Physical Activity, Seasonal Sensitivity and Psychological Well-Being of People of Different Age Groups Living in Extreme Environments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Ethics
2.4. Measures
2.4.1. Seasonal Pattern Assessment Questionnaire (SPAQ)
2.4.2. Psychological Well-Being Ryff Scale
2.4.3. Physical Activity
2.5. Procedures
2.6. Statistical Analysis
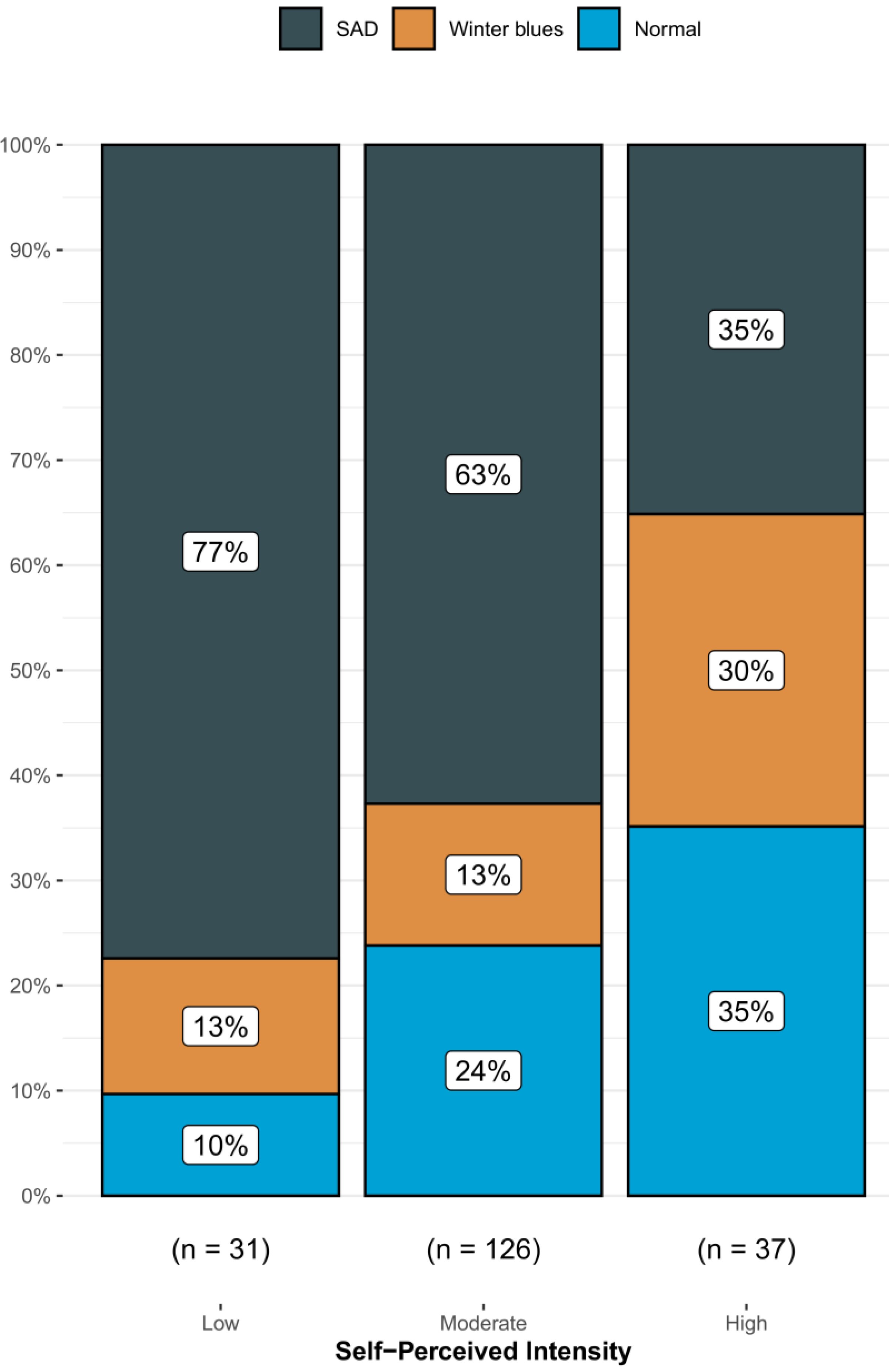
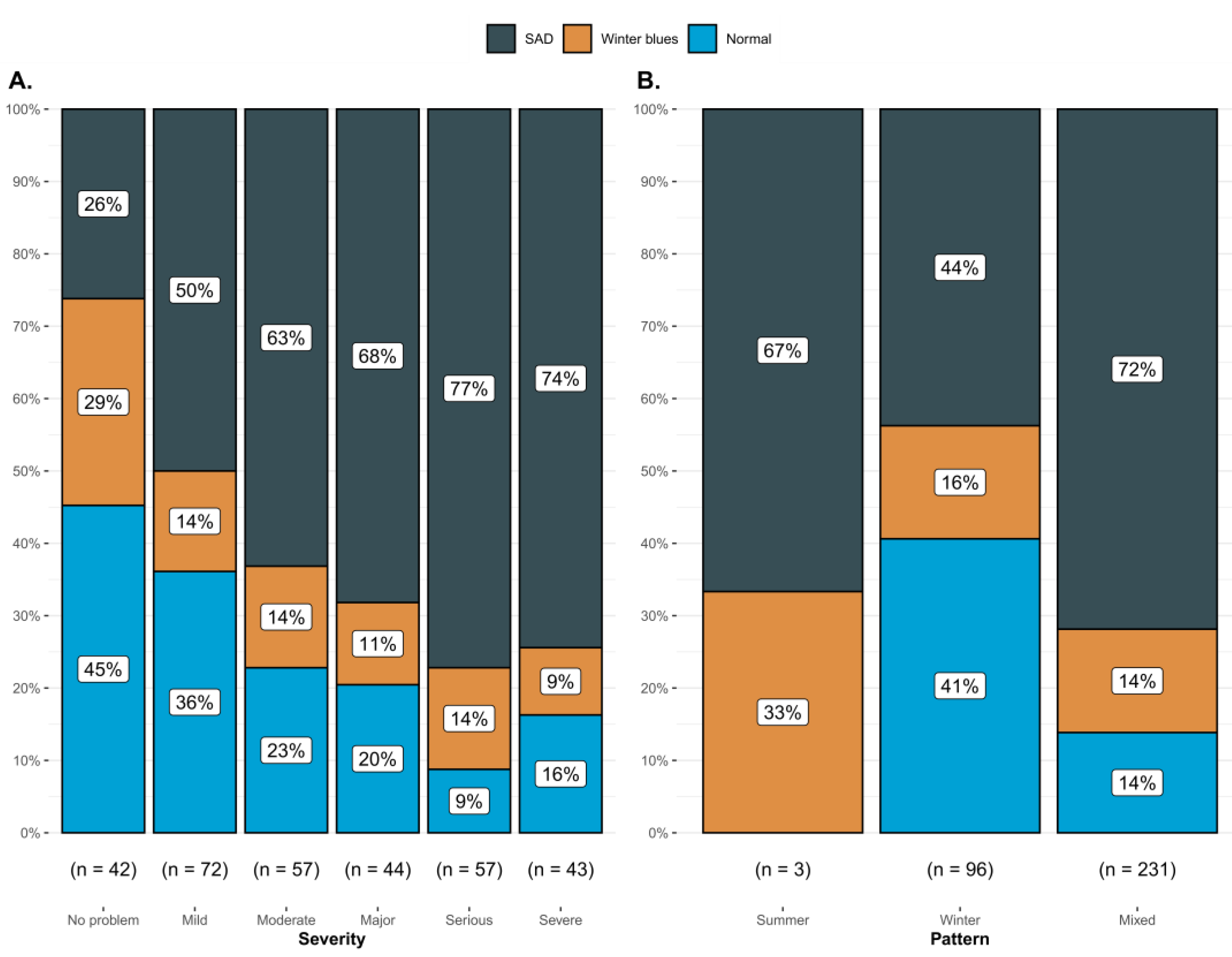
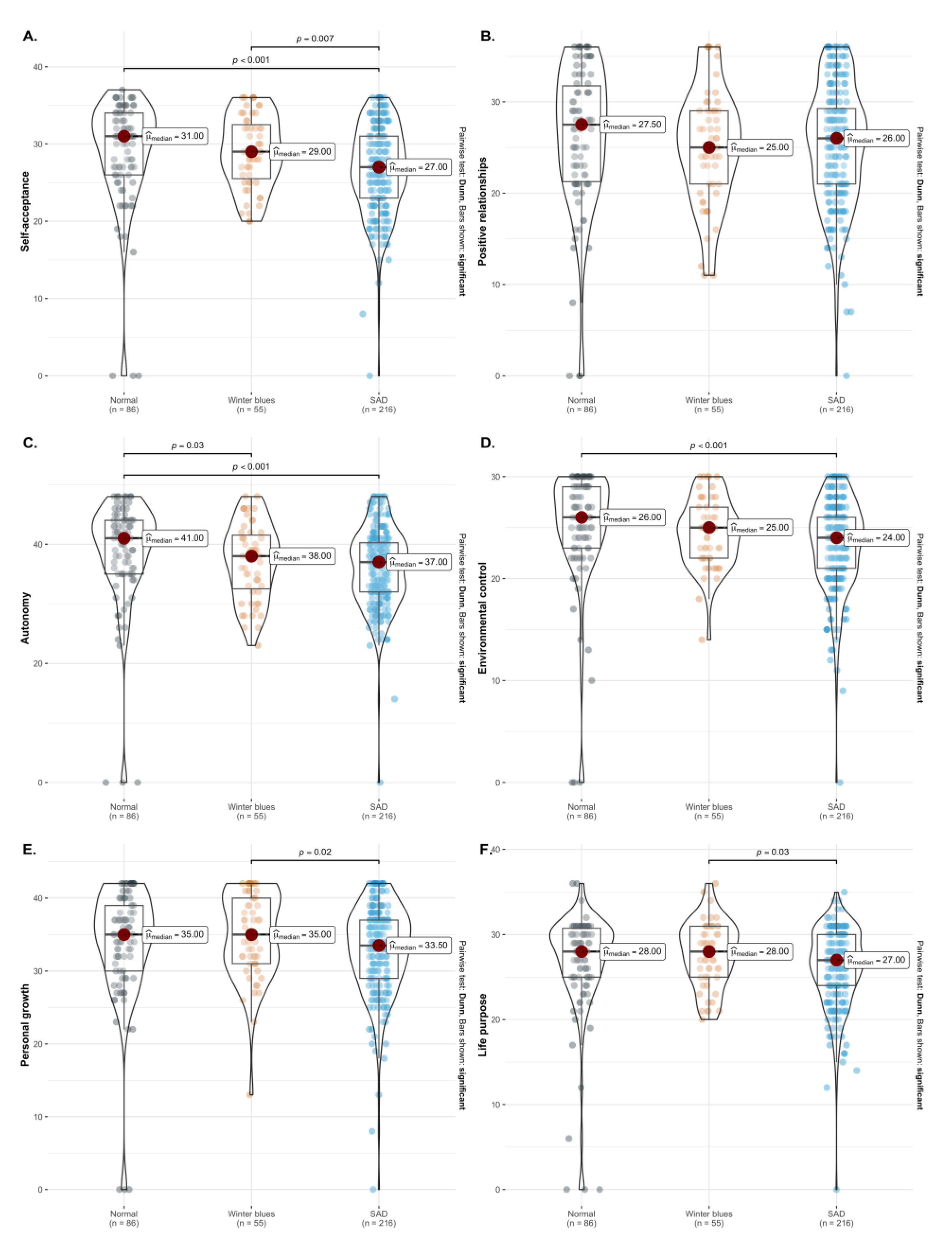
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ministerio del Deporte Ministerio Del Deporte de Chile. Cuenta Publica 2020; Ministerio del Deporte Ministerio Del Deporte de Chile: Santiago, Chile, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Santana, A.; Butorovic, N.; Olave, C. Variación de La Temperatura En Punta Arenas (Chile) En Los Ultimos 120 Años. An. Del Inst. La Patagon. 2009, 37, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leppämäki, S.J.; Partonen, T.T.; Hurme, J.; Haukka, J.K.; Lönnqvist, J.K. Randomized Trial of the Efficacy of Bright-Light Exposure and Aerobic Exercise on Depressive Symptoms and Serum Lipids. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2002, 63, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonte, A.; Coutinho, B. Seasonal Sensitivity and Psychiatric Morbidity: Study about Seasonal Affective Disorder. BMC Psychiatry 2021, 21, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarado-Aravena, C.; Estrada Goic, C.; Nuñez-Espinosa, C. Sintomatología Depresiva y Calidad de Vida En Estudiantes de Medicina de Alta Latitud Sur. Rev. Med. Chil. 2021, 149. in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gueichatureo Asencio, I.; Loezar Tillería, F.; Mellado Quiroz, V.; Vera Vega, C.; Jelincic Vasquez, C.; Nuñez Espinoza, C.; Estrada-Goic, C.; Gueichatureo Asencio, I.; Loezar Tillería, F.; Mellado Quiroz, V.; et al. Seasonal Sensitivity in a High-Latitude Population and Its Relationship to Adaptation Variables and Style of Seasonal Work Organization. Cienc. Psicológicas 2021, 15, e2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewy, A.J.; Sack, R.L.; Singer, C.M.; Whate, D.M.; Hoban, T.M. Winter Depression and the Phase-Shift Hypothesis for Bright Light’s Therapeutic Effects: History, Theory, and Experimental Evidence. J. Biol. Rhythm. 1988, 3, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitan, R.D. The Chronobiology and Neurobiology of Winter Seasonal Affective Disorder. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2007, 9, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirz-Justice, A. Seasonality in Affective Disorders. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2018, 258, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austen, M.L.; Wilson, G.V. Increased Vagal Tone during Winter in Subsyndromal Seasonal Affective Disorder. Biol. Psychiatry 2001, 50, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardell, J.L.; Armour, J.A. Neurocardiology: Structure-Based Function. Compr. Physiol. 2016, 6, 1635–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, S.; Abbas, M. Seasonal Depressive Disorder; StatPearls: Tampa, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Galima, S.V.; Vogel, S.R.; Kowalski, A.W. Seasonal Affective Disorder: Common Questions and Answers. Am. Fam. Physician 2020, 102, 668–672. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lam, R.W.; Tam, E.M.; Yatham, L.N.; Shiah, I.S.; Zis, A.P. Seasonal Depression: The Dual Vulnerability Hypothesis Revisited. J. Affect. Disord. 2001, 63, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peiser, B. Seasonal Affective Disorder and Exercise Treatment: A Review. Biol. Rhythm Res. 2009, 40, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.-L.; Jiang, W.-T.; Wang, X.; Cai, Z.-D.; Liu, Z.-H.; Liu, G.-R. Exercise, Brain Plasticity, and Depression. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2020, 26, 885–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micheli, L.; Ceccarelli, M.; D’Andrea, G.; Tirone, F. Depression and Adult Neurogenesis: Positive Effects of the Antidepressant Fluoxetine and of Physical Exercise. Brain Res. Bull. 2018, 143, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandola, A.; Ashdown-Franks, G.; Hendrikse, J.; Sabiston, C.M.; Stubbs, B. Physical Activity and Depression: Towards Understanding the Antidepressant Mechanisms of Physical Activity. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2019, 107, 525–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bull, F.C.; Al-Ansari, S.S.; Biddle, S.; Borodulin, K.; Buman, M.P.; Cardon, G.; Carty, C.; Chaput, J.-P.; Chastin, S.; Chou, R.; et al. World Health Organization 2020 Guidelines on Physical Activity and Sedentary Behaviour. Br. J. Sport. Med. 2020, 54, 1451–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Pitti, J.; Casajús Mallén, J.A.; Leis Trabazo, R.; Lucía, A.; López de Lara, D.; Moreno Aznar, L.A.; Rodríguez Martínez, G. Ejercicio Físico Como «medicina» En Enfermedades Crónicas Durante La Infancia y La Adolescencia. An. Pediatría 2020, 92, 173.e1–173.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavie, C.J.; Ozemek, C.; Carbone, S.; Katzmarzyk, P.T.; Blair, S.N. Sedentary Behavior, Exercise, and Cardiovascular Health. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 799–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosquera, J.C.G.; Vargas, L.F.A. Sedentarismo, Actividad Física y Salud: Una Revision Narrativa (Sedentary Lifestyle, Physical Activity and Health: A Narrative Review). Retos 2021, 42, 478–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manferdelli, G.; La Torre, A.; Codella, R. Outdoor Physical Activity Bears Multiple Benefits to Health and Society. J. Sport. Med. Phys. Fit. 2019, 59, 868–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paolucci, E.M.; Loukov, D.; Bowdish, D.M.E.; Heisz, J.J. Exercise Reduces Depression and Inflammation but Intensity Matters. Biol. Psychol. 2018, 133, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chekroud, S.R.; Gueorguieva, R.; Zheutlin, A.B.; Paulus, M.; Krumholz, H.M.; Krystal, J.H.; Chekroud, A.M. Association between Physical Exercise and Mental Health in 1·2 Million Individuals in the USA between 2011 and 2015: A Cross-Sectional Study. Lancet. Psychiatry 2018, 5, 739–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuch, F.B.; Vancampfort, D.; Firth, J.; Rosenbaum, S.; Ward, P.B.; Silva, E.S.; Hallgren, M.; Ponce De Leon, A.; Dunn, A.L.; Deslandes, A.C.; et al. Physical Activity and Incident Depression: A Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies. Am. J. Psychiatry 2018, 175, 631–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navalta, J.W.; Bodell, N.G.; Tanner, E.A.; Aguilar, C.D.; Radzak, K.N. Effect of Exercise in a Desert Environment on Physiological and Subjective Measures. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2019, 31, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adan, A.; Natal, V.; Fabbri, M. Propiedades Psicometricas de La Version Castellana Del Cuestionario de Evaluacion de Patrón Estacional. Rev. Latinoam. Psicol. 2006, 38, 59–69. [Google Scholar]
- Goikolea, J.; Miralles, G.; Bulbena Cabré, A.; Vieta, E.; Bulbena, A. Adaptación Española Del Cuestionario de Evaluación de Perfil Estacional (Seasonal Pattern Assessment Questionnaire, SPAQ) En Las Versiones de Adultos e Infanto-Juvenil. Actas Españolas Psiquiatr. 2003, 31, 192–198. [Google Scholar]
- Mersch, P.P.; Middendorp, H.M.; Bouhuys, A.L.; Beersma, D.G.; van den Hoofdakker, R.H. Seasonal Affective Disorder and Latitude: A Review of the Literature. J. Affect. Disord. 1999, 53, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melrose, S. Seasonal Affective Disorder: An Overview of Assessment and Treatment Approaches. Depress. Res. Treat. 2015, 2015, 178564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafka, G.J.; Kozma, A. The Construct Validity of Ryff’s Scales of Psychological Well-Being (SPWB) and Their Relationship to Measures of Subjective Well-Being. Soc. Indic. Res. 2002, 57, 171–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R: The R Project for Statistical Computing. Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 8 January 2023).
- Rivas Cardenas, D. El Clima, Caracteres, Causas, Clasificación, Fenómenos y Alteraciones Climáticas. Bachelor’s Thesis, Universidad Nacional de Educación, Lima, Peru, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ohtani, T.; Kaiya, H.; Utsumi, T.; Inoue, K.; Kato, N.; Sasaki, T. Sensitivity to Seasonal Changes in Panic Disorder Patients. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2006, 60, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacIntosh, B.R.; Murias, J.M.; Keir, D.A.; Weir, J.M. What Is Moderate to Vigorous Exercise Intensity? Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garriga, A.; Sempere-Rubio, N.; Molina-Prados, M.J.; Faubel, R. Impact of Seasonality on Physical Activity: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 19, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escames, G.; Ozturk, G.; Bano-Otalora, B.; Pozo, M.J.; Madrid, J.A.; Reiter, R.J.; Serrano, E.; Concepcion, M.; Acuna-Castroviejo, D. Exercise and Melatonin in Humans: Reciprocal Benefits. J. Pineal Res. 2012, 52, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruegsegger, G.N.; Booth, F.W. Health Benefits of Exercise. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2018, 8, a029694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markotić, V.; Pokrajčić, V.; Babić, M.; Radančević, D.; Grle, M.; Miljko, M.; Kosović, V.; Jurić, I.; Karlović Vidaković, M. The Positive Effects of Running on Mental Health. Psychiatr. Danub. 2020, 32, 233–235. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, S. Physical Exercise and Psychological Well-Being. South Afr. J. Psychol. 2006, 36, 357–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alvarado, C.; Castillo-Aguilar, M.; Villegas, V.; Estrada Goic, C.; Harris, K.; Barria, P.; Moraes, M.M.; Mendes, T.T.; Arantes, R.M.E.; Valdés-Badilla, P.; et al. Physical Activity, Seasonal Sensitivity and Psychological Well-Being of People of Different Age Groups Living in Extreme Environments. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 1719. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20031719
Alvarado C, Castillo-Aguilar M, Villegas V, Estrada Goic C, Harris K, Barria P, Moraes MM, Mendes TT, Arantes RME, Valdés-Badilla P, et al. Physical Activity, Seasonal Sensitivity and Psychological Well-Being of People of Different Age Groups Living in Extreme Environments. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023; 20(3):1719. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20031719
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlvarado, Caren, Matías Castillo-Aguilar, Valeska Villegas, Claudia Estrada Goic, Katherine Harris, Patricio Barria, Michele M. Moraes, Thiago T. Mendes, Rosa M. E. Arantes, Pablo Valdés-Badilla, and et al. 2023. "Physical Activity, Seasonal Sensitivity and Psychological Well-Being of People of Different Age Groups Living in Extreme Environments" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 20, no. 3: 1719. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20031719
APA StyleAlvarado, C., Castillo-Aguilar, M., Villegas, V., Estrada Goic, C., Harris, K., Barria, P., Moraes, M. M., Mendes, T. T., Arantes, R. M. E., Valdés-Badilla, P., & Núñez-Espinosa, C. (2023). Physical Activity, Seasonal Sensitivity and Psychological Well-Being of People of Different Age Groups Living in Extreme Environments. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(3), 1719. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20031719








