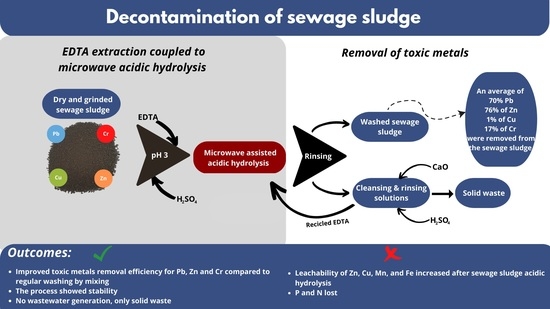
Removal of Toxic Metals from Sewage Sludge by Acid Hydrolysis Coupled with EDTA Washing in a Closed-Loop Process
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. SS Origin and Chemical Properties
2.2. Hydrodynamic Cavitation Coupled with EDTA Washing of SS
2.3. Microwave Irradiation and EDTA Washing of SS
2.4. Microwave-Assisted Acid/Alkaline Hydrolysis and EDTA Washing of SS
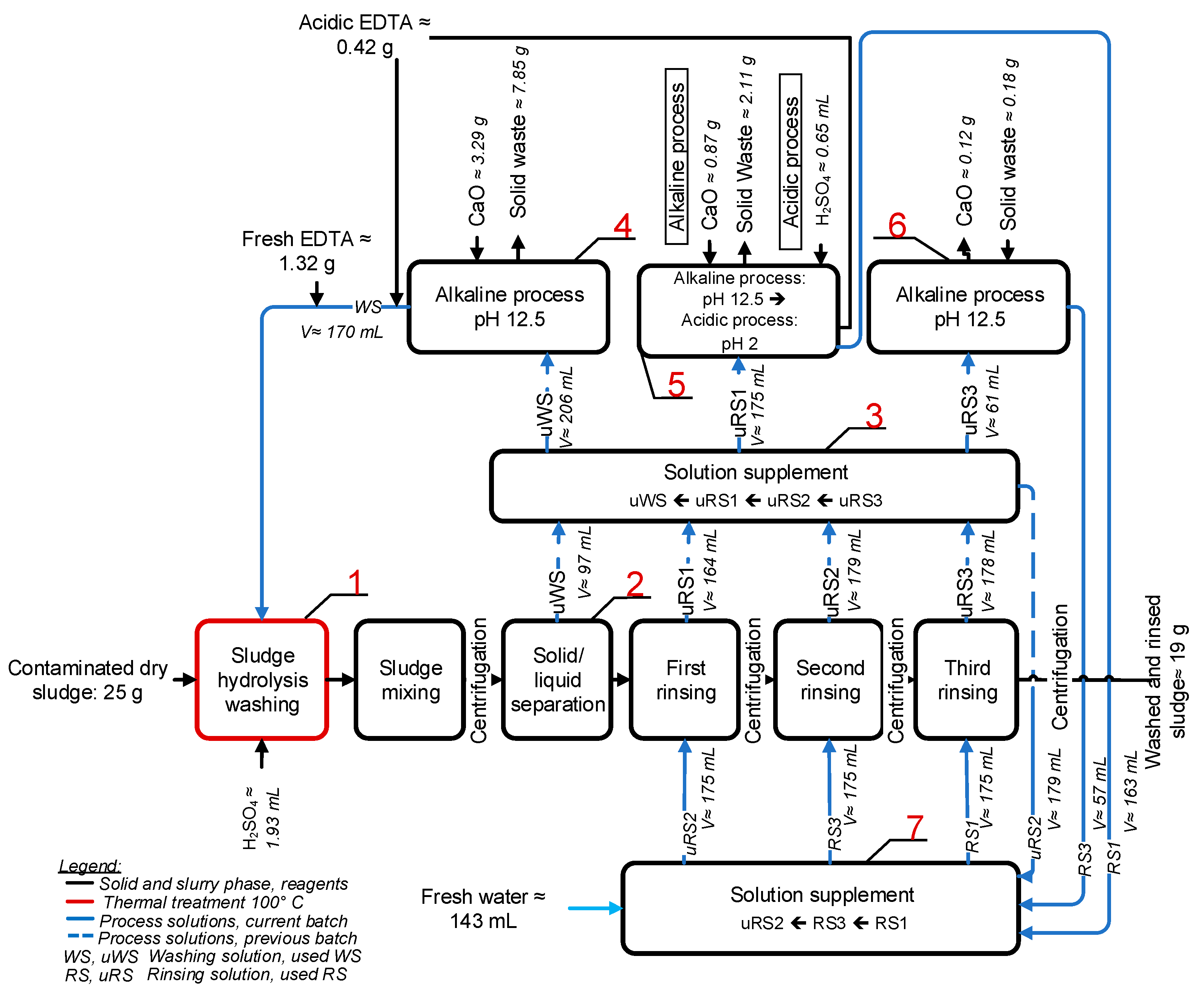
2.5. Washing of SS in Closed Process Loop in Series of Batches
2.6. Determination of TMs
2.7. Determination of EDTA in Process Solutions
2.8. Leachability of Toxic Elements
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemical Properties of SS
3.2. Selection of the Most Efficient Treatment to Remove TMs from SS
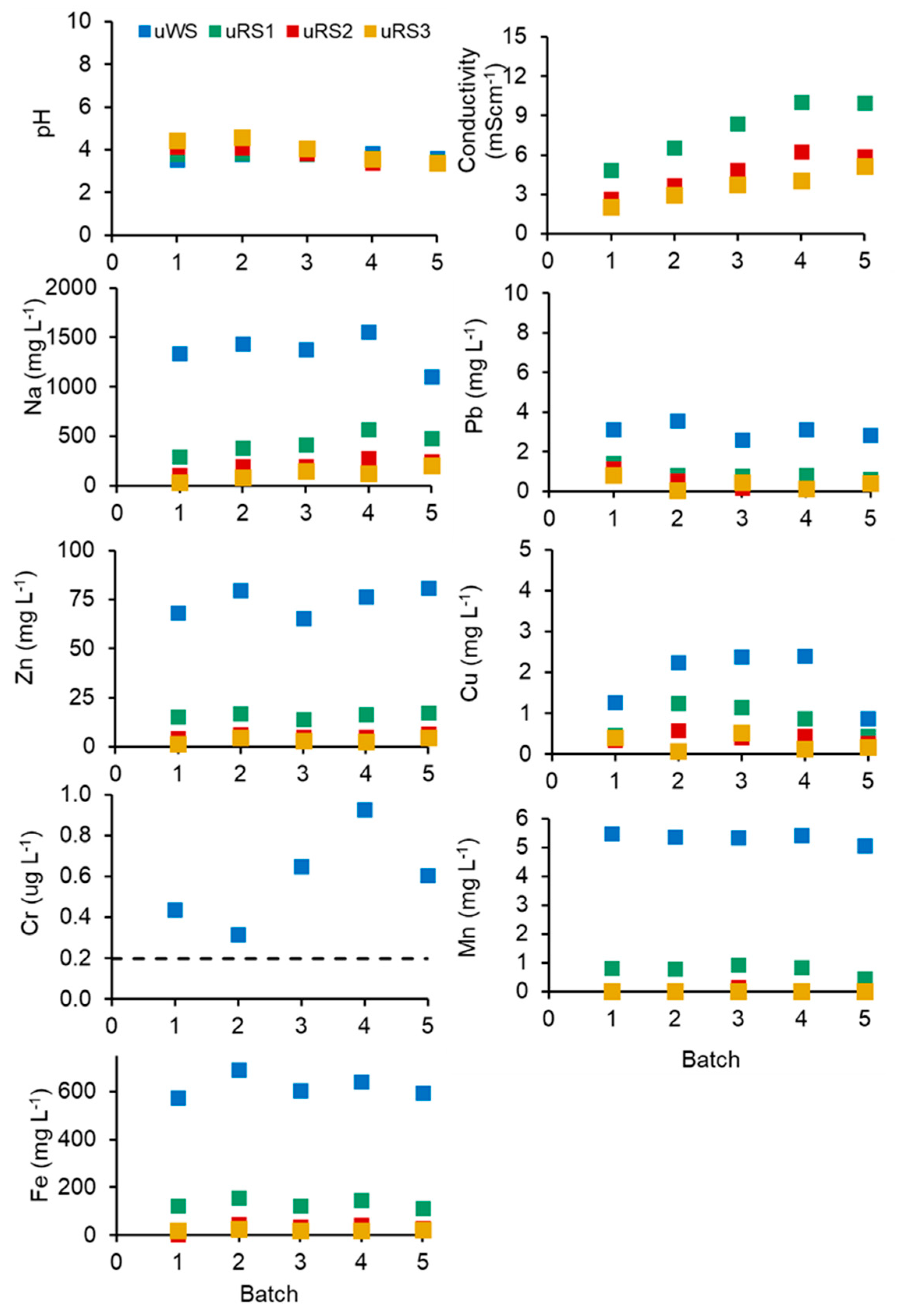
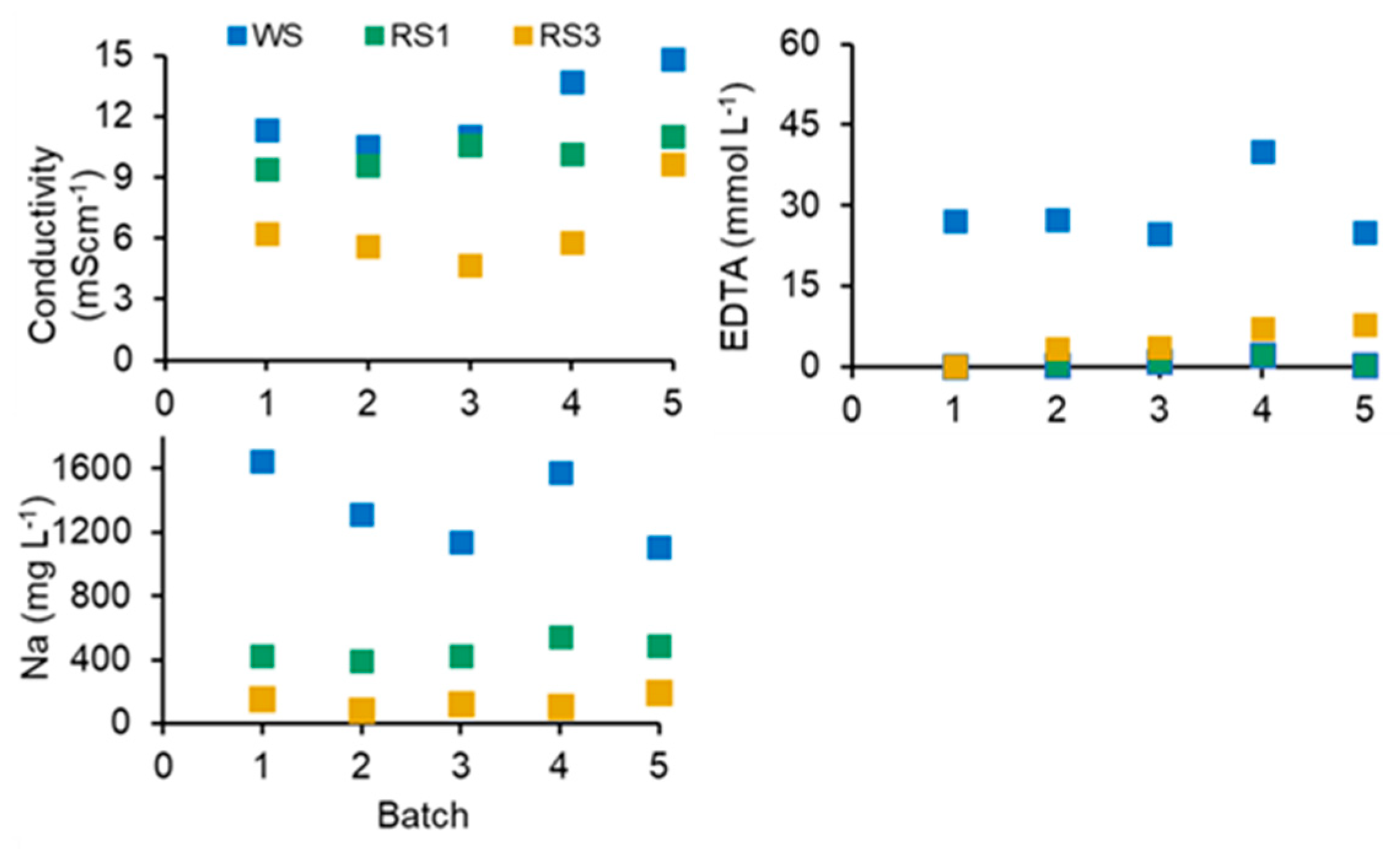
3.3. Acid Hydrolysis and EDTA Washing of SS in a Closed-Loop Process
3.4. Depletion of Nutrients from Washed SS
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bolzonella, D.; Battista, F.; Cavinato, C.; Gottardo, M.; Micolucci, F.; Lyberatos, G.; Pavan, P. Recent Developments in Biohythane Production from Household Food Wastes: A Review. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 257, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwapinski, W.; Kolinovic, I.; Leahy, J.J. Sewage Sludge Thermal Treatment Technologies with a Focus on Phosphorus Recovery: A Review. Waste Biomass Valorization 2021, 12, 5837–5852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroiss, H. What Is the Potential for Utilizing the Resources in Sludge? Water Sci. Technol. 2004, 49, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, A.C.; Warneke, J.E.; Page, A.L.; Lund, L.J. Accumulation of Heavy Metals in Sewage Sludge-Treated Soils. J. Environ. Qual. 1984, 13, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudcová, H.; Vymazal, J.; Rozkošný, M. Present Restrictions of Sewage Sludge Application in Agriculture within the European Union. Soil Water Res. 2019, 14, 104–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelessidis, A.; Stasinakis, A.S. Comparative Study of the Methods Used for Treatment and Final Disposal of Sewage Sludge in European Countries. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 1186–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werther, J.; Ogada, T. Sewage Sludge Combustion. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 1999, 25, 55–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, B.; Hernandez, R.; Fortela, D.L.B.; Sharp, W.; Chistoserdov, A.; Gang, D.; Revellame, E.; Holmes, W.; Zappi, M.E. A Review of Pretreatment Methods to Enhance Solids Reduction during Anaerobic Digestion of Municipal Wastewater Sludges and the Resulting Digester Performance: Implications to Future Urban Biorefineries. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 9141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, M.; Ye, Z.; Yang, C. Effect of Manganese Oxide-Modified Biochar Addition on Methane Production and Heavy Metal Speciation during the Anaerobic Digestion of Sewage Sludge. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 76, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Q.; Xue, Q.; Poon, C.S. Development of a Novel Binder Using Lime and Incinerated Sewage Sludge Ash to Stabilize and Solidify Contaminated Marine Sediments with High Water Content as a Fill Material. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2019, 31, 04019245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Xu, D.; Feng, P.; Hao, B.; Guo, Y.; Wang, S. Municipal Sewage Sludge Incineration and Its Air Pollution Control. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 295, 126456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, C.; Peplinski, B.; Kley, G.; Kratz, S.; Schick, J.; Schnug, E. Phosphorrückgewinnung Aus Klärschlammaschen–Ergebnisse Aus Dem EU-Projekt SUSAN. Österr. Wasser-Abfallwirtsch. 2008, 60, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaber, S.E.; Rizk, M.S.; Yehia, M.M. Extraction of Certain Heavy Metals from Sewage Sludge Using Different Types of Acids. Biokemistri 2011, 23, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suanon, F.; Sun, Q.; Dimon, B.; Mama, D.; Yu, C.-P. Heavy Metal Removal from Sludge with Organic Chelators: Comparative Study of N, N-Bis(Carboxymethyl) Glutamic Acid and Citric Acid. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 166, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaleckas, E.; Paulauskas, V.; Sabienė, N.; Kušlienė, G. Copper and Zinc Removal from Sewage Sludge Using Different Organic Acids. In Proceedings of the International Scientific Conference of Rural Development, Akademija, Lithuania, 15–17 October 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Babel, S.; del Mundo Dacera, D. Heavy Metal Removal from Contaminated Sludge for Land Application: A Review. Waste Manag. 2006, 26, 988–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Wang, Q.; Fang, L.; Xue, Q.; Poon, C.S. Fate of Metals before and after Chemical Extraction of Incinerated Sewage Sludge Ash. Chemosphere 2017, 186, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.B.; Tyagi, R.D.; Blais, J.F. Extraction of Cr(III) and Other Metals from Tannery Sludge by Mineral Acids. Environ. Technol. 2001, 22, 1007–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheju, M.; Pode, R.; Manea, F. Comparative Heavy Metal Chemical Extraction from Anaerobically Digested Biosolids. Hydrometallurgy 2011, 108, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Wu, Y.; Dou, W.; Ren, X. Removal of Heavy Metals in Sludge via Joint EDTA-Acid Treatment: Effects on Seed Germination. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 707, 135866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Cui, Y.; Li, Q.; Sun, J. Effective Removal of Heavy Metals from Industrial Sludge with the Aid of a Biodegradable Chelating Ligand GLDA. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 283, 748–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Li, J.; Guo, M.Z.; Cheeseman, C.R.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Donatello, S.; Poon, C.S. Phosphorus Recovery and Leaching of Trace Elements from Incinerated Sewage Sludge Ash (ISSA). Chemosphere 2018, 193, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewil, R.; Baeyens, J.; Neyens, E. Reducing the Heavy Metal Content of Sewage Sludge by Advanced Sludge Treatment Methods. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2006, 23, 994–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neyens, E.; Baeyens, J.; Creemers, C. Alkaline Thermal Sludge Hydrolysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2003, 97, 295–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neyens, E.; Baeyens, J.; Weemaes, M.; De heyder, B. Hot Acid Hydrolysis as a Potential Treatment of Thickened Sewage Sludge. J. Hazard. Mater. 2003, 98, 275–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zieliński, M.; Ciesielski, S.; Cydzik-Kwiatkowska, A.; Turek, J.; Dębowski, M. Influence of Microwave Radiation on Bacterial Community Structure in Biofilm. Process Biochem. 2007, 42, 1250–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.M.; Park, J.K.; Lee, Y.O. Mechanisms of Microwave Irradiation Involved in the Destruction of Fecal Coliforms from Biosolids. Water Res. 2004, 38, 1615–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.A.; Lelyveld, T.P.; Mavrofidis, S.D.; Kingman, S.W.; Miles, N.J. Microwave Heating Applications in Environmental Engineering—A Review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2002, 34, 75–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, R.; Tang, Y.; Chen, G. Microwave-Induced Heavy Metal Removal from Dewatered Biosolids for Cost-Effective Composting. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 241, 118342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancuso, G.; Langone, M.; Di Maggio, R.; Toscano, A.; Andreottola, G. Effect of Hydrodynamic Cavitation on Flocs Structure in Sewage Sludge to Increase Stabilization for Efficient and Safe Reuse in Agriculture. Bioremed. J. 2022, 26, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Koo, B.; Sun, X.; Yoon, J.Y. Investigation of Sludge Disintegration Using Rotor-Stator Type Hydrodynamic Cavitation Reactor. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 240, 116636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petkovšek, M.; Zupanc, M.; Dular, M.; Kosjek, T.; Heath, E.; Kompare, B.; Širok, B. Rotation Generator of Hydrodynamic Cavitation for Water Treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 118, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suslick, K.S. Sonochemistry. Science 1990, 247, 1439–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repinc, S.K.; Bizjan, B.; Budhiraja, V.; Dular, M.; Gostiša, J.; Brajer Humar, B.; Kaurin, A.; Kržan, A.; Levstek, M.; Arteaga, J.F.M.; et al. Integral Analysis of Hydrodynamic Cavitation Effects on Waste Activated Sludge Characteristics, Potentially Toxic Metals, Microorganisms and Identification of Microplastics. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 151414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales Arteaga, J.F.; Kaurin, A.; Lestan, D. Removal of Toxic Metals from Sewage Sludge by EDTA in a Closed-Loop Washing Process. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejías, C.; Martín, J.; Santos, J.L.; Aparicio, I.; Alonso, E. Occurrence of Pharmaceuticals and Their Metabolites in Sewage Sludge and Soil: A Review on Their Distribution and Environmental Risk Assessment. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2021, 30, e00125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomei, M.C.; BRAGUGLIA, C.M.; CENTO, G.; MININNI, G. Modeling of Anaerobic Digestion of Sludge. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 39, 1003–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raboni, M.; Torretta, V.; Urbini, G. Influence of Strong Diurnal Variations in Sewage Quality on the Performance of Biological Denitrification in Small Community Wastewater Treatment Plants (WWTPs). Sustainability 2013, 5, 3679–3689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DIN 38414-S4; German Standard Procedure for Water, Wastewater and Sludge Analysis, Sludge and Sediments (Group S). Determination of Water Leachability. Benthe-Vertrieb Gmbh: Berlin/Köln, Germany, 1984.
- SIST EN 15936; Sludge, Treated Biowaste, Soil and Waste—Determination of Total Organic Carbon (TOC) by Dry Combustion. AENOR: Madrid, Spain, 2012.
- SIST EN 16168; Sludge, Treated Biowaste and Soil—Determination of Total Nitrogen Using Dry Combustion Method. BSI Standards: London, UK, 2012.
- Hein, H.; Müller, H.; Witte, I. Water and Environmental Analysis with the UV/Vis Spectrometer Lambda 2; Perkin-Elmer Überlingen: Überlingen, Germany, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- ÖNORML1087; Chemical Analysis of Soils: Determination of Plant-Available Phosphate and Potassium by Calcium-Acetate-Lactate. Österreichisches Normungsinstitut: Vienna, Austria, 1993.
- Petkovšek, M.; Mlakar, M.; Levstek, M.; Stražar, M.; Širok, B.; Dular, M. A Novel Rotation Generator of Hydrodynamic Cavitation for Waste-Activated Sludge Disintegration. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2015, 26, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales Arteaga, J.F.; Gluhar, S.; Kaurin, A.; Lestan, D. Simultaneous Removal of Arsenic and Toxic Metals from Contaminated Soil: Laboratory Development and Pilot Scale Demonstration. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 294, 118656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 54321; Soil, Treated Biowaste, Sludge and Waste Digestion of Aqua Regia Soluble Fractions of Elements. ISO Standard: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020.
- Wang, J.; Yu, J.; Kong, X.Z.; Hou, L. Spectrophotometric Determination of EDTA in Aqueous Solution through Ferroin Formation Using Sodium Sulfite as the Reducer. Chemosphere 2013, 91, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PIS. Uredba o Odlagališčih Odpadkov. Uredba o Odlagališčih Odpadkov. Ur. l. RS, no. 10. Available online: http://www.pisrs.si/Pis.web/pregledPredpisa?id=URED6660 (accessed on 24 January 2023).
- Kasselman, G.; Snyman, H.G. A Comparison of Four Leachable Extraction Methods on Sewage Sludge for Metal Determination. In Proceedings of the 2004 Water Institute of Southern Africa (WISA) Biennial Conference, Cape Town, South Africa, 2–6 May 2004. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.; Zhu, G.; Li, H.; Han, X.; Li, J.; Ma, Y. Accumulation and Bioavailability of Heavy Metals in a Soil-Wheat/Maize System with Long-Term Sewage Sludge Amendments. J. Integr. Agric. 2018, 17, 1861–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, R.; Shen, Y.; Zhu, N.; Yin, C.; Yuan, H.; Dai, X. Pretreatment-Promoted Sludge Fermentation Liquor Improves Biological Nitrogen Removal: Molecular Insight into the Role of Dissolved Organic Matter. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 293, 122082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nancharaiah, Y.V.; Mohan, S.V.; Lens, P.N.L. Biological and Bioelectrochemical Recovery of Critical and Scarce Metals. Trends Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 137–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanay, O.; Hasar, H.; Kocer, N.N. Effect of EDTA as Washing Solution on Removing of Heavy Metals from Sewage Sludge by Electrokinetic. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 169, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Lee, Y.; Ong, S.K. Factors Affecting EDTA Extraction of Lead from Lead-Contaminated Soils. Chemosphere 2003, 51, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, C.; Zheng, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, B.; Liu, N.; Wang, D.; Wang, S. Migration and Transformation of Heavy Metals during the Microwave-Assisted Thermal Hydrolysis of Sewage Sludge. Water Sci. Technol. 2021, 84, 917–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, C.E.A.; Morrison, G.M. Fractionation and Toxicity of Metals in Sewage Sludge. Environ. Technol. 1992, 13, 751–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Council of the European Communities. Council Directive 86/278/EEC of 12 June 1986 on the protection of the environment, and in particular of the soil, when sewage sludge is used in agriculture. Off. J. Law 1986, 181, 6–12. [Google Scholar]
- Official Gazette of the Republic of Slovenia: 62/2008; Slovenia Government of the Republic of Slovenia: Ljubljana, Slovenia, 2008. Available online: https://www.uradni-list.si/glasilo-uradni-list-rs/vsebina/2008-01-2630?sop=2008-01-2630 (accessed on 23 January 2023).
- Zhao, S.; Feng, C.; Wang, D.; Liu, Y.; Shen, Z. Salinity Increases the Mobility of Cd, Cu, Mn, and Pb in the Sediments of Yangtze Estuary: Relative Role of Sediments’ Properties and Metal Speciation. Chemosphere 2013, 91, 977–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berde, M.; Jolis, D. Effect of Saltwater Intrusion on Activated Sludge Flocculation. Water Environ. Res. 2021, 93, 750–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, H.Y.; Ong, S.L.; Ng, W.J. Effects of Sodium Chloride on the Performance of a Sequencing Batch Reactor. J. Environ. Eng. 2005, 131, 1557–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Y.; Jia, F.; Ai, Z.; Zhang, L. Iron Oxide Shell Mediated Environmental Remediation Properties of Nano Zero-Valent Iron. Environ. Sci. Nano 2017, 4, 27–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gluhar, S.; Jez, E.; Lestan, D. The Use of Zero-Valent Fe for Curbing Toxic Emissions after EDTA-Based Washing of Pb, Zn and Cd Contaminated Calcareous and Acidic Soil. Chemosphere 2019, 215, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewil, R.; Baeyens, J.; Appels, L. Enhancing the Use of Waste Activated Sludge as Bio-Fuel through Selectively Reducing Its Heavy Metal Content. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 144, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xiao, Q.; Liu, J.; Yan, H.; Wei, Y. Pilot-Scale Study of Sludge Pretreatment by Microwave and Sludge Reduction Based on Lysis–Cryptic Growth. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 190, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veeken, A.H.M.; Hamelers, H.V.M. Removal of Heavy Metals from Sewage Sludge by Extraction with Organic Acids. Water Sci. Technol. 1999, 40, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irving, H.; Williams, R.J.P. Order of Stability of Metal Complexes. Nature 1948, 162, 746–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uysal, A.; Tuncer, D.; Kir, E.; Koseoglu, T.S. Recovery of Nutrients from Digested Sludge as Struvite with a Combination Process of Acid Hydrolysis and Donnan Dialysis. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 76, 2733–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Metals (mg kg−1) | Original SS | Washed SS |
|---|---|---|
| Pb | 40.6 ± 0.2 | 9 ± 0.4 |
| Zn | 634.9 ± 0.8 | 156 ± 14.4 |
| Cu | 134.6 ± 1.0 | 141 ± 4.4 |
| Cr | 36.0 ± 1.4 | 28 ± 1.4 |
| Mn | 84.6 ± 0.1 | 29 ± 0.8 |
| Fe | 10,240 ± 239 | 2803 ± 169 |
| Properties | ||
| pH | 6.91 | 4.35 |
| EC (mS cm−1) | 6.67 | 2.92 |
| Total P (%) | 22,680 ± 145 | 6798 ± 111 |
| P2O5 (mg 100 g−1) | 2065 ± 7 | 150 ± 17 |
| Total N (%) | 6.5 ± 0.0 | 5.0 ± 0.0 |
| Total organic C (%) | 42.4 ± 0.1 | 38.3 ± 0.0 |
| Total C (%) | 42.7 ± 0.1 | 38.4 ± 0.0 |
| K2O (mg 100 g−1) | 877.4 ± 4.1 | 68.6 ± 5.6 |
| CaCO3 (%) | 2.50 ± 0.12 | 0.93 ± 0.07 |
| Batch Number | Removal Efficiency (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | Zn | Cu | Cr | Mn | Fe | |
| 1 | 81 | 67 | 0 | 14 | 61 | 66 |
| 2 | 78 | 77 | 0 | 24 | 68 | 74 |
| 3 | 76 | 76 | 0 | 13 | 67 | 73 |
| 4 | 75 | 79 | 6 | 20 | 69 | 75 |
| 5 | 79 | 80 | 0 | 12 | 70 | 76 |
| Metals (mg kg−1) | Original SS | Washed SS | DIN 38414-S4 * |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | 0.08 ± 0.02 a | 0.09 ± 0.01 a | 10 |
| Zn | 5.99 ± 0.34 a | 70.16 ± 1.37 b | 50 |
| Cu | 10.19 ± 0.26 a | 69.09 ± 2.84 b | 50 |
| Cr | 0.18 ± 0.02 a | 0.28 ± 0.04 a | 10 |
| Mn | 1.36 ± 0.05 a | 1.86 ± 0.05 b | / |
| Fe | 47.77 ± 9.33 a | 249.68 ± 16.73 b | / |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Morales Arteaga, J.F.; Zupanc, M.; Dular, M.; Lestan, D.; Kaurin, A. Removal of Toxic Metals from Sewage Sludge by Acid Hydrolysis Coupled with EDTA Washing in a Closed-Loop Process. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 2544. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20032544
Morales Arteaga JF, Zupanc M, Dular M, Lestan D, Kaurin A. Removal of Toxic Metals from Sewage Sludge by Acid Hydrolysis Coupled with EDTA Washing in a Closed-Loop Process. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023; 20(3):2544. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20032544
Chicago/Turabian StyleMorales Arteaga, Juan Francisco, Mojca Zupanc, Matevž Dular, Domen Lestan, and Anela Kaurin. 2023. "Removal of Toxic Metals from Sewage Sludge by Acid Hydrolysis Coupled with EDTA Washing in a Closed-Loop Process" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 20, no. 3: 2544. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20032544
APA StyleMorales Arteaga, J. F., Zupanc, M., Dular, M., Lestan, D., & Kaurin, A. (2023). Removal of Toxic Metals from Sewage Sludge by Acid Hydrolysis Coupled with EDTA Washing in a Closed-Loop Process. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(3), 2544. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20032544