Correlation Analysis of Attention and Intelligence of Preterm Infants at Preschool Age: A Premature Cohort Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
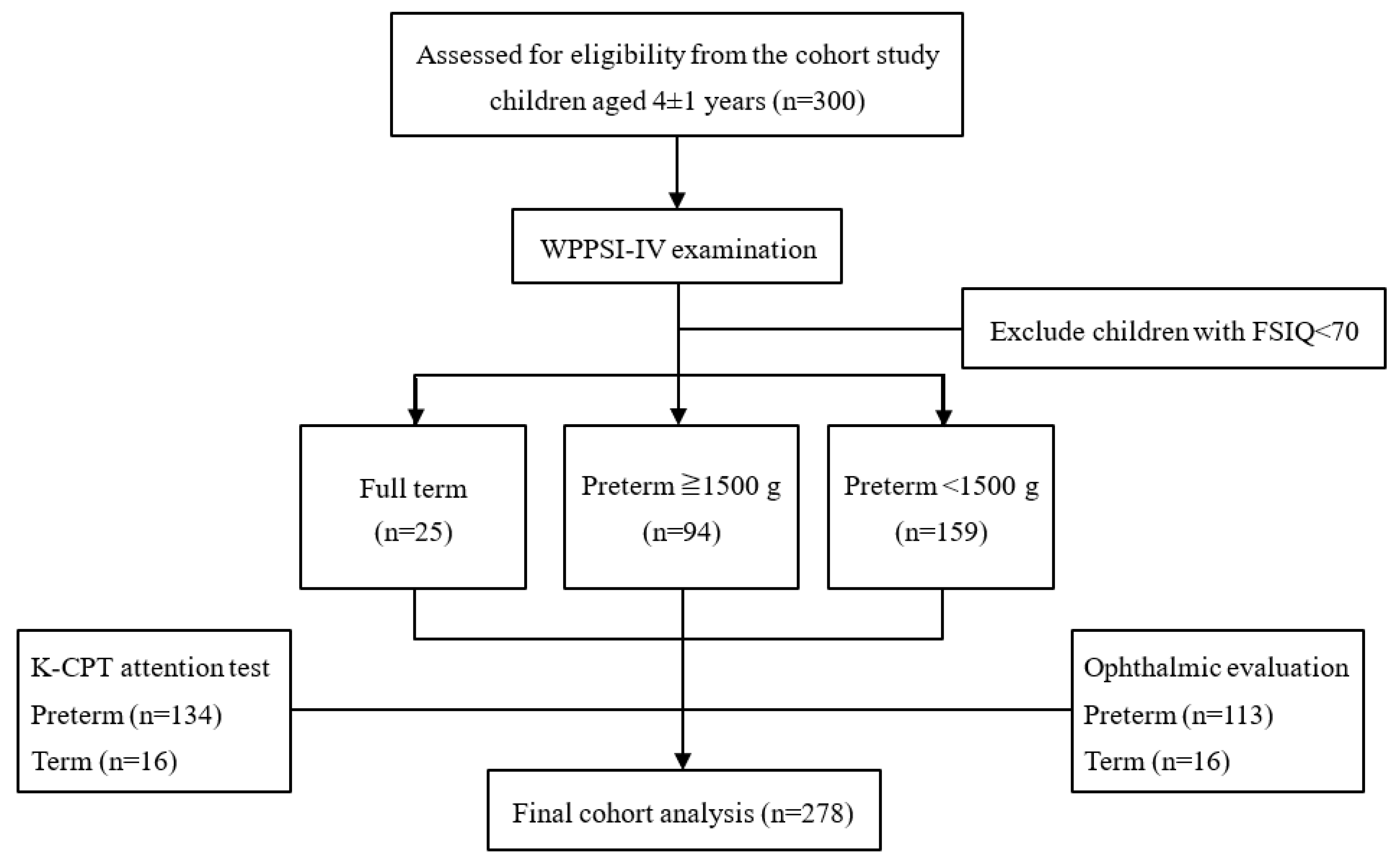
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.1.1. Inclusion Criteria
- (1)
- Term infants born between 37 and 40 gestational weeks with birth weight of more than 2500 g whose parents were willing to sign the informed consent (group 1, the control group).
- (2)
- All infants born before 37 gestational weeks whose parents were willing to sign the informed consent. According to their birth weight, these infants were divided into group 2 (≥1500 g) and group 3 (<1500 g).
- (3)
- Children who were able to complete neurocognitive function tests and had a full-scale intellectual quotient more than 70.
- (4)
- Children whose parents were willing and able to complete questionnaires.
2.1.2. Exclusion Criteria
- (1)
- Since the study aimed to investigate minor neurodevelopmental dysfunction, we had to exclude neonates with severe physical impairments due to perinatal injures, severe hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy, severe congenital malformations, confirmed chromosome anomalies, and the requirement of long-term intubation.
- (2)
- Neonates who were unable to receive the systemic regular follow-up required by this cohort study.
- (3)
- Children who were unable to cooperate with neurocognitive function tests or who had a full-scale intellectual quotient less than 70.
- (4)
- Children whose parents were unwilling or unable to complete questionnaires.
2.2. Procedure
2.3. Intelligence Evaluation
2.4. Attention Evaluation
2.5. Ophthalmic Evaluation
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
- Correlations with K-CPT (Table 4):
- Correlations with WPPSI-IV (Table 5):
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- O’Brien, L.M.; Mervis, C.B.; Holbrook, C.R.; Bruner, J.L.; Smith, N.H.; McNally, N.; McClimment, M.C.; Gozal, D. Neurobehavioral correlates of sleep-disordered breathing in children. J. Sleep Res. 2004, 13, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, R.B.; Kelly, J. Behavior, neurocognition and quality-of-life in children with sleep-disordered breathing. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2006, 70, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owens, J.A. Neurocognitive and behavioral impact of sleep disordered breathing in children. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2009, 44, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halbower, A.C.; Degaonkar, M.; Barker, P.B.; Earley, C.J.; Marcus, C.L.; Smith, P.L.; Prahme, M.C.; Mahone, E.M. Childhood obstructive sleep apnea associates with neuropsychological deficits and neuronal brain injury. PLoS Med. 2006, 3, e301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leversen, K.T.; Sommerfelt, K.; Rønnestad, A.; Kaaresen, P.I.; Farstad, T.; Skranes, J.; Støen, R.; Elgen, I.B.; Rettedal, S.; Eide, G.E.; et al. Prediction of neurodevelopmental and sensory outcome at 5 years in Norwegian children born extremely preterm. Pediatrics 2011, 127, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.; Fawke, J.; Hennessy, E.; Rowell, V.; Thomas, S.; Wolke, D.; Marlow, N. Neurodevelopmental disability through 11 years of age in children born before 26 weeks of gestation. Pediatrics 2009, 124, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarnoudse-Moens, C.S.; Weisglas-Kuperus, N.; van Goudoever, J.B.; Oosterlaan, J. Meta-analysis of neurobehavioral outcomes in very preterm and/or very low birth weight children. Pediatrics 2009, 124, 717–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson-Costello, D.; Friedman, H.; Minich, N.; Siner, B.; Taylor, G.; Schluchter, M.; Hack, M. Improved neurodevelopmental outcomes for extremely low birth weight infants in 2000–2002. Pediatrics 2007, 119, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaud, C.; Daubisse-Marliac, L.; White-Koning, M.; Pierrat, V.; Larroque, B.; Grandjean, H.; Alberge, C.; Marret, S.; Burguet, A.; Ancel, P.Y.; et al. Prevalence and associated factors of minor neuromotor dysfunctions at age 5 years in prematurely born children: The EPIPAGE study. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 2007, 161, 1053–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Nadal, S.; Bosch, L. Cognitive and learning outcomes in late preterm infants at school age: A systematic review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, B.; Whyte, R.K.; Asztalos, E.V.; Moddemann, D.; Poets, C.; Rabi, Y.; Solimano, A.; Roberts, R.S.; Canadian Oxygen Trial (COT) Group. Effects of targeting higher vs lower arterial oxygen saturations on death or disability in extremely preterm infants: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2013, 309, 2111–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenson, B.; Tarnowmordi, W.; Darlow, B.; Simes, J.; Juszczak, E.; Askie, L.M.; Battin, M.R.; Bowler, U.; Broadbent, R.S.; Cairns, P.; et al. Oxygen saturation and outcomes in preterm infants. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 2094–2104. [Google Scholar]
- Vaucher, Y.E.; Peralta-Carcelen, M.; Finer, N.N.; Carlo, W.A.; Gantz, M.G.; Walsh, M.C.; Laptook, A.R.; Yoder, B.A.; Faix, R.G.; Das, A.; et al. Neurodevelopmental outcomes in the early CPAP and pulse oximetry trial. New Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 2495–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litt, J.S.; Gerry Taylor, H.; Margevicius, S.; Schluchter, M.; Andreias, L.; Hack, M. Academic achievement of adolescents born with extremely low birth weight. Acta Paediatr. 2012, 101, 1240–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, V.E.; Bora, S.; Austin, N.C.; Levin, K.J.; Woodward, L.J. Identifying very preterm children at educational risk using a school readiness framework. Pediatrics 2014, 134, e825–e832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strenze, T. Intelligence and socioeconomic success: A meta-analytic review of longitudinal research. Intelligence 2007, 35, 401–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenen, K.C.; Moffitt, T.E.; Roberts, A.L.; Martin, L.T.; Kubzansky, L.; Harrington, H.; Poulton, R.; Caspi, A. Childhood IQ and adult mental disorders: A test of the cognitive reserve hypothesis. Am. J. Psychiatry 2009, 166, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.; Wolke, D.; Hennessy, E.; Marlow, N. Educational outcomes in extremely preterm children: Neuropsychological correlates and predictors of attainment. Dev. Neuropsychol. 2011, 36, 74–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, J.F.; Tsai, M.H.; Chu, S.M.; Fu, R.H.; Chiang, M.C.; Hwang, F.M.; Kuan, M.J.; Huang, Y.S. Early detection of minor neurodevelopmental dysfunctions at age 6 months in prematurely born neonates. Early Hum. Dev. 2013, 89, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-S.; Hsu, J.-F.; Paiva, T.; Chin, W.-C.; Chen, I.-C.; Guilleminault, C. Sleep-disordered breathing, craniofacial development, and neurodevelopment in premature infants: A 2-year follow-up study. Sleep Med. 2019, 60, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taddei, M.; Tinelli, F.; Faccio, F.; Riva, D.; Bulgheroni, S. Sex Influences on the Neurocognitive Outcome of Preterm Children. Available online: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/jnr.24862 (accessed on 16 June 2021).
- Truffert, P.; Paris-Llado, J.; Escande, B.; Magny, J.-F.; Cambonie, G.; Saliba, E.; Thiriez, G.; Zupan-Simunek, V.; Blanc, T.; Rozé, J.-C.; et al. Neuromotor outcome at 2 years of very preterm infants who were treated with high-frequency oscillatory ventilation or conventional ventilation for neonatal respiratory distress syndrome. Pediatrics 2007, 119, 860–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larroque, B.; Ancel, P.-Y.; Marret, S.; Marchand, L.; André, M.; Arnaud, C.; Pierrat, V.; Rozé, J.-C.; Messer, J.; Thiriez, G.; et al. Neurodevelopmental disabilities and special care of 5-year-old children born before 33 weeks of gestation (the EPIPAGE study): A longitudinal cohort study. Lancet 2008, 371, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arpi, E.; D’Amico, R.; Lucaccioni, L.; Bedetti, L.; Berardi, A.; Ferrari, F. Worse global intellectual and worse neuropsychological functioning in preterm-born children at preschool age: A meta-analysis. Acta Paediatr. 2019, 108, 1567–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdei, C.; Austin, N.C.; Cherkerzian, S.; Morris, A.R.; Woodward, L.J. Predicting school-aged cognitive impairment in children born very preterm. Pediatrics 2020, 145, e20191982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaul, Y.F.; Johansson, M.; Månsson, J.; Stjernqvist, K.; Farooqi, A.; Serenius, F.; Thorell, L.B. Cognitive profiles of extremely preterm children: Full-Scale IQ hides strengths and weaknesses. Acta Paediatr. 2021, 110, 1817–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, H.S.; Santhakumaran, S.; Cowan, F.M.; Modi, N. Developmental assessments in preterm children: A meta-analysis. Pediatrics 2016, 138, e20160251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenyhercz, F.; Kósa, K.; Nagy, B.E. Perinatal, neonatal, developmental and demographic predictors of intelligence at 4 years of age among low birth weight children: A panel study with a 2-year follow-up. BMC Pediatr. 2022, 22, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksen, H.L.F.; Kesmodel, U.S.; Underbjerg, M.; Kilburn, T.R.; Bertrand, J.; Mortensen, E.L. Predictors of intelligence at the age of 5: Family, pregnancy and birth characteristics, postnatal influences, and postnatal growth. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matte, T.D.; Bresnahan, M.; Begg, M.D.; Susser, E. Influence of variation in birth weight within normal range and within sibships on IQ at age 7 years: Cohort study. Br. Med. J. 2001, 323, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenkin, S.D.; Starr, J.M.; Deary, I.J. Birth weight and cognitive ability in childhood: A systematic review. Psychol. Bull. 2004, 130, 989–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgen, I.; Sommerfelt, K.; Ellertsen, B. Cognitive performance in a low birth weight cohort at 5 and 11 years of age. Pediatr. Neurol. 2003, 29, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sejer, E.P.F.; Bruun, F.J.; Slavensky, J.A.; Mortensen, E.L.; Kesmodel, U.S. Impact of gestational age on child intelligence, attention and executive function at age 5: A cohort study. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e028982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momany, A.M.; Kamradt, J.M.; Nikolas, M.A. A meta-analysis of the association between birth weight and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. J. Abnorm. Child Psychol. 2018, 46, 1409–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wechsler, D. Wechsler Preschool and Primary Scale of Intelligence, Chinese Version Manual, 4th ed.; Chen, Y.H.; Chen, H.Y., Translators; Chinese Behavioral Science Corporation: Taipei, Taiwan, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Syeda, M.M.; Climie, E.A. Test Review: Wechsler Preschool and Primary Scale of Intelligence-Fourth Edition. J. Psychoeduc. Assess. 2014, 32, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conners, C.K. Conners’ Kiddie Continuous Performance Test; Multi-Health Systems Incorporated: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, P.; Doyle, L.W. Group and the VICS. Neurobehavioral outcomes of school-age children born extremely low birth weight or very preterm in the 1990s. JAMA 2003, 289, 3264–3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundequist, A.; Böhm, B.; Lagercrantz, H.; Forssberg, H.; Smedler, A.C. Cognitive outcome varies in adolescents born preterm, depending on gestational age, intrauterine growth and neonatal complications. Acta Paediatr. 2015, 104, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionio, C.; Lista, G.; Veggiotti, P.; Colombo, C.; Ciuffo, G.; Daniele, I.; Landoni, M.; Scelsa, B.; Alfei, E.; Bova, S. Cognitive, Behavioral and Socioemotional Development in a Cohort of Preterm Infants at School Age: A Cross-Sectional Study. Pediatr. Rep. 2022, 14, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orchinik, L.J.; Taylor, H.G.; Espy, K.A.; Minich, N.; Klein, N.; Sheffield, T.; Hack, M. Cognitive outcomes for extremely preterm/extremely low birth weight children in kindergarten. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2011, 17, 1067–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, I.S.; Kerns, K.A.; Müller, U.; Ahronovich, M.D.; Litman, F.R. Executive functions in extremely low birth weight and late-preterm preschoolers: Effects on working memory and response inhibition. Child Neuropsychol. 2012, 18, 586–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitchen, W.H. The relationship between birth weight and gestational age in an Australian hospital population. J. Paediatr. Child Health 1968, 4, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutta, A.T.; Cleves, M.A.; Casey, P.H.; Cradock, M.M.; Anand, K.J. Cognitive and behavioral outcomes of school-aged children who were born preterm: A meta-analysis. JAMA 2002, 288, 728–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, S.; Marlow, N. Preterm birth and childhood psychiatric disorders. Pediatr. Res. 2011, 69, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnett, A.C.; Anderson, P.J.; Cheong, J.; Doyle, L.W.; Davey, C.G.; Wood, S.J. Prevalence of psychiatric diagnoses in preterm and full-term children, adolescents and young adults: A meta-analysis. Psychol. Med. 2011, 41, 2463–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linsell, L.; Malouf, R.; Morris, J.; Kurinczuk, J.J.; Marlow, N. Prognostic factors for poor cognitive development in children born very preterm or with very low birth weight: A systematic review. JAMA Pediatr. 2015, 169, 1162–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaari, M.; Mankuta, D.; Gadassi, A.H.; Friedlander, E.; Bar-Oz, B.; Eventov-Friedman, S.; Maniv, N.; Zucker, D.; Yirmiya, N. Early developmental trajectories of preterm infants. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2018, 81, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeo, D.M.; Brogna, C.; Sini, F.; Romeo, M.G.; Cota, F.; Ricci, D. Early psychomotor development of low-risk preterm infants: Influence of gestational age and gender. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2016, 20, 518–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broström, L.; Vollmer, B.; Bolk, J.; Eklöf, E.; Ådén, U. Minor neurological dysfunction and associations with motor function, general cognitive abilities, and behaviour in children born extremely preterm. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2018, 60, 826–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, I.S.; Erickson, K.; Ahronovich, M.D.; Baker, R.; Litman, F.R. Cognitive deficit in preschoolers born late-preterm. Early Hum. Dev. 2011, 87, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| (n = 278) | Group 1 Full-Term (n = 25) | Group 2 Preterm ≥ 1500 g (n = 94) | Group 3 Preterm < 1500 g (n = 159) | p-Value | Post Hoc (Scheffe; Bonferroni) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Current age (yr.) | 4.09 ± 1.04 | 4.09 ± 1.06 | 4.14 ± 0.92 | 0.936 | - |
| Male, n (%) | 17 (68.0%) | 53 (56.4%) | 89 (56.0%) | 0.440 | - |
| Perinatal factors: | |||||
| GA (wk.) | 38.35 ± 2.43 | 33.52 ± 1.95 | 27.90 ± 2.77 | <0.001 * | 1 > 2 > 3 |
| BW (g) | 3210.21 ± 442.30 | 2025.63 ± 453.48 | 970.81 ± 266.44 | <0.001 * | 1 > 2 > 3 |
| Apgar score, 1 min | 8.6 ± 0.58 | 7.80 ± 1.51 | 5.47 ± 2.01 | <0.001 * | 1,2 > 3 |
| Apgar score, 5 min | 9.6 ± 0.58 | 9.11 ± 1.29 | 7.60 ± 1.60 | <0.001 * | 1,2 > 3 |
| ASD | 1 (4.0%) | 11 (11.7%) | 45 (28.3%) | 0.001 * | 3 > 1,2 |
| VSD | 0 (0.0%) | 2 (2.1%) | 1 (0.6%) | 0.462 | - |
| BPD | 0 (0.0%) | 4 (4.3%) | 114 (71.7%) | <0.001 * | 3 > 1,2 |
| Pneumonia | 0 (0.0%) | 5 (5.3%) | 65 (40.9%) | <0.001 * | 3 > 1,2 |
| PH | 0 (0.0%) | 2 (2.1%) | 17 (10.7%) | 0.012 * | 3 > 2 |
| PDA | 0 (0.0%) | 10 (10.6%) | 87 (54.7%) | <0.001 * | 3 > 1,2 |
| RDS | 0 (0.0%) | 35 (37.2%) | 151 (95.0%) | <0.001 * | 3 > 2 > 1 |
| NEC | 0 (0.0%) | 2 (2.1%) | 19 (11.9%) | 0.006 * | 3 > 2 |
| IVH | 0 (0.0%) | 6 (6.4%) | 54 (34.0%) | <0.001 * | 3 > 1,2 |
| ROP | 0 (0.0%) | 10 (10.6%) | 99 (62.3%) | <0.001 * | 3 > 1,2 |
| PVL | 0 (0.0%) | 0 (0.0%) | 2 (1.3%) | 0.471 | - |
| Anemia | 0 (0.0%) | 38 (40.4%) | 151 (95.0%) | <0.001 * | 3 > 2 > 1 |
| Sepsis | 1 (4.0%) | 9 (9.6%) | 74 (46.5%) | <0.001 * | 3 > 1,2 |
| Blood transfusion | 0 (0.0%) | 29 (30.9%) | 152 (95.6%) | <0.001 * | 3 > 2>1 |
| Surfactant use | 0 (0.0%) | 7 (7.5%) | 99 (62.7%) | <0.001 * | 3 > 1,2 |
| (n = 150) | Group 1 Full-Term (n = 16) | Group 2 Preterm ≥ 1500 g (n = 72) | Group 3 Preterm < 1500 g (n = 62) | p-Value | Post Hoc (Bonferroni) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical index | 42.54 ± 16.2 | 46.02 ± 17.76 | 51.90 ± 19.37 | 0.083 | - |
| Omissions | 44.90 ± 7.03 | 45.17 ± 7.48 | 52.30 ± 12.45 | 0.000 * | 3 > 1,2 |
| Commissions | 46.81 ± 7.93 | 49.75 ± 12.22 | 48.54 ± 8.97 | 0.560 | - |
| Hit R | 55.53 ± 11.02 | 53.46 ± 11.67 | 58.32 ± 9.38 | 0.035 * | 3 > 2 |
| Hit RT SE | 48.15 ± 10.89 | 49.15 ± 9.04 | 54.83 ± 10.02 | 0.002 * | 3 > 2,1 |
| Variability | 47.87 ± 10.72 | 47.32 ± 8.68 | 51.83 ± 11.01 | 0.029 * | 3 > 2 |
| Detectability | 46.17 ± 9.15 | 47.62 ± 11.80 | 48.82 ± 10.44 | 0.647 | - |
| Response Style | 50.85 ± 15.97 | 52.13 ± 15.69 | 57.45 ± 17.66 | 0.128 | - |
| Perseverations | 52.75 ± 14.67 | 54.41 ± 16.89 | 55.02 ± 16.36 | 0.885 | - |
| Hit RT Block Change | 49.20 ± 6.07 | 45.45 ± 9.94 | 126.77 ± 625.65 | 0.484 | - |
| Hit SE Block Change | 45.64 ± 7.49 | 45.12 ± 8.72 | 47.83 ± 8.73 | 0.186 | - |
| Hit RT ISI Change | 49.90 ± 10.29 | 51.33 ± 11.67 | 64.75 ± 70.07 | 0.202 | - |
| Hit SE ISI Change | 46.90 ± 10.23 | 45.27 ± 8.20 | 50.26 ± 7.63 | 0.003 * | 3 > 2 |
| (n = 278) | Group 1 Full-Term (n = 25) | Group 2 Preterm ≥ 1500 g (n = 94) | Group 3 Preterm < 1500 g (n = 159) | p-Value | Post Hoc (Bonferroni) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FSIQ | 103.36 ± 16.37 | 96.92 ± 13.87 | 88.74 ± 15.46 | <0.001 * | 1,2 > 3 |
| Index scores | |||||
| VCI | 105.24 ± 14.78 | 99.64 ± 15.00 | 95.04 ± 17.59 | 0.007 * | 1 > 3 |
| VSI | 102.00 ± 17.98 | 98.89 ± 14.70 | 89.67 ± 16.53 | <0.001 * | 1,2 > 3 |
| FRI | 106.69 ± 15.17 | 99.48 ± 15.11 | 88.60 ± 14.74 | <0.001 * | 1,2 > 3 |
| WMI | 98.36 ± 16.34 | 97.28 ± 13.19 | 87.22 ± 14.30 | <0.001 * | 1,2 > 3 |
| PSI | 102.15 ± 13.10 | 92.00 ± 18.92 | 82.88 ± 17.37 | <0.001 * | 1,2 > 3 |
| Subtest scores | |||||
| SI | 11.54 ± 1.05 | 10.47 ± 2.48 | 9.01 ± 2.93 | 0.001 * | 1,2 > 3 |
| IN | 10.88 ± 2.79 | 9.65 ± 2.70 | 8.84 ± 2.99 | 0.002 * | 1 > 3 |
| OA | 10.68 ± 3.28 | 9.68 ± 2.98 | 8.03 ± 3.26 | <0.001 * | 1,2 > 3 |
| BD | 9.96 ± 3.61 | 9.85 ± 3.24 | 7.93 ± 3.36 | <0.001 * | 1,2 > 3 |
| PC | 10.62 ± 3.20 | 10.40 ± 3.11 | 7.74 ± 3.08 | <0.001 * | 1,2 > 3 |
| MR | 10.71 ± 2.63 | 9.40 ± 2.78 | 8.59 ± 3.03 | 0.002 * | 1 > 3 |
| ZL | 9.44 ± 2.90 | 10.00 ± 2.43 | 7.82 ± 2.64 | <0.001 * | 1,2 > 3 |
| PM | 9.96 ± 3.58 | 9.13 ± 2.83 | 7.72 ± 3.00 | <0.001 * | 1,2 > 3 |
| CA | 9.62 ± 3.23 | 8.98 ± 2.40 | 7.76 ± 2.94 | 0.023 * | - |
| BS | 11.08 ± 2.43 | 8.61 ± 3.29 | 6.60 ± 3.52 | <0.001 * | 1,2 > 3 |
| Clinical Index | Omissions | Commissions | Hit RT | Hit RT SE | Variability | Detectability | Response Style | Perseverations | Hit RT Block Change | Hit SE Block Change | Hit RT ISI Change | Hit SE ISI Change | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Current age (yr.) | −0.135 | 0.099 | −0.048 | 0.002 | 0.076 | 0.075 | 0.017 | −0.125 | 0.069 | −0.053 | 0.120 | 0.146 | 0.156 |
| Gender | −0.284 ** | 0.036 | 0.155 | −0.038 | 0.033 | −0.029 | 0.208 * | 0.058 | 0.081 | −0.078 | 0.063 | −0.056 | −0.045 |
| Perinatal factors | |||||||||||||
| GA (wk.) | −0.221 ** | −0.353 ** | 0.060 | −0.263 ** | −0.319 ** | −0.212 * | −0.049 | −0.112 | −0.029 | −0.083 | −0.060 | −0.210 * | −0.231 ** |
| BW (g) | −0.105 | −0.301 ** | 0.035 | −0.185 * | −0.239 ** | −0.159 | −0.080 | −0.114 | 0.017 | −0.069 | −0.039 | −0.150 | −0.259 ** |
| Apgar score, 1 min | −0.269 ** | −0.401 ** | −0.079 | −0.230 ** | −0.412 ** | −0.331 ** | −0.168 | 0.053 | −0.136 | −0.130 | −0.022 | −0.103 | −0.089 |
| Apgar score, 5 min | −0.219 * | −0.381 ** | −0.063 | −0.218 * | −0.387 ** | −0.335 ** | −0.138 | 0.030 | −0.119 | −0.145 | 0.007 | −0.102 | −0.059 |
| PH | 0.061 | 0.143 | −0.092 | 0.151 | 0.066 | −0.002 | −0.132 | 0.129 | 0.038 | −0.018 | 0.020 | 0.010 | −0.032 |
| VSD | −0.024 | −0.075 | 0.181 * | 0.037 | 0.083 | 0.042 | 0.085 | −0.090 | 0.298 ** | −0.012 | −0.029 | 0.014 | 0.016 |
| ASD | −0.050 | −0.019 | −0.206 * | 0.122 | −0.106 | −0.116 | −0.229 ** | 0.239 ** | −0.152 | −0.037 | 0.046 | 0.168 | −0.165 |
| PDA | 0.135 | 0.155 | 0.054 | 0.172 * | 0.200 * | 0.068 | 0.030 | 0.100 | 0.125 | 0.152 | 0.024 | 0.000 | −0.009 |
| IVH | −0.011 | 0.037 | −0.035 | 0.027 | 0.013 | 0.034 | −0.028 | −0.001 | 0.033 | 0.200 * | 0.093 | −0.031 | 0.046 |
| ROP | 0.372 ** | 0.438 ** | 0.042 | 0.292 ** | 0.411 ** | 0.229 ** | 0.173 * | −0.053 | 0.134 | 0.189 * | 0.098 | 0.030 | 0.139 |
| RDS | 0.147 | 0.258 ** | −0.061 | 0.129 | 0.256 ** | 0.217 * | −0.019 | 0.128 | 0.046 | 0.075 | 0.014 | 0.105 | 0.220 ** |
| NEC | 0.137 | 0.178 * | 0.216 * | −0.053 | 0.221 ** | 0.224 ** | 0.252 ** | −0.099 | 0.190 * | −0.024 | −0.037 | 0.008 | 0.120 |
| BPD | 0.278 ** | 0.382 ** | −0.008 | 0.275 ** | 0.327 ** | 0.236 ** | 0.110 | 0.132 | 0.057 | 0.133 | 0.112 | 0.185 * | 0.173 * |
| Sepsis | 0.046 | 0.120 | 0.059 | 0.052 | 0.109 | 0.026 | 0.082 | −0.019 | 0.028 | 0.158 | −0.045 | 0.151 | 0.024 |
| Pneumonia | 0.262 ** | 0.354 ** | 0.064 | 0.175 * | 0.299 ** | 0.157 | 0.125 | 0.026 | 0.165 | −0.036 | 0.058 | 0.238 ** | 0.198 * |
| Anemia | 0.088 | 0.232 ** | −0.053 | 0.155 | 0.197 * | 0.147 | 0.007 | 0.173 * | −0.076 | 0.068 | −0.086 | 0.092 | 0.163 |
| Blood transfusion | 0.141 | 0.249 ** | −0.084 | 0.215 * | 0.249 ** | 0.210 * | −0.051 | 0.173 * | 0.017 | 0.070 | −0.057 | 0.112 | 0.228 ** |
| Surfactant use | 0.237 ** | 0.393 ** | −0.009 | 0.247 ** | 0.325 ** | 0.181 * | 0.072 | 0.023 | 0.063 | 0.143 | 0.111 | 0.187 * | 0.165 |
| PVL | 0.004 | −0.069 | 0.146 | −0.041 | 0.009 | 0.036 | 0.088 | −0.056 | −0.006 | −0.008 | −0.021 | 0.002 | 0.098 |
| Vision | |||||||||||||
| BCVA | 0.289 * | 0.254 * | 0.137 | 0.211 | 0.255 * | 0.126 | 0.147 | 0.106 | 0.139 | −0.166 | −0.110 | −0.065 | 0.092 |
| SPH | 0.048 | −0.114 | 0.141 | 0.029 | −0.083 | −0.045 | 0.170 | −0.007 | −0.041 | 0.043 | 0.251 * | 0.014 | −0.182 |
| CYL | 0.104 | 0.123 | 0.115 | 0.053 | −0.003 | −0.068 | 0.120 | 0.033 | 0.103 | −0.132 | −0.129 | −0.053 | −0.269 |
| SE | 0.116 | 0.083 | 0.165 | 0.064 | −0.024 | −0.077 | 0.183 | 0.029 | 0.091 | −0.113 | −0.043 | −0.045 | −0.314 |
| FSIQ | VCI | VSI | FRI | WMI | PSI | BD | IN | MR | BS | PM | SI | PC | CA | ZL | OA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Current age (yr.) | −0.048 | −0.014 | −0.037 | 0.076 | −0.109 | 0.118 | −0.044 | 0.046 | 0.002 | 0.165 | −0.124 * | 0.218 * | 0.099 | 0.026 | −0.053 | 0.02 |
| Gender | 0.11 | 0.062 | 0.150 * | 0.067 | 0.133 * | −0.006 | 0.125 * | 0.042 | 0.074 | −0.006 | 0.081 | 0.135 | 0.119 | 0.194 * | 0.161 * | 0.204 ** |
| Perinatal factors | ||||||||||||||||
| GA (wk.) | 0.356 ** | 0.181 ** | 0.337 ** | 0.385 ** | 0.343 ** | 0.386 ** | 0.332 ** | 0.229 ** | 0.256 ** | 0.398 ** | 0.262 ** | 0.325 ** | 0.368 ** | 0.292 ** | 0.371 ** | 0.334 ** |
| BW (g) | 0.370 ** | 0.232 ** | 0.321 ** | 0.376 ** | 0.364 ** | 0.394 ** | 0.297 ** | 0.241 ** | 0.232 ** | 0.412 ** | 0.310 ** | 0.337 ** | 0.347 ** | 0.319 ** | 0.340 ** | 0.315 ** |
| Apgar score, 1 min | 0.302 ** | 0.157 * | 0.245 ** | 0.305 ** | 0.279 ** | 0.255 ** | 0.253 ** | 0.153 * | 0.211 ** | 0.323 ** | 0.237 ** | 0.211 * | 0.323 ** | 0.211 * | 0.263 ** | 0.275 ** |
| Apgar score, 5 min | 0.246 ** | 0.117 | 0.208 ** | 0.232 ** | 0.240 ** | 0.191 * | 0.241 ** | 0.138 * | 0.169 ** | 0.239 ** | 0.206 ** | 0.159 | 0.263 ** | 0.133 | 0.242 ** | 0.219 ** |
| PH | −0.057 | −0.069 | −0.043 | −0.046 | −0.02 | −0.106 | −0.023 | −0.099 | −0.016 | −0.085 | −0.01 | 0.013 | −0.074 | −0.058 | −0.04 | −0.055 |
| VSD | 0.052 | 0.089 | 0.029 | 0.038 | 0.045 | 0.035 | 0.048 | 0.037 | −0.014 | −0.018 | 0.008 | 0.009 | 0.084 | 0.083 | 0.076 | 0.004 |
| ASD | −0.075 | −0.083 | −0.054 | −0.054 | −0.088 | 0.035 | 0.003 | −0.027 | −0.011 | 0.002 | −0.074 | −0.075 | −0.046 | 0.025 | −0.08 | −0.111 |
| PDA | −0.225 ** | −0.12 | −0.214 ** | −0.237 ** | −0.256 ** | −0.219 * | −0.208 ** | −0.164 ** | −0.142 * | −0.230 * | −0.167 ** | −0.236 ** | −0.257 ** | −0.144 | −0.287 ** | −0.259 ** |
| IVH | −0.173 ** | −0.127 * | −0.195 ** | −0.139 | −0.185 ** | −0.032 | −0.200 ** | −0.045 | −0.131 * | 0.013 | −0.162 * | −0.088 | −0.109 | −0.097 | −0.174 ** | −0.218 ** |
| ROP | −0.350 ** | −0.171 ** | −0.304 ** | −0.465 ** | −0.359 ** | −0.366 ** | −0.315 ** | −0.181 ** | −0.288 ** | −0.421 ** | −0.257 ** | −0.313 ** | −0.449 ** | −0.367 ** | −0.387 ** | −0.299 ** |
| RDS | −0.351 ** | −0.196 ** | −0.313 ** | −0.394 ** | −0.333 ** | −0.378 ** | −0.313 ** | −0.211 ** | −0.288 ** | −0.439 ** | −0.290 ** | −0.278 ** | −0.339 ** | −0.308 ** | −0.316 ** | −0.280 ** |
| NEC | −0.089 | −0.055 | −0.084 | −0.223 * | −0.121 | −0.12 | −0.083 | −0.078 | −0.084 | −0.240 ** | −0.076 | −0.104 | −0.257 ** | −0.184 * | −0.086 | −0.066 |
| BPD | −0.362 ** | −0.175 ** | −0.366 ** | −0.386 ** | −0.325 ** | −0.402 ** | −0.362 ** | −0.239 ** | −0.247 ** | −0.394 ** | −0.246 ** | −0.380 ** | −0.386 ** | −0.306 ** | −0.362 ** | −0.359 ** |
| Sepsis | −0.253 ** | −0.180 ** | −0.274 ** | −0.296 ** | −0.289 ** | −0.222 * | −0.156 ** | −0.189 ** | −0.180 ** | −0.188 * | −0.191 ** | −0.305 ** | −0.291 ** | −0.291 ** | −0.296 ** | −0.295 ** |
| Pneumonia | −0.316 ** | −0.207 ** | −0.311 ** | −0.358 ** | −0.287 ** | −0.207 * | −0.321 ** | −0.190 ** | −0.205 ** | −0.252 ** | −0.194 ** | −0.418 ** | −0.312 ** | −0.266 ** | −0.328 ** | −0.369 ** |
| Anemia | −0.247 ** | −0.169 ** | −0.208 ** | −0.209 * | −0.293 ** | −0.228 * | −0.133 * | −0.168 ** | −0.157 * | −0.283 ** | −0.243 ** | −0.229 ** | −0.242 ** | −0.200 * | −0.284 ** | −0.221 ** |
| Blood transfusion | −0.280 ** | −0.199 ** | −0.234 ** | −0.290 ** | −0.289 ** | −0.291 ** | −0.179 ** | −0.196 ** | −0.165 ** | −0.329 ** | −0.247 ** | −0.273 ** | −0.299 ** | −0.276 ** | −0.278 ** | −0.243 ** |
| Surfactant use | −0.315 ** | −0.141 * | −0.319 ** | −0.345 ** | −0.297 ** | −0.355 ** | −0.339 ** | −0.167 ** | −0.213 ** | −0.333 ** | −0.221 ** | −0.280 ** | −0.387 ** | −0.321 ** | −0.327 ** | −0.326 ** |
| PVL | −0.062 | −0.062 | −0.123 * | 0.06 | −0.05 | 0.02 | −0.106 | −0.039 | 0.082 | 0.007 | −0.042 | −0.052 | 0.002 | 0.02 | −0.04 | −0.035 |
| Vision | ||||||||||||||||
| BCVA | −0.169 | −0.174 | −0.104 | −0.092 | −0.009 | −0.152 | −0.137 | −0.277 ** | −0.058 | −0.310 ** | 0.131 | −0.230 * | −0.07 | −0.097 | −0.137 | −0.055 |
| SPH | −0.033 | −0.08 | 0.044 | 0.039 | 0.058 | −0.033 | 0.034 | −0.025 | −0.067 | −0.004 | 0.071 | −0.194 | 0.049 | 0.033 | 0.008 | 0.041 |
| CYL | 0.095 | 0.062 | −0.105 | 0.057 | 0.158 | −0.031 | −0.001 | 0.136 | 0.083 | 0.117 | 0.03 | 0.00 | −0.032 | −0.17 | 0.237 * | −0.181 |
| SE | 0.086 | 0.04 | −0.061 | 0.063 | 0.171 | −0.029 | 0.031 | 0.137 | 0.041 | 0.12 | 0.058 | −0.043 | −0.012 | −0.136 | 0.222 | −0.13 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chin, W.-C.; Wu, W.-C.; Hsu, J.-F.; Tang, I.; Yao, T.-C.; Huang, Y.-S. Correlation Analysis of Attention and Intelligence of Preterm Infants at Preschool Age: A Premature Cohort Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 3357. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20043357
Chin W-C, Wu W-C, Hsu J-F, Tang I, Yao T-C, Huang Y-S. Correlation Analysis of Attention and Intelligence of Preterm Infants at Preschool Age: A Premature Cohort Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023; 20(4):3357. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20043357
Chicago/Turabian StyleChin, Wei-Chih, Wei-Chi Wu, Jen-Fu Hsu, I. Tang, Tsung-Chieh Yao, and Yu-Shu Huang. 2023. "Correlation Analysis of Attention and Intelligence of Preterm Infants at Preschool Age: A Premature Cohort Study" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 20, no. 4: 3357. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20043357
APA StyleChin, W.-C., Wu, W.-C., Hsu, J.-F., Tang, I., Yao, T.-C., & Huang, Y.-S. (2023). Correlation Analysis of Attention and Intelligence of Preterm Infants at Preschool Age: A Premature Cohort Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(4), 3357. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20043357









