.; Ma, H.; Sun, S.; Liu, H.; Luo, K.; Ren, Y. Modeling regional sustainable development scenarios using the Urbanization and Eco-environment Coupler: Case study of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 689, 820–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Sannigrahi, S.; Bilintoh, T.M.; Zhang, R.; Xiong, B.; Tao, S.; Bilsborrow, R.; Song, C. Understanding human-environment interrelationships under constrained land-use decisions with a spatially explicit agent-based model. Anthropocene 2022, 38, 100337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkan, H. Negative impact of rural settlements on natural resources in the protected areas: Kovada Lake National Park, Turkey. J. Environ. Biol. 2009, 30, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y. Modern human-land relations and human-land system science. Geographicscience 2020, 40, 1221–1234. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, F.; Li, Q.; Xiang, J.; Zhu, J. Economic Growth, Demographic Change and Rural-Urban Migration in China. J. Integr. Agr. 2013, 12, 1884–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Liu, M. Assessment of decoupling between rural settlement area and rural population in China. Land Use Policy 2014, 39, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Wang, Z.; Chi, G.; Zhang, Z. The impacts of population and agglomeration development on land use intensity: New evidence behind urbanization in China. Land Use Policy 2020, 95, 104639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakar, S.V.R.K. A succinct review and analysis of drivers and impacts of agricultural land transformations in Asia. Land Use Policy 2021, 102, 105238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paudel, B.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, J.; Rai, R.; Li, L. Farmers’ perceptions of agricultural land use changes in Nepal and their major drivers. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 235, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, W.; Jiang, G.; Zhang, R.; Li, Y.; Jiang, X. Achieving rural spatial restructuring in China: A suitable framework to understand how structural transitions in rural residential land differ across peri-urban interface? Land Use Policy 2018, 75, 583–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wu, D.; Li, J.; Liang, J.; Zhang, D.; Chen, W. Arable land use efficiency and its driving factors in the Yellow River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 144, 109411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Jiang, G.; Li, Z.; Tian, Y.; Wei, S. Understanding rural land use transition and regional consolidation implications in China. Land Use Policy 2019, 82, 742–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, Y. Arable land protection and rational use in China. Land Use Policy 2021, 106, 105454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Q.; Luo, X. Urban-rural spatial transformation process and influences from the perspective of land use: A case study of the Pearl River Delta Region. Habitat. Int. 2020, 104, 102234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; He, J.; Yue, Q.; Kong, X.; Zhang, M. Linking rural settlements optimization with village development stages: A life cycle perspective. Habitat. Int. 2022, 130, 102696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Ye, C.; Cai, Y.; Xing, X.; Chen, Q. The impact of rural out-migration on land use transition in China: Past, present and trend. Land Use Policy 2014, 40, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.; Liu, Y. Rural restructuring in China. J. Rural. Stud. 2016, 47, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Long, H.; Tang, Y.; Deng, W.; Chen, K.; Zheng, Y. The impact of land consolidation on rural vitalization at village level: A case study of a Chinese village. J. Rural. Stud. 2021, 86, 485–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Zamora, P.; Gallardo-Cobos, R.; Ceña-Delgado, F. Rural areas face the economic crisis: Analyzing the determinants of successful territorial dynamics. J. Rural. Stud. 2014, 35, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razin, E.; Hasson, S. Urban-rural boundary conflicts: The reshaping of Israel’s rural map. J. Rural. Stud. 1994, 10, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Cheng, P.; Kong, X. Spatially explicit restructuring of rural settlements: A dual-scale coupling approach. J. Rural. Stud. 2022, 94, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Long, H.; Liu, Y. Spatio-temporal pattern of China’s rural development: A rurality index perspective. J. Rural. Stud. 2015, 38, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, C.; Zhang, J. The preference for larger cities in China: Evidence from rural-urban migrants. China Econ. Rev. 2017, 43, 72–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, J.; Cui, J. Exploring rural decline with the perspective of demographics: Case study of Hubei, China. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2020, 120, 102917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Woods, M.; Fois, F. Rural decline or restructuring? Implications for sustainability transitions in rural China. Land Use Policy 2020, 94, 104531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.; Xu, Y.; Sun, M.; Liu, C.; Lu, L.; Huang, A.; Duan, Y.; Liu, L. Spatiotemporal characteristics and dynamic mechanism of rural settlements based on typical transects: A case study of Zhangjiakou City, China. Habitat. Int. 2022, 123, 102545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhong, Z.; Cheng, G. arable land loss and construction land expansion in China: Evidence from national land surveys in 1996, 2009 and 2019. Land Use Policy 2023, 125, 106496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, T.; Feng, Z.; Wu, K. Identifying the contradiction between the arable land fragmentation and the construction land expansion from the perspective of urban-rural differences. Ecol. Inform. 2022, 71, 101826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Liu, S.; Tao, T.; Gong, M.; Bai, J. Spatial reconstruction of rural settlements based on livability and population flow. Habitat. Int. 2022, 126, 102614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, M.; Lv, Q. Multi-dimensional hollowing characteristics of traditional villages and its influence mechanism based on the micro-scale: A case study of Dongcun Village in Suzhou, China. Land Use Policy 2020, 101, 105146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Woods, M.; Zou, J. Accelerated restructuring in rural China fueled by ‘increasing vs. decreasing balance’ land-use policy for dealing with hollowed villages. Land Use Policy 2011, 29, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, D.; Long, H.; Qiao, W.; Wang, Z.; Sun, D.; Yang, R. Effects of rural–urban migration on agricultural transformation: A case of Yucheng City, China. J. Rural. Stud. 2020, 76, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, N. Pattern and mechanism of coordinated development of rural people-land-industry in Huang-Huai-Hai area. J. Geogr. Sci. 2019, 74, 1576–1589. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, S.; Kong, X.; Jiang, P. Identification of the human-land relationship involved in the urbanization of rural settlements in Wuhan city circle, China. J. Rural. Stud. 2020, 77, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Sun, H.; Chen, B.; Xia, X.; Li, P. China’s rural human settlements: Qualitative evaluation, quantitative analysis and policy implications. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 105, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Li, X. The changing settlements in rural areas under urban pressure in China: Patterns, driving forces and policy implications. Landscape Urban Plan 2013, 120, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.S.; Lin, W. Transforming rural housing land to farmland in Chongqing, China: The land coupon approach and farmers’ complaints. Land Use Policy 2019, 83, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, J. Conversion from rural settlements and arable land under rapid urbanization in Beijing during 1985–2010. J. Rural. Stud. 2017, 51, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.; Li, T. Characteristics and mechanisms of transformation coupling of arable land and rural homestead utilization in China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2012, 22, 548–562. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Chen, S.; Jiang, G. A review of the potential of rural settlement consolidation in China. Economic. Geography. 2010, 30, 1871–1877. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Long, H. Temporal and spatial changes of rural population and land use in rural settlements in China. J. Nat. Resour. 2010, 25, 1629–1638. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zou, X.; Wang, Y.; Yin, Y.; Tu, X.; Xu, G. The threshold effect of agricultural population transfer on arable land use efficiency in Jiangxi Province. Resour. Sci. 2019, 41, 1576–1588. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.; Wang, H.; Cheng, Y.; Zheng, B.; Lu, Z. The impact of rural out-migration on arable land use intensity: Evidence from mountain areas in Guangdong, China. Land Use Policy 2016, 59, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Jiang, F. Research on ecological protection and high-quality development path of the Yellow River Basin of Henan. China South. Agric. Mach. 2021, 52, 59–61. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Guo, P.; Zhang, F.; Wang, H. The response of ecosystem service value to land use change in the middle and lower Yellow River: A case study of the Henan section. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 140, 109019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Yue, W.; He, X. Decoupling relationship between urban expansion and economic growth in the Yangtze River Economic Belt and its spatial heterogeneity. Nat. Resour. 2018, 33, 219–232. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Chen, K.; Yan, L.; Yu, L.; Zhu, Y. Citizenization of rural migrants in China’s new urbanization: The roles of hukou system reform and rural land marketization. Cities 2023, 132, 103968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, K. Creating land markets for rural revitalization: Land transfer, property rights and gentrification in China. J. Rural. Stud. 2021, 81, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, P.; Tian, Y.; Zou, Y. A novel framework for rural homestead land transfer under collective ownership in China. Land Use Policy 2018, 78, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Liu, Y.; Qu, L. Effect of land-centered urbanization on rural development: A regional analysis in China. Land Use Policy 2019, 87, 104072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, X. Analysis of Suitable Areas for Chinese Farmers to Settle in Urban Areas. J. Geogr. Sci. 2013, 23, 1136–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Li, X.; Yang, J.; Ni, H.; Sang, X. How land use functions evolve in the process of rapid urbanization: Evidence from Jiangsu Province, China. J. Clean Prod. 2022, 380, 134877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Yang, Y.; Chen, F.; Zhu, F.; Qu, J.; Zhang, S. Response of agricultural multifunctionality to farmland loss under rapidly urbanizing processes in Yangtze River Delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 666, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.; de Vries, W.T.; Zhao, Q. Understanding rural resettlement paths under the increasing versus decreasing balance land use policy in China. Land Use Policy 2021, 103, 105325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Long, H.; Ives, C.D.; Deng, W.; Chen, K.; Zhang, Y. Modes and practices of rural vitalisation promoted by land consolidation in a rapidly urbanising China: A perspective of multifunctionality. Habitat. Int. 2022, 121, 102514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, H. Effects of farmland use rights transfer on collective action in the commons: Evidence from rural China. Land Use Policy 2022, 120, 106262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, F.; Feng, S.; Shen, T. Transfer of development rights, farmland preservation, and economic growth: A case study of Chongqing’s land quotas trading program. Land Use Policy 2020, 95, 104611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y. Exploring the outflow of population from poor areas and its main influencing factors. Habitat. Int. 2020, 99, 102161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, K. The transformation of the village collective in urbanising China: A historical institutional analysis. J. Rural. Stud. 2016, 47, 588–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Y. China’s rural regional system and rural revitalization strategy. J. Geogr. Sci. 2019, 74, 2511–2528. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Su, F.; Tao, R. Rural residential properties in China: Land use patterns, efficiency and prospects for reform. Habitat. Int. 2012, 36, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Wu, C.; Tan, Y.; Zhang, X. The dilemma of land expansion and governance in rural China: A comparative study based on three townships in Zhejiang Province. Land Use Policy 2018, 71, 602–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Ke, S. Evaluating the effectiveness of sustainable urban land use in China from the perspective of sustainable urbanization. Habitat. Int. 2018, 77, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| The Decoupling State | Population Growth Rate | Arable Land/Settlements Growth Rate | Decoupling Elasticity Coefficient (PE) | State Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weak decoupling (T1) | >0 | >0 | 0 < PE < 0.8 | The rural population and land have increased together, and the population has grown faster than the land. |
| Expansion inverse decoupling (T2) | >0 | >0 | PE > 1.2 | Rural population and land have increased together, and land has grown faster than population. |
| Strong reverse decoupling (T3) | <0 | >0 | PE < 0 | Land area has increased, and the rural population has decreased. |
| Weak reverse decoupling (T4) | <0 | <0 | 0 < PE < 0.8 | The rural population and land have decreased at the same time, and the population has declined rapidly. |
| Recession decoupling (T5) | <0 | <0 | PE > 1.2 | The rural population and land have decreased at the same time, and the land has declined rapidly. |
| Strong decoupling (T6) | >0 | <0 | PE < 0 | The rural population has increased, and the land area has decreased. |
| Expand the link (T7) | >0 | >0 | 0.8 < PE < 1.2 | The rural population and land increased at the same time, and the growth rate of the two was relatively synchronized. |
| Recession link (T8) | <0 | <0 | 0.8 < PE < 1.2 | The rural population and land have decreased at the same time, and the decline between the two has kept pace. |
| Type | Number of Areas | Arable Land (%) | Settlements Area (%) | Population (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T3 | 14 | 64.01 | 58.69 | 59.79 |
| T4 | 8 | 27.89 | 32.35 | 30.3 |
| T5 | 3 | 8.1 | 8.96 | 9.91 |
| Type | Number of Areas | Arable Land (%) | Settlements Area (%) | Population (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T3 | 21 | 95.53 | 93.66 | 93.57 |
| T4 | 3 | 4.22 | 5.47 | 4.33 |
| T8 | 1 | 0.25 | 0.87 | 2.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, S.; Yin, M. Research on Rural Population/Arable Land/Rural Settlements Association Model and Coordinated Development Path: A Case Analysis of the Yellow River Basin (Henan Section). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 3833. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20053833
Zhao S, Yin M. Research on Rural Population/Arable Land/Rural Settlements Association Model and Coordinated Development Path: A Case Analysis of the Yellow River Basin (Henan Section). International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023; 20(5):3833. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20053833
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Suxia, and Mengmeng Yin. 2023. "Research on Rural Population/Arable Land/Rural Settlements Association Model and Coordinated Development Path: A Case Analysis of the Yellow River Basin (Henan Section)" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 20, no. 5: 3833. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20053833
APA StyleZhao, S., & Yin, M. (2023). Research on Rural Population/Arable Land/Rural Settlements Association Model and Coordinated Development Path: A Case Analysis of the Yellow River Basin (Henan Section). International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(5), 3833. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20053833





